Nugget Formation and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction Stir Welds of Three Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Cycles in the Welds
3.2. Morphology of the Welds
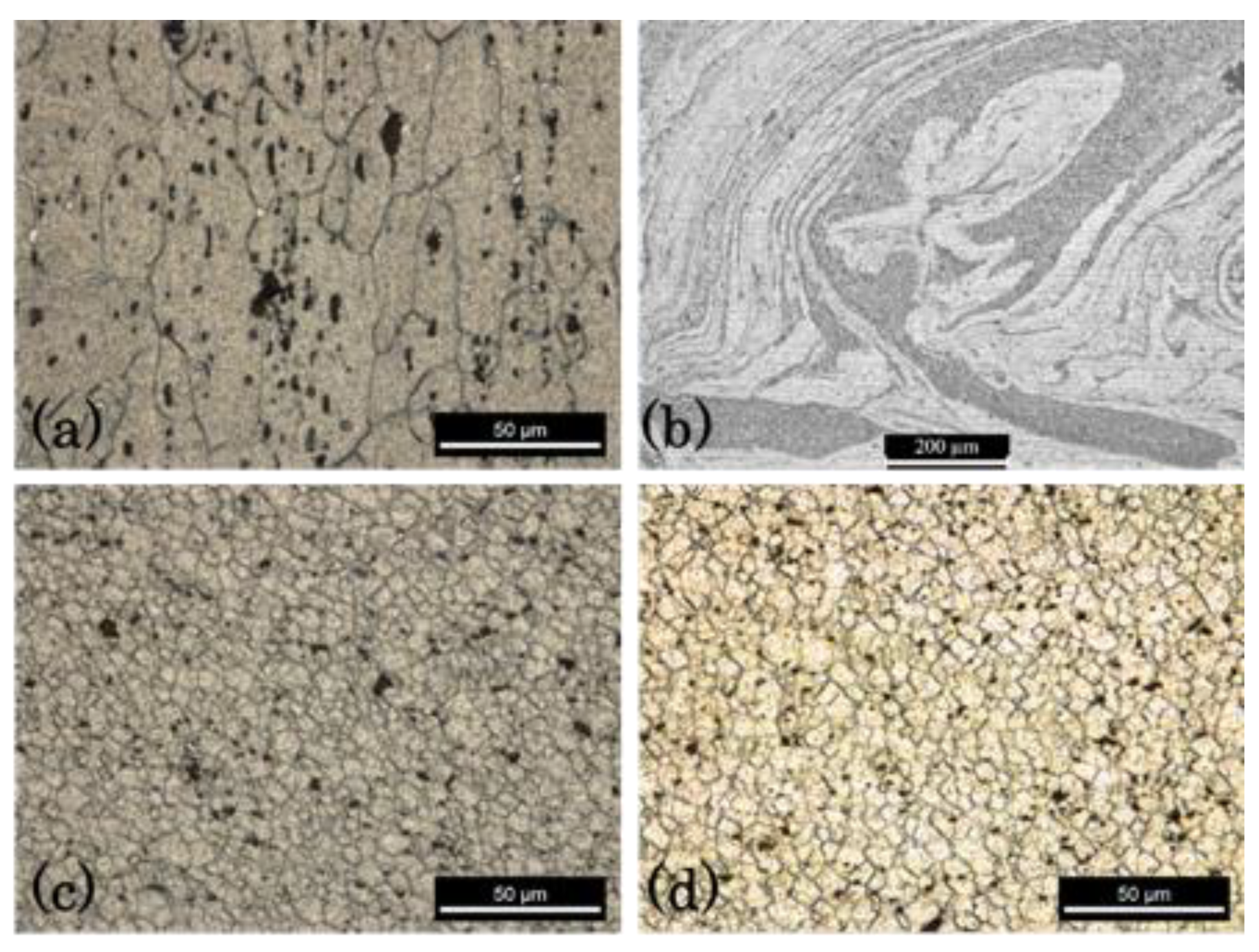
3.3. Microstructure
3.4. Hardness and Tensile Behavior
3.5. Fatigue Strength
4. Conclusions
- It is feasible to achieve good quality FSWs with fillets between three dissimilar aluminum alloys.
- The nugget formation of FS welds between three dissimilar aluminum alloys is greatly influenced by the welding speed, mechanical properties, and location of the alloys, either on the advancing or retreating sides.
- A very low tool rotational to welding speed ratio (w/v) leads to the formation of welding defects.
- The weld nugget has a large dispersion of grain sizes, but the welding speed does not affect the grain size in the nugget.
