Magnetic and Transport Properties of New Dual-Phase High-Entropy Alloy FeRhIrPdPt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
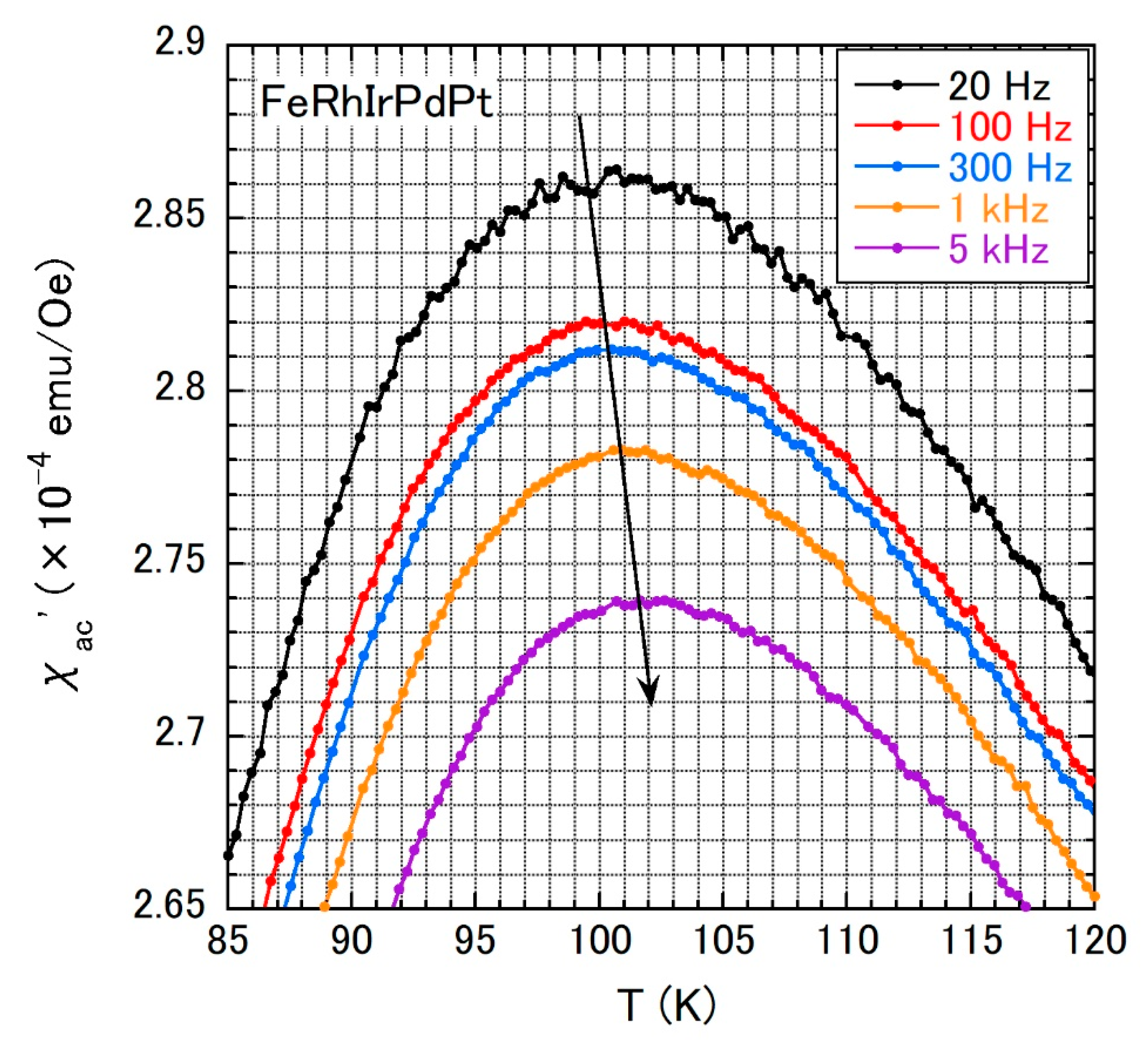
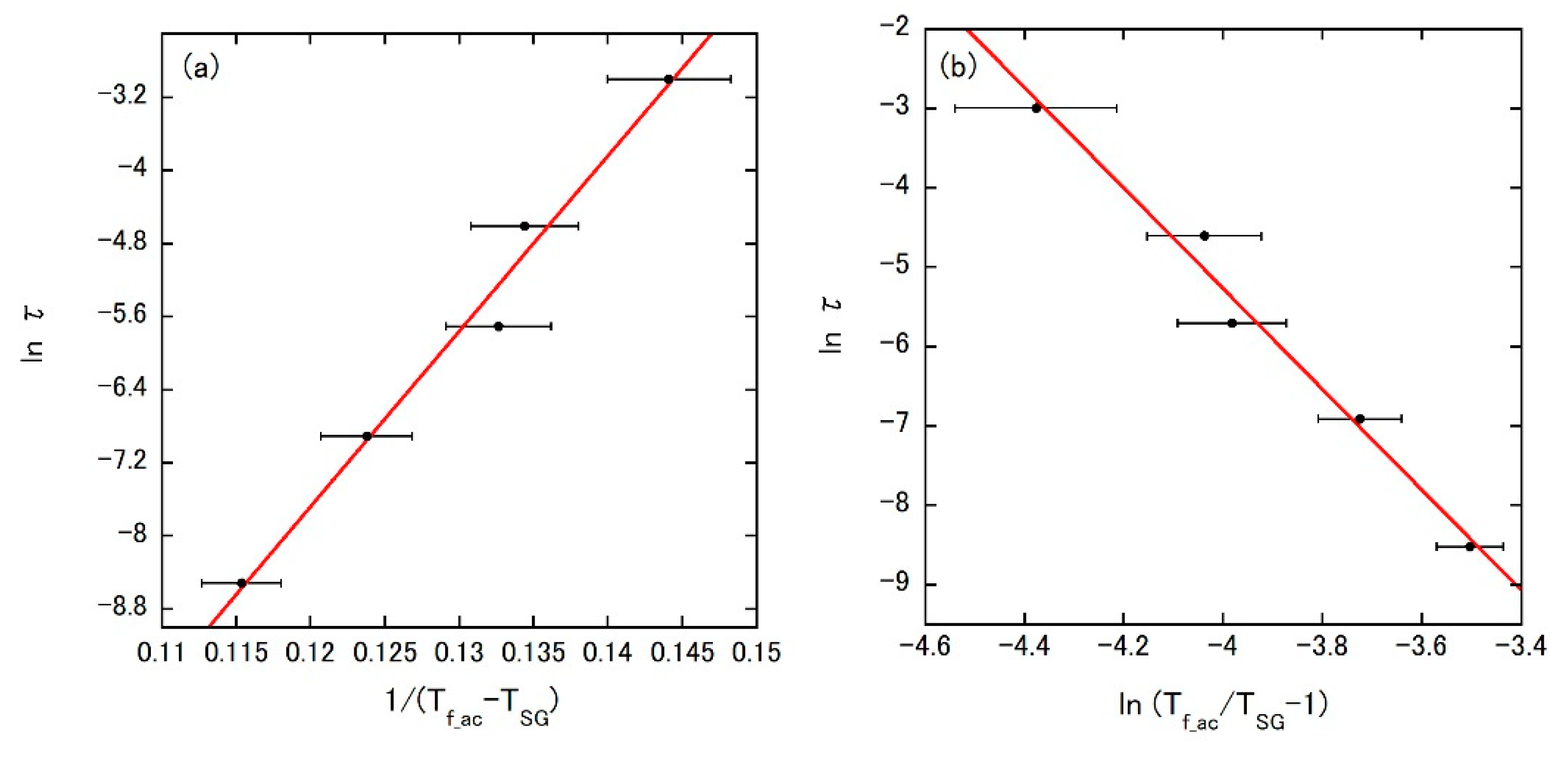
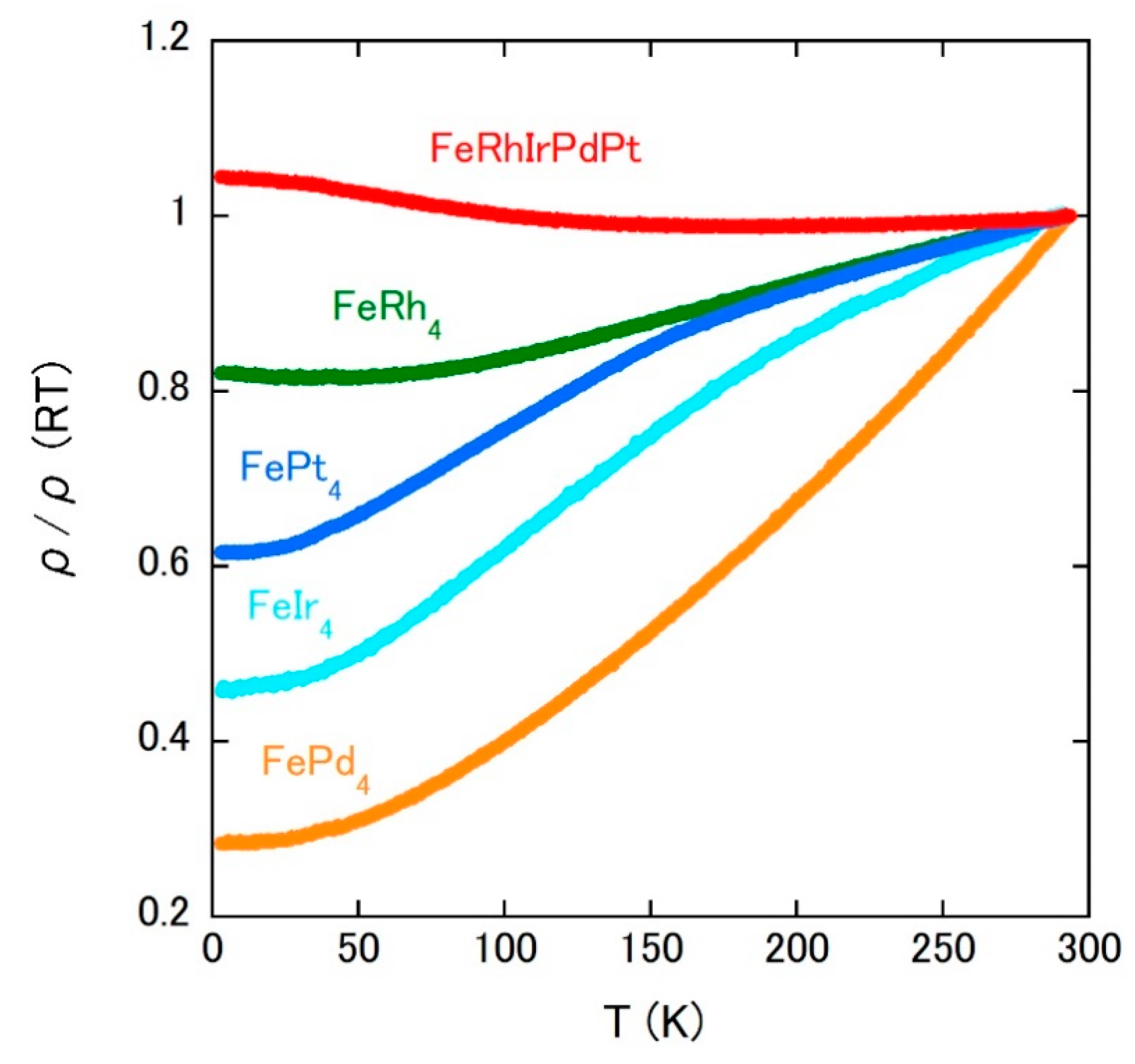
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, M.C.; Yeh, J.-W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.-W.; Ranganathan, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. High-Entropy Alloys, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Musicό, B.L.; Gilbert, D.; Ward, T.Z.; Page, K.; George, E.; Yan, J.; Mandrus, D.; Keppens, V. The emergent field of high entropy oxides: Design, prospects, challenges, and opportunities for tailoring material properties. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 040912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, L.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ning, S.; Jia, B.; et al. High-entropy-stabilized chalcogenides with high thermoelectric performance. Science 2021, 371, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, Z.; Du, T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J. A multicomponent γ-type (Gd1/6Tb1/6Dy1/6Tm1/6Yb1/6Lu1/6)2Si2O7 disilicate with outstanding thermal stability. Mater. Res. Lett. 2020, 8, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Microstructure and compressive properties of multicomponent Alx(TiVCrMnFeCoNiCu)100−x high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454–455, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cava, R.J. High-entropy alloy superconductors: Status, opportunities, and challenges. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 090301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, N.; Kitagawa, J. New high-entropy alloy superconductor Hf21Nb25Ti15V15Zr24. Res. Phys. 2019, 13, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Hamamoto, S.; Ishizu, N. Cutting Edge of High-Entropy Alloy Superconductors from the Perspective of Materials Research. Metals 2020, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, B.; Liaw, P.K. Corrosion-resistant high-entropy alloys: A review. Metals 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M.; Nagase, T.; Hori, T.; Matsugaki, A.; Sekita, A.; Nakano, T. Novel TiNbTaZrMo high-entropy alloys for metallic biomaterials. Scr. Mater. 2017, 129, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Wang, G.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R.; Hu, L.; Wang, C. Highly efficient decomposition of ammonia using high-entropy alloy catalysts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firstov, G.S.; Kosorukova, T.A.; Koval, Y.N.; Odnosum, V.V. High Entropy Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S499–S503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, L.; Suo, H.L.; Lu, Z.P. Rare-earth high-entropy alloys with giant magnetocaloric effect. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-K.; Chen, T.-J.; Chu, P.-C.; Yeh, J.-W.; Lin, S.-J. Electrical, magnetic, and Hall properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, D.; James, A.D.N.; Harris-Lee, E.I.; Lagos, D.A.; O’Neill, D.; Tsuda, N.; Toyoki, K.; Kotani, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Bei, H.; et al. Bulk and element-specific magnetism of medium-entropy and high-entropy Cantor-Wu alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 174405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, O.; Friák, M.; Dudová, M.; Holec, D.; Šob, M.; Kriegner, D.; Holý, V.; Beran, P.; George, E.P.; Neugebauer, J.; et al. Magnetic properties of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 014437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Rao, Z.; Ikeda, Y.; Dutta, B.; Körmann, F.; Neugebauer, J.; Raabe, D. Role of magnetic ordering for the design of quinary TWIP-TRIP high entropy alloys. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2020, 4, 033601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Dutta, B.; Körmann, F.; Lu, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Kwiatkowski da Silva, A.; Wiedwald, U.; Spasova, M.; Farle, M.; et al. Beyond Solid Solution High-Entropy Alloys: Tailoring Magnetic Properties via Spinodal Decomposition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Nedelcos, A.; Leong, Z.; Morley, N.A. Study of dual-phase functionalisation of NiCoFeCr-Alx multicomponent alloys for the enhancement of magnetic properties and magneto-caloric effect. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Kang, K.; Marshal, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Seol, J.-B.; Lee, H.M.; Choi, P.-P. Effects of phase composition and elemental partitioning on soft magnetic properties of AlFeCoCrMn high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 171, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H. A unit cell parameter refinement program on windows computer. J. Crystallogr. 2003, 45, 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nolze, G.; Kraus, W. PowderCell 2.0 for Windows. Powder Diffr. 1998, 13, 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.-H.; Lewis, L.H.; Moodenbaugh, A.R. Large magnetic entropy change in the metallic antiperovskite Mn3GaC. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 10128–10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Skaguchi, K. New room-temperature ferromagnet: B-added Pd0.75Mn0.25 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 468, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, J.; Shirakawa, N.; Setoguchi, Y.; Tsubota, M.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kitagawa, J. Hill Plot Focusing on Ce Compounds with High Magnetic Ordering Temperatures and Consequent Study of Ce2AuP3. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 3559–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Terada, H.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M.; Nose, A.; Tanaka, S. Composition effect in ferromagnetic properties of Tb3Co3Ga. Res. Phys. 2019, 15, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Terada, H.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M.; Kitagawa, J. The Impact of the Composition Effect on Ferromagnetic Properties of Tb2Co2Ga. Metals 2019, 9, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.K.; Kulkarni, R.; Manfrinetti, P.; Fornasini, M.L.; Bernini, C. Structure and magnetic properties of RCu4Mn (R=La-Gd). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 054424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcano, N.; Gómez Sal, J.C.; Espeso, J.I.; De Teresa, J.M.; Algarabel, P.A.; Paulsen, C.; Iglesias, J.R. Mesoscopic Magnetic States in Metallic Alloys with Strong Electronic Correlations: A Percolative Scenario for CeNi1−xCux. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 166406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroder, J.; Gooth, J.; Schnelle, W.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C. Observation of spin glass behavior in chiral Mn48Fe34Si18 with a β-Mn related structure. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 055327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souletie, J.; Tholence, J.L. Critical slowing down in spin glasses and other glasses: Fulcher versus power law. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Garg, A.; Gupta, R. Spin glass-like phase below ∼210 K in magnetoelectric gallium ferrite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 112904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydosh, J.A. Spin Glasses: An Experimental Introduction; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, J.; Sakaguchi, K.; Hara, T.; Hirano, F.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M. Interstitial Atom Engineering in Magnetic Materials. Metals 2020, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Sales, B.C.; Stocks, G.M.; Samolyuk, G.D.; Daene, M.; Weber, W.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bei, H. Tailoring the physical properties of Ni-based single-phase equiatomic alloys by modifying the chemical complexity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troparevsky, M.C.; Morris, J.R.; Kent, P.R.C.; Lupini, A.R.; Stocks, G.M. Criteria for Predicting the Formation of Single-Phase High-Entropy Alloys. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 011041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Gong, P.; Prades-Rodel, S.; Blatter, A.; Scanley, B.E.; Broadbridge, C.C.; Schroers, J. Noble metal high entropy alloys. Scr. Mater. 2017, 126, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusenko, K.V.; Khandarkhaeva, S.; Bykov, M.; Fedotenko, T.; Hanfland, M.; Sukhikh, A.; Gromilov, S.A.; Dubrovinsky, L.S. Face-Centered Cubic Refractory Alloys Prepared from Single-Source