Mechanical Properties of Large Slump Concrete Made by Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Mixing Procedure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportions
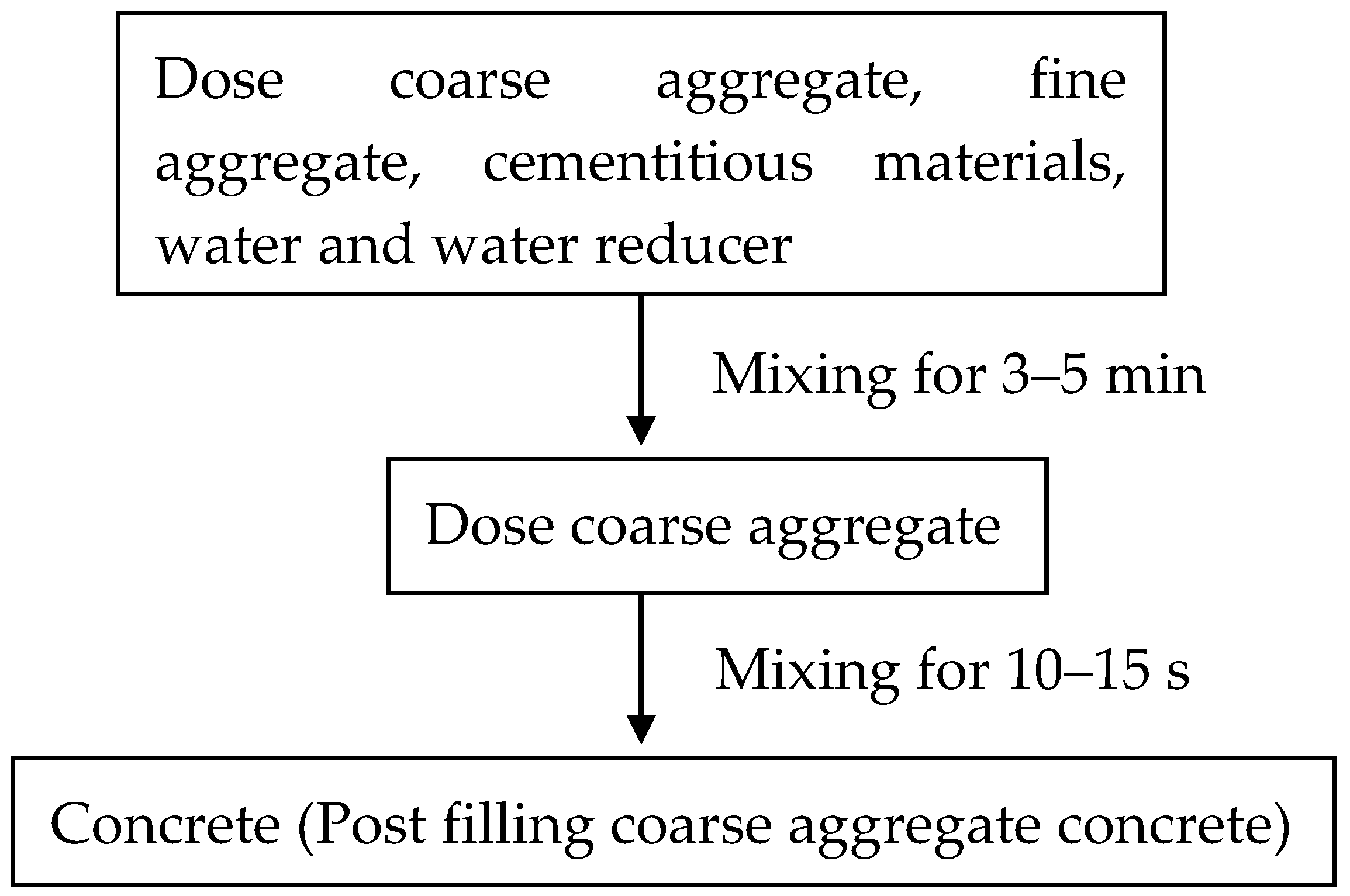
2.3. Mixing Procedures for Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Concrete
2.4. Specimen Preparations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Slump
3.2. Compressive Strength of Cubic Specimens
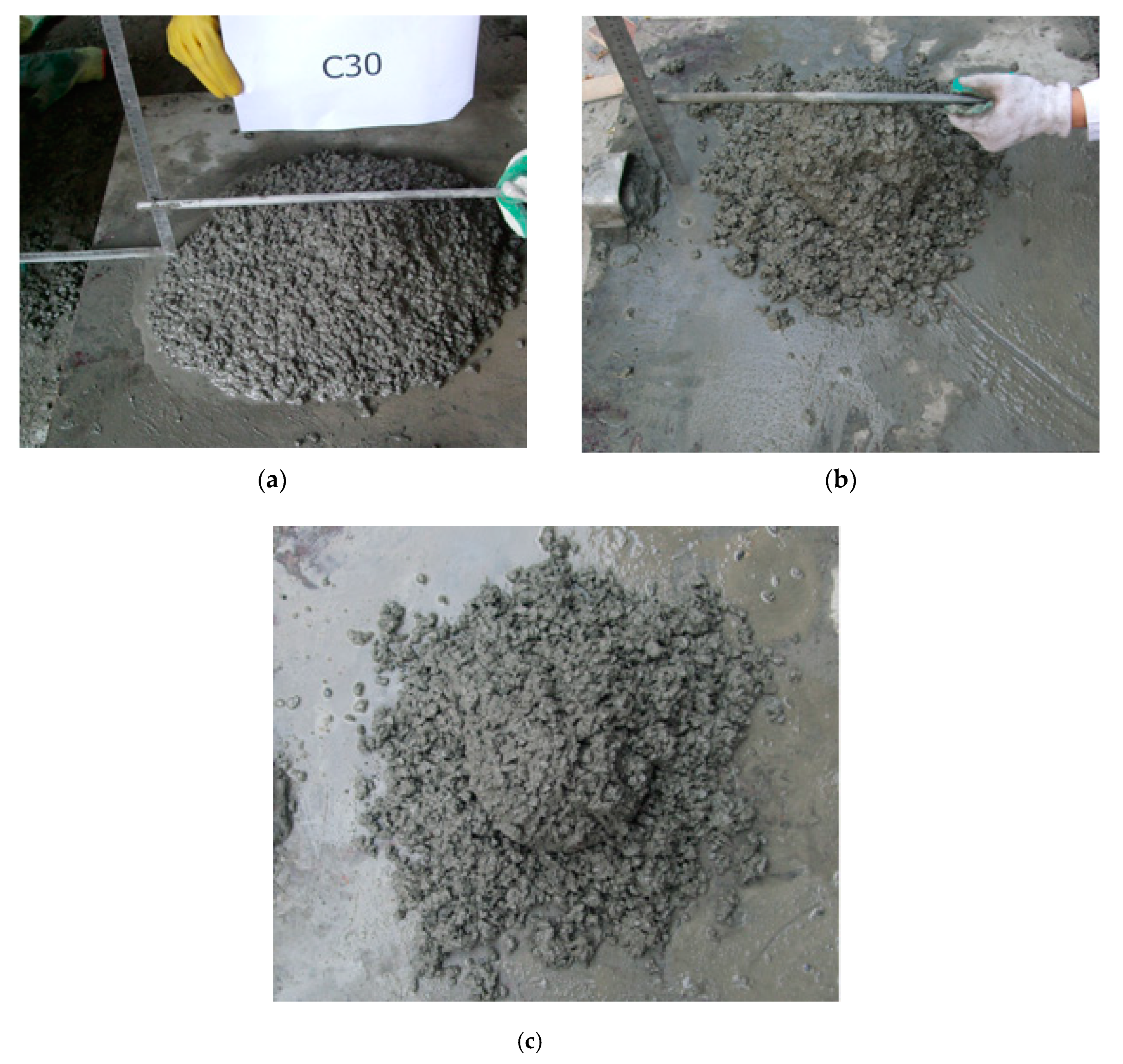
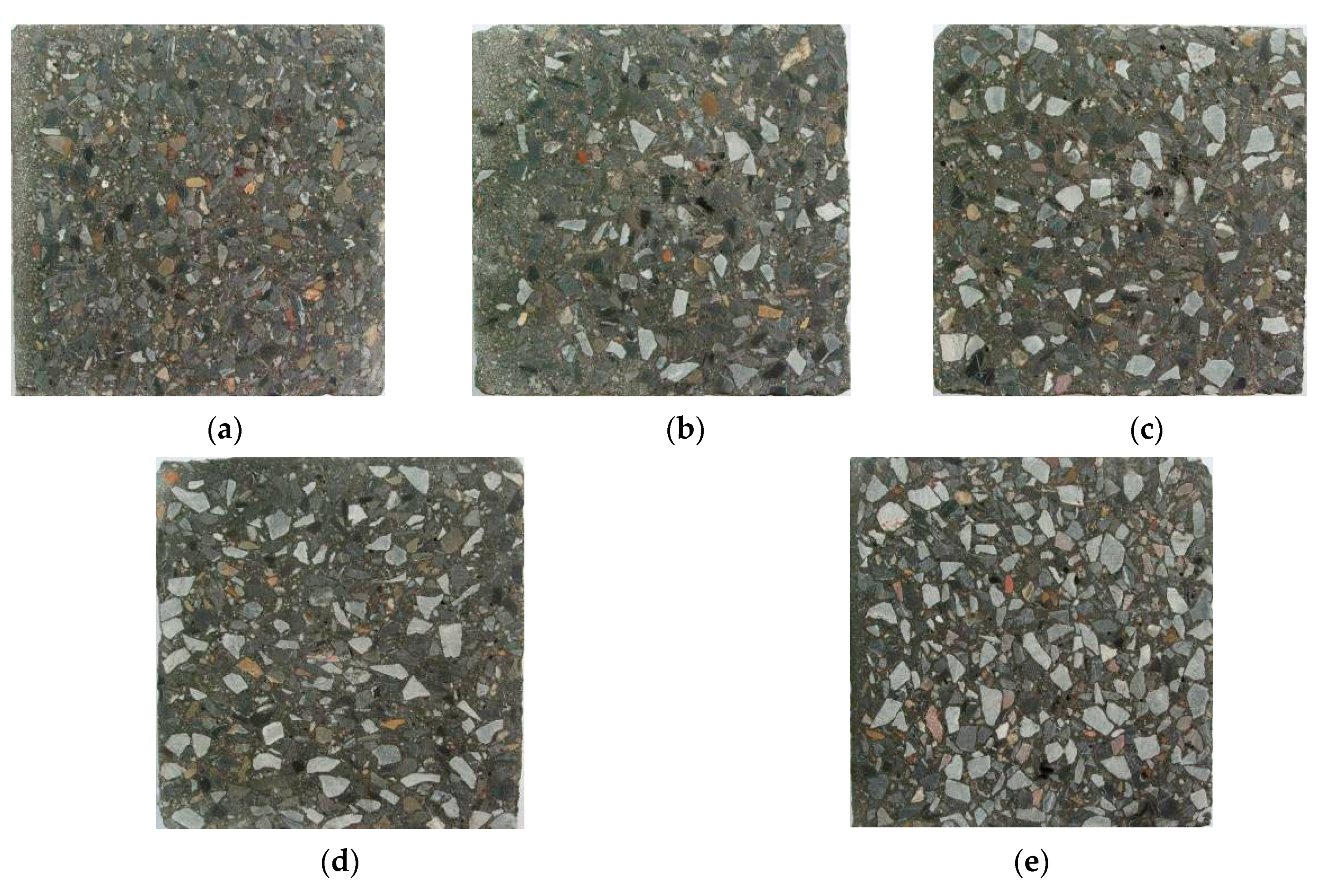
3.2.1. Distribution of Coarse Aggregate
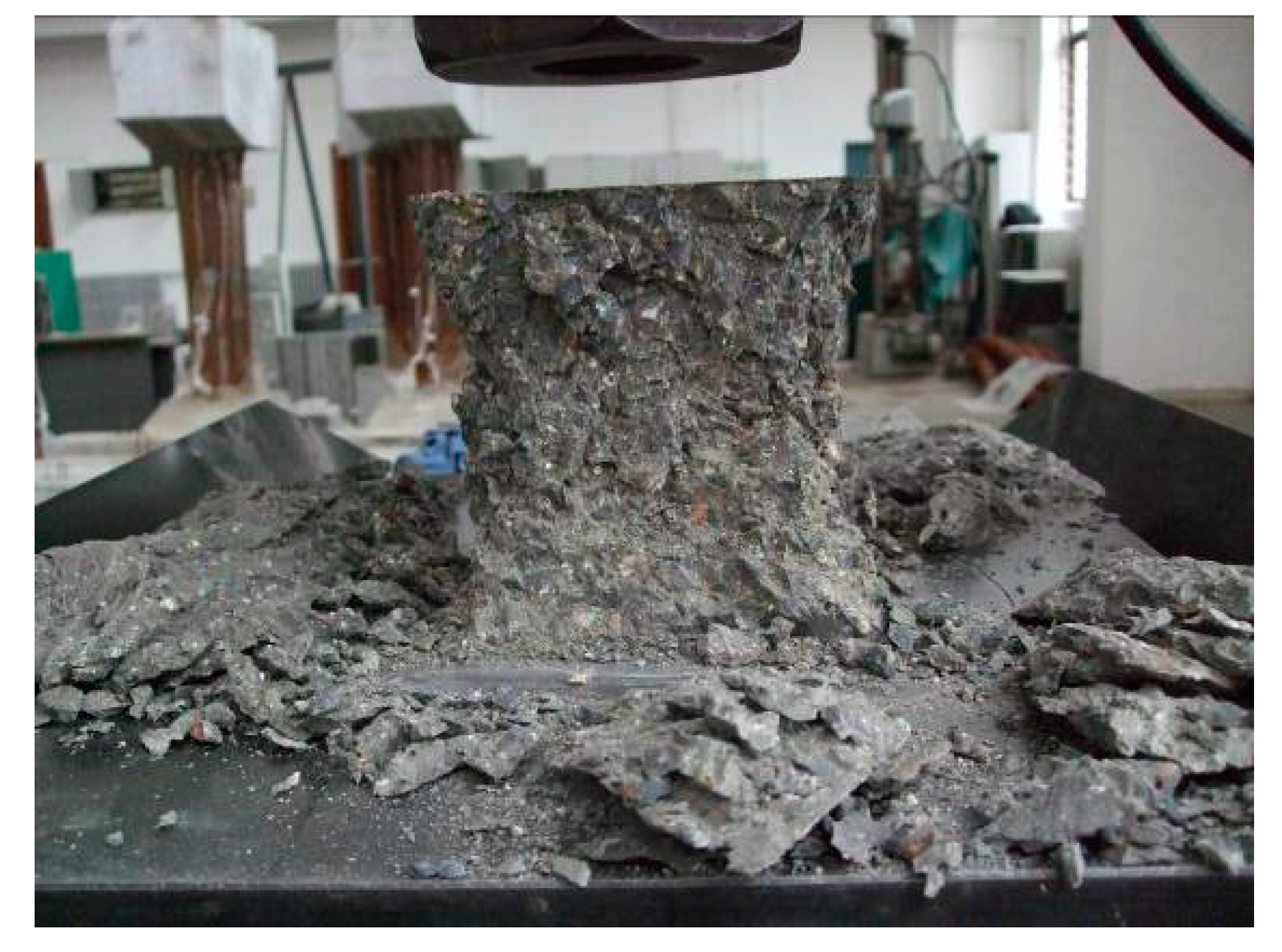
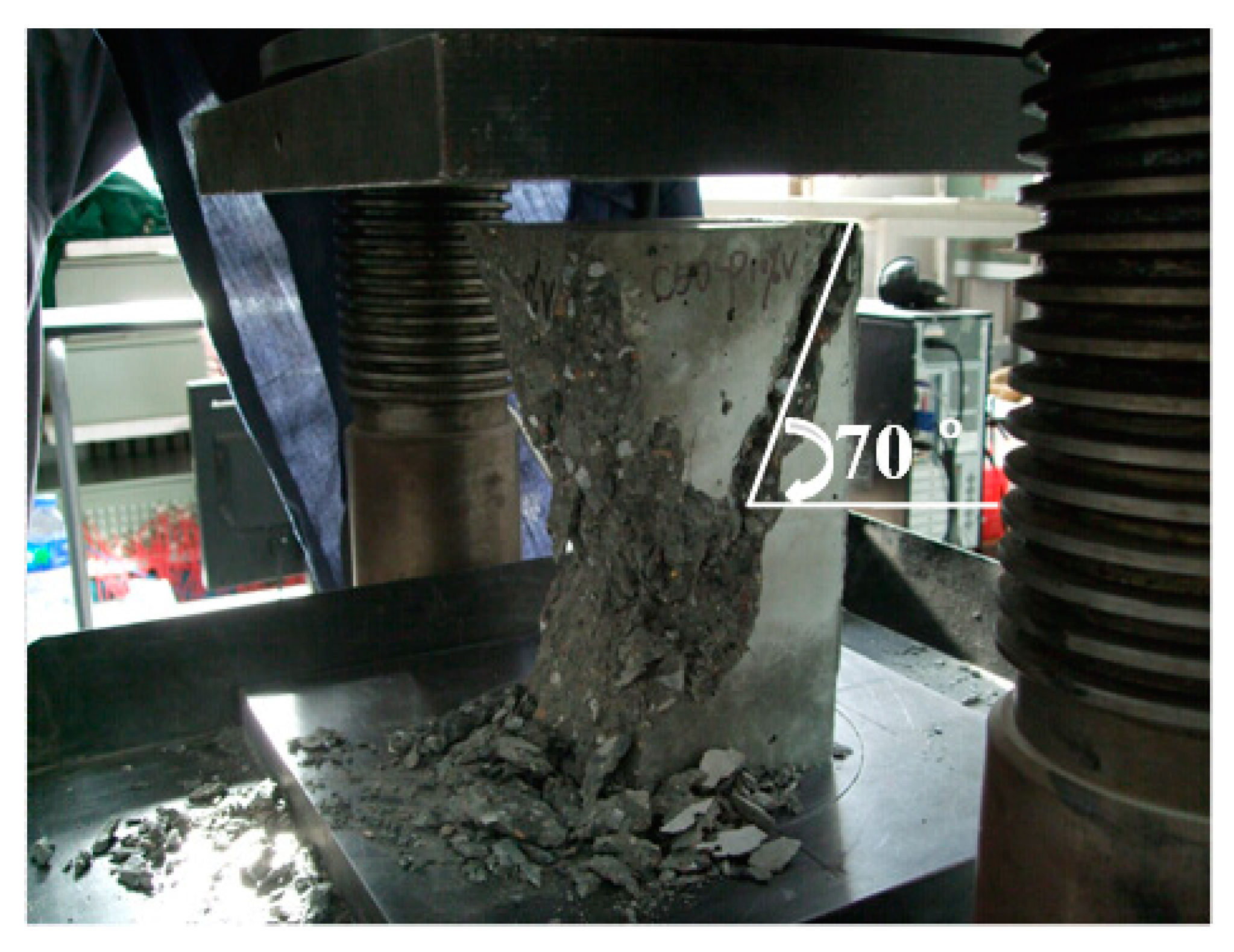
3.2.2. Failure Mode
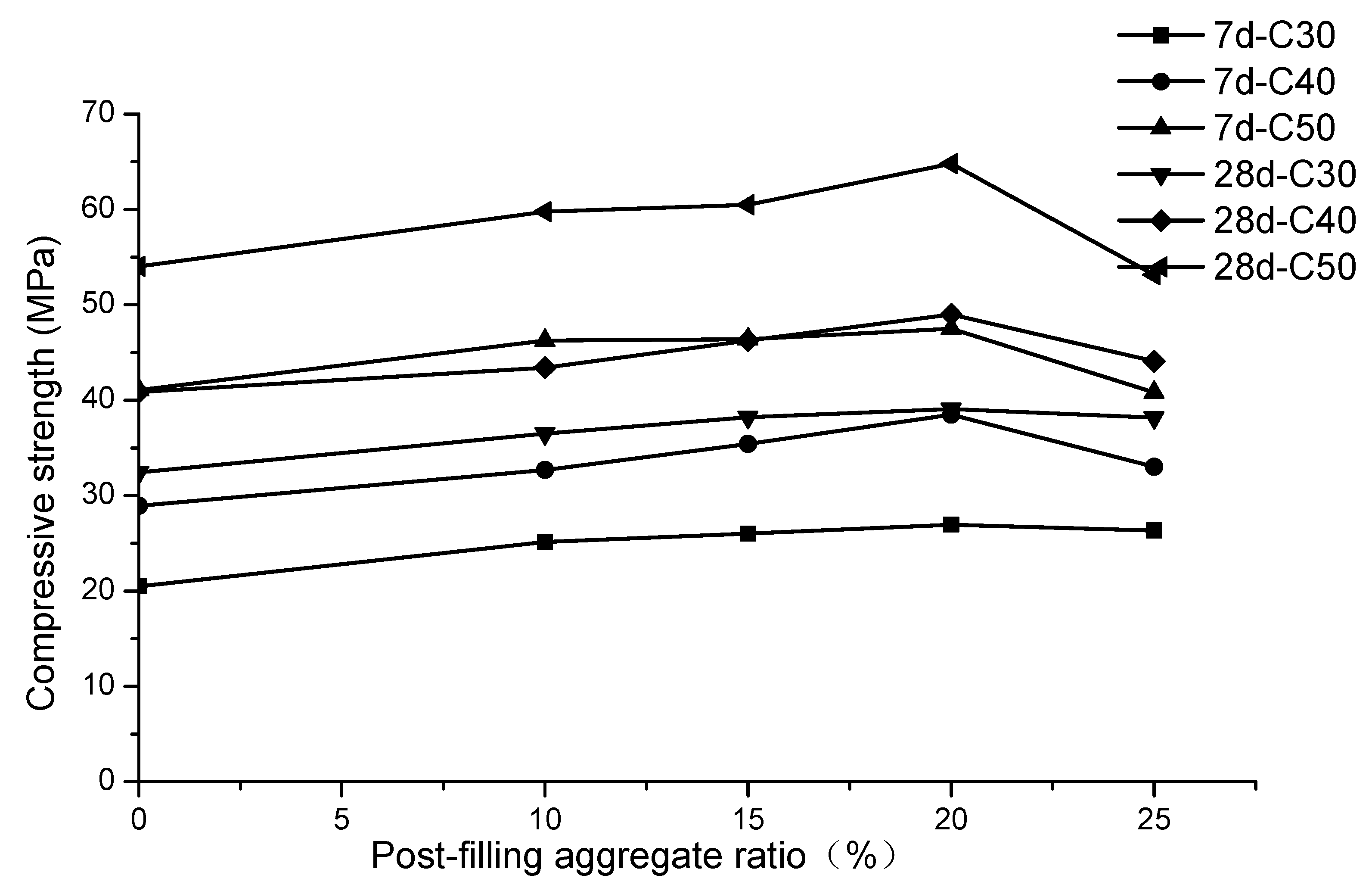
3.2.3. Compressive Strength Results
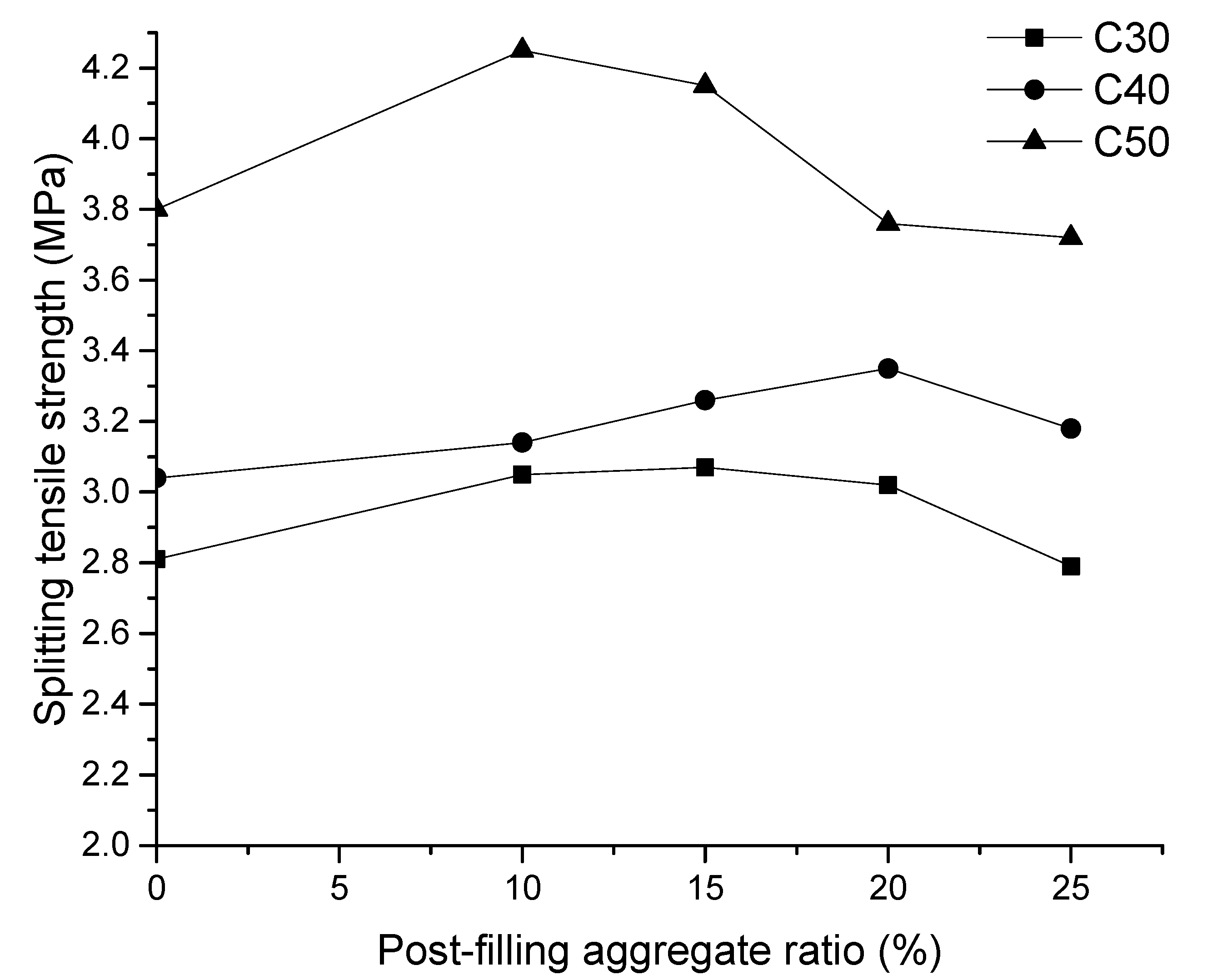
3.3. Splitting Tensile Strength
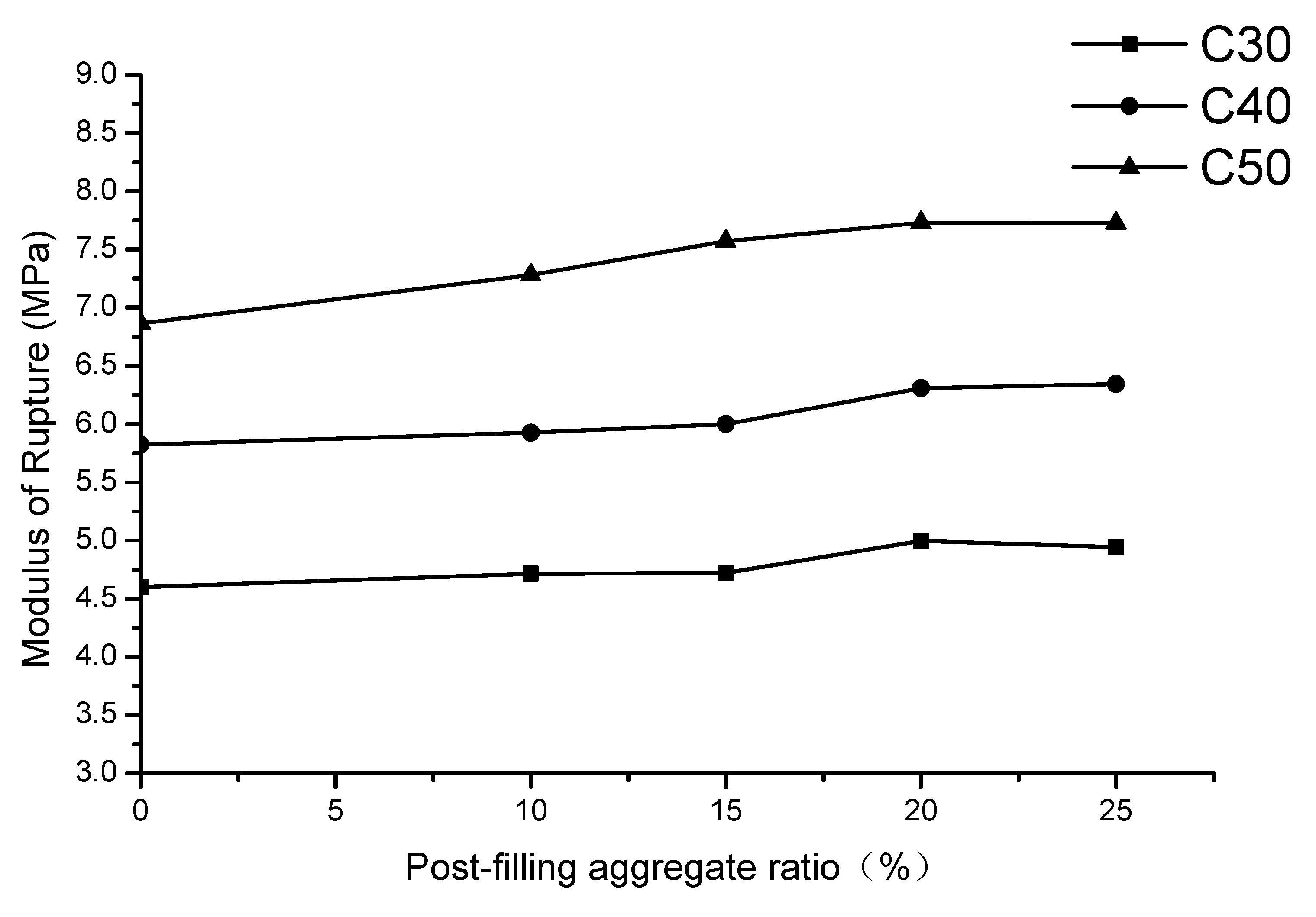
3.4. Modulus of Rupture
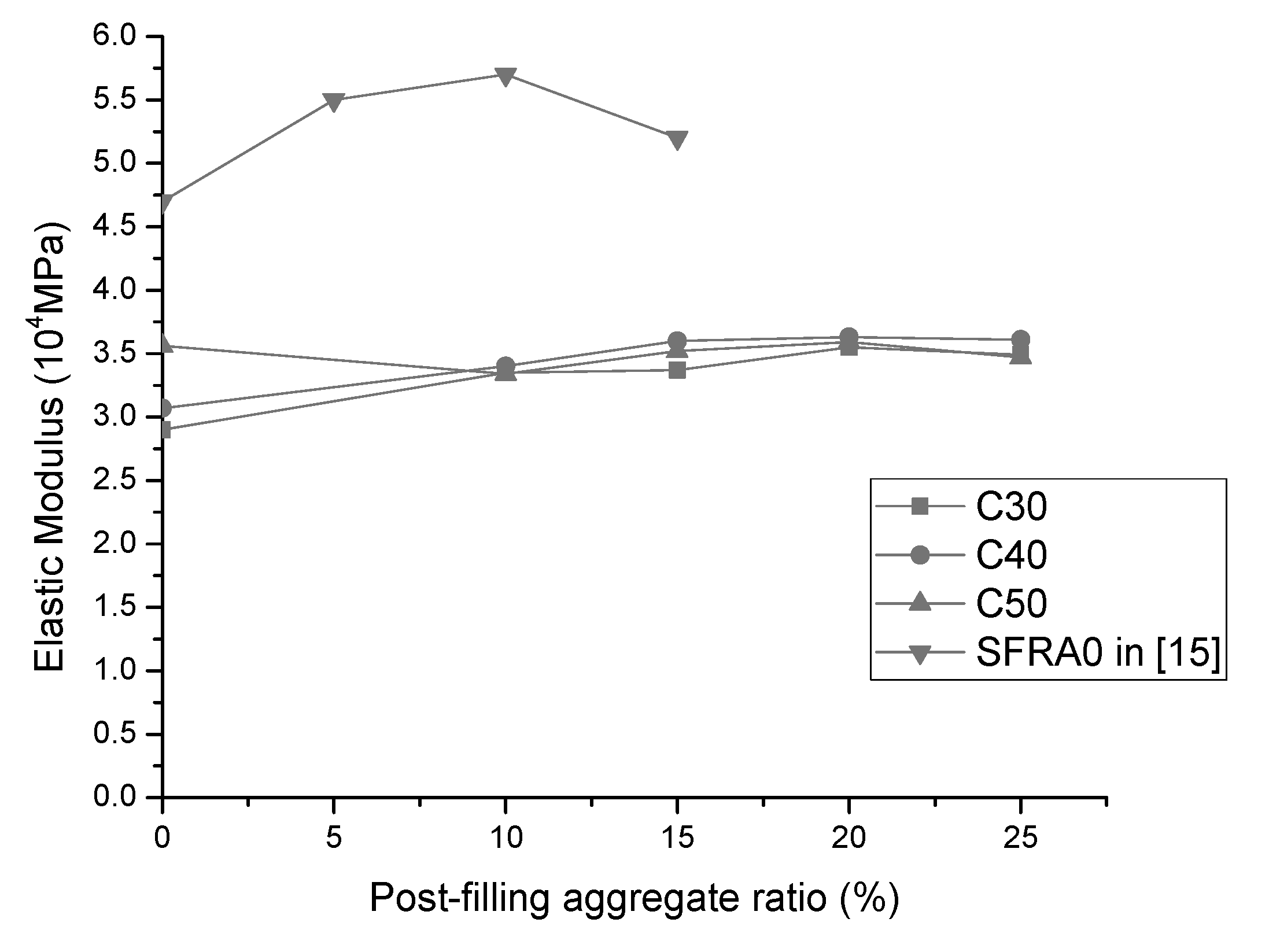
3.5. Modulus of Elasticity
3.6. Axial Compressive Strength of Prism Specimen
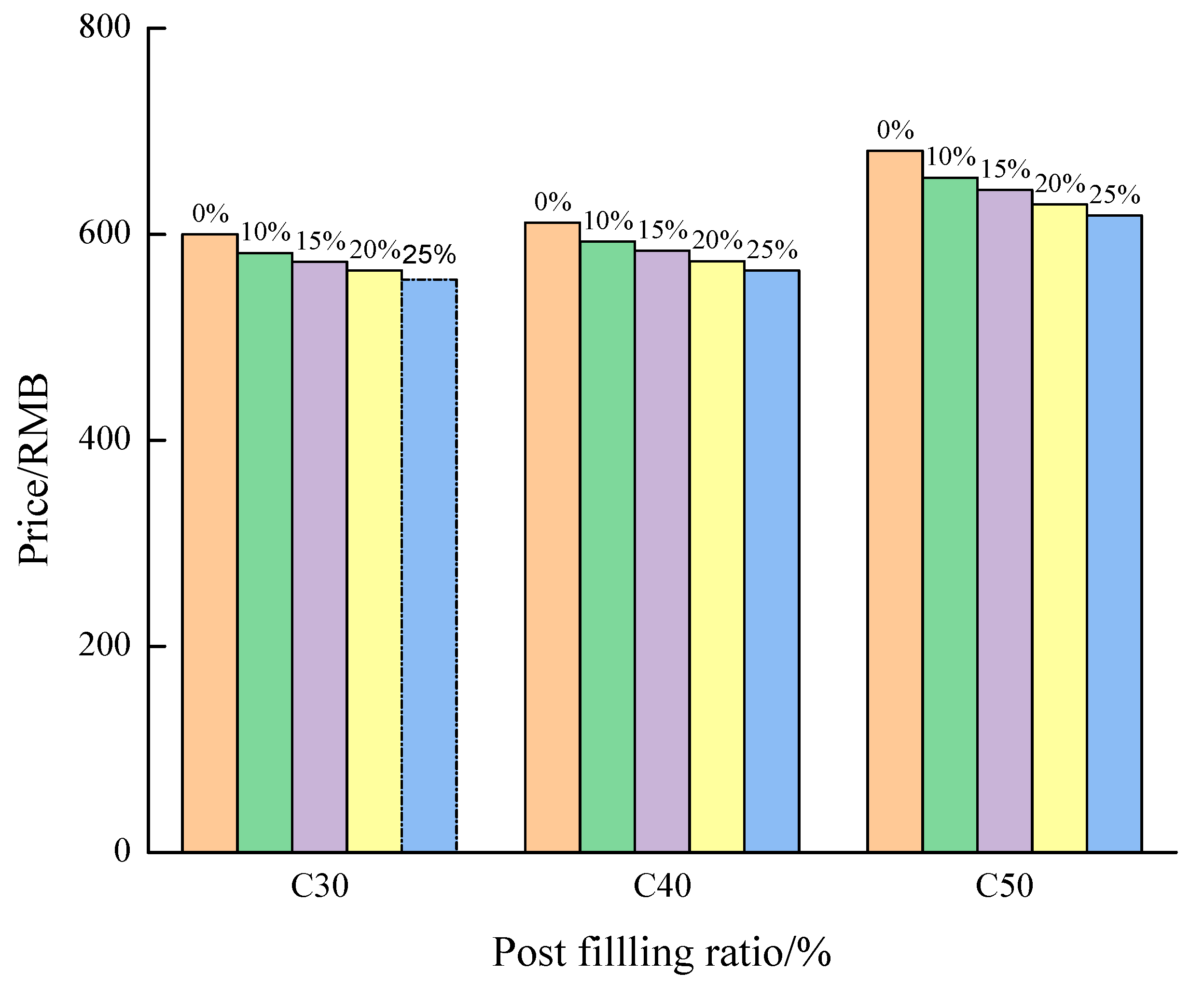
3.7. Economic Cost Analysis of PFCC Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwan, W.H.; Ramli, M.; Kam, K.J.; Sulieman, M.Z. Influence of the amount of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete design and durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Faleschini, F.; Pellegrino, C.; Ricciardi, G. Structural behavior of RC beams containing EAF slag as recycled aggregate: Numerical versus experimental results. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.C.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Barai, S.V. Influence of field recycled coarse aggregate on properties of concrete. Mater. Struct. 