Nailing of Layers: A Promising Way to Reinforce Concrete 3D Printing Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
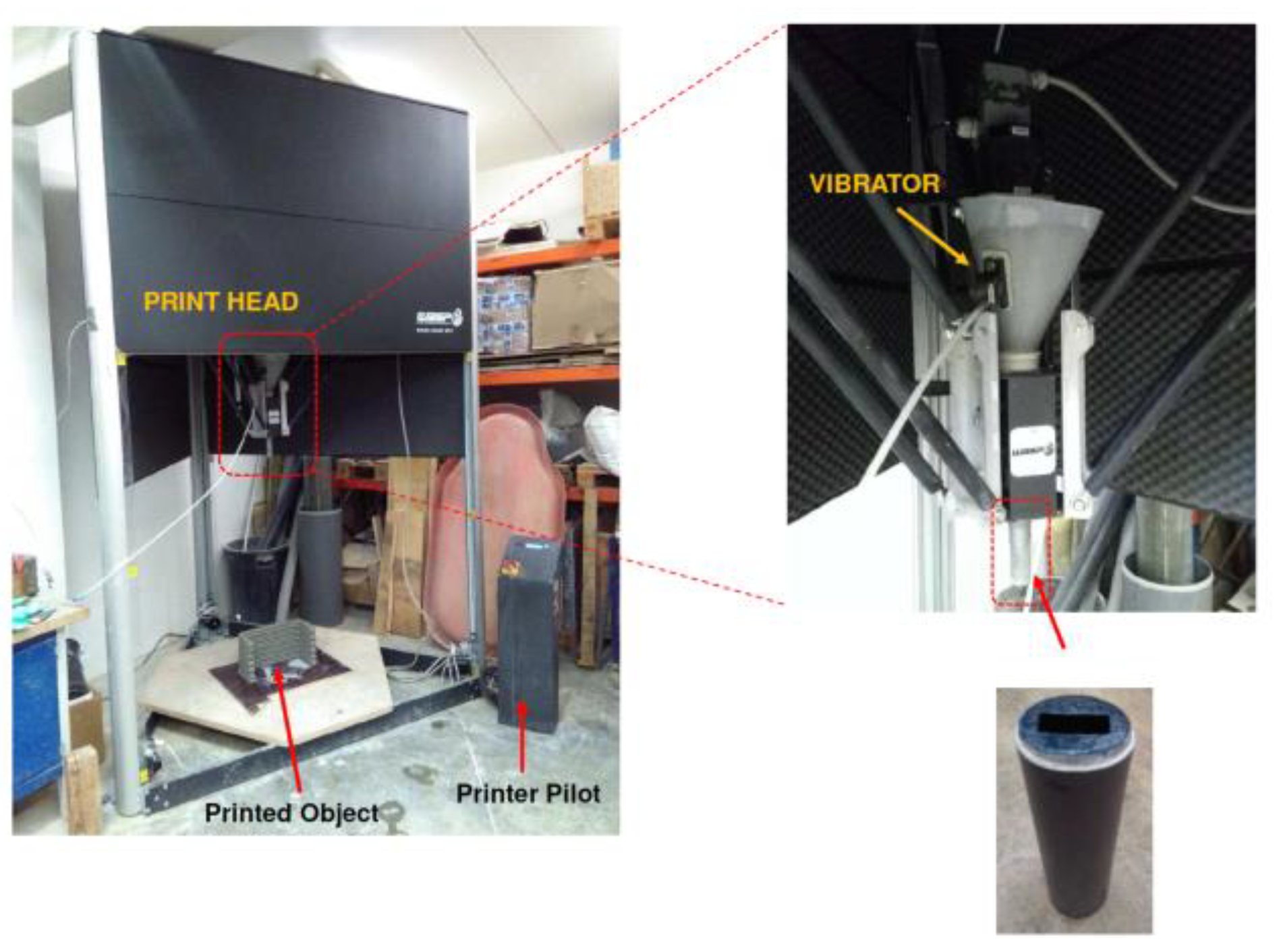
2.2. Samples Geometries and Fabrication
2.3. Mechanical Measurements
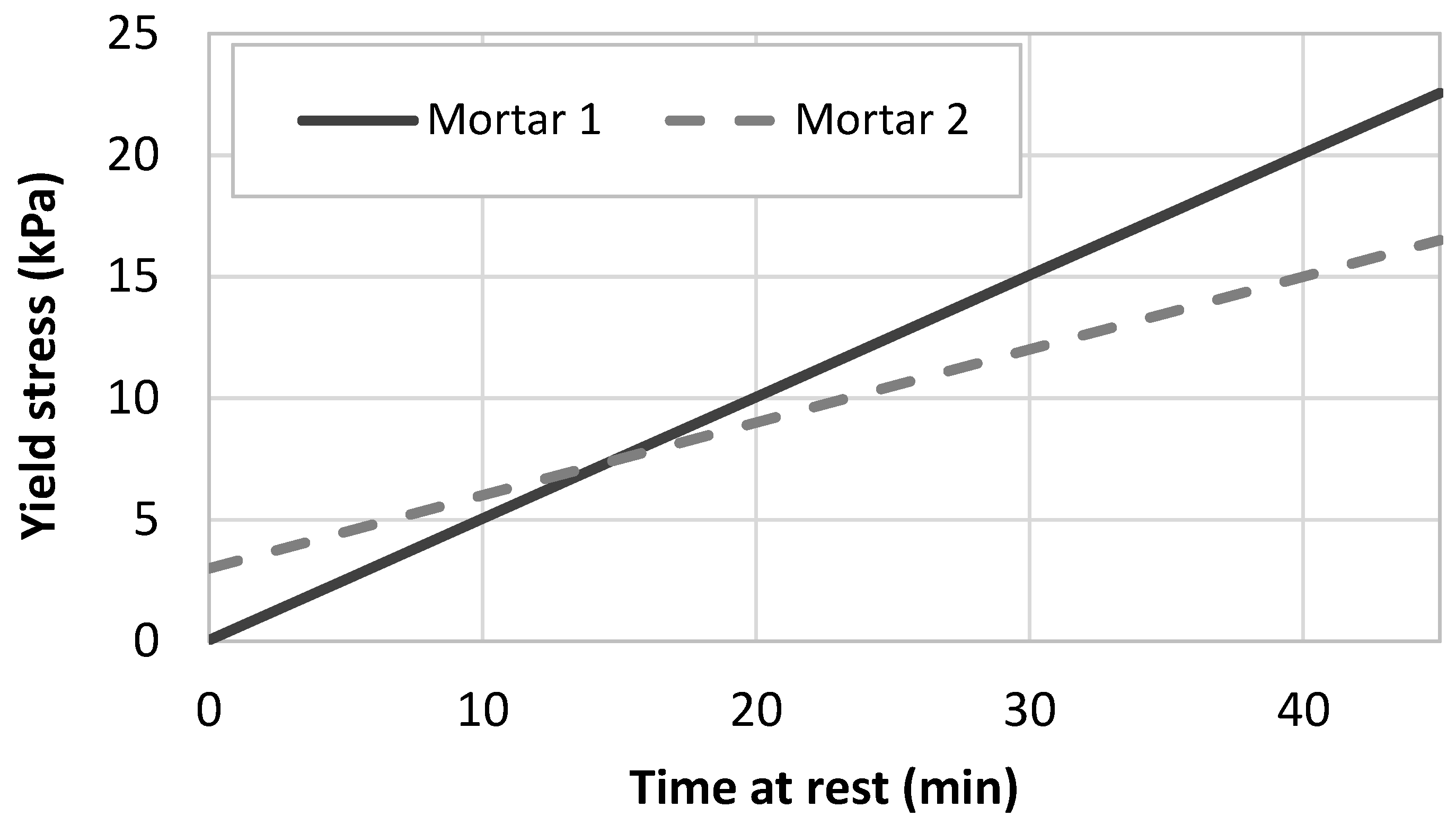
3. Rheological Requirements for the Penetration of Nails
3.1. Penetration Theory
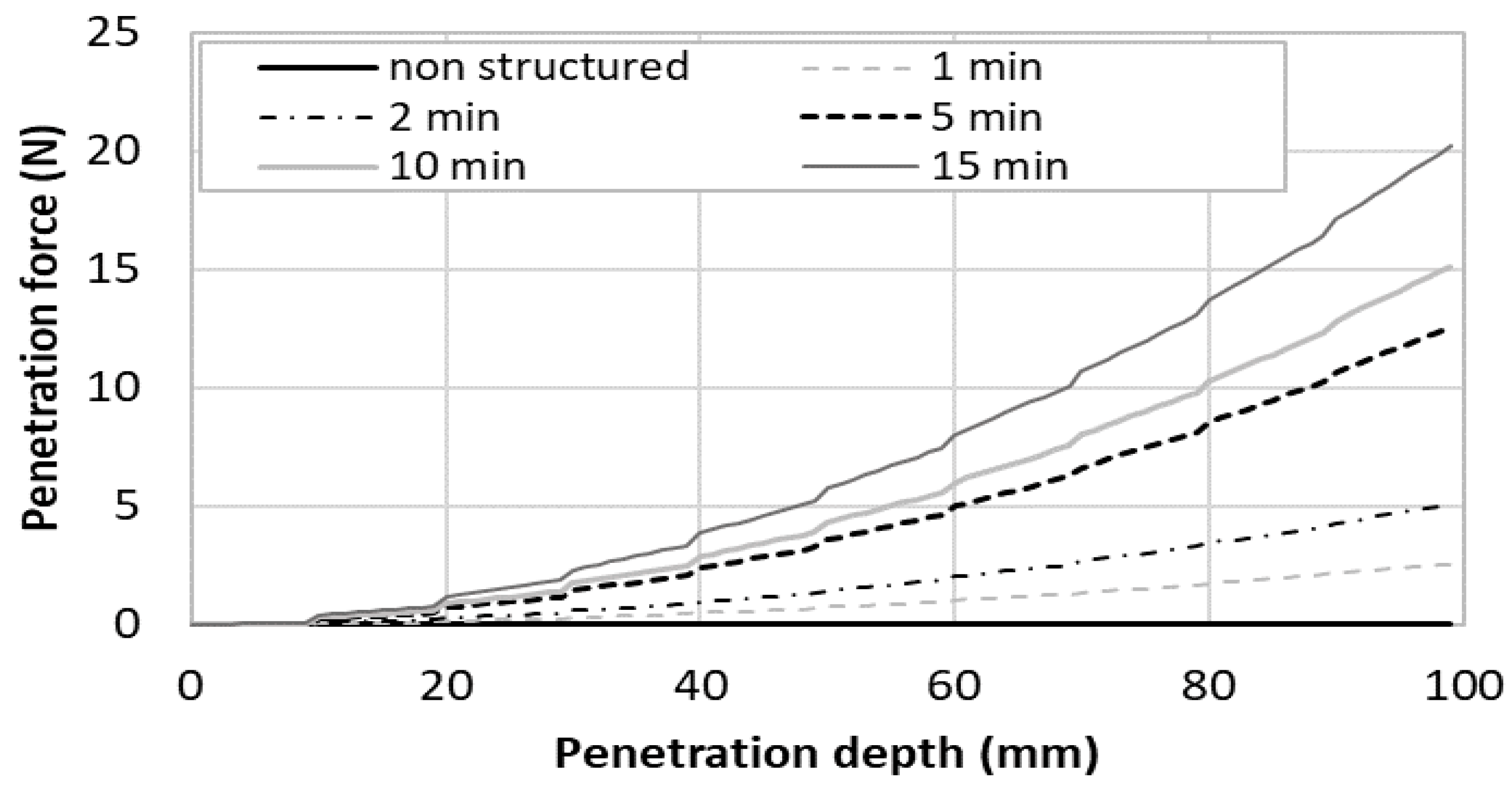
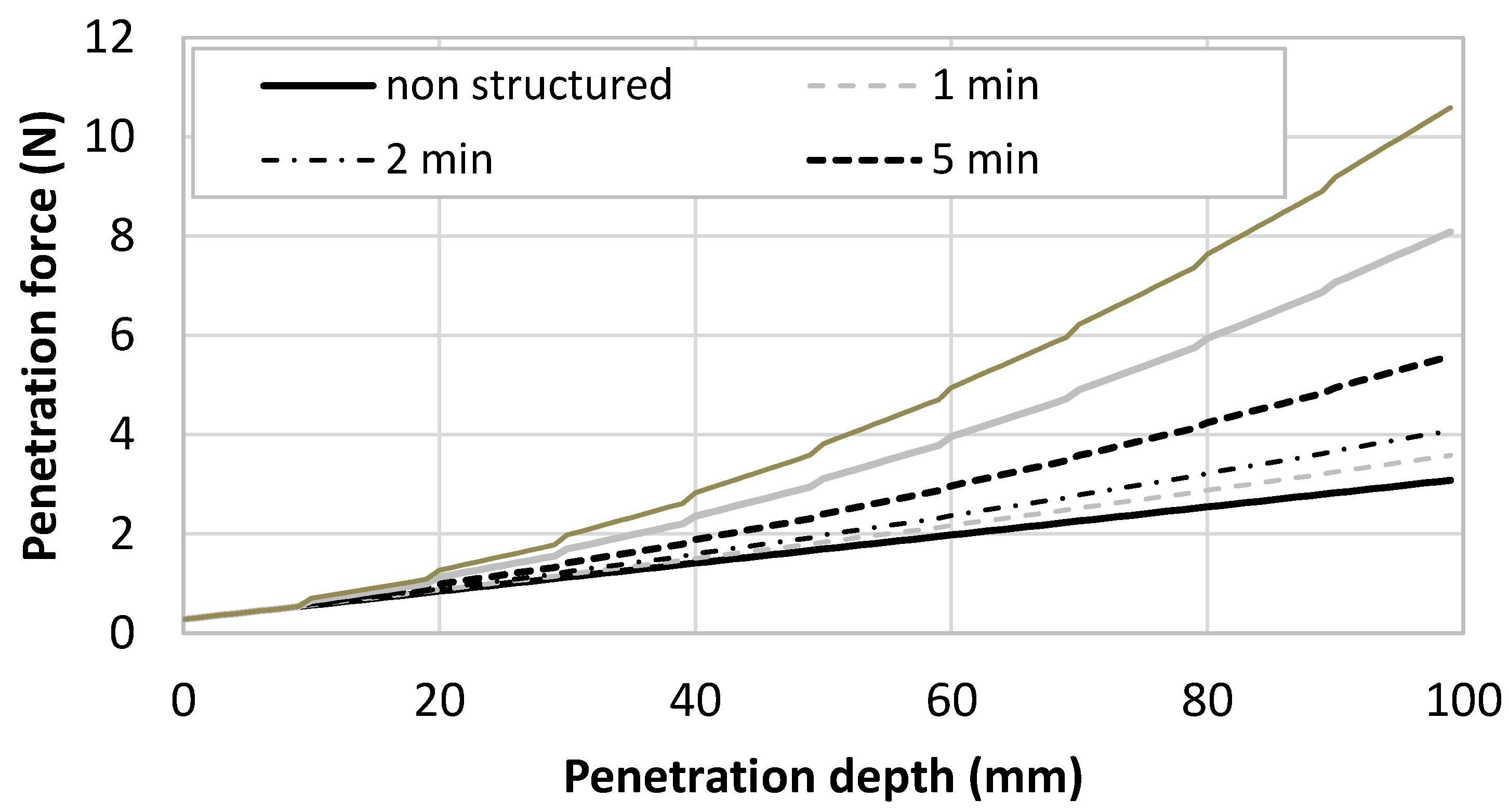
3.2. Penetration of the Nail within a Printed Sample
4. Mechanical Reinforcement
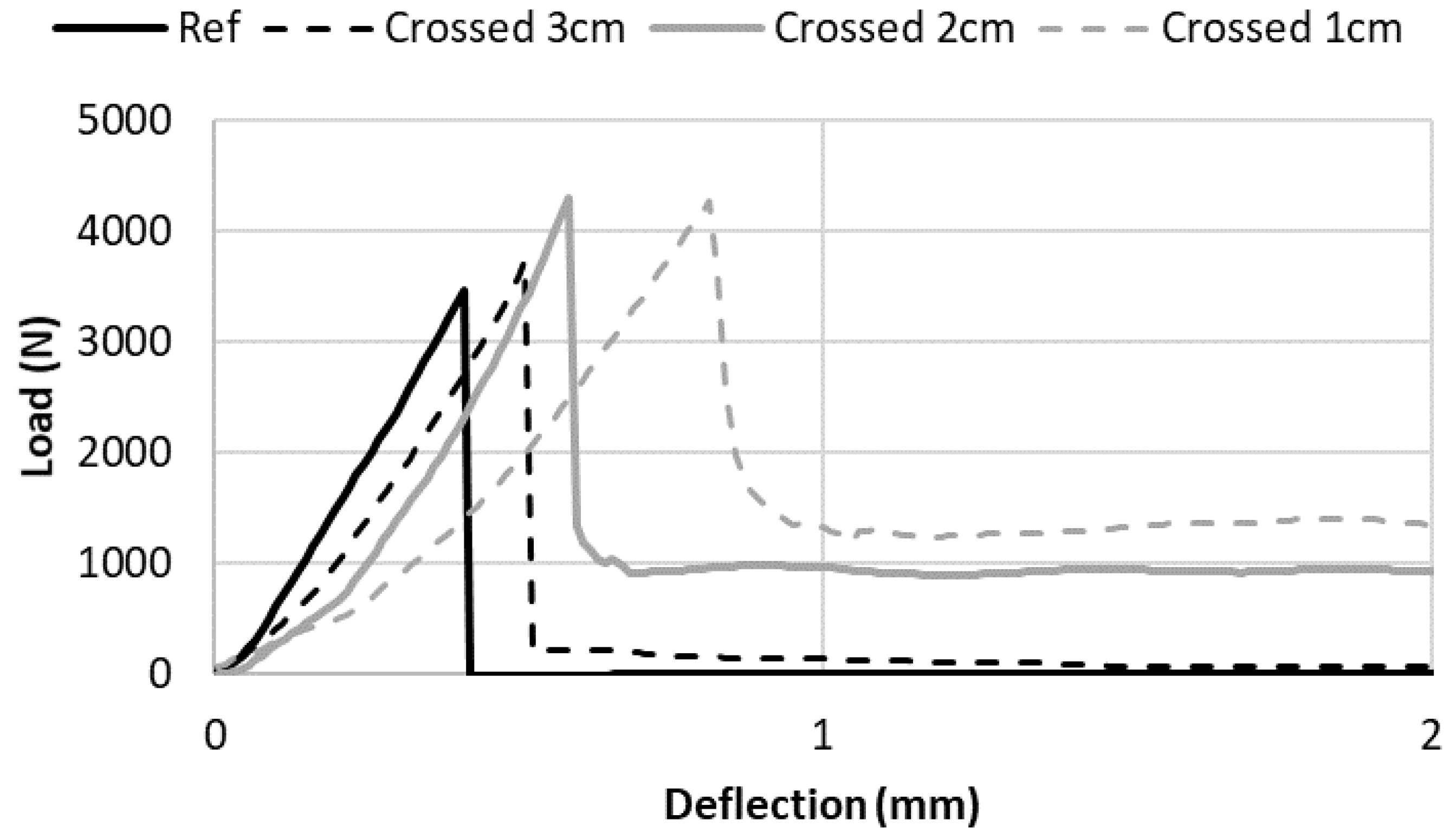
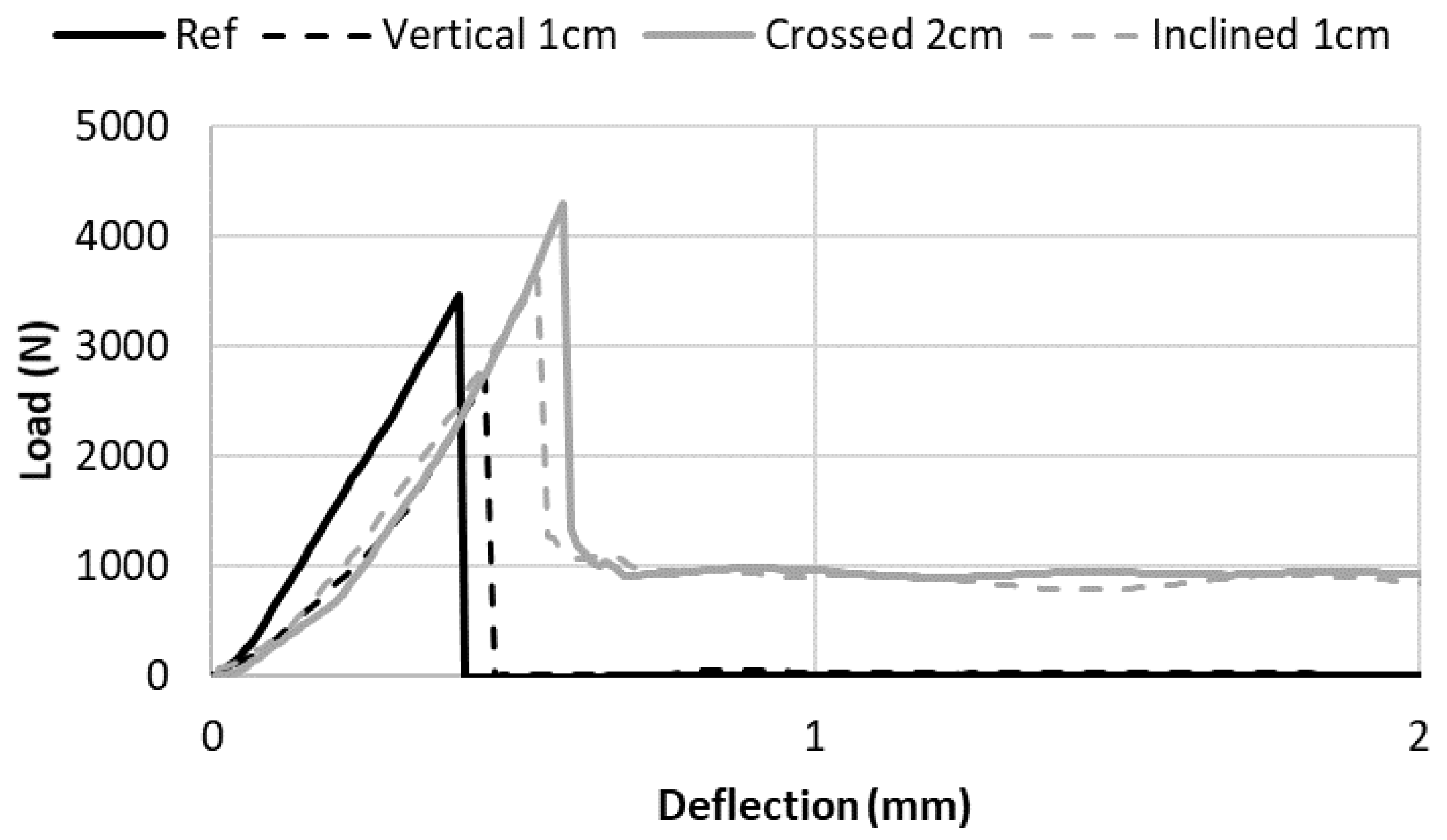
4.1. Bending Resistance
4.2. Post-Peak Behavior
4.3. Possible Durability Issues and Steel Corrosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perrot, A. 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction Revolution; Wiley-ISTE, ISTE: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 1-78630-341-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wangler, T.; Lloret, E.; Reiter, L.; Hack, N.; Gramazio, F.; Kohler, M.; Bernhard, M.; Dillenburger, B.; Buchli, J.; Roussel, N.; et al. Digital Concrete: Opportunities and Challenges. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2016, 1, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.W.D.; Panda, B.; Paul, S.C.; Noor Mohamed, N.A.; Tan, M.J.; Leong, K.F. 3D printing trends in building and construction industry: A review. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2017, 12, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schutter, G.; Lesage, K.; Mechtcherine, V.; Nerella, V.N.; Habert, G.; Agusti-Juan, I. Vision of 3D printing with concrete—technical, economic and environmental potentials. SI Digit. Concr. 