Synthesis, Electrochemical Studies, and Antimicrobial Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis Plant Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Preparation of C. viminalis Leaf and Flower Extracts
2.3. Phytochemical Test of Extracts
2.4. Total Determination of Phenol Content
2.5. Total Determination of Flavonoid Content
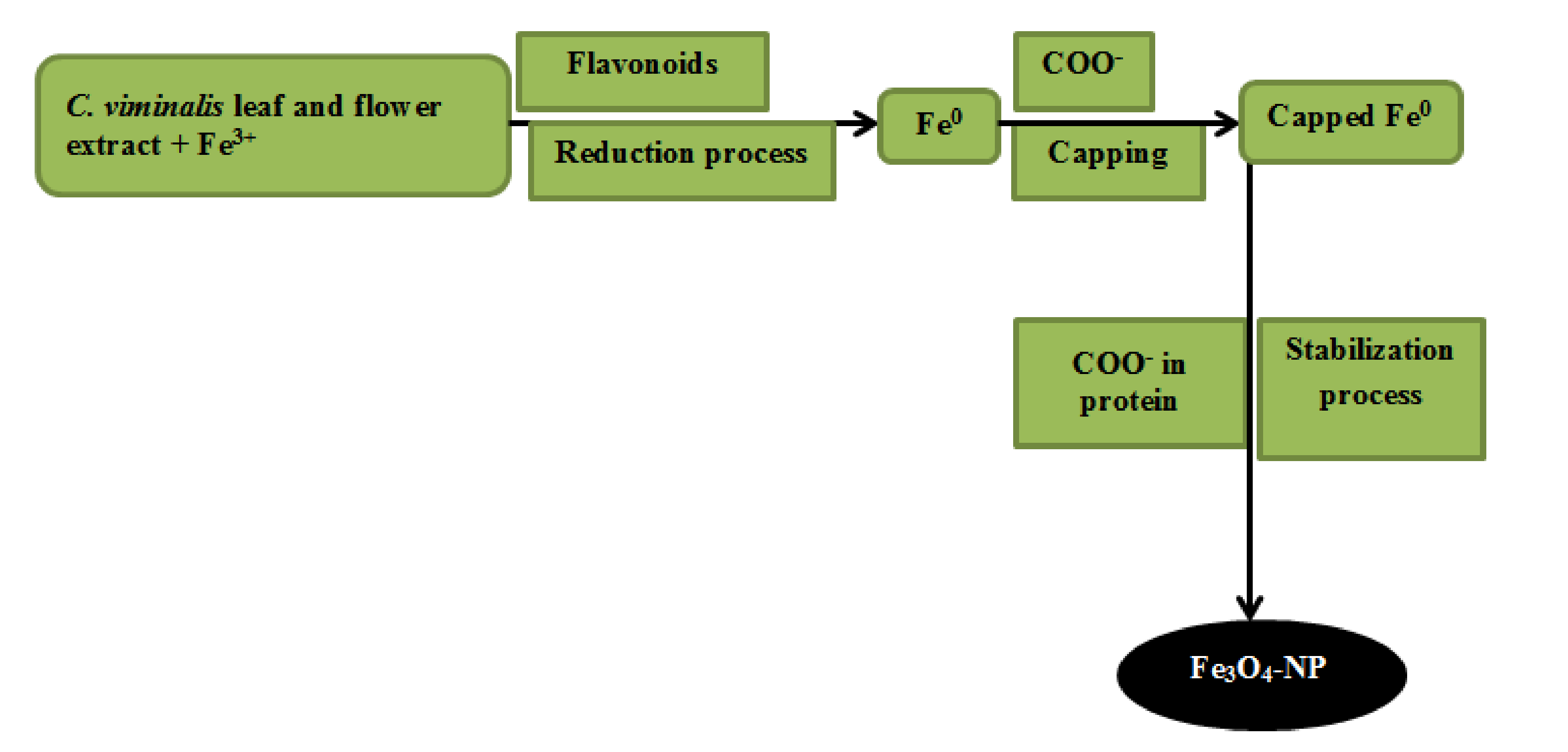
2.6. Synthesis of Fe3O4-NP from Extracts
2.7. Characterization of Iron (III) Oxide Nanoparticles
2.8. Electrochemical Characterization
2.9. Antimicrobial Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytochemical Test
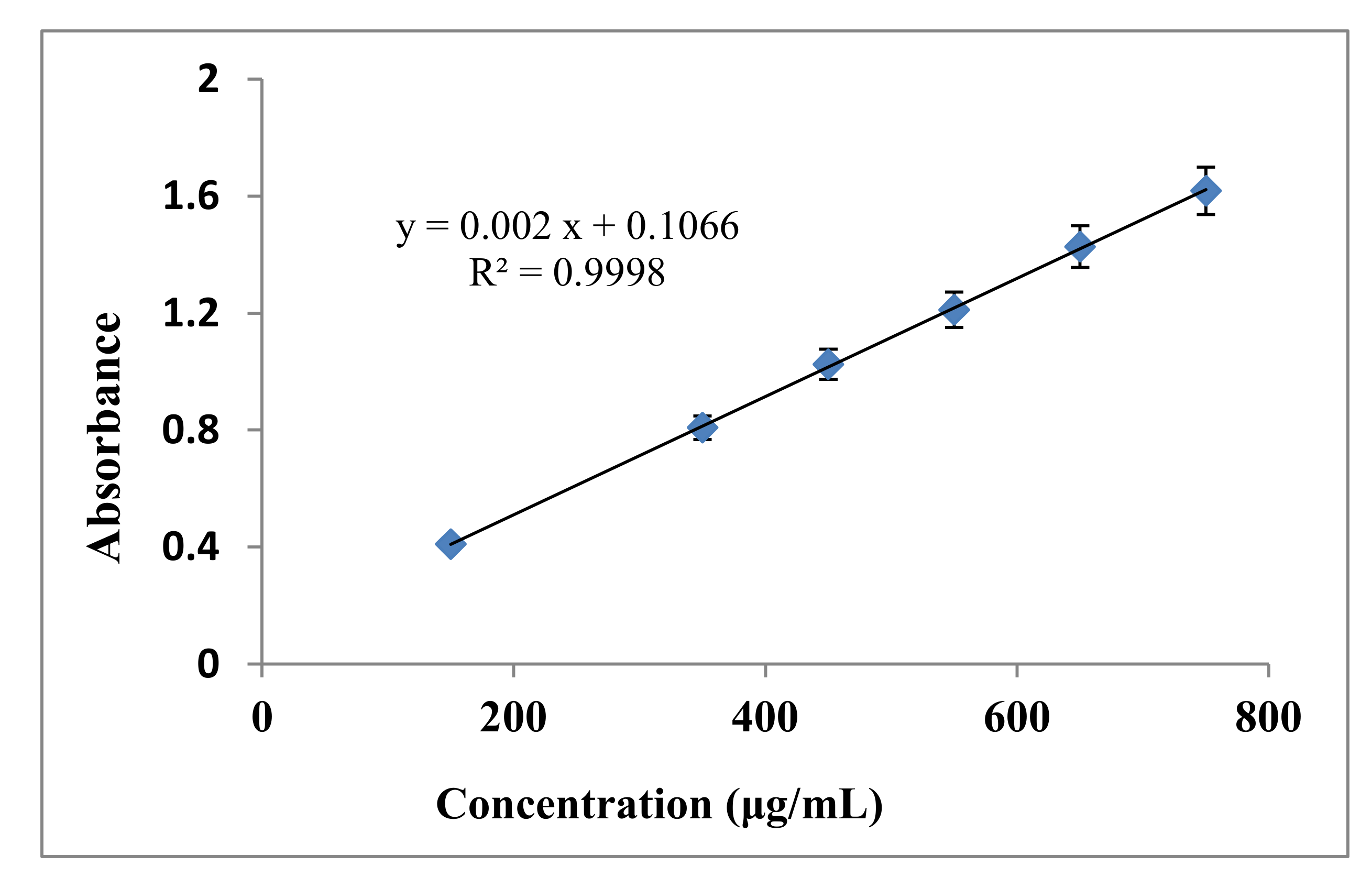
3.2. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC) in Callistemon viminalis
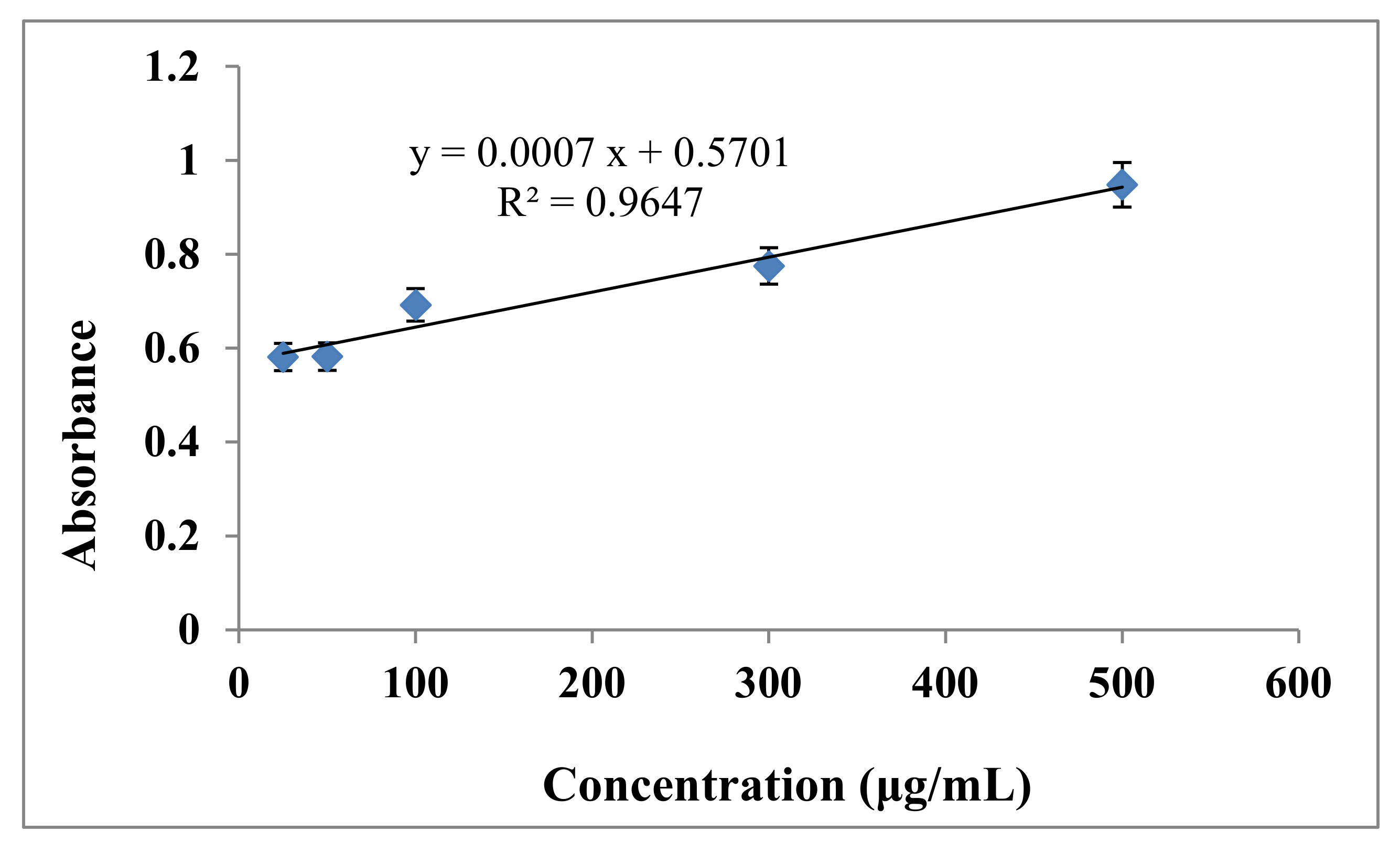
3.3. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content (TFC) in Callistemon viminalis
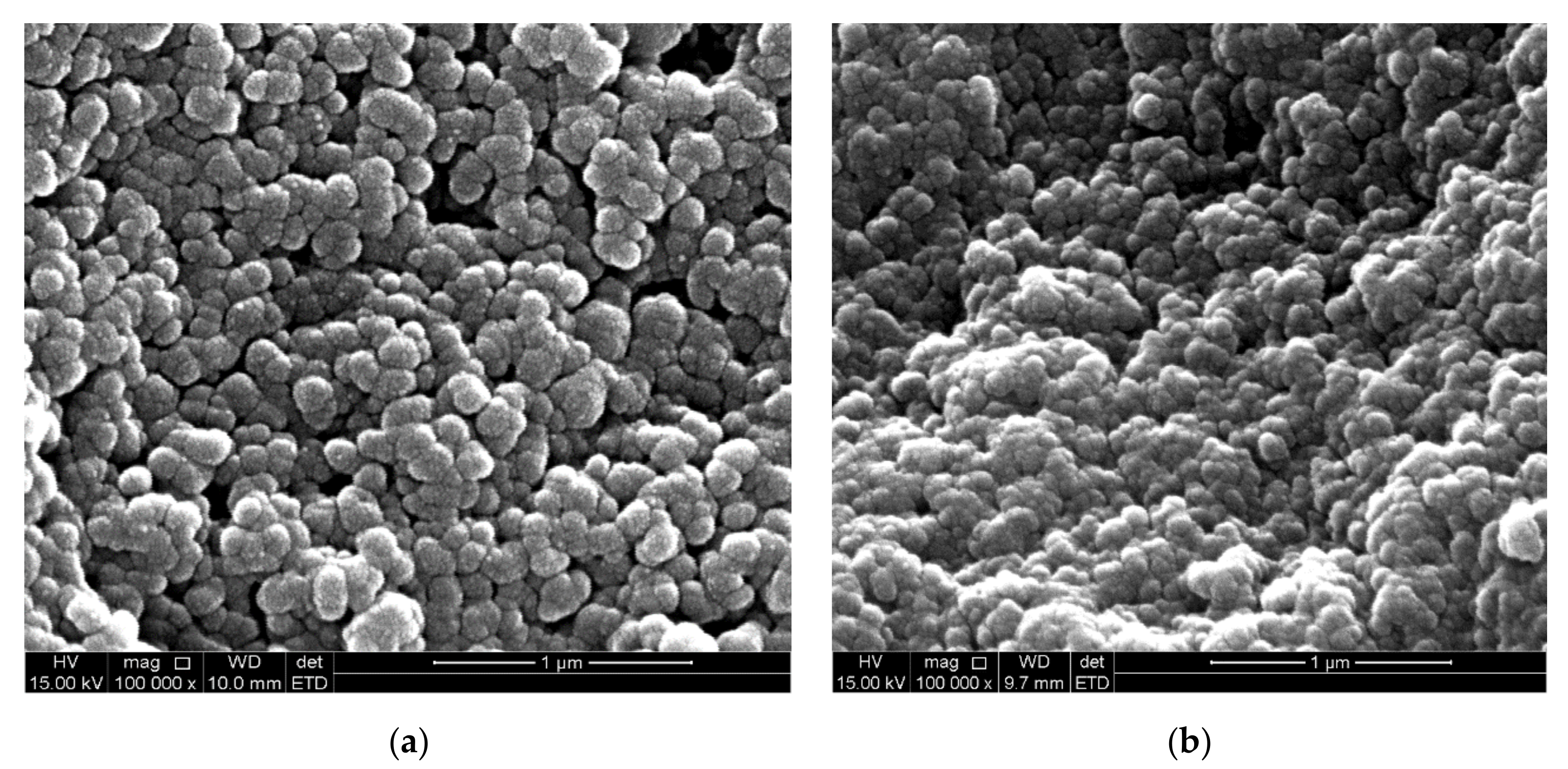
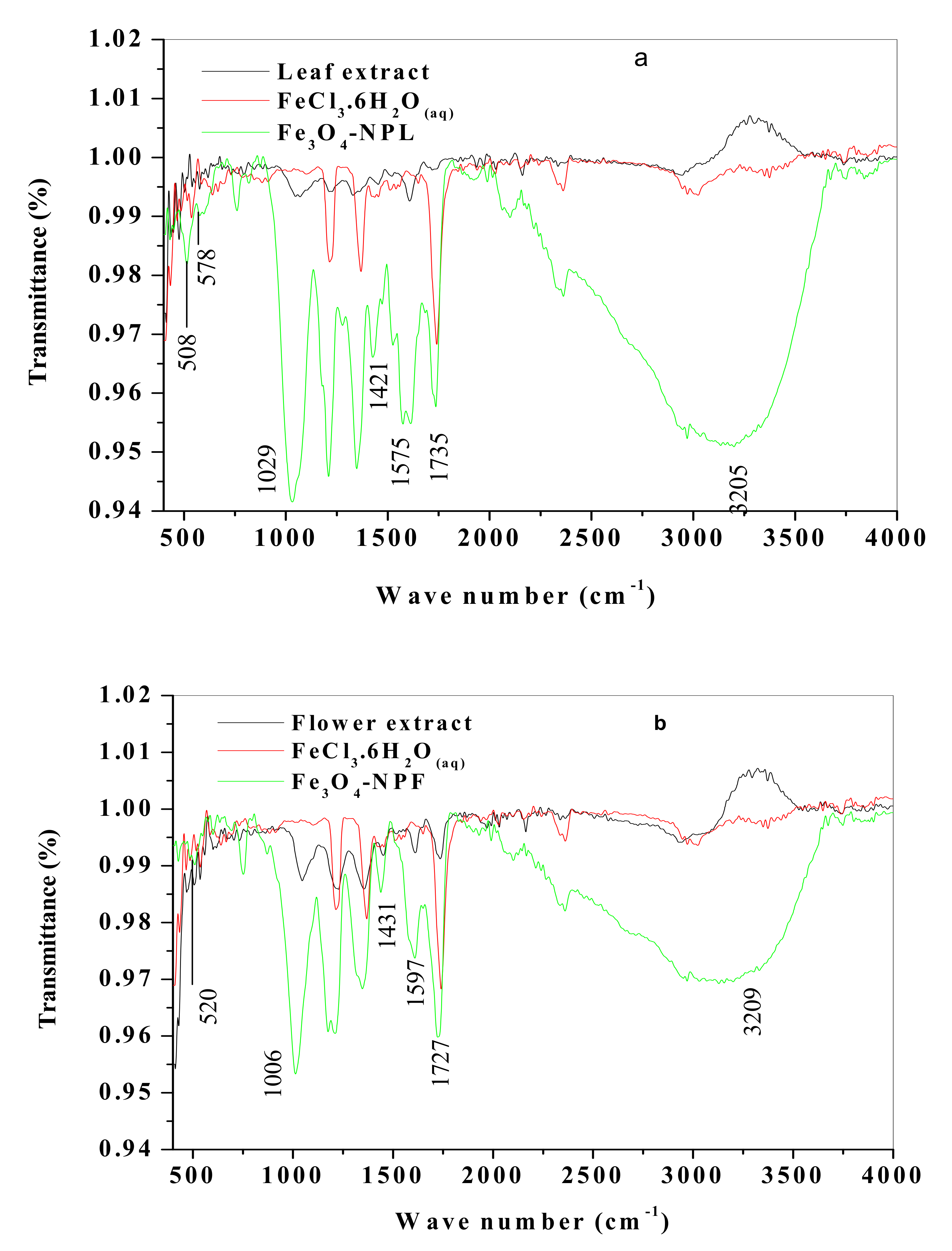
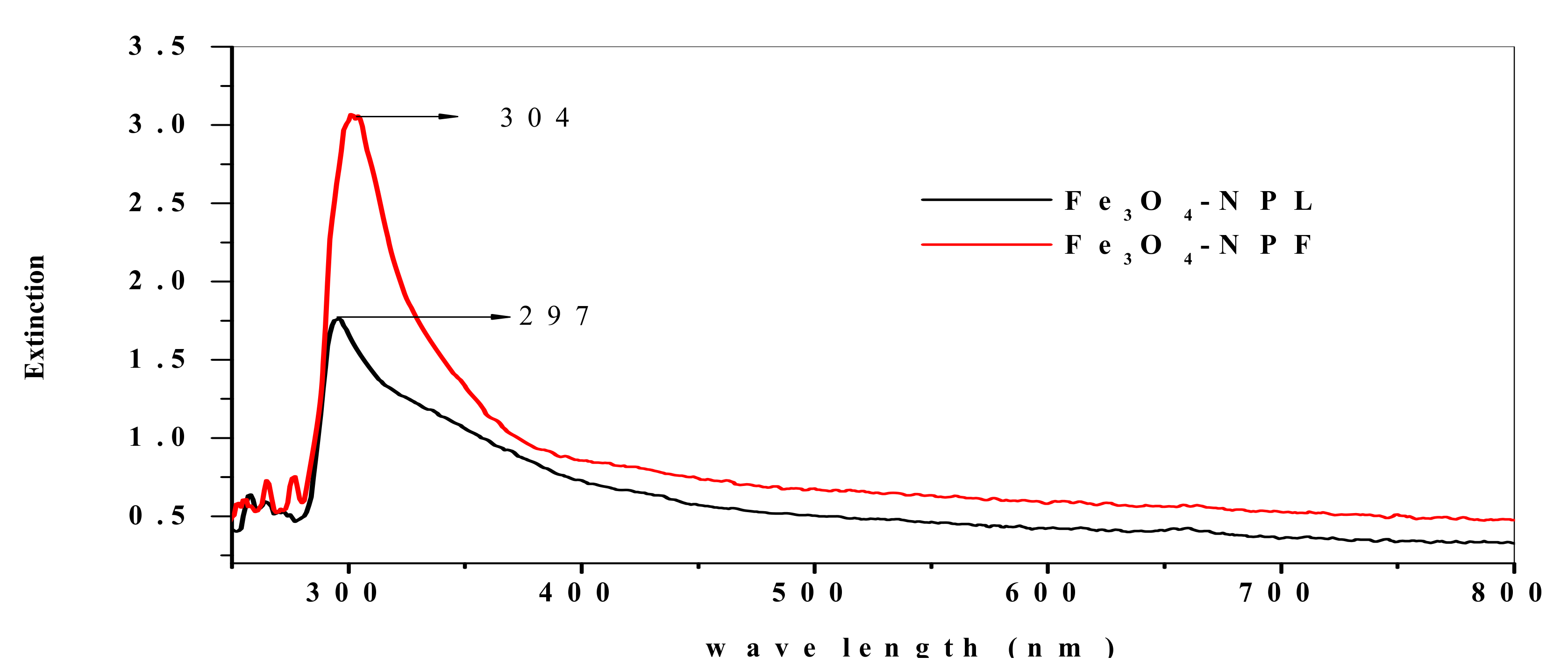
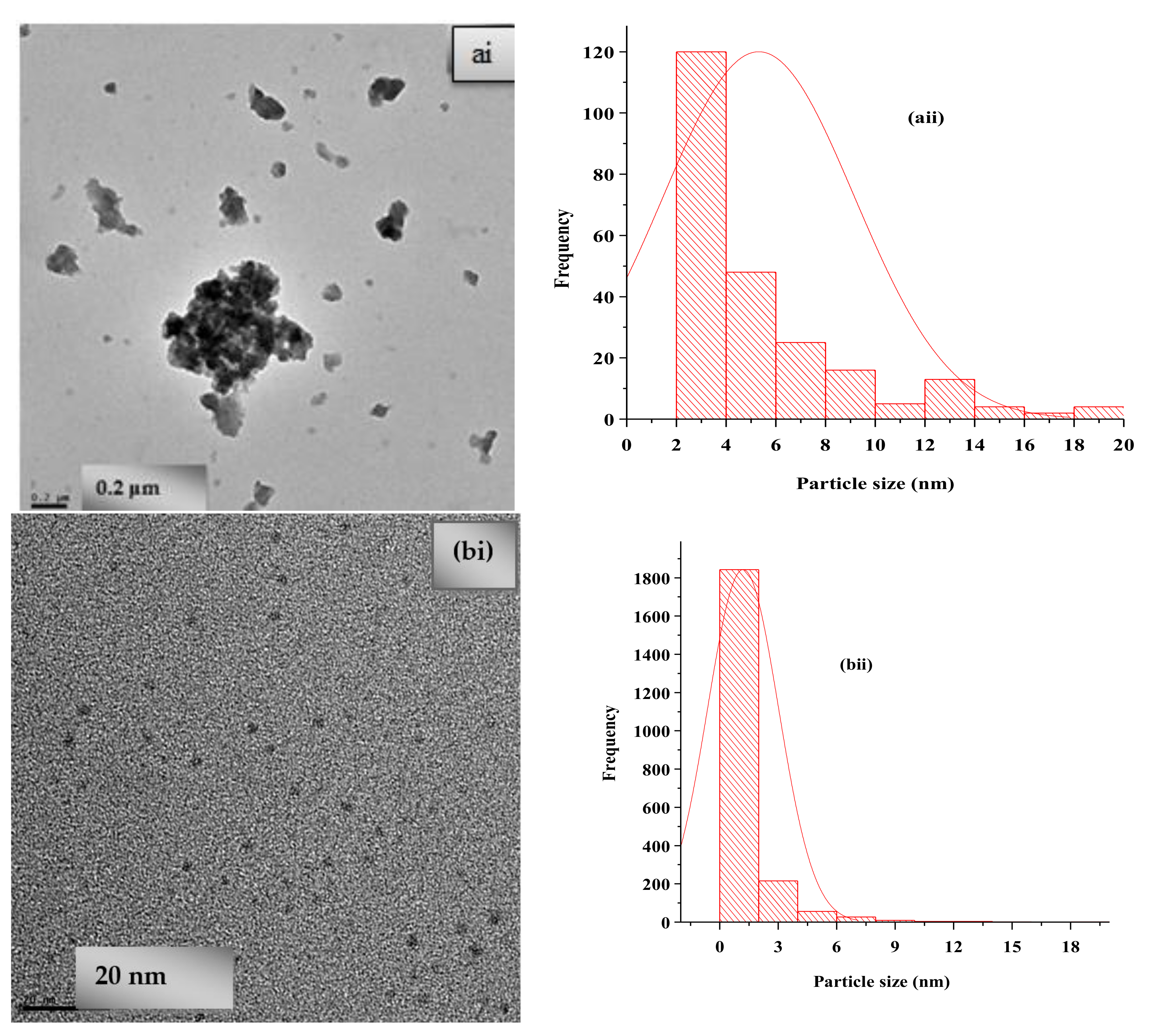
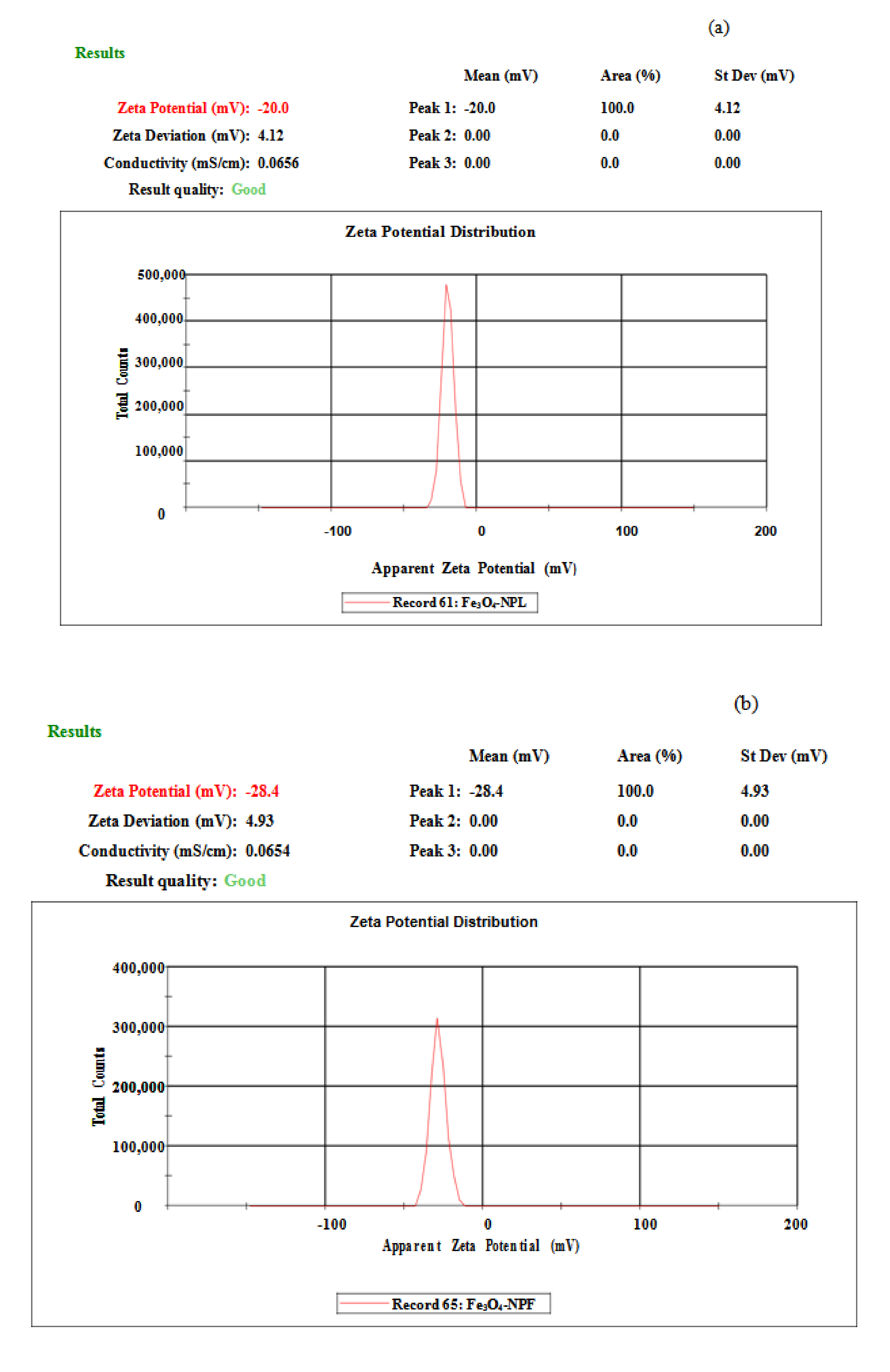
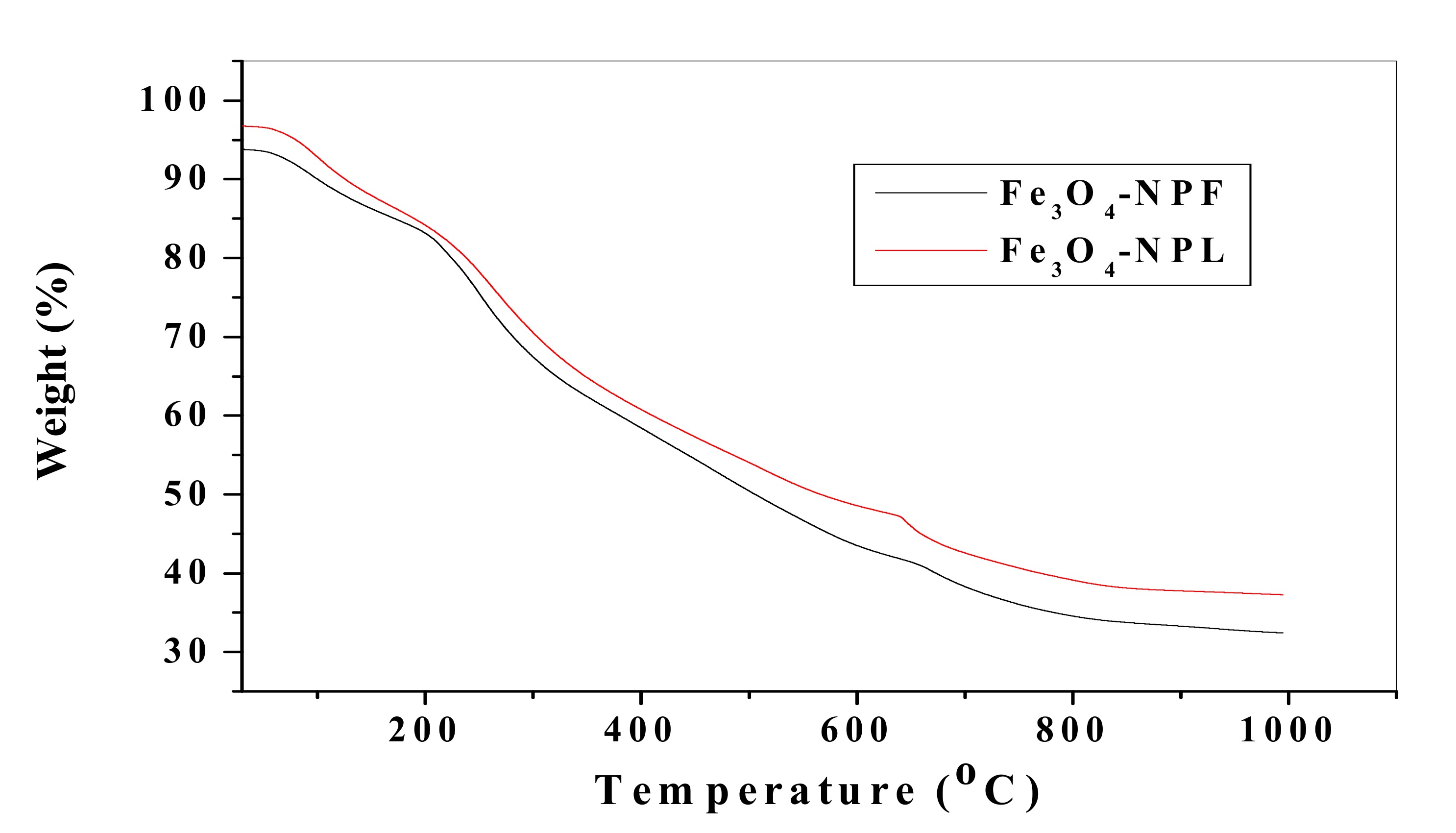
3.4. Spectroscopic and Morphological Characterization
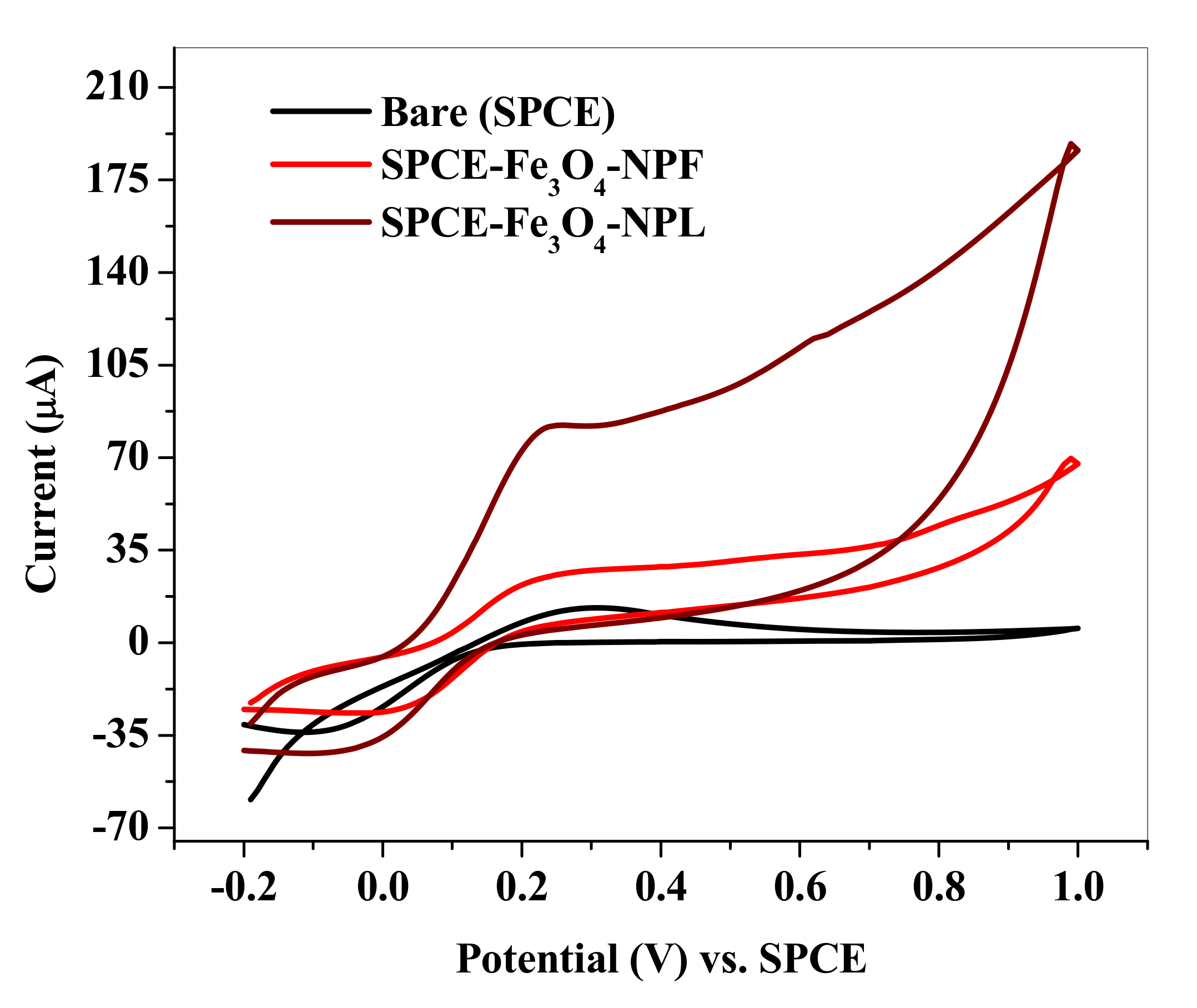
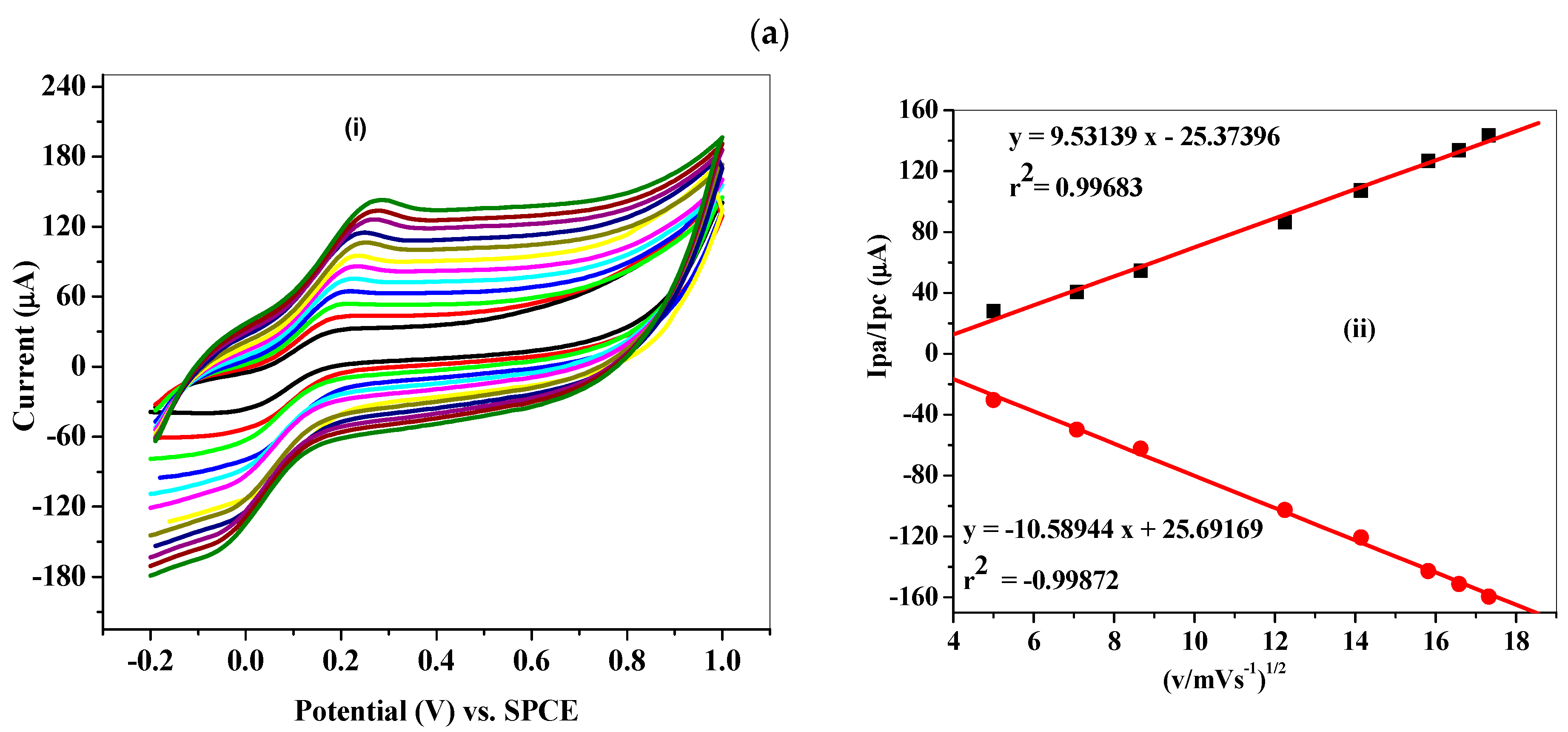
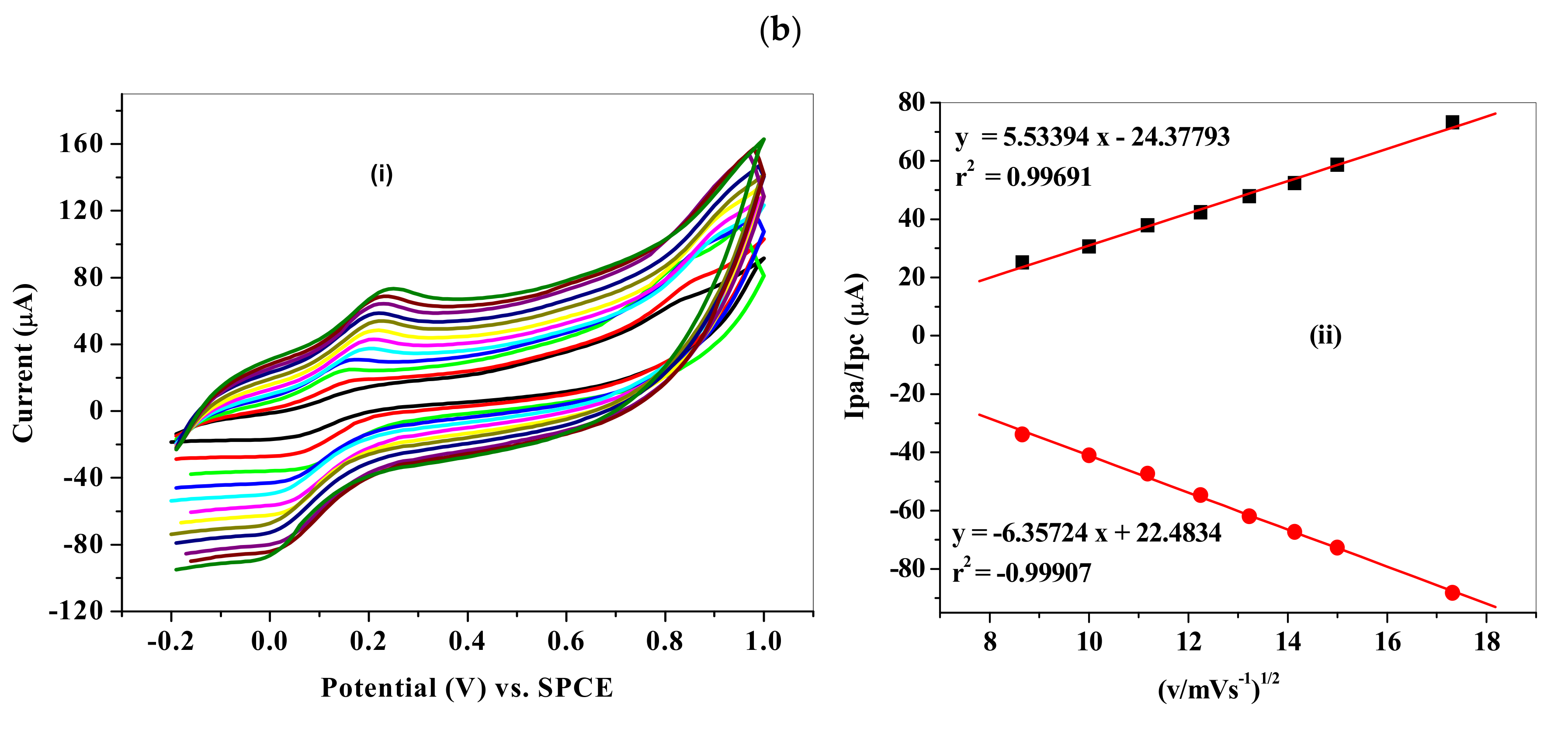
3.5. Electrochemical Characterization of Fe3O4-NP
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity of Green-Mediated Fe3O4-NP on Selected Bacterial Pathogens
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Attarad, A.; Hira, Z.; Muhammad, Z.; Ihsan, U.A.; Abdul, R.P.; Joham, S.A.; Altaf, H. Synthesis, characterization, applications and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanta, K.P.; Kwang-Hyun, B. Green