Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxane Derivatives as Additive or Reactive Components of Epoxy Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analytical Techniques
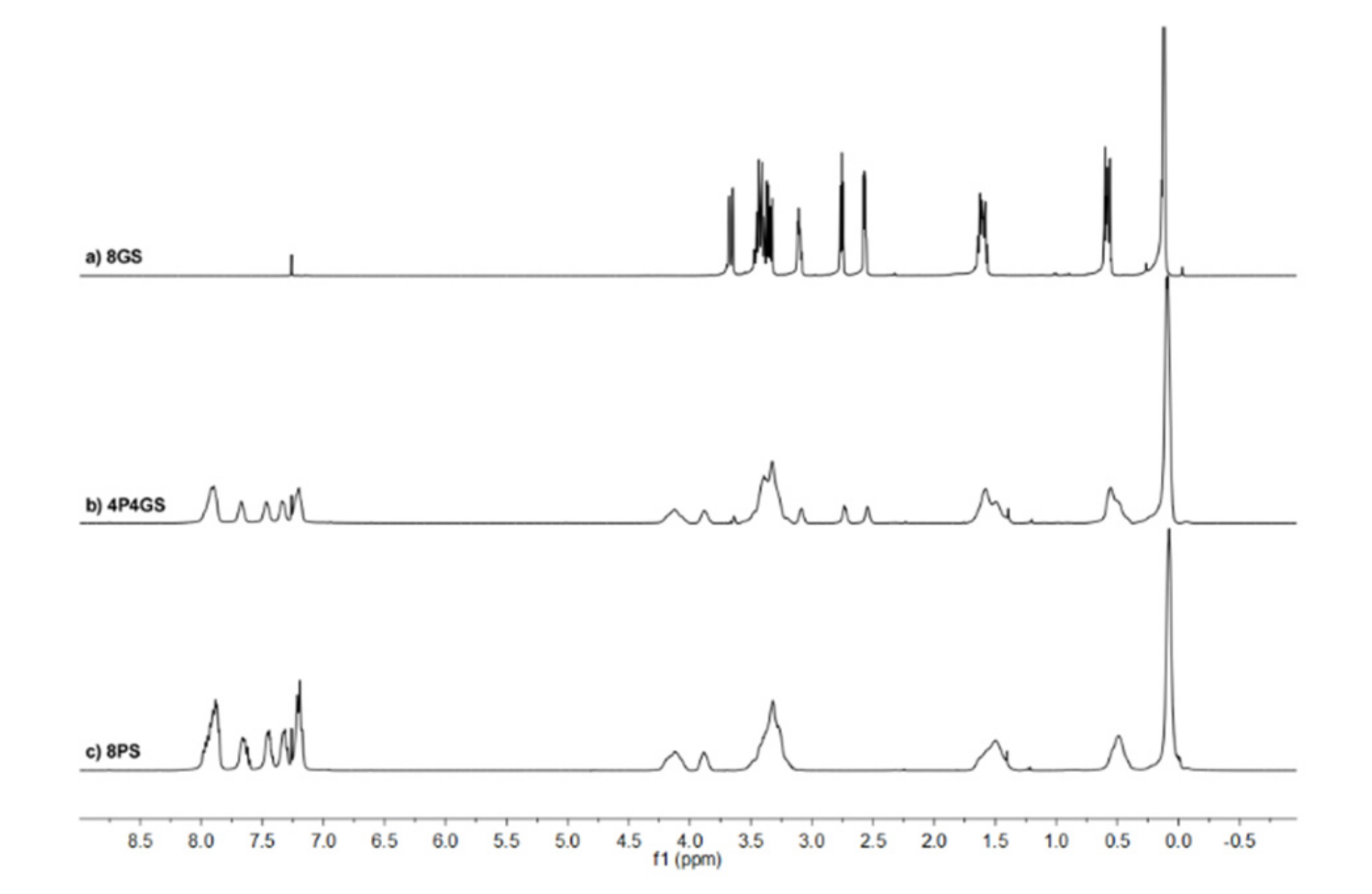
2.2.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
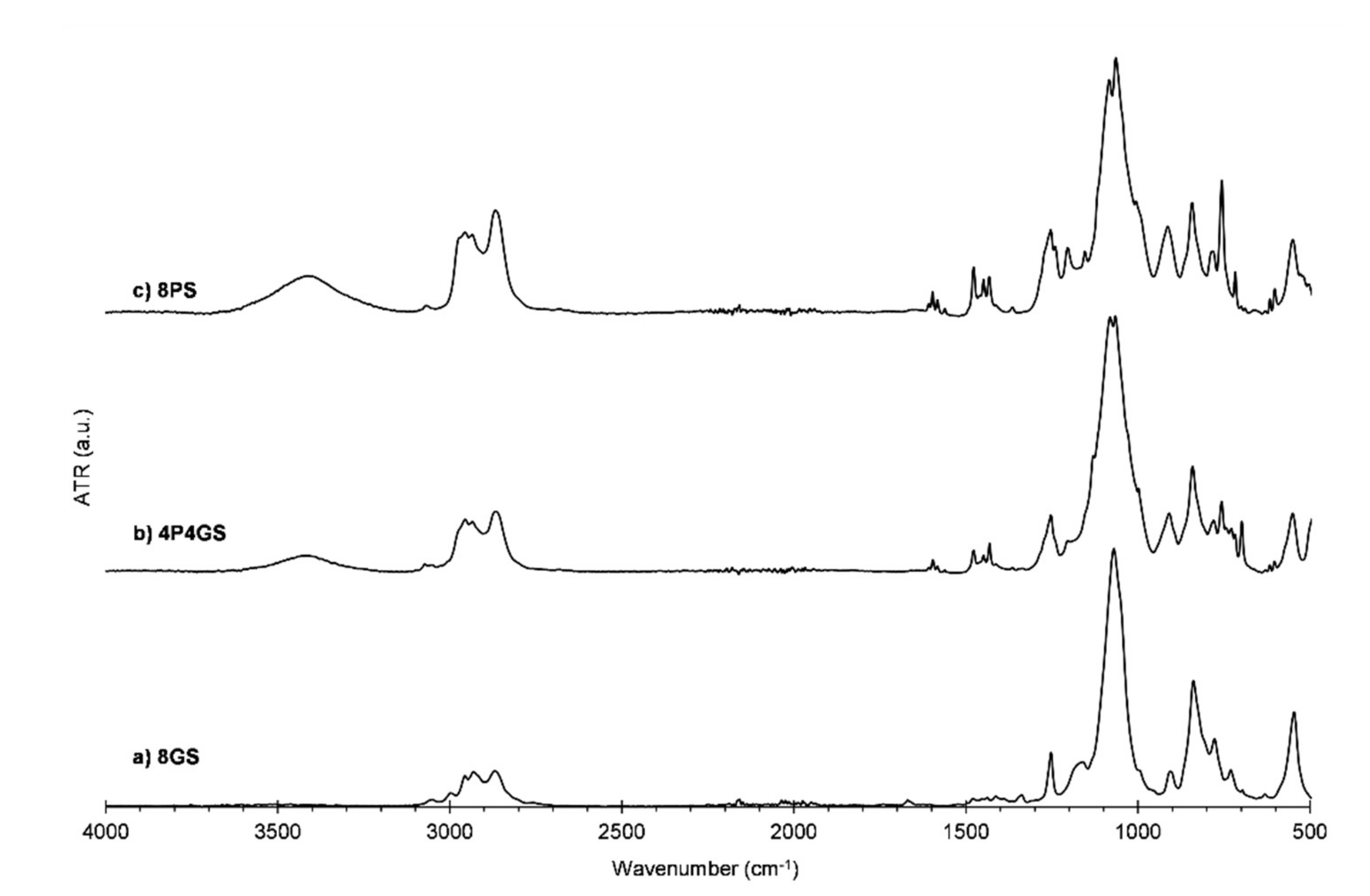
2.2.2. Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
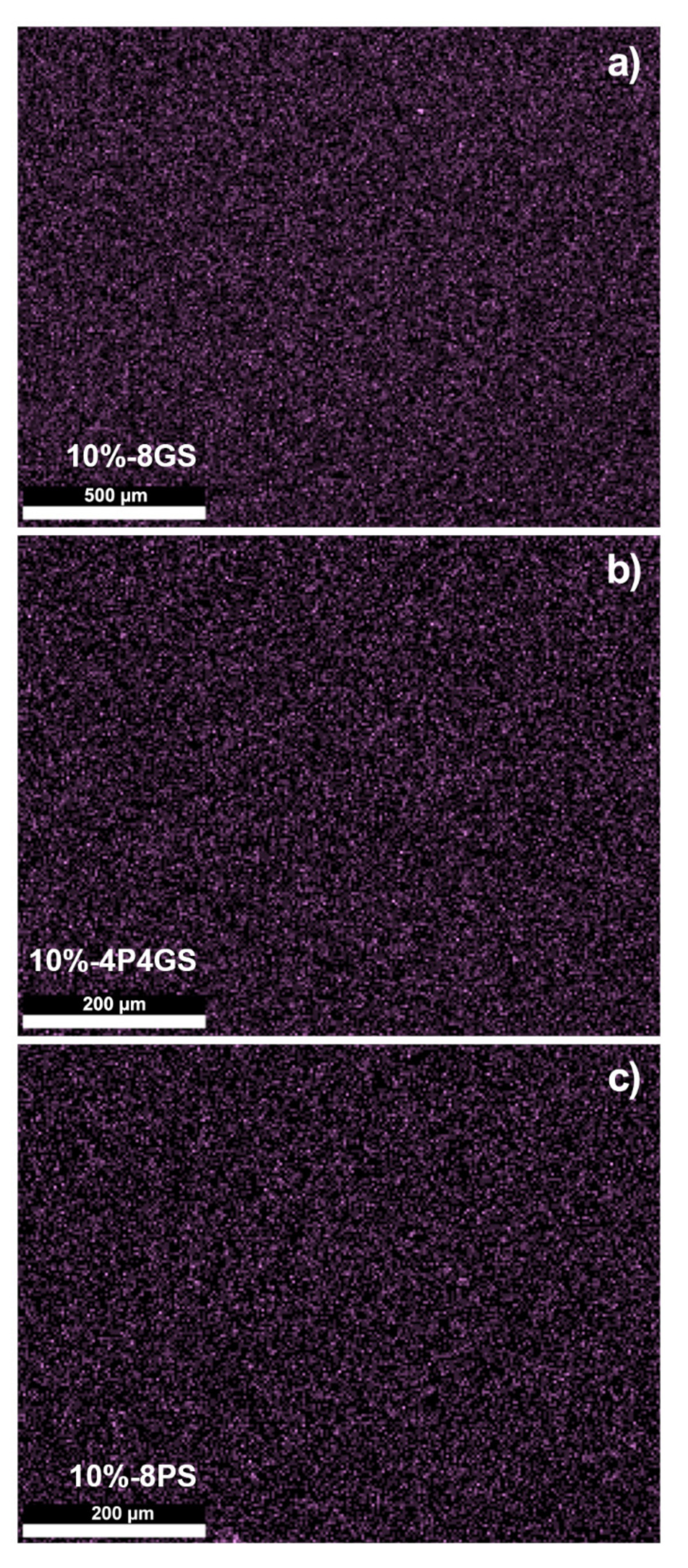
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscope and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM, EDS)
2.2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.6. Cone Calorimetry
2.2.7. Nanomechanical Analysis
2.2.8. Static Water Contact Angle (WCA)
2.3. Synthetic Procedures
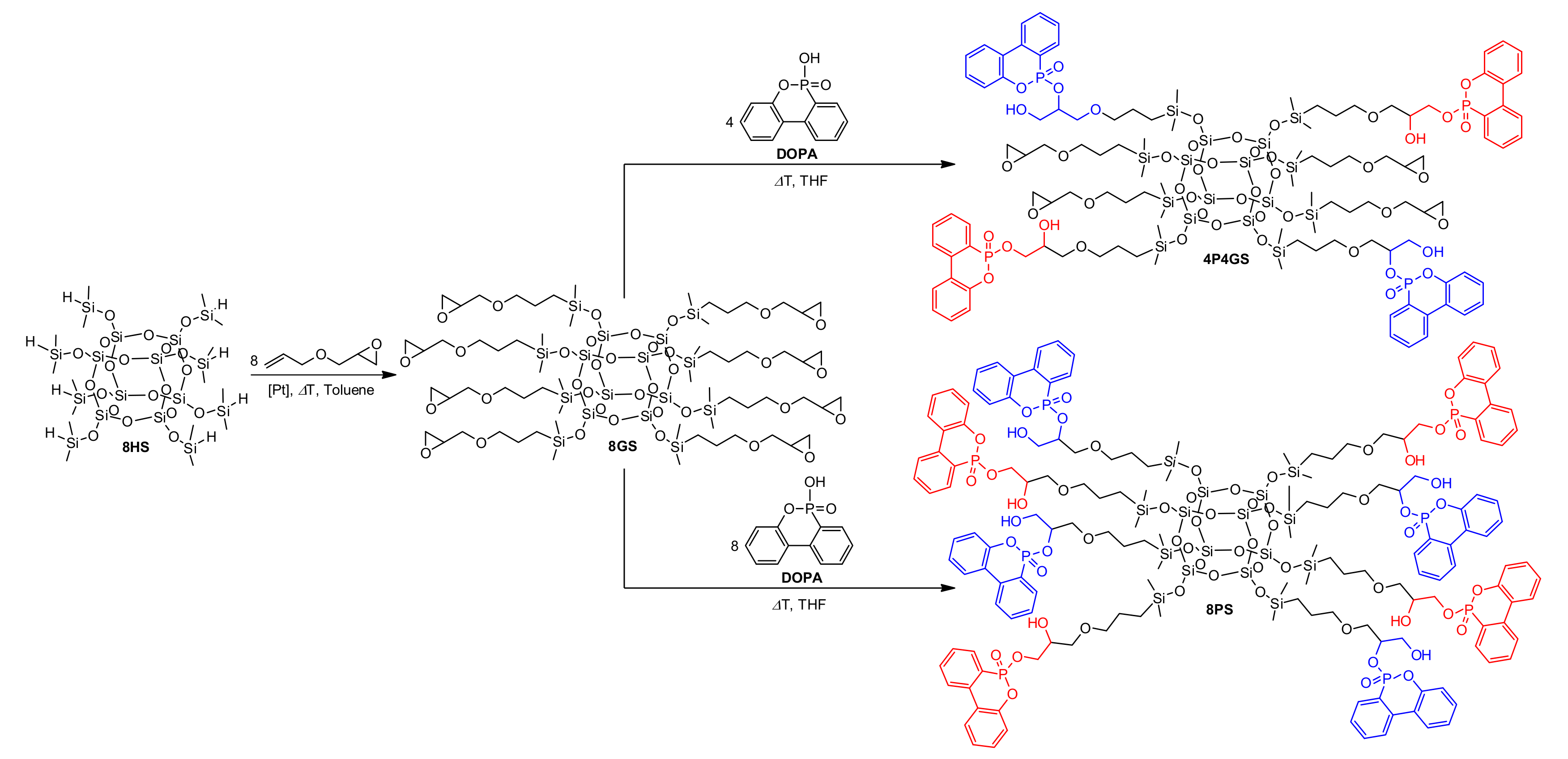
2.3.1. Synthesis of Octakis[(3-glycidoxypropyl)dimethylsiloxy]octasilsesquioxane (8GS)
2.3.2. Synthesis of 10-Hydroxy-9,10-dihydro-9-oxa-10-phosphaphenanthrene-10-oxide (DOPA)
2.3.3. Synthesis of Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxanes (4P4GS and 8PS)
2.3.4. Epoxy Resin Samples Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silsesquioxanes Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy Measurements
3.3. Surface Properties
3.4. Mechanical Properties
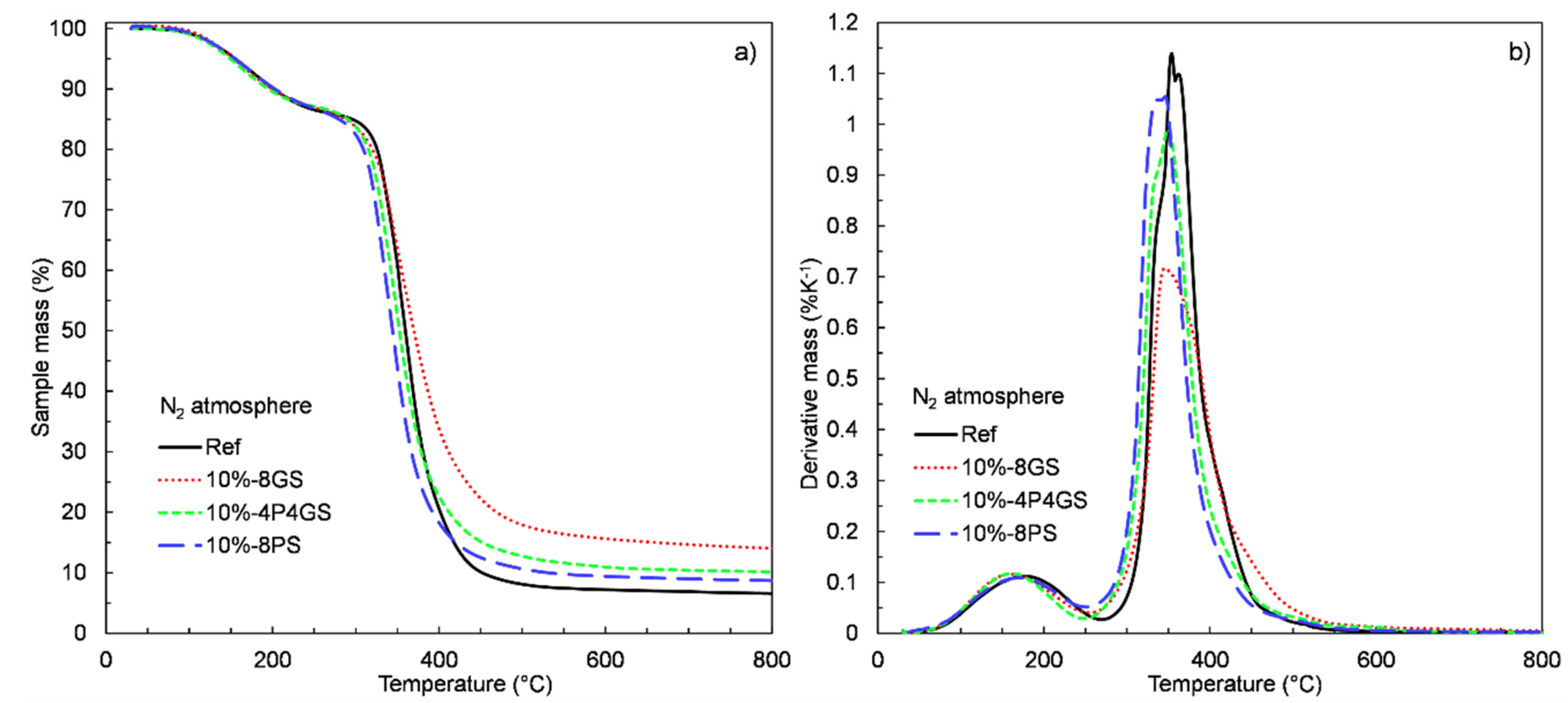
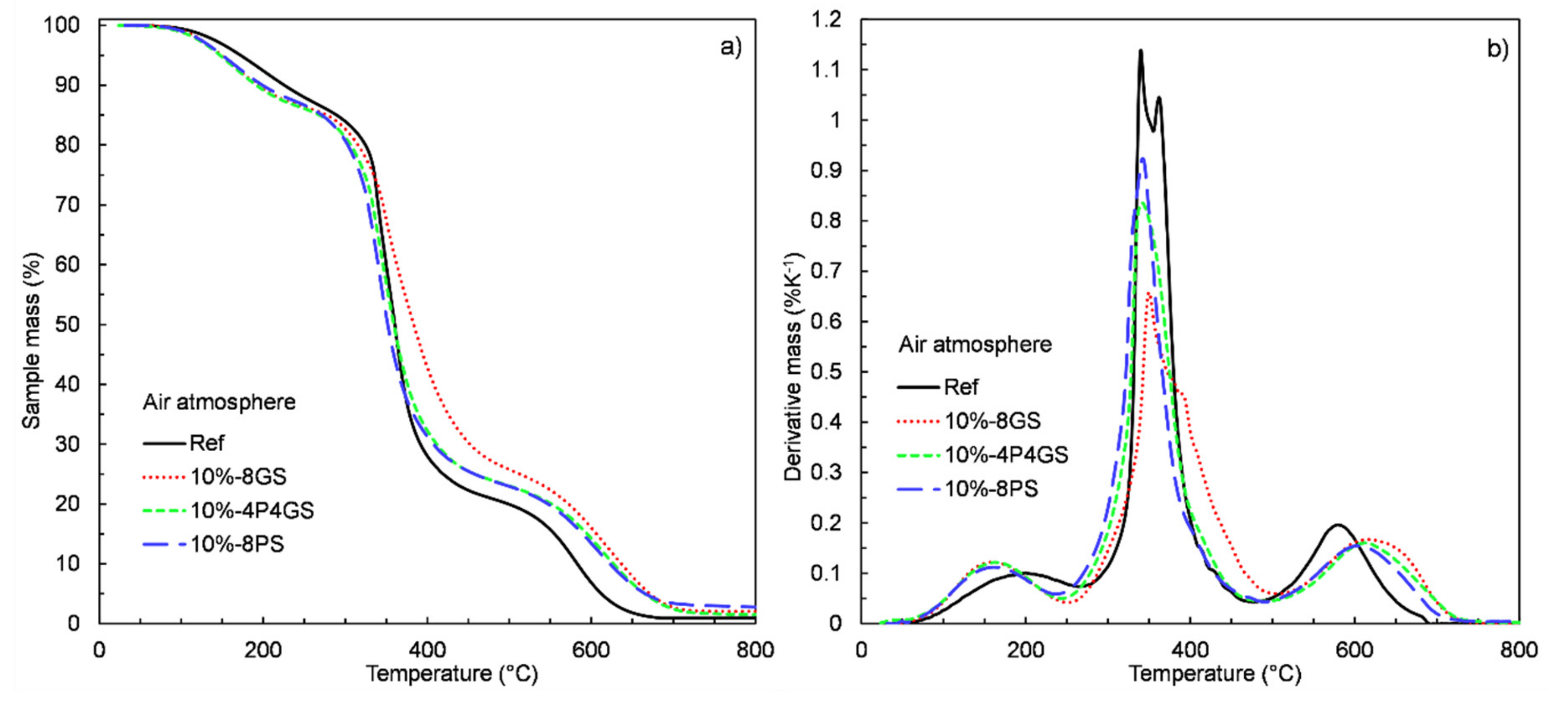
3.5. TGA and DSC Measurements
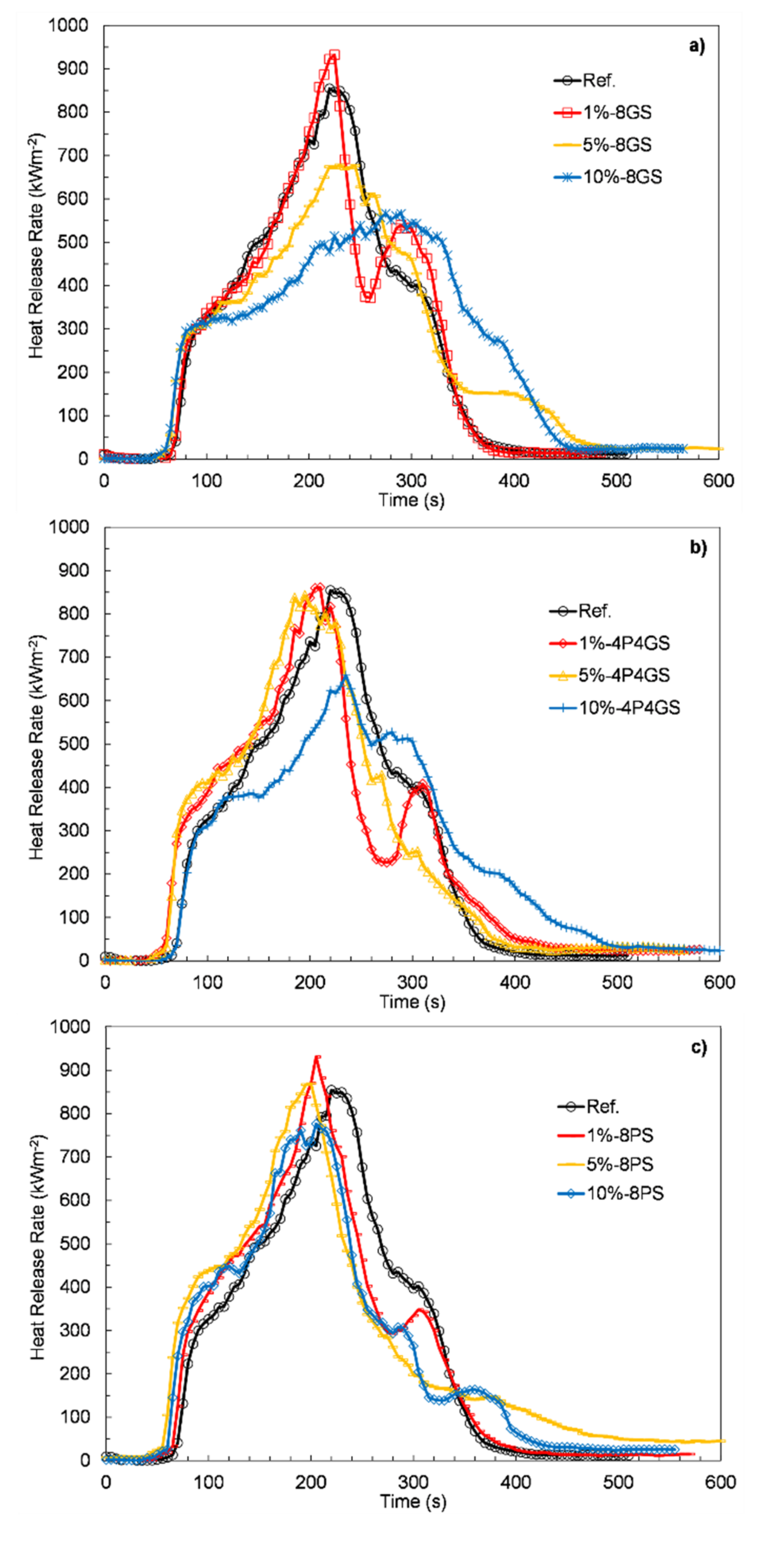
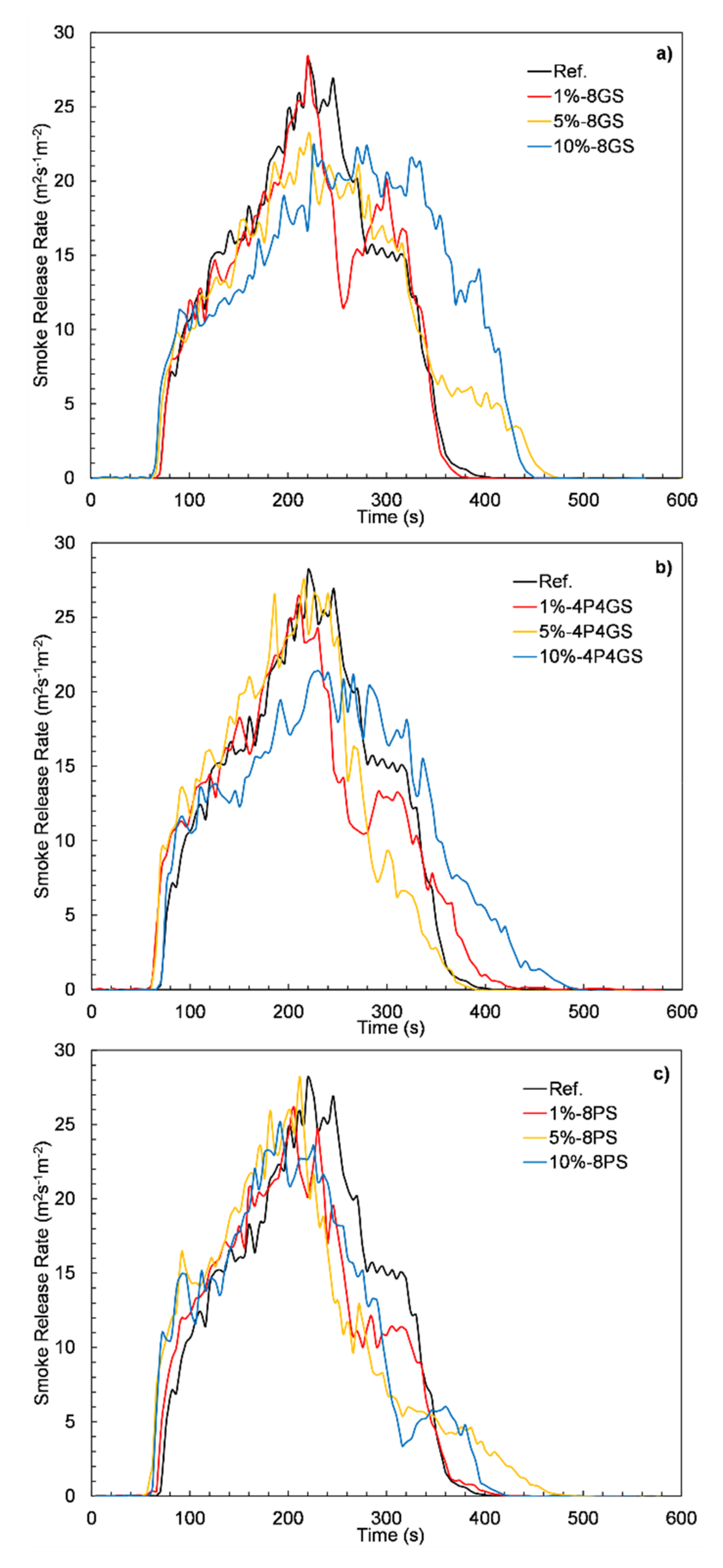
3.6. Flammability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgkin, J. Thermosets: Epoxies and Polyesters in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Buschow, K.H.J., Flemings, M.C., Kramer, E.J., Veyssière, P., Cahn, R.W., Ilschner, B., Mahajan, S., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 9215–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodd, K. 37—Epoxy Resins in Comprehensive Polymer Science and Supplements, 1st ed.; Allen, G., Bevington, J.C., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1989; Volume 5, pp. 667–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, B.; Rosso, P.; Haupert, F.; Friedrich, K. Epoxy nanocomposites—Fracture and toughening mechanisms. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2006, 73, 2375–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.-L.; Li, X.; Park, S.J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domun, N.; Hadavinia, H.; Zhang, T.; Sainsbury, T.; Liaghat, G.H.; Vahid, S. Improving the fracture toughness and the strength of epoxy using nanomaterials-a review of the current status. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10294–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezanzadeh, B.; Niroumandrad, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Mahdavian, M.; Mohamadzadeh Moghadam, M.H. Enhancement of barrier and corrosion protection performance of an epoxy coating through wet transfer of amino functionalized graphene oxide. Corros. Sci. 2016, 103, 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Huang, W.; Yang, D. Preparation and investigation of novel diatomite-supported epoxy resin-modified asphalt binder. J. Test. Eval. 2019, 48, 20180399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A.Y.; Zainelabdeen, I.H.; Dalhat, M.A.; Mohammed, A.S.; Sorour, A.A.; Al-Badour, F.A. Influence of micronized waste tire rubber on the mechanical and tribological properties of epoxy composite coatings. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Liang, C.; Zhao, X.; Gan, B.; Qiu, H.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.-Y. Highly thermally conductive flame-retardant epoxy nanocomposites with reduced ignitability and excellent electrical conductivities. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 139, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Xing, W.; Lu, H.; Lv, P.; Jie, G. Flame retardancy and thermal degradation mechanism of epoxy resin composites based on a DOPO substituted organophosphorus oligomer. Polymer 2010, 51, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotomalala, M.; Wagner, S.; Döring, M. Recent developments in halogen free flame retardants for epoxy resins for electrical and electronic applications. Materials 2010, 3, 4300–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.H. (Ed.) Epoxy Resins in Handbook of Thermoset Plastics, 2nd ed.; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 193–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.-J.; Xu, G.-R.; Leng, Y.; Li, B. Synthesis of a novel flame retardant based on cyclotriphosphazene and DOPO groups and its application in epoxy resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 123, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schartel, B.; Perret, B.; Dittrich, B.; Ciesielski, M.; Kramer, J.; Muller, P.; Altstadt, V.; Zang, L.; Doring, M. Flame Retardancy of Polymers: The Role of Specific Reactions in the Condensed Phase. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoutid, F.; Bonnaud, L.; Alexandre, M.