2018 2018, 112, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, T.; Roussel, N.; Bos, F.P.; Salet, T.A.; Flatt, R.J. Digital concrete: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 123, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Rangeard, D.; Pierre, A. Structural built-up of cement-based materials used for 3D-printing extrusion techniques. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheological requirements for printable concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfs, R.J.M.; Bos, F.P.; Salet, T.A.M. Early age mechanical behaviour of 3D printed concrete: Numerical modelling and experimental testing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprone, D.; Auricchio, F.; Menna, C.; Mercuri, V. 3D printing of reinforced concrete elements: Technology and design approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asprone, D.; Menna, C.; Bos, F.P.; Salet, T.A.; Mata-Falcón, J.; Kaufmann, W. Rethinking reinforcement for digital fabrication with concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjayan, J.G.; Nematollahi, B.; Xia, M.; Marchment, T. Effect of surface moisture on inter-layer strength of 3D printed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, H.; Nerella, V.N.; Mechtcherine, V. Developing and Testing of Strain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites (SHCC) in the Context of 3D-Printing. Materials 2018, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Sanjayan, J. Mechanical anisotropy of aligned fiber reinforced composite for extrusion-based 3D printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Paul, S.C.; Tan, M.J. Anisotropic mechanical performance of 3D printed fiber reinforced sustainable construction material. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.J.-H.; Moon, J.-H.; Kim, W.-W.; Seo, E.-A. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of a 3D-Printed Mortar. Materials 2019, 12, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonebi, M.; Amziane, S.; Perrot, A. Mechanical Behavior of 3D Printed Cement Materials. In 3D Print. Concr. State Art Chall. Digit. Constr. Revolut.; ISTE: London, UK, 2019; pp. 101–124. [Google Scholar]
- Motamedi, M.; Oval, R.; Carneau, P.; Baverel, O. Supportless 3D Printing of Shells: Adaptation of Ancient Vaulting Techniques to Digital Fabrication. In Design Modelling Symposium Berlin; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 714–726. ISBN 978-3-030-29828-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vantyghem, G.; Boel, V.; Corte, W.; Steeman, M. Compliance, Stress-Based and Multi-physics Topology Optimization for 3D-Printed Concrete Structures. In RILEM Bookseries; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 323–332. ISBN 978-3-319-99518-2. [Google Scholar]
- Vantyghem, G.; Corte, W.; Shakour, E.; Amir, O. 3D printing of a post-tensioned concrete girder designed by topology optimization. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí-Juan, I.; Müller, F.; Hack, N.; Wangler, T.; Habert, G. Potential benefits of digital fabrication for complex structures: Environmental assessment of a robotically fabricated concrete wall. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí-Juan, I.; Habert, G. Environmental design guidelines for digital fabrication. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, F.; Wolfs, R.; Ahmed, Z.; Salet, T. Large scale testing of digitally fabricated concrete (DFC) elements. In Proceedings of the RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, Zurich, Switzerland, 10–12 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 129–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mechtcherine, V.; Grafe, J.; Nerella, V.N.; Spaniol, E.; Hertel, M.; Füssel, U. 3D-printed steel reinforcement for digital concrete construction—Manufacture, mechanical properties and bond behaviour. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 179, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, I.; Fabbrocino, F.; Carpentieri, G.; Modano, M.; Amendola, A.; Goodall, R.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F. On the reinforcement of cement mortars through 3D printed polymeric and metallic fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 90, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcherine, V.; Nerella, V.N.; Ogura, H.; Grafe, J.; Spaniol, E.; Hertel, M.; Füssel, U. Alternative Reinforcements for Digital Concrete Construction. In Proceedings of the RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, Zurich, Switzerland, 10–12 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, M.; Sonebi, M.; Amziane, S. “Fresh and rheological properties of 3D printing bio-cement-based materials”. In Proceedings of the 2nd ICBBM (PRO 119), Clermont-Ferrand, France, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hambach, M.; Rutzen, M.; Volkmer, D. Chapter 5—Properties of 3D-Printed Fiber-Reinforced Portland Cement Paste. In 3D Concrete Printing Technology; Sanjayan, J.G., Nazari, A., Nematollahi, B., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 73–113. ISBN 978-0-12-815481-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hambach, M.; Volkmer, D. Properties of 3D-printed fiber-reinforced Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 79, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, F.P.; Ahmed, Z.Y.; Jutinov, E.R.; Salet, T.A. Experimental exploration of metal cable as reinforcement in 3D printed concrete. Materials 2017, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerella, V.N.; Hempel, S.; Mechtcherine, V. Micro-and macroscopic investigations of the interface between layers on the interface of 3D-printed cementitious. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Construction Materials and Systems, Chennai, India, 3–8 September 2017; RILEM: Paris, France, 2017; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Putten, J.; Deprez, M.; Cnudde, V.; De Schutter, G.; Van Tittelboom, K. Microstructural Characterization of 3D Printed Cementitious Materials. Materials 2019, 12, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Putten, J.; De Schutter, G.; Van Tittelboom, K. Surface modification as a technique to improve inter-layer bonding strength in 3D printed cementitious materials. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2019, 4, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Lecompte, T.; Estellé, P.; Amziane, S. Structural build-up of rigid fiber reinforced cement-based materials. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lootens, D.; Jousset, P.; Martinie, L.; Roussel, N.; Flatt, R.J. Yield stress during setting of cement pastes from penetration tests. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Polanco, J.A. Evolution of penetration resistance in fresh concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, H.; Perrot, A.; Amziane, S. A new look at the measurement of cementitious paste setting by Vicat test. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhoud, B.; Perrot, A.; Picandet, V.; Rangeard, D.; Courteille, E. Underwater 3D printing of cement-based mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 214, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. A thixotropy model for fresh fluid concretes: Theory, validation and applications. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G.; Garrault, S.; Brumaud, C. The origins of thixotropy of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecompte, T.; Perrot, A. Non-linear modeling of yield stress increase due to SCC structural build-up at rest. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 92, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Pierre, A.; Vitaloni, S.; Picandet, V. Prediction of lateral form pressure exerted by concrete at low casting rates. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 2315–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Experimental and modeling study on the non-linear structural build-up of fresh cement pastes incorporating viscosity modifying admixtures. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Zeranka, S.; van Zijl, G. 3D concrete printing: A lower bound analytical model for buildability performance quantification. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcherine, V.; Bos, F.P.; Perrot, A.; da Silva, W.R.L.; Nerella, V.N.; Fataei, S.; Wolfs, R.J.M.; Sonebi, M.; Roussel, N. Extrusion-based additive manufacturing with cement-based materials—Production steps, processes, and their underlying physics: A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 132, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinie, L.; Rossi, P.; Roussel, N. Rheology of fiber reinforced cementitious materials: Classification and prediction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, L.K.; Wittel, F.K.; Flatt, R.J.; Herrmann, H.J. Evolution of strength and failure of SCC during early hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 89, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


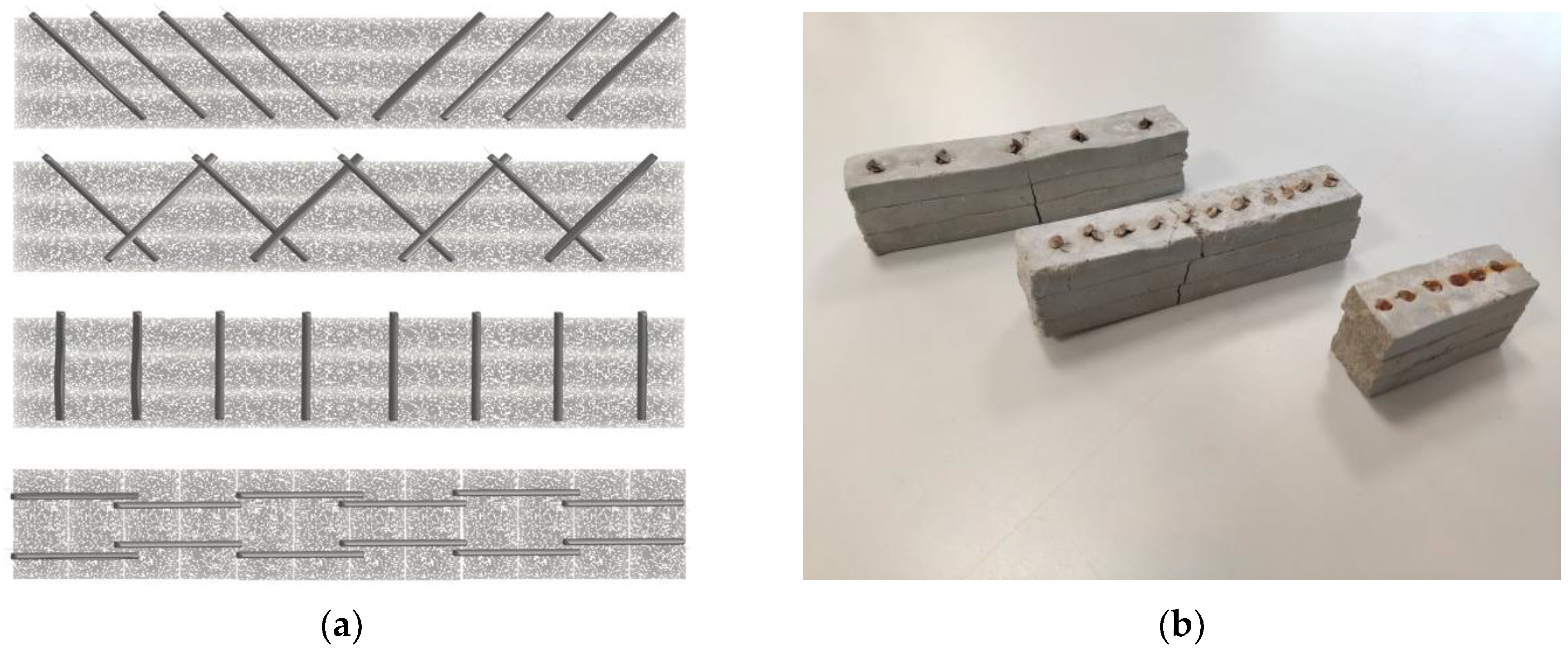

| Reinforcement Geometry | Inclined-Vertical | Crossed | Inclined-Vertical | Crossed | Inclined-Vertical | Crossed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance between nails (mm) | 30 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 |
| Steel weight (kg)/mortar (m3) | 21 | 42 | 32 | 64 | 64 | 127 |
| Reinforcement Direction | No | Vertical | Inclined | Crossed | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance between Nails (cm) | - | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Smooth | Average (N) | 3250 | 3750 | 3667 | 3000 | 4533 | 4167 | 4200 | 4870 | 4533 | 3983 |
