Analysis of Magnetic Anisotropy and Non-Homogeneity of S235 Ship Structure Steel after Plastic Straining by the Use of Barkhausen Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
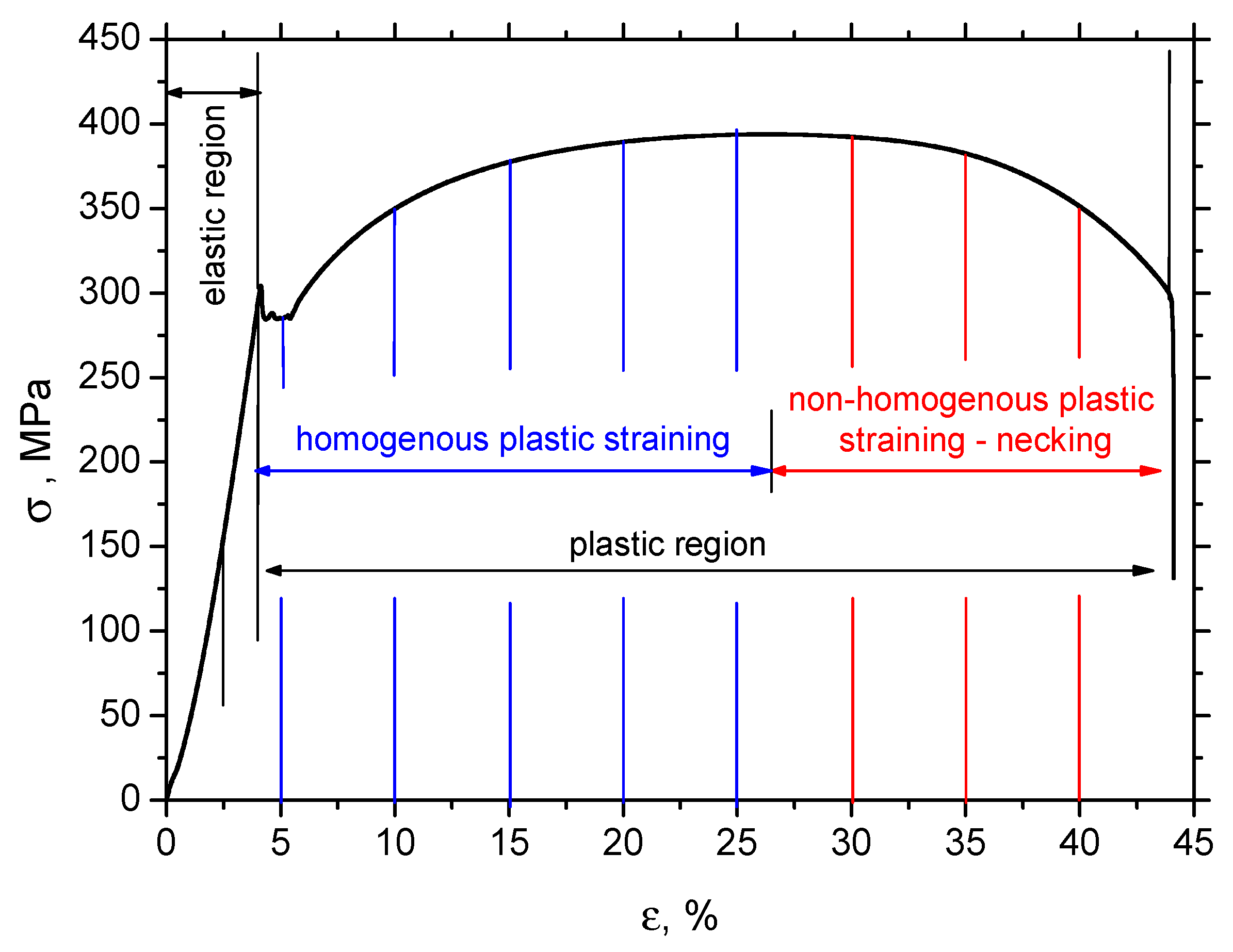
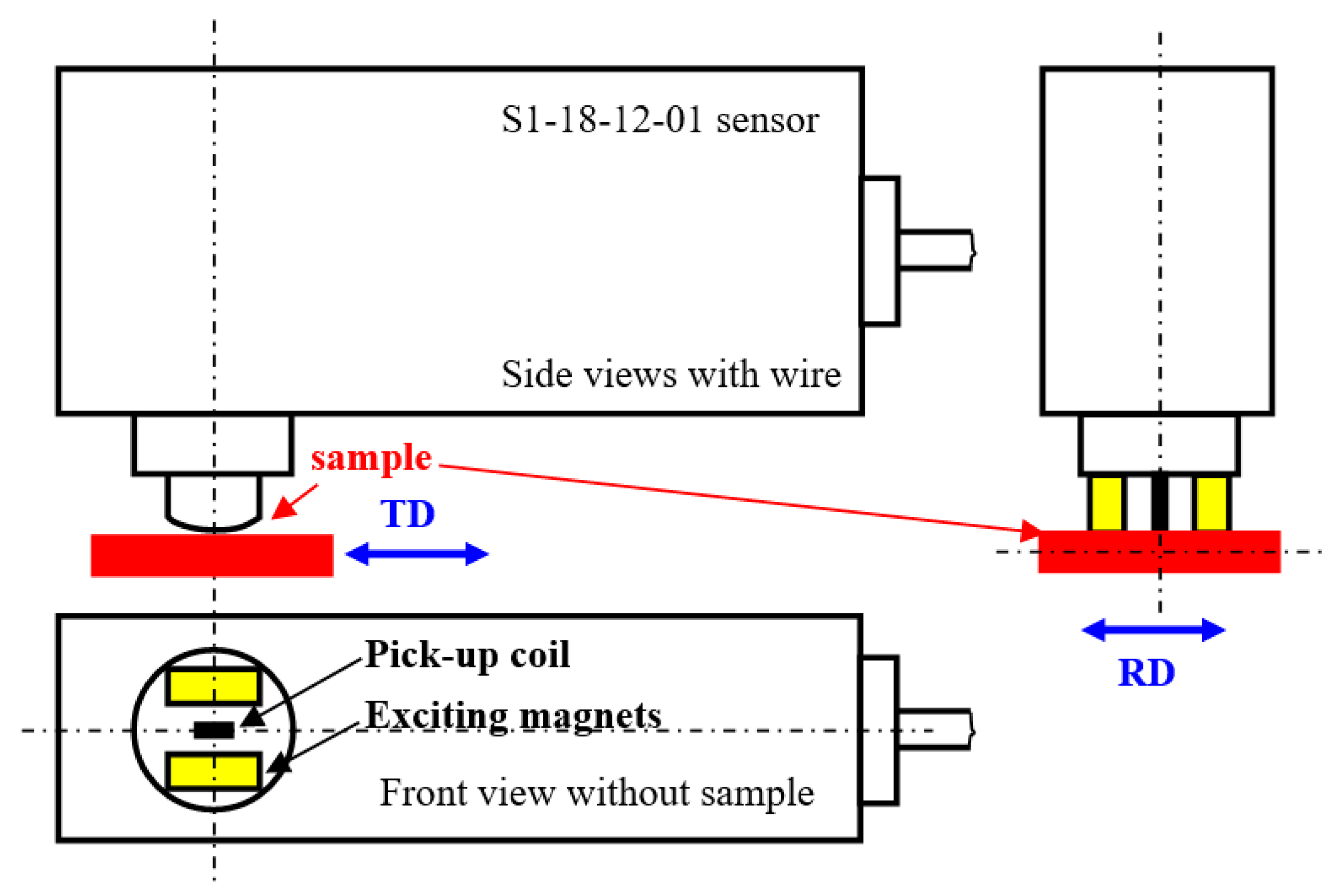
2. Materials and Methods
3. Experimental Results
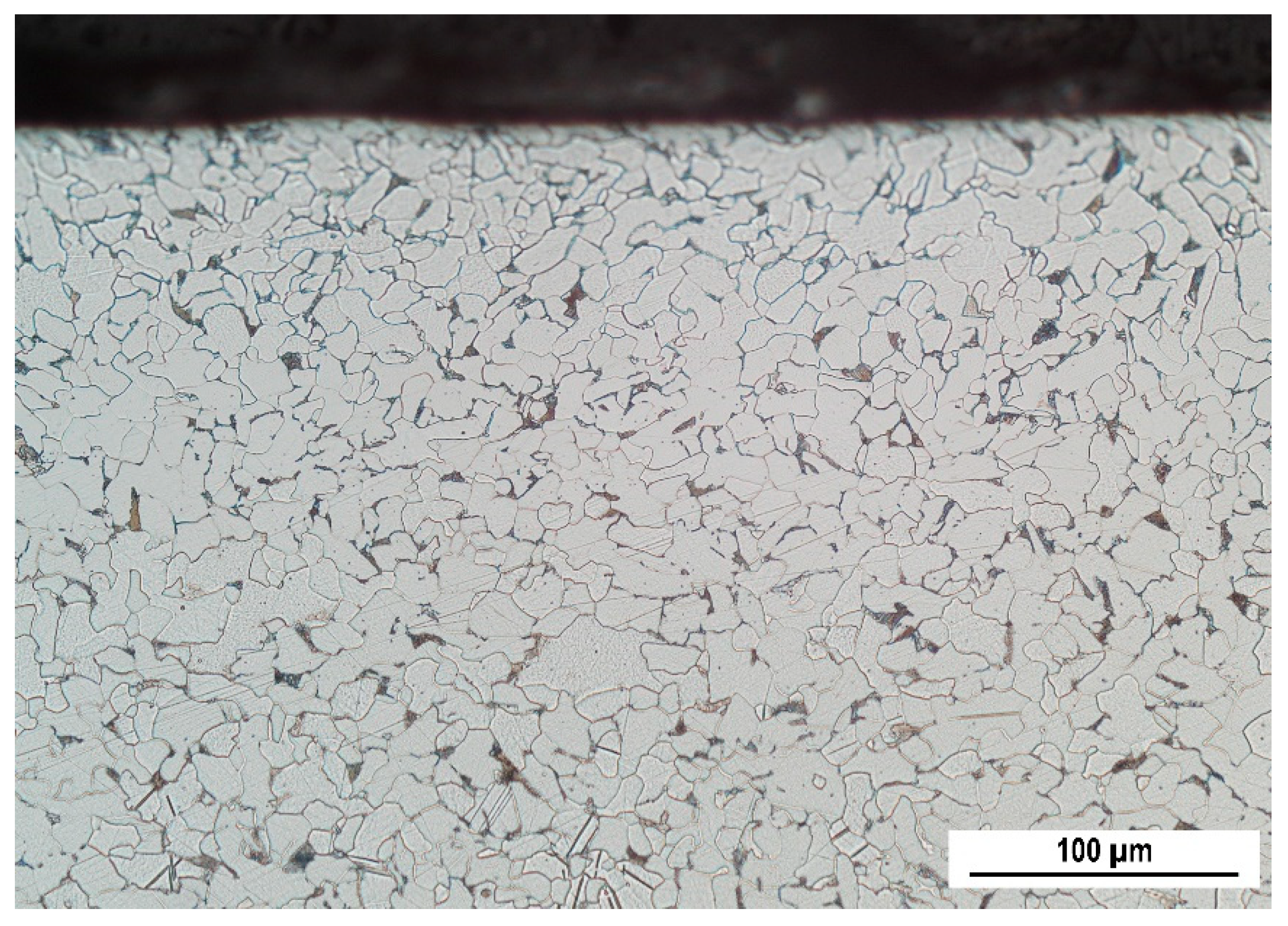
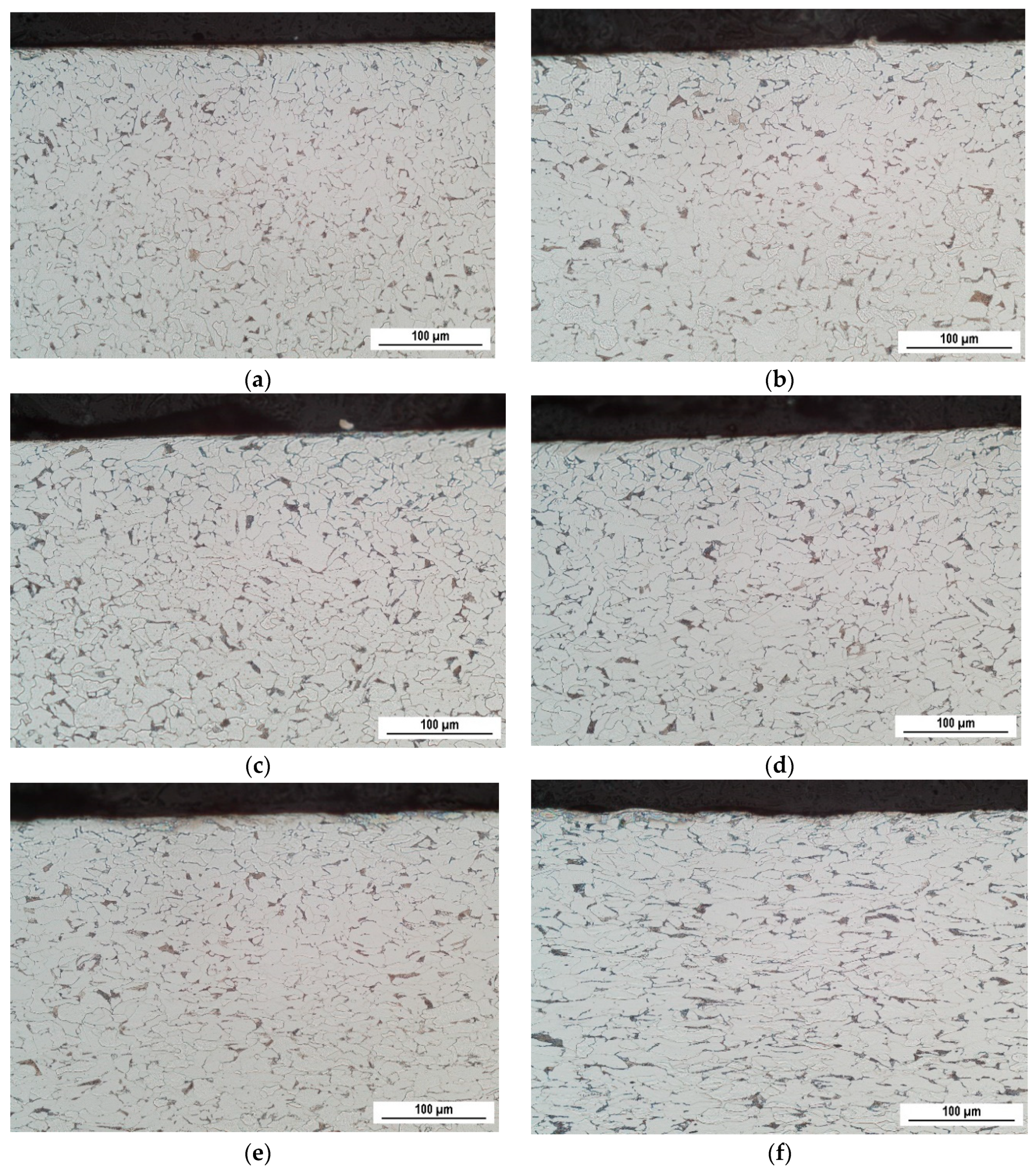
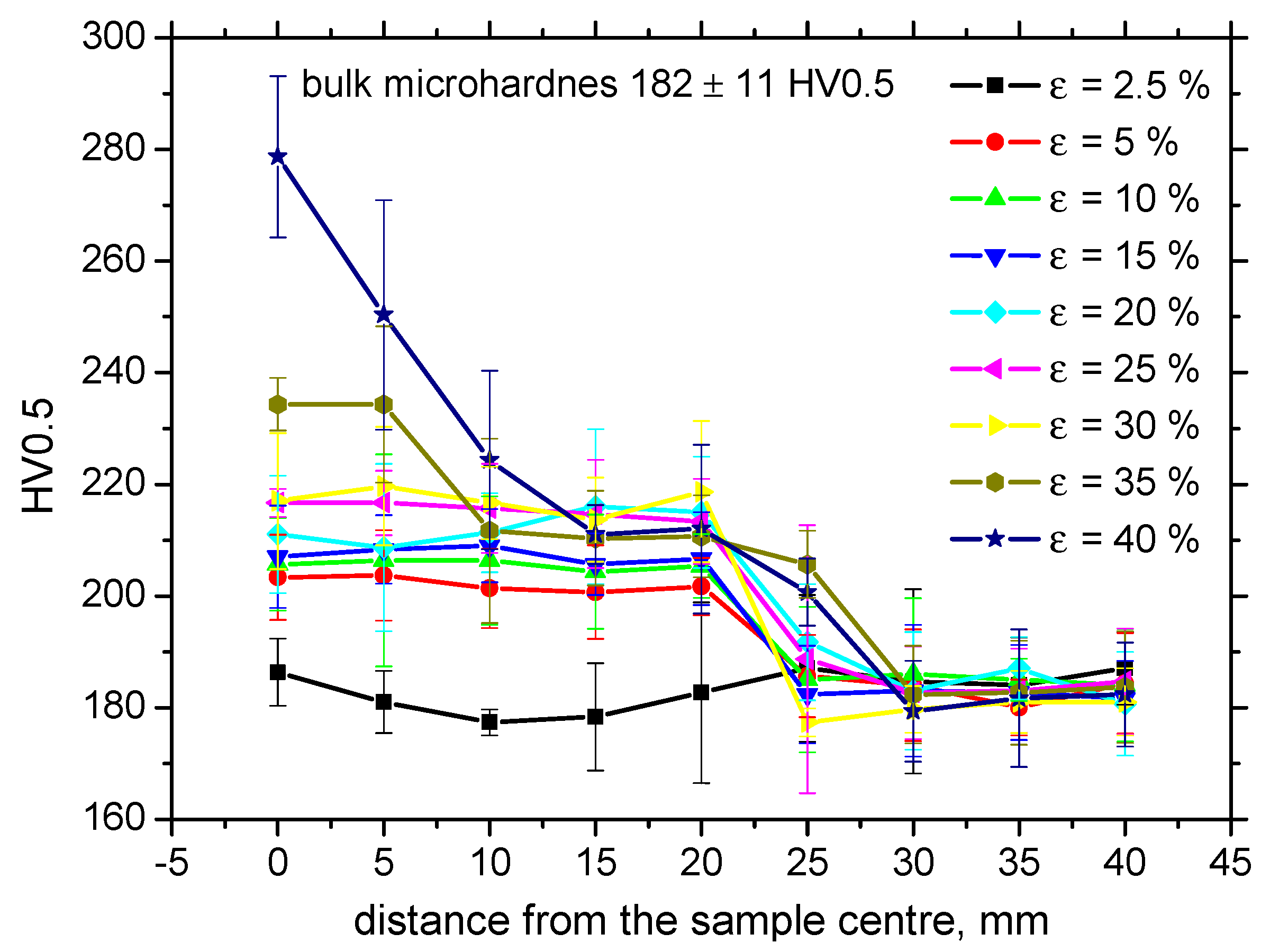
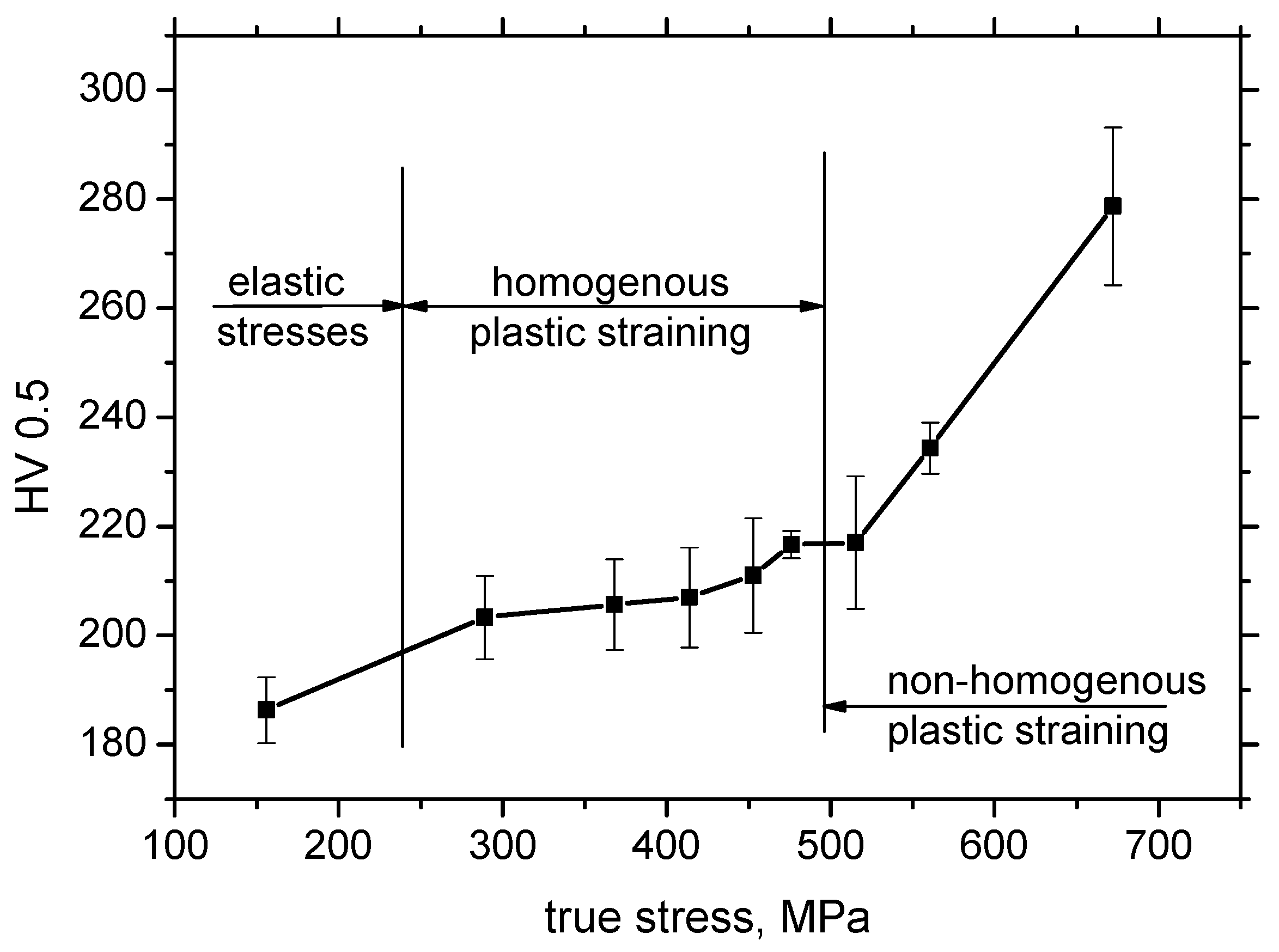
3.1. Light Microscopy and Microhardness
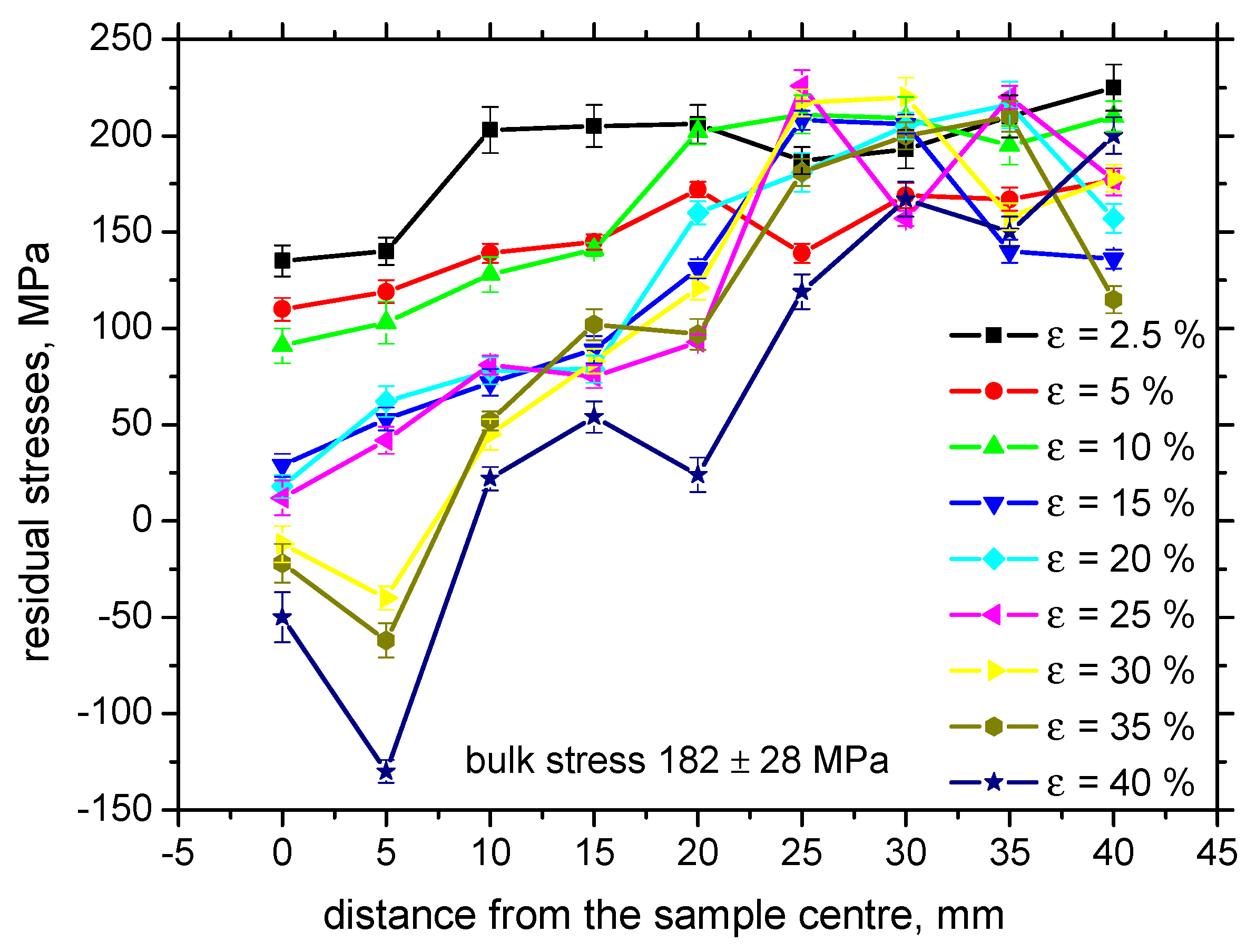
3.2. XRD Measurements
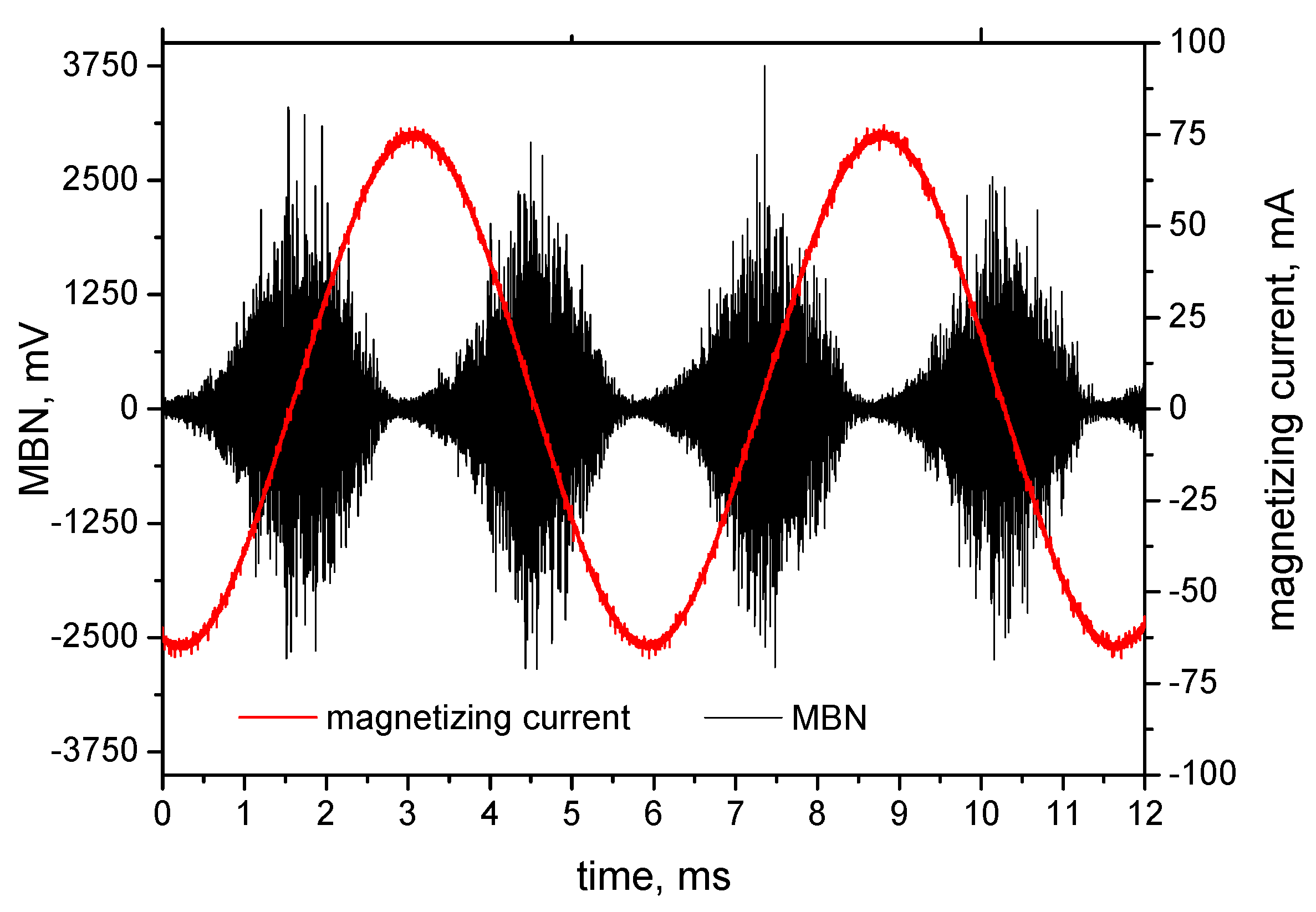
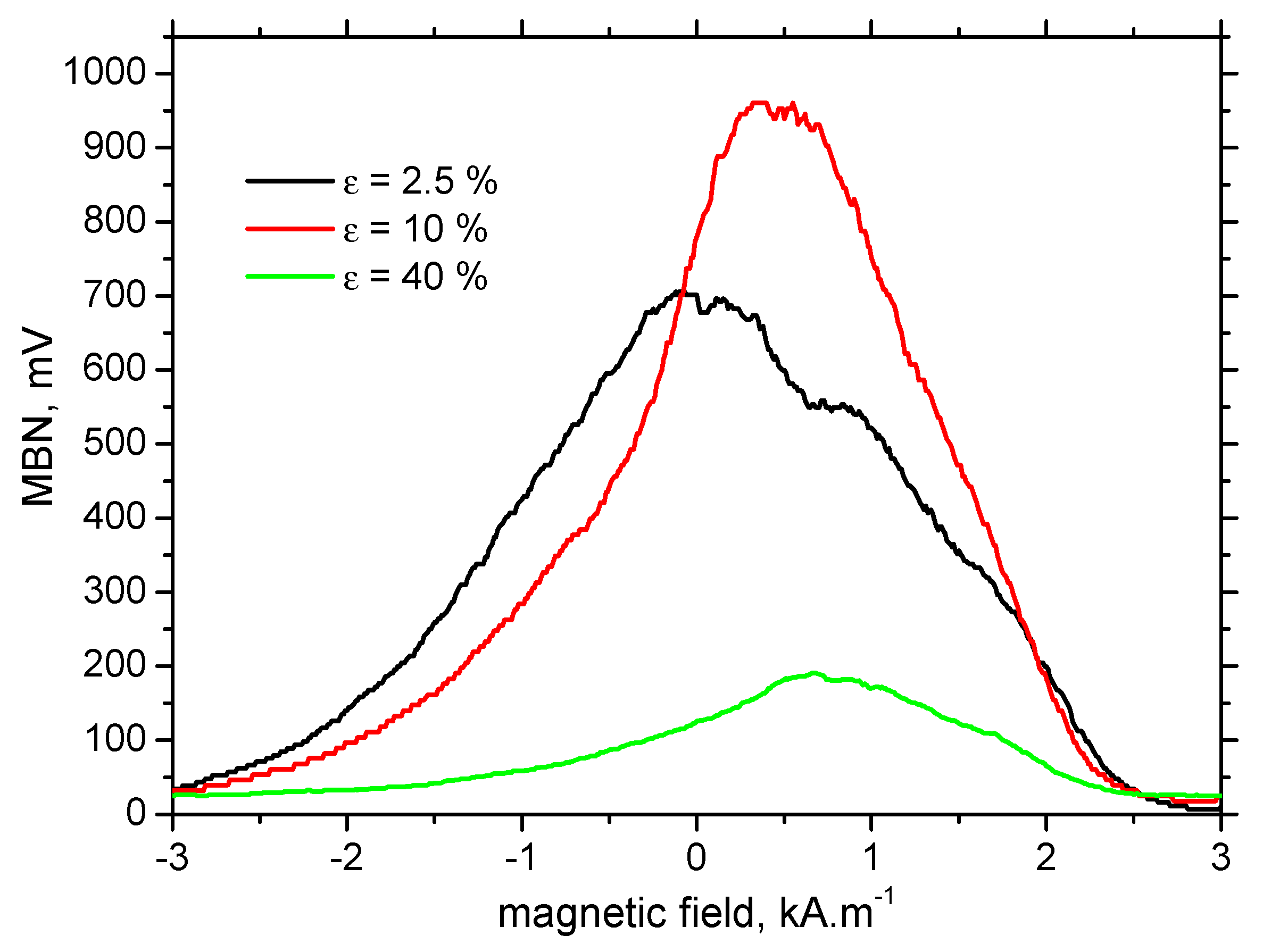
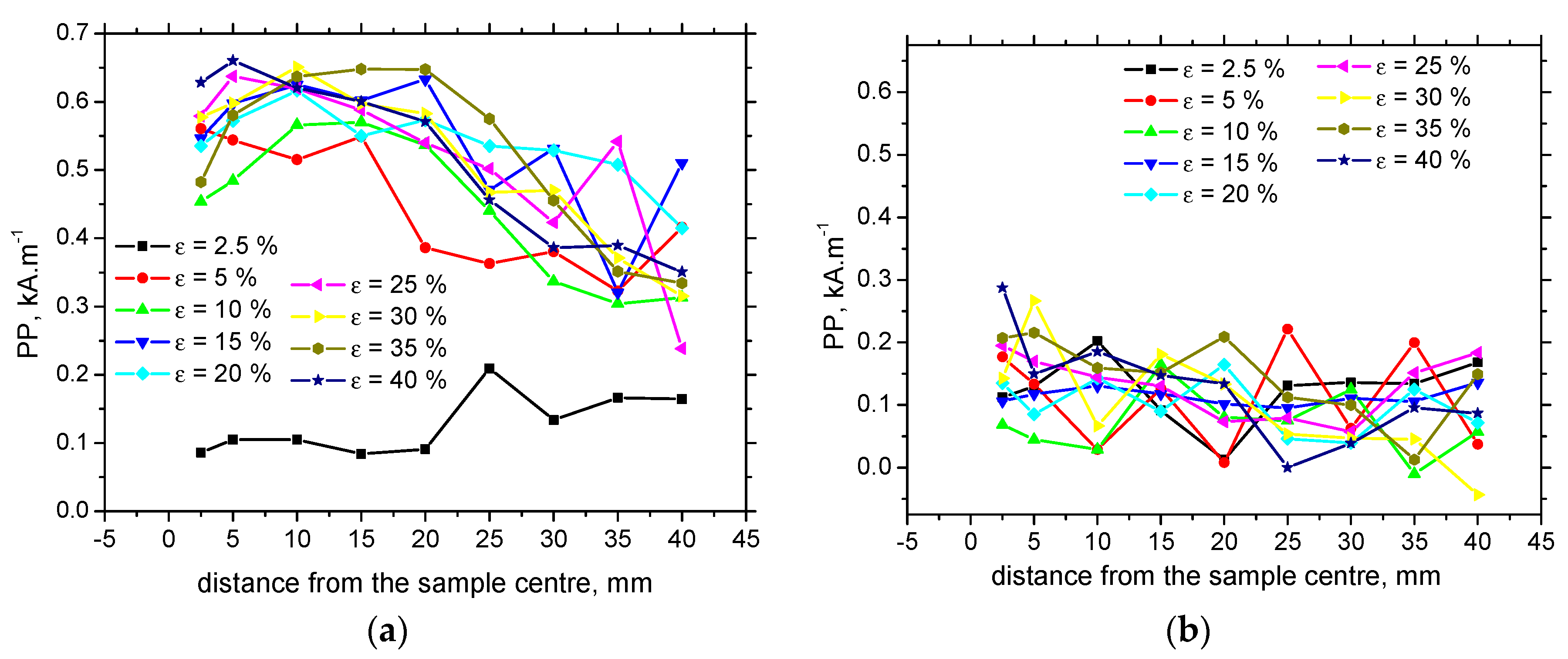
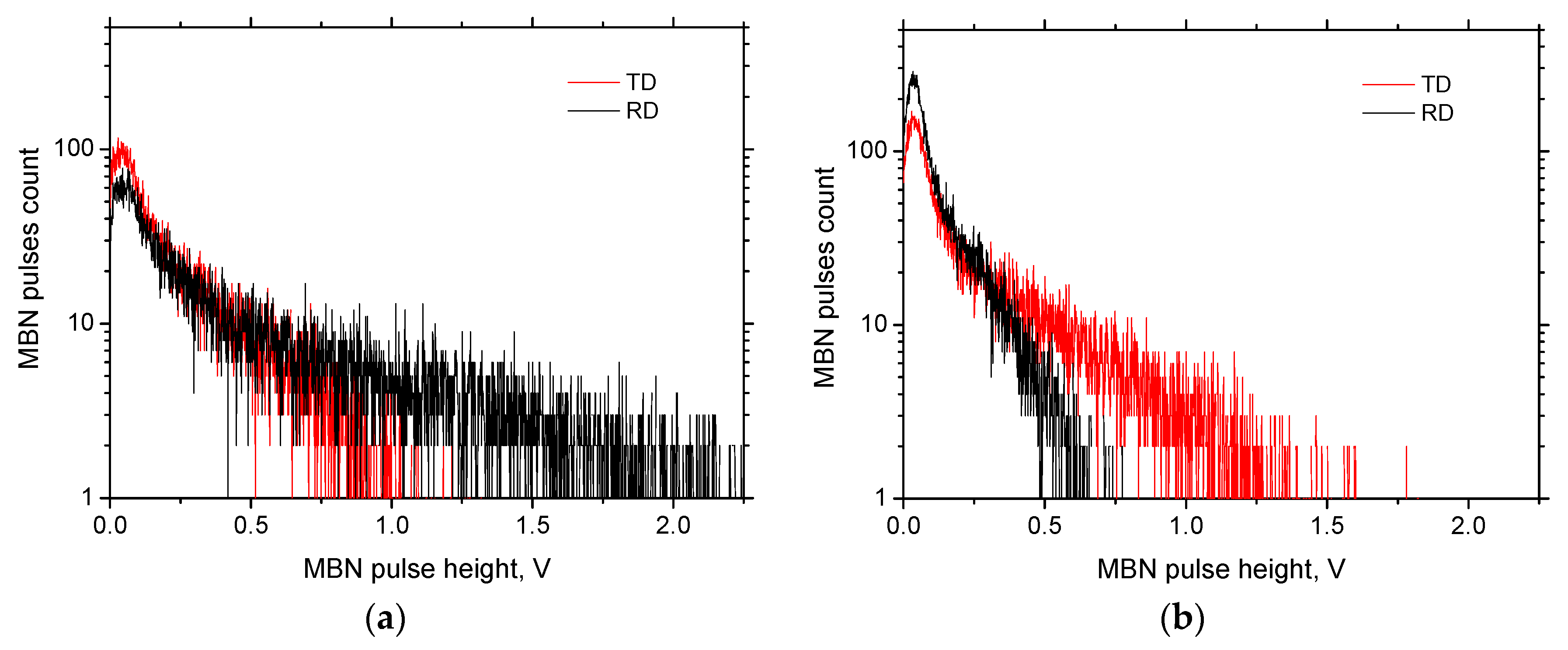
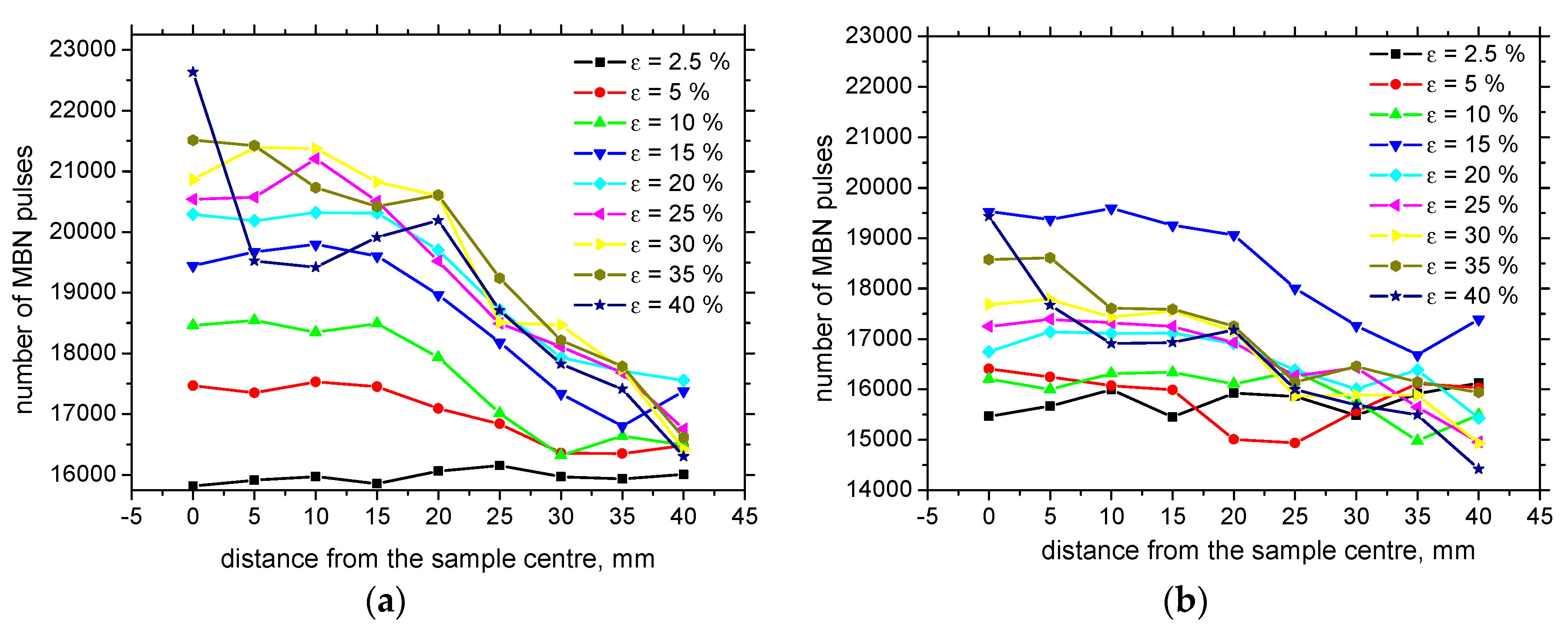
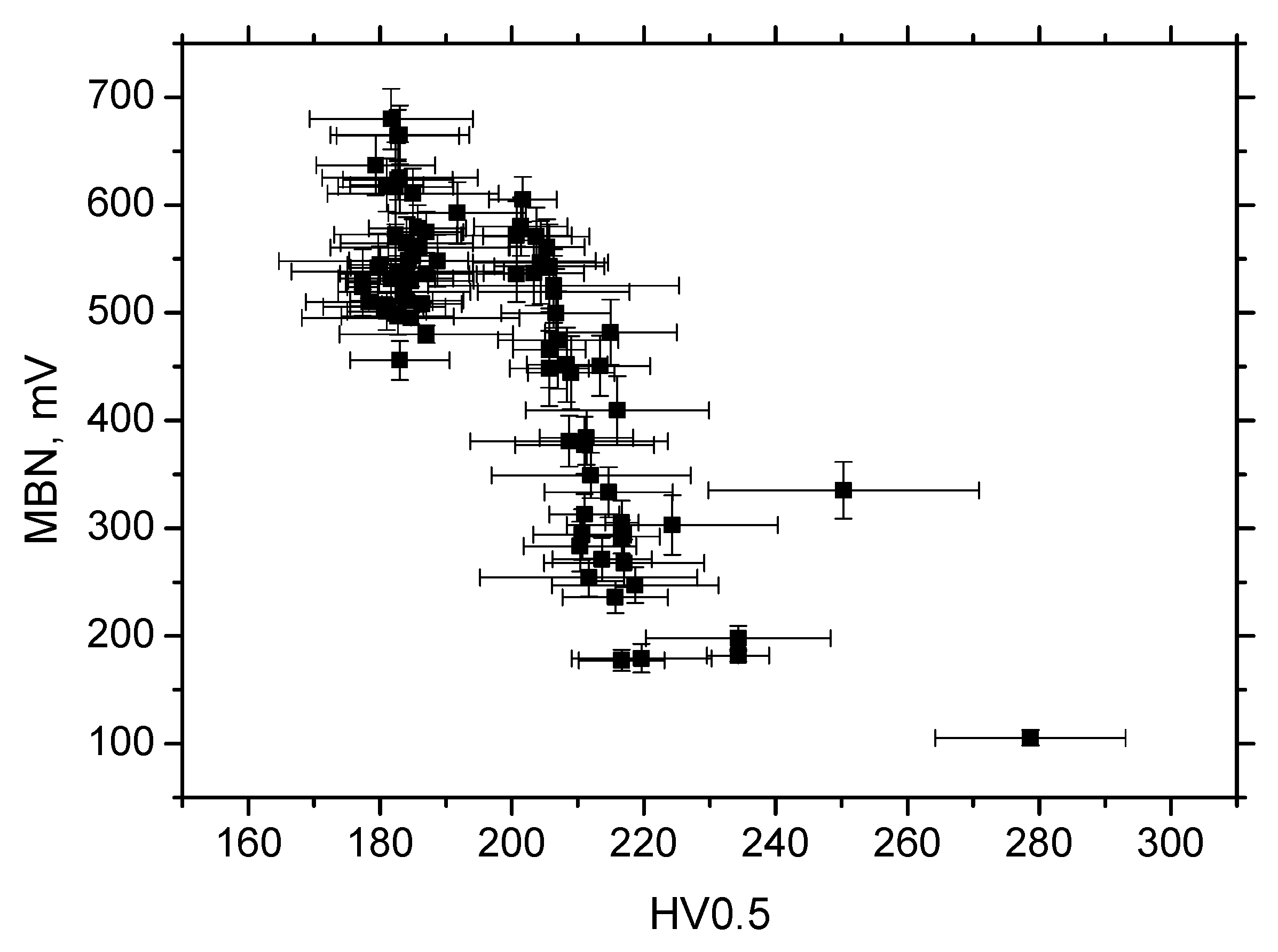
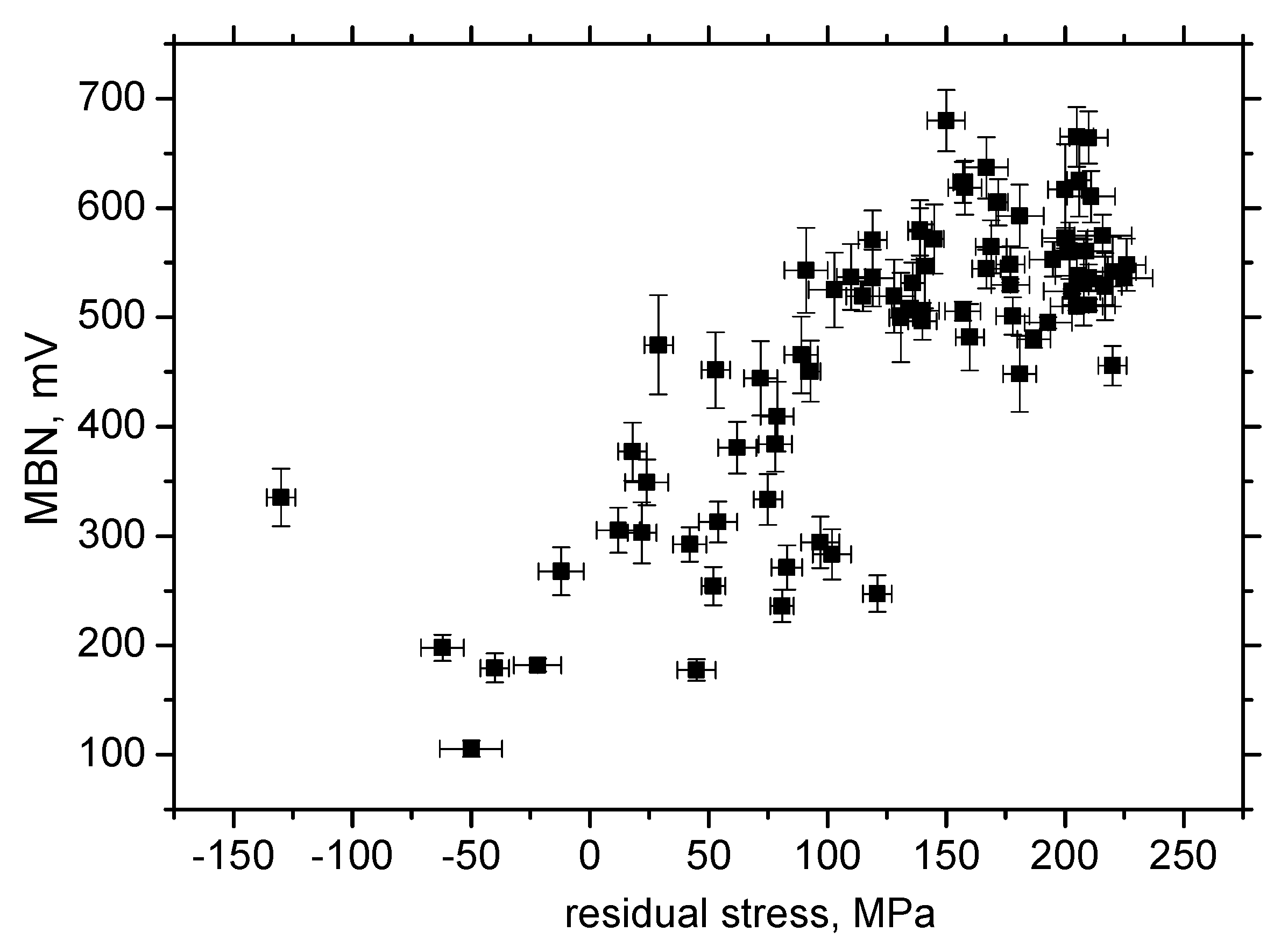
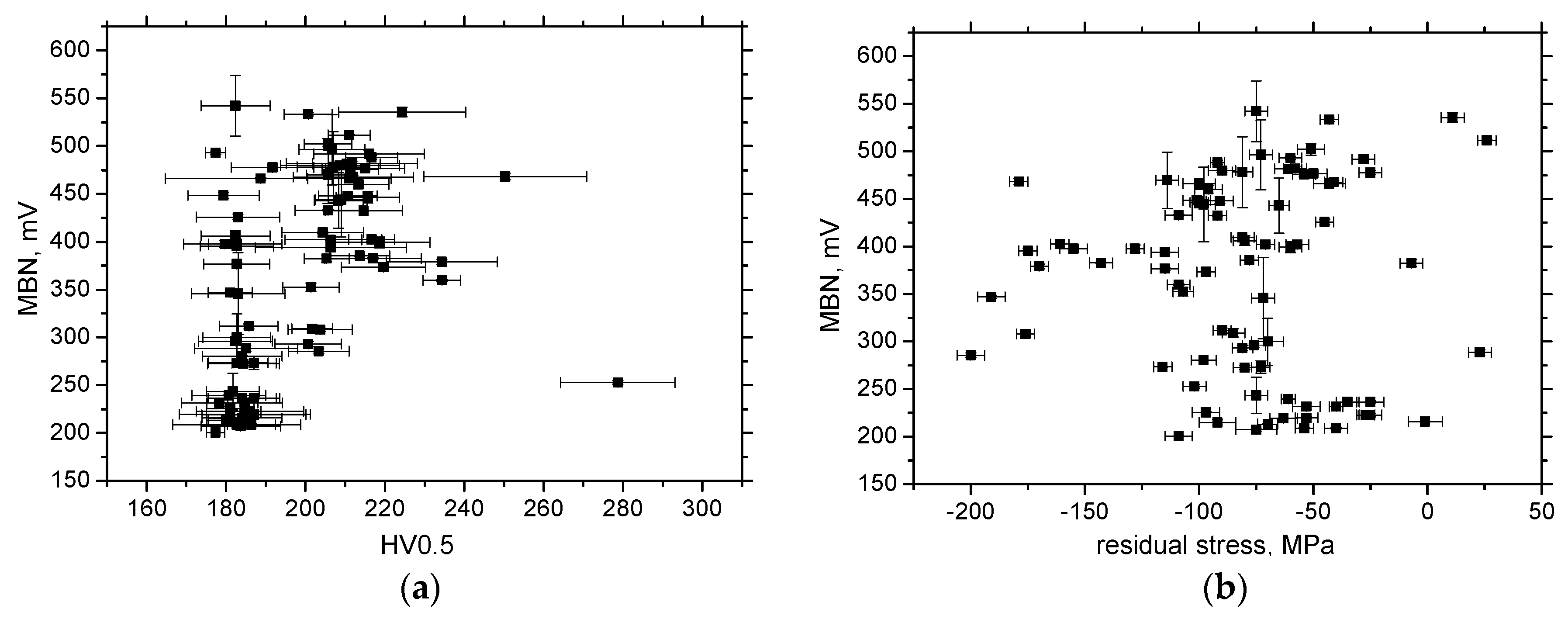
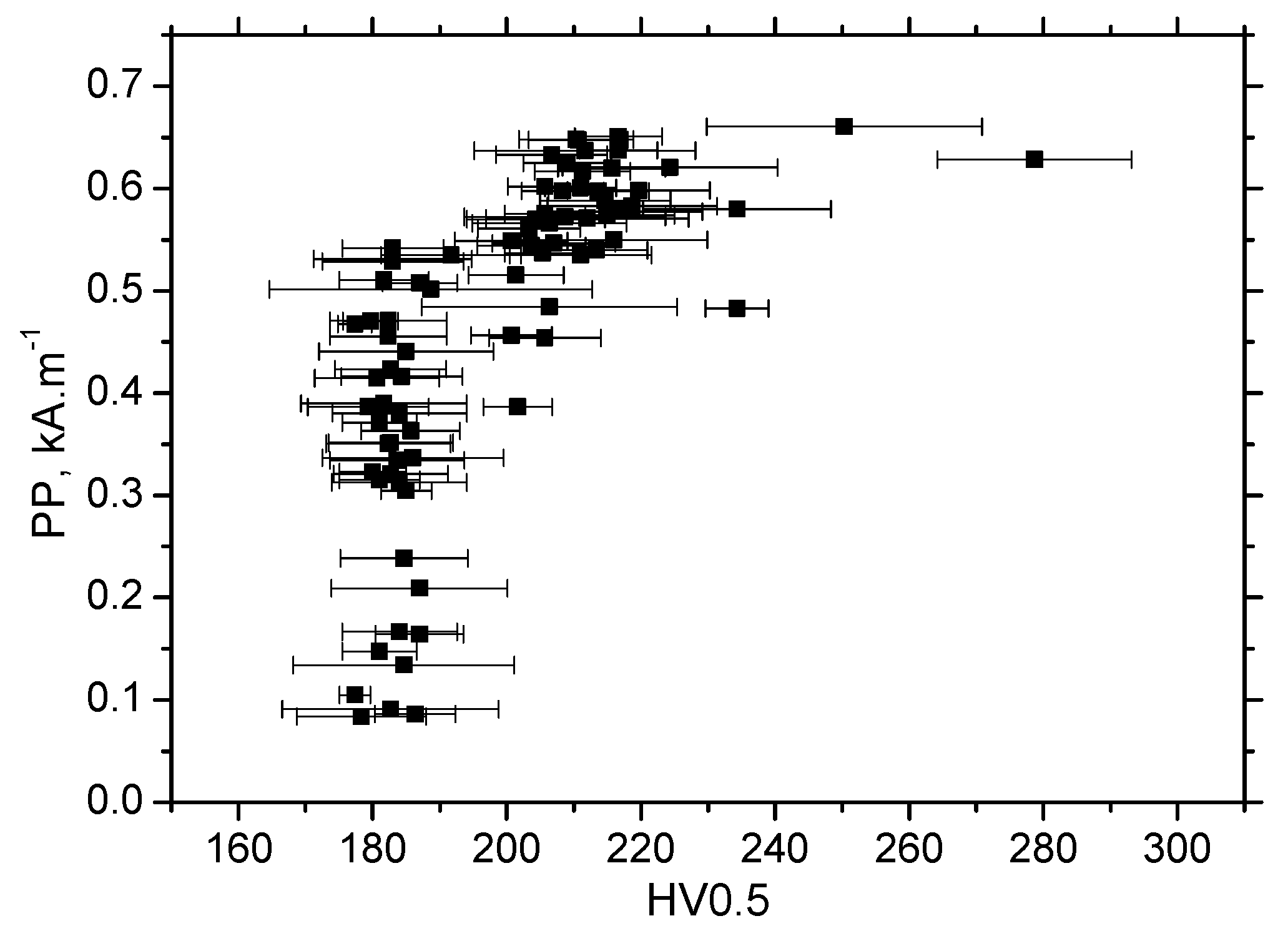
3.3. MBN Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Low MBN alerts incoming rupture of S235 steel;
- Distribution of MBN along the sample length is non-homogenous in the region of localized plastic strain, and the lowest MBN values can be found at the position of necking;
