Effect of the Layer Sequence on the Ballistic Performance and Failure Mechanism of Ti6Al4V/CP-Ti Laminated Composite Armor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
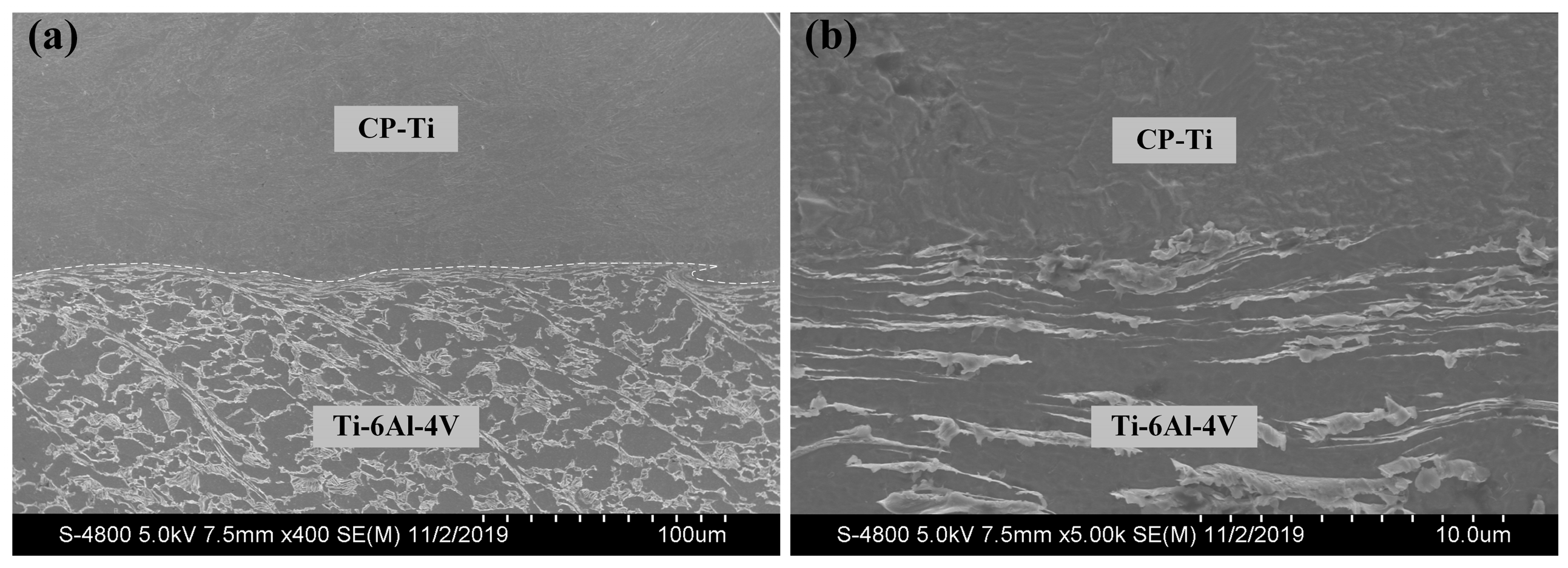
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Numerical Simulation
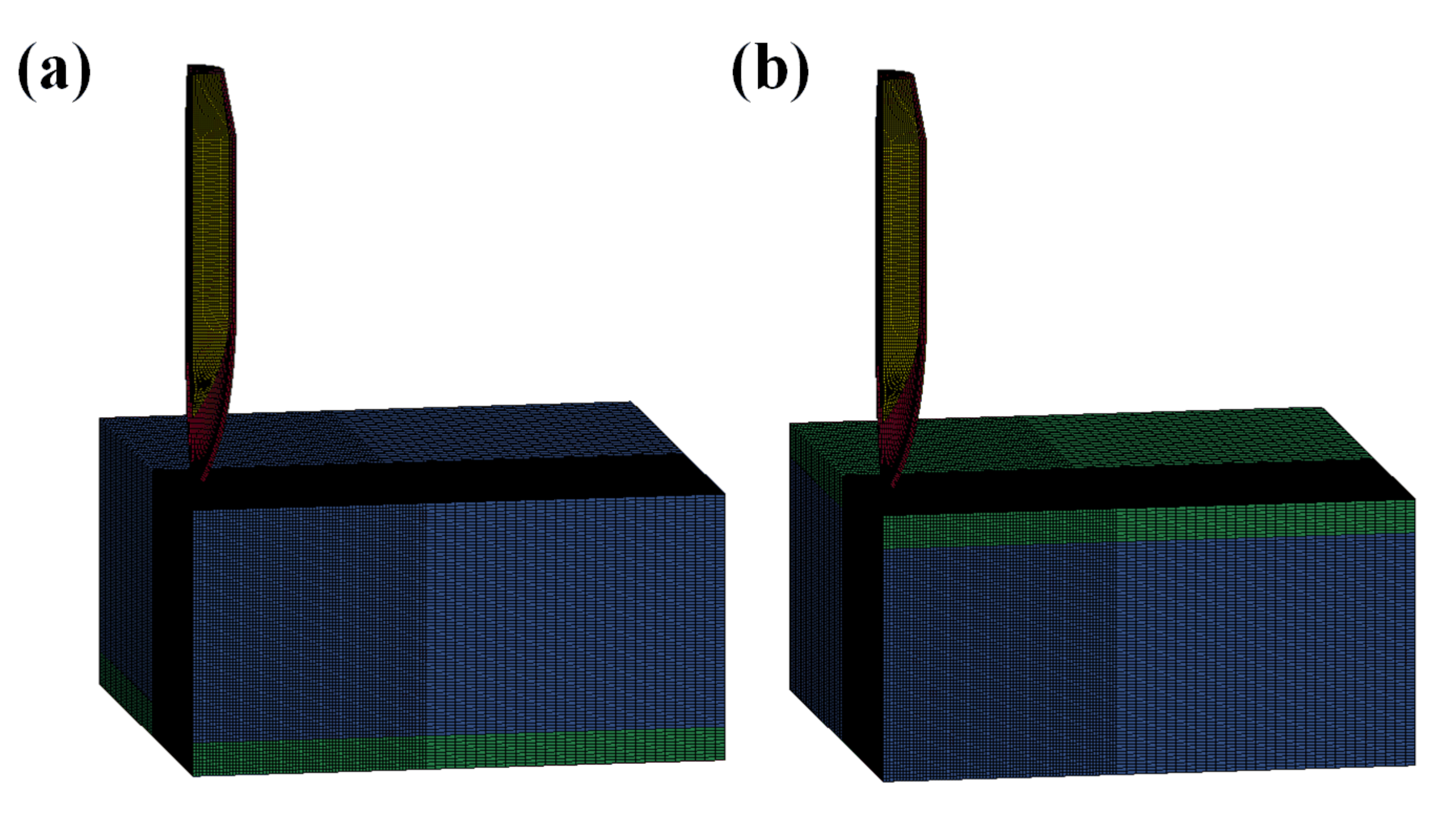
3.1. Finite Element Model
3.2. Material Models
4. Results and Discussion
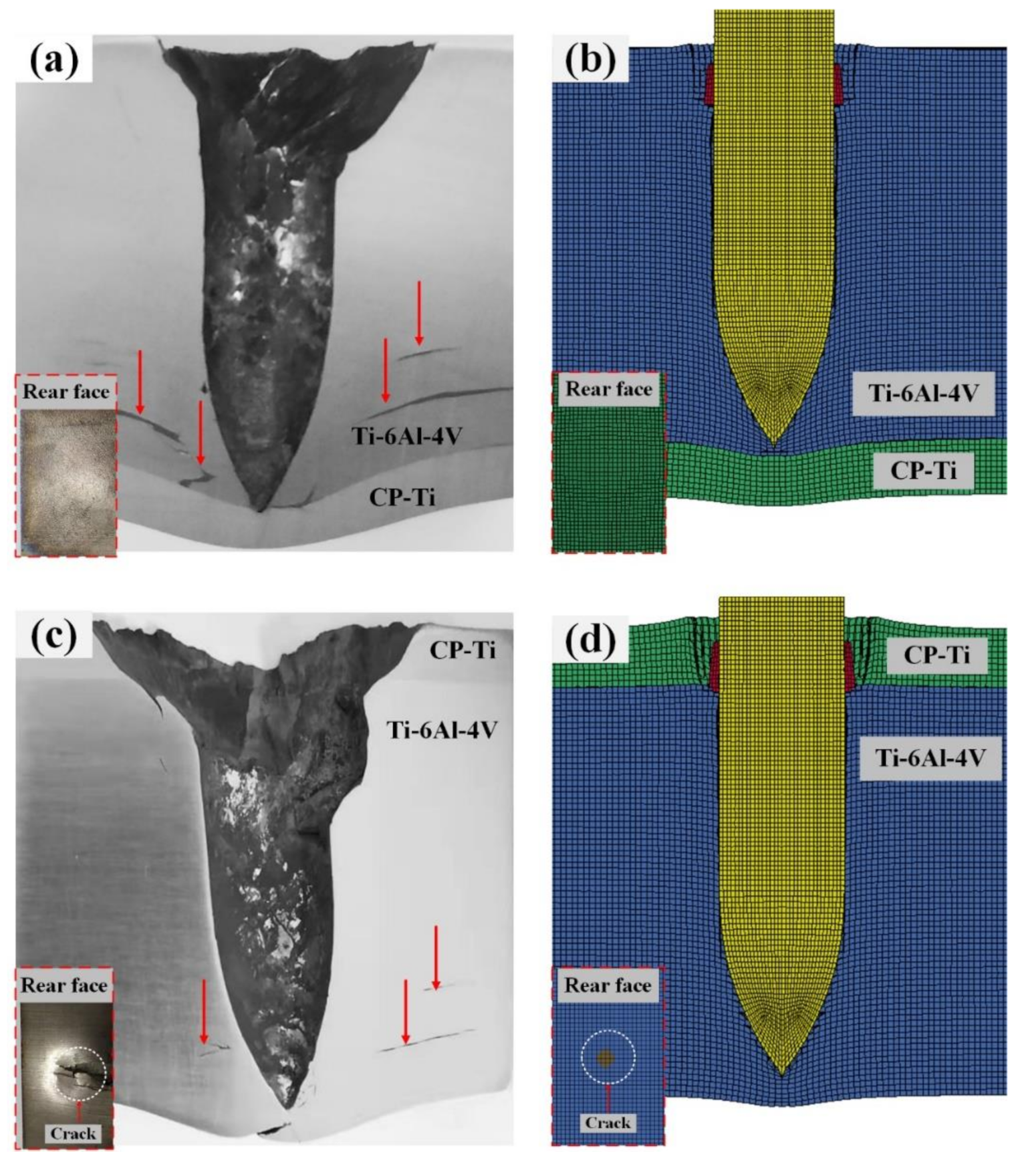
4.1. Penetration Results
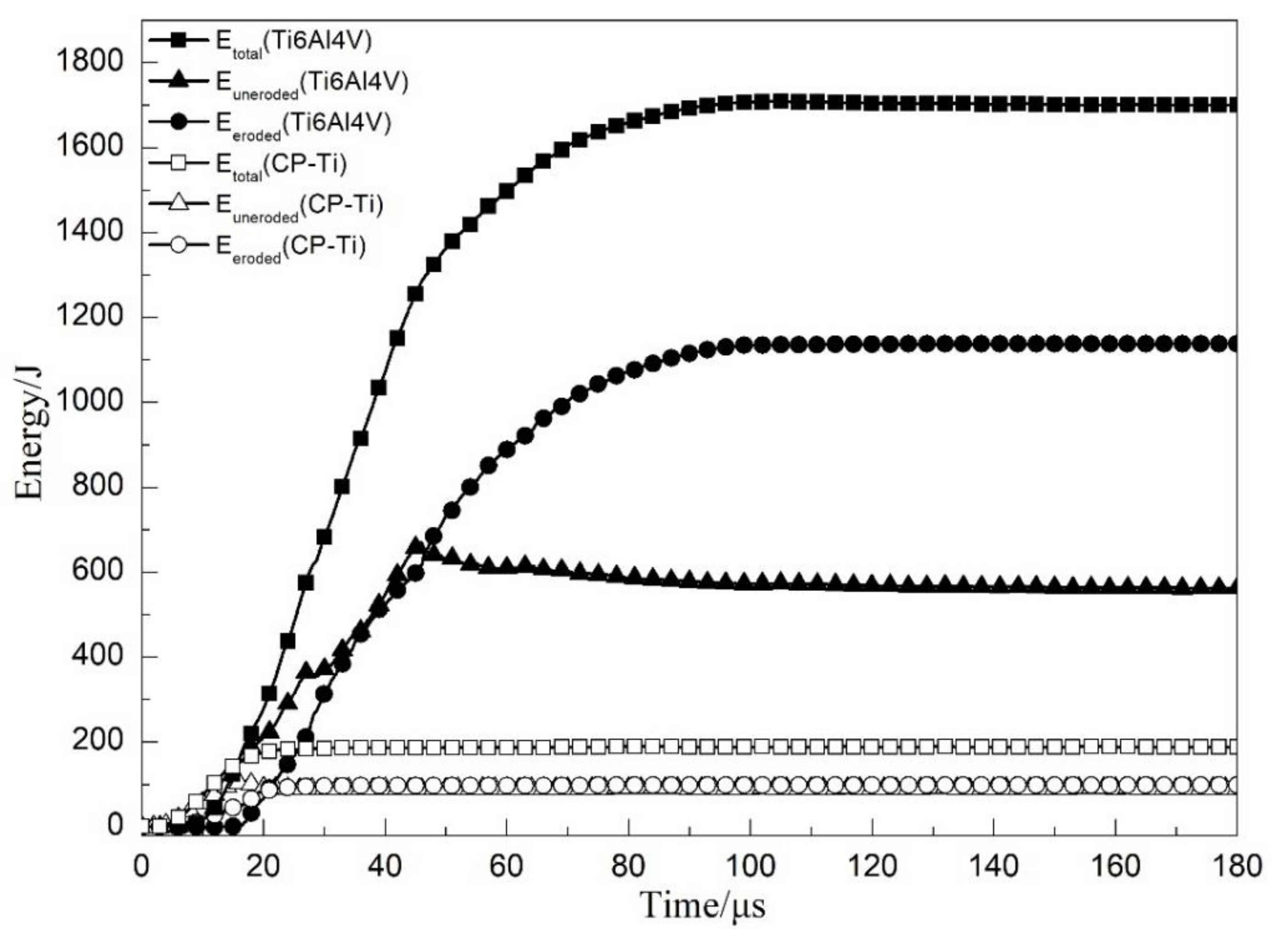
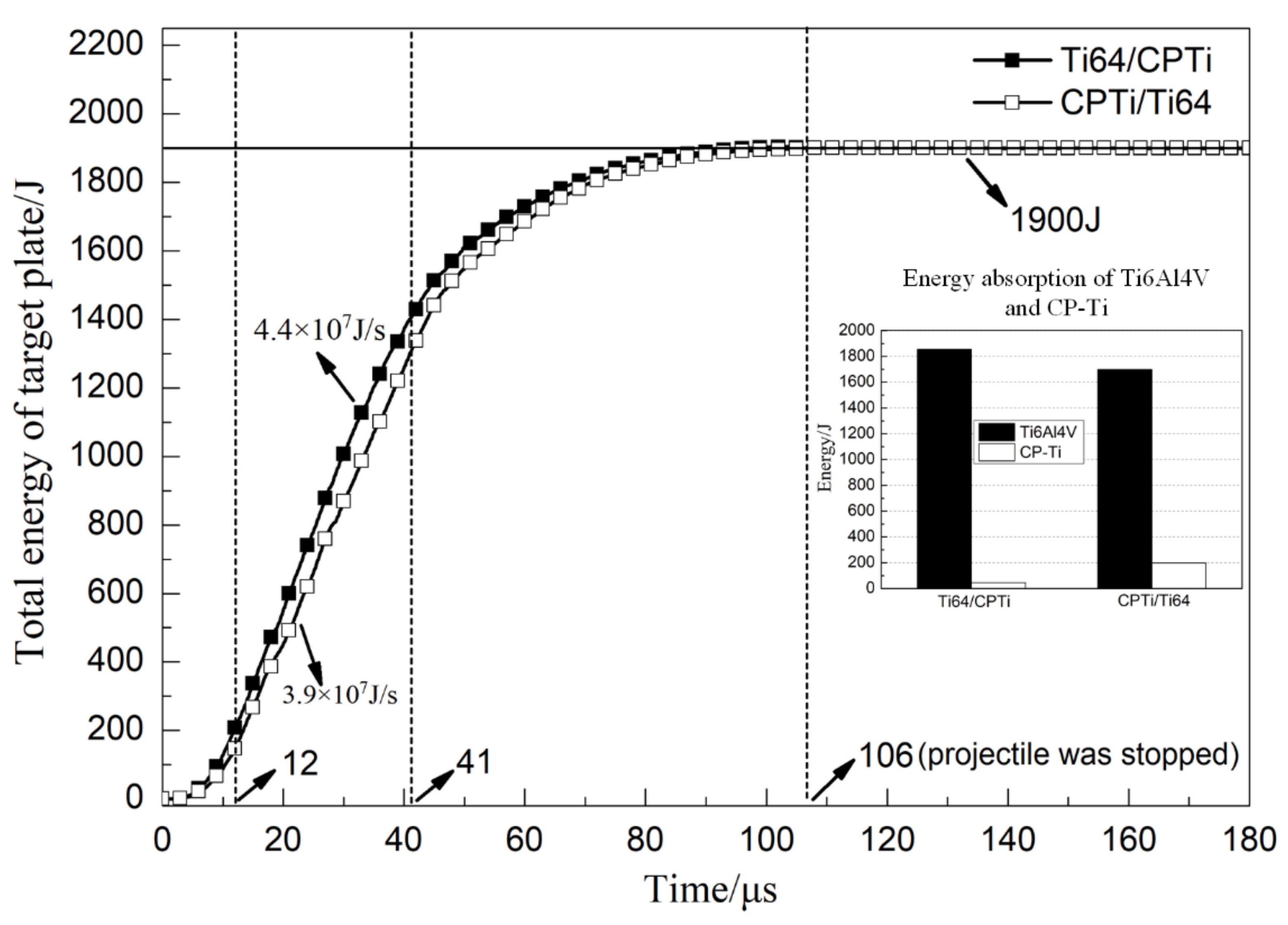
4.2. Energy Analysis of the Penetration Process
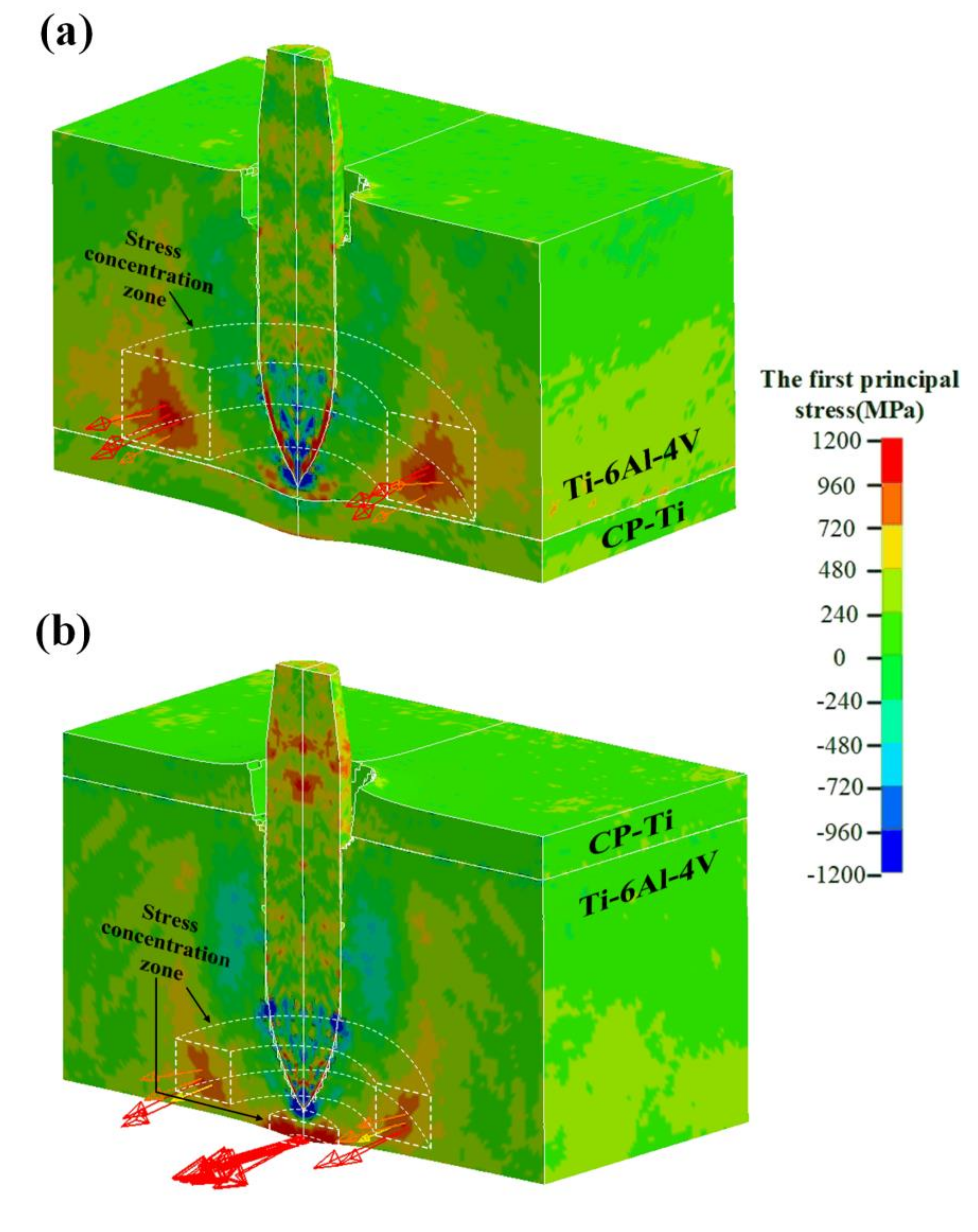
4.3. Stress Analysis of the Target Plate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, N.; Wang, J.X.; Yang, R.; Dong, G. Damage mechanism and anti-penetration performance of multi-layered explosively welded plates impacted by spherical projectile. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2012, 60, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, J.K.; Hopperstad, O.S.; Børvik, T. Low-velocity impact on multi-layered dual-phase steel plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 78, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Johnson, E.; Saleh, M.; Edwards, L. Ballistic performance of multi-layered metallic plates impacted by a 7.62-mm APM2 projectile. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2011, 38, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radin, J.; Goldsmith, W. Normal projectile penetration and perforation of layered targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 1988, 7, 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Z. Experimental investigation on the ballistic resistance of monolithic and multi-layered plates against hemispherical-nosed projectiles impact. Mater. Des. 2012, 41, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cao, Z. Experimental investigation on the ballistic resistance of monolithic and multi-layered plates against ogival-nosed rigid projectiles impact. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qing, G.; Wei, G.; Yang, Y.; Hao, P. The ballistic performance of metal plates subjected to impact by blunt-nosed projectiles of different strength. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wei, G. The ballistic performance of metal plates subjected to impact by projectiles of different strength. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 305–315. [Google Scholar]
- Palta, E.; Gutowski, M.; Fang, H. A numerical study of steel and hybrid armor plates under ballistic impacts. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 136, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.; Ramanjeneyulu, K.; Kumar, K.S.; Bhat, T.B. Ballistic studies on layered structures. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børvik, T.; Dey, S.; Clausen, A. Perforation resistance of five different high-strength steel plates subjected to small-arms projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 948–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wei, G. Experimental investigation on the ballistic performance of monolithic and layered metal plates subjected to impact by blunt rigid projectiles. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2012, 49, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; Gupta, P.; Deore, V.; Tak, S.; Tiwari, G.; Gupta, N. Effect of target span and configuration on the ballistic limit. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2012, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, N. Damage mechanism and anti-penetration performance of explosively welded plates impacted by projectiles with different shapes. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiong, B.; Wang, G.; Tong, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fracture mechanism of a laminated aluminum alloy plate during ballistic impact. Rare Metals 2017, 36, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Wierzbicki, T.; Huang, M. Ballistic resistance of double-layered armor plates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2008, 35, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, G.; Dubinsky, A.; Elperin, T. New results on ballistic performance of multi-layered metal shields. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchar, J.; Voldrich, J.; Rolc, S.; Lisy, J. Ballistic performance of dual hardness armor. In Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Ballistics, Orlando, FL, USA, 23–27 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fan, Q.; Cai, H.; Wang,, F. Underlying mechanism of periodical adiabatic shear bands generated in Ti-6Al-4V target by projectile impact. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fan, Q.; Gao, R.; Huo, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Effects of dynamic mechanical properties on the ballistic performance of a new near-β titanium alloy Ti684. Mater. Des. 2014, 62, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, G.; Singh, B.B.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sivakumar, K.; Gogia, A. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and ballistic performance of Ti-4Al-2.3V-1.9 Fe alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, K.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, W.; Peng, M.; Jin, D. Failure mechanisms in ballistic performance of Ti-6Al-4V targets having equiaxed and lamellar microstructures. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 85, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkins, M.; Hansen, J.; Page, J.; Turner, P. Effect of thermomechanical processing on the ballistic performance of titanium. In Proceedings of the Non-Aerospace Applications of Titanium Symposium Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, San Antonio, TX, USA, 16–19 February 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Sukumar, G.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Kumar, K.; Bhat, T.; Gogia, A. Effect of heat treatment on ballistic impact behavior of Ti–6Al–4V against 7.62 mm deformable projectile. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaurin, B. Dual-Hardness Titanium Body Armor for Concealable Applications. Master’s Thesis, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, CA, USA, June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, R.; Rennhack, E. Evaluation of Dual-Hardness Titanium Alloy Armor; Lockheed Missiles and Space Company: Palo Alto, CA, USA, January 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Fras, T.; Szachogluchowicz, I.; Sniezek, L. Ti6Al4V-AA1050-AA2519 explosively-cladded plates under impact loading. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2018, 227, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchey, W.J. Suppression of Material Failure Modes in Titanium Armors; No. ARL-TR-3124; Army Research Laboratory: Aberdeen Proving Ground, MD, USA, December 2003; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Acarer, M.; Demir, B. An investigation of mechanical and metallurgical properties of explosive welded aluminum-dual phase steel. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4158–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchely, M.F.; Maranon, A.; Silberschmidt, V.V. Material model for modeling clay at high strain rates. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 90, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, G.; Cook, W. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, American Defense Preparedness Association, Hague, The Netherlands, 19–21 April 1983; pp. 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Hallquist, J. LS-DYNA Theory Manual; Livermore Software Technology Corporation: Livermore, CA, USA, March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lesuer, D. Experimental Investigations of Material Models for Ti-6Al-4V Titanium and 2024-T3 Aluminum; Final report, DOT/FAA/AR-00/25; US Department of Transportation and Federal Aviation Administration: Washington, DC, USA, September 2000.
- Nassiri, A.; Zhang, S.; Lee, T.; Abke, T.; Vivek, A.; Kinsey, B.; Daehn, G. Numerical investigation of CP-Ti & Cu110 impact welding using smoothed particle hydrodynamics and arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian methods. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 28, 558–564. [Google Scholar]




| Materials | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V | 920 | 974 | 15 |
| CP-Ti | 285 | 428 | 37 |
| Material | E (GPa) | ρ (g/cm3) | υ | (MPa) | G (GPa) | C | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| steel | 210 | 7.85 | 0.33 | 1200 | 80.0 | 100 | 10 |
| lead | 17 | 11.27 | 0.4 | 24 | 6.1 | 600 | 3 |
| brass | 115 | 8.52 | 0.31 | 206 | 44.0 | - | - |
| Materials Parameters | Ti6Al4V | CP-Ti |
|---|---|---|
