Finite Element-Based Numerical Simulations to Evaluate the Influence of Wollastonite Microfibers on the Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Cementitious Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
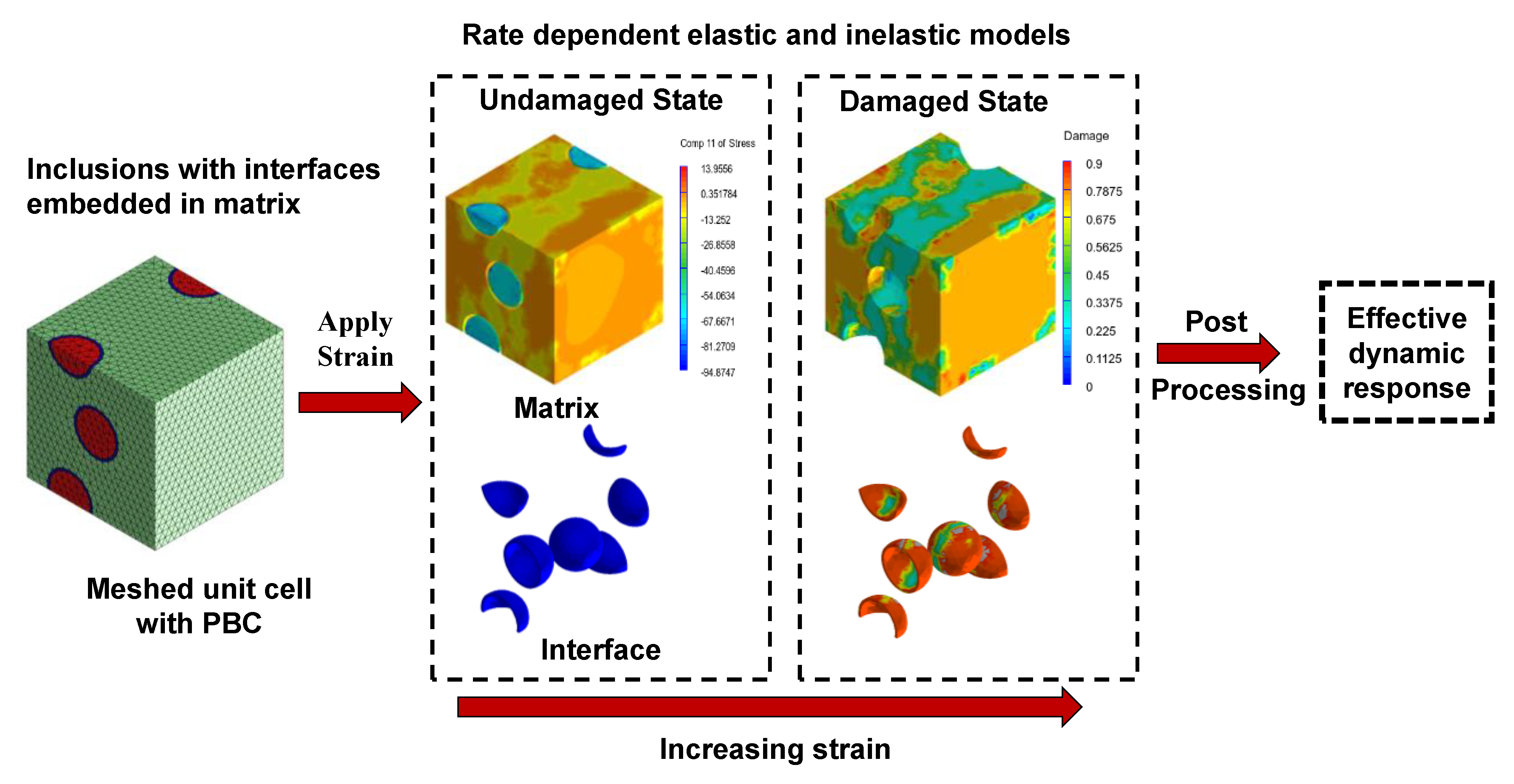
2. Multiscale Numerical Simulations for Dynamic Response Prediction of Fiber-Reinforced Mortars
2.1. Multiscale Simulation Strategy
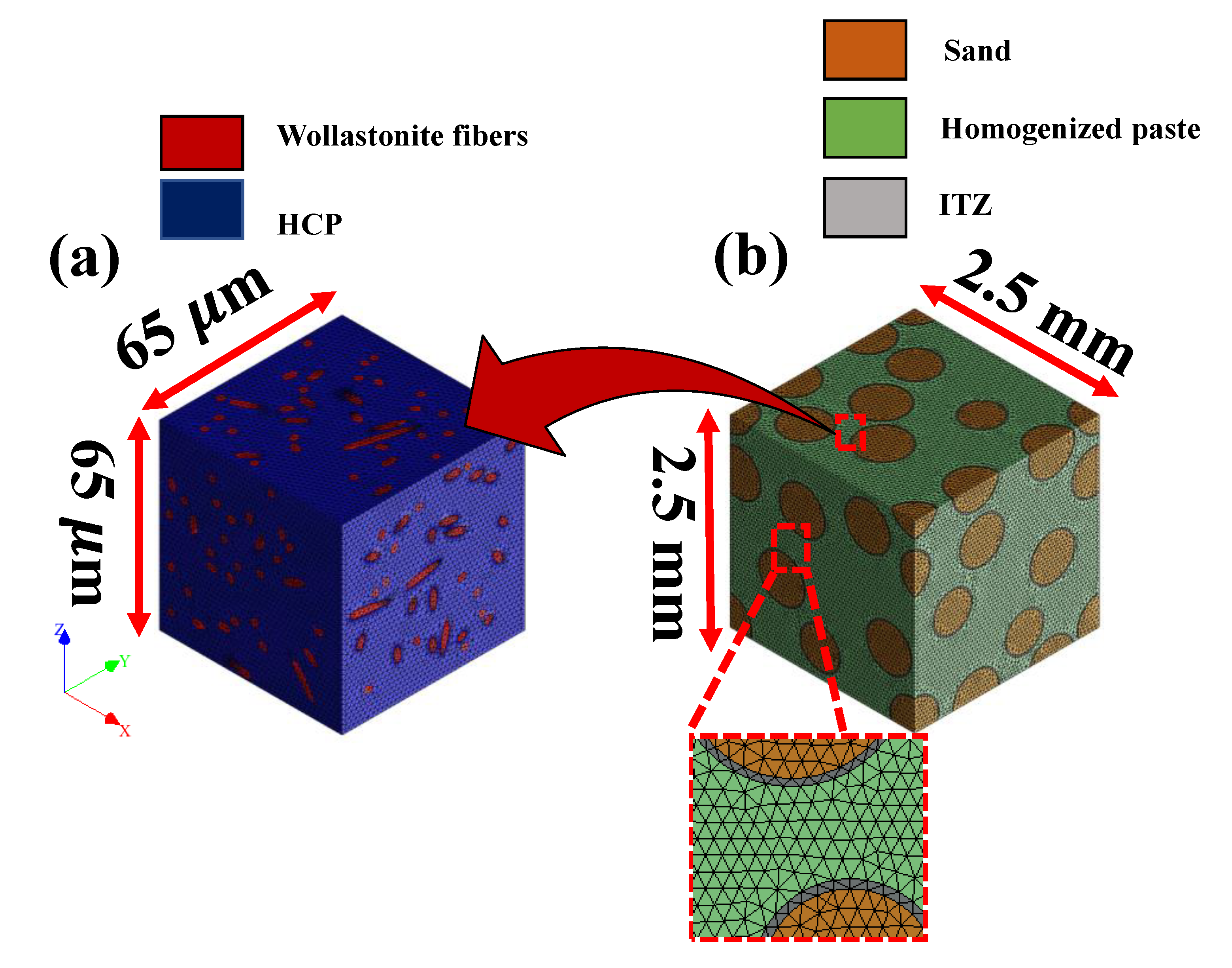
2.1.1. Representative Geometry Generation
2.1.2. Periodically Bounded Unit Cells
2.1.3. Constitutive Behavior Prediction
2.1.4. Rate Dependent Damage
2.1.5. Post-Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Representative Length Scales for Numerical Simulation
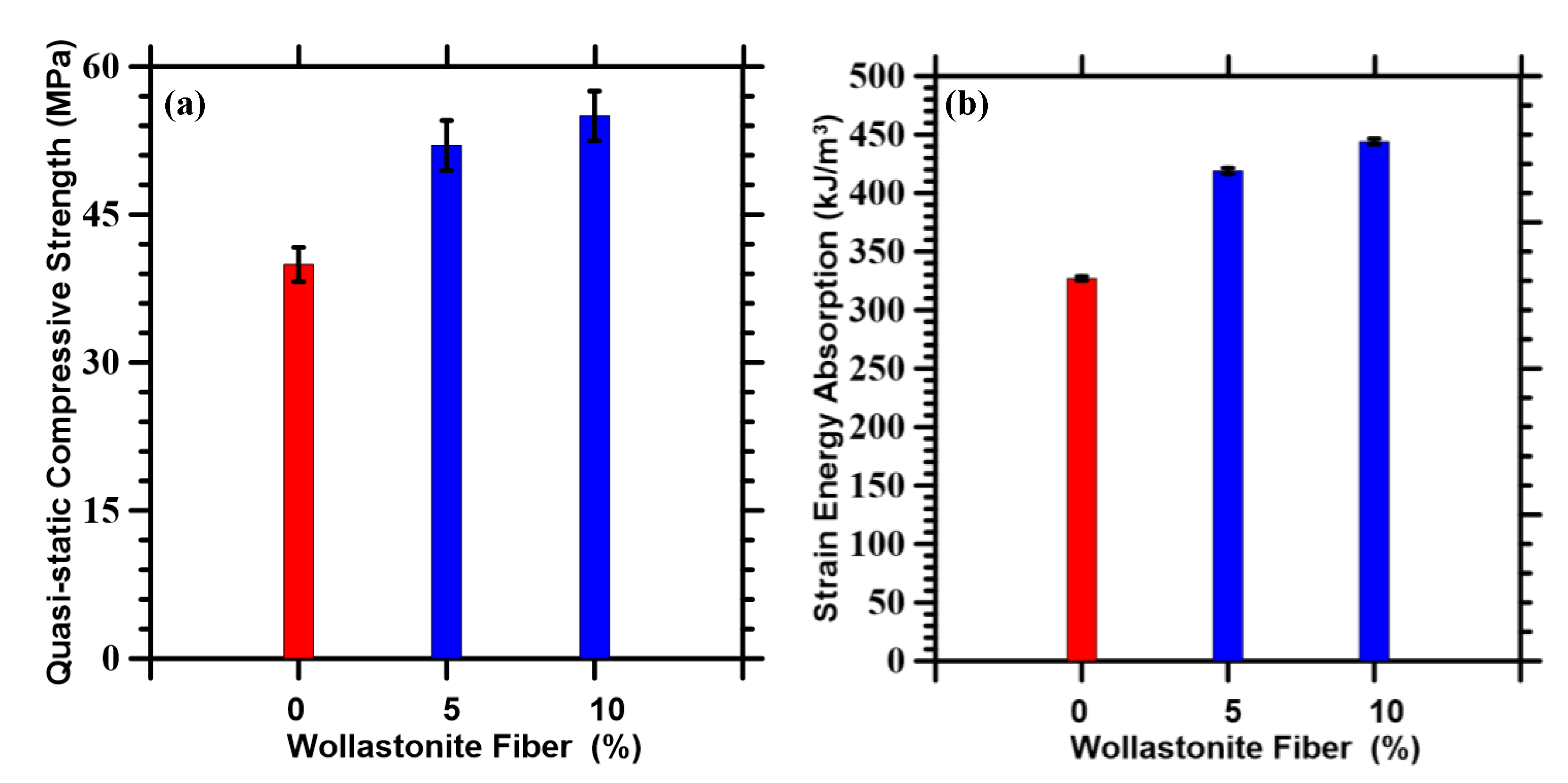
3.2. Quasi-Static Compressive Behavior
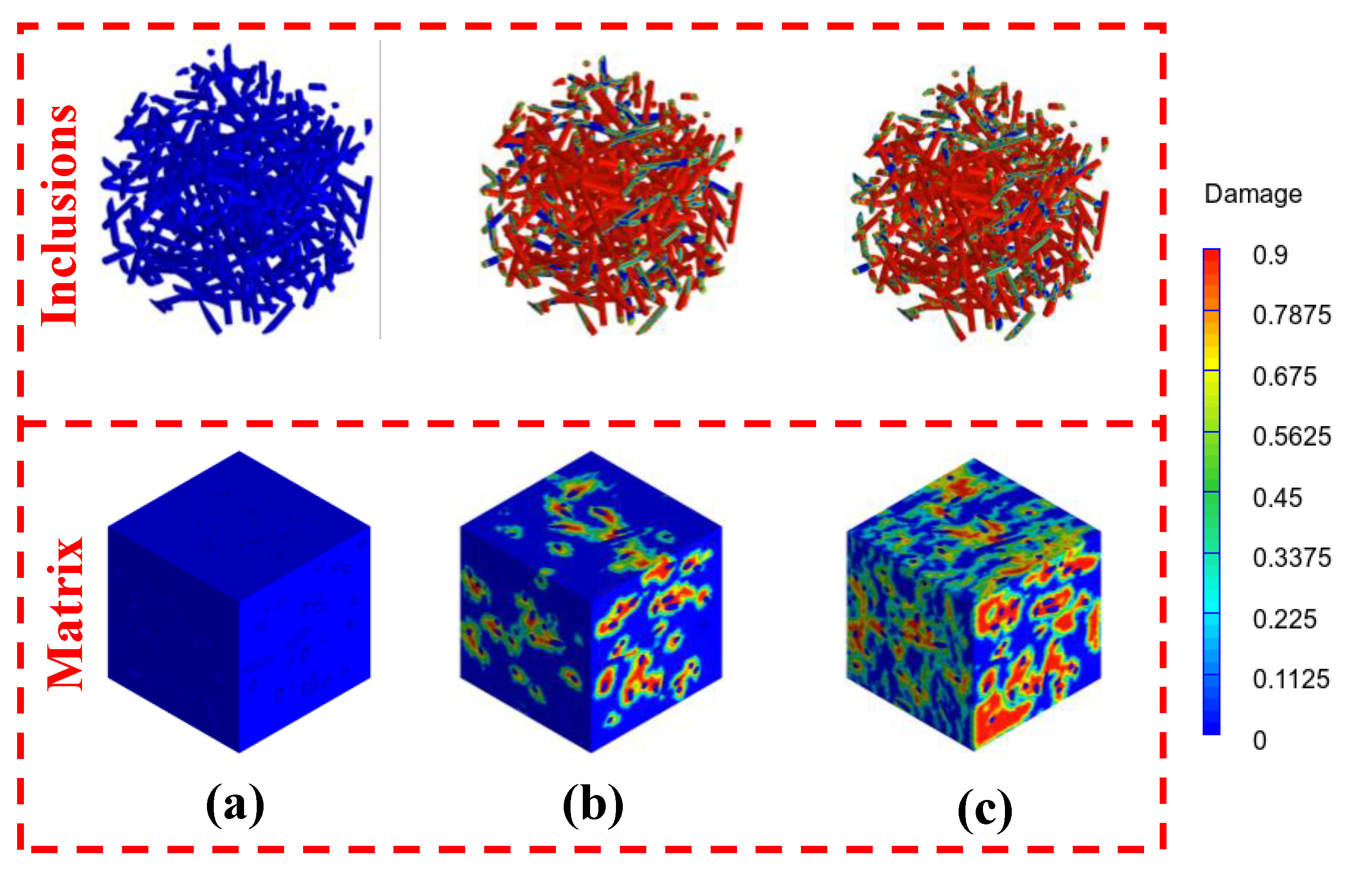
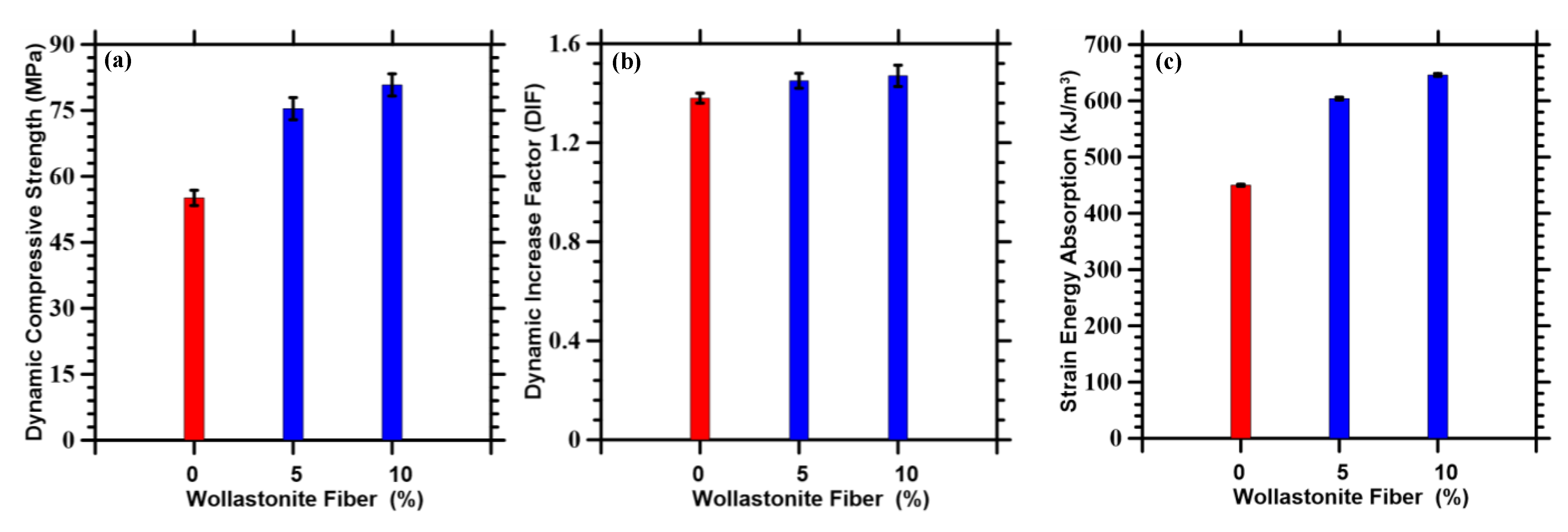
3.3. Compressive Response under Dynamic Loads
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bažant, Z.P.; Cedolin, L. Fracture Mechanics of Reinforced Concrete. J. Eng. Mech. Div. 1980, 106, 1287–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.F. Crack Propagation and the Fracture of Concrete. J. Proc. 1961, 58, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ding, W.; Qiao, Y. Experimental Investigation on the Tensile Behavior of Hybrid Steel-PVA Fiber Reinforced Concrete Containing Fly Ash and Slag Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 118000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turatsinze, A.; Garros, M. On the Modulus of Elasticity and Strain Capacity of Self-Compacting Concrete Incorporating Rubber Aggregates. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ožbolt, J.; Bede, N.; Sharma, A.; Mayer, U. Dynamic Fracture of Concrete L-Specimen: Experimental and Numerical Study. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 148, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ožbolt, J.; Sharma, A.; Reinhardt, H.-W. Dynamic Fracture of Concrete—Compact Tension Specimen. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2011, 48, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, J.G. On the Strength and Toughness Properties of SFRC under Static-Dynamic Compression. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic Compression Behavior of Ultra-High Performance Cement Based Composites. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, S.G.; Molyneaux, T.C.K.; Barnett, S.J.; Gao, X. Dynamic Enhancement of Blast-Resistant Ultra High Performance Fibre-Reinforced Concrete under Flexural and Shear Loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2010, 37, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Xu, J. Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Ceramic Fiber Reinforced Concrete under Impact Load. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 45, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, A.A.; Ransinchung, G.D.; Kumar, P. Micro Fiber Reinforced Cement Paste and Mortar Overlays—A Review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2013, 6, 765. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalaratnam, V.S.; Shah, S.P. Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Subjected to Impact Loading. J. Proc. 1986, 83, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraja, M.C.; Dhang, N.; Gupta, A.P. Stress–Strain Curves for Steel-Fiber Reinforced Concrete under Compression. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1999, 21, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, C.; Seliem, H.M.; El-Safty, A.; Rizkalla, S.H. Use of Basalt Fibers for Concrete Structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.; Park, C.; Moon, D.Y. Characteristics of Basalt Fiber as a Strengthening Material for Concrete Structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2005, 36, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passuello, A.; Moriconi, G.; Shah, S.P. Cracking Behavior of Concrete with Shrinkage Reducing Admixtures and PVA Fibers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, C.A.; Fajardo, G.; Monroy, S.; Duran-Herrera, A.; Valdez, P.; Magniont, C. Comparative Study between Natural and PVA Fibers to Reduce Plastic Shrinkage Cracking in Cement-Based Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhosseini, H.; Tahir, M.M.; Alaskar, A.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Alyousef, R. Enhancement of Strength and Transport Properties of a Novel Preplaced Aggregate Fiber Reinforced Concrete by Adding Waste Polypropylene Carpet Fibers. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 101003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadhosseini, H.; Yatim, J.M.; Sam, A.R.M.; Awal, A.S.M.A. Durability Performance of Green Concrete Composites Containing Waste Carpet Fibers and Palm Oil Fuel Ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Study on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Nano-Calcium Carbonate/Epoxy Composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4521–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, S.; Ramachandra Murthy, A.; Ramesh Kumar, V.; Karunanithi, A. Characterisation Studies on the Particle Size Effect of Calcium Carbonate in High-Strength Concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 2021, 73, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriço, A.; Bogas, J.A.; Hawreen, A.; Guedes, M. Durability of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, M.; Ardakani, S.H.; Mohammadi, S. An XFEM Multiscale Approach for Fracture Analysis of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Concrete. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2014, 72, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimov, D.; Amit, I.; Gorrie, O.; Barnes, M. Ultrahigh Performance Nanoengineered Graphene–Concrete Composites for Multifunctional Applications—Dimov—2018—Advanced Functional Materials—Wiley Online Library. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsaei, E.; de Souza, F.B.; Yao, X.; Benhelal, E.; Akbari, A.; Duan, W. Graphene-Based Nanosheets for Stronger and More Durable Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 642–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.; El-Tawil, S.; Naaman, A.E. Direct Tensile Behavior of Ultra High Performance Fiber Reinforced Concrete (UHP-FRC) at High Strain Rates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, H. Dynamic Compressive Behaviour of Spiral Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete in Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar Tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, P.; Li, Z.-X. Effects of Steel Fibres on Dynamic Strength of UHPC. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaris, W.; Shah, S.P. Constitutive Model for Dynamic Loading of Concrete. J. Struct. Eng. 1985, 111, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, D.L.; Park, S.W.; Zhou, M. Dynamic Behavior of Concrete at High Strain Rates and Pressures: I. Experimental Characterization. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2001, 25, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, A.; Guo, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Li, D.; Qin, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z. Cement-Based Materials Modified with Superabsorbent Polymers: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doner, S.; Nayak, S.; Senol, K.; Shukla, A.; Krishnan, N.M.A.; Yilmazcoban, I.K.; Das, S. Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Metallic Particulate-Reinforced Cementitious Composites: SHPB Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nili, M.; Afroughsabet, V. The Effects of Silica Fume and Polypropylene Fibers on the Impact Resistance and Mechanical Properties of Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, V.T.; Baeza, F.J.; Ivorra, S.; Zornoza, E.; Galao, Ó. Effect of Steel and Carbon Fiber Additions on the Dynamic Properties of Concrete Containing Silica Fume. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannawi, K.; Bian, H.; Prince-Agbodjan, W.; Raghavan, B. Effect of Different Types of Fibers on the Microstructure and the Mechanical Behavior of Ultra-High Performance Fiber-Reinforced Concretes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 86, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, R.; Khatib, J.; Kaur, I. Use of Recycled Plastic in Concrete: A Review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1835–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorneycroft, J.; Orr, J.; Savoikar, P.; Ball, R.J. Performance of Structural Concrete with Recycled Plastic Waste as a Partial Replacement for Sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R.; Moriconi, G. Environmental-Friendly Durable Concrete Made with Recycled Materials for Sustainable Concrete Construction. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Sustainable Development of Cement, Concrete and Concrete Structures, Toronto, ON, Canada, 5–7 October 2005; pp. 485–505. [Google Scholar]
