Ion-Enhanced Etching Characteristics of sp2-Rich Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbons in CF4 Plasmas and O2 Plasmas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Procedures
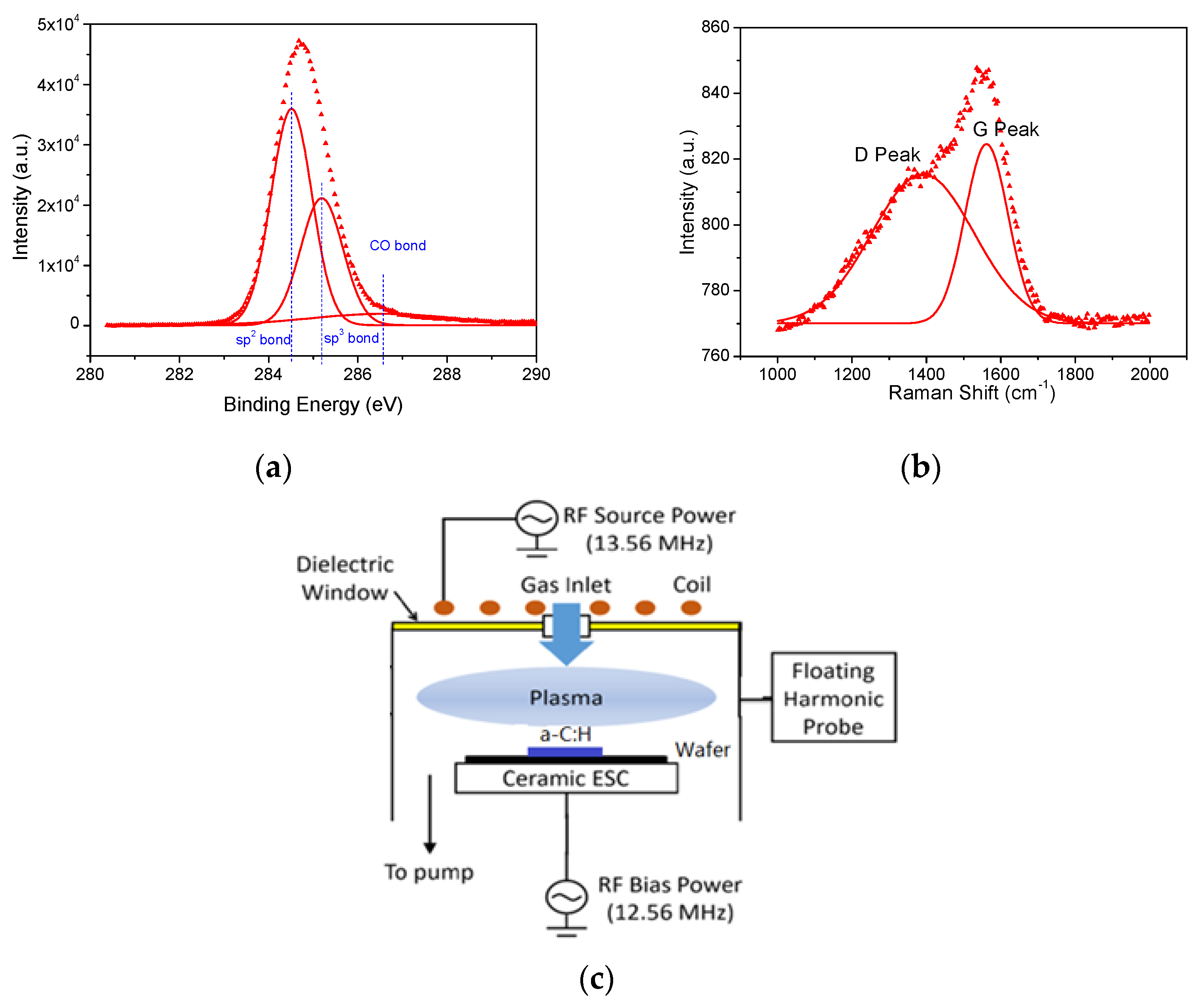
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Y.-M.; Valdes-Garcia, A.; Han, S.-J.; Farmer, D.B.; Meric, I.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dimitrakopoulos, C.; Grill, A.; Avouris, P.; et al. Wafer-scale graphene integrated circuit. Science 2011, 332, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.-S.; Pei, S.; Ren, W.; Tang, D.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Li, F.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.-M. Field emission of single-layer graphene films prepared by electrophoretic deposition. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliev, A.E.; Oh, J.; Kozlov, M.E.; Kuznetsov, A.A.; Fang, S.; Fonseca, A.F.; Ovalle, R.; Lima, M.D.; Haque, M.H.; Gartstein, Y.N.; et al. Giant-Stroke, Superelastic Carbon nanotube aerogel muscles. Science 2009, 323, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueckes, T.; Kim, K.; Joselevich, E.; Tseng, G.Y.; Cheung, C.-L.; Lieber, C.M. Carbon nanotube–based nonvolatile random access memory for molecular computing. Science 2000, 289, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhi, L.; Müllen, K. Transparent, Conductive graphene electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Gogotsi, Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, X.; Su, D.S.; Centi, G.; Perathoner, S. Catalysis by hybrid sp2/sp3nanodiamonds and their role in the design of advanced nanocarbon materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8438–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akay, G. Plasma generating—Chemical looping catalyst synthesis by microwave plasma shock for nitrogen fixation from air and hydrogen production from water for agriculture and energy technologies in global warming prevention. Catalysts 2020, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2002, 37, 129–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, B.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, N.-E.; Shon, J.W. Ultrahigh Selective Etching of SiO2 Using an Amorphous Carbon Mask in Dual-Frequency Capacitively Coupled C4F8/CH2F2 / O2/Ar Plasmas. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D135–D141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.H.; Park, J.W.; Yun, D.H.; Kim, K.N.; Yeom, G.Y. Etch properties of amorphous carbon material using RF pulsing in the O2/N2/CHF3 plasma. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 8577–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, J. Amorphous carbon. Adv. Phys. 1986, 35, 317–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; O’Reilly, E.P. Electronic and atomic structure of amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 2946–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Hard amorphous (diamond-like) carbons. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1991, 21, 199–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman, Z.L.; Efstathiadis, H.; Smith, F.W. Thermal stability of diamondlike carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 80, 3068–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Ho, K.M. Structure, dynamics, and electronic properties of diamondlike amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, N.; Girardeau, T.; Camelio, S.; Barranco, A.; Vouagner, D.; Breelle, E. Effects of negative low self-bias on hydrogenated amorphous carbon films deposited by PECVD technique. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Turban, G. Etching process of hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) thin films in a dual ECR-r.f. nitrogen plasma. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, R.D.; Polk, J.E.; Goebel, D.; Johnson, L.K. Carbon sputtering yield measurements at grazing incidence. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, C.; Schlüter, M.; Jacob, W. Chemical sputtering of carbon films by argon ions and molecular oxygen at cryogenic temperatures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 224106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, T.T.; Weber, J.J.-W.; Colsters, P.G.J.; Mestrom, D.M.H.G.; Van De Sanden, M.R.; Engeln, R.R. Synergistic etch rates during low-energetic plasma etching of hydrogenated amorphous carbon. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 013302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salonen, E.; Nordlund, K.; Keinonen, J.; Wu, C.H. Swift chemical sputtering of amorphous hydrogenated carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 195415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralchenko, V.G.; Kononenko, T.V.; Foursova, T.; Loubnin, E.N. Comparison of laser and O2 plasma etching of diamond-like carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1993, 2, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachova, O.; Alves, M.; Swart, J.; Braga, E.; Cescato, L. CF4 plasma etching of materials used in microelectronics manufacturing. Microelectron. J. 2000, 31, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andújar, J.; Vives, M.; Corbella, C.; Bertran, E. Growth of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films in pulsed d.c. methane discharges. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.C.; Lee, S.C.; Wei, C.H.; Tyan, S.L. Correlation between ID⁄IG ratio from visible raman spectra and sp2/sp3 ratio from XPS spectra of annealed hydrogenated DLC film. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobolewski, M.A.; Olthoff, J.K.; Wang, Y. Ion energy distributions and sheath voltages in a radio-frequency-biased, inductively coupled, high-density plasma reactor. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 3966–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Hsieh, C.-T. Activation energy for oxygen chemisorption on carbon at low temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L.; Ojha, S. The chemical sputtering of graphite in an oxygen plasma. Vacuum 1976, 26, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, A.; Bittencourt, C.; Pireaux, J.J.; Van Lier, G.; Charlier, J.C. Radio-frequency plasma functionalization of carbon nanotubes surface O2, NH3, and CF4 treatments. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 74308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, N.; Ananina, O.; Ryazanova, A. Fluorine and carbon fluoride interaction with a diamond surface: Quantum-chemical modeling. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 124, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, W.; Hopf, C.; Schlüter, M. Chemical sputtering of carbon materials due to combined bombardment by ions and atomic hydrogen. Phys. Scr. 2006, T124, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.; Sawin, H.H. Plasma kinetic study of silicon-dioxide removal with fluorocompounds in a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition chamber. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2007, 51, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbruchel, C. Universal energy dependence of physical and ion-enhanced chemical etch yields at low ion energy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1989, 55, 1960–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, C.; Von Keudell, A.; Jacob, W. Chemical sputtering of hydrocarbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, C.; Von Keudell, A.; Jacob, W. Chemical sputtering of hydrocarbon films by low-energy Ar ion and H atom impact. Nucl. Fusion 2002, 42, L27–L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, P.; Gissler, W. Chemical sputtering of carbon films by low energy N2+ ion bombardment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1996, 5, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froberg, R.W.; Essenhigh, R. Reaction order and activation energy of carbon oxidation during internal burning. Symp. (Int.) Combust. 1979, 17, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| a-C:H | b(eV−1/2) | |
|---|---|---|
| in CF4 plasmas | 0.4 | 156 |
| in O2 plasmas | 0.65 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.; Chae, H. Ion-Enhanced Etching Characteristics of sp2-Rich Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbons in CF4 Plasmas and O2 Plasmas. Materials 2021, 14, 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112941
Li J, Kim Y, Han S, Chae H. Ion-Enhanced Etching Characteristics of sp2-Rich Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbons in CF4 Plasmas and O2 Plasmas. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112941
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Yongjae Kim, Seunghun Han, and Heeyeop Chae. 2021. "Ion-Enhanced Etching Characteristics of sp2-Rich Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbons in CF4 Plasmas and O2 Plasmas" Materials 14, no. 11: 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112941
APA StyleLi, J., Kim, Y., Han, S., & Chae, H. (2021). Ion-Enhanced Etching Characteristics of sp2-Rich Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbons in CF4 Plasmas and O2 Plasmas. Materials, 14(11), 2941. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112941






