Preparation and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Oriented Fiber Arrays by Electrospinning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Analysis
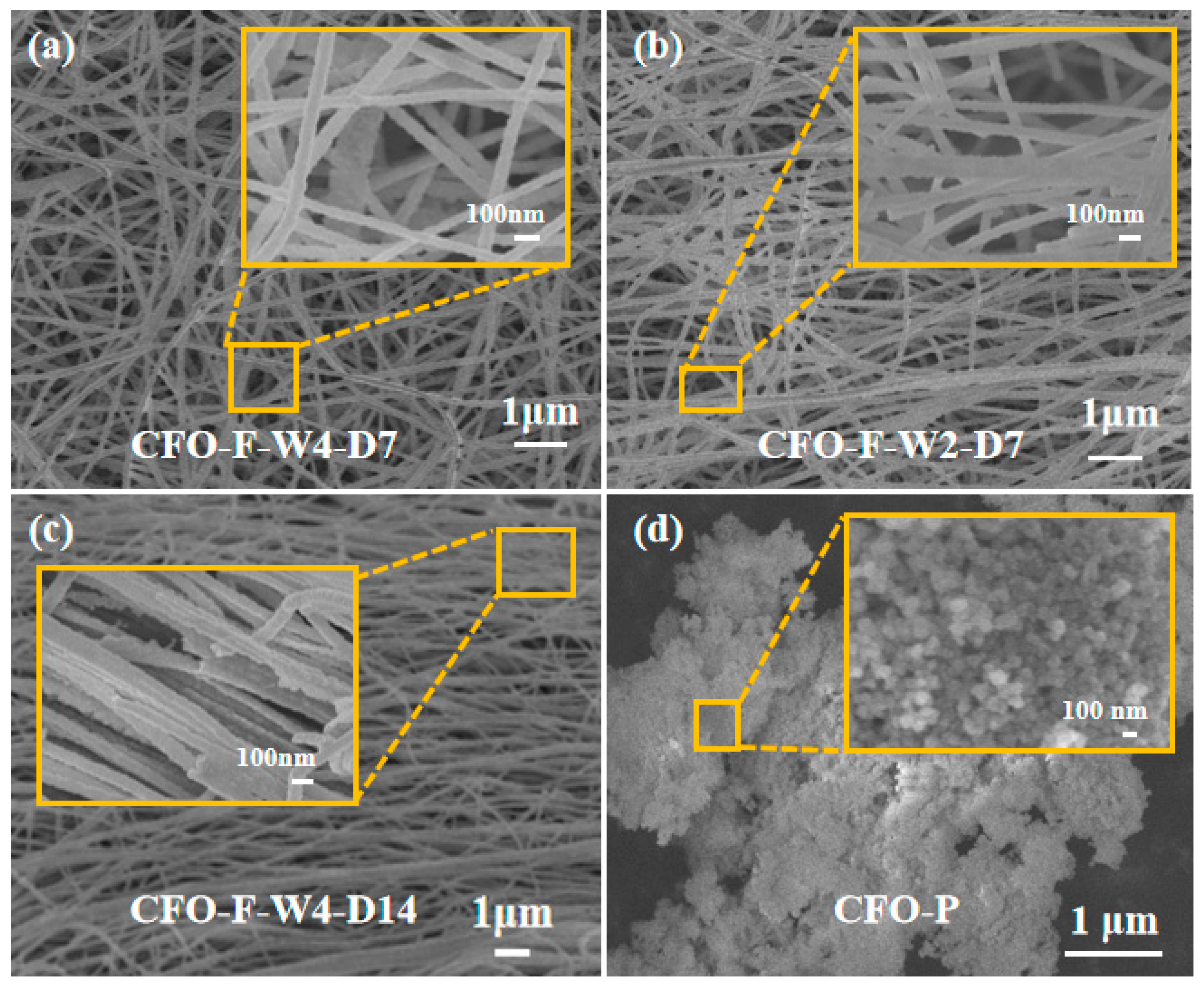
3.2. Morphological Analysis
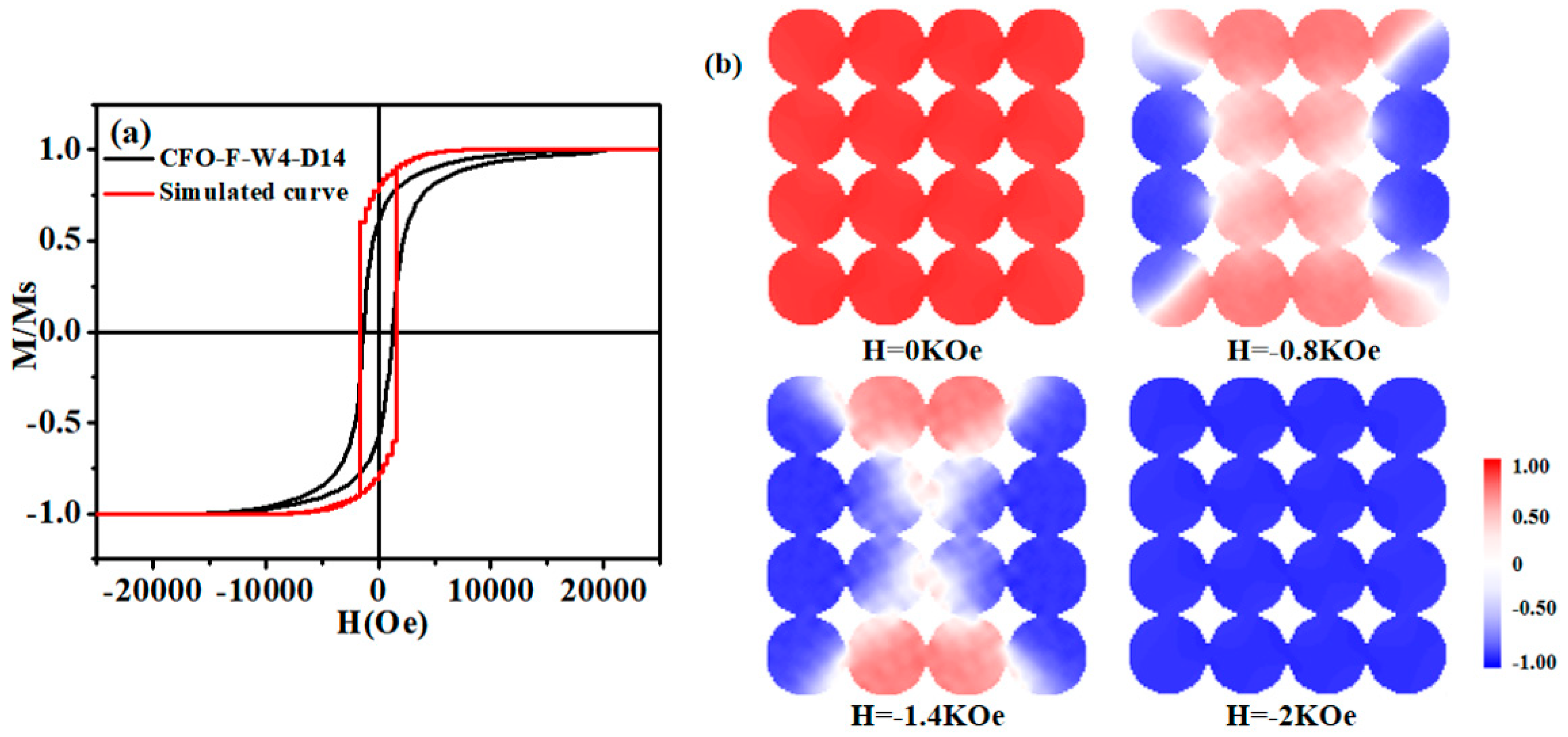
3.3. Magnetic Performance Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, A.; Chang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. The phase diagram and exotic magnetostrictive behaviors in spinel oxide Co(Fe1−xAlx)2O4 system. Materials 2019, 12, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartunek, V.; Sedmidubsky, D.; Huber, S.; Svecova, M.; Ulbrich, P.; Jankovsky, O. Synthesis and properties of nanosized stoichiometric cobalt ferrite spinel. Materials 2018, 11, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmin, N.; Abdulsatar, S.; Hashim, M.; Zahid, M.; Gillani, S.F.; Kalsoom, A.; Ashiq, M.N.; Inam, I.; Safdar, M.; Mirza, M. Structural and magnetic studies of Ce-Mn doped M-type SrFe12O19 hexagonal ferrites by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 473, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, H. A review of the magnetic properties, synthesis methods and applications of maghemite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, M.P.; Orlov, A.V.; Znoyko, S.L.; Bragina, V.A.; Gorshkov, B.G.; Ksenevich, T.I.; Cherkasov, V.R.; Nikitin, P.I. Multiplex biosensing with highly sensitive magnetic nanoparticle quantification method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.S.; Deng, G.C.; Cao, Y.M.; McIntyre, G.J.; Li, R.B.; Yuan, N.; Feng, Z.J.; Ge, J.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Cao, S.X. Tuning the magnetic anisotropy via Mn substitution in single crystal CO4Nb2O9. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Qian, K.; Yu, K.J.; Zhou, H.F.; Weng, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.W. Controllable synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4@f-GNPs nanocomposites. Compos. Commun. 2020, 20, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shu, X.F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ma, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Shu, R.W.; Kong, L.B. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of (1−x)CoFe2O4/xCoFe composites at multiple frequency bands. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 493, 165699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Chu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Shen, X.Q. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of electrospun Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanofibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiong, L.Y.; Yu, X.; He, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Shen, J.L. Magnetically controlled terahertz modulator based on Fe3O4 nanoparticle ferrofluids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning jets and polymer nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, N.