Fabrication of Eco-Friendly Betanin Hybrid Materials Based on Palygorskite and Halloysite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
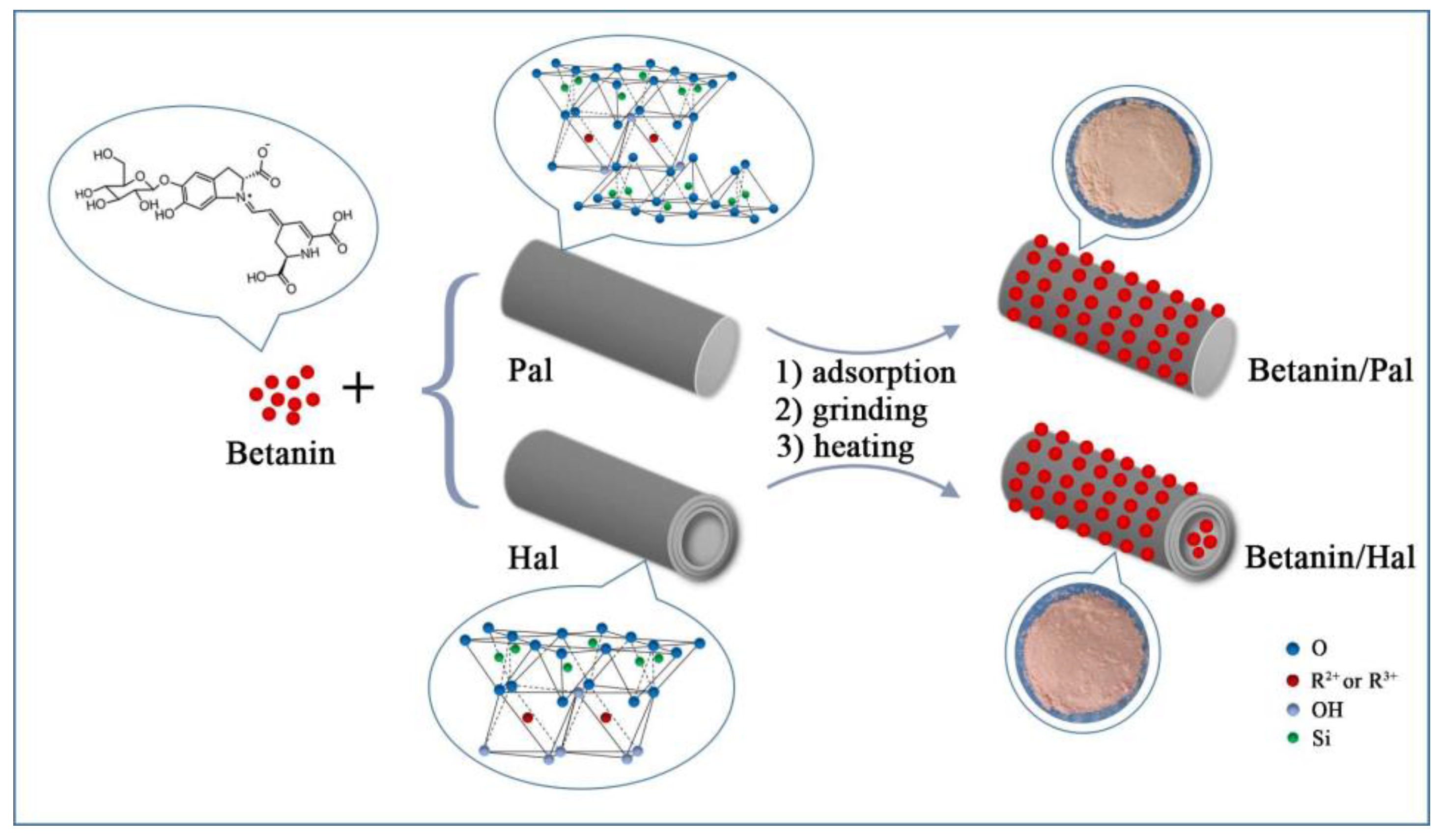
2.2. Preparation of Betanin/Clay Mineral Hybrid Materials
2.3. Stability Tests
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
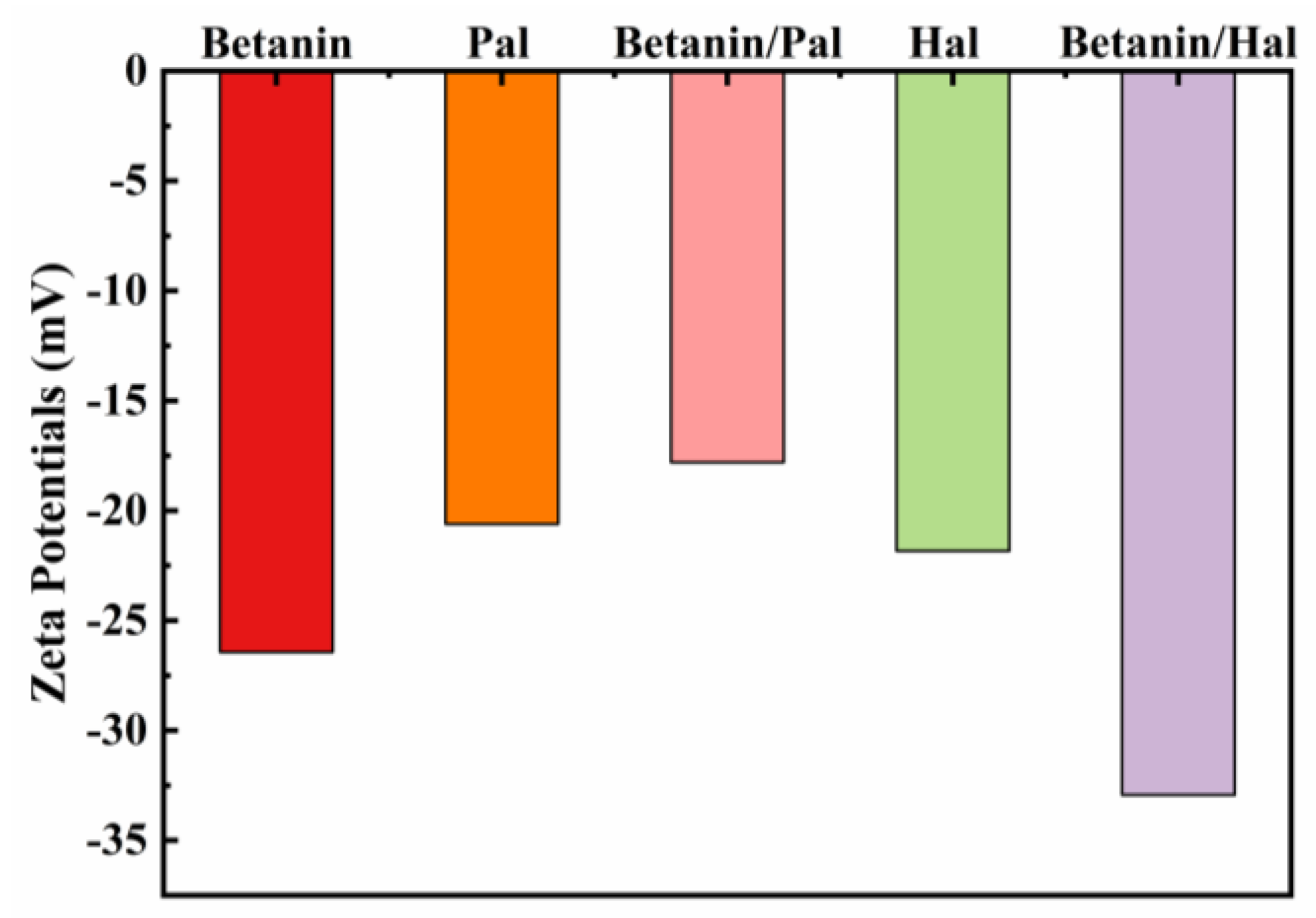
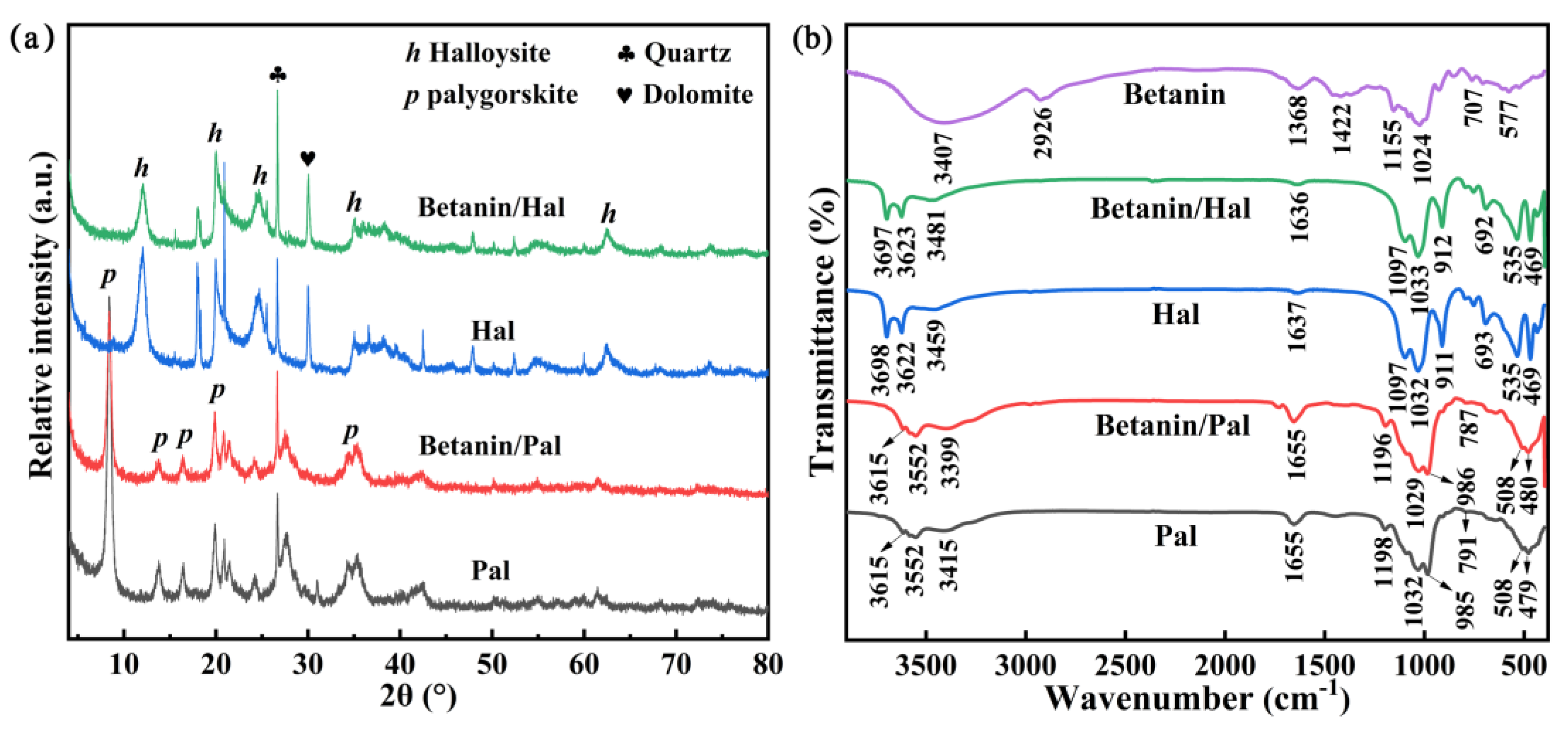
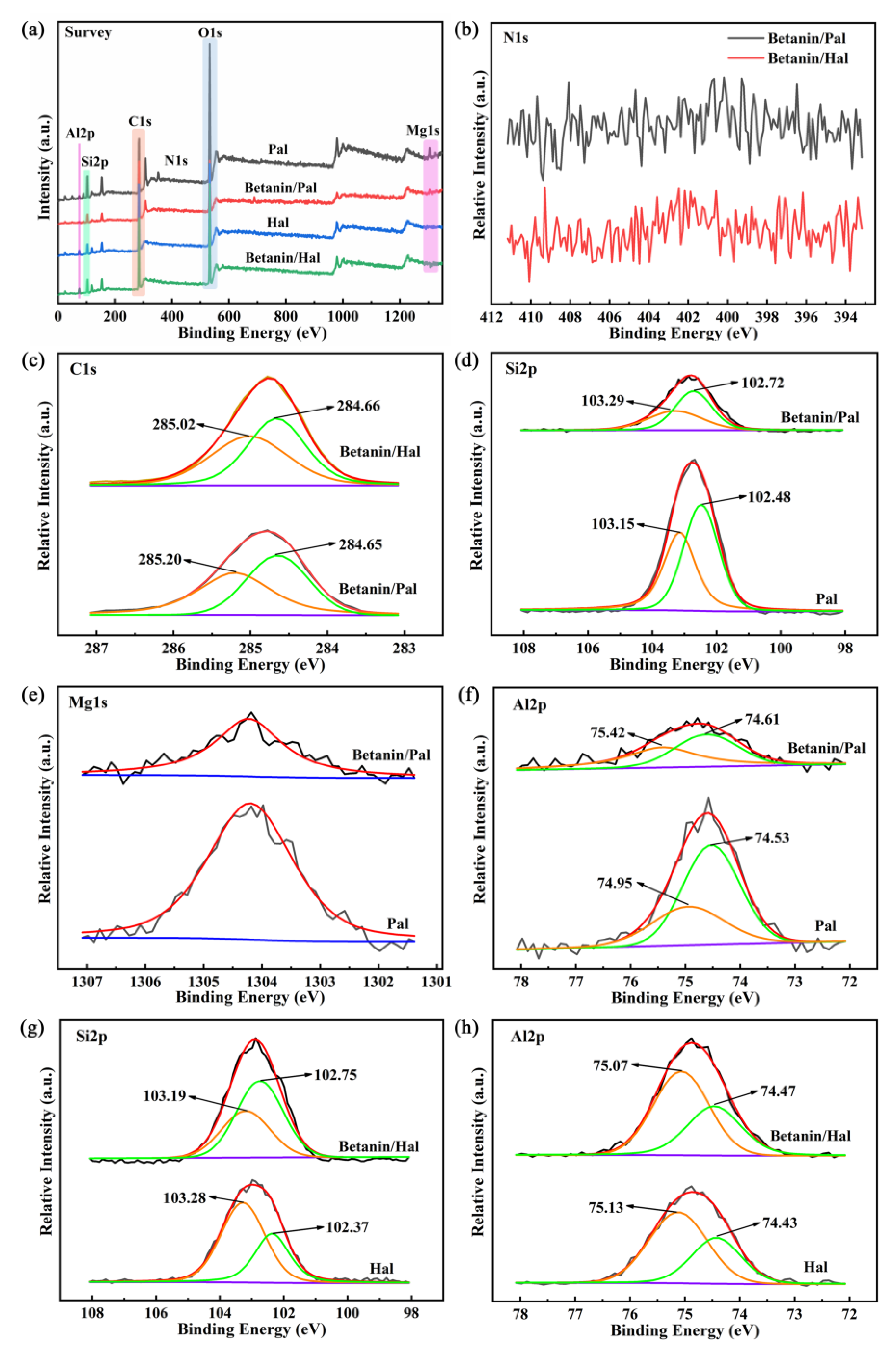
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Hybrid Materials
3.2. Thermal and Chemical Stability of the Hybrid Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jose-Yacaman, M.; Rendón, L.; Arenas, J.; Puche, M.C.S. Maya Blue Paint: An Ancient Nanostructured Material. Science 1996, 273, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristea, D.; Vilarem, G. Improving light fastness of natural dyes on cotton yarn. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 70, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leona, M. Microanalysis of organic pigments and glazes in polychrome works of art by surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14757–14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, M.; Nazarpoor, K.; Karimi, L. Eco-friendly dyeing of wool using natural dye from weld as co-partner with synthetic dye. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrie, B.H. Rethinking the History of Artists’ Pigments Through Chemical Analysis. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Nasir, H.; Abd-Talib, N.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Wong, L.P.; Idham, Z.; Casillas, A.C.; Ahmad, A. Natural colorants from plants for wellness industry. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2018, 9, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Olphen, H. Maya Blue: A Clay-Organic Pigment? Sciences 1966, 154, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, B.; Kuang, W.; Moser, A.; Facey, G.A.; Detellier, C. Structural study of Maya Blue: Textural, thermal and solidstate multinuclear magnetic resonance characterization of the palygorskite-indigo and sepiolite-indigo adducts. Clays Clay Miner. 