Precursors. Materials 2020, 13, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusenko, K.V.; Riva, S.; Carvalho, P.A.; Yusenko, M.V.; Arnaboldi, S.; Sukhikh, A.S.; Hanfland, M.; Gromilov, S.A. First hexagonal close packed high-entropy alloy with outstanding stability under extreme conditions and electrocatalytic activity for methanol oxidation. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.O.; Trofimov, E.A. Toward expanding the realm of high entropy materials to platinum group metals: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
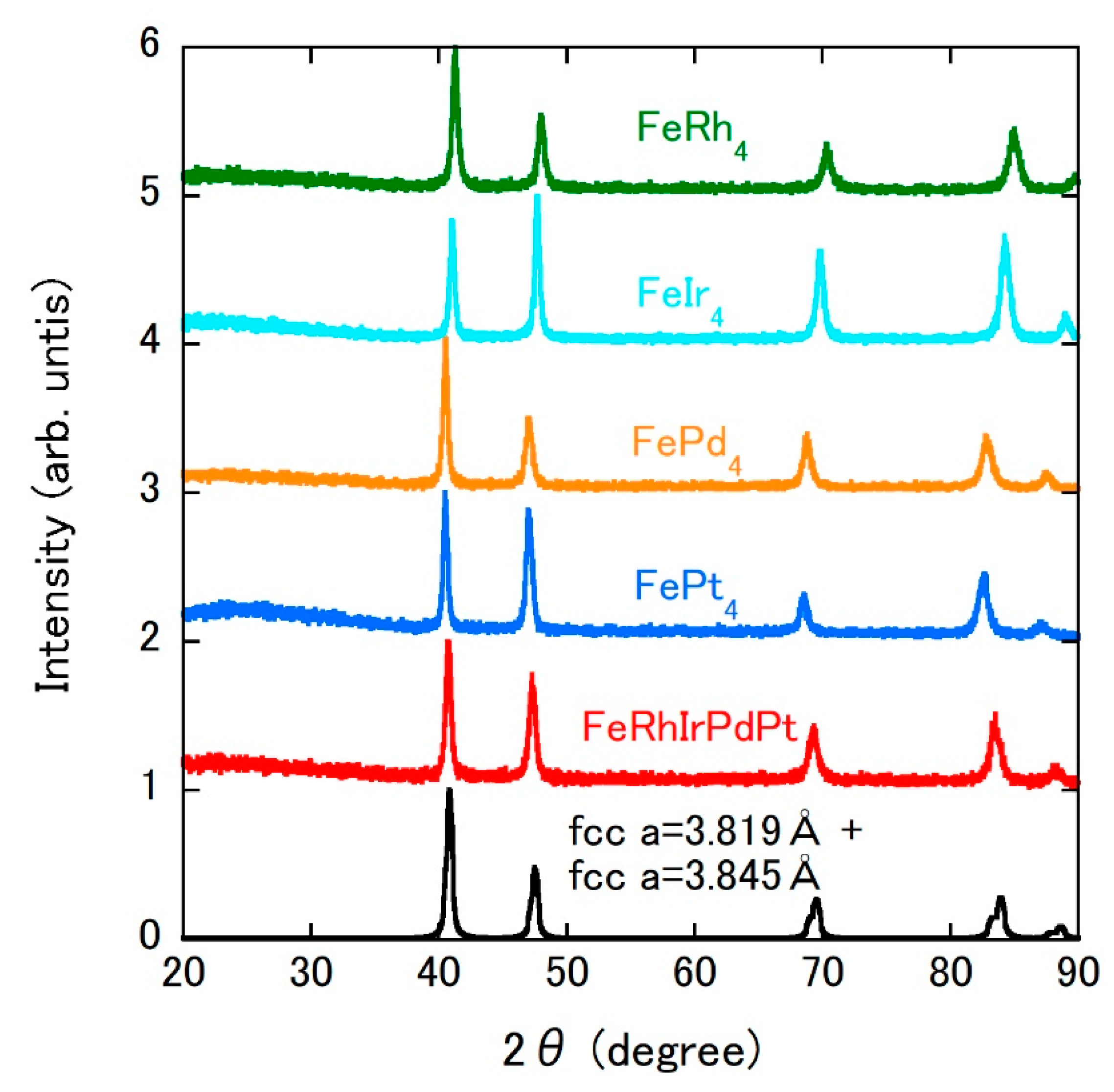
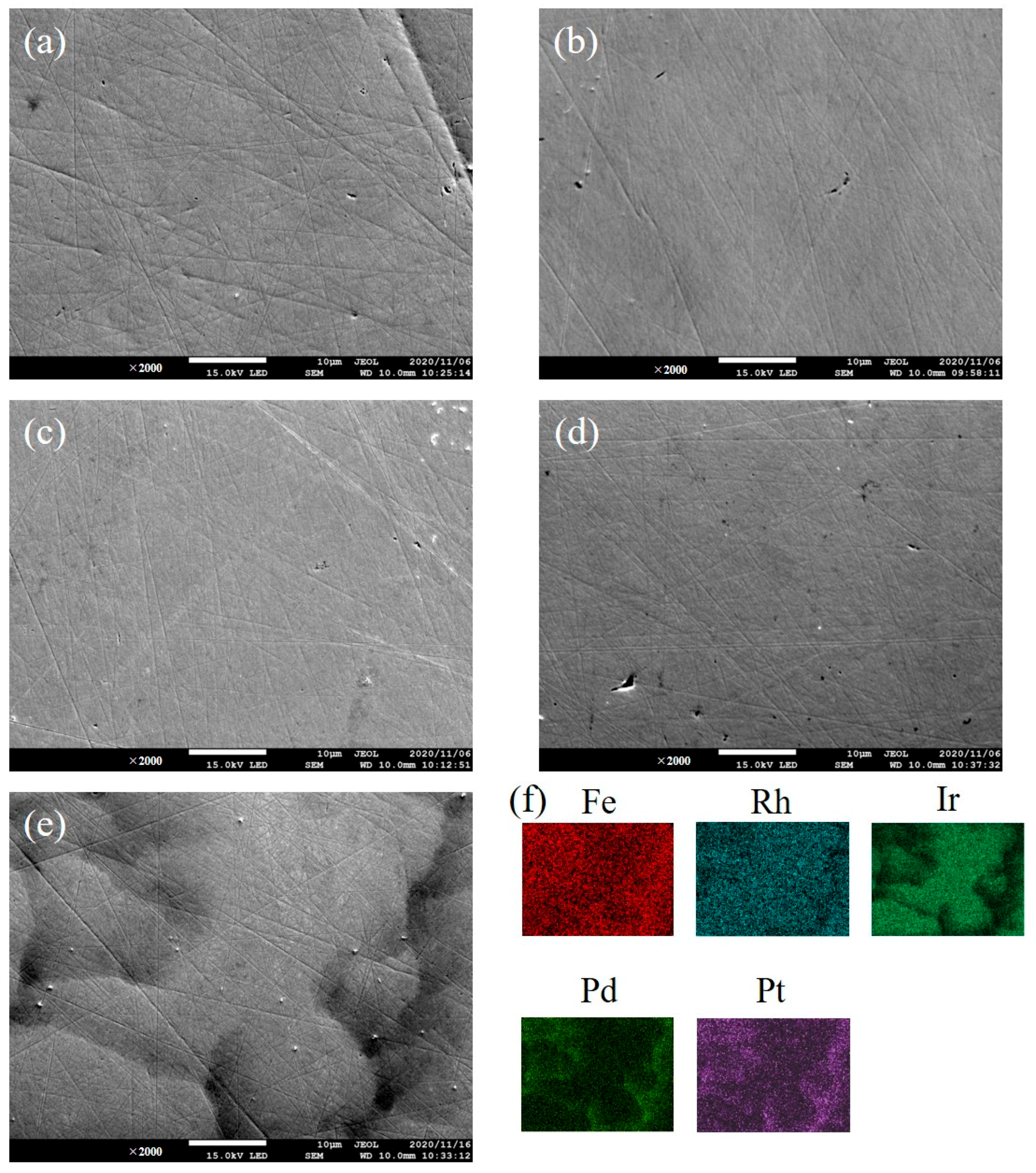

| Sample | Composition | Lattice Parameter (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| FeRh4 | Fe19.2(8)Rh80.8(8) | 3.782(1) |
| FeIr4 | Fe18.5(6)Ir81.5(6) | 3.807(1) |
| FePd4 | Fe19.3(9)Pd80.7(9) | 3.858(1) |
| FePt4 | Fe19.2(6)Pt80.8(6) | 3.871(2) |
| FeIrRhPtPd | main: Fe15.8(5)Rh24.5(5)Ir32.6(1)Pd10.7(6)Pt16.4(6) minor: Fe23.7(7)Rh14.0(8)Ir5.4(9)Pd32.5(9)Pt24.4(6) | 3.834(1) |
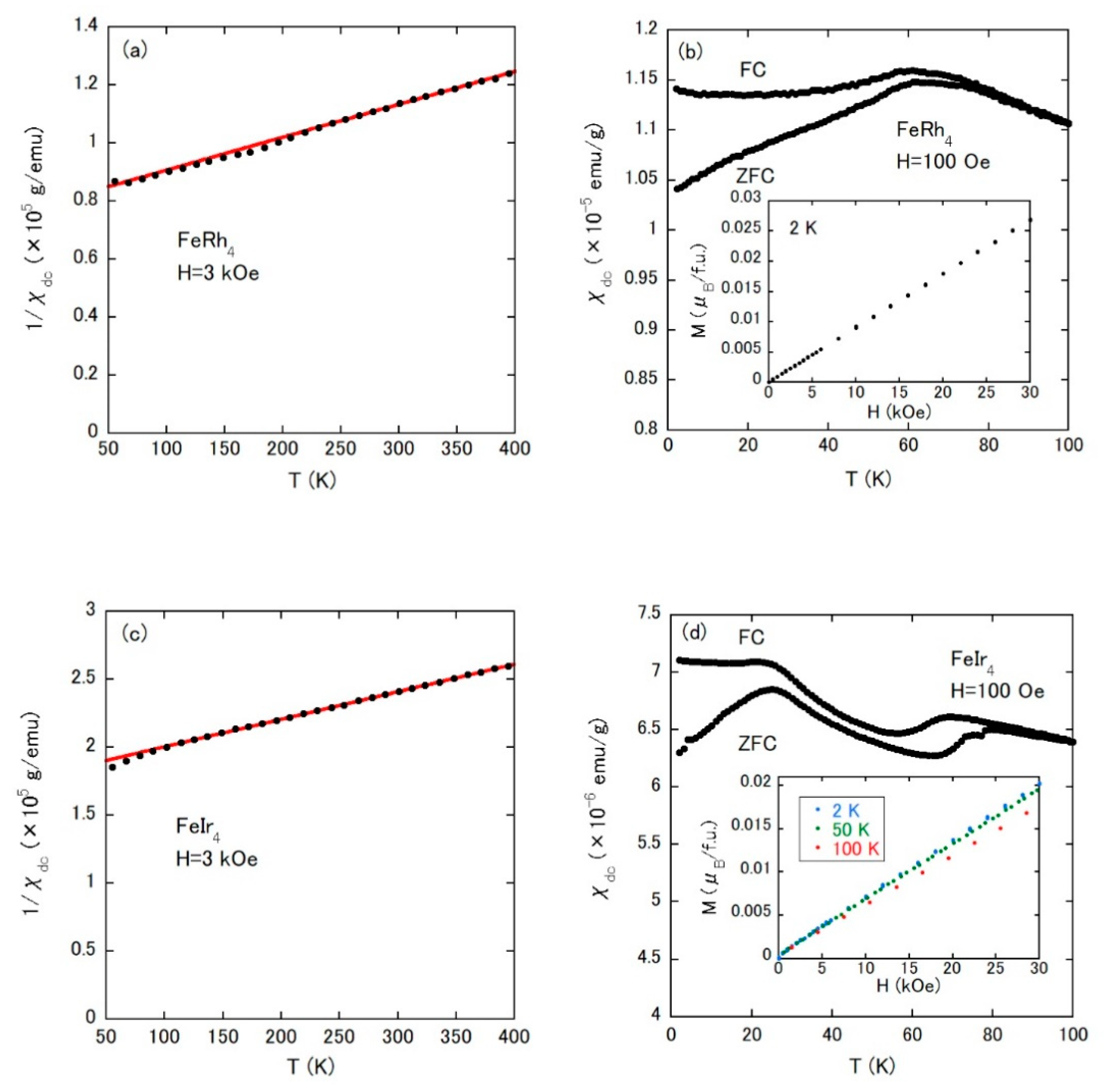
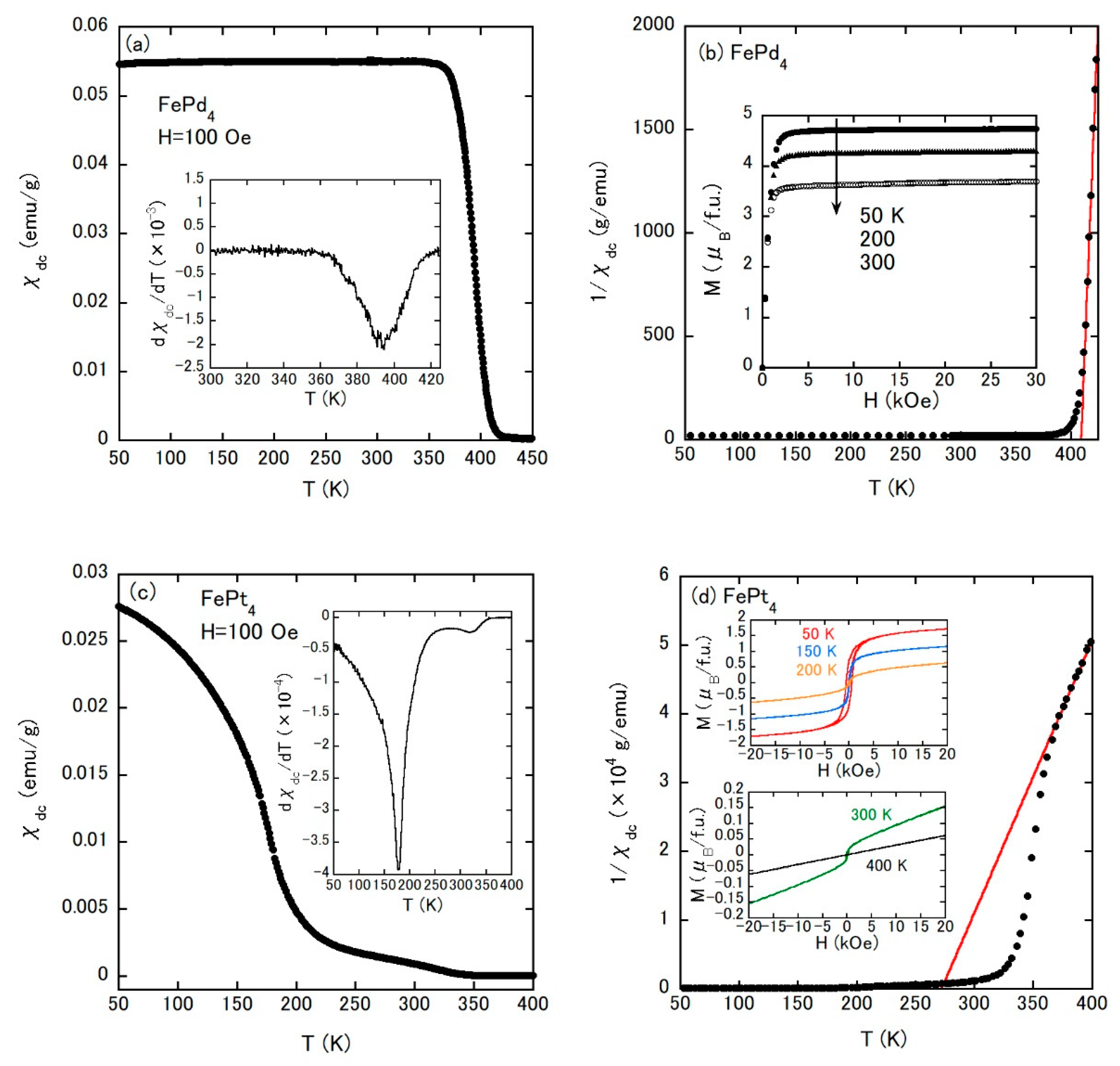
| Sample | Magnetism | Magnetic Ordering Temperature (K) | μeff (μB/Fe) | ΘCW (K) | ρ (RT) (μΩcm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeRh4 | SG | Tf = 59 | 5.74 | −700 | 39.0 |
| FeIr4 | SG | Tf = 23, 69 | 5.71 | −890 | 21.2 |
| FePd4 | FM | TC = 393 | 5.44 | 409 | 59.5 |
| FePt4 | FM | TC = 177, 317 | 4.11 | 272 | 107 |