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Dubois, P. New prospects in flame retardant polymer materials: From fundamentals to nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 63, 100–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Harcup, J.; Yee, A.F.; Zhu, Q.; Laine, R.M. Organic/inorganic hybrid composites from cubic silsesquioxanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11420–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byczyński, Ł.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Januszewski, R. Thermal behaviour and flame retardancy of polyurethane high-solid coatings modified with hexakis(2,3-epoxypropyl)cyclotriphosphazene. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 108, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, M.; Szołyga, M.; Maciejewski, H.; Marciniec, B. Thiirane functional spherosilicate as epoxy resin modifier: Synthesis and thermal stability. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 117, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Wang, C.S. Synthesis and properties of phosphorus-containing advanced epoxy resins. II. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. Thermal decomposition, combustion and flame-retardancy of epoxy resins—A review of the recent literature. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1901–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, B.; Pan, Z.; Hu, Y. A combination of POSS and polyphosphazene for reducing fire hazards of epoxy resin. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmakci, E. Allylamino diphenylphosphine oxide and POSS containing flameretardant photocured hybrid coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 105, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, R. Pyrolysis and fire behaviour of epoxy resin composites based on a phosphorus-containing polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (DOPO-POSS). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, X.; Song, T.; Jiao, Q.; Yang, R. The influence of the phosphorus-based flame retardant on the flame retardancy of the epoxy resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Xing, W.; Lu, H. Thermal degradation behaviors of epoxy resin/poss hybrids and phosphorus-silicon synergism of flame retardancy. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B: Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, L.; Dong, L.-P.; Li, L.