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Klocker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Dopke, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Hutten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic properties of electrospun magnetic nanofiber mats after stabilization and carbonization. Materials 2020, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquet, I.; Presmanes, L.; Bonningue, C.; Tailhades, P. Patterned ferrimagnetic thin films of spinel ferrites obtained directly by laser irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 283, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Homogeneous growth of conducting polymer nanofibers by electrodeposition for superhydrophobic and superoleophilic stainless steel meshes. Rsc. Adv. 2014, 4, 50401–50405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.L.; Dong, J.P.; Xu, J.Q. Direct electrodeposition of highly ordered gold nanotube arrays for use in non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.L.; Cheng, L.; Chen, R.S.; Ni, H.W. Quasi-aligned nanorod arrays composed of Nickel–Cobalt nanoparticles anchored on TiO2/C nanofiber arrays as free standing electrode for enzymeless glucose sensors. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodaee, T.; Ghasemi, A.; Razavi, R.S. Controlled growth of large-area arrays of gadolinium-substituted cobalt ferrite nanorods by hydrothermal processing without use of any template. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 17420–17428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, J.L.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Sabantina, L.; Klocker, M.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Orientation of electrospun magnetic nanofibers near conductive areas. Materials 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Huang, L.B.; Zang, D.Y.; Li, C.; Dang, J.; Wang, D.W. Segmented polymer nanowires and nanorods by one-step template wetting with a hyperbranched polymer and linear polymer blend. Rsc. Adv. 2014, 4, 53021–53027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Xu, L. Preparation and formation mechanism of highly aligned electrospun nanofibers using a modified parallel electrode method. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.P.; Peng, Q.Q.; Chen, Q.P.; Xiong, J.Y.; Zhang, F.; Sun, D.H. Alignment of electrospun fibers using the whipping instability. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.W.; MacEwan, M.R.; Ray, W.Z.; Liu, W.Y.; Siewe, D.Y.; Xia, Y.N. Radially aligned, electrospun nanofibers as dural substitutes for wound closure and tissue regeneration applications. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5027–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhugra, V.S.; Williams, G.V.M.; Chong, S.V.; Nann, T. Electrospun, oriented, ferromagnetic Ni1-xFex Nanofibers. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Xu, Q.W.; Li, C.; Huang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wu, D.C.; Wang, Z.L. Engineering 3D aligned nanofibers for regulation of cell growth behavior. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.Q.; Yin, D.H.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Li, C.L. Facile synthesis and characterization of spinel ferrite NiFe2O4 nanowire arrays with a high-aspect-ratio. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 22997–23000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Yang, D.Y. Fabrication of aligned electrospun nanofibers by inclined gap method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.P.; Xia, Y.N.; Yang, H. Magnetic-field-assisted electrospinning of aligned straight and wavy polymeric nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2454–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X. Fabrication of aligned fibrous arrays by magnetic electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3702–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning nanofibers as uniaxially aligned arrays and layer-by-layer stacked films. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katta, P.; Alessandro, M.; Ramsier, R.D.; Chase, G.G. Continuous Electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers onto a wire drum collector. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, J.G.; Tan, G.G.; Mellors, N.J.; Xie, E.Q.; Han, W.H. Unique magnetic properties and magnetization reversal process of CoFe2O4 nanotubes fabricated by electrospinning. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3932–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Feng, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.F.; Yuan, Y. Fiber-guided and particle-localized microwave absorption of nanoscale CoFe2O4 derived from citric acid-based precursor. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 561, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordina, B.; Tiwari, R.K.; Setua, D.K.; Sharma, A. Superior elastomeric nanocomposites with electrospun nanofibers and nanoparticles of CoFe2O4 for magnetorheological applications. Rsc. Adv. 2015, 5, 19091–19105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Jung, H.R.; Lee, W.J. Hollow cobalt ferrite–polyaniline nanofibers as magnetically separable visible-light photocatalyst for photodegradation of methyl orange. J. Photoch. Photobiol. A 2016, 321, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiscan, O.; Dumitru, I.; Tura, V.; Chiriac, H.; Stancu, A. High frequency absorption of PVC/iron oxides and PVC/CoFe2O4 /CoO nanofibers produced by electrospinning technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.W.; Park, J.H.; Jung, H.R.