Fabrication, Structure and Mechanical and Ultrasonic Properties of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloys Part I: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloys Suitable for Ultrasonic Scalpel
Abstract
1. Introduction
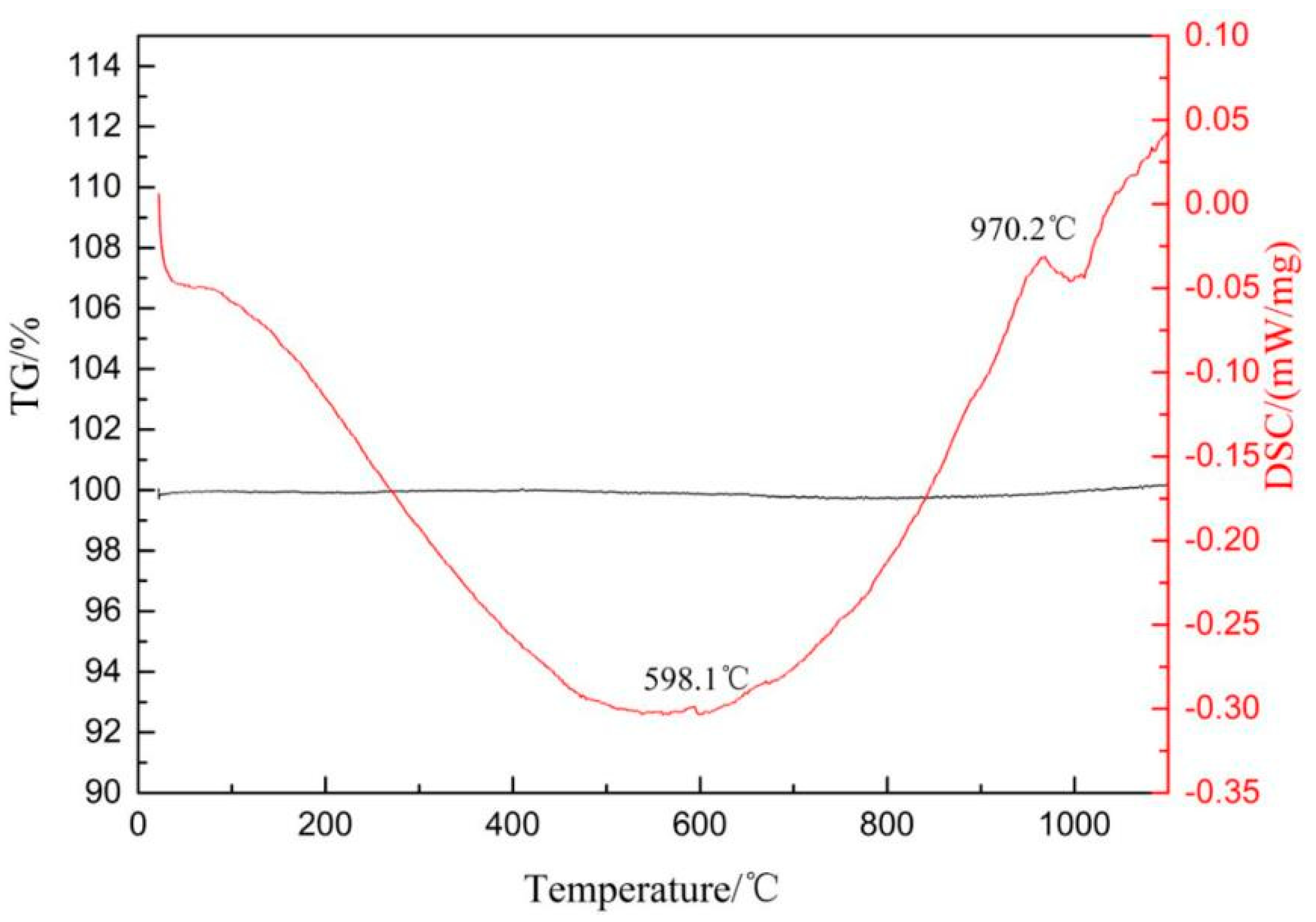
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
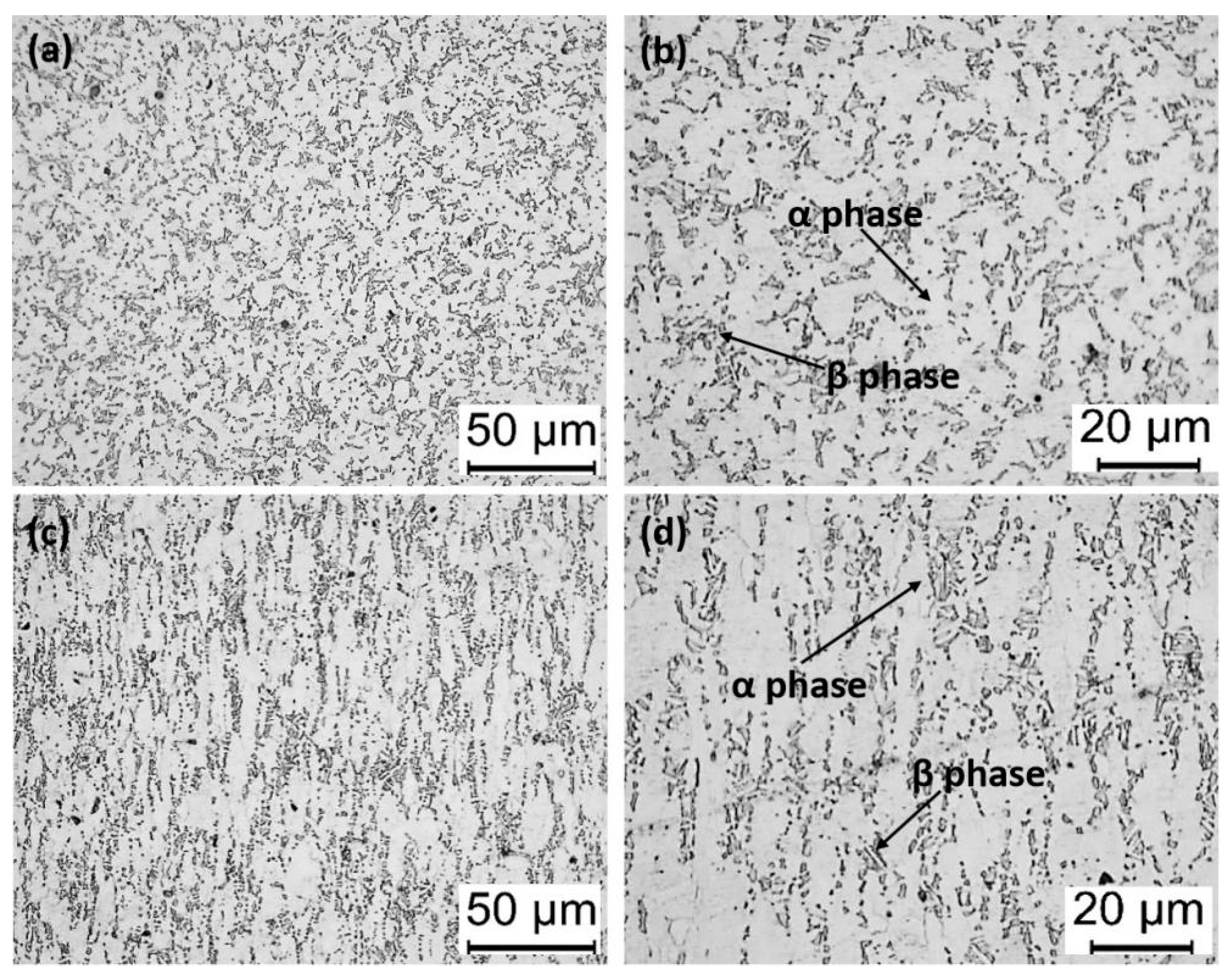
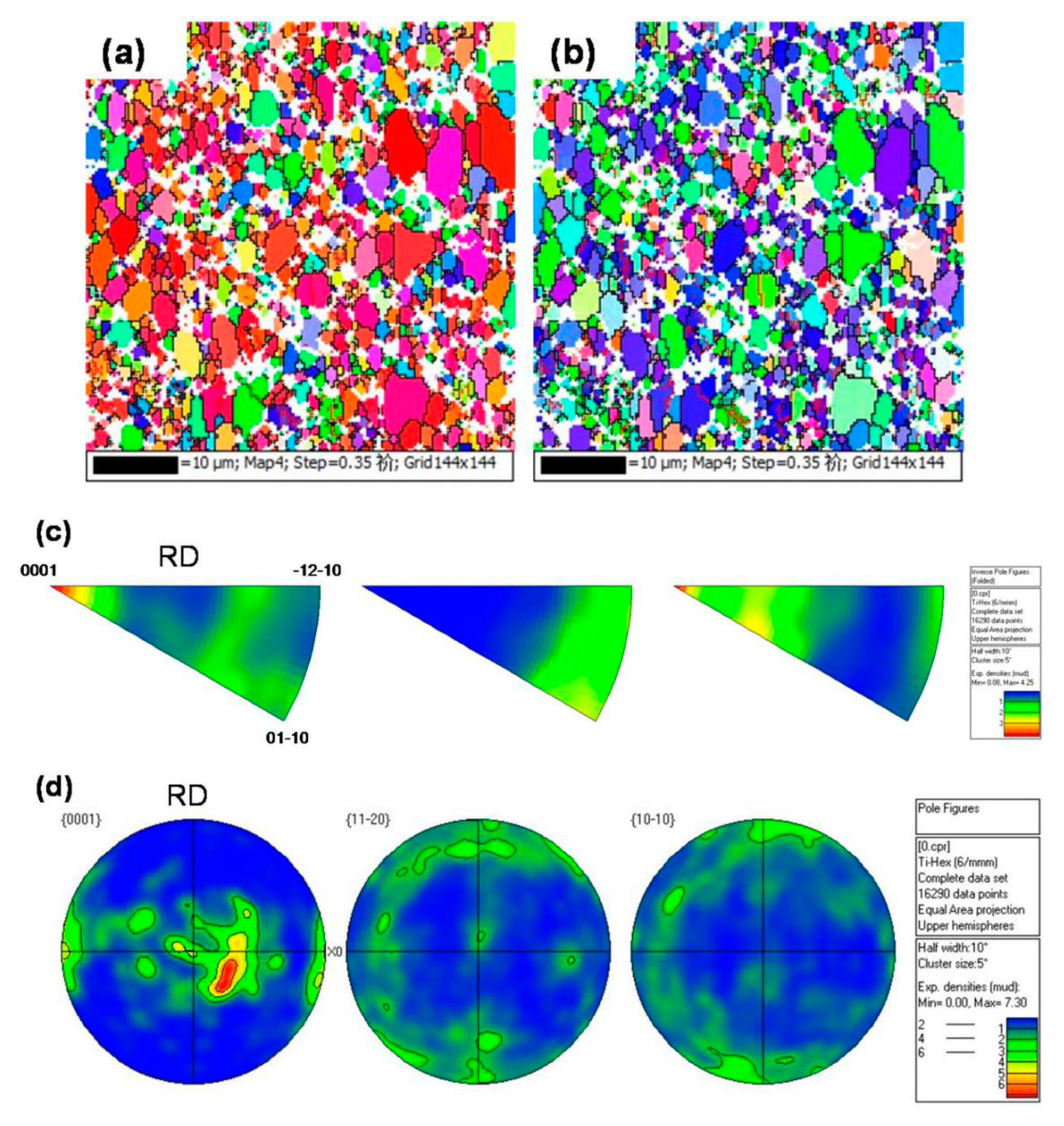
