Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.N.; Sundberg, M.; Flivik, G. Comparable Results With Porous Metal Augments in Combination With Either Cemented or Uncemented Cups in Revision Hip Arthroplasty: An Analysis of One Hundred Forty-Seven Revisions at a Mean of Five Years. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, F.H.; Whiteside, L.A. The fate of massive allografts in total hip acetabular revision surgery. J. Arthroplast. 1992, 7, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, N.A.; Weiss, S.; Klotz, M.C.; Gondan, M.; Jaeger, S.; Bitsch, R.G. Loosening after acetabular revision: Comparison of trabecular metal and reinforcement rings. A systematic review. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.C.; Hungerford, D.S. Cement disease. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1987, 225, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, H.A.H.; El-Bakoury, A.; Srinivasan, S.C.M.; Yarlagadda, R.; Keenan, J. Tritanium Acetabular Cup in Revision Hip Replacement: A Six to Ten Years of Follow-Up Study. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2566–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, R.M.; Meyer, C.; Buckley, C.A.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Mechanical stability of novel highly porous metal acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärrholm, J.; Mohaddes, M.; Odin, D.; Vinblad, J.; Rogmark, C.; Rolfson, O. Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register Annual Report 2017; Svenska Höftprotesregistret Registercentrum Västra Götaland SE-413 45: Göteborg, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann, M.; Ansorge, C.; Lausmann, C.; Suero, E.M.; Gehrke, T.; Citak, M. An alternative treatment option for Paprosky Type IIIb acetabular defect using multiple tantalum wedges—A case report. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2020, 11, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houdek, M.T.; Abdel, M.P.; Perry, K.I.; Salduz, A.; Rose, P.S.; Sim, F.H.; Lewallen, D.G. Outcome of Patients Treated With Porous Tantalum Acetabular Implants for Neoplastic Periacetabular Lesions. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Lee, J.M.; Maniatopoulos, C. Observations on the effect of movement on bone ingrowth into porous-surfaced implants. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 208, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspenberg, P.; Goodman, S.; Toksvig-Larsen, S.; Ryd, L.; Albrektsson, T. Intermittent micromotion inhibits bone ingrowth. Titanium implants in rabbits. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1992, 63, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, N.A.; Bitsch, R.G.; Gondan, M.; Schonhoff, M.; Jaeger, S. Comparison of the stability of three fixation techniques between porous metal acetabular components and augments. Bone Jt. Res. 2018, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paprosky, W.G.; Perona, P.G.; Lawrence, J.M. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J. Arthroplast. 1994, 9, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.; Graichen, F.; Rohlmann, A.; Bender, A.; Heinlein, B.; Duda, G.N.; Heller, M.O.; Morlock, M.M. Realistic loads for testing hip implants. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2010, 20, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, G.; Deuretzbacher, G.; Heller, M.; Graichen, F.; Rohlmann, A.; Strauss, J.; Duda, G.N. Hip contact forces and gait patterns from routine activities. J. Biomech. 2001, 34, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, G.; Bender, A.; Dymke, J.; Duda, G.; Damm, P. Standardized Loads Acting in Hip Implants. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.D.; Seyler, T.M.; Bennett, D.; Delanois, R.E.; Saleh, K.J.; Thongtrangan, I.; Kuskowski, M.; Cheng, E.Y.; Sharkey, P.F.; Parvizi, J.; et al. Total hip arthroplasties: What are the reasons for revision? Int. Orthop. 2008, 32, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.H.; Laflamme, G.Y.; Delisle, J.; Fernandes, J. Trabecular metal used for major bone loss in acetabular hip revision. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolghasemian, M.; Tangsataporn, S.; Sternheim, A.; Backstein, D.; Safir, O.; Gross, A.E. Combined trabecular metal acetabular shell and augment for acetabular revision with substantial bone loss: A mid-term review. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Bender, B.; Coyle, C.; Parvizi, J.; Sharkey, P.F.; Hozack, W.J. Do tantalum and titanium cups show similar results in revision hip arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steno, B.; Kokavec, M.; Necas, L. Acetabular revision arthroplasty using trabecular titanium implants. Int. Orthop. 2015, 39, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delanois, R.E.; Gwam, C.U.; Mohamed, N.; Khlopas, A.; Chughtai, M.; Malkani, A.L.; Mont, M.A. Midterm Outcomes of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty With the Use of a Multihole Highly-Porous Titanium Shell. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 2806–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallart, X.; Fernandez-Valencia, J.A.; Riba, J.; Bori, G.; Garcia, S.; Tornero, E.; Combalia, A. Trabecular TitaniumTM cups and augments in revision total hip arthroplasty: Clinical results, radiology and survival outcomes. HIP Int. 2016, 26, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meo, F.; Cacciola, G.; Bellotti, V.; Bruschetta, A.; Cavaliere, P. Trabecular Titanium acetabular cups in hip revision surgery: Mid-term clinical and radiological outcomes. HIP Int. 2018, 28, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Issa, K.; Kapadia, B.H.; Pivec, R.; Khanuja, H.S.; Mont, M.A. Systematic review on outcomes of acetabular revisions with highly-porous metals. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Della Valle, C.J.; Jacobs, J.J. Applications of porous tantalum in total hip arthroplasty. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2006, 14, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggemann, A.; Mallmin, H.; Bengtsson, M.; Hailer, N.P. Safety of Use of Tantalum in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggemann, A.; Fredlund, E.; Mallmin, H.; Hailer, N.P. Are porous tantalum cups superior to conventional reinforcement rings? Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, L.; Rachala, S.R.; Cabanela, M.E. Cementless acetabular revision: Past, present, and future. Revision total hip arthroplasty: The acetabular side using cementless implants. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goldman, A.H.; Armstrong, L.C.; Owen, J.R.; Wayne, J.S.; Jiranek, W.A. Does Increased Coefficient of Friction of Highly Porous Metal Increase Initial Stability at the Acetabular Interface? J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, C.A.; O’Connor, D.; Jasty, M.; McGovern, T.F.; Bobyn, J.D.; Harris, W.H. Quantification of implant micromotion, strain shielding, and bone resorption with porous-coated anatomic medullary locking femoral prostheses. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 285, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, J.R.; Callaghan, J.J.; Pedersen, D.R.; Brown, T.D. Areas of contact and extent of gaps with implantation of oversized acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1994, 298, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.T., Jr.; Engh, C.A.; Forte, M.R.; Kukita, Y.; Grandia, S.K. Evaluation of initial surface apposition in porous-coated acetabular components. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 293, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.L.; Lehman, J.; Notz, W.I.; Santner, T.J.; Bartel, D.L. Acetabular cup geometry and bone-implant interference have more influence on initial periprosthetic joint space than joint loading and surgical cup insertion. J. Biomech. Eng. 2006, 128, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, S.; Dedukh, N.; Filipenko, V.; Akonjom, M.; Badnaoui, A.A.; Schwarzkopf, R. Comparative analysis of osseointegration in various types of acetabular implant materials. HIP Int. 2018, 28, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochel, J.; Janz, V.; Hipfl, C.; Perka, C.; Wassilew, G.I. Reconstruction of acetabular defects with porous tantalum shells and augments in revision total hip arthroplasty at ten-year follow-up. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraile Suari, A.; Marques Lopez, F.; Cuenca Llavall, M.; Tey Pons, M.; Leon Garcia, A. Reconstruction for pelvic discontinuity and massive acetabular defects. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2020, 64, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, M.R.; Masri, B.A.; Duncan, C.P.; Garbuz, D.S. Continued good results with modular trabecular metal augments for acetabular defects in hip arthroplasty at 7 to 11 years. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, R.M.; Hull, J.R.; Russo, G.S.; Lieberman, J.R.; Jiranek, W.A. Porous Tantalum Buttress Augments for Severe Acetabular Posterior Column Deficiency. Surg. Technol. Int. 2015, 27, 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Konan, S.; Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S. Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: A minimum ten-year clinical, radiological and quality of life outcome study. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, V.; Agrawal, P.; Porter, M.L.; Board, T.N. Early results of a high friction surface coated uncemented socket in revision hip arthroplasty. HIP Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziri, Q.; Issa, K.; Pivec, R.; Harwin, S.F.; Delanois, R.E.; Mont, M.A. Excellent results of primary THA using a highly porous titanium cup. Orthopedics 2013, 36, e390–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
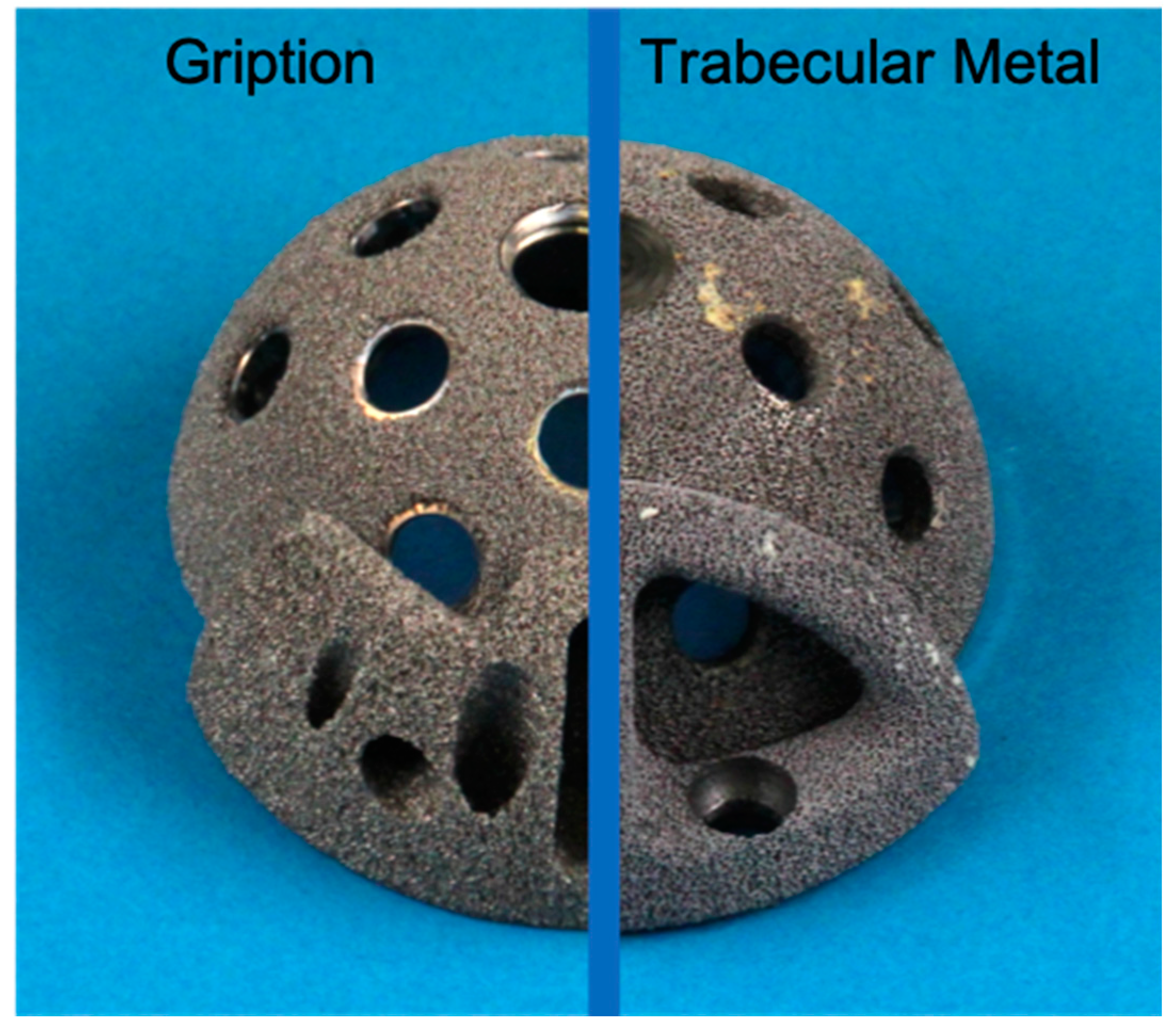
