Determination of Iron Valence States Around Pits and the Influence of Fe3+ on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
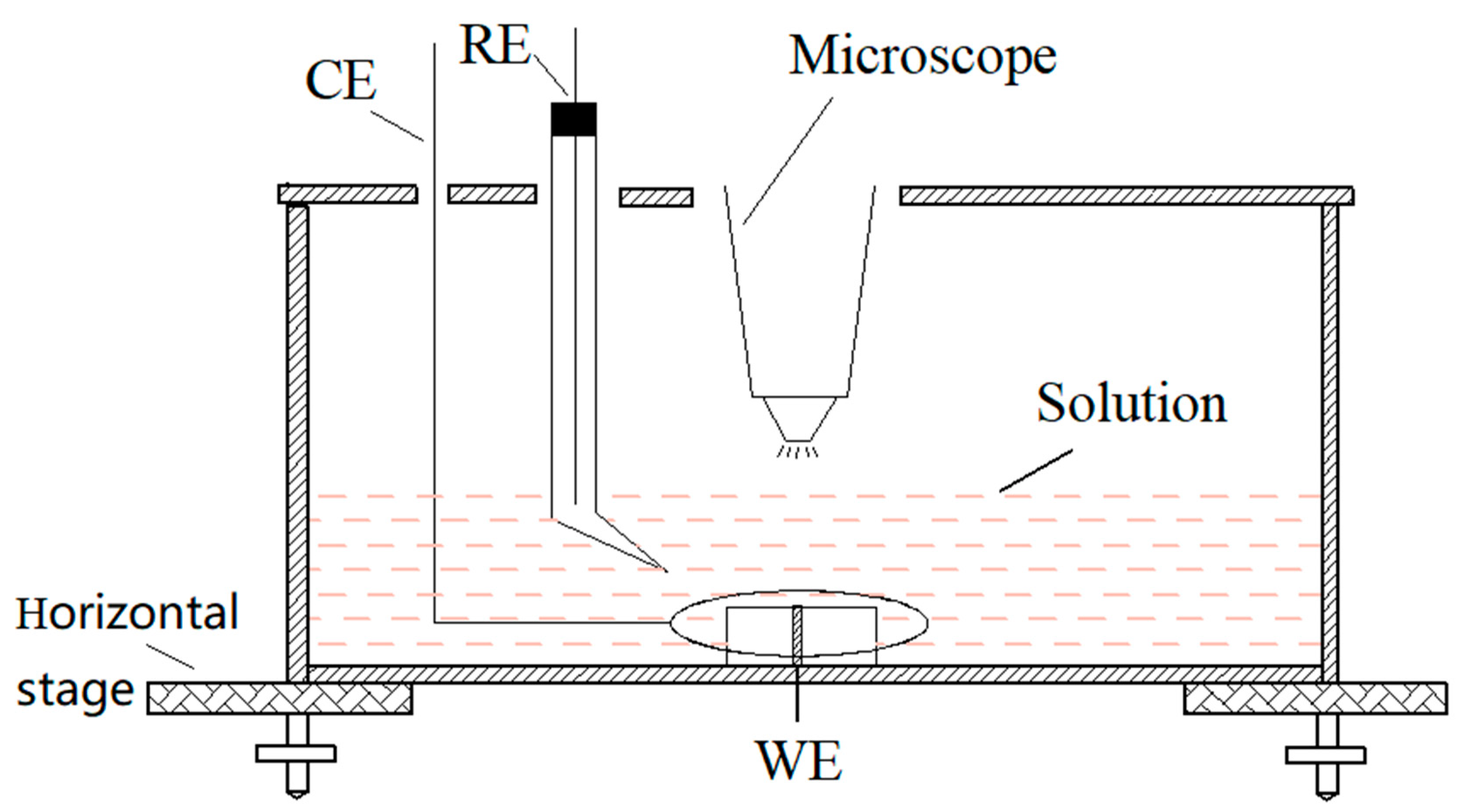
2.2. Chromogenic Testing
2.3. Electrochemical Testing of 304 SS in Different Iron Ion Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
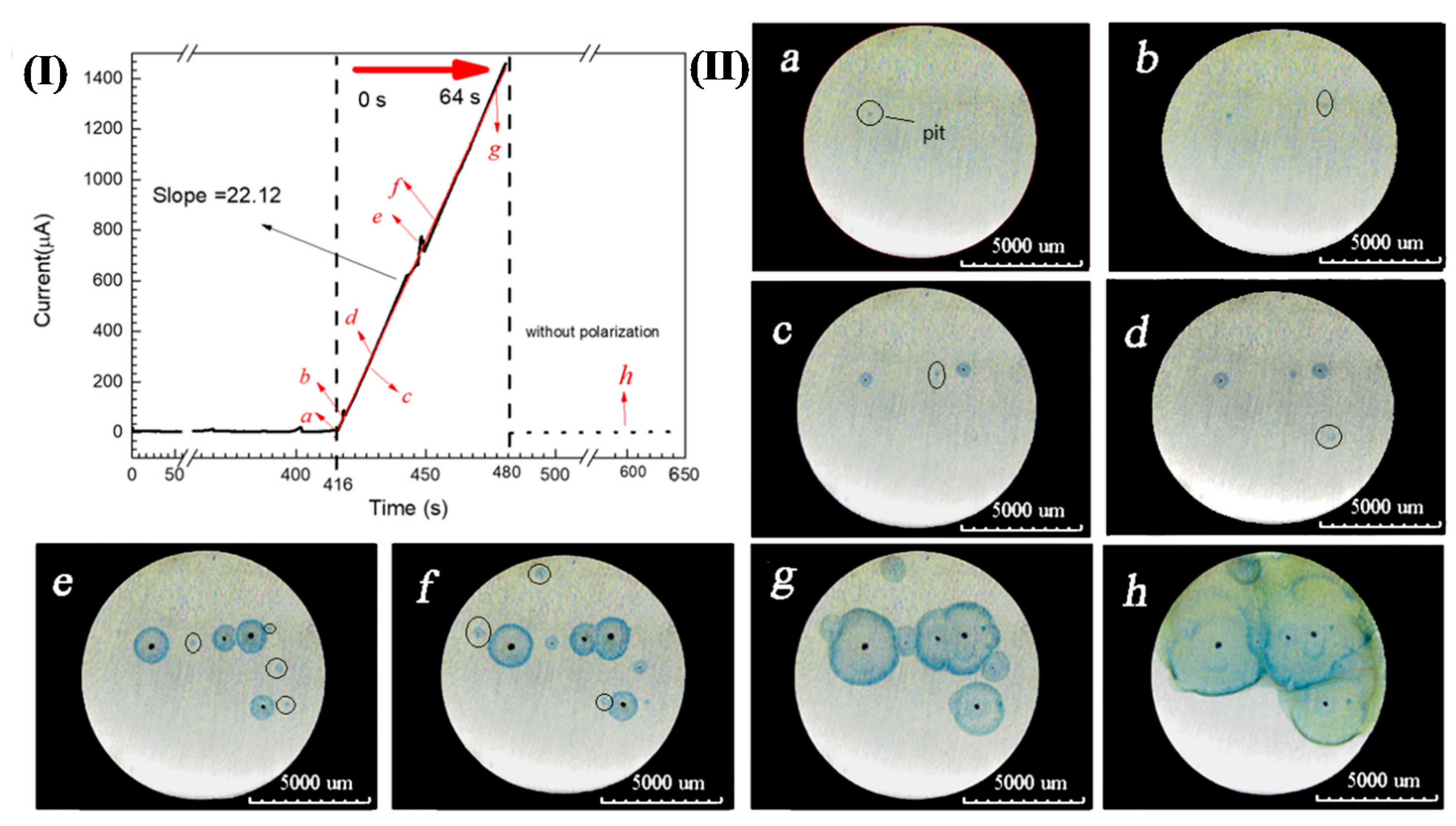
3.1. Chromogenic Testing Results
3.2. Electrochemical Testing Results of 304 SS in Different Iron Ion Solutions
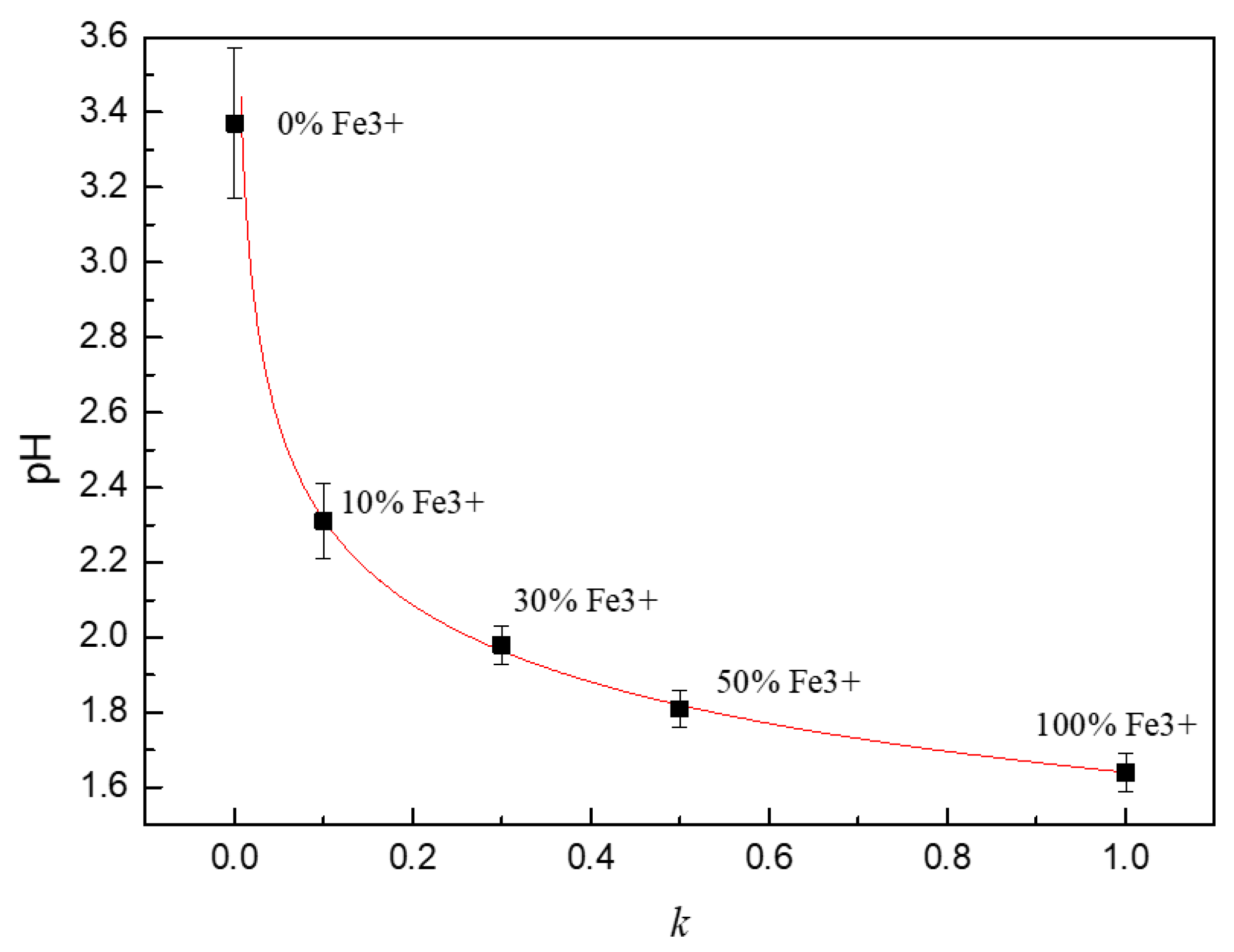
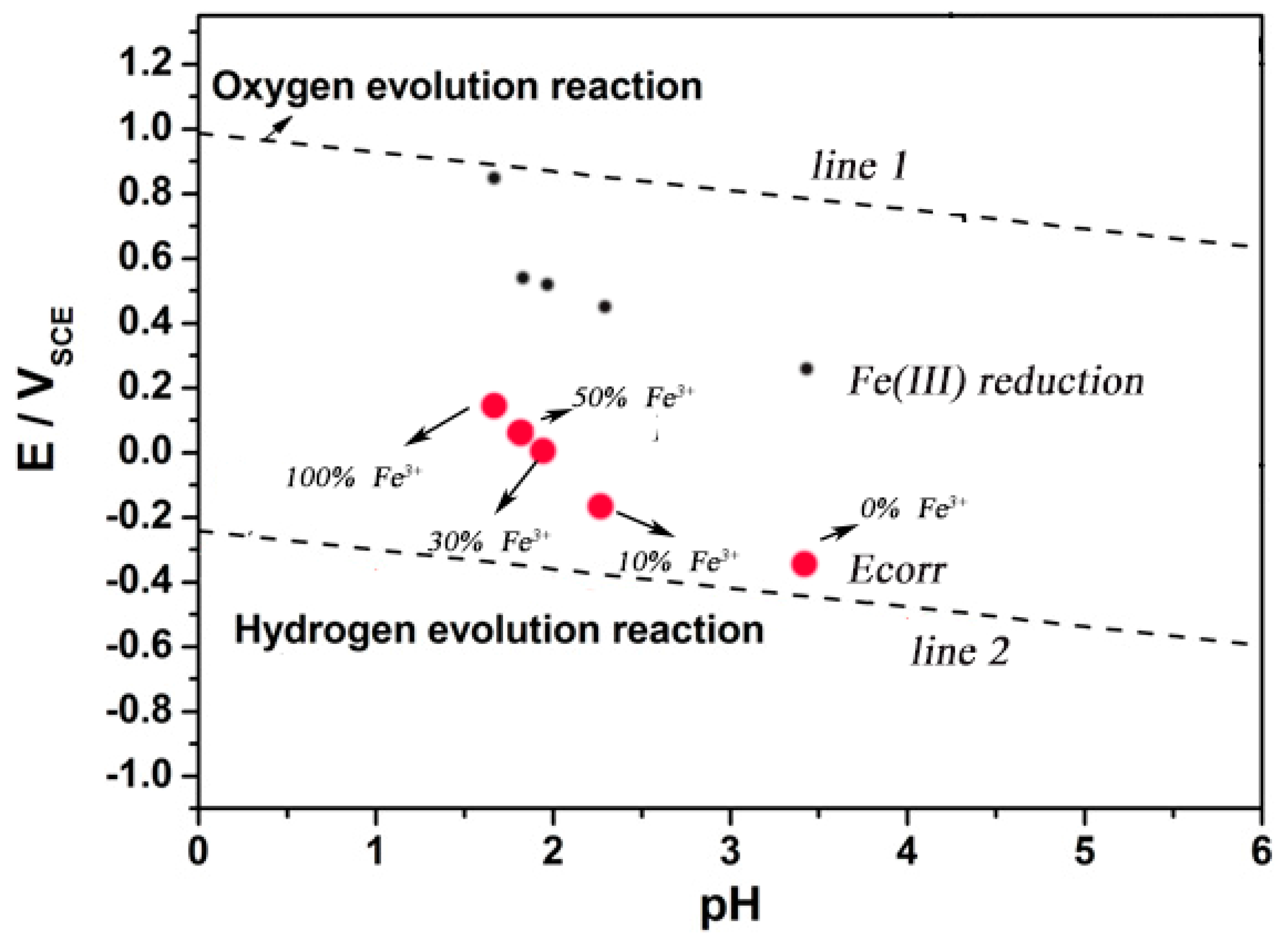
3.3. Analysis of Thermodynamic Conditions
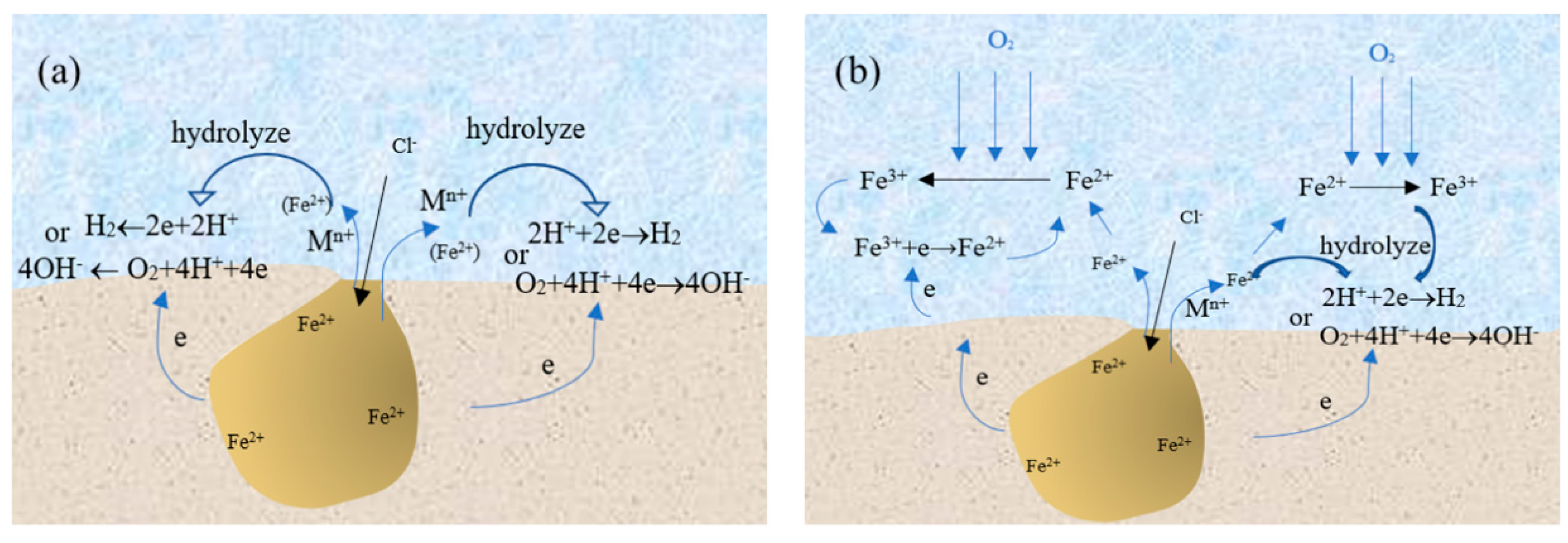
3.4. Cathodic Reaction
3.5. Effect of Fe3+ Around the Pit on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 SS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burstein, G.T.; Liu, C.; Souto, R.M.; Vines, S.P. Origins of pitting corrosion. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, G.T.; Liu, C. Nucleation of corrosion pits in Ringer’s solution containing bovine serum. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4296–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.M.; Du, N.; Li, S.M.; Chen, S.B.; Wu, Q.Y. Metastable pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, M.; Raeissi, K.; Atapour, M.; Fernández-Pérez, B.M.; Betancor-Abreu, A.; Llorente, I.; Fajardo, S.; Salarvand, Z.; Meghdadi, S.; Amirnasr, M.; et al. Pitting corrosion inhibition of 304 stainless steel in NaCl solution by three newly synthesized carboxylic Schiff bases. Corros. Sci. 2019, 160, 