2010, 44, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malešev, M.; Radonjanin, V.; Marinković, S. Recycled concrete as aggregate for structural concrete production. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1204–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.-C.; Huang, R.; Hwang, H.; Chao, S.-J. The effects of different fine recycled concrete aggregates on the properties of mortar. Materials 2015, 8, 2658–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E. Prepakt method of concrete repair. J. Proc. 1960, 57, 155–172. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.M.; Fu, G. Introduction of foreign preplaced aggregate concrete. J. China. Foreign. Highw. 2005, 25, 111–114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.M. Sand enveloped with cement – a new type of reinforced concrete. Sci. Tech. Inf. Hehai Univ. 1986, 3, 63–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.Q. Construction Technology of Roller Compacted Concrete Pavement; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khosravani, M.R.; Nasiri, S.; Anders, D.; Weinberg, K. Prediction of dynamic properties of ultra-high performance concrete by an artificial intelligence approach. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2019, 127, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.R.; Wagner, P.; Fröhlich, D.; Weinberg, K. Dynamic fracture investigations of ultra-high performance concrete by spalling tests. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z. Preliminary study the reinforcing mechanism of sand enveloped with cement. China. Concr. Cem. Prod. 1895, 6, 3–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Jin, F.; Zhang, C.H. Experimental research on mechanical behavior of self-compacting rock-fill concrete. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng. 2007, 26, 3232–3236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Dong, R.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Ma, W.; Zha, J. Experimental investigation on aggregate interlocking concrete prepared with scattering–filling coarse aggregate process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2312–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Ji, X.; Ye, Y. Properties of recycled aggregate concrete prepared with scattering-filling coarse aggregate process. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özturan, T.; Çeçen, C. Effect of coarse aggregate type on mechanical properties of concretes with different strengths. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshr, H.; Almusallam, A.; Maslehuddin, M. Effect of coarse aggregate quality on the mechanical properties of high strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2003, 17, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddah, M.S.; Zitouni, S.; Belâabes, S. Effect of content and particle size distribution of coarse aggregate on the compressive strength of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.F.; Hannant, D.J.; Williams, R.I.T.; Hobbs, D.W.; Akman, M.S.; Bartoš, P. Discussion: The effect of aggregate concentration upon the strength and modulus of elasticity of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1980, 32, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counto, U.J. The effect of the elastic modulus of the aggregate on the elastic modulus, creep and creep recovery of concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1964, 16, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, T.J. Modulus of elasticity of concrete affected by elastic moduli of cement paste matrix and aggregate. J. Proc. 1962, 59, 427–451. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemi, M.A.; Karihaloo, B.L. Effect of aggregate volume fraction on the fracture parameters of concrete: A mesomechanical approach. Mag. Concr. Res. 2001, 53, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.G. Preparation and properties of high strength and high performance coarse aggregate interlocking concrete. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 35, 624–628. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.G.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, T.; Abu, D.; Hu, J.Q.; Zhou, M.K. Influence of scattering-filling coarse aggregate on properties of self-compacting concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2009, 12, 345–347. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.G. Effect of scattering-filling aggregate technology on the mechanical properties of concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2007, 10, 711–716. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.G.; Ma, W.; Hao, W.X.; Sun, J.P. Parallel investigation on three kinds of concrete placing process. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2007, 29, 46–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 50081-2002. Standard for Test. Method of Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete; China Architecture and Building Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]







| Water Reduction Efficiency | Matrix | Appearance | Specific Gravity | pH Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30% | Modified polycarboxylate solution | Light brown | 1.06–1.2 | 6–8 |