| FeRhIrPdPt | SG +FM corr. | Tf = 90 | 3.40 | 308 | 70.8 |
| Model | τ0 (s) | Ea (K) | TSG (K) | zv |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vogel–Fulcher law | 4.8 × 10−14 | 192 | 93 | - |
| Critical scaling approach | 5.1 × 10−14 | - | 90 | 6.3 |
| Fe | Rh | Ir | Pd | Pt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 0 | −57 | −63 | −116 | −244 |
| Rh | −57 | 0 | −21 | 37 | −24 |
| Ir | −63 | −21 | 0 | 40 | 11 |
| Pd | −116 | 37 | 40 | 0 | −36 |
| Pt | −244 | −24 | 11 | −36 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baba, K.; Ishizu, N.; Nishizaki, T.; Kitagawa, J. Magnetic and Transport Properties of New Dual-Phase High-Entropy Alloy FeRhIrPdPt. Materials 2021, 14, 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112877
Baba K, Ishizu N, Nishizaki T, Kitagawa J. Magnetic and Transport Properties of New Dual-Phase High-Entropy Alloy FeRhIrPdPt. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112877
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaba, Kohei, Naoki Ishizu, Terukazu Nishizaki, and Jiro Kitagawa. 2021. "Magnetic and Transport Properties of New Dual-Phase High-Entropy Alloy FeRhIrPdPt" Materials 14, no. 11: 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112877
APA StyleBaba, K., Ishizu, N., Nishizaki, T., & Kitagawa, J. (2021). Magnetic and Transport Properties of New Dual-Phase High-Entropy Alloy FeRhIrPdPt. Materials, 14(11), 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112877







