Effect of Calcium Acetate Content on Apatite-Forming Ability and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement Modified with Quaternary Ammonium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cement Preparation
2.3. Setting Time Measurement
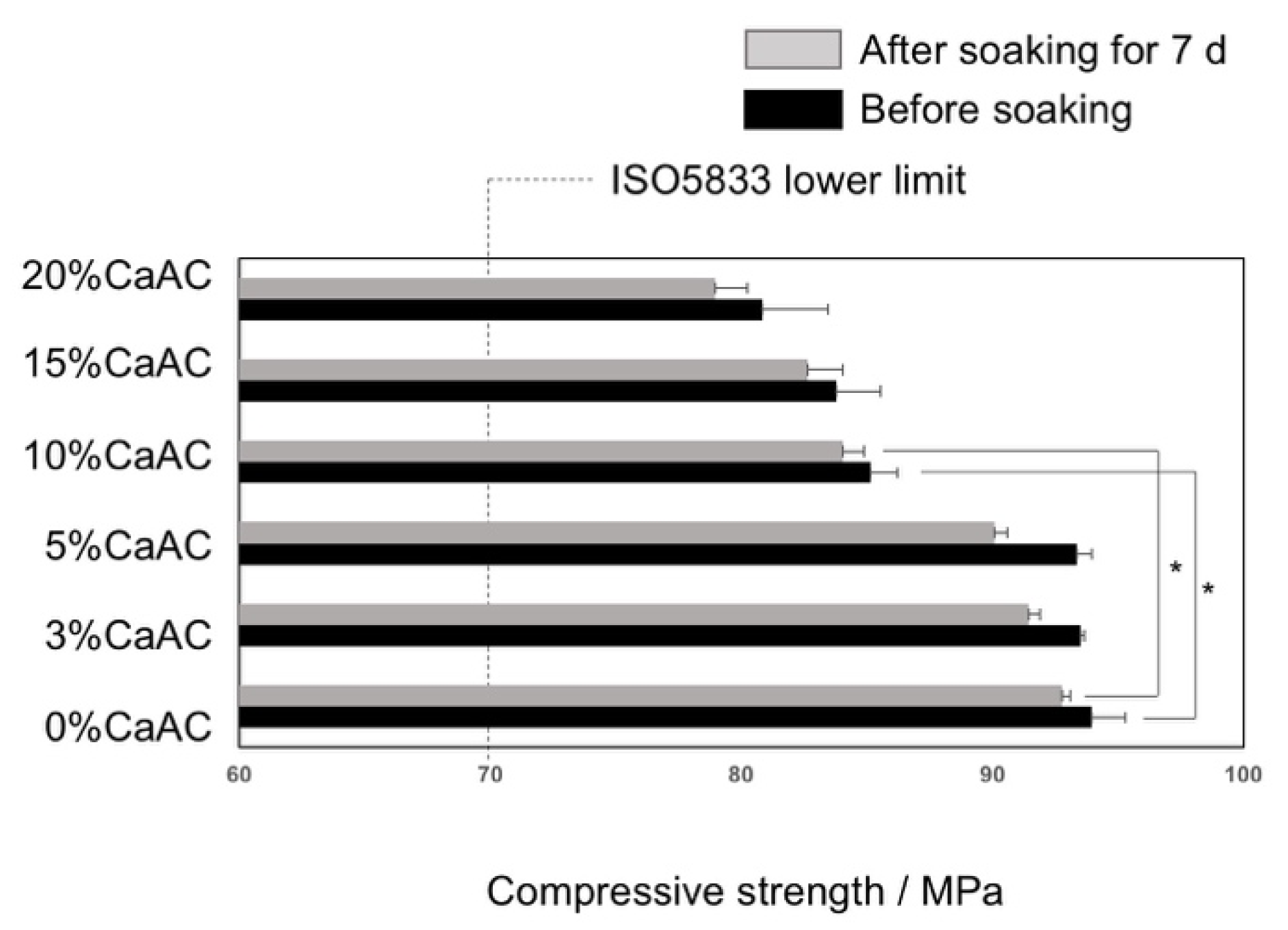
2.4. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Bioactivity Test in SBF
2.6. pH Changes in SBF
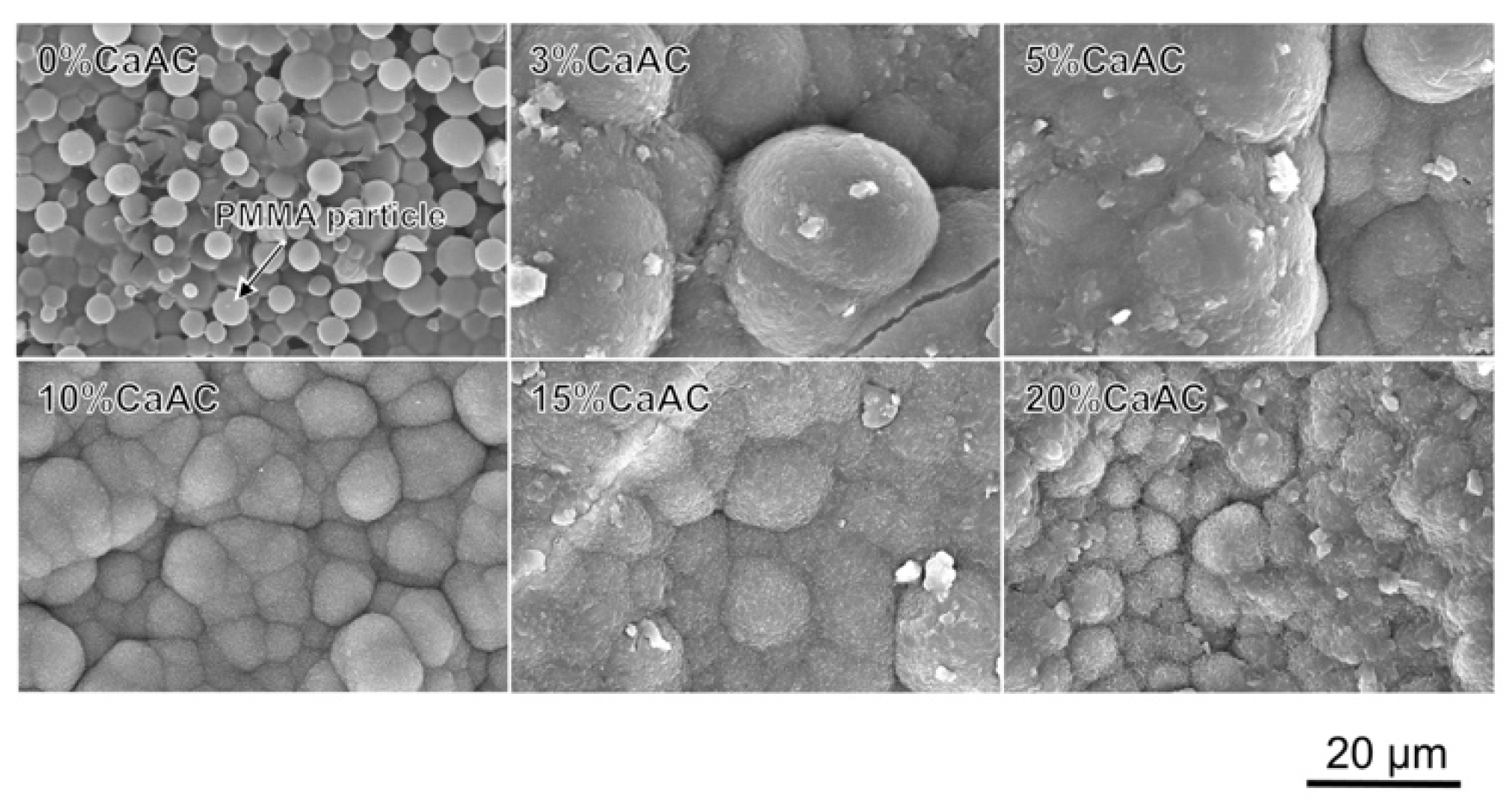
2.7. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harper, E.J. Bioactive bone cements. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 1998, 212, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breusch, S.J.; Aldinger, P.R.; Thomsen, M.; Ewerbeck, V.; Lukoschek, M. Anchoring principles in hip endoprostheses I: Prosthesis stem. Unfallchirurg 2000, 103, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Okada, Y.; Fukumoto, A.; Furukawa, T.; Kato, H.; Kokubo, T.; Kikutani, T. Bioactive bone cement: Comparison of apatite and wollastonite containing glass-ceramic, hydroxyapatite, and β-tricalcium phosphate fillers on bone-bonding strength. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 42, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, W.F.; Kobayashi, M.; Shinzato, S.; Kamimura, M.; Neo, M.; Yoshihara, S.; Nakamura, T. Biological and mechanical properties of PMMA-based bioactive bone cements. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. The story of Bioglass®. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, C.; Miyazaki, T.; Kyomoto, M.; Tanihara, M.; Osaka, A. Development of bioactive PMMA-based cement by modification with alkoxysilane and calcium salt. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ohtsuki, C.; Kyomoto, M.; Tanihara, M.; Mori, A.; Kuramoto, K. Bioactive PMMA bone cement prepared by modification with methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane and calcium chloride. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 67A, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thölmann, D.; Kossmann, B.; Sosna, F. Polymers with antimicrobial properties. Eur. Coat. J. 2003, 1, 16–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, C.J.; Franke, R.; Marx, A.; Kossmann, B.; Ottersbach, P. A study into the anti-microbial properties of an amino functionalised polymer using multi-parameter flow cytometry. Biotech. Lett. 2004, 26, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, S.; Pagnoulle, C.; Galleni, M.; Compère, P.; Jérôme, R.; Detrembleur, C. Polyolefin matrixes with permanent antibacterial activity: Preparation, antibacterial activity, and action mode of the active species. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Wu, D.; Fu, R. Preparation of antibacterial poly (methyl methacrylate) by solution blending with water-insoluble antibacterial agent poly [(tert-buty1amino) ethyl methacrylate]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maeda, T.; Miyazaki, T. Bioactive and antibacterial PMMA-based bone cements prepared by chemical modification. In Abstract of 25th Annual Meeting of Japanese Association of Apatite Science; Japanese Association of Apatite Science: Tokyo, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Maeda, T.; Miyazaki, T. Preparation of bioactive and antibacterial PMMA-based bone cement by modification with quaternary ammonium and alkoxysilane. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. submitted.
- Kamitakahara, M.; Kawashita, M.; Miyata, N.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Degradation of Bioactive Polydimethylsiloxane–CaO–SiO2–TiO2 and Poly(tetramethylene oxide)–CaO–TiO2 Hybrids in a Simulated Body Fluid. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Ohtsuki, C.; Miyazaki, T.; Sugino, A.; Tanihara, M.; Kuramoto, K. Synthesis of Bioactive PMMA Bone Cement via Modification with Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane and Calcium Acetate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2005, 16, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.B.; Nakanishi, K.; Kokubo, T.; Soga, N.; Ohtsuki, C.; Nakamura, T.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Dependence of apatite formation on silica gel on its structure: Effect of heat treatment. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO Standard. Implants for Surgery—Acrylic Resin Cements, ISO5833; International Organization for Standardization: Genève, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chuan, D.; Zhang, L.; Leng, C.; Chen, Q.; Miyazaki, T.; Liu, J. Setting Behavior, Apatite-forming Ability, Mechanical strength of Polymethylmethacrylate Bone Cement through Bioactivity Modification of Phosphate Functional Groups Combined with Ca2+ Ions. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 2128–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrodeguas, R.G.; Lasa, B.V.; Del Barrio, J.S. Injectable acrylic bone cements for vertebroplasty with improved properties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 68, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.; Davidenko, N.; García, R.; Alonso, A.; Rodríguez, R.; Guerra, R.M.; Sastre, R. Kinetic study of the photopolymerization of a bisphenol-A–bis(glycidylmethacrylate)/triethyleneglycol dimethacrylate system in hydroxyapatite-filled composites. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Ito, S.; Huang, Z.T.; Hayashi, T.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Ca,P-rich layer formed on high-strength bioactive glass-ceramic A-W. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ohtsuki, C.; Tanihara, M. Synthesis of Bioactive Organic-inorganic Nano-hybrid for Bone Repair through Sol-gel Processing. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2003, 3, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.H.; Tanaka, J. Effect of citric acid on the nucleation of hydroxyapatite in a simulated body fluid. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2155–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerrum, J.; Sillen, L.G.; Martell, A.E. Stability Constants of Metal-ion Complexes; Sillen, L.G., Martell, A.E., Eds.; The Chemical Society: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
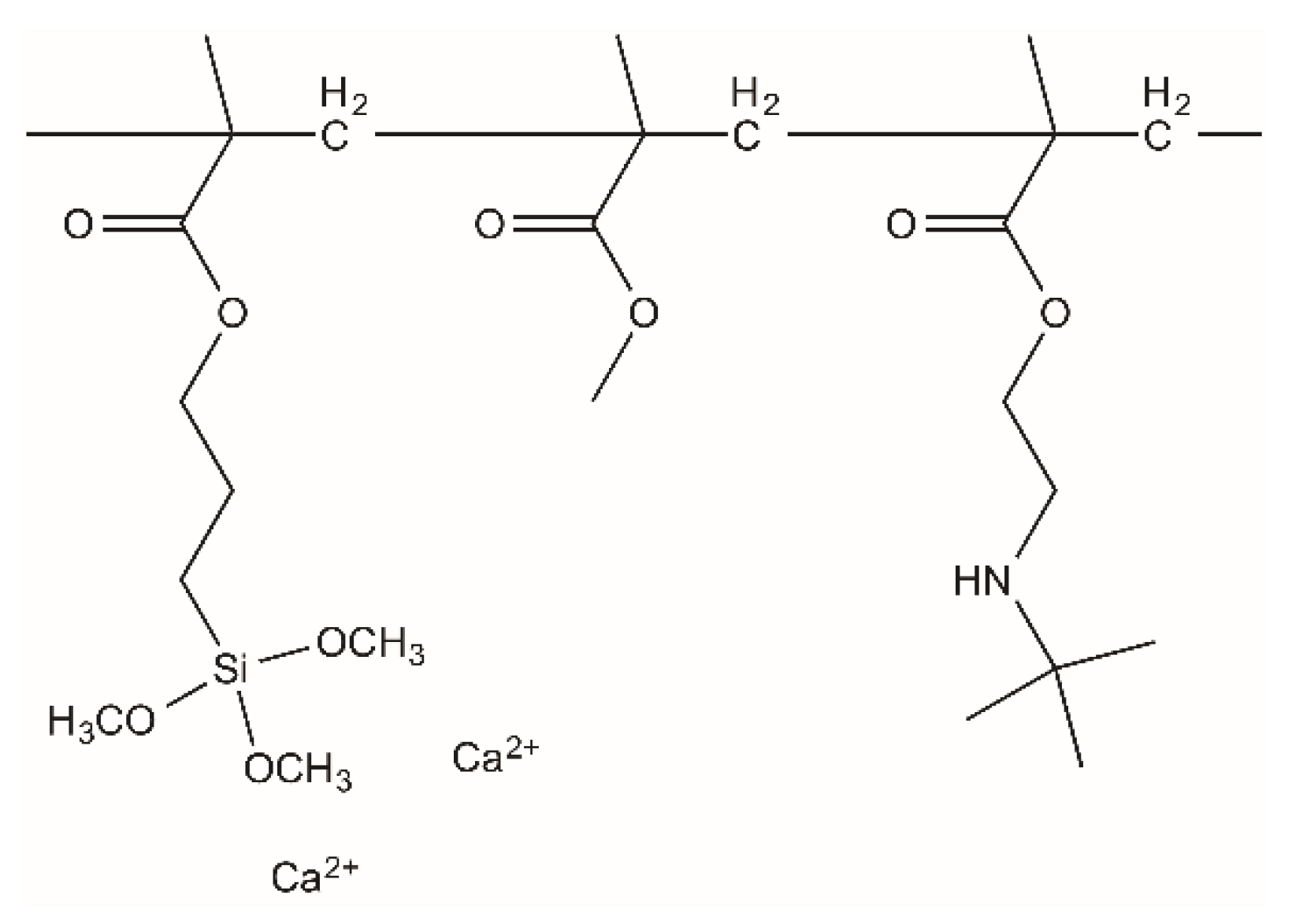

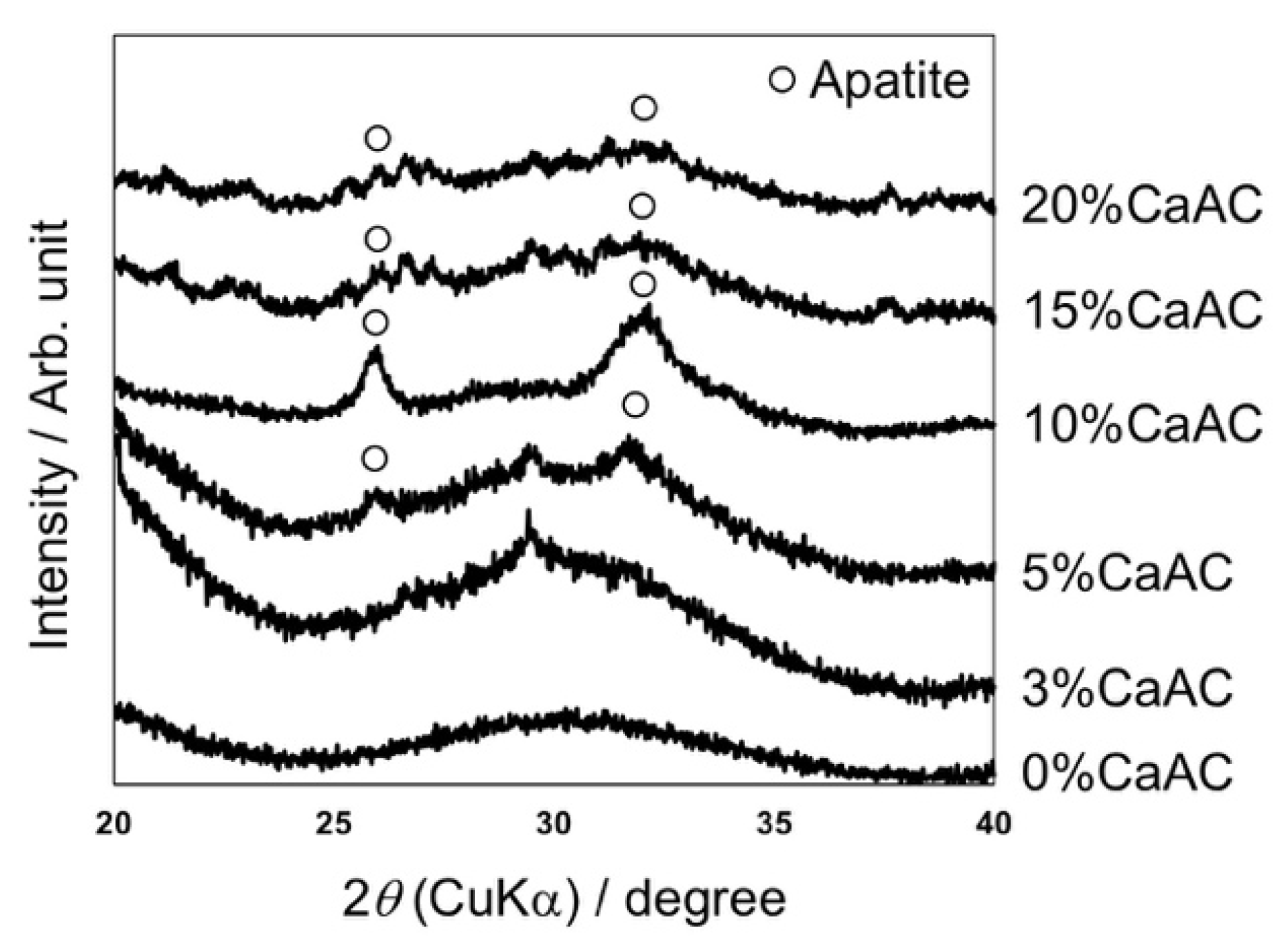

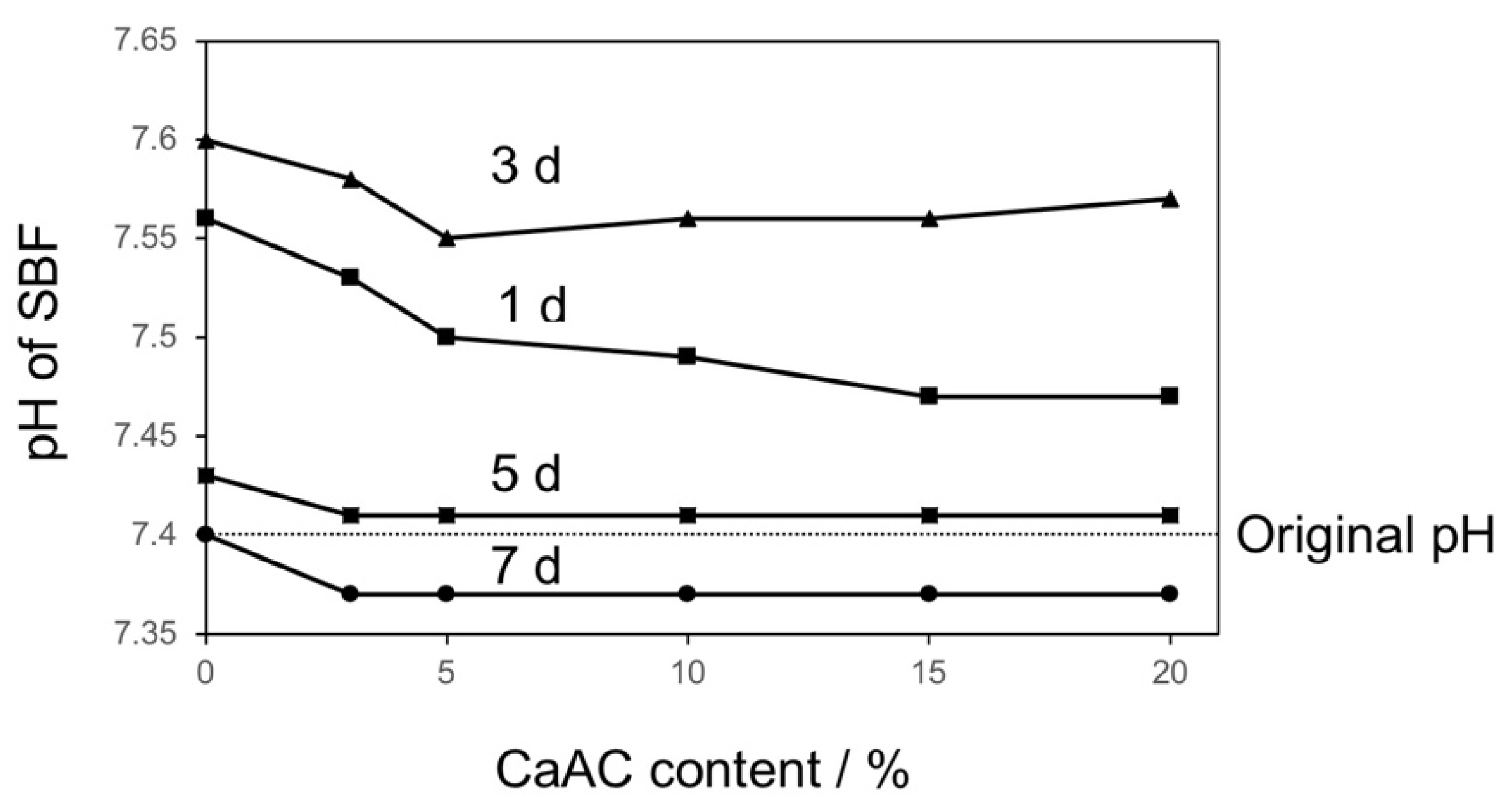
| Powder (per 1 g)/mg | Liquid (per 0.51 g)/mg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | BPO | Calcium Acetate | MMA | TBAEMA | MPS | NDT |
| (971−x) | 29 | x | 486 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Maeda, T.; Miyazaki, T. Effect of Calcium Acetate Content on Apatite-Forming Ability and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement Modified with Quaternary Ammonium. Materials 2020, 13, 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214998
Wang H, Maeda T, Miyazaki T. Effect of Calcium Acetate Content on Apatite-Forming Ability and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement Modified with Quaternary Ammonium. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214998
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haiyang, Toshinari Maeda, and Toshiki Miyazaki. 2020. "Effect of Calcium Acetate Content on Apatite-Forming Ability and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement Modified with Quaternary Ammonium" Materials 13, no. 21: 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214998
APA StyleWang, H., Maeda, T., & Miyazaki, T. (2020). Effect of Calcium Acetate Content on Apatite-Forming Ability and Mechanical Property of PMMA Bone Cement Modified with Quaternary Ammonium. Materials, 13(21), 4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214998