Effect of Surface Integrity on Hot Fatigue Life of Ti2AlNb Intermetallic Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
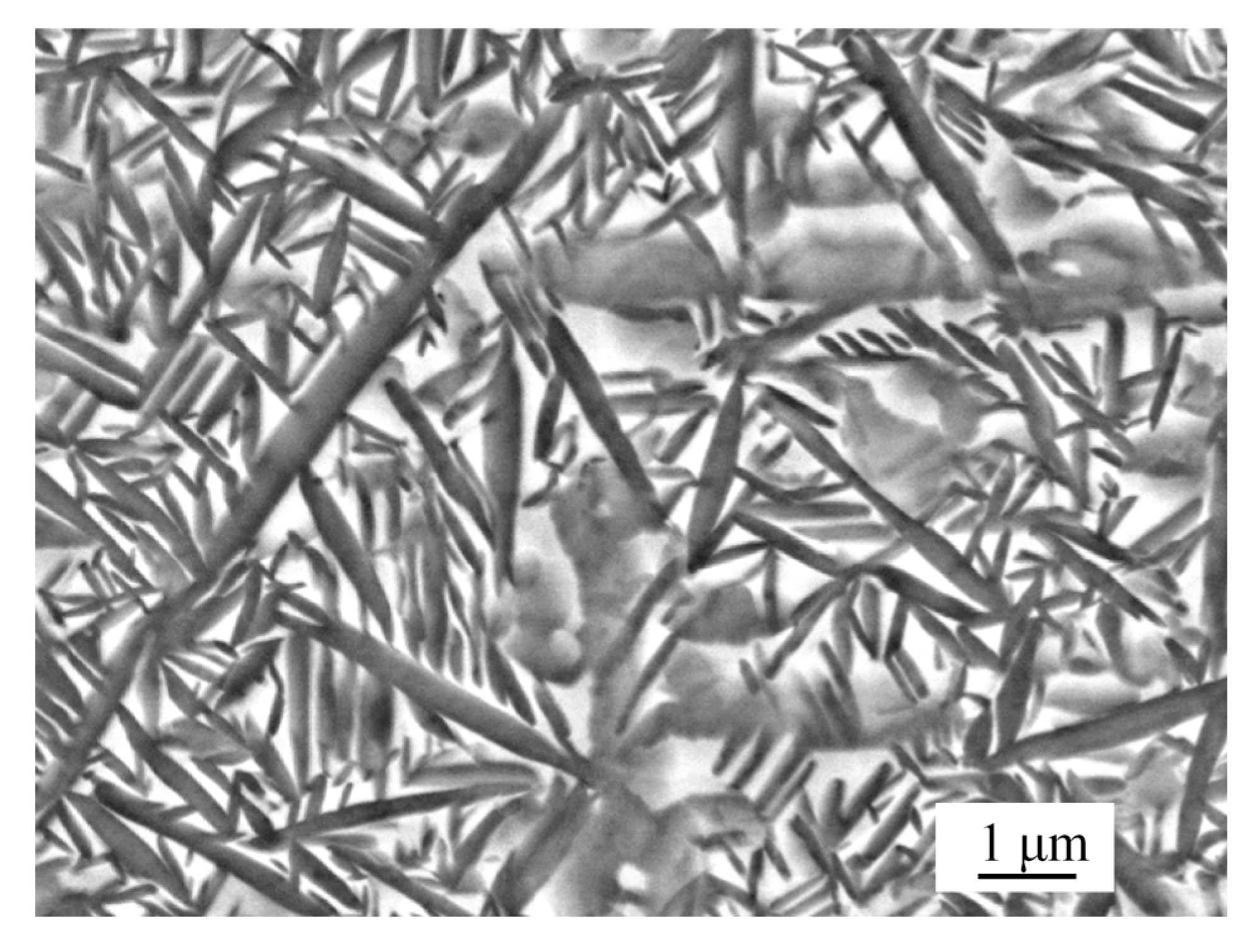
2.1. Material Properties
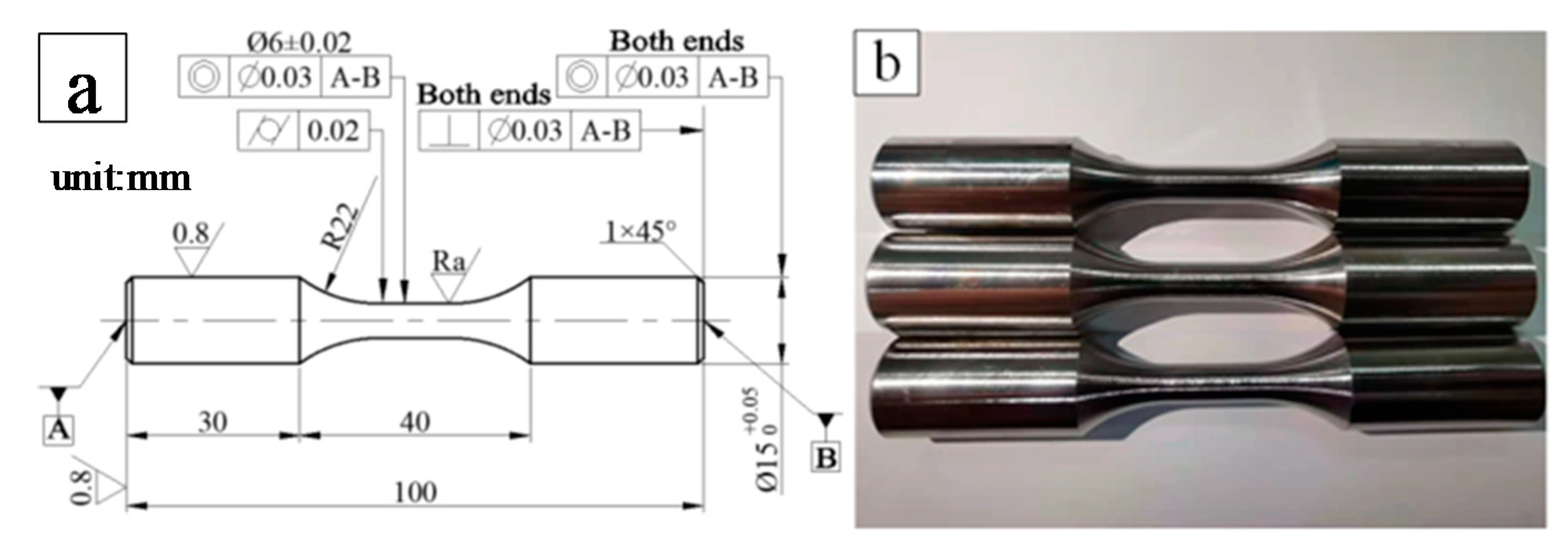
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Surface Integrity Characterization
2.4. Fatigue Test Setup
3. Results and Discussion
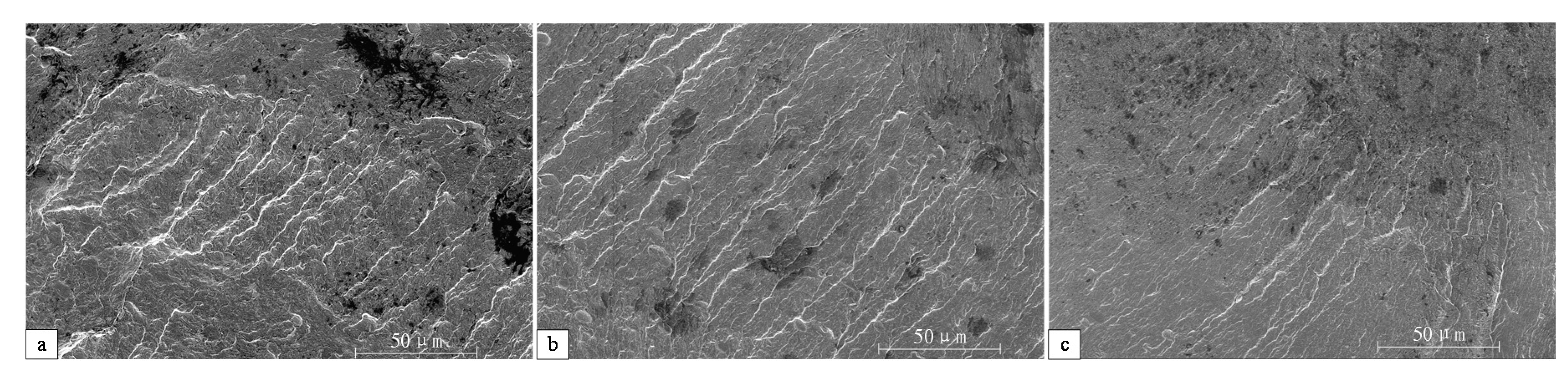
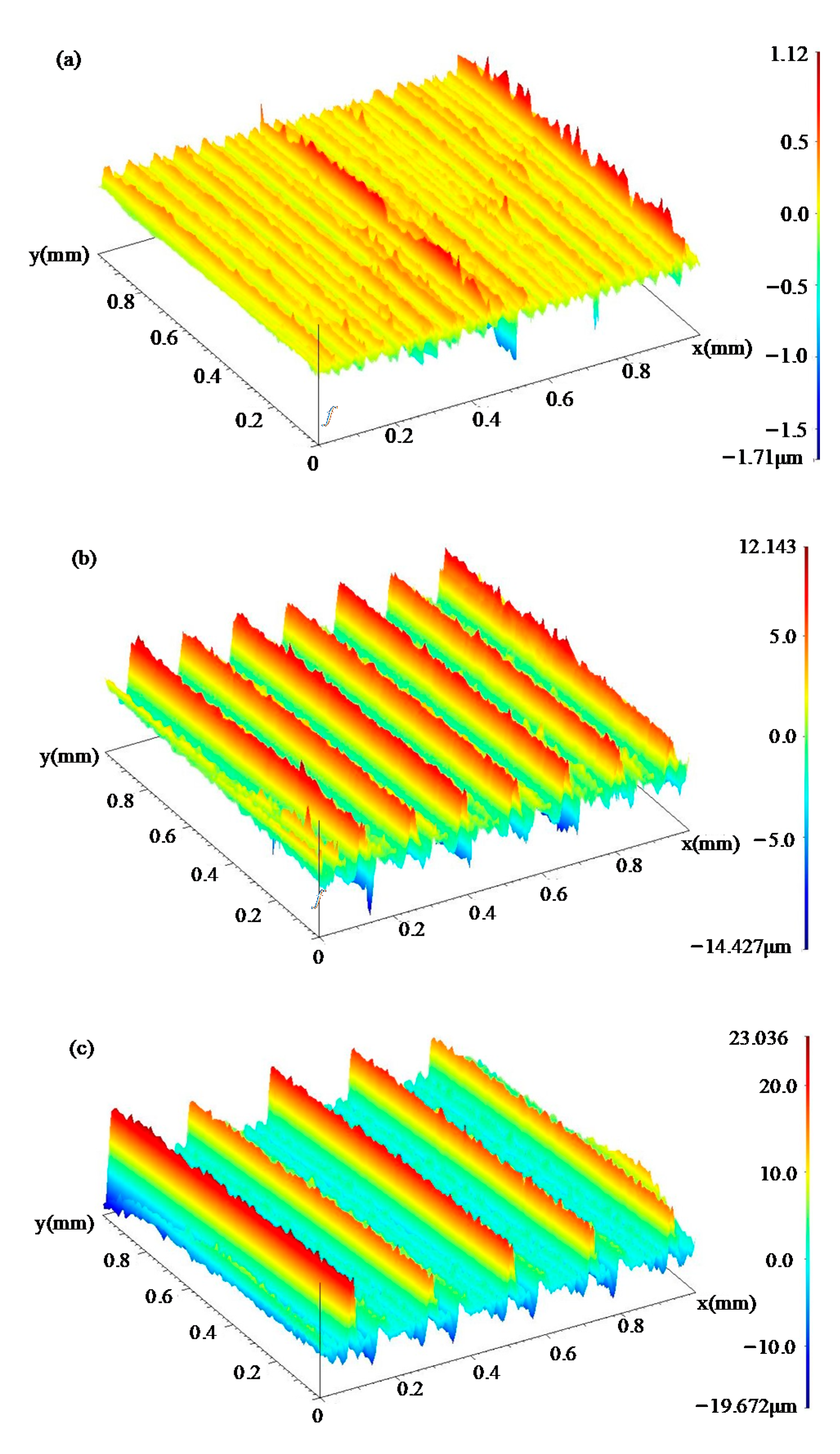
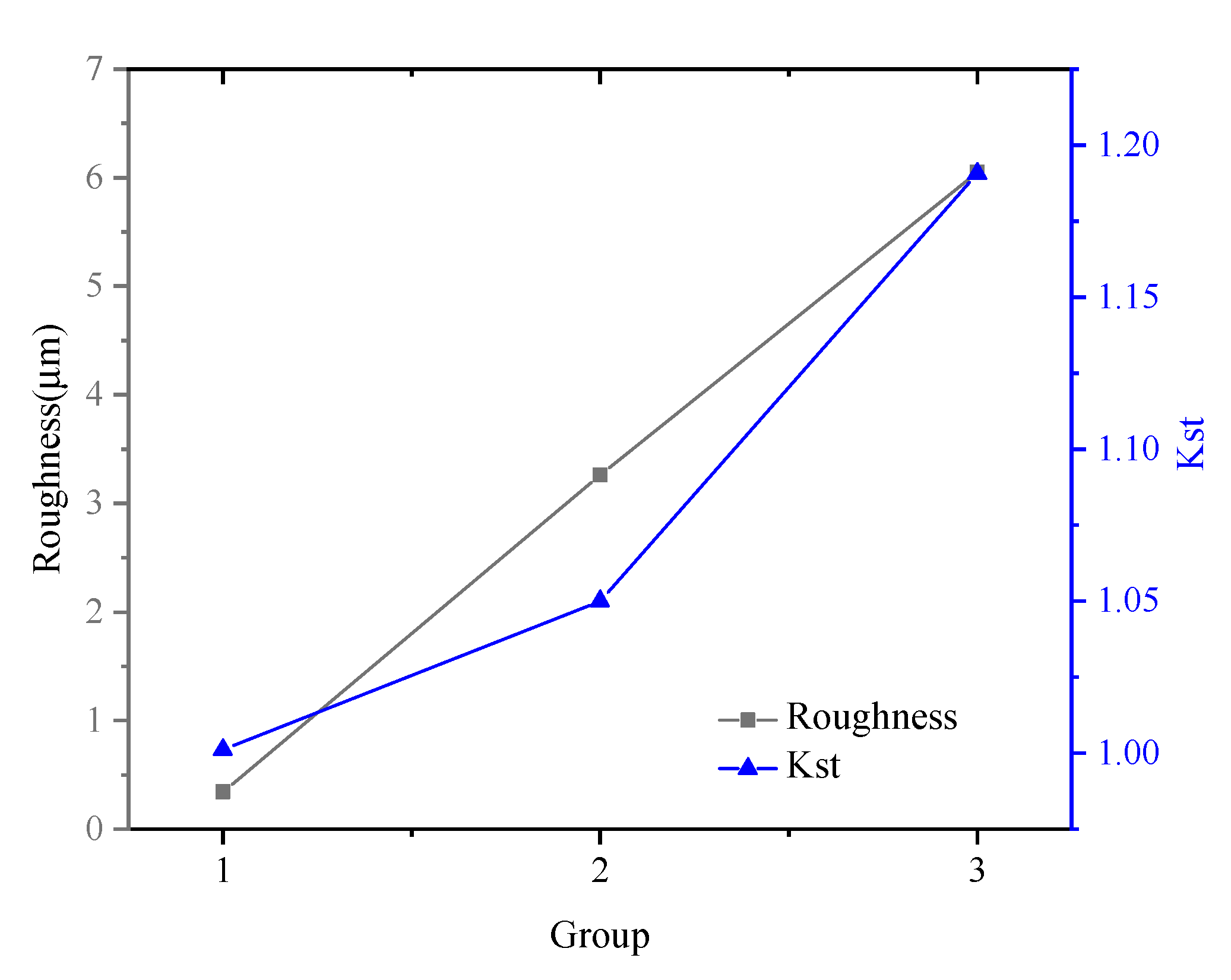
3.1. Surface Topography
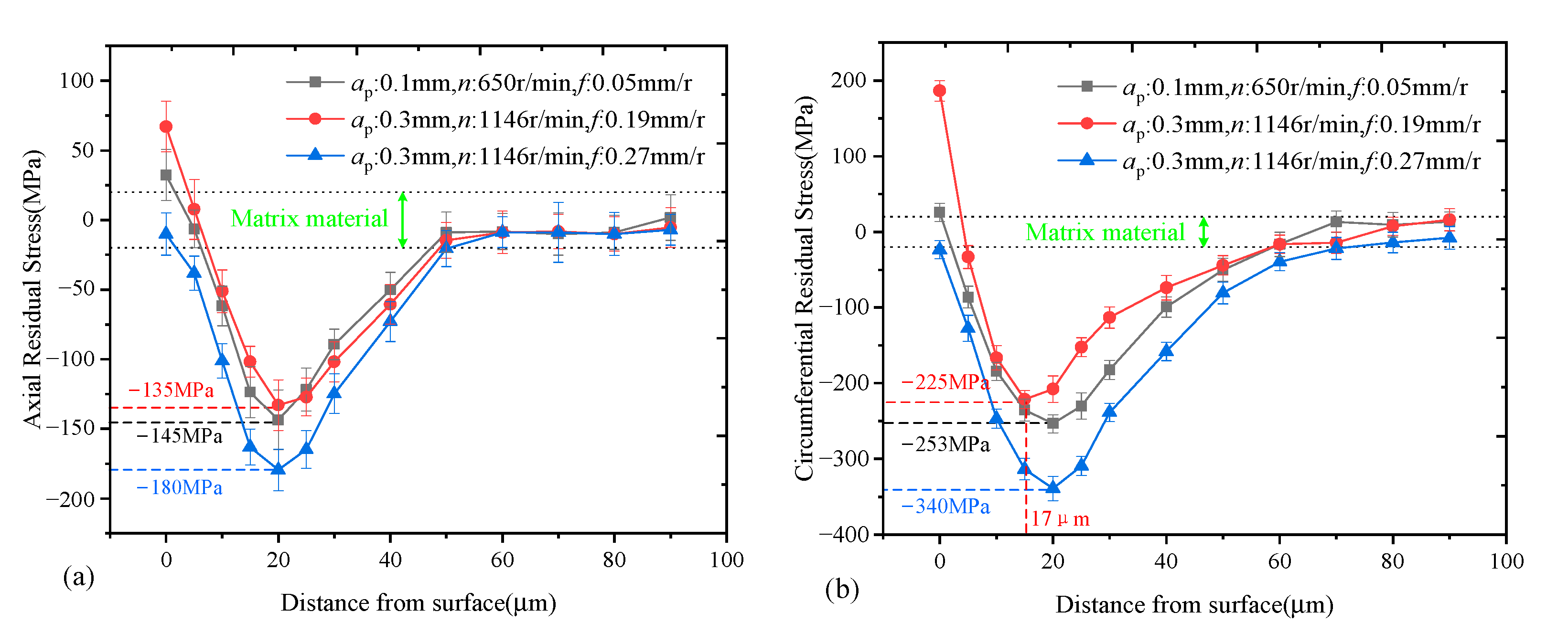
3.2. Residual Stress Distribution
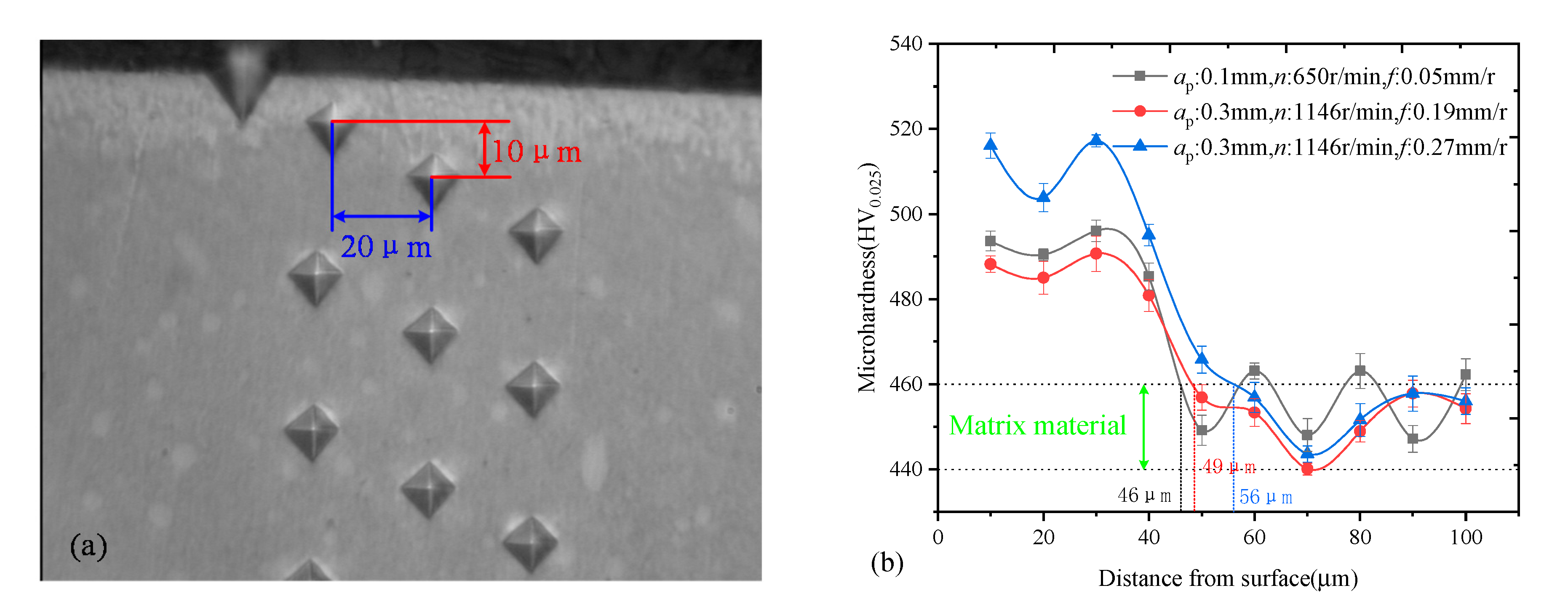
3.3. Micro Hardness Distribution
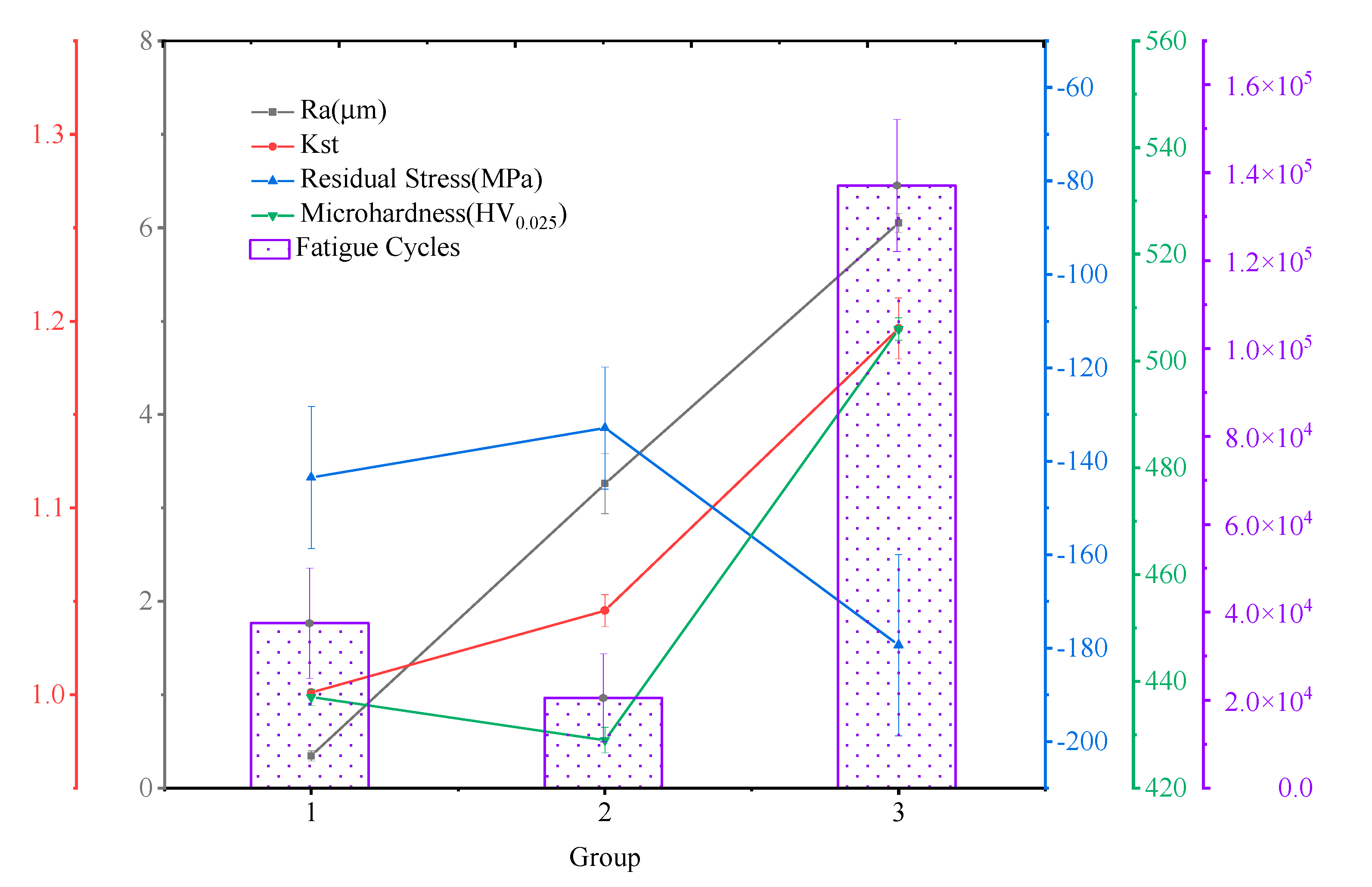
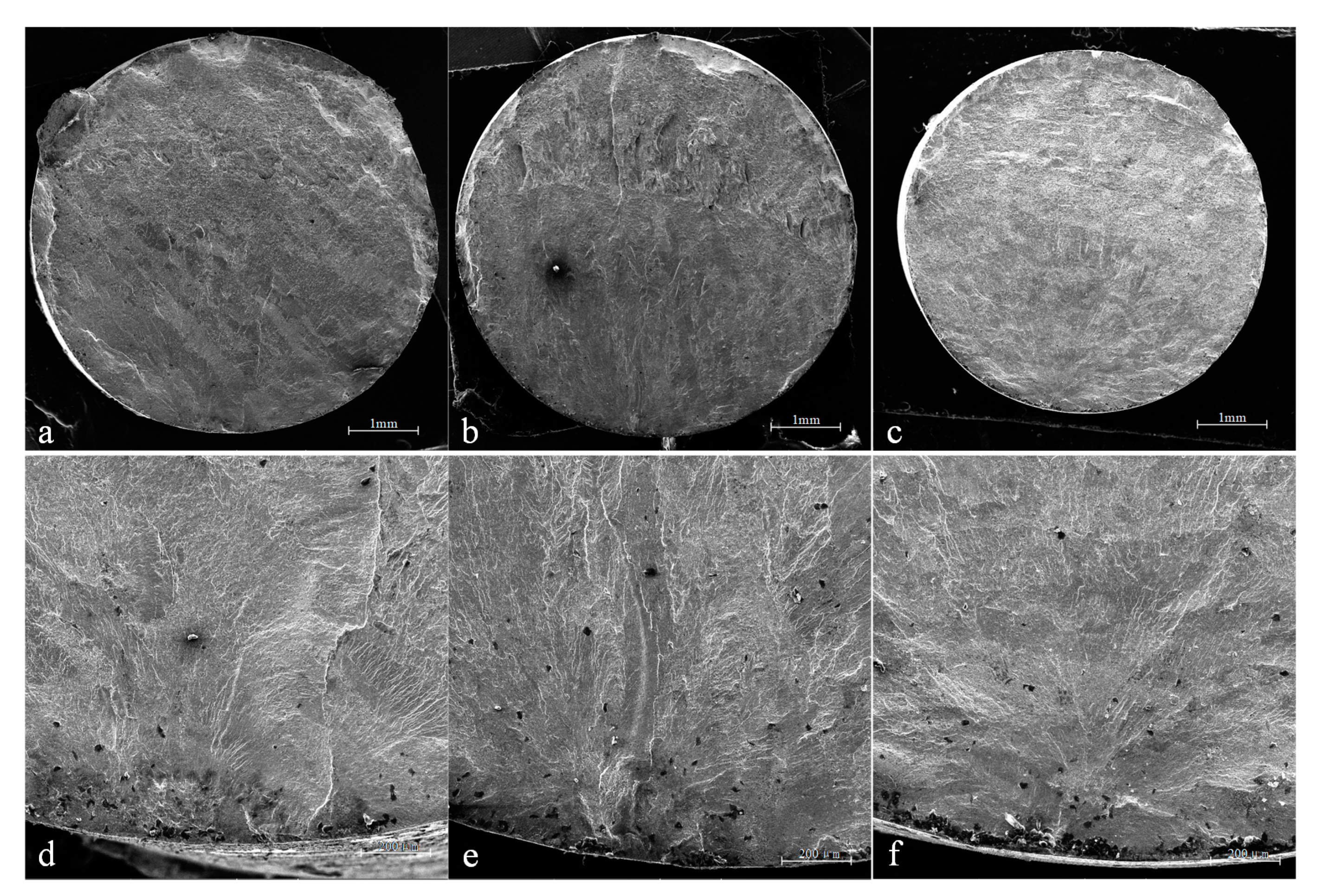
3.4. Fatigue Life and Fracture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Mao, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, X. Microstructure controlling by heat treatment and complex processing