- Frigione, M. Recycling of PET Bottles as Fine Aggregate in Concrete. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, P.; Rana, A.; Chad, Y.B.; Misra, A.; Csetenyi, L. Durability Studies on Concrete Containing Wollastonite. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, V.; Kachala, R.; Bonakdar, A.; Mobasher, B. Mechanical Properties of Micro and Sub-Micron Wollastonite Fibers in Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 82, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareei, S.A.; Ameri, F.; Shoaei, P.; Bahrami, N. Recycled Ceramic Waste High Strength Concrete Containing Wollastonite Particles and Micro-Silica: A Comprehensive Experimental Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shen, A.; Lyu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, W. Effect of Wollastonite Microfibers as Cement Replacement on the Properties of Cementitious Composites: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Yan, C.; Duan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Yan, Z. Durability Performances of Wollastonite, Tremolite and Basalt Fiber-Reinforced Metakaolin Geopolymer Composites under Sulfate and Chloride Attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites Reinforced with Cellulose Based Fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprone, D.; Cadoni, E.; Iucolano, F.; Prota, A. Analysis of the Strain-Rate Behavior of a Basalt Fiber Reinforced Natural Hydraulic Mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 53, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralegaonkar, R.; Gavali, H.; Aswath, P.; Abolmaali, S. Application of Chopped Basalt Fibers in Reinforced Mortar: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabi, A.; Chehlatt, S. Preparation Process of a Highly Resistant Wollastonite Bioceramics Using Local Raw Materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.M. Crystallization of Synthetic Wollastonite Prepared from Local Raw Materials. Int. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 4, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsudin, R.; Abdul Azam, F. ‘Atiqah; Abdul Hamid, M.A.; Ismail, H. Bioactivity and Cell Compatibility of β-Wollastonite Derived from Rice Husk Ash and Limestone. Materials 2017, 10, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yücel, H.E.; Özcan, S. Strength Characteristics and Microstructural Properties of Cement Mortars Incorporating Synthetic Wollastonite Produced with a New Technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Guo, Q.; Xi, X.; Hou, G.; Wei, G.; Qu, J. The Environmental Sustainability of Synthetic Wollastonite Using Waste from Zirconium Oxychloride Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, V.; Kachala, R.; Bonakdar, A.; Neithalath, N.; Mobasher, B. Quantitative 2D Restrained Shrinkage Cracking of Cement Paste with Wollastonite Microfibers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J. Experimental and Modeling Study of Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Cement Paste, Mortar and Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Zhou, F.-H.; Sun, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Shi, S.-Q. Studies on Rate-Dependent Macro-Damage Evolution of Materials at High Strain Rates. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2010, 19, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhelal, E.; Zahedi, G.; Shamsaei, E.; Bahadori, A. Global Strategies and Potentials to Curb CO2 Emissions in Cement Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubachevsky, B.D.; Stillinger, F.H.; Pinson, E.N. Disks vs. Spheres: Contrasting Properties of Random Packings. J. Stat. Phys. 1991, 64, 501–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubachevsky, B.D.; Stillinger, F.H. Geometric Properties of Random Disk Packings. J. Stat. Phys. 1990, 60, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Krishnan, N.M.A.; Das, S. Fracture Response of Metallic Particulate-Reinforced Cementitious Composites: Insights from Experiments and Multiscale Numerical Simulations. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 97, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Maroli, A.; Singh, S.S.; Stannard, T.; Xiao, X.; Chawla, N.; Neithalath, N. A Microstructure-Guided Constitutive Modeling Approach for Random Heterogeneous Materials: Application to Structural Binders. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 119, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Aguayo, M.; Rajan, S.D.; Sant, G.; Neithalath, N. Microstructure-Guided Numerical Simulations to Predict the Thermal Performance of a Hierarchical Cement-Based Composite Material. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 87, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayak, S.; Das, S. A Microstructure-Guided Numerical Approach to Evaluate Strain Sensing and Damage Detection Ability of Random Heterogeneous Self-Sensing Structural Materials. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 156, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nayak, S.; Krishnan, N.M.A.; Das, S. Microstructure-Guided Numerical Simulation to Evaluate the Influence of Phase Change Materials (PCMs) on the Freeze-Thaw Response of Concrete Pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Sluis, O.; Schreurs, P.J.G.; Brekelmans, W.A.M.; Meijer, H.E.H. Overall Behaviour of Heterogeneous Elastoviscoplastic Materials: Effect of Microstructural Modelling. Mech. Mater. 2000, 32, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Yang, P.; Singh, S.S.; Mertens, J.C.E.; Xiao, X.; Chawla, N.; Neithalath, N. Effective Properties of a Fly Ash Geopolymer: Synergistic Application of X-ray Synchrotron Tomography, Nanoindentation, and Homogenization Models. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.A.; Kuhl, E.; Steinmann, P. A Note on the Generation of Periodic Granular Microstructures Based on Grain Size Distributions. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2008, 32, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hoffarth, C.; Ren, B.; Spencer, B.; Sant, G.; Rajan, S.D.; Neithalath, N. Simulating the Fracture of Notched Mortar Beams through Extended Finite-Element Method and Peridynamics. J. Eng. Mech. 2019, 145, 04019049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, M.P.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Zimmerman, R.W. inhomogeneous Interfacial transition zone model for the bulk modulus of mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, S.; Huang, J. The ITZ in Concrete—A Different View Based on Image Analysis and SEM Observations. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2001, 23, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wriggers, P. Multiscale Diffusion–Thermal–Mechanical Cohesive Zone Model for Concrete. Comput. Mech. 2015, 55, 999–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X. Stress-Strain Behavior and Statistical Continuous Damage Model of Cement Mortar under High Strain Rates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadal, R.S.; Misra, R.D.K. The