-J.; Wang, Y.-Z. Organic-inorganic hybrid flame retardant: Preparation, characterization and application in EVA. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 17812–17821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Franczyk, A.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Marciniec, B. Synthesis of Bifunctional Silsesquioxanes (RSiMe2O)∼4(R′SiMe2O)∼4Si8O12 via Hydrosilylation of Alkenes. Organometallics 2019, 38, 3018–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Januszewski, R.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Franczyk, A.; Marciniec, B. A facile approach for the synthesis of novel silsesquioxanes with mixed functional groups. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 18141–18145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y. Definitions for Hydrophilicity, Hydrophobicity, and Superhydrophobicity: Getting the Basics Right. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.P.; Liu, J. Nanoindentation Techniques in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Buschow, K.H.J., Flemings, M.C., Kramer, E.J., Veyssière, P., Cahn, R.W., Ilschner, B., Mahajan, S., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 5908–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Landingham, M.R.; Villarrubia, J.S.; Guthrie, W.F.; Meyers, G.F. Nanoindentation of Polymers: An Overview. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 167, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beake, B.D.; Harris, A.J.; Liskiewicz, T.W. Advanced nanomechanical test techniques. In Materials Characterization Modern Methods and Applications; Ranganathan, N., Ed.; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapico, G.F.; Ohtake, N.; Akasaka, H.; Munoz-Guijosa, J.M. Epoxy toughening through high pressure and shear rate preprocessing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Yuan, C.; Chang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zeng, B.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Dai, L. Highly transparent and flame-retardant epoxy composites based on a hybrid multi-element containing POSS derivative. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 46139–46147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, T.; Yuan, C.H.; Song, C.F.; Chang, Y.; Chen, G.R.; Xu, Y.T.; Dai, L.Z. Modification of epoxy resin through the self-assembly of a surfactant-like multi-element flame retardant. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3462–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, R. Novel flame retardancy effects of DOPO-POSS on epoxy resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, R. Blowing-out effect in epoxy composites flame retarded by DOPO-POSS and its correlation with amide curing agents. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.D.; Fontaine, G.; Samyn, F.; Delva, X.; Louisy, J.; Bellayer, S.; Bourgeois, Y.; Bourbigot, S. Outlining the mechanism of flame retardancy in polyamide 66 blended with melamine-poly(zinc phosphate). Fire Saf. J. 2014, 70, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Dai, J.; Jia, H.; Gao, S. Synergistic effects of lanthanum oxide on a novel intumescent flame retardant polypropylene system. Polymer Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | E 652 (g) | IDA (g) | Modifier | Modifier Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | 40 | 20 | - | - |
| 1%-8GS | 20.166 | 8GS | 0.4 | |
| 5%-8GS | 20.828 | 8GS | 2 | |
| 10%-8GS | 21.656 | 8GS | 4 | |
| 1%-4P4GS | 20.056 | 4P4GS | 0.4 | |
| 5%-4P4GS | 20.28 | 4P4GS | 2 | |
| 10%-4P4GS | 20.56 | 4P4GS | 4 | |
| 1%-8PS | 20 | 8PS | 0.4 | |
| 5%-8PS | 20 | 8PS | 2 | |
| 10%-8PS | 20 | 8PS | 4 |
| Sample | Calculated Element Weight (%) | Measured Element Weight (%) | Error (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | P | Si | P | Si | P | |
| Ref | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1%-8GS | 0.15 | - | 0.19 | 0.01 | 7.05 | 55.63 |
| 5%-8GS | 0.74 | - | 0.91 | 0.01 | 3.59 | 56.14 |
| 10%-8GS | 1.42 | - | 1.69 | 0.01 | 3.13 | 55.94 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 18.71 | 54.88 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 4.86 | 12.84 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 0.97 | 0.27 | 0.88 | 0.25 | 3.48 | 6.61 |
| 1%-8PS | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 11.79 | 19.81 |
| 5%-8PS | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.3 | 0.17 | 5.21 | 8.55 |
| 10%-8PS | 0.74 | 0.41 | 0.73 | 0.41 | 3.68 | 4.99 |
| Sample | WCA (°) |
|---|---|
| Ref | 77.1 ± 3.4 |
| 1%-8GS | 81 ± 4.69 |
| 5%-8GS | 81.7 ± 1.93 |
| 10%-8GS | 80.2 ± 3.9 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 82.7 ± 2.55 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 81 ± 0.97 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 81.3 ± 1.75 |
| 1%-8PS | 82.5 ± 0.8 |
| 5%-8PS | 79.7 ± 1.04 |
| 10%-8PS | 50.1 ± 3.31 |
