Size Effect of a Piezoelectric Patch on a Rectangular Plate with the Neural Network Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical Model
2.1. Dynamic Equation of the Thin Plate
2.2. Neural Network Modeling
3. Case Study
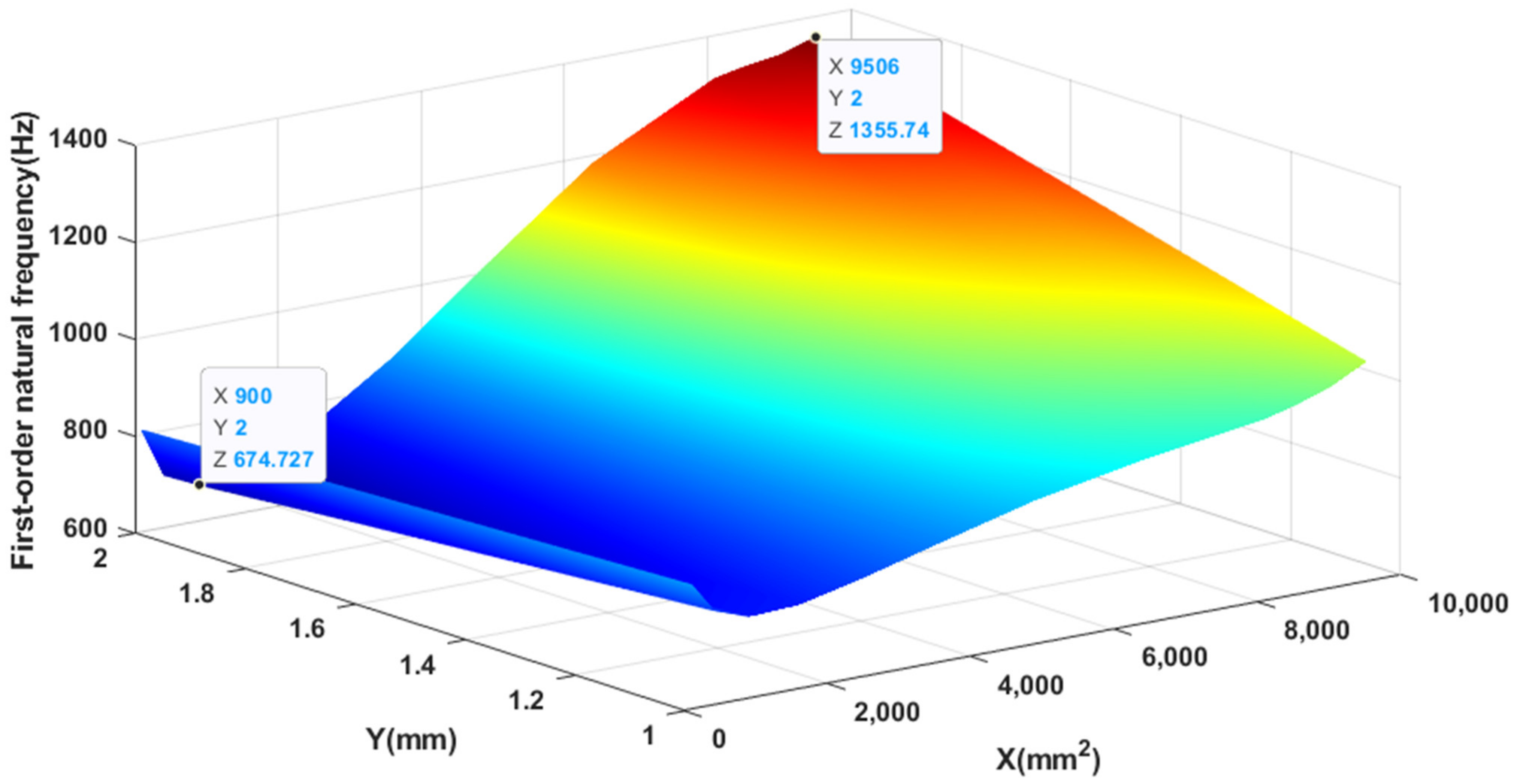
3.1. CASE 1: Input Side Length and Thickness
3.2. CASE 2: Input Area and Thickness
3.3. CASE 3: Input Volume
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katzir, S. The discovery of the piezoelectric effect. Arch. Hist. Exact Sci. 2003, 57, 61–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krommer, M.; Irschik, H. A Reissner-Mindlin-type plate theory including the direct piezoelectric and the pyroelectric effect. Acta Mech. 2000, 141, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, H.S.; Tseng, C.I. Distributed vibration control and identification of coupled elastic/piezoelectric systems: Finite element formulation and applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1991, 5, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Takezawa, A. Topology optimization of piezoelectric smart structures for minimum energy consumption under active control. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 58, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, Z. Dynamic topology optimization of piezoelectric structures with active control for reducing transient response. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2014, 281, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, H.S.; Tseng, C.I. Distributed piezoelectric sensor/actuator design for dynamic measurement/control of distributed parameter systems: A piezoelectric finite element approach. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 138, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, Y. Functionally graded piezoelectric cantilever beam under load. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2004, 74, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, H.S.; Zhong, J.P. Adaptive piezoelectric shell structures: Theory and experiments. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 1993, 7, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J. On laminated composite plates with integrated sensors and actuators. Eng. Struct. 1999, 21, 568–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Raudys, S.J.; Jain, A.K. Small sample size effects in statistical pattern recognition: Recommendations for practitioners. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, S. Robot manipulator control using neural networks: A survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 285, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-J.; Tan, M. Sliding mode control for flexible-link manipulators based on adaptive neural networks. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2018, 15, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufman: Burlington, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mair, C.; Kadoda, G. An investigation of machine learning based prediction systems. J. Syst. Softw. 2000, 53, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, H. User-friendly optimization approach of fed-batch fermentation conditions for the production of iturin A using artificial neural networks and support vector machine. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Gerlich, D.W. Machine learning in cell biology–teaching computers to recognize phenotypes. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarca, A.L.; Carey, V.J. Machine learning and its applications to biology. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernick, M.N.; Yang, Y. Machine learning in medical imaging. RadioGraphics 2010, 27, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Wei, J.S. Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural networks. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C. Machine learning in medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varian, H. Artificial Intelligence, Economics, and Industrial Organization; 0898-2937; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Milačić, L.; Jović, S. Application of artificial neural network with extreme learning machine for economic growth estimation. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2017, 465, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, M.; Singh, T. Prediction of blast-induced ground vibration using artificial neural network. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebraeel, N.; Lawley, M. Residual life predictions from vibration-based degradation signals: A neural network approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Dandy, G.C. The use of artificial neural networks for the prediction of water quality parameters. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadrakakis, M.; Lagaros, N.D. Structural optimization using evolution strategies and neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1998, 156, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.Z.; Xu, Y. A phase field and deep-learning based approach for accurate prediction of structural residual useful life. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 383, 113885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolpour, A.R.; Mailah, M. Self-learning active vibration control of a flexible plate structure with piezoelectric actuator. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2010, 18, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.; Kim, J. Dynamics of elastic-piezoelectric two-layer beams using spectral element method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 4403–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H. Dynamics modelling of beams with shunted piezoelectric elements. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 268, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofooei, F.R.; Nikkhoo, A. Application of active piezoelectric patches in controlling the dynamic response of a thin rectangular plate under a moving mass. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 2429–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
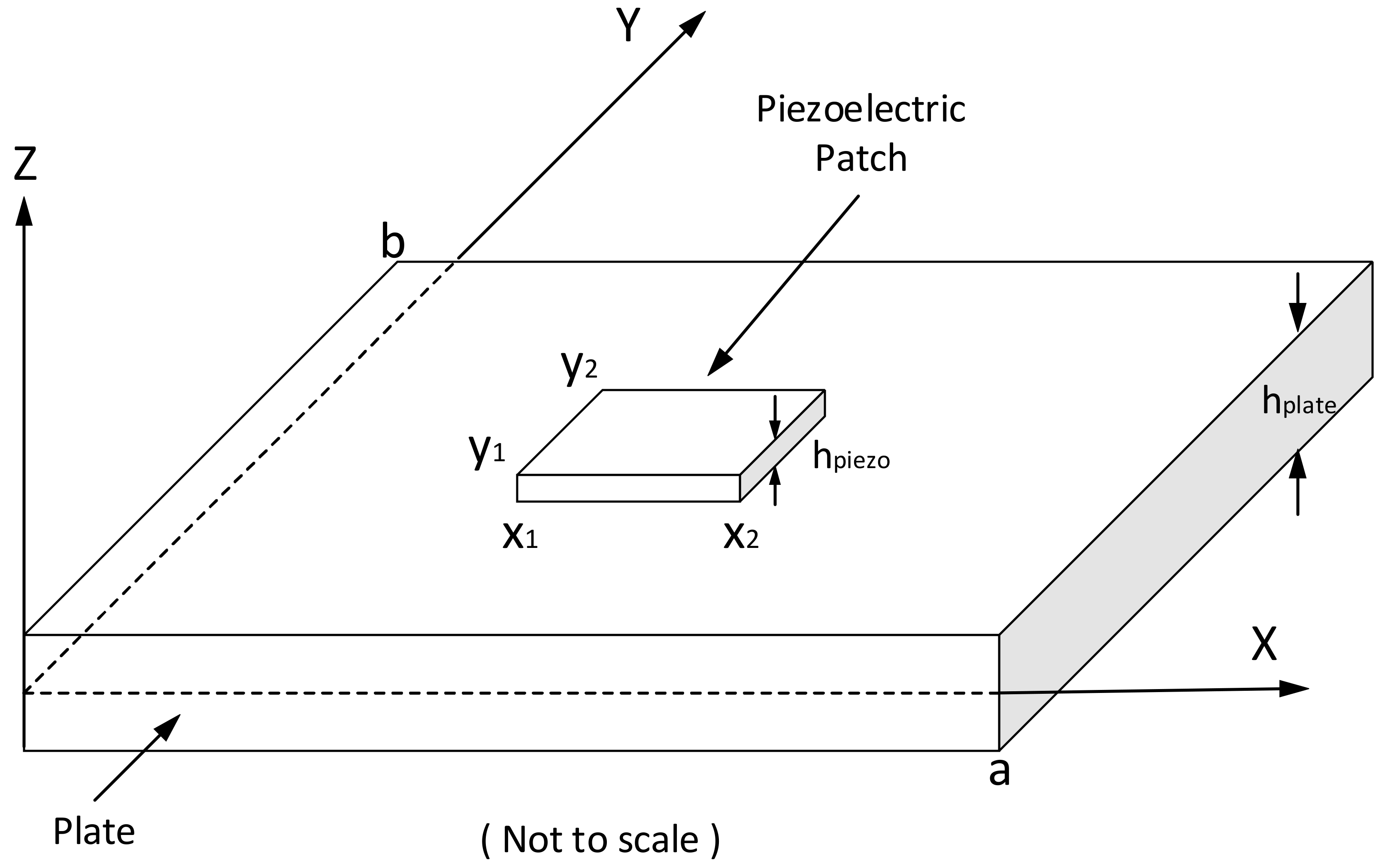

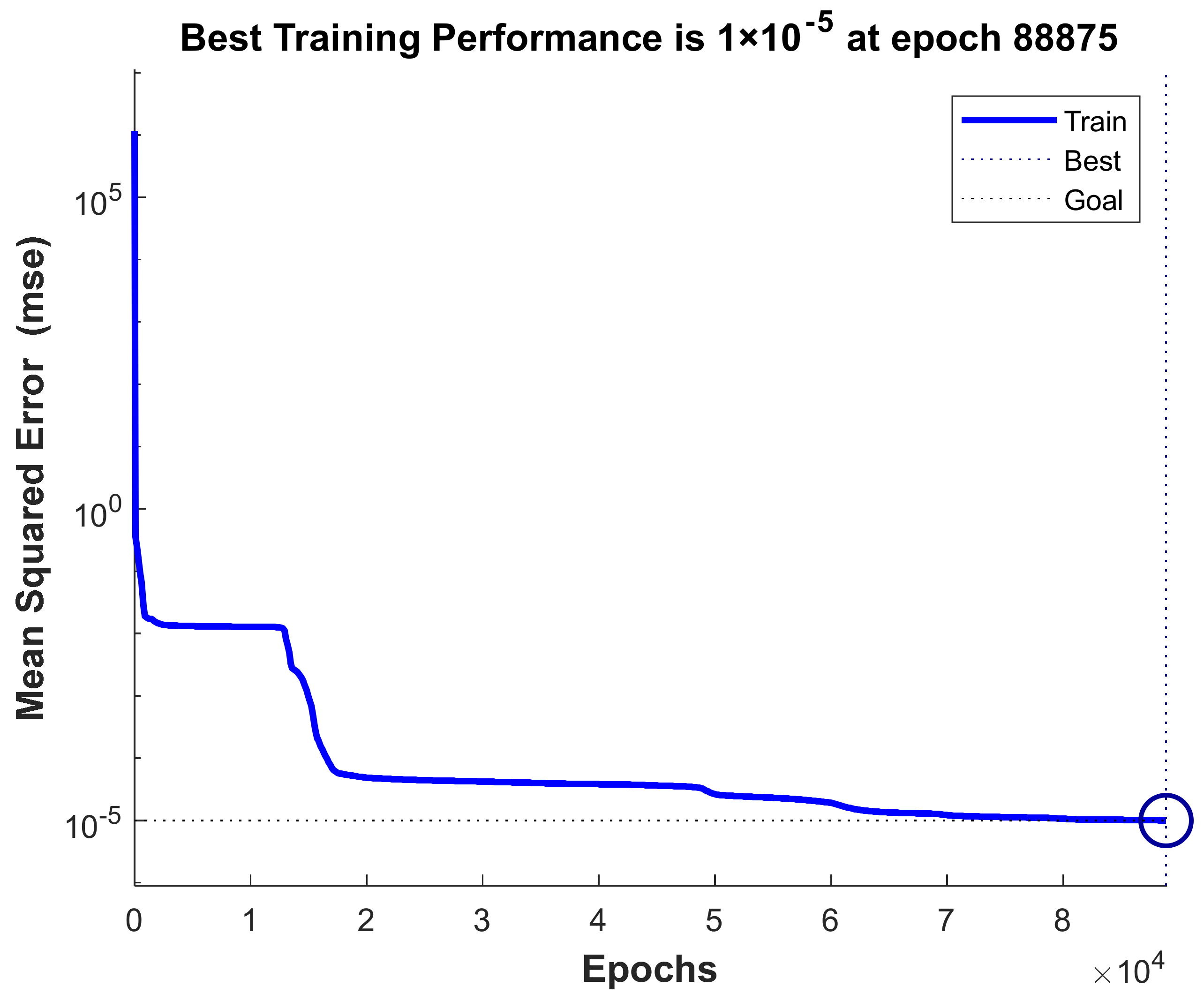


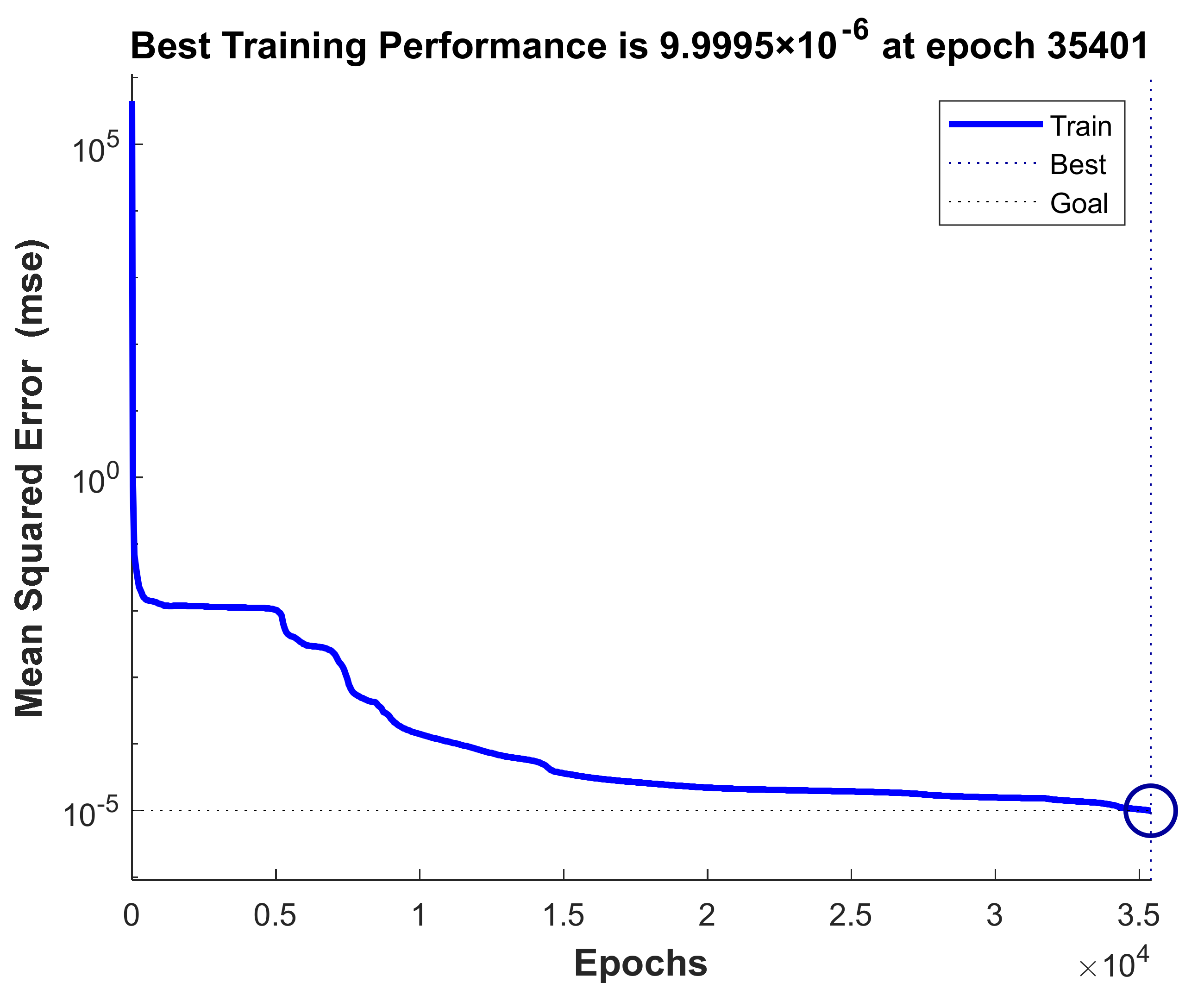

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length , mm | 100 |
| Width , mm | 100 |
| Thickness , mm | 1.0 |
| Density , | 2700 |
| Modulus of elasticity , Pa | 70 × |
| Poisson ratio | 0.33 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length , mm | 1.0~100 |
| Width , mm | 1.0~100 |
| Thickness , mm | 1.0~2.0 |
| Density , | 2500 |
| Modulus of elasticity , Pa | 56 × |
| Poisson ratio | 0.36 |
| Length | Thickness/mm | First-Order Natural Frequency/Hz | Error/% | Displacement Amplitude/mm | Error/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMSOL | ANN | COMSOL | ANN | ||||
| 10.0 | 1.0 | 856.87 | 856.87 | 0.00 | 0.69 × | 0.72 × | 4.35 |
| 15.0 | 1.1 | 816.18 | 816.18 | 0.00 | 1.38 × | 1.32 × | −4.35 |
| 20.0 | 1.2 | 778.09 | 778.10 | 0.00 | 2.11 × | 2.09 × | −0.95 |
| 22.5 | 1.3 | 757.29 | 757.29 | 0.00 | 2.33 × | 2.35 × | 0.86 |
| 27.5 | 1.4 | 733.13 | 733.13 | 0.00 | 2.91 × | 2.90 × | −0.34 |
| 35.0 | 1.5 | 722.68 | 722.68 | 0.00 | 3.82 × | 3.83 × | 0.26 |
| 40.0 | 1.6 | 725.77 | 725.77 | 0.00 | 4.20 × | 4.21 × | 0.24 |
| 57.5 | 1.7 | 841.62 | 841.62 | 0.00 | 7.18 × | 7.13 × | −0.70 |
| 65.0 | 1.8 | 930.04 | 930.04 | 0.00 | 8.63 × | 8.61 × | −0.23 |
| 82.5 | 1.9 | 1202.42 | 1202.42 | 0.00 | 17.46 × | 17.45 × | −0.06 |