Influence of Loading Rate and Concurrent Microstructural Evolution in Micrometric Talc- and Wollastonite-Reinforced High Isotactic Polypropylene Composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 374, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.R.L.; Němeček, J.; Štemberk, P. Application of Multiscale Elastic Homogenization Based on Nanoindentation for High Performance Concrete. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2013, 62–63, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, S.-S. Four-Phase Sphere Modeling of Effective Bulk Modulus of Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, J.A.; Abrantes, A.E.; Lade, P.V. Effect of Strain Rate on the Stress-Strain Behavior of Sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
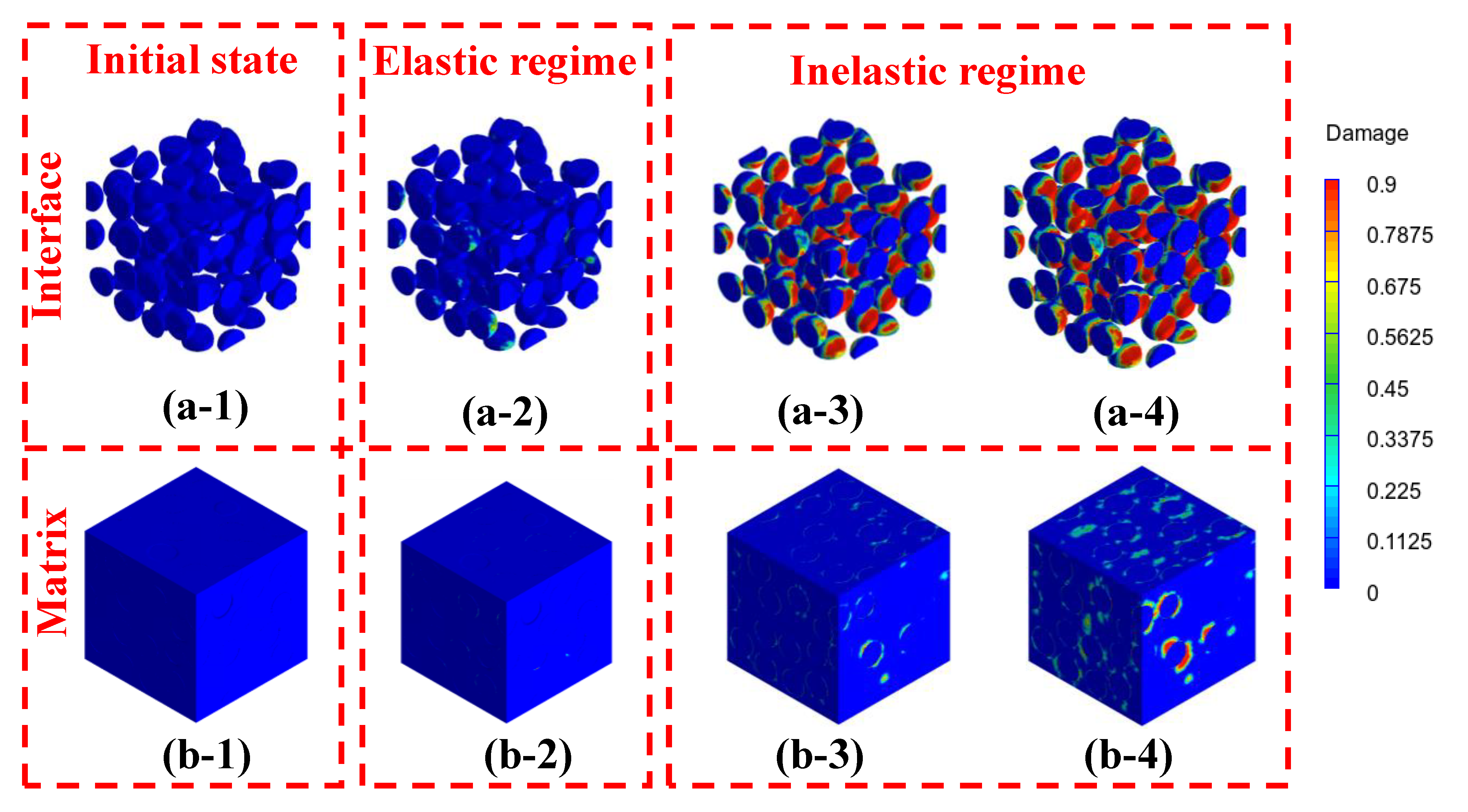
| Fiber Content (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 6501 | 3.92 | 1.691 | 0.468 | 0.014 | 0.687 | 0.0014 |
| 10% | 10,298 | 4.53 | 1.701 | 0.502 | 0.015 | 0.702 | 0.0018 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyngdoh, G.A.; Doner, S.; Nayak, S.; Das, S. Finite Element-Based Numerical Simulations to Evaluate the Influence of Wollastonite Microfibers on the Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Cementitious Composites. Materials 2021, 14, 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164435
Lyngdoh GA, Doner S, Nayak S, Das S. Finite Element-Based Numerical Simulations to Evaluate the Influence of Wollastonite Microfibers on the Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Cementitious Composites. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyngdoh, Gideon A., Sami Doner, Sumeru Nayak, and Sumanta Das. 2021. "Finite Element-Based Numerical Simulations to Evaluate the Influence of Wollastonite Microfibers on the Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Cementitious Composites" Materials 14, no. 16: 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164435
APA StyleLyngdoh, G. A., Doner, S., Nayak, S., & Das, S. (2021). Finite Element-Based Numerical Simulations to Evaluate the Influence of Wollastonite Microfibers on the Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Cementitious Composites. Materials, 14(16), 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164435