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, W.J. Fabrication and characterization of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanofibers by electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Adv. 2008, 147, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugendar, K.; Vaithyanathan, V.; Patro, L.N.; Inbanathan, S.S.R.; Bharathi, K.K. Temperature-dependent magnetization, anisotropy and conductivity of CoFe2-xSnxO4 (x = 0.025, 0.05, 0.075): Appearance of grain boundary conductivity at high temperatures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 305001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivel, M.; Babu, R.R.; Ramamurthi, K.; Arivanandhan, M. CTAB cationic surfactant assisted synthesis of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19320–19328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadifard, M.; Farhadi, S.; Mohebbi, S. Sonocatalytic performance of magnetic flower-like CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared from a heterometallic oxo-centered trinuclear complex under microwave irradiation. Polyhedron 2018, 155, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labchir, N.; Hannour, A.; Hssi, A.A.; Vincent, D.; Chatelon, J.P.; Dufeu, D.; Ihlal, A.; Sajieddine, M. Microwave response of coplanar waveguide based on electrodeposited CoFe2O4 nanowires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 510, 166952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Yang, G.J.; Wei, J.X.; Bian, H.Q.; Gao, J.M.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, T. Morphology and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanocables fabricated by electrospinning based on the Kirkendall effect. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 445, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.J.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, Y.S.; Liu, Z.G.; Du, X.B.; Wen, G.H. Synthesis and magnetic properties of spinel CoFe2O4 nanowire arrays. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2795–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Meng, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.D. Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in 70 nm CoFe2O4 thin films fabricated on SiO2/Si(100) by the sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 7803–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvandi-Tabrizi, Y.; Schwartz, J. Micromagnetic analysis of crystallographic texturing and substrate-induced strain effects in NiFe2O4 and CoFe2O4 thin films. Acta Mater. 