| 97.5 | 2.0 | 1355.75 | 1356.81 | 0.08 | 15.87 × | 15.69 × | −1.13 |
| Area | Thickness/mm | First-Order Natural Frequency/Hz | Error/% | Displacement Amplitude/mm | Error/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMSOL | ANN | COMSOL | ANN | ||||
| 100 | 1.0 | 856.87 | 856.87 | 0.00 | 0.69 × | 0.83 × | 20.23 |
| 400 | 1.1 | 787.51 | 787.51 | 0.00 | 2.38 × | 2.29 × | −3.74 |
| 900 | 1.2 | 750.04 | 750.05 | 0.00 | 4.27 × | 4.28 × | 0.13 |
| 1600 | 1.3 | 751.44 | 751.44 | 0.00 | 6.07 × | 6.10 × | 0.47 |
| 2500 | 1.4 | 791.77 | 791.77 | 0.00 | 7.94 × | 7.91 × | −0.39 |
| 3600 | 1.5 | 867.70 | 867.70 | 0.00 | 10.29 × | 10.29 × | −0.05 |
| 4900 | 1.6 | 982.22 | 982.22 | 0.00 | 13.87 × | 13.74 × | −0.93 |
| 6400 | 1.7 | 1117.52 | 1117.52 | 0.00 | 18.99 × | 18.98 × | −0.07 |
| 8100 | 1.8 | 1238.61 | 1238.61 | 0.00 | 23.26 × | 23.22 × | −0.16 |
| Area | Thickness/mm | First-Order Natural Frequency/Hz | Error/% | Displacement Amplitude/mm | Error/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMSOL | ANN | COMSOL | ANN | ||||
| 100 | 1.0 | 856.87 | 856.87 | 0.00 | 0.69 × | 0.83 × | 20.23 |
| 4 × 25 | 869.34 | −1.43 | 1.06 × | −21.39 | |||
| 2.5 × 40 | 878.65 | −2.48 | 1.34 × | −38.20 | |||
| 2 × 50 | 881.17 | −2.76 | 1.37 × | −39.56 | |||
| 400 | 1.1 | 787.51 | 787.51 | 0.00 | 2.38 × | 2.29 × | −3.74 |
| 16 × 25 | 790.67 | −0.40 | 2.46 × | −7.17 | |||
| 10 × 40 | 816.50 | −3.55 | 3.23 × | −29.18 | |||
| 5 × 80 | 851.29 | −7.49 | 3.52 × | −35.04 | |||
| 900 | 1.2 | 750.04 | 750.05 | 0.00 | 4.27 × | 4.28 × | 0.13 |
| 25 × 36 | 754.72 | −0.62 | 4.42 × | −3.27 | |||
| 18 × 50 | 783.56 | −4.28 | 5.52 × | −22.48 | |||
| 15 × 60 | 802.80 | −6.57 | 6.52 × | −34.40 | |||
| 10 × 90 | 831.08 | −9.75 | 5.50 × | −22.18 | |||
| 1600 | 1.3 | 751.44 | 751.44 | 0.00 | 6.07 × | 6.10 × | 0.47 |
| 32 × 50 | 763.72 | −1.61 | 6.62 × | −7.82 | |||