108130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, G.T.; Pistorius, P.C.; Mattin, S.P. The nucleation and growth of corrosion pits on stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistorius, P.C.; Burstein, G.T. Metastable pitting corrosion of stainless steel and the transition to stability. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1992, 341, 531–559. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Byeon, J.W. Morphological estimation of pitting corrosion on vertically positioned 304 stainless steel using acoustic-emission duration parameter. Corros. Sci. 2019, 148, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.B.; Dong, C.F.; Sun, M.; Xiao, K.; Zhong, P.; Li, X.G. Effects of solution pH and Cl− on electrochemical behaviour of an Aermet100 ultra–high strength steel in acidic environments. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 4159–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, M.; Müller, J. The mechanism of the oxygen reduction on rust-covered metal substrates. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 327–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.M.; Ai, Y.J.; Li, S.M.; Du, N.; Ye, C. Pitting Kinetics of 304 Stainless Steel Using ESPI Detection Technique. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.F.; Li, X.G.; Du, N.; Huang, Y.Z.; Korsunsky, A. Direct evidence of initial pitting corrosion. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Spikes, H.; Wong, J.S.S. In situ pH responsive fluorescent probing of localized iron corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wranglen, G. Pitting and sulphide inclusions in steel. Corros. Sci. 1974, 14, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, B.T.; Nishikata, A.; Tsuru, T. Scanning electrochemical microscope study on pitting corrosion of iron. Electrochemistry 2003, 71, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazarnezhad-Bajestani, M.; Neshati, J.; Siadati, M.H. Determination of SS321 pitting stage in FeCl3 solution based on electrochemical noise measurement data using artificial neural network. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 845, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikowski, J.; Jazdzewska, A.; Mazur, R.; Darowicki, K. Determination of pitting corrosion stage of stainless steel by galvanodynamic impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 253, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, P.; Snoeyink, V.L.; Lytle, D.A.; Kriven, W.M. Iron Corrosion Scales: Model for Scale Growth, Iron Release, and Colored Water Formation. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Zheng, Z.J.; Gao, Y. The bi-layer structure and the higher compactness of a passive film on nanocrystalline 304 stainless steel. Thin Solid Films 2016, 599, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Macdonald, D.D.; Dong, C. Passive film on 2205 duplex stainless steel studied by photo-electrochemistry and ARXPS methods. Corros. Sci. 2019, 146, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, Q. Spectrophotometric determination of methimazole in