2003, 51, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet-Plamondon, C.M.; Aranda, P.; Favier, A.; Habert, G.; Van Damme, H.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. The Maya blue nanostructured material concept applied to colouring geopolymers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98834–98841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, C.L.; Heleno, S.A.; Carocho, M.; Rodrigues, P.; Pinela, J.; Dias, M.I.; Fernandes, I.P.; Barreiro, M.F.; Morales, P.; Barros, L.; et al. Betacyanins from Gomphrena globosa L. flowers: Incorporation in cookies as natural colouring agents. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, X.; Sun, D.; Ding, S.; Cai, P.; Yuan, L.; Tian, Y.; Tu, W.; Hu, Q.-N. AdditiveChem: A comprehensive bioinformatics knowledge-base for food additive chemicals. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, I.; Gashti, M.P. Extraction of polyphenolic dyes from henna, pomegranate rind, andPterocarya fraxinifoliafor nylon 6 dyeing. Color. Technol. 2016, 132, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micó-Vicent, B.; Martínez-Verdú, F.; Novikov, A.; Stavitskaya, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Yendluri, R.; Lvov, Y. Stabilized Dye-Pigment Formulations with Platy and Tubular Nanoclays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, H.A. Anthocyanins and betalains: Evolution of the mutually exclusive pathways. Plant Sci. 1994, 101, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M. Betalains: Properties, sources, applications, and stability—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Stabilization of betalains: A review. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TuTunchi, P.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Hamishehkar, H.; Alizadeh, A. Extraction of red beet extract with β-cyclodextrin-enhanced ultrasound assisted extraction: A strategy for enhancing the extraction efficacy of bioactive compounds and their stability in food models. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, J.; Cabanes, J.; Jiménez-Atiénzar, M.; Ibañez-Tremolada, M.; Gómez-Pando, L.R.; García-Carmona, F.; Gandía-Herrero, F. Characterization of betalains, saponins and antioxidant power in differently colored quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) varieties. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhananjayan, I.; Kathiroli, S.; Subramani, S.; Veerasamy, V. Ameliorating effect of betanin, a natural chromoalkaloid by modulating hepatic carbohydrate metabolic enzyme activities and glycogen content in streptozotocin—Nicotinamide induced experimental rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Ghorbani, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Roufegarinejad, L. Improvement in the stability of betanin by liposomal nanocarriers: Its application in gummy candy as a food model. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Ahmad, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Assessment of free radicals scavenging activity of seven natural pigments and protective effects in AAPH-challenged chicken erythrocytes. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, N.; Roriz, C.L.; Morales, P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C. Coloring attributes of betalains: A key emphasis on stability and future applications. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elbe, J.H.; Maing, I.-Y.; Amundson, C.H. Color stability of betanin. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsley, M.W.; Katsaboxakis, K.Z. Stability and use of natural colours in foods Red beet powder, copper chlorophyll powder and cochineal. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1980, 15, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Nazari, M.; Alizadeh, S.A.; Hamishehkar, H. Multifunctional betanin nanoliposomes-incorporated gelatin/chitosan nanofiber/ZnO nanoparticles nanocomposite film for fresh beef preservation. Meat Sci. 2020, 167, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyles, C.; Sobeck, S.J.S. Photostability of organic red food dyes. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Abbasi, M.M.; Shokouhi, B.; Ghorbani, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of betanin for diabetes treatment by liposomal nanocarriers. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 59, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, H.; Falsafi, S.R.; Jafari, S.M. Nanoencapsulation of carotenoids within lipid-based nanocarriers. J. Control. Release 2019, 298, 38–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theng, B.K.G. Clay-Polymer Interactions: Summary and Perspectives. Clays Clay Miner. 1982, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Chrzanowski, W.; Rohanizadeh, R. Biomedical applications of cationic clay minerals. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29467–29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Xiong, L.; Chen, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Enhanced Electrochemical Properties of Gel Polymer Electrolyte with Hybrid Copolymer of Organic Palygorskite and Methyl Methacrylate. Materials 2018, 11, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Wang, A. Adsorption of dyes onto palygorskite and its composites: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1274–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dong, W.; Wang, A.; Ding, J.; Wang, Q.; Hui, A.; Wang, A. Optimal Synthesis of Environment-Friendly Iron Red Pigment from Natural Nanostructured Clay Minerals. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Mu, B.; Wang, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. A Comparative Study on Color Stability of Anthocyanin Hybrid Pigments Derived from 1D and 2D Clay Minerals. Materials 2019, 12, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drits, V.A.; Sokolova, G.V. Structure of palygorskite. Am. Inst. Phys. 1971, 16, 183–185. [Google Scholar]
- Galan, E. Properties and applications of palygorskite-sepiolite clays. Clay Miner. 1996, 31, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. Novel environment friendly inorganic red pigments based on attapulgite. Powder Technol. 2017, 315, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ding, J.; Mu, B.; Wang, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Acid/base reversible allochroic anthocyanin/palygorskite hybrid pigments: Preparation, stability and potential applications. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 171, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Vinokurov, V.; Stavitskaya, A.V.; Lvov, Y. Development of Marine Antifouling Epoxy Coating Enhanced with Clay Nanotubes. Materials 2019, 12, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchman, G.J.; Davy, T.J.; Aylmore, L.A.G.; Gilkes, R.; Self, P.G. Characteristics of fine pores in some halloysites. Clay Miner. 1995, 30, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, A.; Yang, H.; Ouyang, J. Applications and interfaces of halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Baglioni, P.; Ridi, F. Halloysite Nanotubes as Nano-Carriers of Corrosion Inhibitors in Cement Formulations. Materials 2020, 13, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, K.; Singh, G.; Lakhi, K.S.; Benzigar, M.R.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Almajid, A.M.; Belperio, T.; Vinu, A. Halloysite nanotubes: Novel and eco-friendly adsorbents for high-pressure CO2 capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Nassir, M.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Impact of Sulfuric Acid Treatment of Halloysite on Physico-Chemic Property Modification. Materials 2016, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Du, Y.; Ma, X. Selective fabrication of iron oxide particles in halloysite lumen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 151, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Controlled Release of Protective Agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mu, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. Effect of grinding time on fabricating a stable methylene blue/palygorskite hybrid nanocomposite. Powder Technol. 2015, 280, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite Clay Nanotubes for Loading and Sustained Release of Functional Compounds. Adv. Mater. 2015, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.C.; Ferreira, C.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Panchal, A.; Lvov, Y.; Agarwal, A. Halloysite clay nanotubes for life sciences applications: From drug encapsulation to bioscaffold. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 257, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zong, L.; Mu, B.