biosynthesis of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using the aqueous extracts of food processing wastes under photo catalyzed condition and investigation of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. J. Photoch Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; He, T. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Synthesis and application in water treatment. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Onar, K.; Yakinci, M.E. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Phys. 2016, 667, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, C.; Dai, Y.; Song, M.; Gutmann, S.; Gao, F.; Lv, G.; Li, J.; Li, X.; et al. The application of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in cancer research: A new strategy to inhibit drug resistance. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 80, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinali, R.; Alireza, E.; Merilyn, M.-H.; Younes, G.; Aydin, B. The effect of iron oxide nanoparticles on Bacillus subtilis biofilm, growth and viability. Process. Biochem. 2017, 62, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omolola, E.F.; Abolanle, S.A.; Eno, E.E. Electrochemical determination of Serotonin in urine samples based on metal oxide nanoparticles/MWCNT on modified glass carbon electrode. Sens. Biosensing Res. 2017, 13, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, W.; Muhammad, M.; Nisar, U. Nanomaterials-based electrochemical detection of heavy metals in water: Current status, challenges and future direction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghui, Y.; Yunhui, Y.; Yanli, L.; Guoli, S.; Ruqin, Y. Platinum nanoparticles–doped sol gel/carbon nanotubes composite electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Biosens. Bio. Electron. 