| A(MPa) | 1098 | 359 |
| B(MPa) | 1092 | 668 |
| n | 0.93 | 0.49 |
| C | 0.014 | 0.0194 |
| m | 1.1 | 0.5816 |
| D1 | –0.09 | 0.5 |
| D2 | 0.25 | 3.89 |
| D3 | –0.5 | –1.74 |
| D4 | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| D5 | 3.87 | 0.95 |
| Scheme | Experiment Penetration Depth (mm) | Simulation Penetration Depth (mm) | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti64/CP-Ti | 35.8 | 34.0 | 5.3% |
| CP-Ti/Ti64 | 37.1 | 36.8 | 0.8% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhu, X. Effect of the Layer Sequence on the Ballistic Performance and Failure Mechanism of Ti6Al4V/CP-Ti Laminated Composite Armor. Materials 2020, 13, 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173886
Yu H, Fan Q, Zhu X. Effect of the Layer Sequence on the Ballistic Performance and Failure Mechanism of Ti6Al4V/CP-Ti Laminated Composite Armor. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173886
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hong, Qunbo Fan, and Xinjie Zhu. 2020. "Effect of the Layer Sequence on the Ballistic Performance and Failure Mechanism of Ti6Al4V/CP-Ti Laminated Composite Armor" Materials 13, no. 17: 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173886
APA StyleYu, H., Fan, Q., & Zhu, X. (2020). Effect of the Layer Sequence on the Ballistic Performance and Failure Mechanism of Ti6Al4V/CP-Ti Laminated Composite Armor. Materials, 13(17), 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173886