| Concrete Strength Grade | Cement + Fly Ash + Mineral Powder | Sand | Coarse Aggregate | Water | Water Reducer | Slump (mm) | 7d Compressive Strength (MPa) | 28d Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C30 | 352 + 88 + 0 | 716 | 1074 | 220 | 4.4 | 200 | 21 | 32 |
| 0.8:0.2:0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1% | ||||
| C40 | 352 + 44 + 44 | 716 | 1074 | 202 | 5.72 | 190 | 28 | 41 |
| 0.8:0.1:0.1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.46 | 1.3% | ||||
| C50 | 388 + 97 + 0 | 705 | 1058 | 194 | 7.28 | 200 | 41 | 54 |
| 0.8:0.2:0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.5% |
| Mechanical Property | Dimension |
|---|---|
| Compressive strength for cubic specimen () | 150 mm × 150 mm × 150 mm |
| Compressive strength for prism specimen () | 150 mm × 150 mm × 300 mm |
| Modulus of elasticity () | 150 mm × 150 mm × 300 mm |
| Splitting tensile strength () | 150 mm × 150 mm × 150 mm |
| Modulus of rupture () | 150 mm × 150 mm × 700 mm |
| Concrete Grade | Slump (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-Filling Ratio 0% | Post-Filling Ratio 10% | Post-Filling Ratio 15% | Post-Filling Ratio 20% | Post-Filling Ratio 25% | |
| C30 | 200 | 150 | 145 | 120 | 110 |
| C40 | 190 | 150 | 140 | 90 | 80 |
| C50 | 220 | 170 | 150 | 115 | 90 |
| Concrete Grade | Post-Filling Aggregate Ratio | Compressive Strength (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7d | 28d | ||
| C30 | 0% | 20.5 (1.3) | 32.4 (1.4) |
| 10% | 25.1 (1.1) | 36.5 (1.9) | |
| 15% | 26.0 (1.2) | 38.2 (2.4) | |
| 20% | 26.9 (0.4) | 39.1 (3.6) | |
| 25% | 26.3 (1.5) | 38.2 (4.5) | |
| C40 | 0% | 28.9 (1.3) | 40.9 (0.7) |
| 10% | 32.7 (3.0) | 43.4 (0.3) | |
