Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
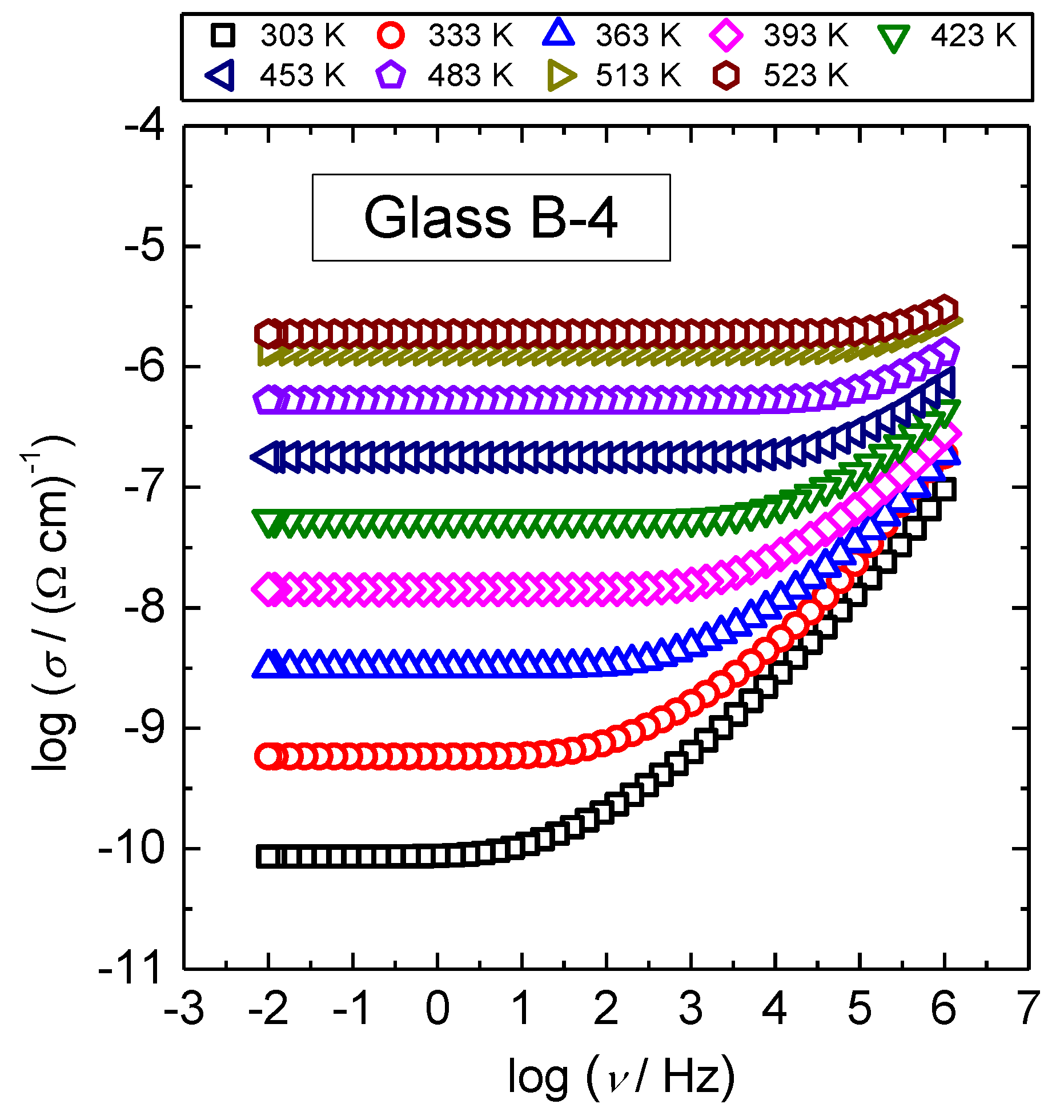
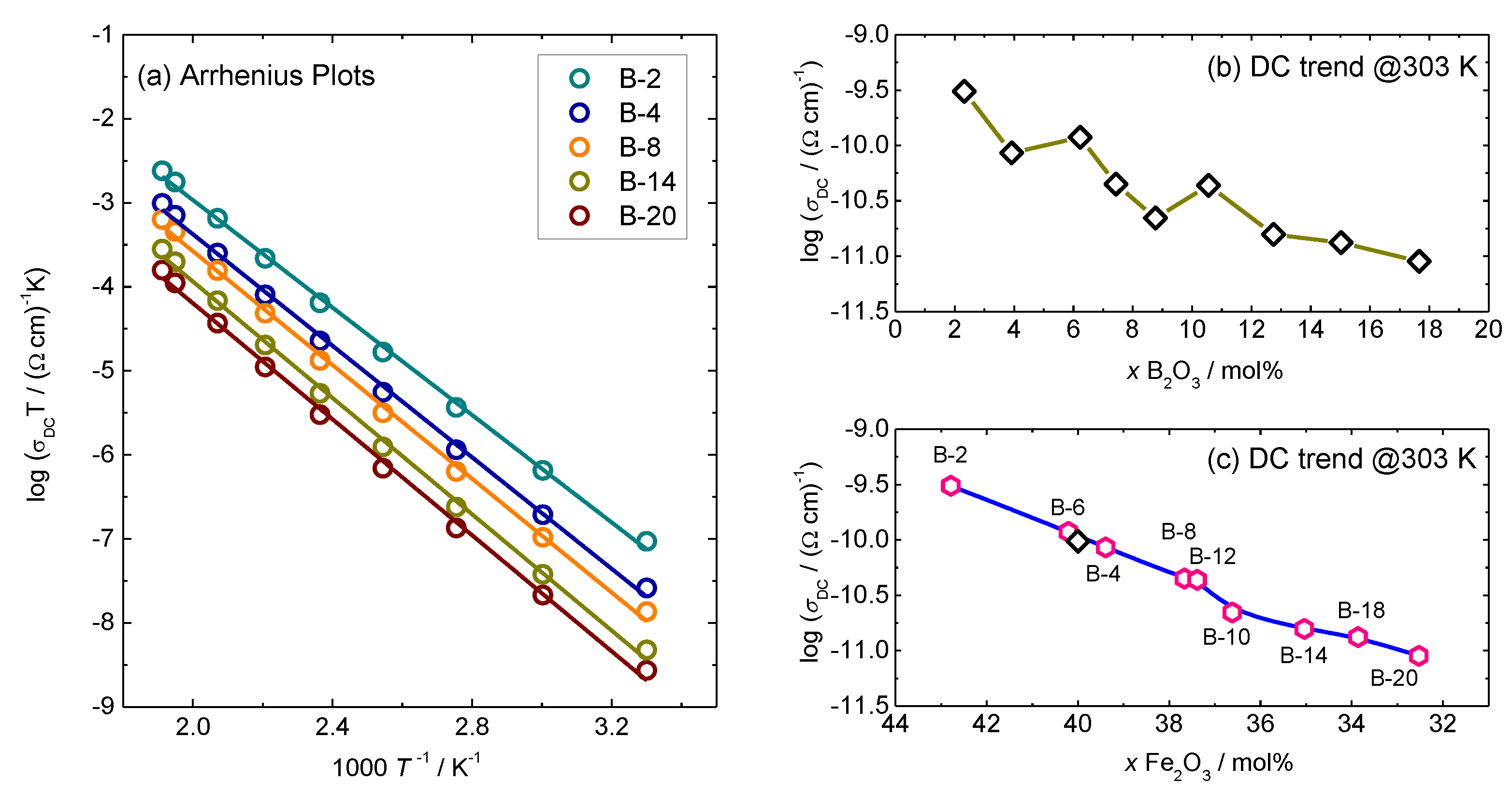
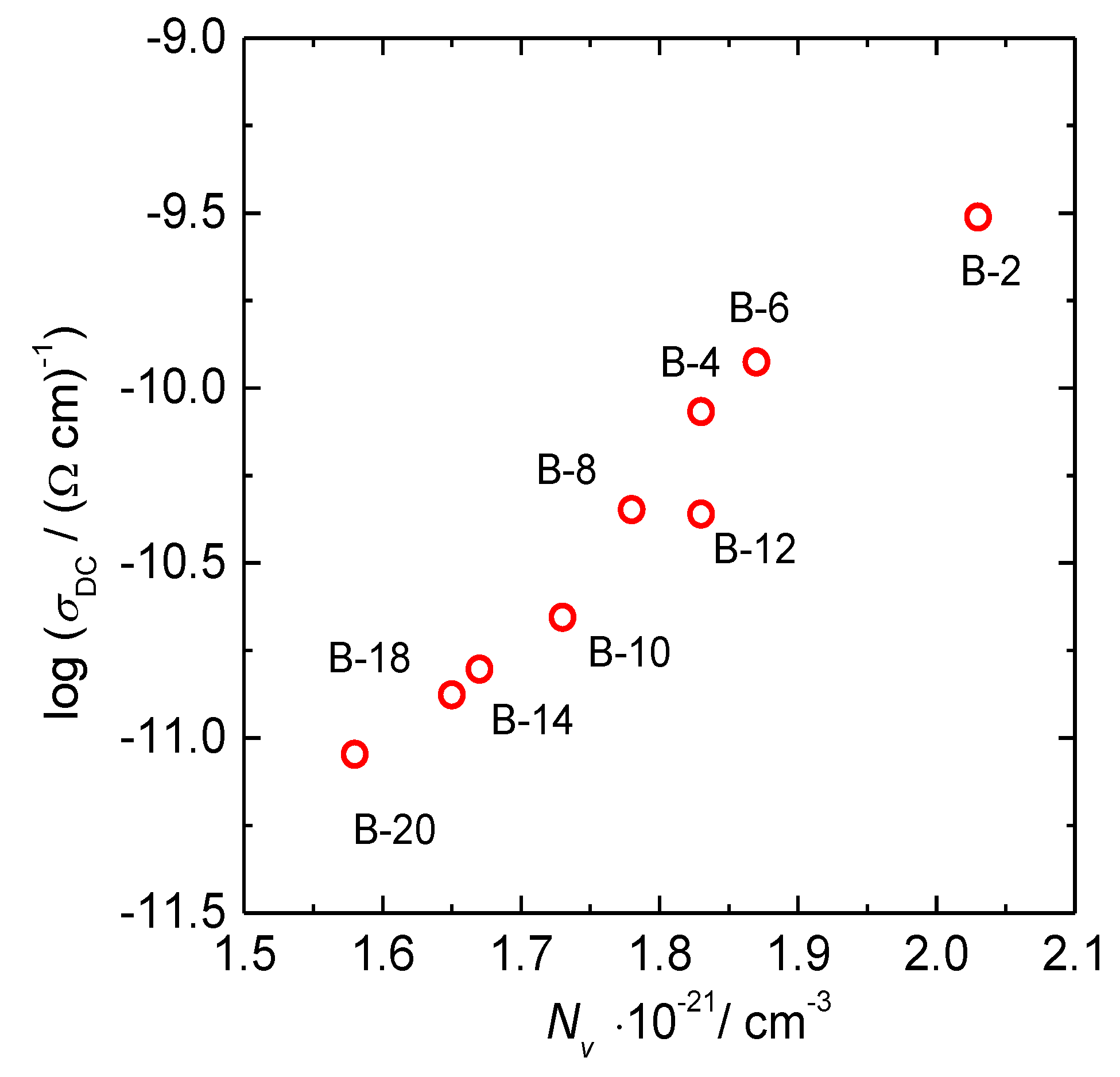
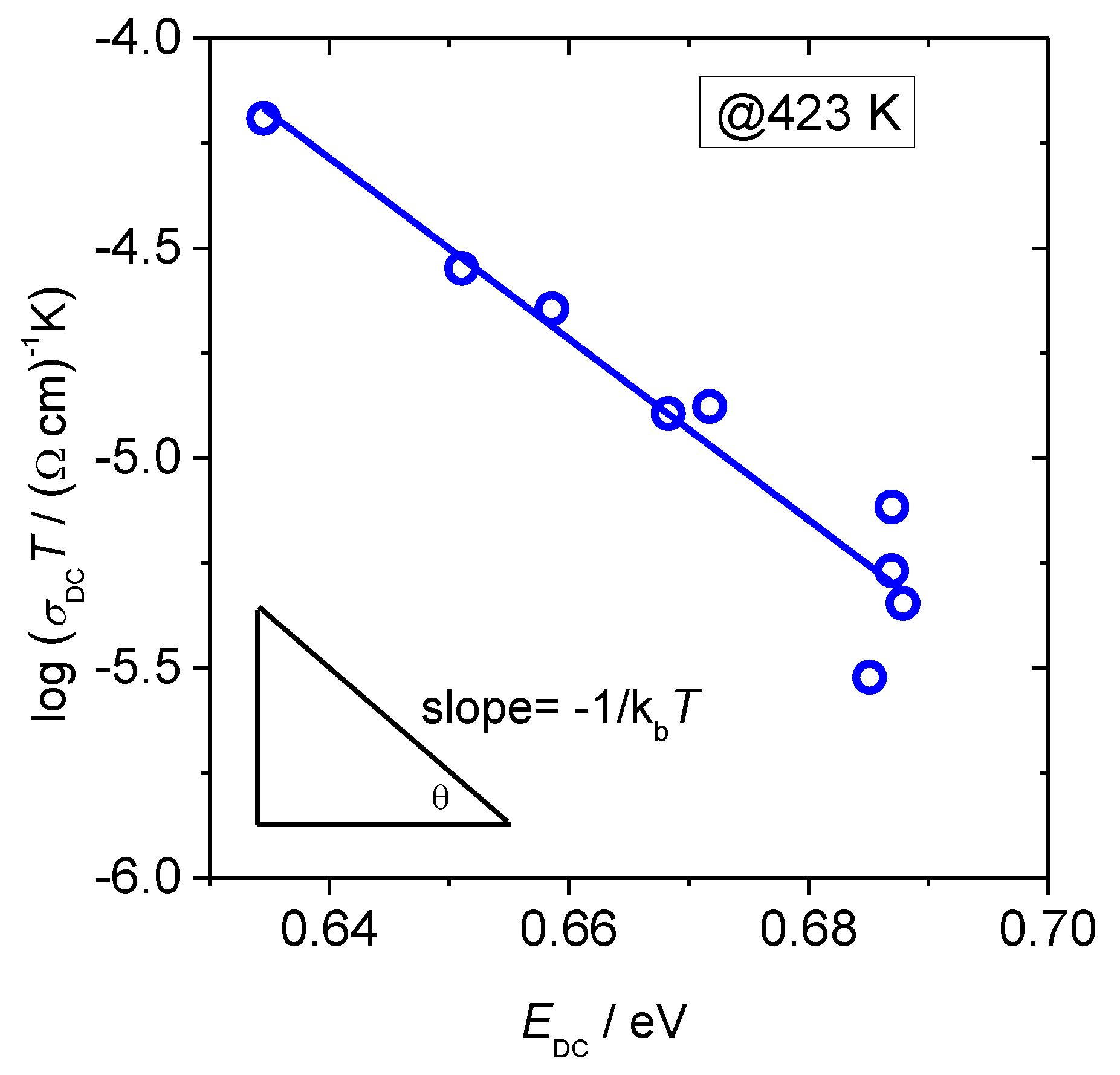
3.1. DC Conductivity
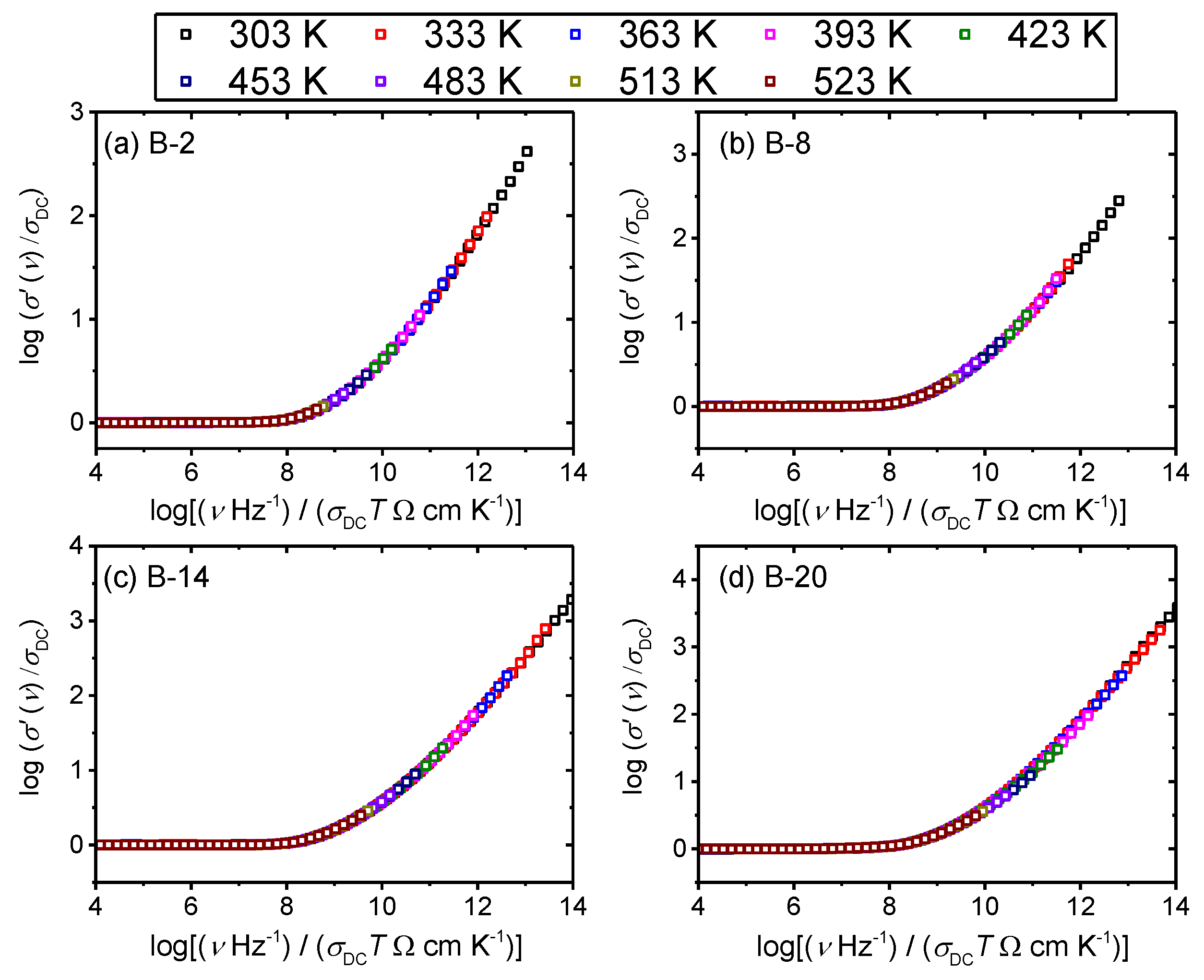
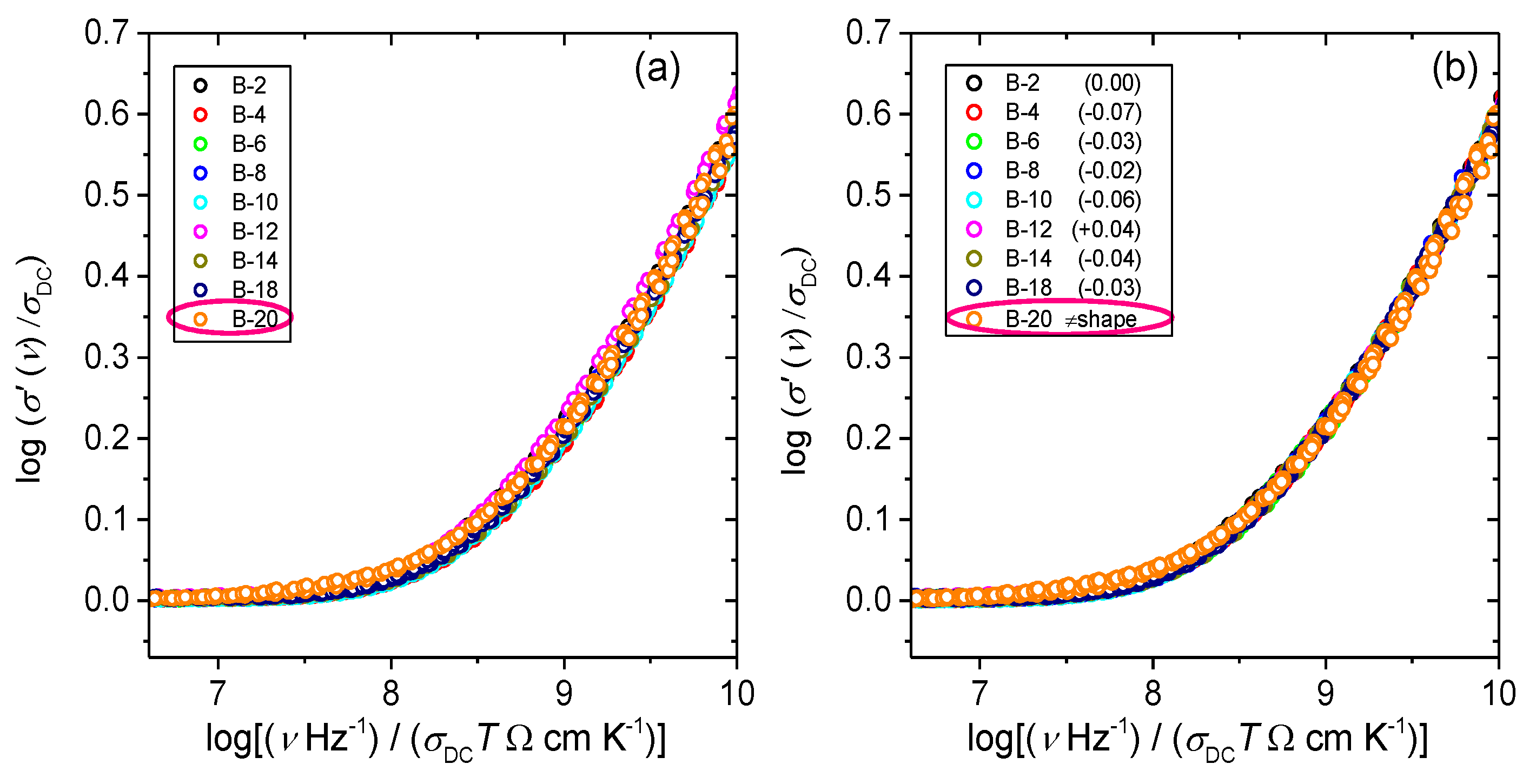
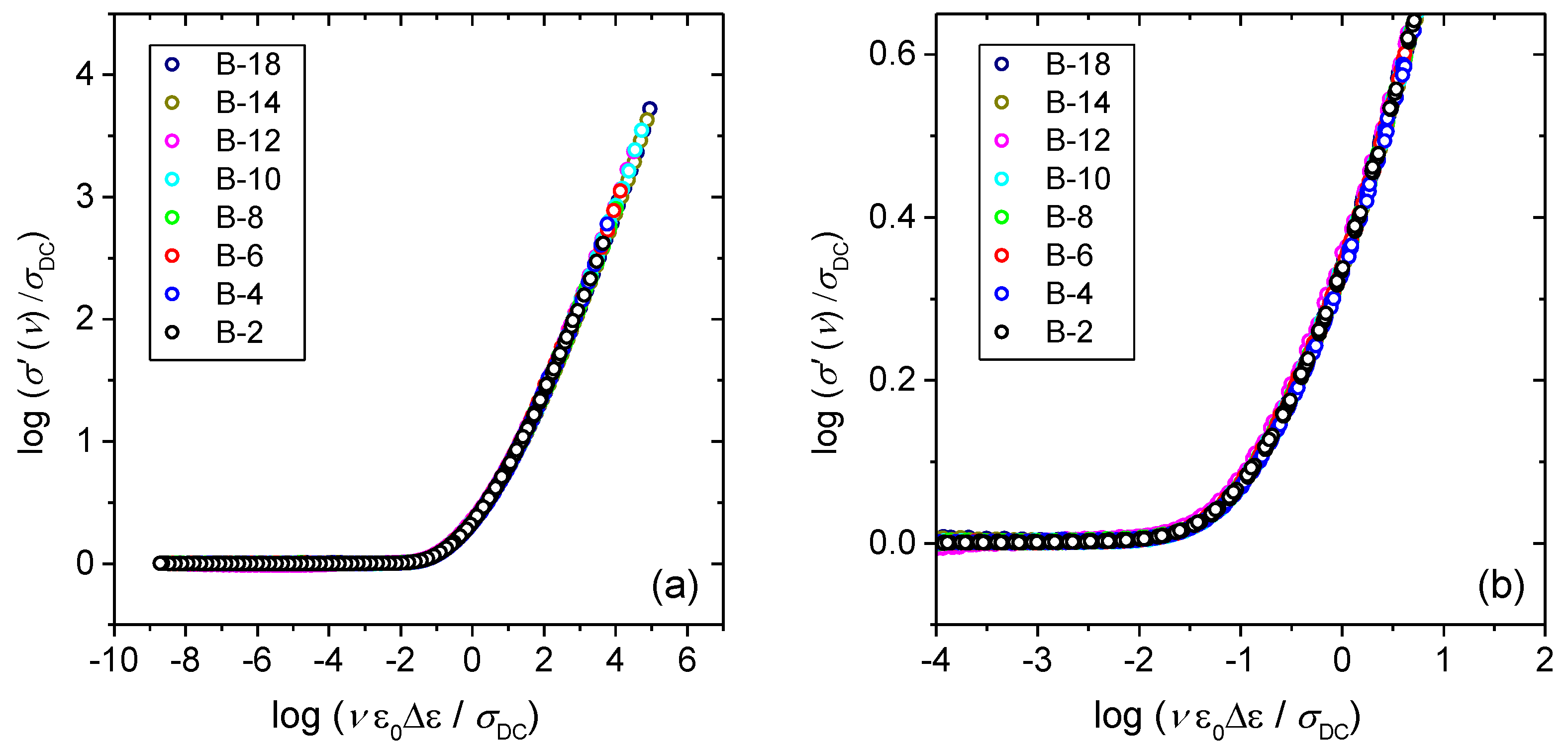
3.2. Frequency-Dependent Conductivity and Scaling Properties
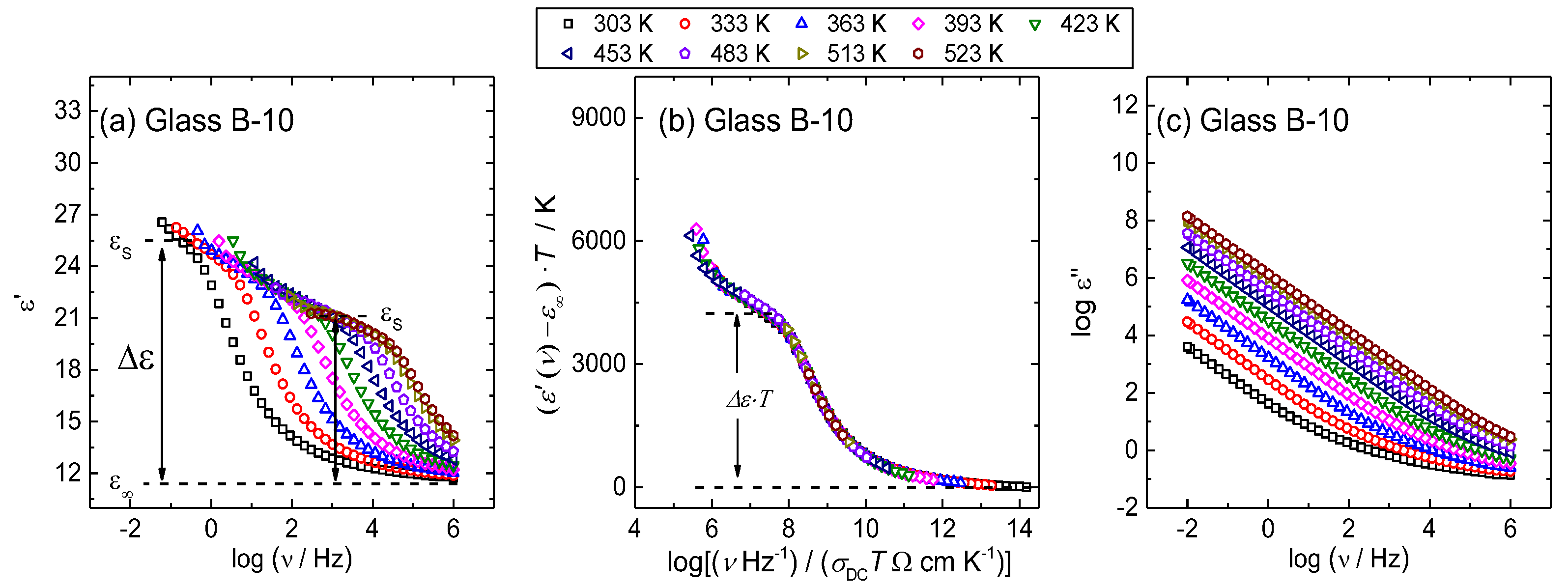
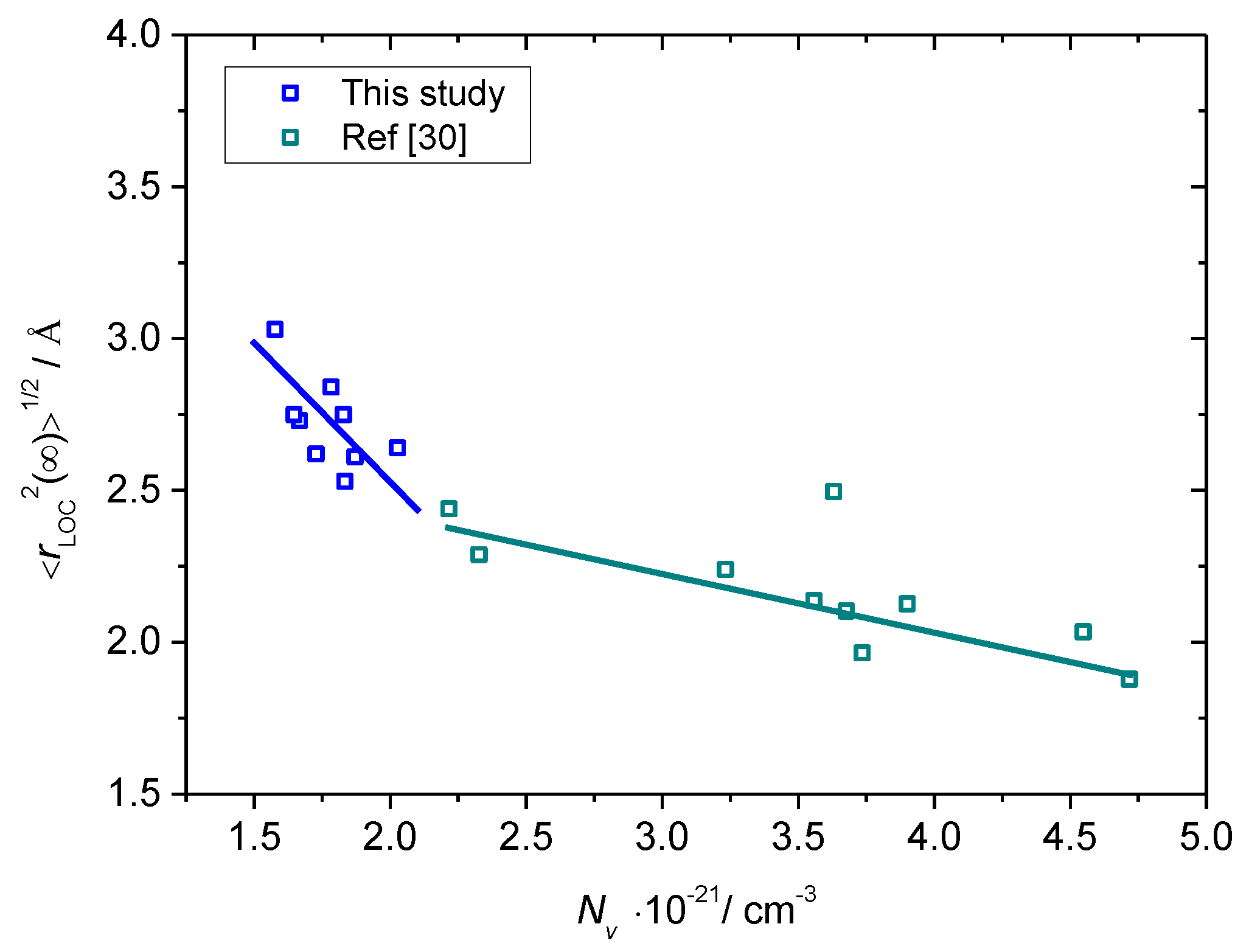
3.3. Scaling of Permittivity Spectra and Length Scales of Polaronic Transport
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mott, N. Conduction in glasses containing transition metal ions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1968, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, I.; Mott, N. Polarons in crystalline and non-crystalline materials. Adv. Phys. 1969, 18, 