- A more or less homogenous distribution of MBN is typical for homogenous plastic strains;
- Due to the preferential elongation of the matrix during loading, the RD direction exhibits higher values as comparted with the TD; however, the easy axis of magnetization tends to turn into the TD for the higher ε;
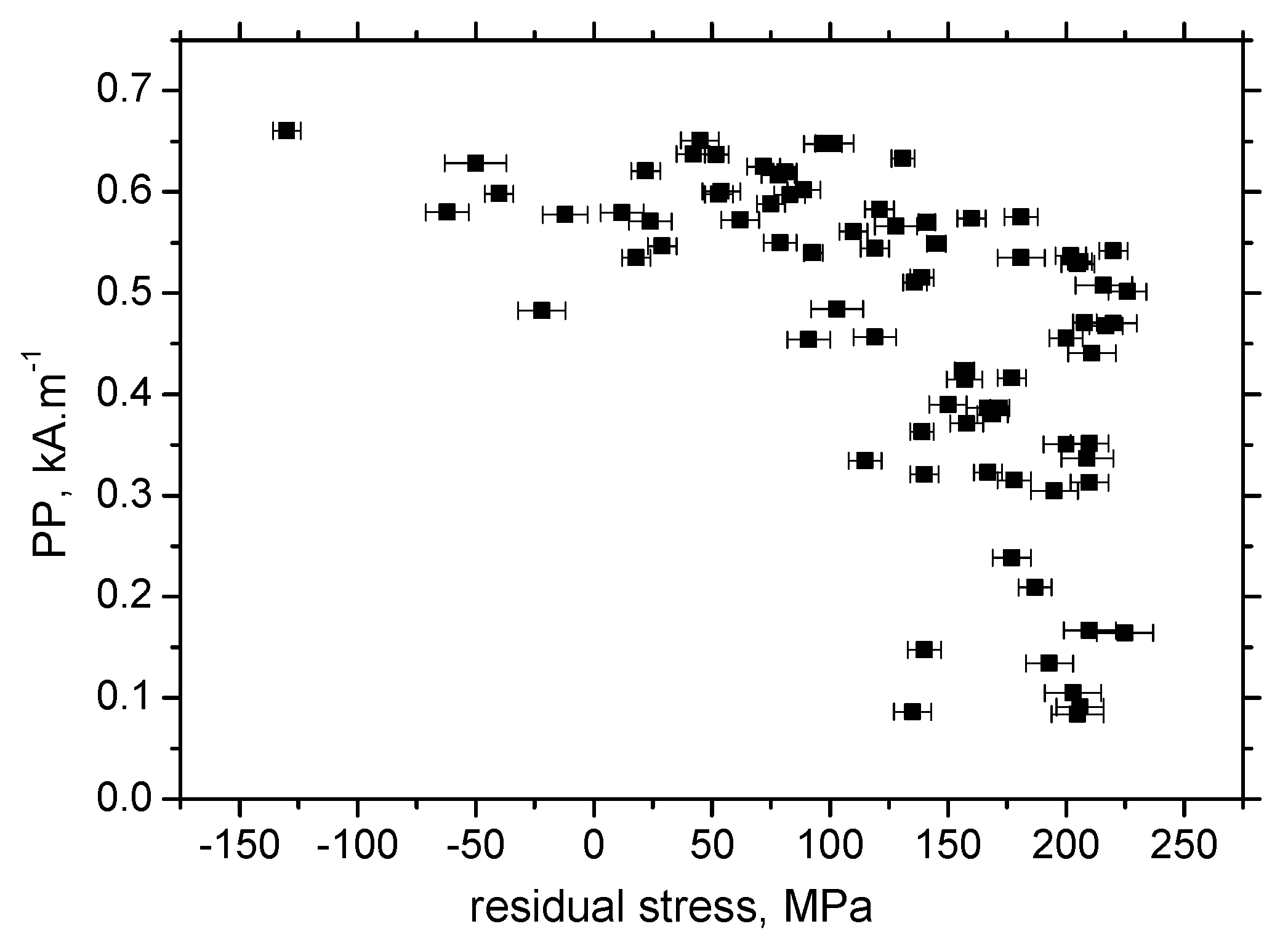
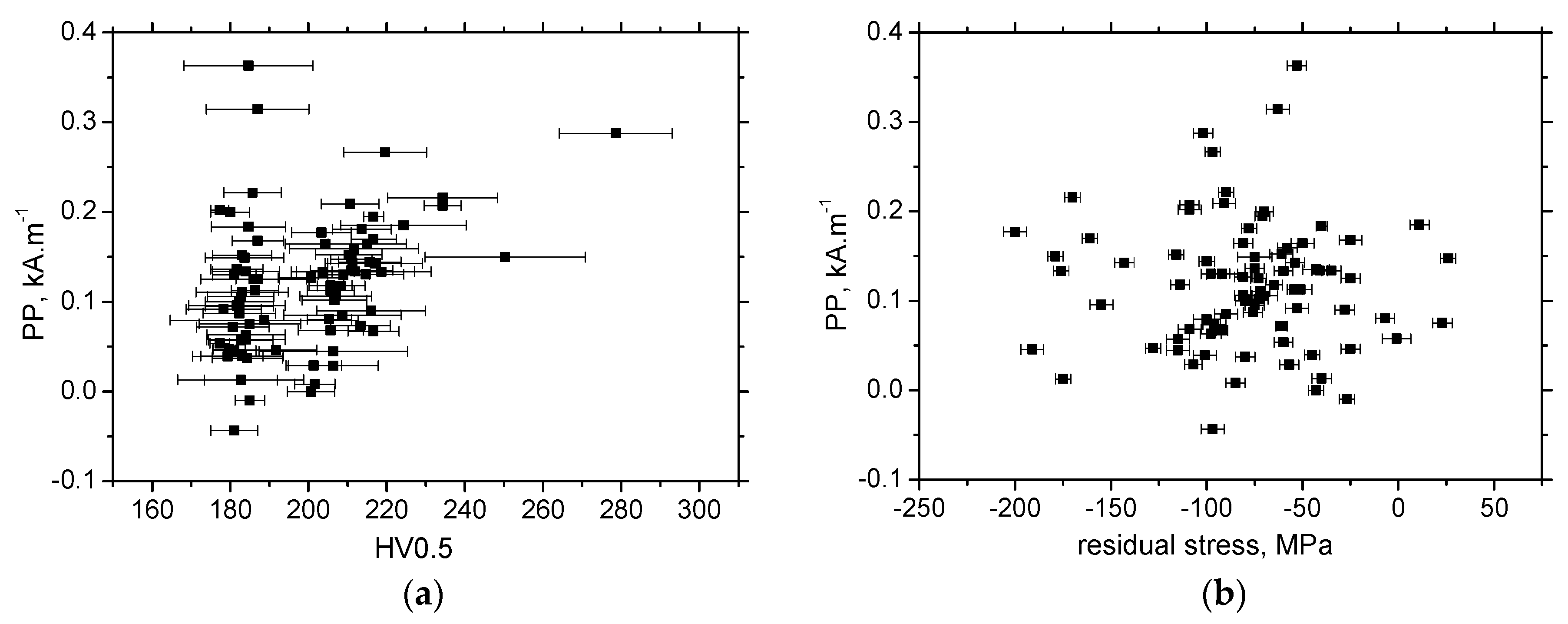
- MBN is a function of residual stresses as well as microhardness in the RD;
- Sensitivity of PP against developed ε is lower as compared with MBN, and the correlation of PP versus HV0.5, as well as residual stress, is weak.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Illes, L.; Kalina, T.; Jurkovic, M.; Luptak, V. Distributed Propulsion Systems for Shallow Draft Vessels. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, L.D.; Wang, H.; Mao, W.; Osawa, N.; Rychlik, I. Comparison of two statistical wave models for fatigue and fracture analysis of ship structures. Ocean Eng. 2019, 187, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Spencer, B.F. Fatigue life prediction for parallel-wire stay cables considering corrosion effects. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 114, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, W. Recommended hot-spot analysis procedure for structural details of ships and FPSOs based on round-robin FE analyses. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2002, 12, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.G.; Yamada, K. A method of determining geometric stress for fatigue strength evaluation of steel welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2004, 26, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Bahleda, F.; Minárik, P.; Zgútová, K.; Jambor, M. Non-destructive monitoring of corrosion extent in steel rope wires via Barkhausen noise emission. J. Magn. Mater. 2019, 484, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wharton, J.; Shenoi, J.A. Ultimate strength analysis of aged steel-plated structures exposed to marine corrosion damage: A review. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, R. Domain Walls and Their Dynamics, 1st ed.; Pavol Jozef Šafárik University: Košice, Slovakia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 3rd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Tian, G.Y.; Gao, B.; Zeng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J. Micro-macro characteristics between domain wall motion and magnetic Barkhausen noise under tensile stress. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, V.; Shaw, B.A.; Mountford, P.; Hopkins, P. Magnetic Barkhausen noise emission technique for evaluation of residual stress alteration by grinding in case-carburized En36 steel. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4997–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorsa, A.; Santa-Aho, S.; Wartiainen, J.; Souminen, L.; Vippola, M.; Leviskä, K. Effect of shot peening parameters to residual stress profiles and Barkhausen noise. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2018, 37, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, X.; Vincent, A. On the role of residual internal stresses and dislocations on Barkhausen noise in plastically deformed steel. NDTE Int. 2004, 37, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, S.; Gür, C.H.; Alexandrov, I.V.; Abramova, M.M. Characterization of ultra-fine grained steel samples produced by high pressure torsion via magnetic Barkhausen noise analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatelier-Rothea, C.; Chicois, J.; Fougeres, R.; Fleischmann, P. Characterization of pure iron and (130 p.p.m.) carbon-iron binary alloy by Barkhausen noise measurements: Study of the influence of stress and microstructure. Acta Metal. 