| Sample | Modulus (500–1500 nm) | Hardness (500–1500 nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (MPa) | Std. Dev. (%) | Mean (MPa) | Std. Dev. (%) | |
| Ref. | 3064 | 1.6 | 127 | 1.7 |
| 1%-8GS | 3555 | 1.6 | 163 | 1.7 |
| 5%-8GS | 3149 | 1.4 | 136 | 1.7 |
| 10%-8GS | 3149 | 0.9 | 137 | 1.2 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 3071 | 1.2 | 129 | 1.4 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 3112 | 0.8 | 130 | 2.8 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 3086 | 1 | 132 | 1.1 |
| 1%-8PS | 3127 | 0.6 | 137 | 1.1 |
| 5%-8PS | 3210 | 1.8 | 139 | 2.1 |
| 10%-8PS | 3230 | 0.7 | 145 | 0.9 |
| Sample | Mass Loss Temperature (°C) | Char Yield @ 800 °C (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1% | T5% | T10% | T20% | T40% | T60% | T80% | ||
| Ref. | 104.2 | 155.4 | 201.3 | 325.7 | 350.8 | 368.8 | 401.6 | 6.6 |
| 1%-8GS | 96.7 | 146.8 | 190.3 | 325.4 | 352 | 369.7 | 404.4 | 7.6 |
| 5%-8GS | 100.1 | 143.8 | 189 | 329.1 | 356.3 | 377.7 | 424.9 | 10.9 |
| 10%-8GS | 111 | 153.3 | 199.6 | 320 | 355.1 | 386.6 | 469.2 | 14.1 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 104 | 151.7 | 196 | 326.3 | 351.7 | 368.8 | 401.5 | 6.9 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 105.6 | 152.4 | 198.2 | 318.5 | 344.6 | 364 | 400 | 8 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 101.3 | 149.3 | 194.9 | 315.1 | 342.2 | 363.4 | 412.1 | 10.2 |
| 1%-8PS | 110.7 | 161.4 | 208.9 | 321.8 | 347.6 | 366.9 | 400.2 | 7.2 |
| 5%-8PS | 104.1 | 152.3 | 197.6 | 317.8 | 343.2 | 361.9 | 392.6 | 7.8 |
| 10%-8PS | 106.6 | 154.9 | 202.9 | 309.2 | 334.7 | 353.9 | 392.2 | 8.7 |
| Sample | Step I | Step II | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (°C) | Change (%) | Tmax (°C) | Rate (%K−1) | Range (°C) | Change (%) | Tmax (°C) | Rate (%K−1) | |
| Ref. | 41–270 | 14.1 | 176 | 0.11 | 270–600 | 78.7 | 353.8 | 1.14 |
| 1%-8GS | 52–260 | 13.6 | 161.3 | 0.12 | 260–600 | 77.7 | 362.8 | 1.15 |
| 5%-8GS | 44–255 | 12.7 | 150.5 | 0.12 | 255–600 | 75.9 | 361.8 | 0.99 |
| 10%-8GS | 40–255 | 13.8 | 161.3 | 0.12 | 255–600 | 71.1 | 345.7 | 0.72 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 46–263 | 13.5 | 167.8 | 0.12 | 263–600 | 79 | 356.7 | 1.26 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 41–260 | 13.9 | 167.7 | 0.11 | 260–600 | 77.5 | 354.5 | 1 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 40–250 | 12.8 | 161.3 | 0.12 | 250–650 | 76.6 | 349.8 | 1 |
| 1%-8PS | 50–270 | 14.2 | 180.5 | 0.11 | 270–600 | 78.1 | 359.8 | 1.1 |