| 15% | 35.4 (2.0) | 46.3 (0.3) | |
| 20% | 38.5 (2.2) | 49.0 (2.8) | |
| 25% | 33.0 (1.6) | 44.1 (0.2) | |
| C50 | 0% | 41.1 (0.4) | 54.0 (2.8) |
| 10% | 46.3 (1.0) | 59.7 (3.1) | |
| 15% | 46.4 (1.7) | 60.5 (0.8) | |
| 20% | 47.5 (0.2) | 64.8 (0.7) | |
| 25% | 40.8 (1.1) | 53.1 (3.1) | |
| Concrete Strength Grade | PFA Ratio | Modulus of Rupture (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| C30 | 0% | 4.60 (0.14) |
| 10% | 4.71 (0.46) | |
| 15% | 4.72 (0.31) | |
| 20% | 5.00 (1.34) | |
| 25% | 4.94 (1.47) | |
| C40 | 0% | 5.82 (0.12) |
| 10% | 5.93 (0.16) | |
| 15% | 6.00 (0.31) | |
| 20% | 6.31 (0.44) | |
| 25% | 6.34 (0.22) | |
| C50 | 0% | 6.87 (0.04) |
| 10% | 7.28 (0.46) | |
| 15% | 7.57 (0.39) | |
| 20% | 7.73 (0.18) | |
| 25% | 7.72 (0.95) |
| Concrete Strength | PFA Ratio | Average of Axial Compressive Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| C30 | 0% | 28.5 (3.7) |
| 10% | 31.9 (2.4) | |
| 15% | 30.8 (2.1) | |
| 20% | 29.2 (0.7) | |
| 25% | 29.9 (1.7) | |
| C40 | 0% | 33.7 (1.1) |
| 10% | 36.4 (0.7) | |
| 15% | 38.2 (0.3) | |
| 20% | 36.0 (1.8) | |
| 25% | 34.0 (1.1) | |
| C50 | 0% | 42.7 (4.0) |
| 10% | 45.8 (2.1) | |
| 15% | 47.4 (0.3) | |
| 20% | 49.7 (2.5) | |
| 25% | 49.0 (2.0) |
| Material | Cement | Fly Ash | CA | FA | Water | WR | Cost (RMB)/m3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Price/(RMB·kg−1) | 0.55 | 0.4 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.0025 | 15 | ||
| Reference concrete | Proportion | 352 | 88 | 1074 | 716 | 220 | 4.4 | 599.65 |
| cost | 193.6 | 35.2 | 182.58 | 121.72 | 0.55 | 66 | ||
| PFCC 10% | Proportion | 316.8 | 79.2 | 1216.6 | 644.4 | 198 | 3.96 | 582.19 |
| cost | 174.24 | 31.68 | 206.82 | 109.55 | 0.495 | 59.4 | ||