pharmaceutical, serum and urine samples by reaction with potassium ferricyanide-Fe(III). J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 65, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q. Spectrophotometric determination of perphenazine with the detection system of potassium ferricyanide-Fe(III) in pharmaceutical and serum samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2009, 74, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, S.K. Prussian Blue Still a Hot Topic. Chem. Eng. News 2005, 83, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, H.; Meguro, R.; Asano, Y.; Shoumura, K. Changes in non-heme iron histochemistry in the ischemic brains of cats and Mongolian gerbils. Int. Congr. Ser. 2003, 1251, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.M.; Li, S.M.; Du, N.; Chen, S.B.; Wu, Q.Y. Effects of applied potential on stable pitting of 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Chen, S.; Dou, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, L.; Man, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Cheng, Y.F.; Li, X. Passivation behavior and surface chemistry of 2507 super duplex stainless steel in artificial seawater: Influence of dissolved oxygen and pH. Corros. Sci. 2019, 150, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgerdi, A.A.; Brenna, A.; Ormellese, M.; Pedeferri, M.; Bolzoni, F. Experimental design to study the influence of temperature, pH, and chloride concentration on the pitting and crevice corrosion of UNS S30403 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2019, 159, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Vafaeian, S. Effect of solution pH on the electrochemical behaviour of AISI 304 austenitic and AISI 430 ferritic stainless steels in concentrated acidic media. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shojaei, E.; Mirjalili, M.; Moayed, M.H. The influence of the crevice induced IR drop on polarization measurement of localized corrosion behavior of 316L stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2019, 156, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, J.W.; Sutton, W.H. Crevice Corrosion of Stainless Steels: I. A Mathematical Model. Br. Corros. J. 1978, 13, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Q.; Wu, J.X.; Zhang, W.Q.; Lu, X.Y.; Wang, K. A pitting mechanism for passive 304 stainless steel in sulphuric acid media containing chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 1993, 34, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Composition | Solutions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% Fe3+ | 10% Fe3+ | 50% Fe3+ | 100% Fe3+ | |
| FeCl2 (mol/L) | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0 |
| FeCl3 (mol/L) | 0 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| Testing Conditions | Ecorr/mV | Jcorr/μA·cm−2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mol/FeCl2 | −0.316 | 1.09 |
| 0.09 mol/FeCl2 + 0.01 mol/FeCl3 | −0.174 | 0.98 |
| 0.07 mol/FeCl2 + 0.03 mol/FeCl3 | 0.003 | 2.68 |
| 0.05 mol/FeCl2 + 0.05 mol/FeCl3 | 0.069 | 2.95 |
| 0.1 mol/FeCl3 | 0.123 | 3.42 |