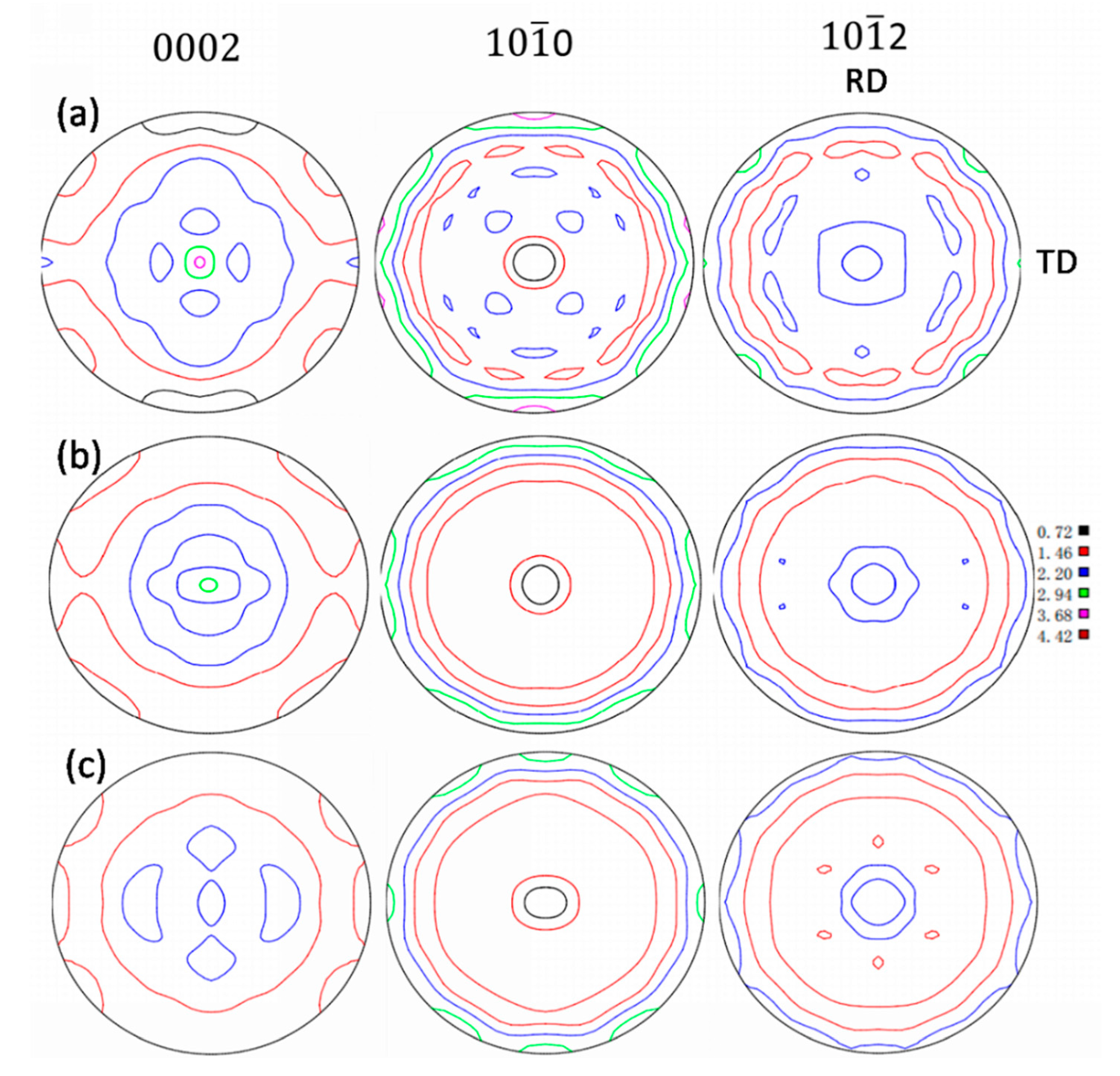
3.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties after Solution Treatment
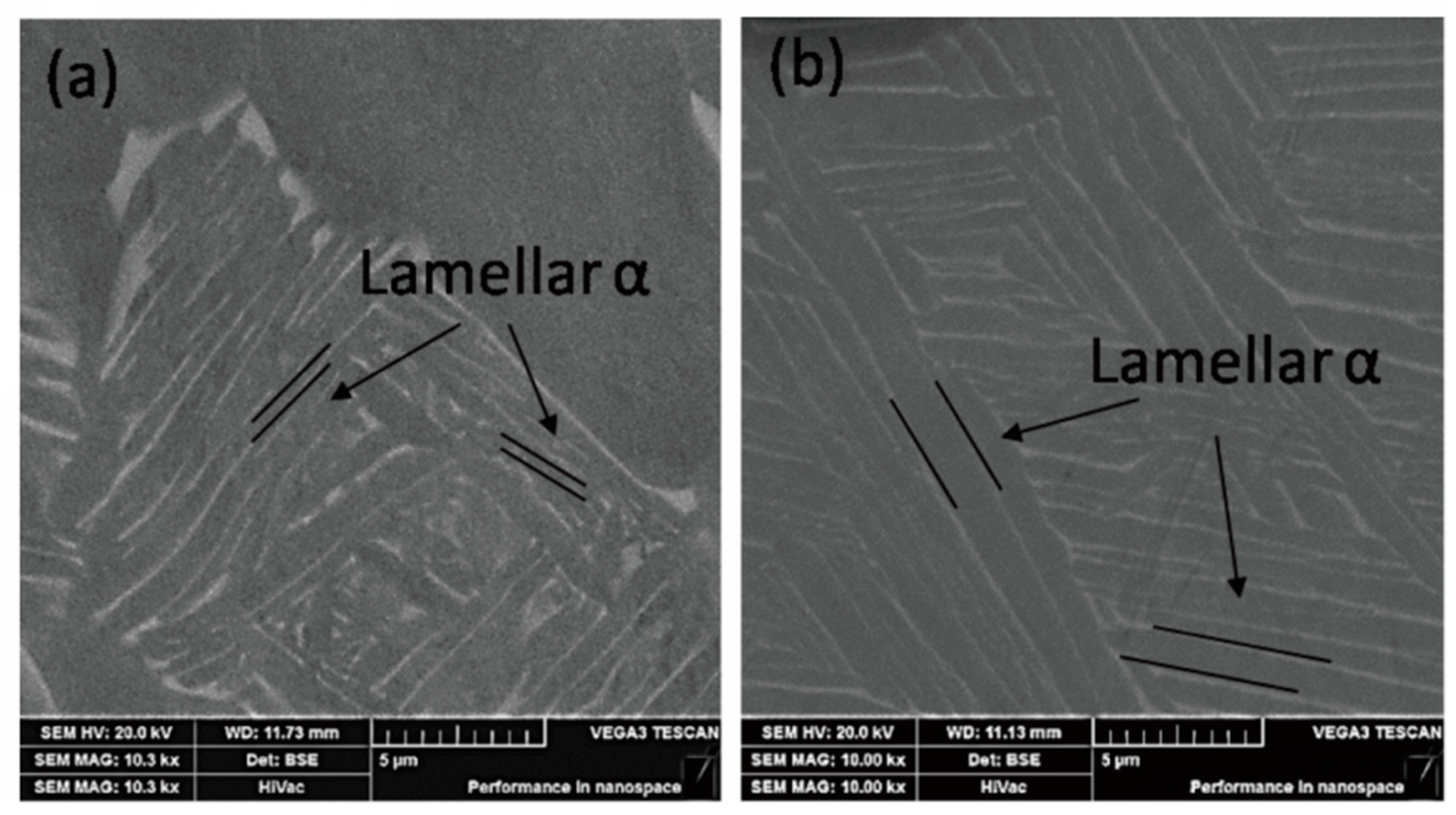