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Attapulgite/carbon composites as a recyclable adsorbent for antibiotics removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1650–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, A.; Zong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. A new route to fabricate high-efficient porous silicate adsorbents by simultaneous inorganic-organic functionalization of low-grade palygorskite clay for removal of Congo red. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 277, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchuk, M.; Selig, M.J.; Celli, G.B.; Lawrence, P.; Smilgies, D.-M.; Abbaspourrad, A. Mechanistic investigation via QCM-D into the color stability imparted to betacyanins by the presence of food grade anionic polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Jaber, M.; Rodrigues, F.; Rigaud, B.; Walter, P.; Zhang, Z. A new durable pigment with hydrophobic surface based on natural nanotubes and indigo: Interactions and stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mu, B.; Hui, A.; Wang, Q.; Wang, A. Low-cost bismuth yellow hybrid pigments derived from attapulgite. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 149, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Frost, R.L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J. Infrared and infrared emission spectroscopic study of typical Chinese kaolinite and halloysite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Mu, B.; Luo, Z.; Wang, A. Bright blue halloysite/CoAl 2 O 4 hybrid pigments: Preparation, characterization and application in water-based painting. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 139, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Cui, H.; Wang, C.; Hao, F.; Liu, P.; Xiong, W. In situ self-assembled preparation of the hybrid nanopigment from raw sepiolite with excellent stability and optical performance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 163, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yuan, P.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. Infrared spectroscopic evidence of a direct addition reaction between palygorskite and pyromellitic dianhydride. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carazo, E.; Borrego-Sánchez, A.; García-Villén, F.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Iborra, C.V.; Cerezo, P.; Aguzzi, C. Adsorption and characterization of palygorskite-isoniazid nanohybrids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Xi, Y.; He, H. Synthesis, characterization of palygorskite supported zero-valent iron and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Facile preparation of stable palygorskite/methyl violet@SiO2 “Maya Violet” pigment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 457, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.D.; Khot, K.V.; Dongale, T.; Musselman, K.P.; Bhosale, P.N. Development of dye sensitized TiO2 thin films for efficient energy harvesting. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 790, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aztatzi-Rugerio, L.; Granados-Balbuena, S.Y.; Zainos-Cuapio, Y.; Ocaranza-Sánchez, E.; Rojas-López, M. Analysis of the degradation of betanin obtained from beetroot using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.N.A.; Ritesh, S.K.; Sharmila, G.; Muthukumaran, C. Extraction optimization and characterization of water soluble red purple pigment from floral bracts of Bougainvillea glabra. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2145–S2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tian, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, A. From naturally low-grade palygorskite to hybrid silicate adsorbent for efficient capture of Cu(II) ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 132, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoufis, T.; Katsaros, F.; Kooi, B.J.; Bletsa, E.; Papageorgiou, S.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Panagiotopoulos, I. Halloysite nanotube-magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle hybrids for the rapid catalytic decomposition of pentachlorophenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidecka, K.; Giacoboni, J.; Picconi, P.; Vago, R.; Licandro, E. Quantification of amino groups on halloysite surfaces using the Fmoc-method. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13944–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and intercalation structure model of halloysite-stearic acid intercalation compound. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