| PFCC 15% | Proportion | 299.2 | 74.8 | 1287.9 | 608.6 | 187 | 3.74 | 573.45 |
| cost | 164.56 | 29.92 | 218.94 | 103.46 | 0.468 | 56.1 | ||
| PFCC 20% | Proportion | 281.6 | 70.4 | 1359.2 | 572.8 | 176 | 3.52 | 564.72 |
| cost | 154.88 | 28.16 | 231.06 | 97.38 | 0.44 | 52.8 | ||
| PFCC 25% | Proportion | 264 | 66 | 1430.5 | 537 | 165 | 3.3 | 555.99 |
| cost | 145.2 | 26.4 | 243.19 | 91.29 | 0.41 | 49.5 | ||
| Material | Cement | Fly Ash | Mineral Powder | CA | FA | Water | WR | Cost (RMB)/m3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Price/(RMB·kg−1) | 0.55 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.0025 | 15 | ||
| Reference concrete | Proportion | 352 | 44 | 44 | 1074 | 716 | 202 | 5.72 | 611.49 |
| Cost | 193.6 | 5.28 | 22 | 182.58 | 121.72 | 0.51 | 85.8 | ||
| PFCC 10% | Proportion | 316.8 | 39.6 | 39.6 | 1216.6 | 644.4 | 181.8 | 5.15 | 592.82 |
| Cost | 174.2 | 4.75 | 19.8 | 206.82 | 109.55 | 0.45 | 77.25 | ||
| PFCC 15% | Proportion | 299.2 | 37.4 | 37.4 | 1287.9 | 608.6 | 171.7 | 4.86 | 583.52 |
| Cost | 164.6 | 4.49 | 18.7 | 218.94 | 103.46 | 0.43 | 72.9 | ||
| PFCC 20% | Quantity | 281.6 | 35.2 | 35.2 | 1359.2 | 572.8 | 161.6 | 4.58 | 574.26 |
| Cost | 154.9 | 4.22 | 17.6 | 231.06 | 97.38 | 0.4 | 68.7 | ||
| PFCC 25% | Proportion | 264 | 33 | 33 | 1430.5 | 537 | 151.5 | 4.29 | 564.87 |
| Cost | 145.2 | 3.96 | 16.5 | 243.19 | 91.29 | 0.38 | 64.35 | ||
| Material | Cement | Fly Ash | CA | FA | Water | WR | Cost (RMB)/m3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price/(RMB·kg−1) | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.0025 | 15 | ||
| Reference concrete | Quantity | 388 | 97 | 1058 | 705 | 194 | 7.275 | 680.93 |