| Standard dev. (N) | 507 | 71 | 416 | 283 | 503 | 321 | 346 | 44 | 115 | 305 | |
| Rusty | Average (N) | 3250 | 3550 | 3250 | 3300 | 4200 | 4267 | 3767 | 4550 | 4267 | 3790 |
| Standard dev. (N) | 507 | 495 | 495 | 608 | 265 | 702 | 115 | 71 | 321 | 115 | |
| Reinforcement Direction. | No | Vertical | Inclined | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance between Nails (cm) | ||||
| Smooth | Average (N) | 640 | 845 | 895 |
| Standard dev. (N) | 53 | 87 | 42 | |
| Rusty | Average (N) | 640 | 974 | 995 |
| Standard dev. (N) | 53 | 98 | 148 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrot, A.; Jacquet, Y.; Rangeard, D.; Courteille, E.; Sonebi, M. Nailing of Layers: A Promising Way to Reinforce Concrete 3D Printing Structures. Materials 2020, 13, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071518
Perrot A, Jacquet Y, Rangeard D, Courteille E, Sonebi M. Nailing of Layers: A Promising Way to Reinforce Concrete 3D Printing Structures. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071518
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrot, A., Y. Jacquet, D. Rangeard, E. Courteille, and M. Sonebi. 2020. "Nailing of Layers: A Promising Way to Reinforce Concrete 3D Printing Structures" Materials 13, no. 7: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071518
APA StylePerrot, A., Jacquet, Y., Rangeard, D., Courteille, E., & Sonebi, M. (2020). Nailing of Layers: A Promising Way to Reinforce Concrete 3D Printing Structures. Materials, 13(7), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071518





