Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi-Based Eutectic Shape Memory Alloy Produced via Selective Laser Melting In-Situ Alloying by Nb
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- heating to 500 °C and holding at 500 °C for 2 h;
- -
- heating to 900 °C and holding at 900 °C for 30 min;
- -
- heating to 900 °C and holding at 900 °C for 2 h.
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- -
- NiTiNb shape memory alloy can be produced by SLM in-situ alloying by Nb with a relative density of 99%.
- -
- The microstructure of the in-situ alloyed material consists of B2-NiTi matrix, fine NiTi + β-Nb eutectic phase, and residual unmelted Nb particles.
- -
- The use of increased laser spot size with simultaneous increase of layer thickness and laser power allows to obtain more homogeneous element distribution and homogeneous microstructure of NiTiNb alloy.
- -
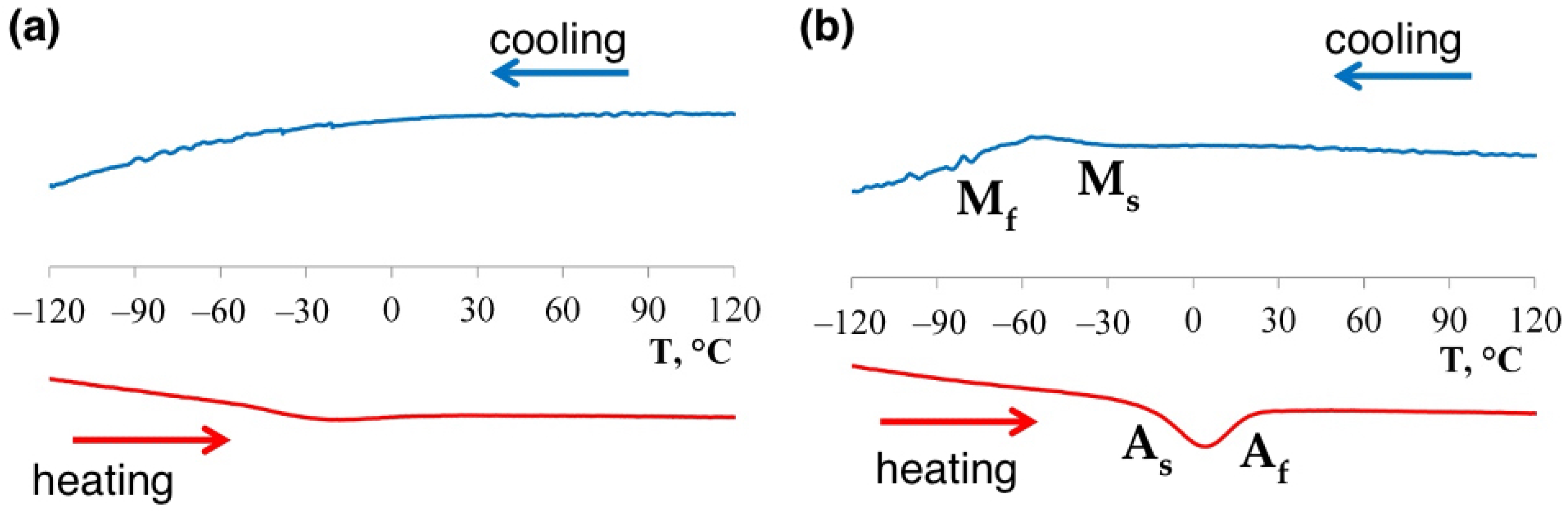
- The SLM in-situ alloying of NiTi by Nb allowed increasing the martensitic transformation hysteresis as compared to the alloy without Nb addition from 22 to 50 °C while the Af temperature increased from −5 to 22 °C.