for Ti2AlNb based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 299, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Nakazawa, S.; Hagiwara, M. The effect of quaternary additions on the microstructures and mechanical properties of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 329, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D. The intermetallic Ti2AlNb. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1997, 42, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liang, X.B.; Zhang, J.W. Recent work on alloy and process development of Ti2AlNb based alloys. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2005; Volume 475, pp. 795–800. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, A.H.; Li, B.B.; Shen, J. Recent advances on Ti2AlNb-based alloys. J. Mater. Metall. 2011, 10, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann, J.; Buque, C.; Appel, F. Effect of shot peening on fatigue performance of a lamellar titanium aluminide alloy. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.W.; Lin, J.P.; Zhao, Z.X.; Sun, H.L. Fatigue response of a grain refined TiAl alloy Ti-44Al-5Nb-1W-1B with varied surface quality and thermal exposure history. Intermetallics 2017, 85, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.F.; Jin, Q.C.; Huang, X.C.; Wu, D.X.; Ren, J.X.; Zhang, D.H. Research on surface integrity of grinding Inconel718. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 65, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.X.; Yao, C.F.; Tan, L.; Ren, J.X.; Zhang, D.H. Experimental Study on Surface Integrity in High-Speed End Milling of Titanium Alloy TB6. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 328, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraratchai, M.; Limido, J.; Mabru, C.; Chieragatti, R. Modelling the influence of machined surface roughness on the fatigue life of aluminium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arola, D.; Williams, C.L. Estimating the fatigue stress concentration factor of machined surfaces. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ås, S.K.; Skallerud, B.; Tveiten, B.W.; Holme, B. Fatigue life prediction of machined components using finite element analysis of surface topography. Int. J. Fatigue 2005, 27, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasahara, H. The effect on fatigue life of residual stress and surface hardness resulting from different cutting conditions of 0.45% C steel. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.X.; Liu, D.X.; Sun, Y.F.; Tang, J.G.; Zhang, X.H. The effects of machined workpiece surface integrity on the fatigue life of TC21 titanium alloy. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 503, pp. 382–389. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Wen, Z.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yue, Z.F. Effect mechanism and equivalent model of surface roughness on fatigue behavior of nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 125, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiya, P.S.; Busch, D.E. Effect of surface roughness on low-cycle fatigue behavior of type 304 stainless steel. Metall. Trans. A 1975, 6, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novovic, D.; Dewes, R.C.; Aspinwall, D.K.; Voice, W.; Bowen, P. The effect of machined topography and integrity on fatigue life. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, A.; Rieger, U.; Eichlseder, W. The effect of machining on the surface integrity and fatigue life. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liang, X.L.; Cui, P.C. Effects of Machined Surface Integrity on High-Temperature Low-Cycle Fatigue Life and Process Parameters Optimization of Turning Superalloy Inconel 718. Materials 2021, 14, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.X.; Wang, J.C.; Gao, Y.K.; Feng, A.H. Effect