Effect of Chromium and Molybdenum Addition on the Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
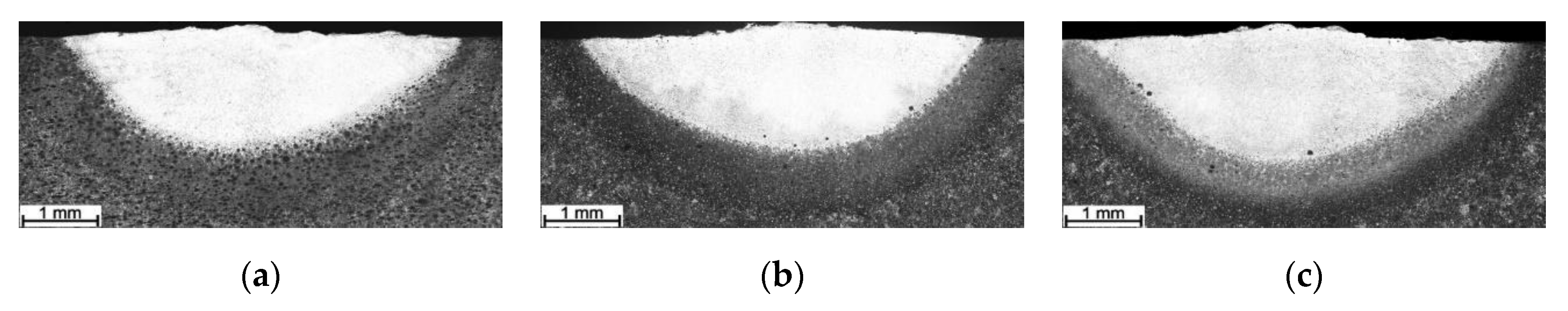
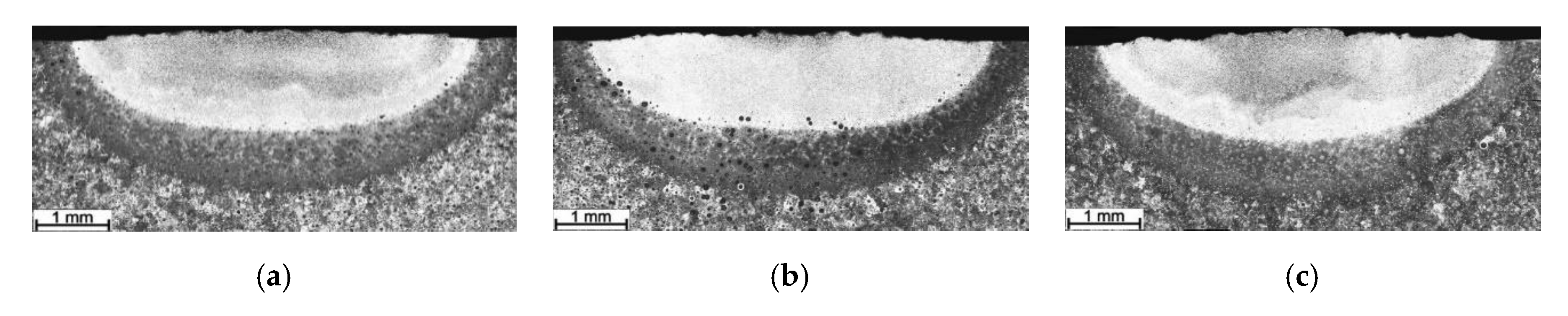
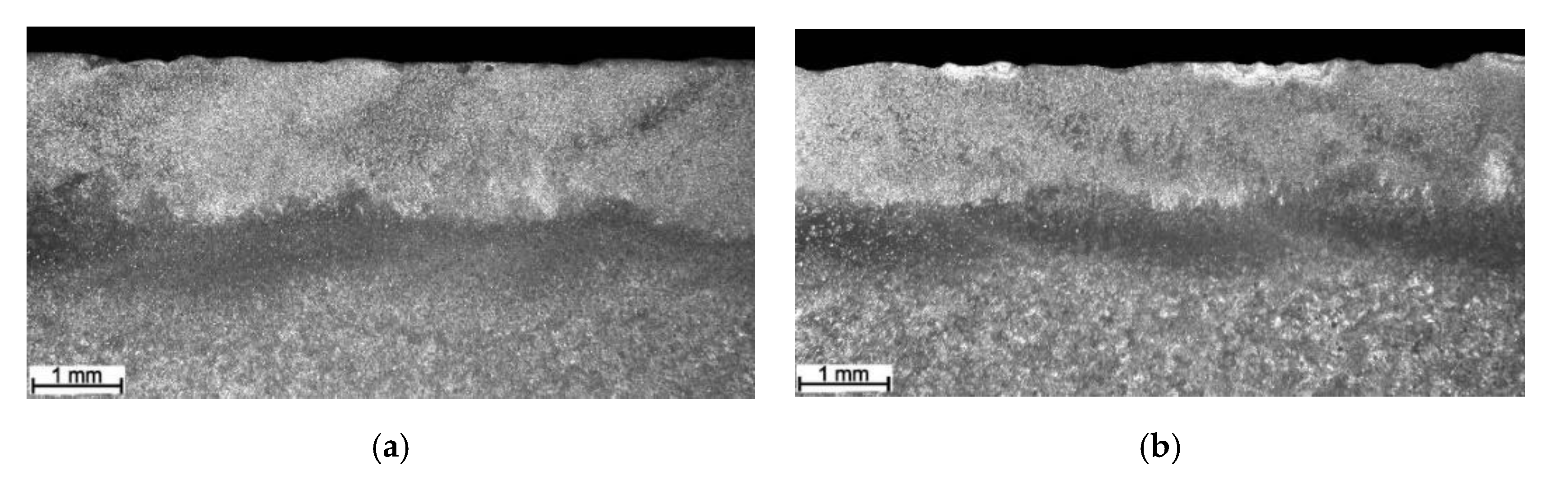
3.1. Macrostructure Analysis
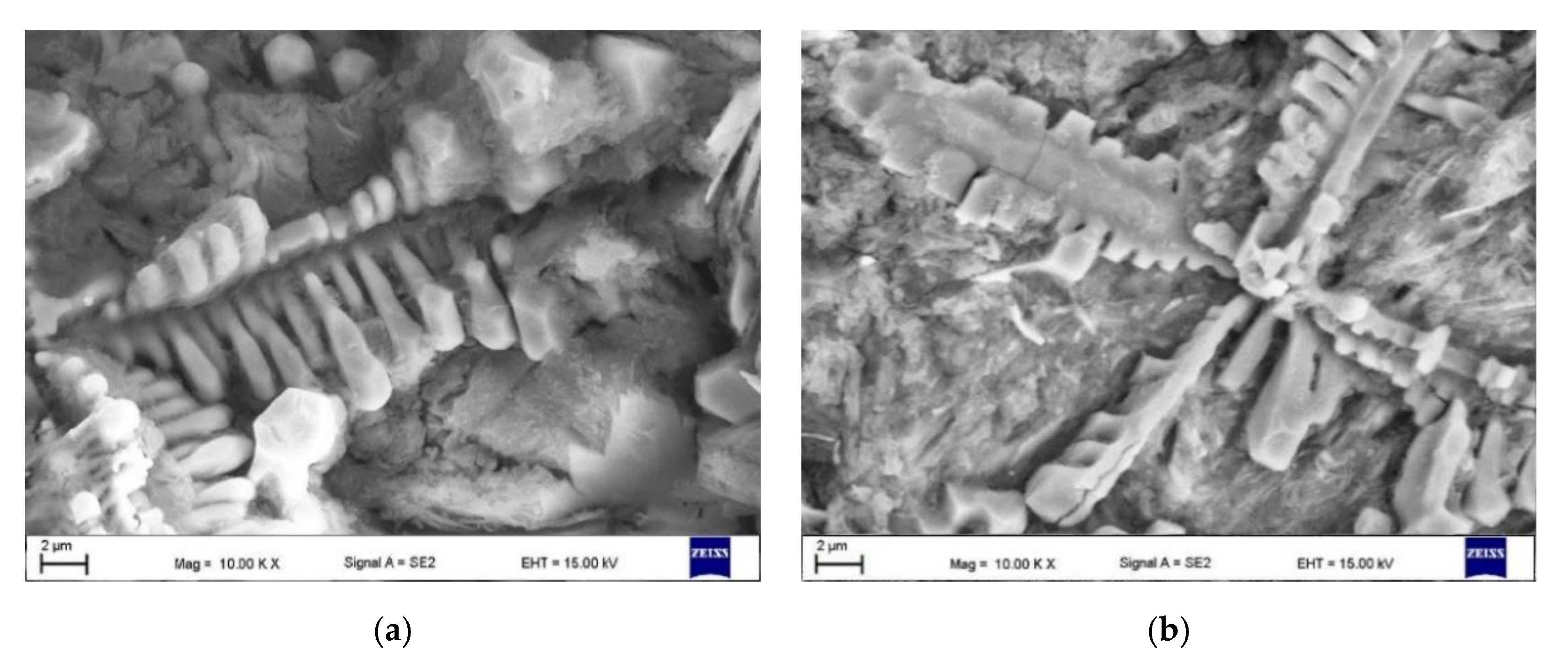
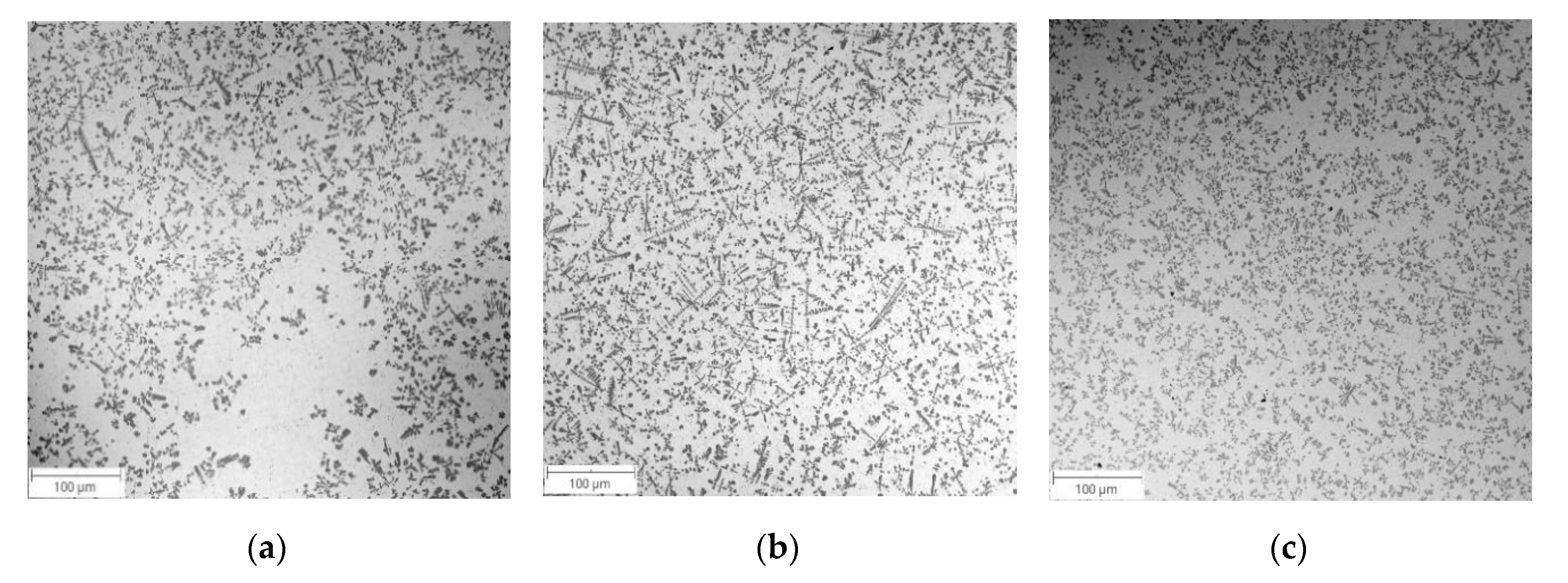
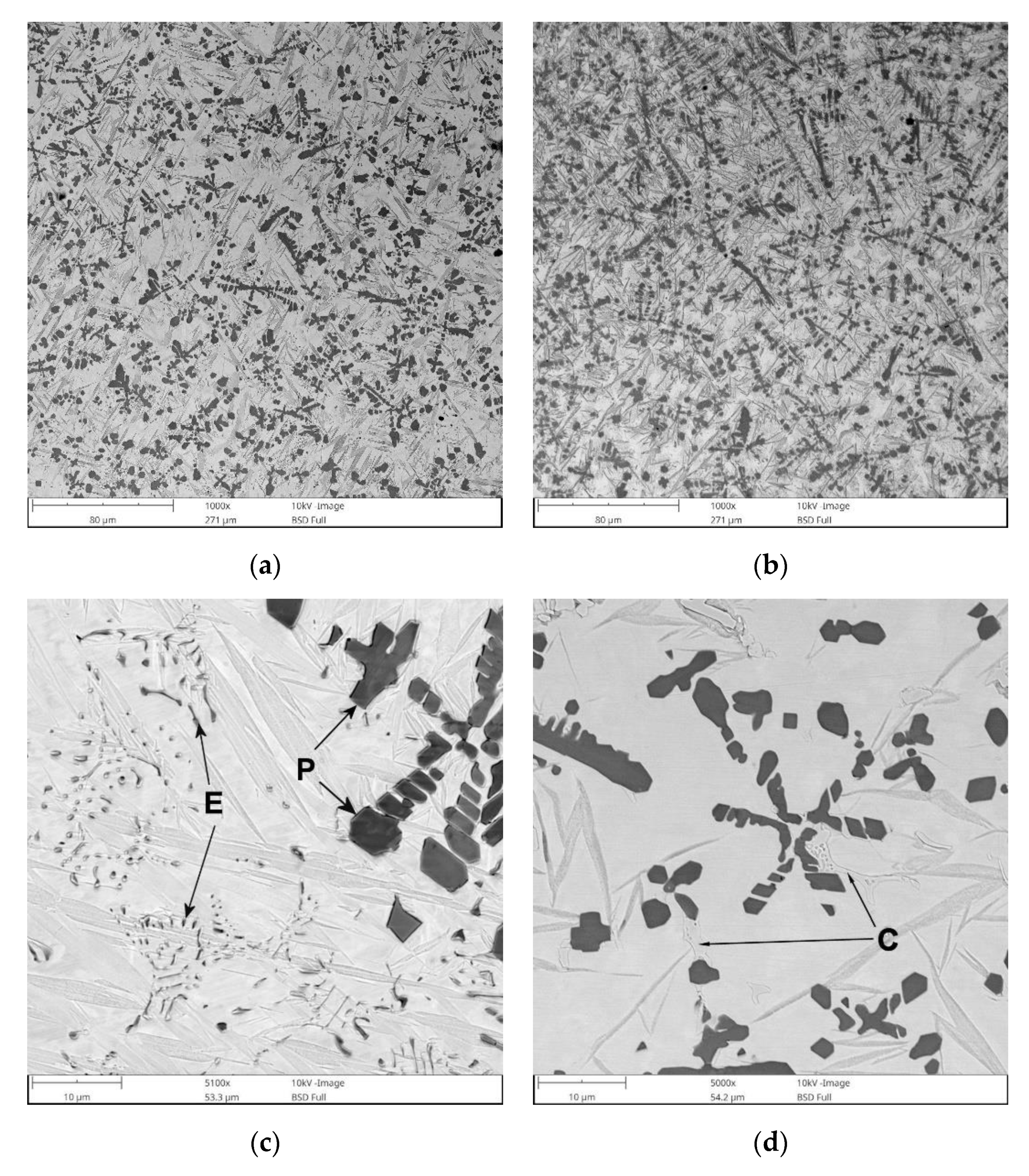
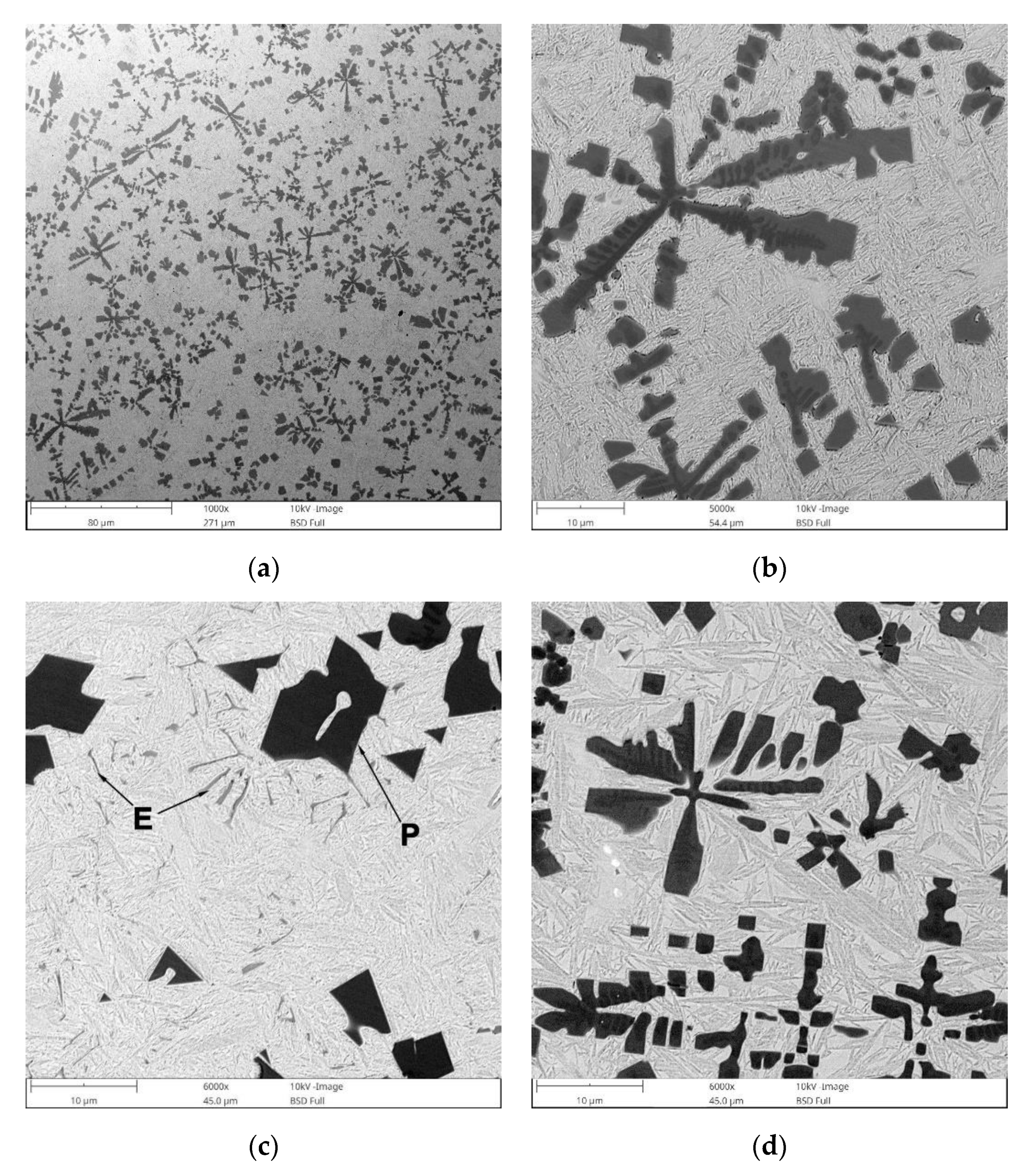
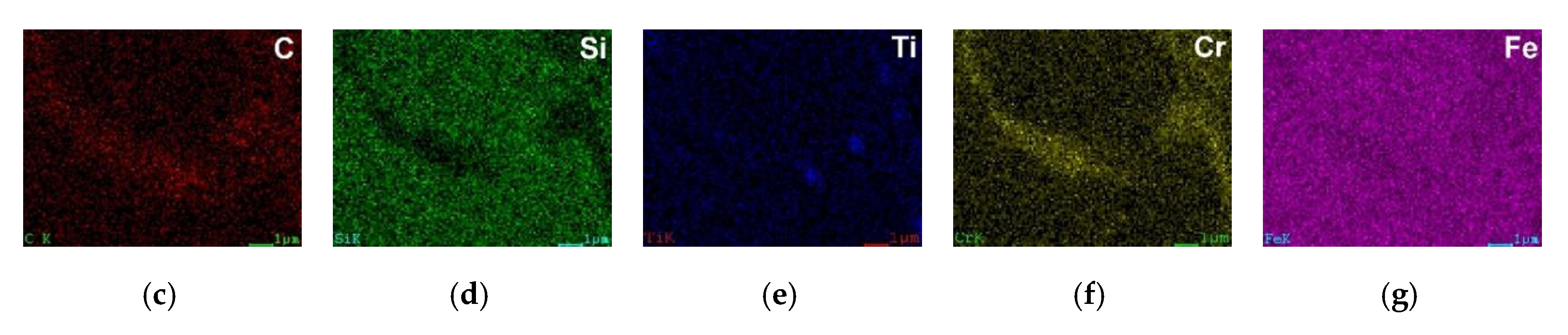
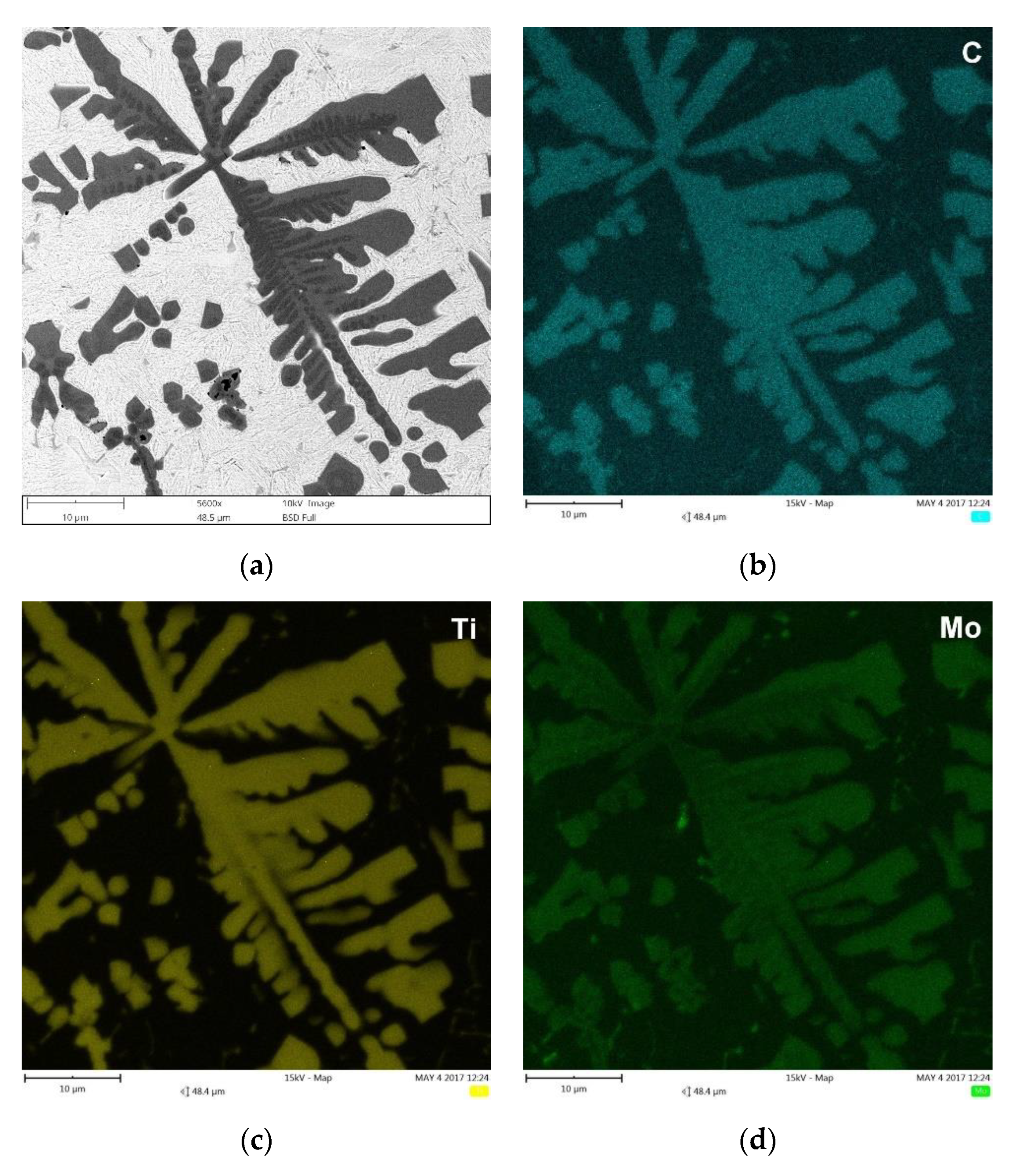
3.2. Microstructural Analysis
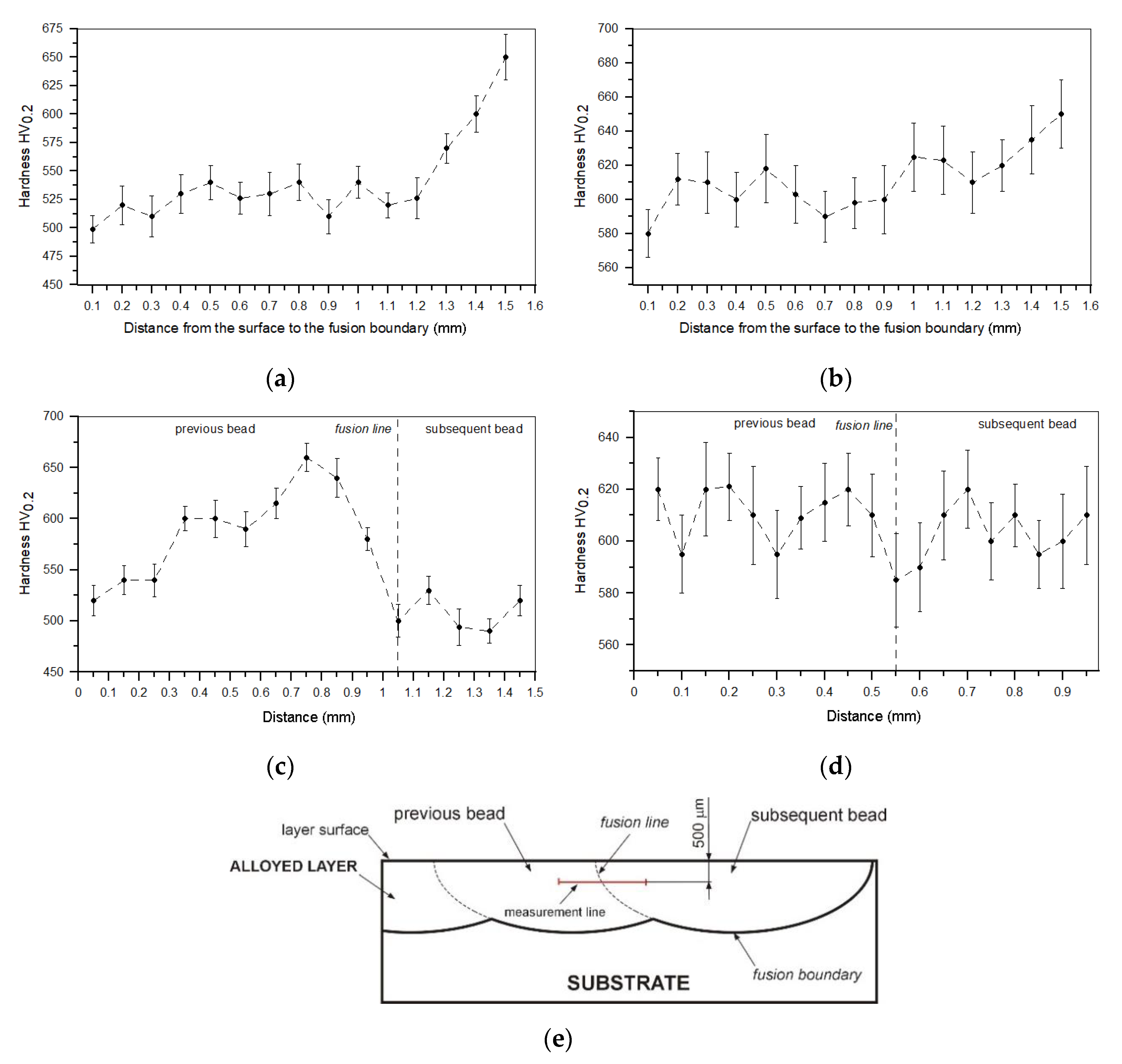
3.3. Hardness Analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| TRL | TiC-reinforced composite surface layer |
| LA | Laser surface alloying |
| DCI | Ductile cast iron |
| MMC | Metal matrix composite |
| SM | Substrate material |
| SAB | Single-alloyed bead |
| SAL | Surface alloyed layer (the layer produced via a multi-pass overlapping alloying process) |
| TRC | SAL produced using a powder mixture of Ti-Cr |
| TRM | SAL produced using a powder mixture of Ti-Mo |
| TR | SAL produced using a pure Ti powder |
| HAZ | Heat-affected zone |
| MFP | Mean free path |
| BSE | Back-Scattered Electron |
References
- Paczkowska, M.; Makuch, N.; Kulka, M. The influence of various cooling rates during laser alloying on nodular iron surface layer. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 102, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, N.; Yang, C.; Duraiselvam, M.; Prabu, G.; Tseng, S.; Kumar, D.R. Investigation of high temperature wear performance on laser processed nodular iron using optimization technique. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. Direct diode laser surface melting of nodular cast iron. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 809–810, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschini, L.; Campana, G.; Pagano, N.; Angelin, V. Effect of laser surface treatment on the dry sliding behaviour of the EN-GJS400-12 ductile cast iron. Tribol. Int. 2016, 104, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Shi, Y. Investigation on wear resistance of nodular cast iron by laser surface treatment. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, N.; Angelini, V.; Ceschini, L.; Campana, G. Laser remelting for enhancing tribological preferences of a ductile iron. Procedia CIRP 2016, 41, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D.; Górka, J.; Kwaśny, W.; Pakieła, W.; Matus, K. Influence of solidification conditions on the microstructure of laser-surface-melted ductile cast iron. Materials 2020, 13, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, N.; Yang, C.; Duraiselvam, M.; Prabu, G. Microstructure and tribological evolution during laser alloying WC-12%Co and Cr3C2−25%NiCr powders on nodular iron surface. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tański, T.; Pakieła, W.; Janicki, D.; Tomiczek, B.; Król, M. Properties of the aluminium alloy EN AC-51100 after laser surface treatment. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, A. Titanium matrix composite Ti/TiN produced by diode laser gas nitriding. Metals 2015, 5, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Łatka, L.; Walczak, M.; Winnicki, M. Comparative study on the cavitation erosion and sliding wear of cold-sprayed Al/Al2O3 and Cu/Al2O3 coatings, and stainless steel, aluminium alloy, copper and brass. Metals 2020, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Mridha, S.; Stack, M.M. Mapping