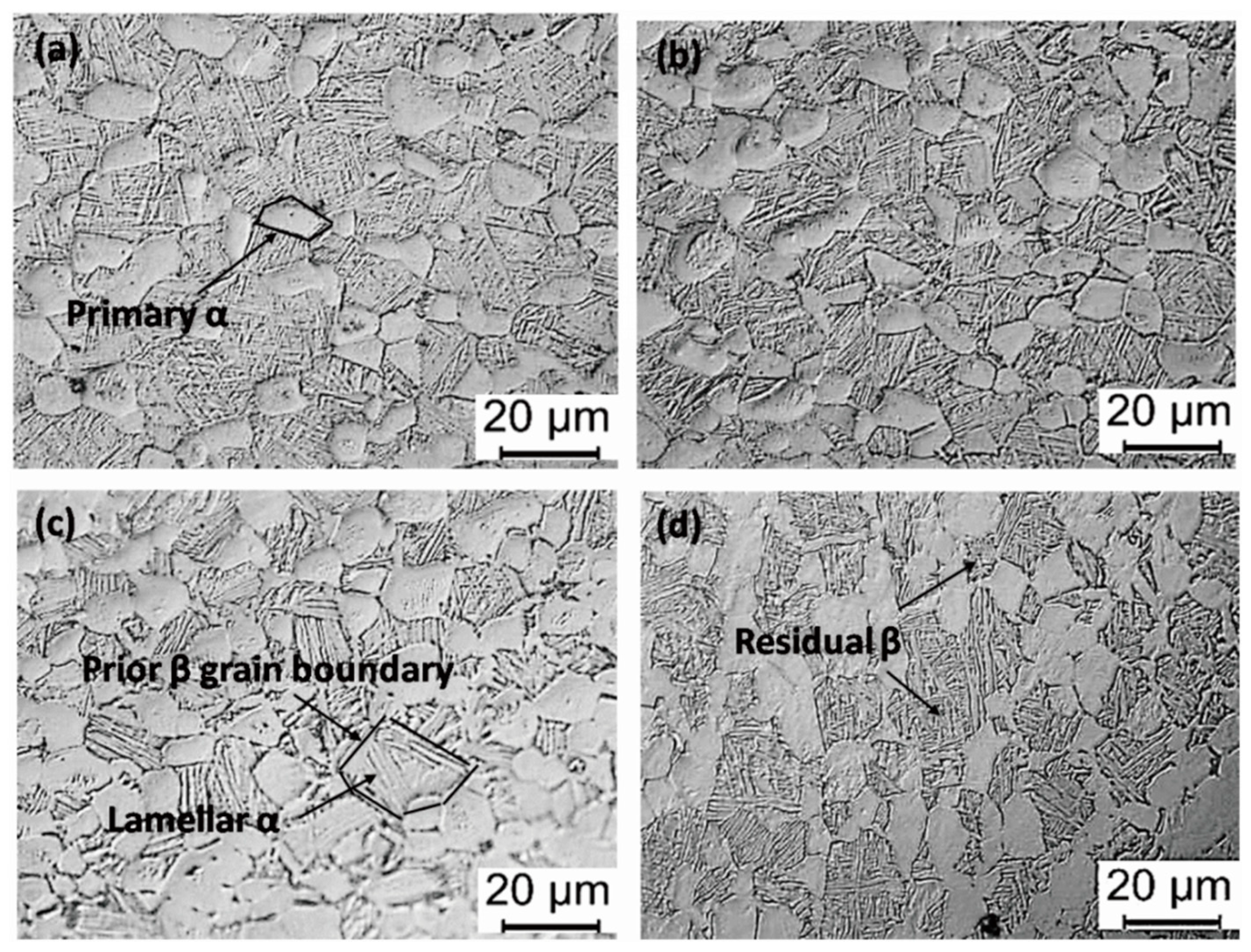
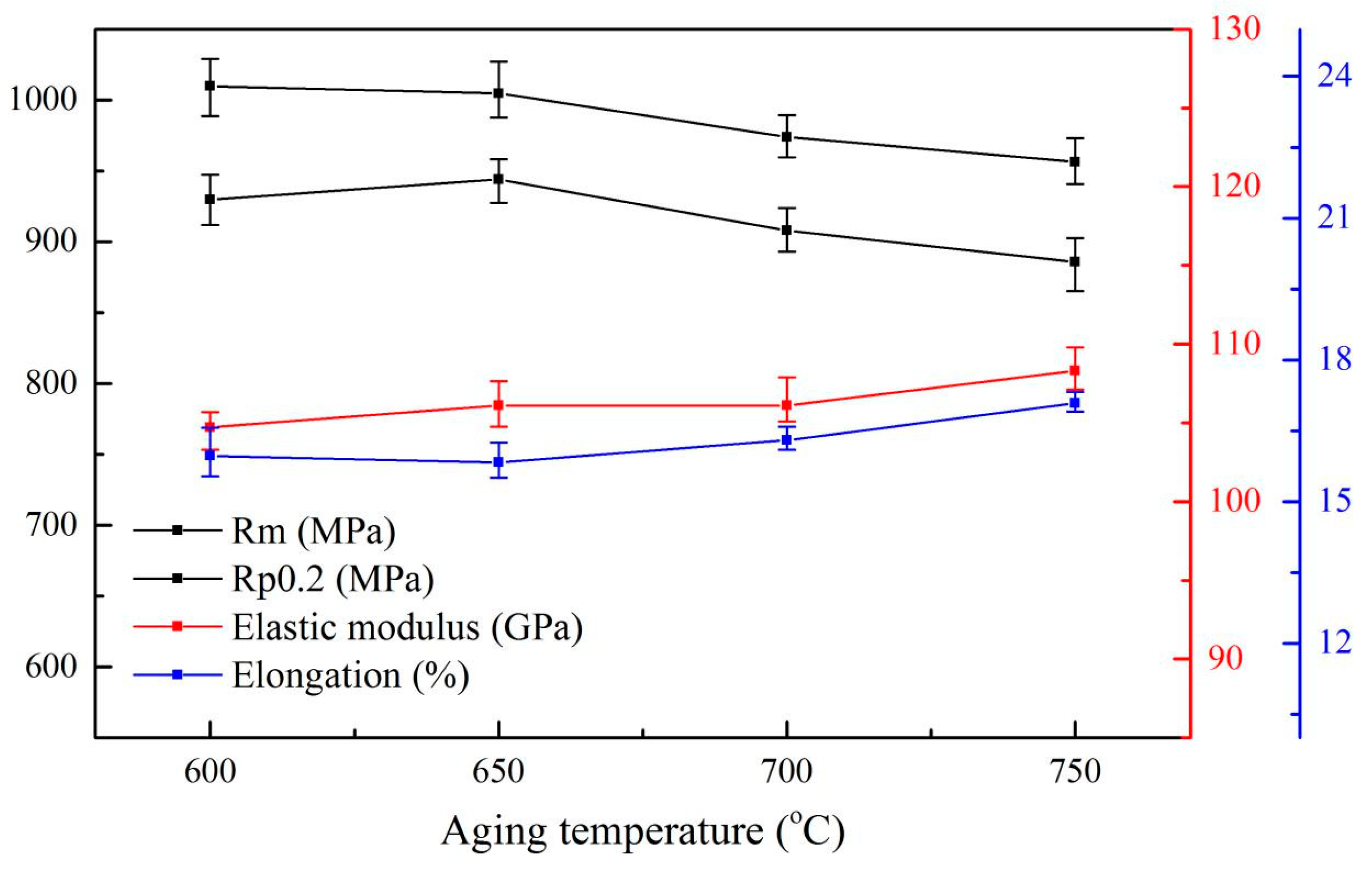
3.2. Microstructure and its Mechanical Properties after Aging Treatment
4. Conclusions
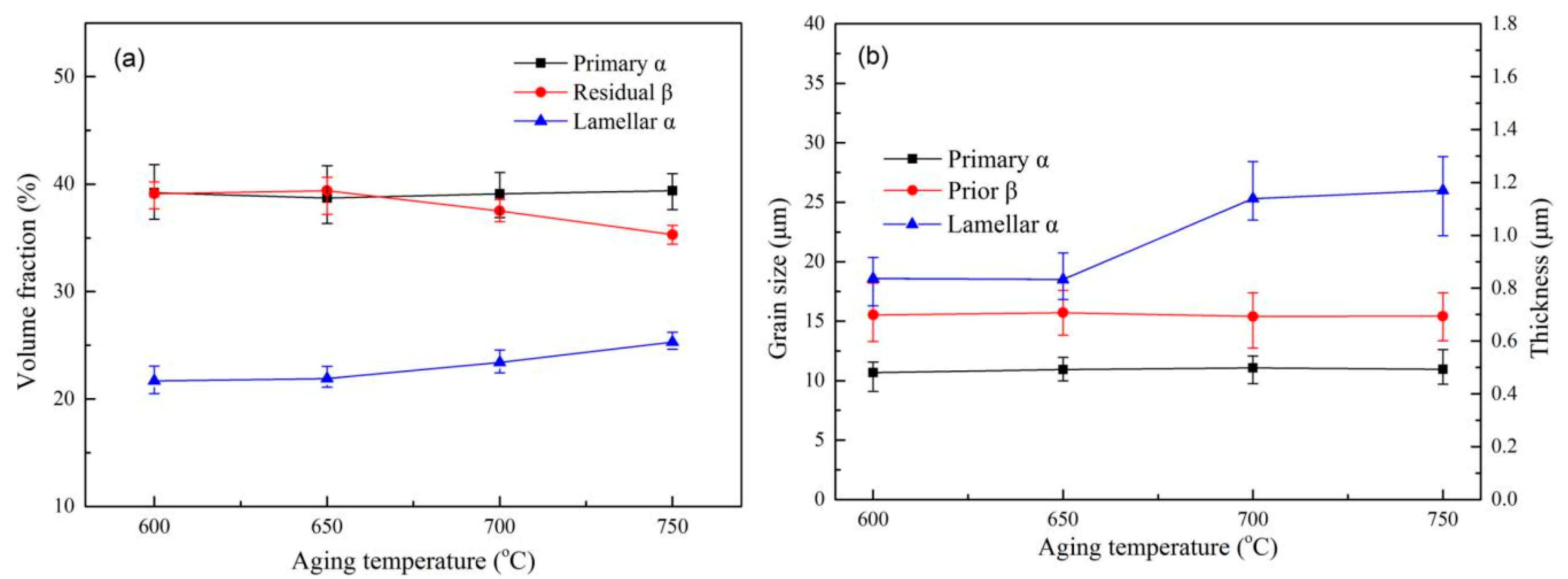
- The content and size of the primary α phase of the Ti6Al4V alloy decrease with an increase in solid solution temperature. The lamellar α phase exhibited the opposite trend, i.e., the β phase content first increases and then decreases. The increase in the aging temperature has little effect on the content and size of the primary α phase but causes a slight increase in the thickness of the lamellar α phase.