| 5%-8PS | 45–255 | 13.2 | 167.2 | 0.12 | 255–600 | 78.4 | 350.8 | 1.1 |
| 10%-8PS | −250 | 13.7 | 170.2 | 0.11 | 250–600 | 77.3 | 346.2 | 1.1 |
| Sample | Mass Loss Temperature (°C) | Residue @ 800 °C (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1% | T5% | T10% | T20% | T40% | T60% | T80% | ||
| Ref | 113.5 | 171.3 | 222.8 | 318.7 | 343.3 | 363.5 | 490 | 0.96 |
| 1%-8GS | 104.7 | 153.1 | 197.8 | 312.8 | 346.4 | 374.4 | 457 | 0.44 |
| 5%-8GS | 94.7 | 143.2 | 184.3 | 305.8 | 350.7 | 387.1 | 543.9 | 0.59 |
| 10%-8GS | 104.3 | 148.6 | 191.6 | 309.8 | 355.8 | 400 | 561.9 | 2 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 106.1 | 157 | 202.4 | 312.3 | 345 | 369.7 | 431.3 | 0 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 105.2 | 154.4 | 198.3 | 308.1 | 340.4 | 364.4 | 497.8 | 0.8 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 98.8 | 147.5 | 190.3 | 301.3 | 339.6 | 368.7 | 542 | 1.48 |
| 1%-8PS | 109.4 | 158 | 202.7 | 312.3 | 343.9 | 371 | 436.2 | 0.23 |
| 5%-8PS | 99 | 147.4 | 190.2 | 300.7 | 337.8 | 359.7 | 501.2 | 0 |
| 10%-8PS | 102.2 | 149.9 | 197.2 | 297.6 | 333.5 | 361.3 | 537.7 | 2.73 |
| Sample | Step I | Step II | Step III | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (°C) | Change (%) | Tmax (°C) | Rate (%K−1) | Range (°C) | Change (%) | Tmax (°C) | Rate (%K−1) | Range (°C) | Change (%) | Tmax (°C) | Rate (%K−1) | |
| Ref. | 55–260 | 13.4 | 196.8 | 0.1 | 260–470 | 65.6 | 333.5 | 1.14 | 470–680 | 20.1 | 569.5 | 0.2 |
| 1%-8GS | 45–257 | 14 | 169.3 | 0.12 | 257–503 | 68.6 | 341.5 | 0.9 | 503–738 | 17 | 587.5 | 0.14 |
| 5%-8GS | 30–246 | 14.1 | 158 | 0.13 | 246–489 | 61.7 | 350.5 | 0.67 | 489–733 | 23.5 | 593.8 | 0.18 |
| 10%-8GS | 30–247 | 13.7 | 159.3 | 0.12 | 247–498 | 61 | 343 | 0.66 | 498–746 | 23.3 | 606.3 | 0.17 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 42–257 | 14 | 177 | 0.11 | 257–514 | 72.4 | 348.2 | 0.97 | 514–714 | 13.6 | 600.2 | 0.13 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 41–251 | 14 | 172.8 | 0.12 | 251–483 | 65.3 | 336.8 | 1 | 483–734 | 19.9 | 580.3 | 0.16 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 47–240 | 13.6 | 162 | 0.12 | 240–483 | 62.9 | 335.7 | 0.8 | 483–754 | 21.9 | 604.5 | 0.16 |
| 1%-8PS | 30–255 | 13.9 | 175.3 | 0.12 | 255–413 | 71.4 | 335.3 | 0.9 | 513–733 | 14.5 | 612.3 | 0.13 |
| 5%-8PS | 52–243 | 13.9 | 164.7 | 0.12 | 243–479 | 65.1 | 344.7 | 0.96 | 479–743 | 21 | 589.7 | 0.16 |