| Cost | 232.8 | 38.8 | 179.86 | 119.85 | 0.49 | 109.13 | ||
| PFCC 10% | Quantity | 349.2 | 87.3 | 1202.2 | 634.5 | 174.6 | 6.5 | 654.62 |
| Cost | 209.52 | 34.92 | 204.37 | 107.87 | 0.44 | 97.5 | ||
| PFCC 15% | Quantity | 329.8 | 82.5 | 1274.3 | 599.3 | 164.9 | 6.2 | 642.80 |
| Cost | 197.88 | 33 | 216.63 | 101.88 | 0.41 | 93 | ||
| PFCC 20% | Quantity | 310.4 | 77.6 | 1346.4 | 564 | 155.2 | 5.8 | 629.44 |
| Cost | 186.24 | 31.04 | 228.89 | 95.88 | 0.39 | 87 | ||
| PFCC 25% | Quantity | 291 | 72.8 | 1418.5 | 528.8 | 145.5 | 5.5 | 617.63 |
| Cost | 174.6 | 29.12 | 241.15 | 89.90 | 0.36 | 82.5 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, J.; Cao, Q.; Luan, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Mechanical Properties of Large Slump Concrete Made by Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Mixing Procedure. Materials 2020, 13, 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122761
Jia J, Cao Q, Luan L, Wang Z, Zhang L. Mechanical Properties of Large Slump Concrete Made by Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Mixing Procedure. Materials. 2020; 13(12):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122761
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Jinqing, Qi Cao, Lan Luan, Ziyi Wang, and Lihua Zhang. 2020. "Mechanical Properties of Large Slump Concrete Made by Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Mixing Procedure" Materials 13, no. 12: 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122761
APA StyleJia, J., Cao, Q., Luan, L., Wang, Z., & Zhang, L. (2020). Mechanical Properties of Large Slump Concrete Made by Post-Filling Coarse Aggregate Mixing Procedure. Materials, 13(12), 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13122761