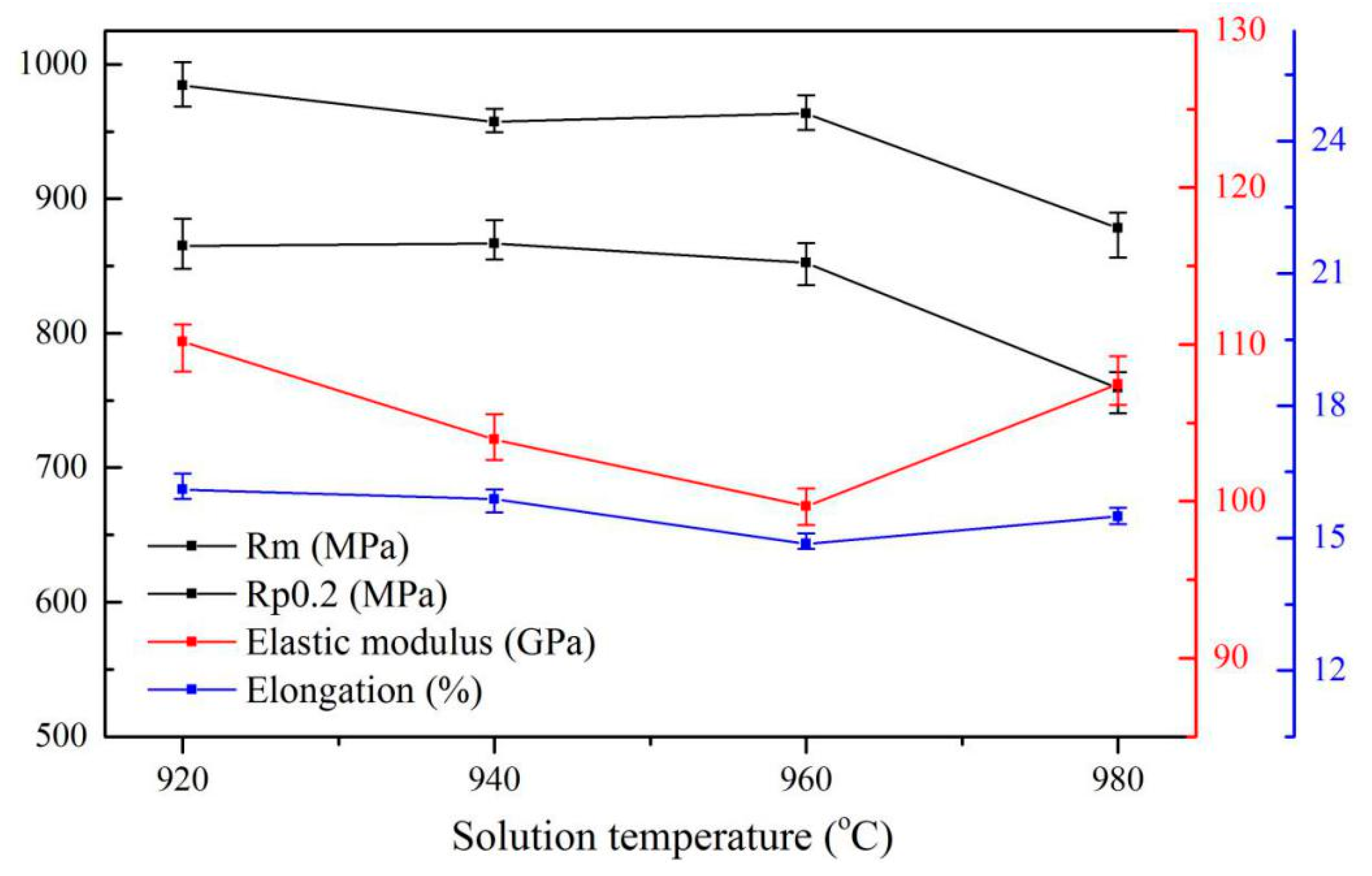
- For the solution and aging-treated Ti6Al4V alloys, the main factor affecting the tensile strength is lamellar α. As the solid solution temperature increases from 960 °C to 980 °C, the average thickness of lamellar α increased by 1.09 µm, and the average yield strength decreased by 93 MPa. As aging temperature increases from 600 °C to 750 °C, the thickness of lamellar α slightly increases by 0.33 µm and causes the yield strength of the specimens remained at about 900 MPa.