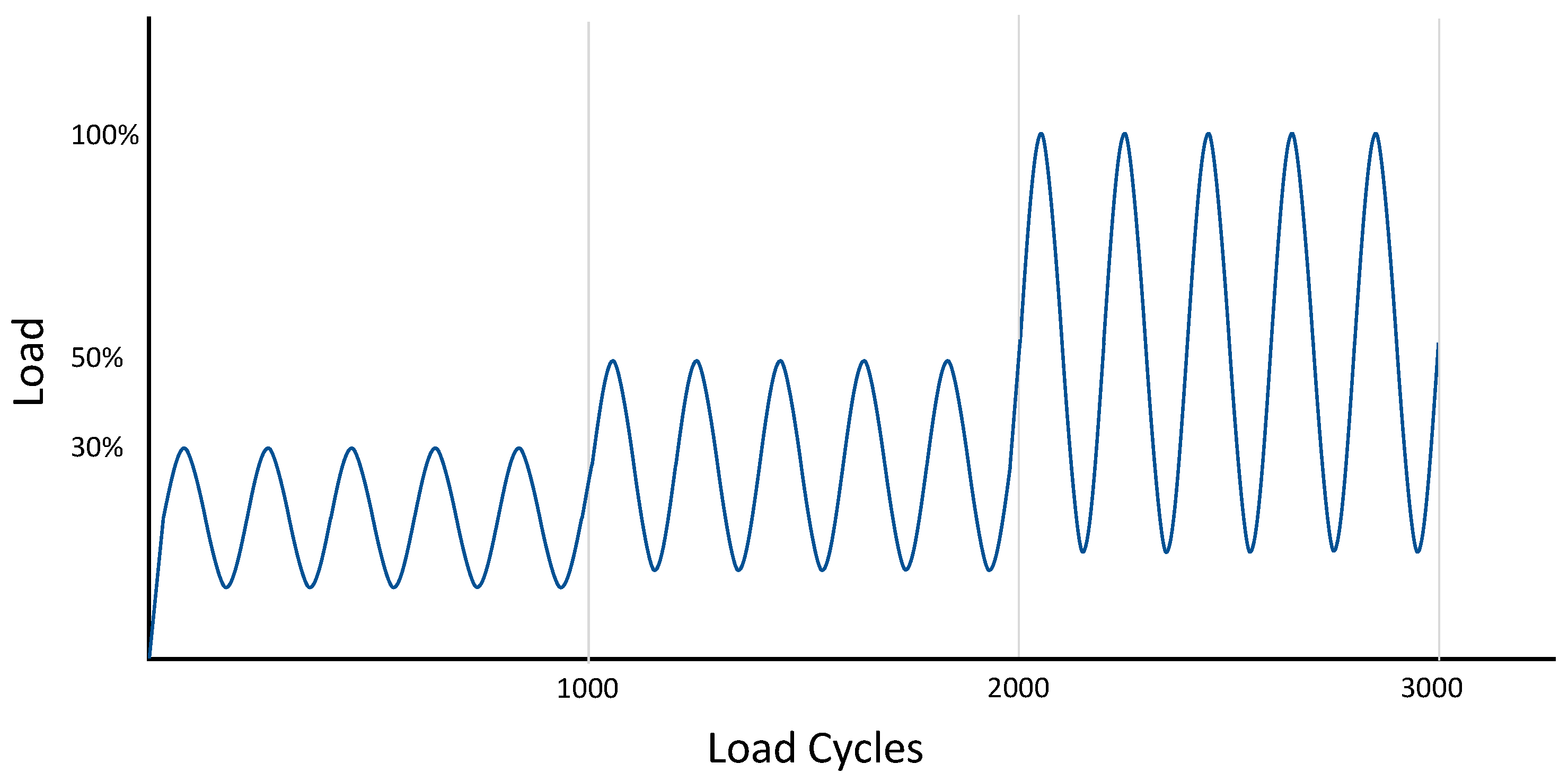
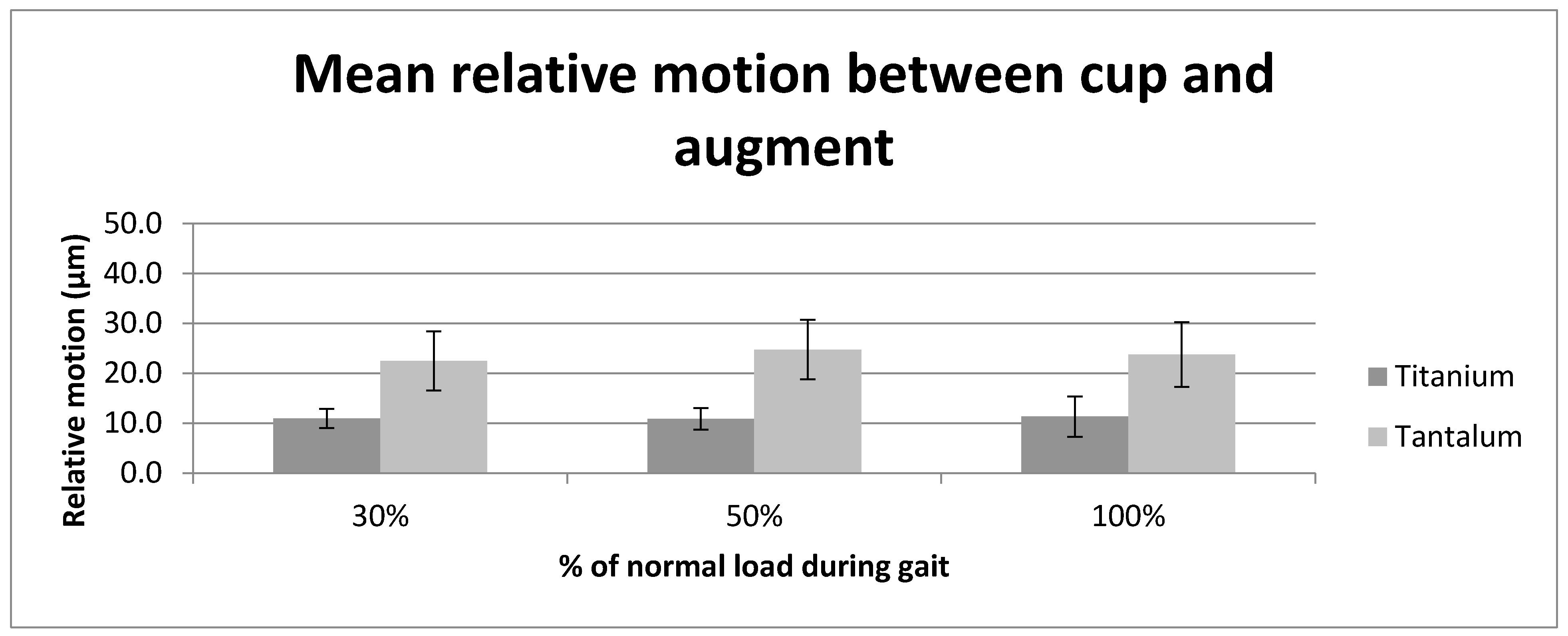
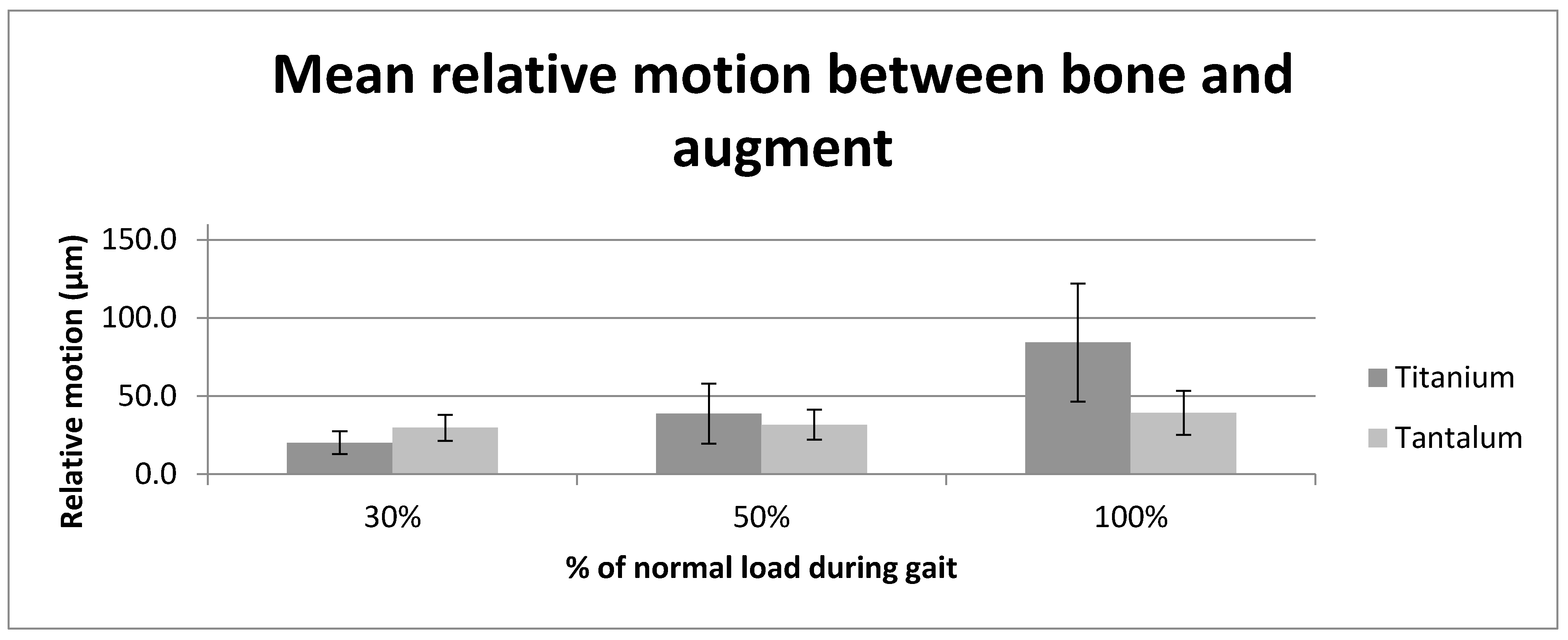
| Interface | Augment/Cup | Bone/Augment | Bone/Cup | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implant Material | Titanium | Tantalum | Titanium | Tantalum | Titanium | Tantalum |
| Load | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) |
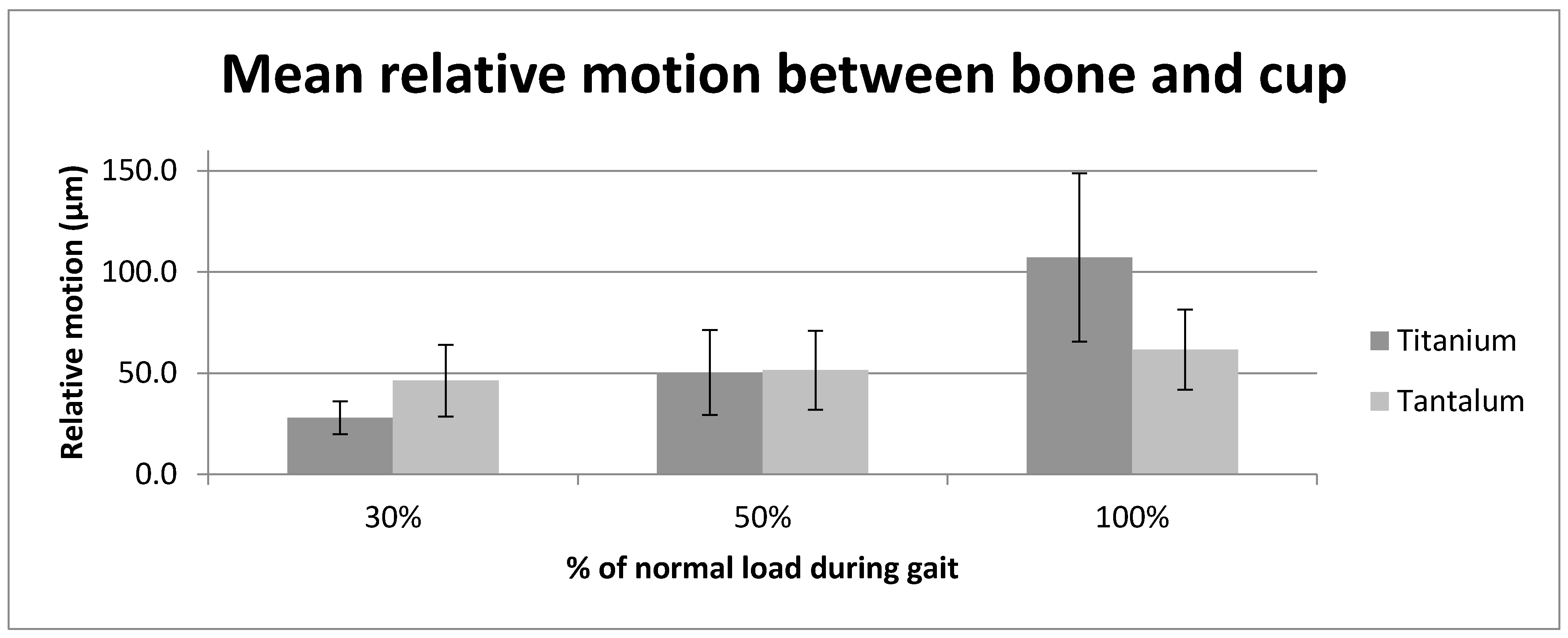
| 30% | 11.0 (1.9) | 22.5 (6.1) | 20.0 (7.3) | 29.7 (8.1) | 27.9 (8.0) | 46.3 (18.6) |
| 50% | 10.9 (2.1) | 24.7 (5.7) | 38.7 (17.8) | 31.7 (9.7) | 50.2 (18.6) | 51.4 (19.8) |
| 100% | 11.3 (4.2) | 23.7 (6.6) | 84.3 (40.2) | 39.4 (15.0) | 107.2 (44.0) | 61.6 (20.5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beckmann, N.A.; Bitsch, R.G.; Schonhoff, M.; Siebenrock, K.-A.; Schwarze, M.; Jaeger, S. Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs. Materials 2020, 13, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071783
Beckmann NA, Bitsch RG, Schonhoff M, Siebenrock K-A, Schwarze M, Jaeger S. Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071783
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeckmann, Nicholas A., Rudi G. Bitsch, Mareike Schonhoff, Klaus-Arno Siebenrock, Martin Schwarze, and Sebastian Jaeger. 2020. "Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs" Materials 13, no. 7: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071783
APA StyleBeckmann, N. A., Bitsch, R. G., Schonhoff, M., Siebenrock, K.-A., Schwarze, M., & Jaeger, S. (2020). Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs. Materials, 13(7), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071783