- -
- Annealing of the in-situ alloyed material at 900 °C resulted in improved microstructural homogeneity and higher tensile strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Choi, E. Flexural capacity and crack-closing performance of NiTi and NiTiNb shape-memory alloy fibers randomly distributed in mortar beams. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 153, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, E.; Zhu, J.-N.; Popovich, A.; Popovich, V. A review of NiTi shape memory alloy as a smart material produced by additive manufacturing. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 30, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Jani, J.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A review of shape memory alloy research, applications and opportunities. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.-C.; Chen, L.; Lu, W.; Zhang, D. Phase transformation and deformation behavior of NiTi-Nb eutectic joined NiTi wires. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlari, K.; Shi, Q.; Li, K.; Xu, P.; Cao, P.; Liu, X. An investigation into the possibility to eliminate the microstructural defects of parts printed using a Ni-rich Ni-Ti elemental powder mixture. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BAO, Z.; GUO, S.; XIAO, F.; ZHAO, X. Development of NiTiNb in-situ composite with high damping capacity and high yield strength. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, L. Surface Modification of Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Technologies, Developments, and Future Interests. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Z.; Zhou, S.L.; Liu, W.X. A Study of NiTiNb Shape-Memory Alloy Pipe-Joint with Improved Properties. Mater. Sci. Forum 2002, 394–395, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xinqing, Z. Mechanical Properties and Transformation Behavior of NiTiNb Shape Memory Alloys. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.; Hai-chang, J.; Li-jian, R.; Li, X.; Xin-qing, Z. Mechanical behavior in NiTiNb shape memory alloys with low Nb content. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Guojun, M.; Xinqing, Z.; Huibin, X. Effects of Nb Content on Yield Strength of NiTiNb Alloys in Martensite State. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, S.L.; Ibeh, A.J.; Jakus, A.E.; Shah, R.N.; Dunand, D.C. NiTi-Nb micro-trusses fabricated via extrusion-based 3D-printing of powders and transient-liquid-phase sintering. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y. Processing Map of NiTiNb Shape Memory Alloy Subjected to Plastic Deformation at High Temperatures. Metals 2017, 7, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slipchenko, V.N.; Koval, Y.N.; Koshovy, O.V. Influence of casting technology on the phase transformation in NiTiNb alloys. J. Phys. IV 2003, 112, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wei, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; et al. Effect of process parameters on the phase transformation behavior and tensile properties of NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polozov, I.; Sufiiarov, V.; Kantyukov, A.; Razumov, N.; Goncharov, I.; Makhmutov, T.; Silin, A.; Kim, A.; Starikov, K.; Shamshurin, A.; et al. Microstructure, densification, and mechanical properties of titanium intermetallic alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing with high-temperature preheating using gas atomized and mechanically alloyed plasma spheroidized powders. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, A.; Polozov, I.; Sufiiarov, V.; Popovich, A. In-situ synthesis of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloy by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Joguet, D.; Robin, G.; Peltier, L.; Laheurte, P. In situ elaboration of a binary Ti–26Nb alloy by selective laser melting of elemental titanium and niobium mixed powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonelli, M.; Aboulkhair, N.T.; Cohen, P.; Murray, J.W.; Clare, A.T.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R.J.M. A comparison of Ti-6Al-4V in-situ alloying in Selective Laser Melting using simply-mixed and satellited powder blend feedstocks. Mater. Charact. 2018, 143, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanemann, T.; Carter, L.N.; Habschied, M.; Adkins, N.J.E.; Attallah, M.M.; Heilmaier, M. In-situ alloying of AlSi10Mg+Si using Selective Laser Melting to control the coefficient of thermal expansion. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 795, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Demyanetz, A.; Koptyug, A.; Popov, V.V. In-situ Alloying as a Novel Methodology in Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 10th International Conference Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties (NAP), Sumy, Ukraine, 9–13 November 2020; pp. 02SAMA05-1–02SAMA05-4. [Google Scholar]
- Polozov, I.; Sufiiarov, V.; Kantyukov, A.; Popovich, A. Selective Laser Melting of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloy using elemental powders: Effect of process parameters and post-treatment on microstructure, composition, and properties. Intermetallics 2019, 112, 106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Qin, P.; Liang, S.X.; Sercombe, T.B.; Zhang, L.C. Selective laser melting of Ti–35Nb composite from elemental powder mixture: Microstructure, mechanical behavior and corrosion behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hao, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Cui, L.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Z. The microstructure of a selective laser melting (SLM)-fabricated NiTi shape memory alloy with superior tensile property and shape memory recoverability. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 19, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Duan, L.; Li, F.; Che, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, S.; Yan, C. Effect of laser energy density on the evolution of Ni4Ti3 precipitate and property of NiTi shape memory alloys prepared by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 869, 159338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, I.S.; Masaylo, D.V.; Orlov, A.; Razumov, N.G.; Obrosov, A. The Effect of Laser Power on the Microstructure of the Nb-Si Based In Situ Composite, Fabricated by Laser Metal Deposition. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 822, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enneti, R.K.; Morgan, R.; Atre, S.V. Effect of process parameters on the Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of tungsten. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 71, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandwana, P.; Elliott, A.M.; Siddel, D.; Merriman, A.; Peter, W.H.; Babu, S.S. Powder bed binder jet 3D printing of Inconel 718: Densification, microstructural evolution and challenges. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, R.; Amato, G.; McCrum, D. Heat-activated prestressing of NiTiNb shape memory alloy wires. Eng. Struct. 2020, 206, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperovich, G.; Haubrich, J.; Gussone, J.; Requena, G. Correlation between porosity and processing parameters in TiAl6V4 produced by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2016, 105, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Krakhmalev, P.; Yadroitsava, I. Hierarchical design principles of selective laser melting for high quality metallic objects. Addit. Manuf. 2014, 7, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Mohanty, S.; Hattel, J.H. Multiphysics modelling of lack-of-fusion voids formation and evolution in IN718 made by multi-track/multi-layer L-PBF. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 139, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.A.; Calta, N.P.; Khairallah, S.A.; Wang, J.; Depond, P.J.; Fong, A.Y.; Thampy, V.; Guss, G.M.; Kiss, A.M.; Stone, K.H.; et al. Dynamics of pore formation during laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.; Miyazaki, S.; Otsuka, K.; Nishida, N. Effects of Nb Addition on the Microstructure of Ti–Ni Alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 1992, 33, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yan, E.H.; Huang, S.K.; Wen, Y.H. Influence of Ni/Ti ratio and Nb addition on martensite transformation behavior of NiTiNb alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhou, K.; Kuang, T. Selective laser melting of tungsten-copper functionally graded material. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufiiarov, V.S.; Popovich, A.A.; Borisov, E.V.; Polozov, I.A.; Masaylo, D.V.; Orlov, A.V. The Effect of Layer Thickness at Selective Laser Melting. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tan, X.P.; Du, Z.; Chandra, S.; Sun, Z.; Lim, C.W.J.; Tor, S.B.; Lim, C.S.; Wong, C.H. Additive manufacturing of NiTi shape memory alloys using pre-mixed powders. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 271, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, M.; Liao, G.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X. Martensitic transformation involved mechanical behaviors and wide hysteresis of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
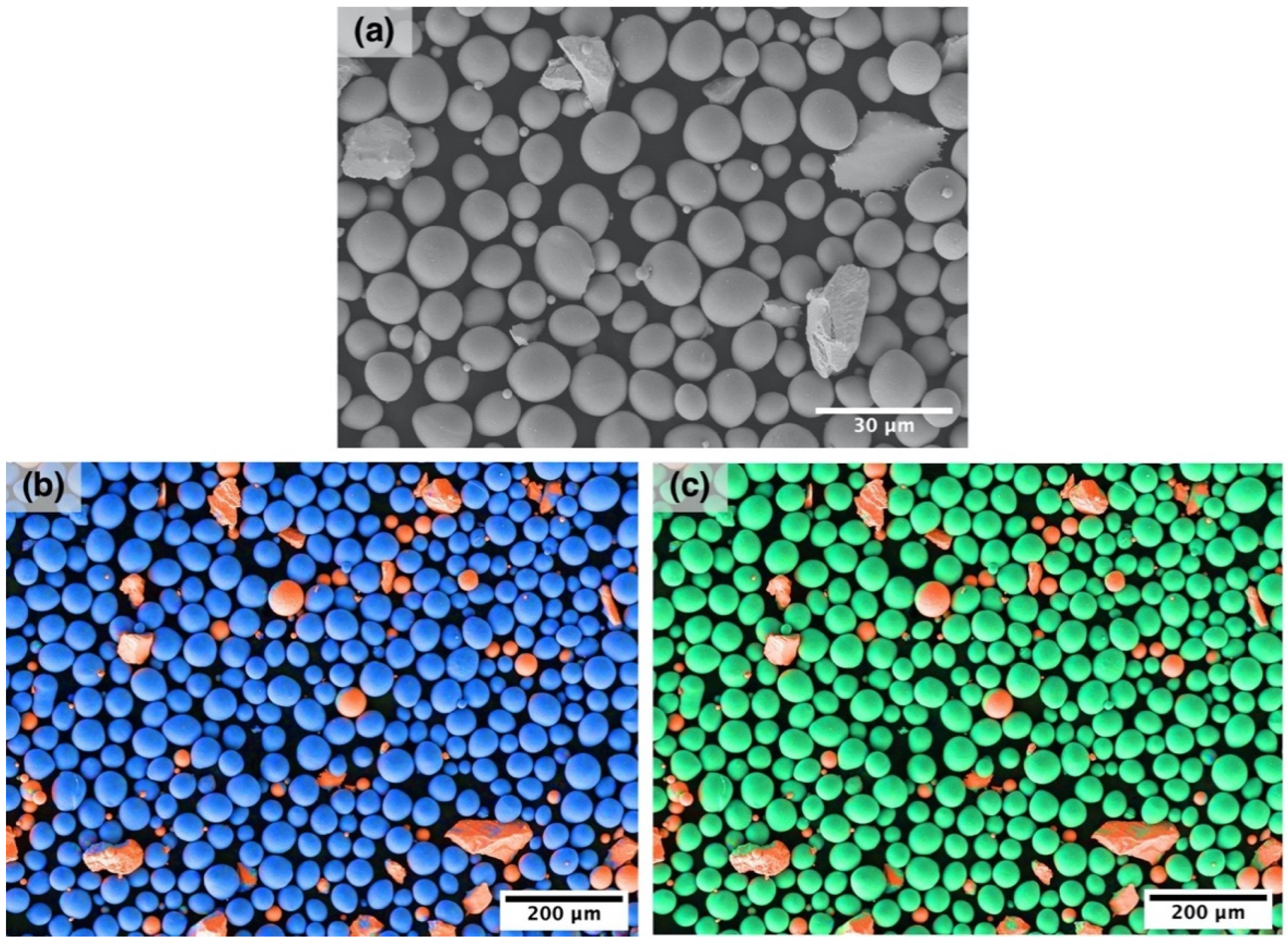
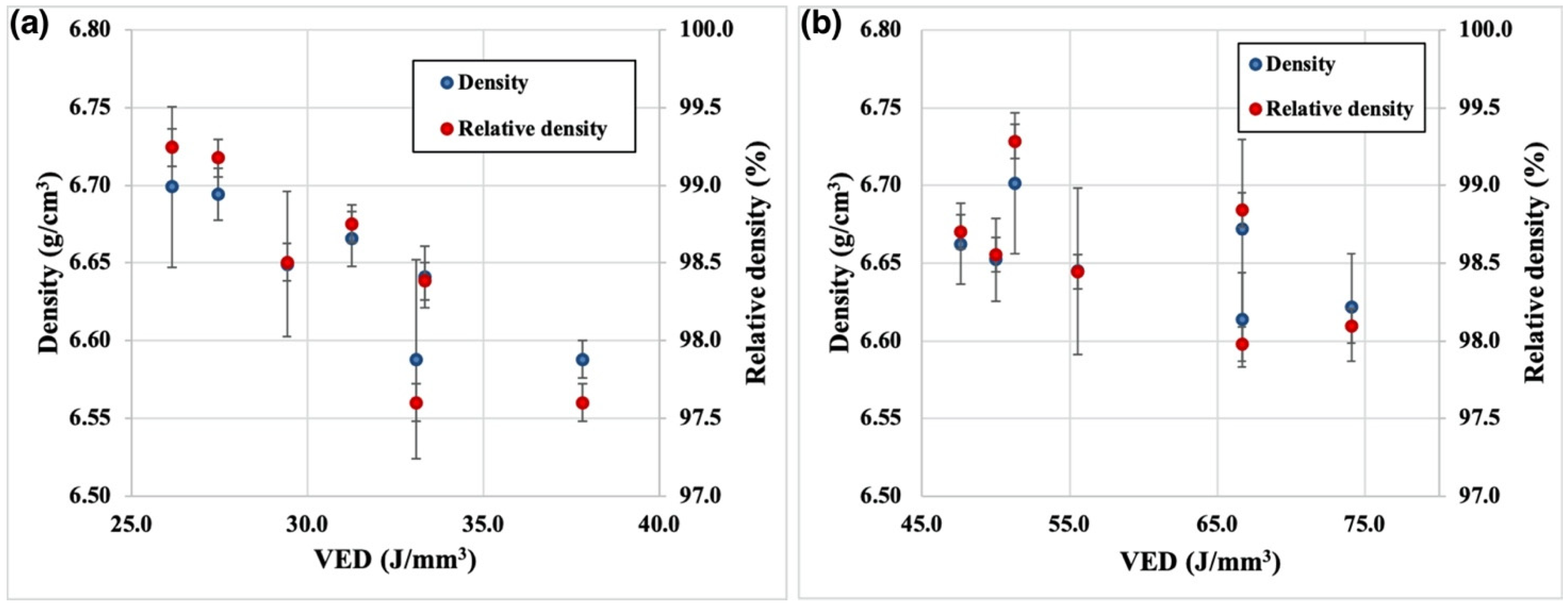
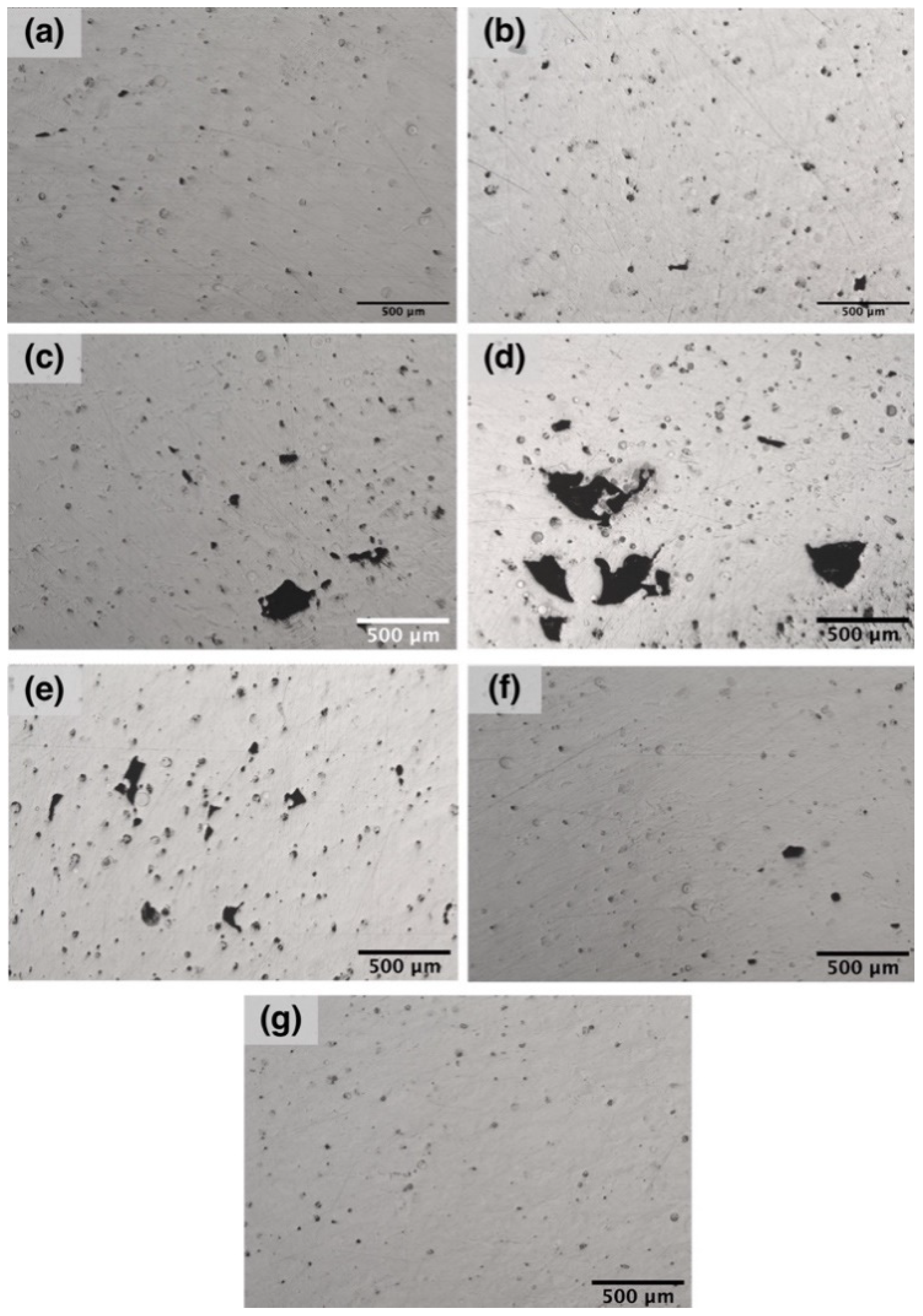
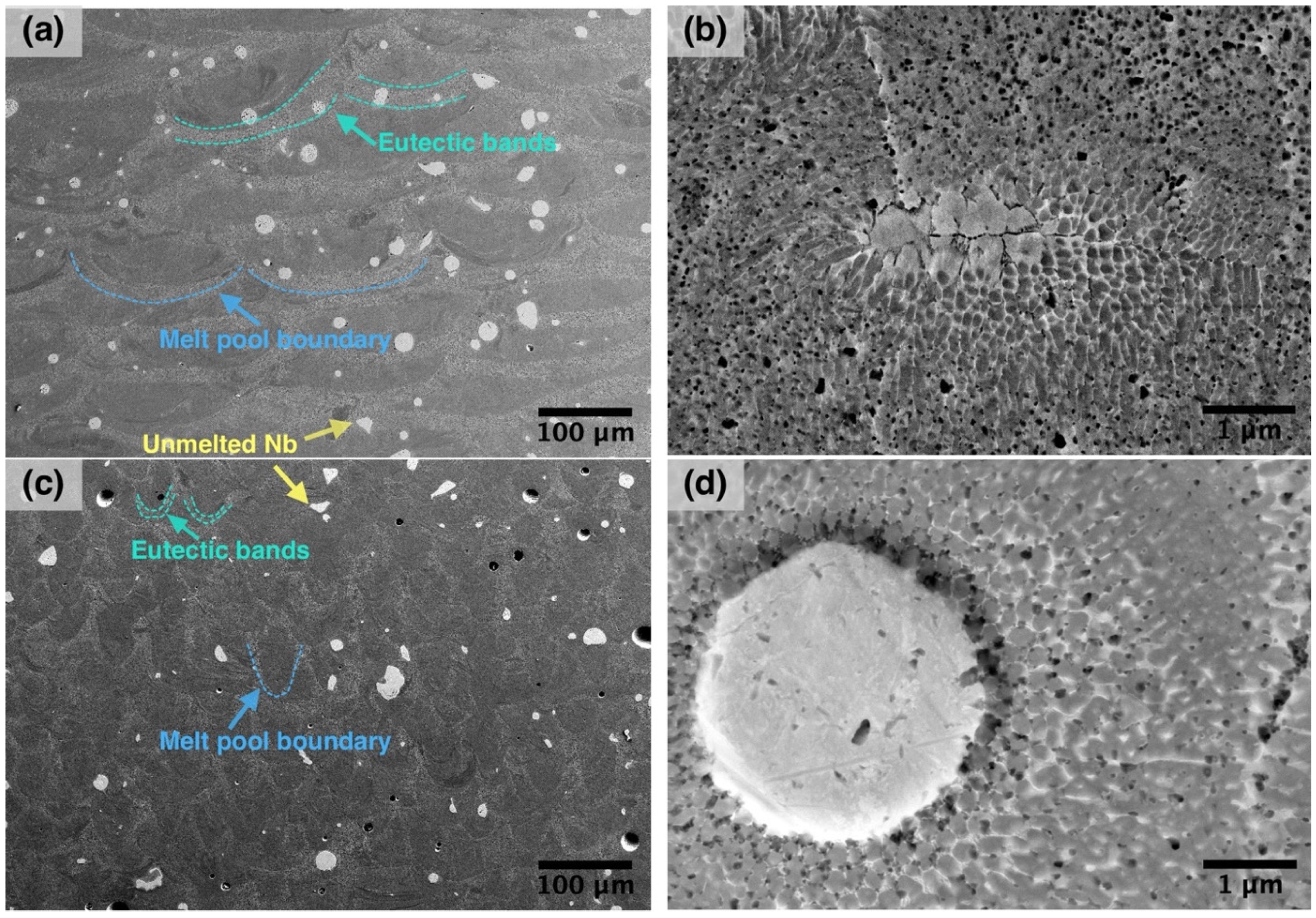
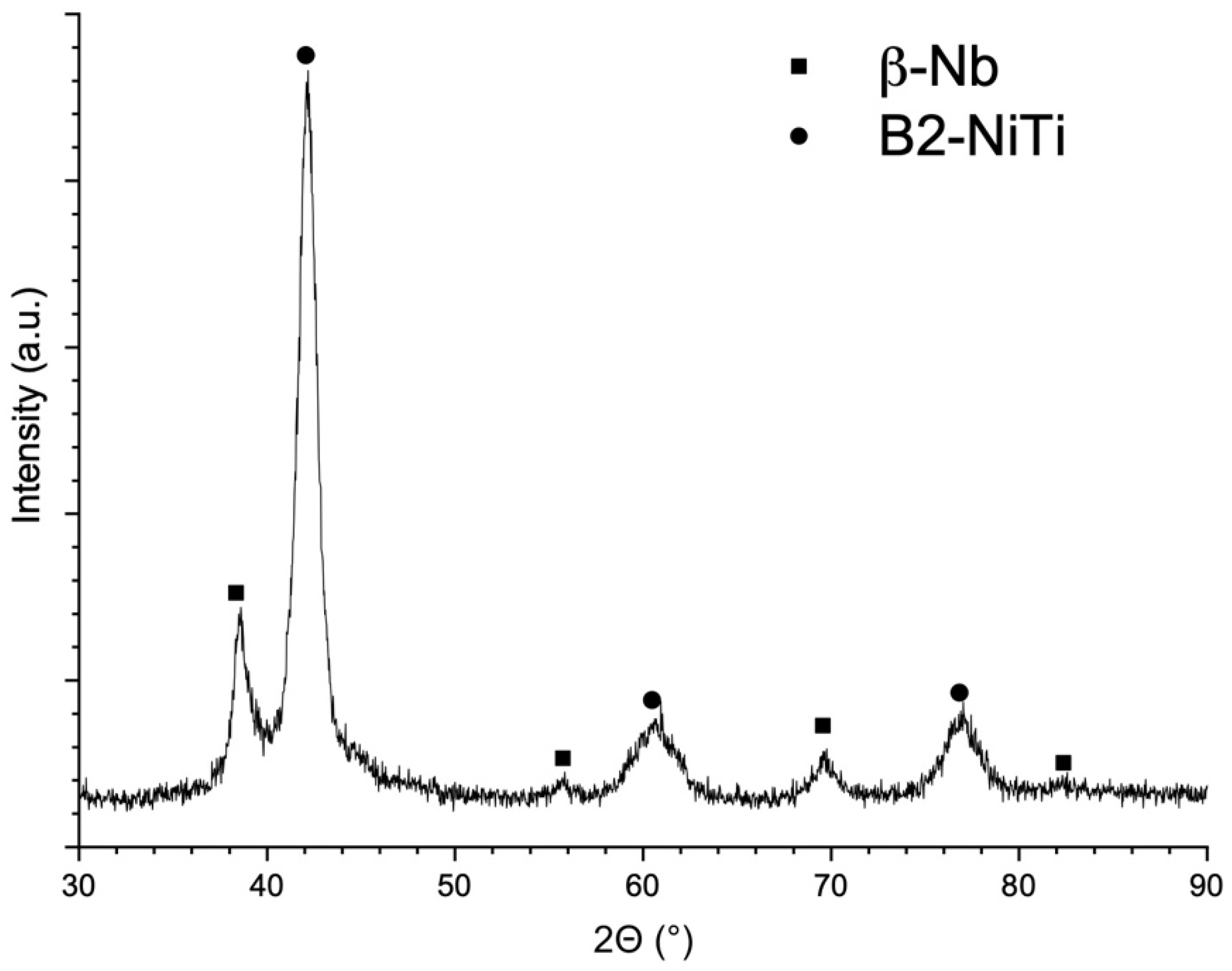
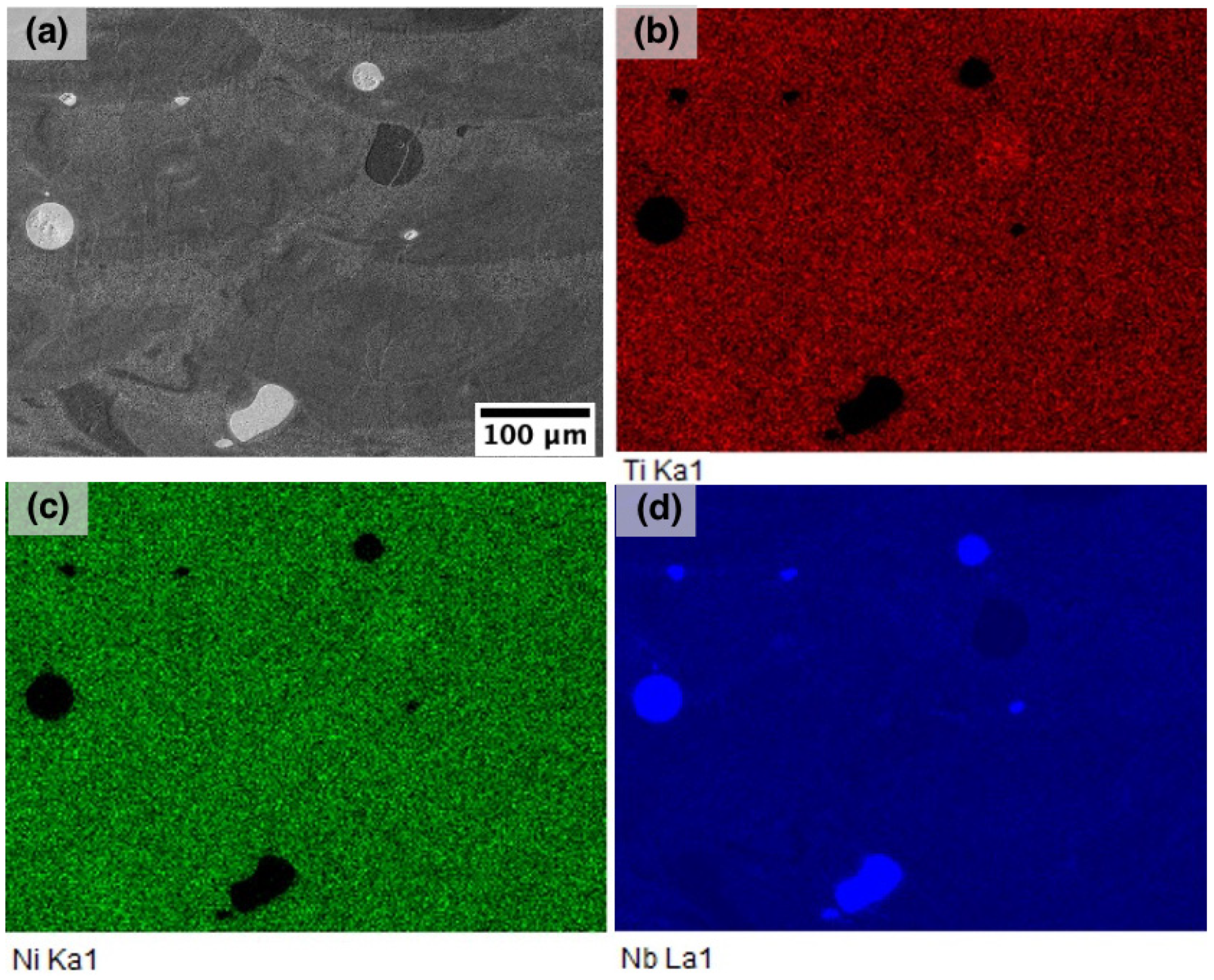
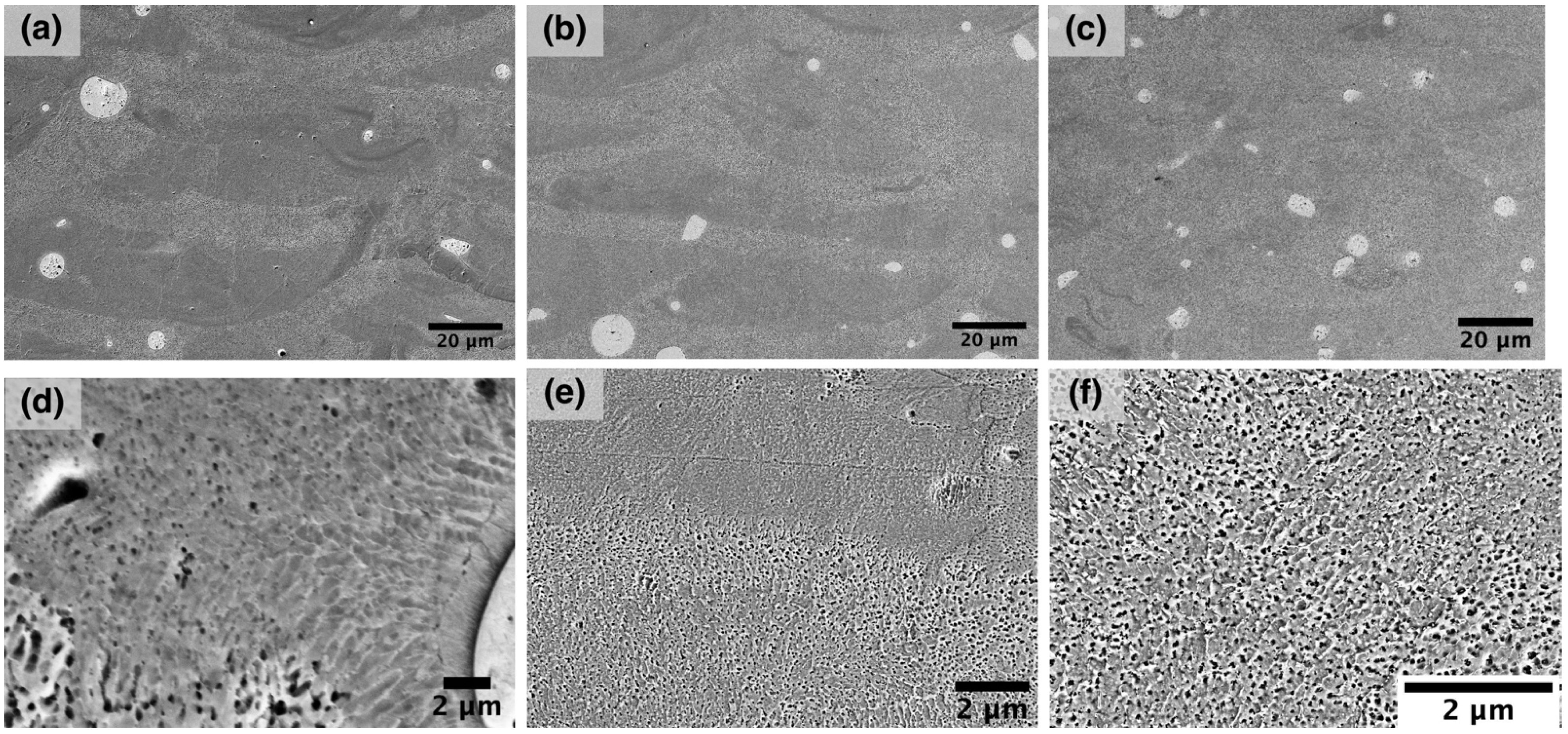
| Process Parameter Set | Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/s) | Hatch Distance (µm) | Layer Thickness (µm) | VED (J/mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 200 | 600 | 120 | 50 | 55.6 |
| A2 | 200 | 650 | 120 | 51.3 | |
| A3 | 200 | 700 | 120 | 47.6 | |
| B1 | 180 | 600 | 120 | 50.0 | |
| B2 | 240 | 600 | 120 | 66.7 | |
| C1 | 200 | 600 | 100 | 66.7 | |
| C2 | 200 | 600 | 90 | 74.1 | |
| D1 | 450 | 300 | 450 | 100 | 33.3 |
| D2 | 450 | 320 | 450 | 31.3 | |
| D3 | 450 | 340 | 450 | 29.4 | |
| E1 | 400 | 340 | 450 | 26.1 | |
| E2 | 420 | 340 | 450 | 27.5 | |
| F1 | 450 | 340 | 400 | 33.1 | |
| F2 | 450 | 340 | 350 | 37.8 |
| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiTi-+Nb, SLM, as-fabricated | 390 ± 10 | 590 ± 60 | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| NiTi-+Nb, SLM, after H/T (900 °C for 2 h) | 410 ± 20 | 680 ± 20 | 3.8 ± 0.3 |
| Ni47Ti44Nb9, casted [10] | ~500 | ~650 | ~40 |
| Sample | Ms (°C) | Mf (°C) | As, (°C) | Af (°C) | Аf-As (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiTi+Nb, SLM as-fabricated | −50 | −78 | −52 | 5 | 57 |
| NiTi+Nb, SLM+H/T (900 °C for 2 h) | −30 | −76 | −28 | 22 | 50 |
| NiTi, SLM as-fabricated | −34 | −69 | −27 | −5 | 22 |
| Ni47Ti44Nb9, casted [40] | −73 | −90 | −25 | −11 | 14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polozov, I.; Popovich, A. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi-Based Eutectic Shape Memory Alloy Produced via Selective Laser Melting In-Situ Alloying by Nb. Materials 2021, 14, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102696
Polozov I, Popovich A. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi-Based Eutectic Shape Memory Alloy Produced via Selective Laser Melting In-Situ Alloying by Nb. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102696
Chicago/Turabian StylePolozov, Igor, and Anatoly Popovich. 2021. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi-Based Eutectic Shape Memory Alloy Produced via Selective Laser Melting In-Situ Alloying by Nb" Materials 14, no. 10: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102696
APA StylePolozov, I., & Popovich, A. (2021). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of NiTi-Based Eutectic Shape Memory Alloy Produced via Selective Laser Melting In-Situ Alloying by Nb. Materials, 14(10), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102696