1998, 46, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Čížek, J.; Kolařík, K.; Minárik, P.; Čilliková, M.; Melikhová, O. Monitoring of grinding burn via Barkhausen noise emission in case-hardened steel in large-bearing production. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 240, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktena, A.; Hristoforou, E.; Gerhardt, G.J.L.; Missell, F.P.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Rodrigues, D.L.; Albertis-Campos, M. Barkhausen noise as a microstructure characterization tool. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 2014, 435, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Jurkovič, M.; Kalina, T.; Pitoňák, M.; Zgútová, K. Monitoring of S235 steel over-stressing by the use of Barkhausen noise technique. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupakov, A.; Perevertov, A.; Neslušan, M. Reading depth of the magnetic Barkhausen noise. I. One phase semi-hard ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupakov, A.; Perevertov, A.; Neslušan, M. Reading depth of the magnetic Barkhausen noise. II. Two-phase surface-treated steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuschewski, B.; Bleicher, O.; Beutner, M. Surface integrity inspection on gears using Barkhausen noise analysis. Proc. Eng. 2011, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S. Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Čížek, J.; Neslušan, M.; Čilliková, M.; Mičietová, A.; Melikhova, O. Modification of steel surfaces induced by turning: Non-destructive characterization using Barkhausen noise and positron annihilation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 445301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neslušan, M.; Trško, L.; Minárik, P.; Čapek, J.; Bronček, J.; Pastorek, F.; Čížek, J.; Moravec, J. Non-destructive evaluation of steel surface after severe plastic deformation via Barkhausen noise technique. Metals 2018, 8, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feaugas, X. On the origin of the tensile flow stress in the stainless steel AISI 316 L at 300 K: Back stress and effective stress. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 3617–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorth, R.M. Ferromagnetism, 3rd ed.; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Néel, L. Principles of a new general theory of the coercive field. Ann. Univ. Grenoble 1946, 22, 299–343. [Google Scholar]

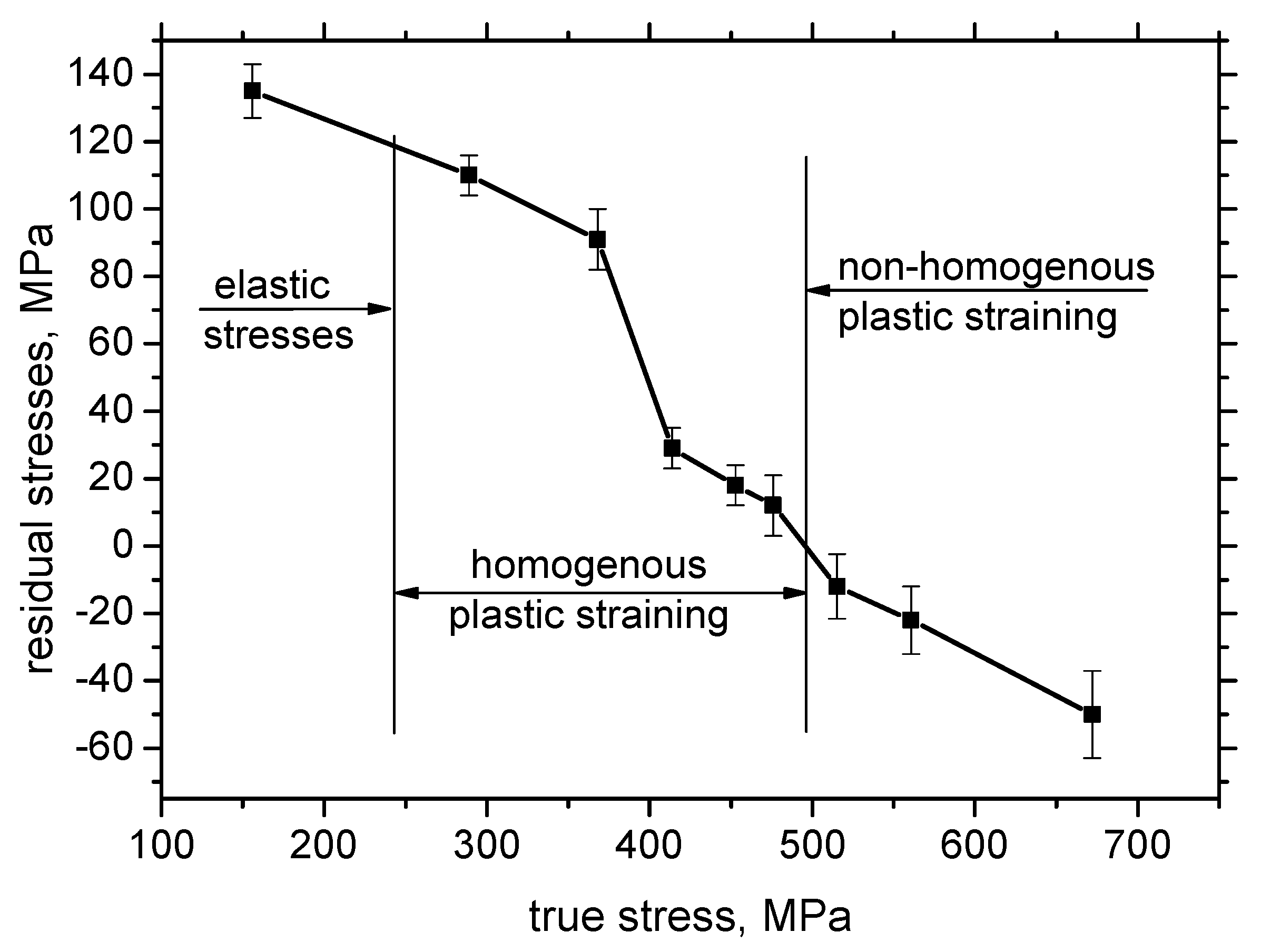
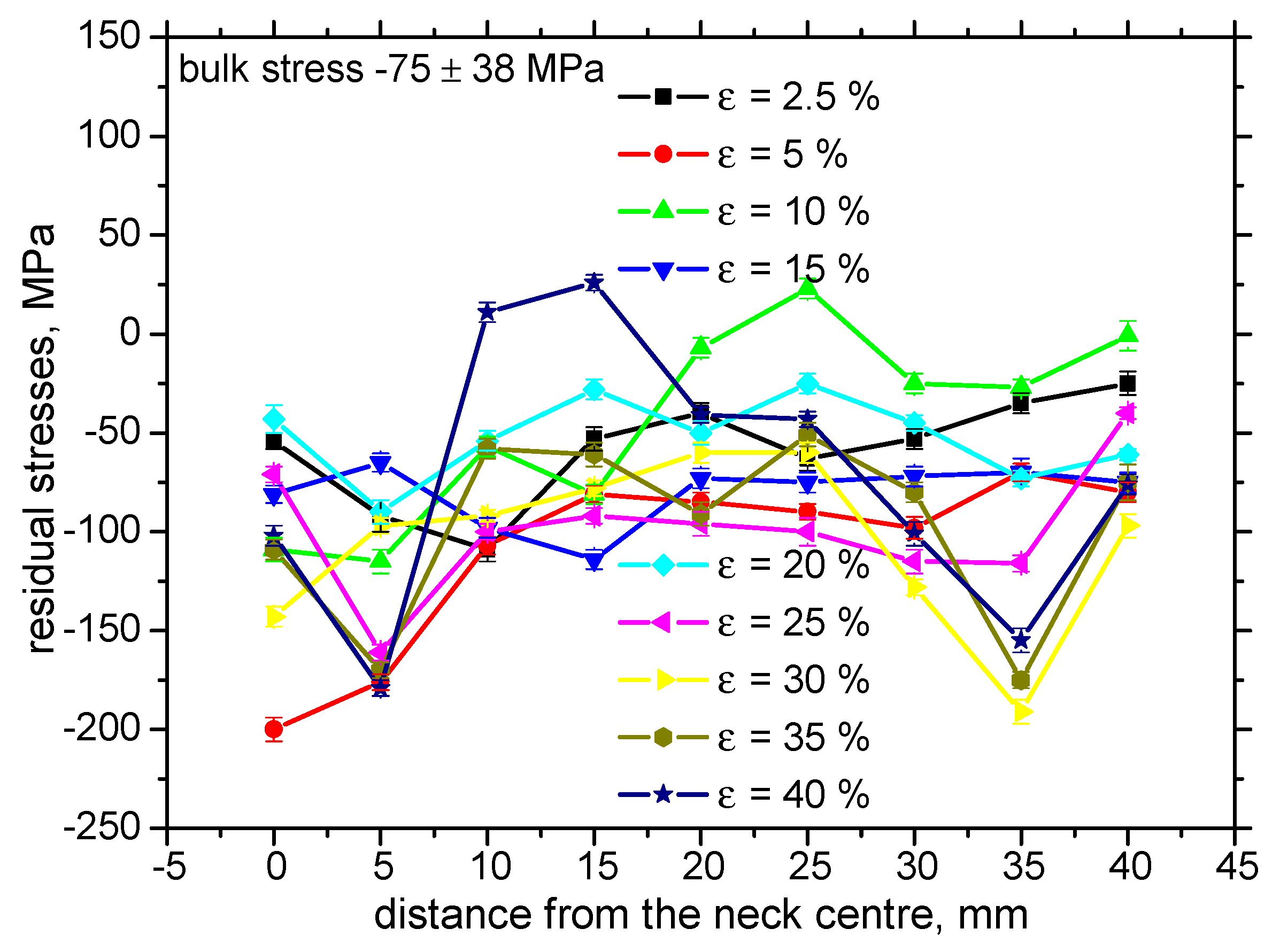
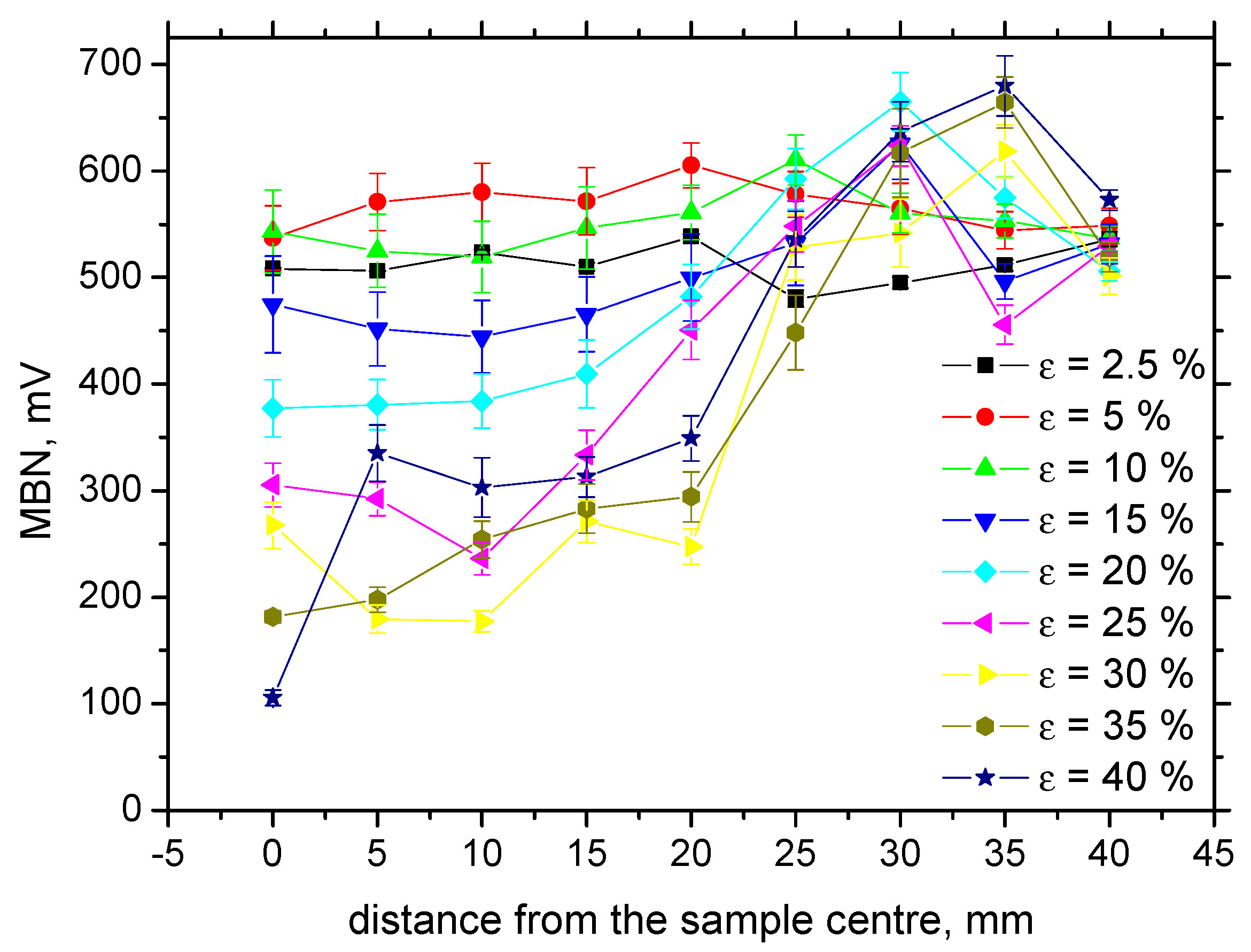
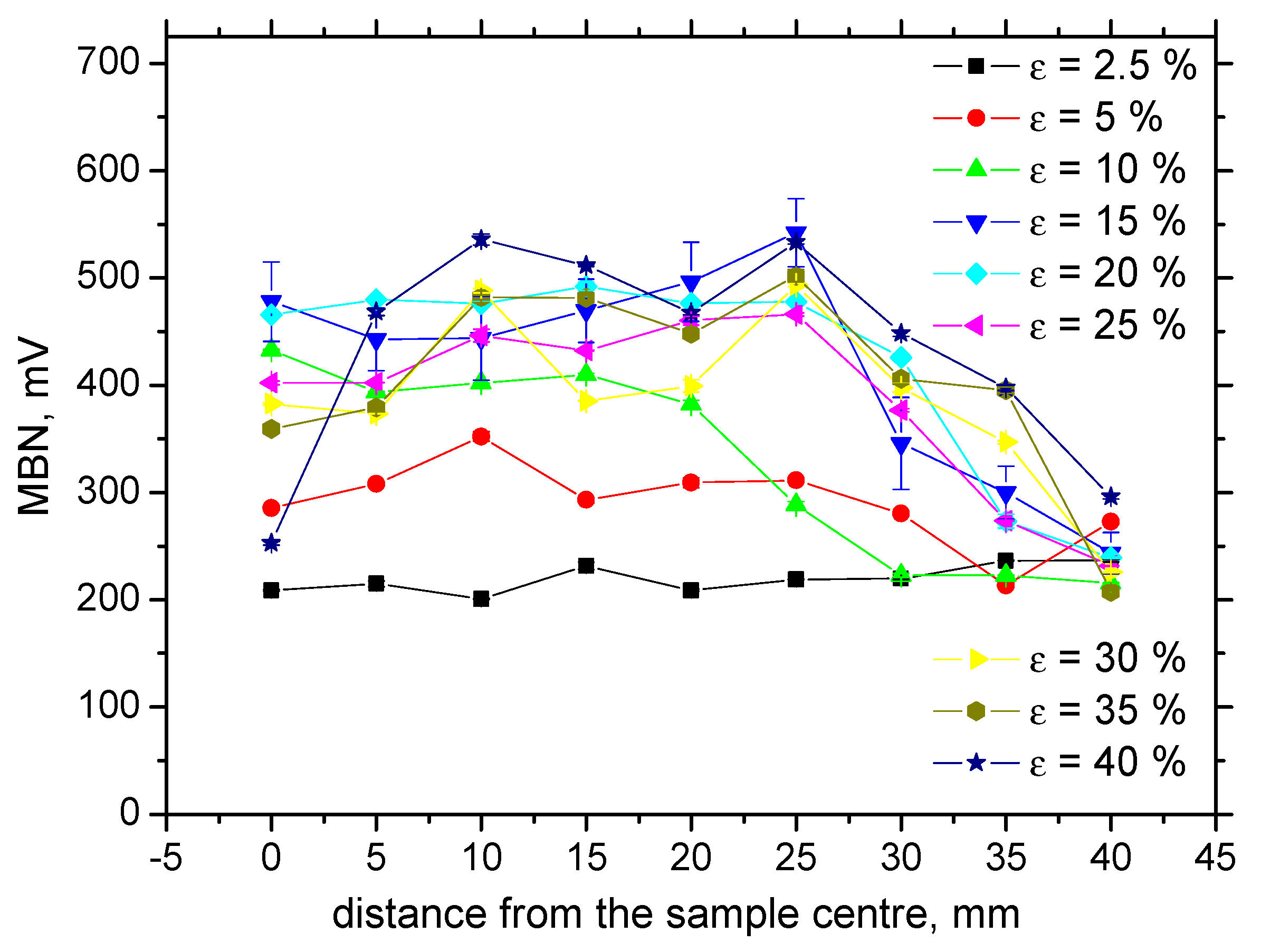
| Fe | C | Mn | Si | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| balance | 0.22 | 1.6 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Parameter | Elastic Deformation | Plastic Deformations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homogenous Plastic Straining | Non-Homogenous (Localized) Plastic Straining—Necking | ||||||||
| ε, % | 2.5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| T, mm | 7.84 | 7.78 | 7.65 | 7.48 | 7.30 | 7.13 | 6.84 | 6.45 | 5.66 |
| W, mm | 12.41 | 12.30 | 12.06 | 11.84 | 11.44 | 11.31 | 10.81 | 10.27 | 8.96 |
| L, mm | 49.80 | 50.40 | 52.00 | 53.80 | 56.03 | 57.93 | 59.67 | 61.38 | 63.61 |
| σ, MPa | 156 | 284 | 349 | 376 | 388 | 392 | 391 | 381 | 350 |