of shot peening on fatigue performance of Ti2AlNb intermetallic alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 127, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.N.; Hughes, D.J.; Chen, Z.; Lombard, H.; Hattingh, D.G.; Asquith, D.; Yates, J.R.; Webster, P.J. Residual stresses and fatigue performance. Eng. Failure Anal. 2007, 14, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arola, D.; McCain, M.L. Surface texture and the stress concentration factorfor FRP components with holes. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 37, 1439–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | Al | Nb | Mo | Zr | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 10.95 | 37.74 | 1.79 | 1.67 | Other |
| Parameters | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ap (mm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| n (r/min) | 650 | 1146 | 1146 |
| f (mm/r) | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| Specimen No. | Ra (μm) | Ry (μm) | Rz (μm) | ρ (μm) | Kst | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.3964 | 2.0512 | 2.0194 | 697.6331 | 1.0012 | Group 1 ap, 0.1 mm; n, 650 r/min; f, 0.05 mm/r |
| 2 | 0.3427 | 2.029 | 1.9891 | 717.5242 | 1.0010 | |
| 3 | 0.3752 | 2.0905 | 2.0496 | 706.1372 | 1.0011 | |
| 4 | 2.9380 | 13.257 | 13.1901 | 143.5176 | 1.0412 | Group 2 ap, 0.3 mm; n, 1146 r/min; f, 0.19 mm/r |
| 5 | 3.2589 | 13.0042 | 12.9865 | 130.9969 | 1.0498 | |
| 6 | 3.0105 | 13.601 | 13.5711 | 136.4176 | 1.0442 | |
| 7 | 6.1271 | 26.5943 | 26.7299 | 59.4716 | 1.2050 | Group 3 ap, 0.3 mm; n, 1146 r/min; f, 0.27 mm/r |
| 8 | 6.0504 | 25.1128 | 24.9831 | 64.4499 | 1.1887 | |
| 9 | 6.0255 | 25.8038 | 25.9345 | 61.6457 | 1.1944 |
| No. Specimen | A | λ | ω | θ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 6.889 | −4.615 | 1.590 | 1.555 |
| 5 | 26.893 | −3.929 | 0.357 | 1.569 |
| 8 | 2.175 | −3.368 | 4.783 | 1.510 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sha, A.; Li, X. Effect of Surface Integrity on Hot Fatigue Life of Ti2AlNb Intermetallic Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174841
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Sha A, Li X. Effect of Surface Integrity on Hot Fatigue Life of Ti2AlNb Intermetallic Alloy. Materials. 2021; 14(17):4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174841
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanju, Yi Zhou, Aixue Sha, and Xingwu Li. 2021. "Effect of Surface Integrity on Hot Fatigue Life of Ti2AlNb Intermetallic Alloy" Materials 14, no. 17: 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174841
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, Y., Sha, A., & Li, X. (2021). Effect of Surface Integrity on Hot Fatigue Life of Ti2AlNb Intermetallic Alloy. Materials, 14(17), 4841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174841