wear mechanisms of TiC/Ti composite coatings. Wear 2015, 328–329, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Hejwowski, T. Cavitation erosion resistance and wear mechanism model of flame-sprayed Al2O3-40% TiO2/NiMoAl cermet coatings. Coatings 2018, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wang, A.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, K.; Huang, Z. Microstructure and wear resistance of composite layers on a ductile iron with multicarbide by laser surface alloying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 7001–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, H.C.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, F.T.; Yue, T.M. In situ synthesis of TiC reinforced surface MMC on Al6061 by laser surface alloying. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.I.; Nakata, K.; Tomida, S. In situ formation of TiC particulate composite layer on cast iron by laser alloying of thermal sprayed titanium coating. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D.; Górka, J.; Kwaśny, W.; Gołombek, K.; Kondracki, M.; Żuk, M. Diode laser surface alloying of armor steel with tungsten carbide. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikin, R.M. The mechanical properties of in-situ composites. JOM 1997, 49, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashivamurthy, K.I.; Kumar, R.K.; Seetharamu, S.; Chandrasekharaiah, M.N. Review on TiC reinforced steel composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 4519–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. In-situ synthesis of titanium carbide particles in an iron matrix during diode-laser surface alloying of ductile cast iron. Mater. Technol. 2016, 51, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilev, V.G.; Morozov, E.A. Laser melt injection of austenitic cast iron Ch16D7GKh with titanium. Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Met. 2016, 57, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, W.; Su, Y. TiC reinforcement composite coating produced using graphite of the cast iron by laser cladding. Materials 2016, 9, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicki, D. Microstructural evolution during laser surface alloying of ductile cast iron with titanium. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 2425–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. Microstructure and sliding wear behaviour of in-situ TiC-reinforced composite surface layers fabricated on ductile cast iron by laser alloying. Materials 2018, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. Fabrication of TiC-reinforced surface layers on ductile cast iron substrate by laser surface alloying. Solid State Phenom. 2020, 308, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y. Microstructure and properties of a titanium carbide reinforced coating on grey iron applied with laser cladding. Mater. Technol. 2019, 53, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.N.; Hawk, J.A.; Tylczak, J.H.; Wilson, R.D.; Govier, R.D. Wear of titanium carbide reinforced metal matrix composite. Wear 1999, 225–229, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, E.; Szymański, Ł.; Kurtyka, P.; Tokarski, T.; Maziarz, W.; Grabowska, B.; Czapla, P. Locally reinforcement TiC-Fe type produced in situ in castings. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Hua, B.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, Z. Dry sliding wear behaviour of TiC/Fe composites fabricated by exothermic dispersion of Fe–Ti–C powders. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2014, 8, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. The Effect of Melt Composition on Microstructure of In-Situ Tic-Reinforced Fe-Based Composite Surface Layers Synthesized via a Laser Surface Alloying; Department of Welding, Silesian University of Technology: Gliwice, Poland, 2017; unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Janicki, D. The effect of cooling rate on microstructure of in-situ TiC-reinforced Fe-based composite surface layers synthesized on the ductile cast iron via a laser surface alloying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021. in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Heiple, C.R.; Roper, J.R. Mechanism for minor element effect on GTA fusion zone geometry. Weld. J. 1982, 61, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Heiple, C.R.; Roper, J.R.; Stagner, R.T.; Aden, R.J. Surface active element effects on the shape of GTA, laser, and electron beam welds. Weld. J. 1983, 62, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Heiple, C.R.; Burgardt, P. Effects of SO2 shielding gas additions on GTA weld shape. Weld. J. 1985, 64, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Janicki, D. Fabrication of high chromium white iron surface layers on ductile cast iron substrate by laser surface alloying. Stroj. Vestn. 2017, 63, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Heo, Y.U.; Suh, D.W. Stability of (Ti, M)C (M = Nb, V, Mo and W) carbide in steals using first-principle calculations. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. The friction and wear behaviour of in-situ titanium carbide reinforced composite layers manufactured on ductile cast iron by laser surface alloying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 126634, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, H.O. Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides: Properties Characteristic, Processing and Application; Noyes Publications: Westwood, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Storms, E.K. The Refractory Carbides; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Zum Ghar, K.-H. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; Tribology Series 10; Elsevier Science Publishers, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Thakare, M.R.; Wharton, J.A.; Wood, R.J.K.; Menger, C. Effect of abrasive particle size and the influence of microstructure on the wear mechanisms in wear-resistant materials. Wear 2012, 276–277, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzeciwilk, D.; Wokulski, Z.; Tkacz, P. Growth and TEM and HREM characterisation of TiC crystals grown from high-temperature solutions. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2003, 38, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Influence of trace boron on the morphology of titanium carbide in an Al–Ti–C–B master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 491, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzeciwilk, D.; Wokulski, Z.; Tkacz, P. Microstructure of TiC crystals obtained from high temperature nickel solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 350, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, L. Microstructure and mechanical behaviors of in situ TiC particulates reinforced Ni matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3898–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopagoni, S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Singh, A.R.P.; Mensah, B.A.; Bunce, N.; Tiley, J.; Scharf, T.W.; Banerjee, R. Microstructural evolution in laser deposited nickel–titanium–carbon in situ metal matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Morphological evolution of TiC from octahedron to cube induced by elemental nickel. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| C | Si | Cu | Mn | Cr | Ni | Ti | Mo | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.60 | 2.51 | 0.78 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.016 | balance |
| Processing Condition No./SAB No. | Alloying Material | Powder Feed Rate 2 (mg/mm) | Fusion Area of the SAB (mm2) | Average Ti Content, (wt%) | Average Cr Content, (wt%) | Average Mo Content, (wt%) | Quality 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | Ti | 8.0 | 7.34 ± 0.61 | 7.0 ± 0.8 | − | − | U |
| T2 | 10.0 | 7.05 ± 0.58 | 8.8 ± 1.1 | − | − | U | |
| T3 | 11.0 | 6.80 ± 0.50 | − | − | − | N | |
| TC1 | Ti-Cr 1 | 9.0 | 7.73 ± 0.63 | 8.4 ± 0.29 | 1.6 ± 0.11 | − | U |
| TC2 | 11.0 | 7.89 ± 0.65 | 10.3 ± 0.38 | 1.9 ± 0.15 | − | U | |
| TC3 | 12.0 | 8.50 ± 0.67 | 11.6 ± 0.58 | 2.3 ± 0.24 | − | U | |
| TC4 | 13.0 | 8.42 ± 0.71 | − | − | − | N | |
| TM1 | Ti-Mo 1 | 10.0 | 8.20 ± 0.63 | 7.0 ± 0.38 | − | 1.8 ± 0.16 | U |
| TM2 | 12.5 | 8.09 ± 0.62 | 8.4 ± 0.46 | − | 2.3 ± 0.23 | U | |
| TM3 | 13.5 | 8.10 ± 0.64 | 9.9 ± 0.69 | − | 2.8 ± 0.32 | U | |
| TM4 | 14.0 | 8.07 ± 0.69 | − | − | − | N |
| TRL No. | Processing Condition No. (Table 2) 1 | α-Fe (Martensite) Fraction (wt%) 2 | Retained Austenite Fraction (wt%) 2 | Cementite Fraction (vol%) | TiC Fraction (vol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR | T2 | 66.4 ± 1.1 | 15.3 ± 1.4 | 8.1 ± 2.9 | 15.4 ± 2.1 |
| TRC | TC3 | 52.9 ± 1.6 | 23.7 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 20.8 ± 1.1 |
| TRM | TM3 | 69.1 ± 1.4 | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 21.1 ± 1.3 |
| TRL No. | Element (wt%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Ti | Cr | Mo | Mn | Si | Cu | S | P | Fe | |
| TR | 3.15 | 9.5 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 1.99 | 0.79 | 0.148 | 0.023 | balance |
| TRC | 3.10 | 12.4 | 2.87 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 1.90 | 0.81 | 0.181 | 0.025 | balance |
| TRM | 3.07 | 10.5 | 0.06 | 3.15 | 0.14 | 1.85 | 0.76 | 0.177 | 0.023 | balance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janicki, D. Effect of Chromium and Molybdenum Addition on the Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying. Materials 2020, 13, 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245750
Janicki D. Effect of Chromium and Molybdenum Addition on the Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying. Materials. 2020; 13(24):5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245750
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanicki, Damian. 2020. "Effect of Chromium and Molybdenum Addition on the Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying" Materials 13, no. 24: 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245750
APA StyleJanicki, D. (2020). Effect of Chromium and Molybdenum Addition on the Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Fabricated on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying. Materials, 13(24), 5750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245750