2018, 149, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Maashani, M.S.; Khalaf, K.A.; Gismelseed, A.M.; Al-Omari, I.A. The structural and magnetic properties of the nano-CoFe2O4 ferrite prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Munjal, S.; Khare, N. Strain/defect induced enhanced coercivity in single domain CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 386, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, G.P.; Yuan, X.H.; Ye, L.N. 3D and 1D micromagnetic calculation for hard/soft bilayers with in-plane easy axes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 4231–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, M.; Vivas, L.G. Magnetization reversal in Co-base nanowire arrays. Phys. Status Solidi B 2011, 248, 2368–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Sampaio, L.C.; Sinnecker, E.H.C.P.; Vargas, P.; Altbir, D. Dipolar magnetic interactions among magnetic microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 249, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Xu, H.H.; Zhang, J.X.; Yue, M. Magnetic properties and magnetization reversal in Co nanowires with different morphology. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


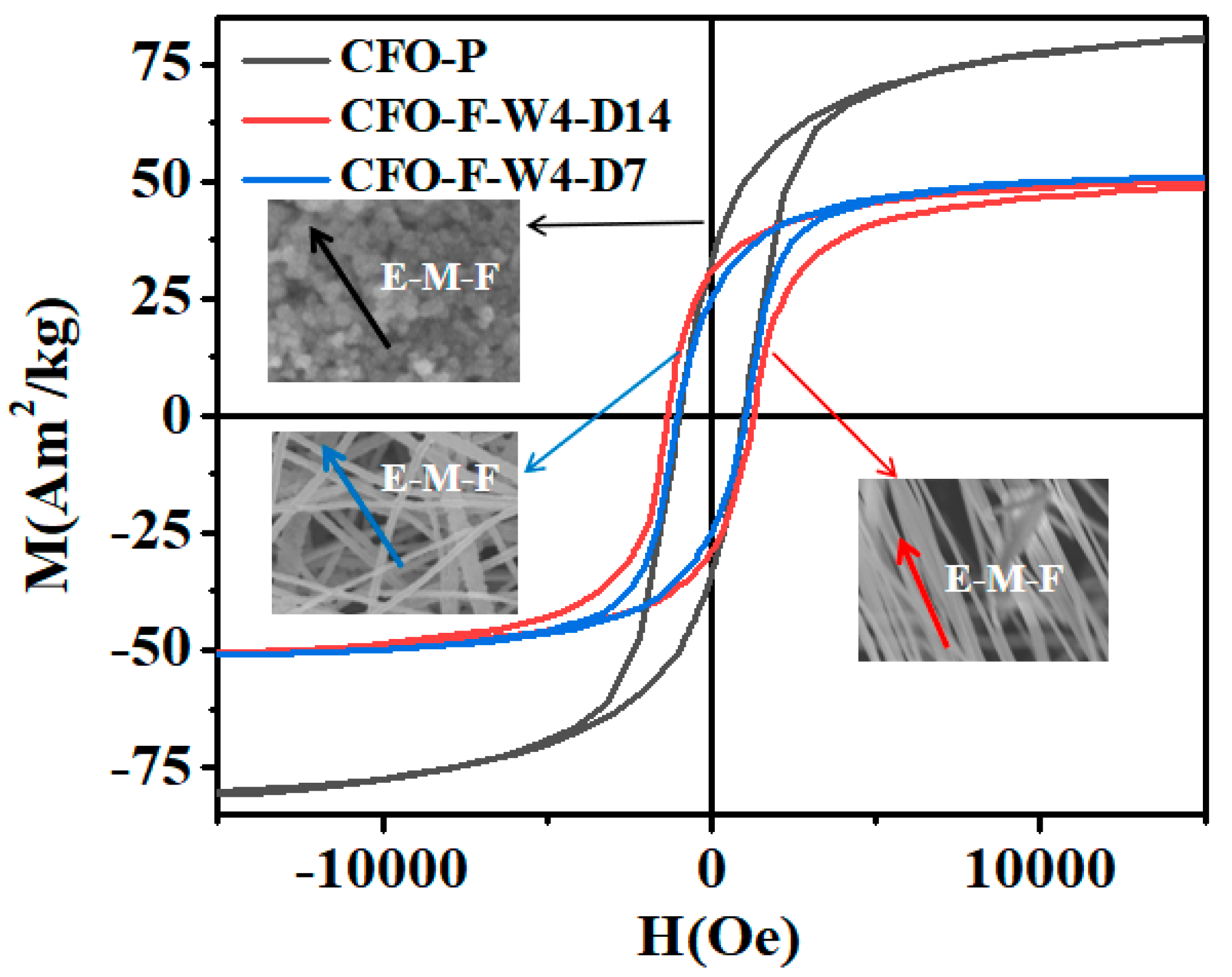
| Samples | Ms (Am2/kg) | Hc (Oe) | Mr (Am2/kg) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-oriented nanofibers (parallel-CFO-F-W4-D7) | 49.95 | 1126.2 | 24.83 | 0.50 |
| Non-oriented nanofibers (perpendicular-CFO-F-W4-D7) | 50.67 | 1118.2 | 25.12 | 0.49 |
| Aligned nanofibers (parallel-CFO-F-W4-D14) | 50.89 | 1330.5 | 32.39 | 0.64 |
| Aligned nanofibers (perpendicular-CFO-F-W4-D14) | 51.11 | 857.2 | 24.80 | 0.48 |
| CFO-P | 80.23 | 979.3 | 32.33 | 0.40 |
| Morphology | Method | Ms | Hc | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Co-Precipitation Method | 64.45 emu/g | 681.04 Oe | [39] |
| Nanoparticles | Microwave Heating Method | 23.88 emu/g | 237 Oe | [40] |
| Nanowires | Electrodeposited | \ | 1300 Oe | [41] |
| Nanocables | Electrospinning | \ | 878 Oe | [42] |
| Nanowire Arrays | Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template | \ | 1100 Oe | [43] |
| Thin Films | Sol–Gel Method | 200 emu/cm3 | 1000 Oe | [44] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Dai, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, W. Preparation and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Oriented Fiber Arrays by Electrospinning. Materials 2020, 13, 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173860
Cheng C, Dai J, Li Z, Feng W. Preparation and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Oriented Fiber Arrays by Electrospinning. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173860
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chen, Jianfeng Dai, Zengpeng Li, and Wei Feng. 2020. "Preparation and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Oriented Fiber Arrays by Electrospinning" Materials 13, no. 17: 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173860
APA StyleCheng, C., Dai, J., Li, Z., & Feng, W. (2020). Preparation and Magnetic Properties of CoFe2O4 Oriented Fiber Arrays by Electrospinning. Materials, 13(17), 3860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173860