| 10%-8PS | 57–233 | 12.6 | 160.2 | 0.11 | 233–480 | 64 | 335.3 | 0.92 | 480–736 | 20.4 | 591.7 | 0.15 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|
| Ref. | 43.93 |
| 1%-8GS | 44.44 |
| 10%-8GS | 42.24 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 45.91 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 41.47 |
| 1%-8PS | 43.57 |
| 10%-8PS | 39.88 |
| Sample | TTI (s) | TTF (s) | pHRR (kWm−2) | MARHE (kWm−2) | FIGRA (kWm−2s−1) | THR (MJm−2) | SEA (m2kg−1) | TSR (m2m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | 63 | 393 | 854.5 | 405.9 | 3.9 | 139.4 | 842.2 | 4733.4 |
| 1%-8GS | 65 | 380 | 932 | 399.2 | 4.1 | 138.2 | 796.7 | 4435 |
| 5%-8GS | 56 | 485 | 678.2 | 372.5 | 2.9 | 143.1 | 832.4 | 4844 |
| 10%-8GS | 58 | 455 | 566 | 348.8 | 2.1 | 144.6 | 932.7 | 5538.4 |
| 1%-4P4GS | 51 | 470 | 861.3 | 412.7 | 4.1 | 141.1 | 822.1 | 4527.6 |
| 5%-4P4GS | 60 | 402 | 845.3 | 436.7 | 4.3 | 143.7 | 755.1 | 4480.1 |
| 10%-4P4GS | 67 | 528 | 658.5 | 349.8 | 2.8 | 143.3 | 833.4 | 4970.4 |
| 1%-8PS | 60 | 425 | 931.1 | 413.1 | 4.5 | 137.9 | 790.8 | 4309.9 |
| 5%-8PS | 57 | 526 | 869.2 | 430.8 | 4.3 | 153.2 | 830.4 | 4574.1 |
| 10%-8PS | 60 | 438 | 776.6 | 399.7 | 3.8 | 134.9 | 835.6 | 4529.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szołyga, M.; Dutkiewicz, M.; Nowicki, M.; Sałasińska, K.; Celiński, M.; Marciniec, B. Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxane Derivatives as Additive or Reactive Components of Epoxy Resins. Materials 2020, 13, 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235373
Szołyga M, Dutkiewicz M, Nowicki M, Sałasińska K, Celiński M, Marciniec B. Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxane Derivatives as Additive or Reactive Components of Epoxy Resins. Materials. 2020; 13(23):5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235373
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzołyga, Mariusz, Michał Dutkiewicz, Marek Nowicki, Kamila Sałasińska, Maciej Celiński, and Bogdan Marciniec. 2020. "Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxane Derivatives as Additive or Reactive Components of Epoxy Resins" Materials 13, no. 23: 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235373
APA StyleSzołyga, M., Dutkiewicz, M., Nowicki, M., Sałasińska, K., Celiński, M., & Marciniec, B. (2020). Phosphorus-Containing Silsesquioxane Derivatives as Additive or Reactive Components of Epoxy Resins. Materials, 13(23), 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235373