2006, 21, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin-Hua, C.; Sarani, Z.; Kasra, S.; Nilofar, A. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanocrystals using hydrothermal approach. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 4147–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, S.I.U.; Pal, U.; Jesus, F.S.-D. Controlling size and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 clusters in solvothermal process. Adv. Nano. Res. 2014, 2, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashan, S.; Dagher, S.; Tit, N.; Alazzam, A.; Obaidat, I. Novel method for synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2016, 53, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurughan, M.G.; Mohanraj, S.; Kodhaiyolii, S.; Pugalenthi, V. Ocimum sanctum leaf extract mediated green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: Spectroscopic and microscopic studies. J. Chem. Pharm. 2014, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Atul, B.; Debabrata, R.; Vipul, B.; Absar, A.; Indranil, S.; Seikh, M.Y.; Milan, S.; Murali, S. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small Nano Micro 2005, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, V.M.; Svetlana, S.M.; Andrew, J.L.; Olga, V.S.; Anna, O.D.; Igor, V.Y.; Michael, E.T.; Natalia, O.K. Biosynthesis of stable iron oxide nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Hordeum vulgare and Rumex acetosa plants. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5982–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasubbulakshmi, S.; Kadirvelu, K. Green synthesis of Iron oxide nanoparticles using lagenaria Siceraria and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity. Def. Life Sci. J. 2017, 2, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; EL-Hefny, M.; Nasser, R.A.; Ali, H.M.; El-Shanhorey, N.A.; Elansary, H.O. Medicinal and biological values of Callistemon viminalis extracts: History, current situation and prospects. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenielle, D.; Lois, R.; Alison, N.; Sylvia, M.; John, L.; Mohammed, A. Antibacterial and antifungal analysis of crude extracts from the leaves of Callistemon viminalis. J. Med. Biol. Sci. 2009, 3, 1934–7189. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, P.; Kumari, K.; Mozumdar, S.; Chandra, R. A green approach for the synthesis of gold nano triangles using aqueous leaf extract of Callistemon viminalis. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, B.T.; Manikandana, E.; Gurib-Fakima, A.; Maaza, M. Sm2O3 nanoparticles green synthesis via callistemon viminalis’ extract. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 650, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sone, B.T.; Manikandan, E.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Single-phase α-Cr2O3 nanoparticles’ green synthesis using Callistemon viminalis’ red flower extract. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2016, 9, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Ali, H.M.; El-Shanhorey, N.A.; Abdel-Megeed, A. Evaluation of extracts and essential oil from Callistemon viminalis leaves: Antibacterial and antioxidant activities, total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Nandhakumar, E.; Priya, D.; Soni, M.; Vimalane, I.; Vetha, P. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Tectona grandis (L.) and their anti-bacterial, antiarthritic, anti-oxidant and in vitro cytotoxicity activities. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10347–10356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Weli, A.M.; Ahmed, S.H.I. Comparison of total phenols, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of various crude extracts of Hyoscyamus gallagheri traditionally used for the treatment of epilepsy. Clin. Phytosci. 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.A.; Mohammad, O.; Rukhsana, S.; Anish, K.; Syed, I.A.; Mohammad, A.J.; Syed, K.Z.; Mohammad, H.A. Antibacterial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation technology against Bacillus cereus and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 110–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hombach, M.; Bloemberg, G.V.; Bottger, E.C. Effects of clinical breakpoint changes in CLSI guidelines 2010/2011 and EUCAST guidelines 2011 on antibiotic susceptibility test reporting of Gram-negative bacilli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboonchian, F.; Jamei, R.; Sarghein, S.H. Phenolic and flavonoid content of Elaeagnus angustifolia L.(leaf and flower). Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2014, 4, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, O.M.; Markham, K.R. Flavonoids Chemistry, Biochemistry and Applications; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitzer, V.; Veberic, R.; Osterc, G.; Stampar, F. Color and phenolic content changes during flower development in groundcover rose. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, M.A.; Khan, R.; Park, D.R.; Lee, Y.W.; Yeom, I.T. Removal of Sb (III) and Sb (V) by ferric chloride coagulation: Implications of Fe solubility. Water 2018, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.V.; Dharmasoth, R.D.; Satish, M.B.; Basavaiah, K. Facile green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Zanthoxylum armatum DC. For efficient adsorption of methylene blue. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, G.; Logeshwaran, V.; Sarathbabu, S.; Jha, P.K.; Jeyaraj, M.; Rajkuberan, C.; Senthilkumar, N.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticle using Couroupita guianensis Aubl. Fruit extract for their antibacterial and Cytotoxicity activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ghandoor, H.; Zidan, H.M.; Khalil, M.M.; Ismail, M.I.M. Synthesis and some physical properties of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5734–5745. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential—What they are and what they are not? J. Control Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Haron, M.J.; Namvar, F.; Nadi, B.; Rahman, M.Z.A.; Amin, J. Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 2013, 18, 7533–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Amani, A.M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Beigi, V.; Bazmandeh, A.Z.; Khalaf, N. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Artemisia vulgaris leaf extract and their application as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of methyl orange. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 115013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Taghizadeh, S.; Ali Mohammad Amani, A.M.; Alimardani, V. One-step green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Teucrium polium and their catalytic application in dye degradation. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviron, E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1979, 101, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, N.; Chen, H.; Dong, S. Biopolymer and carbon nanotubes interface prepared by self-assembly for studying the electrochemistry of microperoxidase-11. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10808–10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, R.; Nihan Aydemir, N.; Carraher, C.; Hamiaux, C.; Baek, P.; Cheema, J.; Kralicek, A.; Travas-Sejdic, J. Investigating electrochemical stability and reliability of gold electrode-electrolyte systems to develop bioelectronic nose using insect olfactory receptor. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkarran, A.A. Bacterial effects and protein corona evaluations: Crucial ignored factors for prediction of bio-efficacy of various forms of silver nanoparticles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katherine, B.H.; Allen, J.B. Interaction of silver (II) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: An electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micro molar Ag. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13214–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.W.; An, Y.J. Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Streptococcus aureus. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pathogens | 100 µg/mL of Fe3O4-NP Synthesized from Leaves | 150 µg/mL Fe3O4-NP Synthesized from Leaves | 100 µg/mL vFe3O4-NP Synthesized from Flowers | 150 µg/mL Fe3O4-NP Synthesized from Flowers | Ciprofloxacin * (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus (ATCC 10876) | 8 | 12 | 10 | 13 | 30 |
| E. coli (ATCC 25922) | 11 | 13 | 11 | 14 | 40 |
| Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212) | 11 | 13 | 12 | 14 | 37 |
| Enterococcus gallinarum (ATCC 700425) | 7 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 28 |
| Enterococcus faecium (ATCC 701221) | 8 | 14 | 10 | 12 | 38 |
| Salmonella typhimurium (ATCC 14028) | 12 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 31 |
| Salmonella enteritidis (ATCC 13076) | 10 | 13 | 12 | 15 | 35 |
| Vibrio cholerae | 13 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uwaya, G.E.; Fayemi, O.E.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Junaedi, H.; Ebenso, E.E. Synthesis, Electrochemical Studies, and Antimicrobial Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis Plant Extracts. Materials 2020, 13, 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214894
Uwaya GE, Fayemi OE, Sherif E-SM, Junaedi H, Ebenso EE. Synthesis, Electrochemical Studies, and Antimicrobial Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis Plant Extracts. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214894
Chicago/Turabian StyleUwaya, Gloria E., Omolola E. Fayemi, El-Sayed M. Sherif, Harri Junaedi, and Eno E. Ebenso. 2020. "Synthesis, Electrochemical Studies, and Antimicrobial Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis Plant Extracts" Materials 13, no. 21: 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214894
APA StyleUwaya, G. E., Fayemi, O. E., Sherif, E.-S. M., Junaedi, H., & Ebenso, E. E. (2020). Synthesis, Electrochemical Studies, and Antimicrobial Properties of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles from Callistemon viminalis Plant Extracts. Materials, 13(21), 4894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214894