41–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, L.; Chung, C.; MacKenzie, J. Electrical properties of semiconducting oxide glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1979, 32, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, M.; Mansingh, A. Transport Properties of Semiconducting Phosphate Glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4629–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, I. Polaron conduction in disordered 3d oxides. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1970, 2, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šantić, A.; Moguš-Milanković, A. Charge carrier dynamics in materials with disordered structures: A case study of iron phosphate glasses. Croat. Chem. Acta 2012, 85, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banday, A.; Murugavel, S. Small polaron hopping conduction mechanism in LiFePO4 glass and crystal. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 45111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguš-Milanković, A.; Day, D.E.; Šantić, B. DC conductivity and polarisation in iron phosphate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 1999, 40, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Ray, C.S.; Mogus-Milankovic, A.; Day, D.E. Iron redox equilibrium, structure and properties of iron phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 283, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, Y.; El-Egili, K.; Doweidar, H.; Abbas, I. Structure and electric conduction of Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2004, 353, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahrani, A.; El-Desoky, M.M. Electrical transport studies in alkali iron phosphate glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2006, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Fahmy, N.A.; Pegg, I.L. Effect of mixing transition ions in glasses. II. The P2O5–Fe2O3–MnO system. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahrani, A.; Al-Hajry, A.; El-Desoky, M. Electrical relaxation in mixed lithium and sodium iron phosphate glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 364, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, L. Electronic conductivity in Na2O–FeO–P2O5 glasses. Solid State Ionics 2003, 157, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguš-Milanković, A.; Šantić, B.; Day, D.; Ray, C. Electrical conductivity in mixed-alkali iron phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 283, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguš-Milanković, A.; Šantić, A.; Reis, S.; Furic, K.; Day, D. Mixed ion–polaron transport in Na2O–PbO–Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2004, 342, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguš-Milanković, A.; Šantić, A.; Karabulut, M.; Day, D. Study of electrical properties of MoO3–Fe2O3–P2O5 and SrO–Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses by impedance spectroscopy. II. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 330, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šantić, A.; Kim, C.; Day, D.; Moguš-Milanković, A. Electrical properties of Cr2O3–Fe2O3–P2O5 glasses. Part II. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielniok, D.; Cramer, C.; Eckert, H. Structure/property correlations in ion-conducting mixed-network former glasses: Solid-state NMR studies of the system Na2O−B2O3−P2O5. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3162–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Seth, V.; Gahlot, P.; Khasa, S.; Arora, M.; Gupta, S. Study of electron paramagnetic resonance, optical transmission and dc conductivity of vanadyl doped Bi2O3·B2O3·Li2O glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2004, 377, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, F.; Montagne, L.; Pascual, L.; Durán, A. Composition and structure dependence of the properties of lithium borophosphate glasses showing boron anomaly. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rao, K. Lithium ion transport in germanophosphate glasses. Solid State Ionics 2004, 170, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.S.S.; Rani, A.; Radhakrishna, S. Mixed glass former effect in AgI-Ag2O-V2O5-P2O5 quaternary amorphous solid electrolytes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1990, 25, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, M.; Yuce, B.; Bozdogan, O.; Ertap, H.; Mammadov, G. Effect of boron addition on the structure and properties of iron phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, P.A.; Yang, G.; Hand, R.; Möbus, G. Boron