| Potential V/SCE | Solutions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% Fe3+ | 10% Fe3+ | 30% Fe3+ | 50% Fe3+ | 100% Fe3+ | |
| 0.786 ± 0.012 | 0.849 ± 0.006 | 0.868 ± 0.003 | 0.878 ± 0.003 | 0.888 ± 0.003 | |
| −0.443 ± 0.012 | −0.380 ± 0.006 | −0.361 ± 0.003 | −0.351 ± 0.003 | −0.341 ± 0.003 | |
| 0.232 | 0.471 | 0.505 | 0.527 | 0.823 | |
| Ecorr | −0.316 | −0.174 | 0.003 | 0.069 | 0.123 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Du, N.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, W. Determination of Iron Valence States Around Pits and the Influence of Fe3+ on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel. Materials 2020, 13, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030726
Zhang H, Du N, Wang S, Zhao Q, Zhou W. Determination of Iron Valence States Around Pits and the Influence of Fe3+ on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel. Materials. 2020; 13(3):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, Nan Du, Shuaixing Wang, Qing Zhao, and Wenjie Zhou. 2020. "Determination of Iron Valence States Around Pits and the Influence of Fe3+ on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel" Materials 13, no. 3: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030726
APA StyleZhang, H., Du, N., Wang, S., Zhao, Q., & Zhou, W. (2020). Determination of Iron Valence States Around Pits and the Influence of Fe3+ on the Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel. Materials, 13(3), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030726