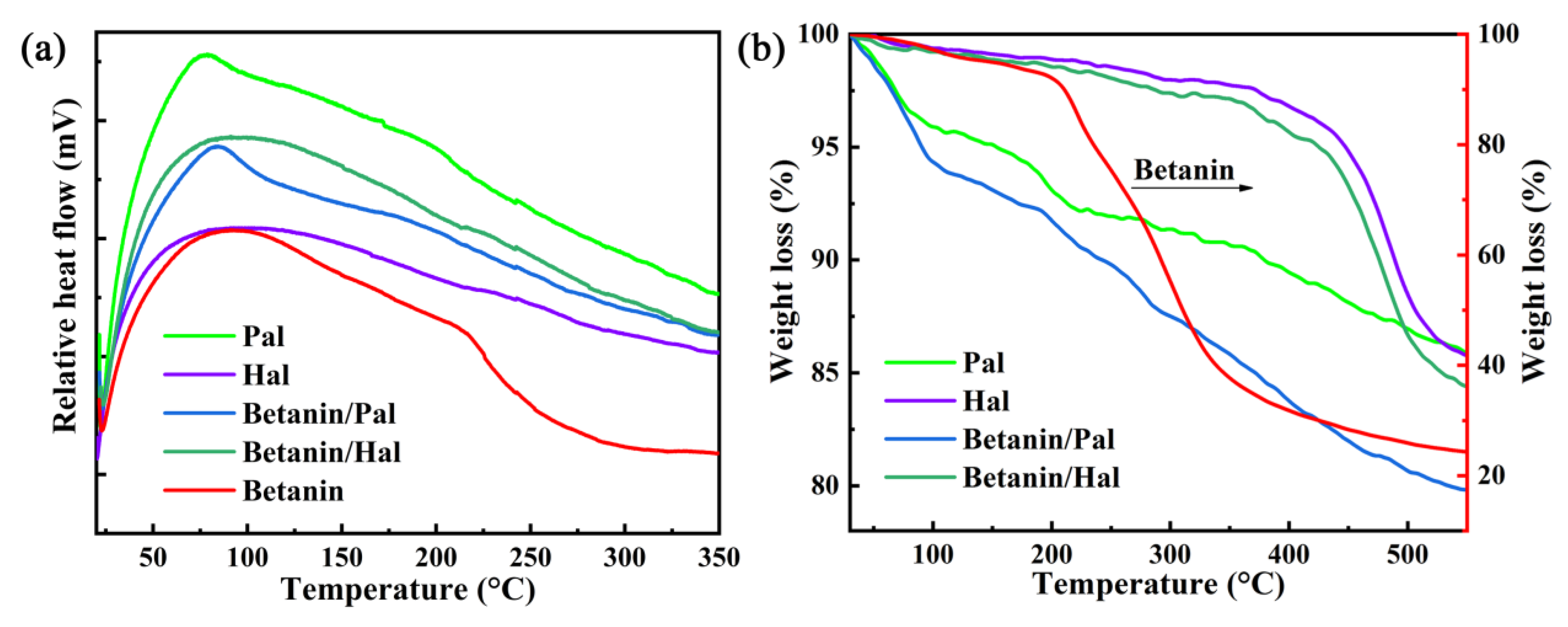
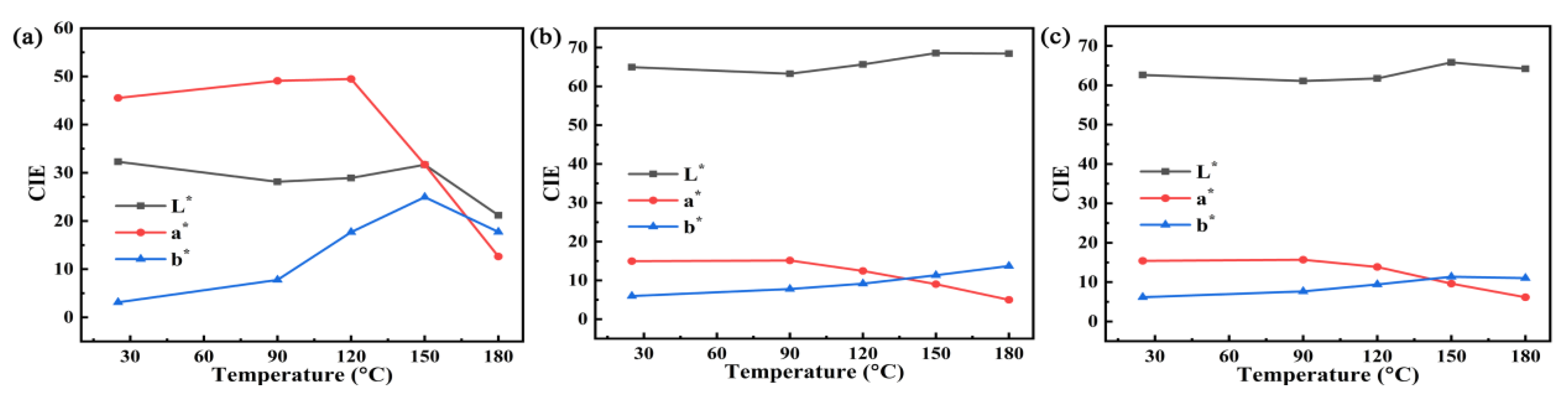
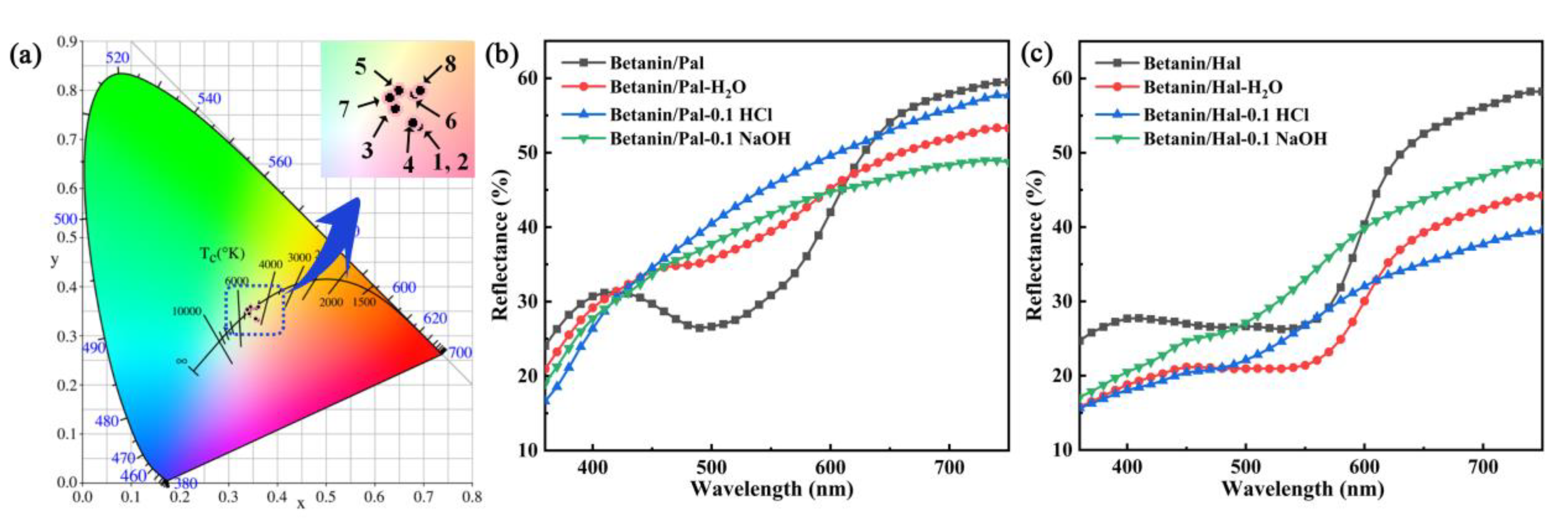
| Samples | SBET (m2/g) | Smicro (m2/g) | Sext (m2/g) | Vtotal (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pal | 185.85 | 26.93 | 158.93 | 0.4243 |
| Betanin/Pal | 129.19 | 11.40 | 117.79 | 0.4288 |
| Hal | 58.10 | 1.43 | 56.67 | 0.2064 |
| Betanin/Hal | 48.29 | - | 52.43 | 0.1752 |
| Different Medium | Betanin/Pal | Betanin/Hal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | |
| Before immersion | 64.94 ± 0.50 | 14.96 ± 0.25 | 5.99 ± 0.05 | 62.64 ± 0.10 | 15.43 ± 0.08 | 6.18 ± 0.06 |
| Distilled water | 69.59 ± 0.07 | 5.13 ± 0.01 | 8.34 ± 0.02 | 56.23 ± 0.01 | 12.02 ± 0.01 | 6.01 ± 0.01 |
| 0.1 M HCl | 73.13 ± 0.22 | 1.89 ± 0.02 | 13.00 ± 0.08 | 59.23 ± 0.14 | 6.32 ± 0.05 | 11.80 ± 0.08 |
| 0.1 M NaOH | 70.47 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.02 | 9.98 ± 0.02 | 64.60 ± 0.12 | 6.85 ± 0.01 | 13.91 ± 0.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Mu, B.; Wang, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, A. Fabrication of Eco-Friendly Betanin Hybrid Materials Based on Palygorskite and Halloysite. Materials 2020, 13, 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204649
Li S, Mu B, Wang X, Kang Y, Wang A. Fabrication of Eco-Friendly Betanin Hybrid Materials Based on Palygorskite and Halloysite. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shue, Bin Mu, Xiaowen Wang, Yuru Kang, and Aiqin Wang. 2020. "Fabrication of Eco-Friendly Betanin Hybrid Materials Based on Palygorskite and Halloysite" Materials 13, no. 20: 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204649
APA StyleLi, S., Mu, B., Wang, X., Kang, Y., & Wang, A. (2020). Fabrication of Eco-Friendly Betanin Hybrid Materials Based on Palygorskite and Halloysite. Materials, 13(20), 4649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204649