- Increasing the welding speed increases the static and fatigue resistance of the welded joints.
- Placing the more resistant alloy (AA2017) on the advancing side rather than on the retreating side generates higher local weld temperature and provides stronger joints and with better fatigue behavior.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burcu, E.; Kumruoglu, L.C. 5083 type Al-Mg and 6082 type Al-Mg-Si alloys for ship building. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2015, 4, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, K.; Squillacioti, R.; Cheeseman, B.; Placzankis, B.; Gallardy, D. Expanding the Availability of Lightweight Aluminum Alloy Armor Plate Procured from Detailed Military Specifications. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Aluminum Alloys, Pittsburgh, Russia, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Fujii, H.; Tsumura, T.; Komazaki, T.; Nakata, K. Three defect types in friction stir welding of aluminum die casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 415, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Ishak, M.; Rejab, M.R.M. Effect of pin tool flute radius on the material flow and tensile properties of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, L.; Buffa, G.; Shivpuri, R. Influence of material characteristics on plastomechanics of the FSW process for T-joints. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, T.; Das, H.; Pal, T. Influence of welding parameters on material flow, mechanical property and intermetallic characterization of friction stir welded AA6063 to HCP copper dissimilar butt joint without offset. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2833–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-W.; Liu, H.; Fujii, H. Dissimilar friction stir welding of pure Ti and pure Al. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 730, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.; Arruti, E.; Janeiro, G.; Aldanondo, E.; Alvarez, P.; Echeverria, A. Material flow and mechanical behaviour of dissimilar AA2024-T3 and AA7075-T6 aluminium alloys friction stir welds. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinaharan, I.; Kalaiselvan, K.; Vijay, S.J.; Raja, P. Effect of material location and tool rotational speed on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded aluminum alloys. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2012, 12, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbini, A.; Carstensen, J.; Dos Santos, J.F. Influence of Alloys Position, Rolling and Welding Directions on Properties of AA2024/AA7050 Dissimilar Butt Weld Obtained by Friction Stir Welding. Metals 2018, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabandi, H.K.; Jashnani, H.R.; Paidar, M. Effect of precipitation hardening heat treatment on mechanical and microstructure features of dissimilar friction stir welded AA2024-T6 and AA6061-T6 alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel, N.; Silva, C.; Da Costa, J.M.D.; Loureiro, A. Friction stir welding of T-joints in dissimilar materials: Influence of tool geometry and materials properties. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boșneag, A.; Constantin, M.A.; Nitu, E.; Iordache, M. Friction Stir Welding of three dissimilar aluminium alloy: AA2024, AA6061 and AA7075. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 400, 022013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boşneag, A.; Constantin, M.A.; Nitu, E.L.; Iordache, M. Friction Stir Welding of three dissimilar aluminium alloy used in aeronautics industry. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 252, 12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnar, B.; Kazeminezhad, M.; Kokabi, A. Effects of heat input in friction stir welding on microstructure and mechanical properties of AA3003-H18 plates. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. E8/E8M—13a—Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Al-Ahmari, A.; Abidi, M.H. Analysis of defects in clean fabrication process of friction stir welding. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aval, H.J.; Serajzadeh, S.; Kokabi, A.H.; Loureiro, A. Effect of tool geometry on mechanical and microstructural behaviours in dissimilar friction stir welding of AA 5086–AA 6061. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Roy, G.G.; Debroy, T. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional heat transfer and plastic flow during friction stir welding. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.; Janeiro, G.; Da Silva, A.A.M.; Aldanondo, E.; Echeverria, A. Material flow and mixing patterns during dissimilar FSW. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.-J.; Yun, J.-G.; Kang, C.-Y. Formation mechanism of typical onion ring structures and void defects in friction stir lap welded dissimilar aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Lai, J.; Chen, X.-G. Microstructural Evolution and Dynamic Softening Mechanisms of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy during Hot Compressive Deformation. Materials 2014, 7, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Deng, B.; Liu, A.; Li, L. Dynamic Mechanical Behavior and Microstructure Evolution of an Extruded 6013-T4 Alloy at Elevated Temperatures. Metals 2019, 9, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Krajewski, P.; Briant, C.L. Dynamic Recrystallization of AA5083 at 450 °C: The Effects of Strain Rate and Particle Size. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, M.; Sun, Y.; Fujii, H.; Ma, N.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ahmed, S.; Chintapenta, V.; Murakawa, H. Deformation characteristics and microstructural evolution in friction stir welding of thick 5083 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, C.; Louro, R.; Rodrigues, D. Analysis of high temperature plastic behaviour and its relation with weldability in friction stir welding for aluminium alloys AA5083-H111 and AA6082-T6. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemba-Rec, I.; Kopyściański, M.; Miara, D.; Krasnowski, K. Effect of process parameters on mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar 7075-T651 and 5083-H111 aluminum alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 2767–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Ataia, S.; Seleman, M.E.-S.; Ammar, H.; Ahmed, E. Friction stir welding of similar and dissimilar AA7075 and AA5083. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 242, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Li, H.; Sun, D.; Gong, W.; Liu, J. Effects of welding speed on the microstructure and hardness in friction stir welding joints of 6005A-T6 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, M. Influence of welding speed on the fatigue of friction stir welds, and comparison with MIG and TIG. Int. J. Fatigue 2003, 25, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, V.I.; Ioda, E.N.; Skupov, A.A.; Panteleev, M.D.; Ovchinnikov, V.V.; Malov, D.V. Effect of the surface roughness of friction stir welded joints on the fatigue characteristics of welded joints in V-1461 and V-1469 aluminium–lithium alloys. Weld. Int. 2017, 31, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Alloy | Cu | Mg | Mn | Si | Cr | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA2017-T4 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | ≤0.1 | Bal. |
| AA5083-H111 | 0.025 | 4.5 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 0.25 | Bal. |
| AA6082-T6 | 0.09 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.53 | <0.25 | Bal. |
| Properties | AA2017-T4 | AA5083-H111 | AA6082-T6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | 416.8 ± 3 | 317.5 ± 5.8 | 344.6 ± 5.7 |
| Tensile Yield Strength (MPa) | 293 ± 9.2 | 145 ± 4.1 | 286 ± 13.4 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 18 ± 3.9 | 22.7 ± 1.4 | 18.4 ± 1.6 |
| Vickers Hardness (HV0.2) | 116.7 ± 4.2 | 82.3 ± 1.4 | 115 ± 0.8 |
| Material Position | Series | V (mm/min) | w/v (r/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 562 | 562-30 | 30 | 16.7 |
| 562-120 | 120 | 4.2 | |
| 562-280 | 280 | 1.8 | |
| 265 | 265-30 | 30 | 16.7 |
| 265-120 | 120 | 4.2 | |
| 265-230 | 230 | 2.2 |
| Welds Series | Zone | Mg | Si | Cu | Material Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 562-30 | Z1 | 0.66 | 0.45 | 1.75 | 2017 |
| Z2 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.14 | 2017/5083/6082 | |
| Z3 | 2.3 | 0.57 | 0.4 | 2017/5083/6082 | |
| Z4 | 3.32 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 5083/2017 | |
| Z5 | 4.85 | … | … | 5083 | |
| Z6 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.4 | 2017/6082 | |
| Z7 | 1.29 | 0.51 | 0.6 | 2017/5083/6082 | |
| 265-30 | Z1 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0 | 6082 |
| Z2 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 4.7 | 2017/5083/6082 | |
| Z3 | 1.2 | … | 3 | 2017/5083 | |
| Z4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2017/6082 |
| Weld Series | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Efficiency (%) | Strain (%) | Fracture Zone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 562 | 562-30 | 273.3 ± 0.5 | 86.0 | 10.6 ± 1.8 | HAZ |
| 562-120 | 277.4 ± 0.4 | 87.4 | 8.3 ± 2.6 | HAZ | |
| 265 | 265-30 | 271.7 ± 0.4 | 85.6 | 8.9 ± 0.4 | HAZ |
| 265-120 | 296.2 ± 4.2 | 93.3 | 8.2 ± 2.5 | HAZ | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manuel, N.; Galvão, I.; Leal, R.M.; Costa, J.D.; Loureiro, A. Nugget Formation and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction Stir Welds of Three Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. Materials 2020, 13, 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112664
Manuel N, Galvão I, Leal RM, Costa JD, Loureiro A. Nugget Formation and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction Stir Welds of Three Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. Materials. 2020; 13(11):2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112664
Chicago/Turabian StyleManuel, Neves, Ivan Galvão, Rui M. Leal, José D. Costa, and Altino Loureiro. 2020. "Nugget Formation and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction Stir Welds of Three Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys" Materials 13, no. 11: 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112664
APA StyleManuel, N., Galvão, I., Leal, R. M., Costa, J. D., & Loureiro, A. (2020). Nugget Formation and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction Stir Welds of Three Dissimilar Aluminum Alloys. Materials, 13(11), 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112664