| σtrue, MPa | 156 | 289 | 368 | 413 | 452 | 475 | 515 | 560 | 672 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurkovič, M.; Kalina, T.; Zgútová, K.; Neslušan, M.; Pitoňák, M. Analysis of Magnetic Anisotropy and Non-Homogeneity of S235 Ship Structure Steel after Plastic Straining by the Use of Barkhausen Noise. Materials 2020, 13, 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204588
Jurkovič M, Kalina T, Zgútová K, Neslušan M, Pitoňák M. Analysis of Magnetic Anisotropy and Non-Homogeneity of S235 Ship Structure Steel after Plastic Straining by the Use of Barkhausen Noise. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204588
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurkovič, Martin, Tomáš Kalina, Katarína Zgútová, Miroslav Neslušan, and Martin Pitoňák. 2020. "Analysis of Magnetic Anisotropy and Non-Homogeneity of S235 Ship Structure Steel after Plastic Straining by the Use of Barkhausen Noise" Materials 13, no. 20: 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204588
APA StyleJurkovič, M., Kalina, T., Zgútová, K., Neslušan, M., & Pitoňák, M. (2020). Analysis of Magnetic Anisotropy and Non-Homogeneity of S235 Ship Structure Steel after Plastic Straining by the Use of Barkhausen Noise. Materials, 13(20), 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204588