- The elastic modulus of the Ti6Al4V alloy is mainly controlled by the texture of the α phase and content of the β phase. However, the β phase content is the main factor affecting the elastic modulus of the alloys treated by solution and aging treatment. Specifically, the specimen’s solid solution treated at 960 °C has the highest residual β content, hence the average elastic modulus is the lowest at 99.69 GPa. Additionally, the elastic modulus of the alloys after aging treatment remained at about 105 GPa, which is attributed to the stable residual β phase content.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G. Effects of different tissue loads on high power ultrasonic surgery scalpel. Ultrasound. Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, G.P.; McGuinness, G.B.; Dolan, F.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Performance characteristics of a therapeutic ultrasound wire waveguide apparatus. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2007, 49, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Shi, W.; Zhou, Z. The application and development of ultrasonic scalpel. J. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 22, 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, M.; Lucas, M. The effect of Ti-6Al-4V microstructure on the performance of ultrasonic soft tissue cutting tips. Proc. Meet. Acoust. 2017, 32, 020010. [Google Scholar]
- Lobkis, O.I.; Rokhlin, S. Characterization of polycrystals with elongated duplex microstructure by inversion of ultrasonic backscattering data. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 161905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, C.; Carreon, M. Assessment of precipitates of aged Ti-6Al-4V alloy by ultrasonic attenuation. Philos. Mag. 2017, 97, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Pilchak, A.L.; Lobkis, O.I.; Foltz, J.W.; Rokhlin, S.I.; Williams, J.C. Correlating Ultrasonic Attenuation and Microtexture in a Near-Alpha Titanium Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2358–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Kou, Z. Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and High-Temperature Wear Resistance of Ti–Al–B alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Wu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X. The Microstructural Evolution, Tensile Properties, and Phase Hardness of a TiAl Alloy with a High Content of the β Phase. Materials 2019, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Huang, L. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Underwater Laser Welding of Titanium Alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjering, G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Investigation of the grain size effect on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with equiaxed and bimodal microstructures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 219, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zherebtsov, S.; Murzinova, M.; Salishchev, G.; Semiatin, S.L. Spheroidization of the lamellar microstructure in Ti–6Al–4V alloy during warm deformation and annealing. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4138–4150. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, H.; Bin, L.; Lee, S.-H.; Li, Y.; Ono, Y.; Chiba, A. Frequent Occurrence of Discontinuous Dynamic Recrystallization in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy with α Martensite Starting Microstructure. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yoshida, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Ono, Y.; Chiba, A. Ti–6Al–4V alloy with an ultrafine-grained microstructure exhibiting low-temperature–high-strain-rate superplasticity. Mater. Lett. 2013, 98, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Nishihara, T.; Velay, V.; Vidal, V. Superplastic Property of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy with Ultrafine-Grained Heterogeneous Microstructure. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 20, 1700317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Murzinova, M.; Zherebtsov, S.; Salishchev, G.A.; Semiatin, S.L. Microstructure evolution during warm working of Ti–6Al–4V with a colony-α microstructure. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhou, S.; Luo, W.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, Y. Influence of primary α-phase volume fraction on the mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy at different strain rates and temperatures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 322, 022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z. Effects of β treatments on microstructures and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 533, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donachie, M.J., Jr. Titanium: A Technical Guide, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ankem, S.; Margolin, H.; Greene, C.A.; Neuberger, B.W.; Oberson, P.G. Mechanical properties of alloys consisting of two ductile phases. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 632–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.N.; Guo, H.Z.; Shi, Z.F.; Qin, C.; Zhao, Z.L. Microstructure characterization and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy after thermomechanical treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Hong, Q. The effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 563, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancken, B.; Thijs, L.; Kruth, J.-P.; van Humbeeck, J. Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by Selective Laser Melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 541, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M.; Kobayashi, T. Fracture characteristics analysis related to the microstructures in titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 213, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization Administration of the P.R.C. GB/T 6394-2017: Determination of Estimating the Average Grain Size of Metal; Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Standardization Administration of the P.R.C. GB/T 228.1-2010: Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature; Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Standardization Administration of the P.R.C. Metallic Materials—Determination of Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson’s Ratio; Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Z.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wang, G.D.; Chen, L.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, R. Microstructural evolution during aging of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2009, 16, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marker, C.; Shang, S.-L.; Zhao, J.-C.; Liu, Z.-K. Elastic knowledge base of bcc Ti alloys from first-principles calculations and CALPHAD-based modeling. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 140, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Song, X. First principles study of low Young’s modulus Ti–Nb–Zr alloy system. Mater. Lett. 2012, 80, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Song, X. A study of low Young’s modulus Ti–Nb–Zr alloys using d electrons alloy theory. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ti | Al/% | V/% | Fe/% | C/% | N/% | H/% | O/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reminder | 6.05 | 4.61 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.012 | 0.18 |
| Specimen No. | Heat Treatment |
|---|---|
| A | 920 °C, 1 h, AC |
| B | 940 °C, 1 h, AC |
| C | 960 °C, 1 h, AC |
| D | 980 °C, 1 h, AC |
| E | (960 °C, 1 h, AC) + (600 °C, 2 h, AC) |
| F | (960 °C, 1 h, AC) + (650 °C, 2 h, AC) |
| G | (960 °C, 1 h, AC) + (700 °C, 2 h, AC) |
| H | (960 °C, 1 h, AC) + (750 °C, 2 h, AC) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; He, H.; Lou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S. Fabrication, Structure and Mechanical and Ultrasonic Properties of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloys Part I: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloys Suitable for Ultrasonic Scalpel. Materials 2020, 13, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020478
He Z, He H, Lou J, Li Y, Li D, Chen Y, Liu S. Fabrication, Structure and Mechanical and Ultrasonic Properties of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloys Part I: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloys Suitable for Ultrasonic Scalpel. Materials. 2020; 13(2):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020478
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zheyu, Hao He, Jia Lou, Yimin Li, Dongyang Li, Yongzhi Chen, and Shaojun Liu. 2020. "Fabrication, Structure and Mechanical and Ultrasonic Properties of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloys Part I: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloys Suitable for Ultrasonic Scalpel" Materials 13, no. 2: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020478
APA StyleHe, Z., He, H., Lou, J., Li, Y., Li, D., Chen, Y., & Liu, S. (2020). Fabrication, Structure and Mechanical and Ultrasonic Properties of Medical Ti6Al4V Alloys Part I: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti6Al4V Alloys Suitable for Ultrasonic Scalpel. Materials, 13(2), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020478