| 20 × 80 | 802.82 | −6.40 | 9.79 × | −37.65 | |||
| 2500 | 1.4 | 791.77 | 791.77 | 0.00 | 7.94 × | 7.91 × | −0.39 |
| 40 × 62.5 | 804.92 | −1.63 | 9.12 × | −13.30 | |||
| Volume | First-Order Natural Frequency/Hz | Error/% | Displacement Amplitude/mm | Error/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMSOL | ANN | COMSOL | ANN | |||
| 405.00 | 764.52 | 764.52 | 0.00 | 0.70 × | 2.89 × | 310.74 |
| 506.25 | 786.92 | 786.92 | 0.00 | 3.33 × | 2.60 × | −22.14 |
| 2531.25 | 700.76 | 674.24 | −3.78 | 3.07 × | 10.73 × | 249.79 |
| 2890.00 | 736.39 | 736.39 | 0.00 | 4.63 × | 7.41 × | 59.82 |
| 3307.50 | 813.20 | 813.20 | 0.00 | 11.63 × | 14.74 × | 26.74 |
| 4000.00 | 780.70 | 780.70 | 0.00 | 6.13 × | 4.81 × | −21.48 |
| 7290.00 | 953.00 | 953.00 | 0.00 | 12.41 × | 12.42 × | 0.09 |
| 10,890.00 | 1120.99 | 1341.22 | 19.65 | 23.11 × | 27.42 × | 18.66 |
| 13,537.50 | 1161.84 | 1161.84 | 0.00 | 22.07 × | 23.27 × | 5.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, H.; Zhang, J.; Fan, M. Size Effect of a Piezoelectric Patch on a Rectangular Plate with the Neural Network Model. Materials 2021, 14, 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123240
Min H, Zhang J, Fan M. Size Effect of a Piezoelectric Patch on a Rectangular Plate with the Neural Network Model. Materials. 2021; 14(12):3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123240
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Hequn, Jie Zhang, and Mu Fan. 2021. "Size Effect of a Piezoelectric Patch on a Rectangular Plate with the Neural Network Model" Materials 14, no. 12: 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123240
APA StyleMin, H., Zhang, J., & Fan, M. (2021). Size Effect of a Piezoelectric Patch on a Rectangular Plate with the Neural Network Model. Materials, 14(12), 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123240