environments and irradiation stability of iron borophosphate glasses analysed by EELS. Solid State Sci. 2008, 10, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, K.; Pan, S.; Zhu, H.; Lu, M.; Qin, J. FTIR spectra and properties of iron borophosphate glasses containing simulated nuclear wastes. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1092, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguš-Milanković, A.; Pavić, L.; Ertap, H.; Karabulut, M. Polaronic mobility in boron doped iron phosphate glasses: Influence of structural disorder on summerfield scaling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 2007–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räisänen, J. Handbook of Modern Ion Beam Analysis, 2nd ed.; Materials Research Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 147–173, and Appendices, Appendix 12 pp. 177–223. [Google Scholar]
- Topić, N.; Radović, I.B.; Fazinić, S.; Skoko, Ž. Analysis of medieval and post-medieval glass finds from dubrovnik region (Croatia). Archaeometry 2016, 58, 574–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šantić, A.; Banhatti, R.D.; Pavić, L.; Ertap, H.; Yüksek, M.; Karabulut, M.; Moguš-Milanković, A. Polaronic transport in iron phosphate glasses containing HfO2 and CeO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3999–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, M.; Kashif, I. Electrical conductivity in mixed calcium and barium iron phosphate glasses. Phys. Status Solidi A 2002, 194, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajry, A.; Tashtoush, N.; El-Desoky, M. Characterization and transport properties of semiconducting Fe2O3–Bi2O3–Na2B4O7 glasses. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 368, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assiri, M.S.; Salem, S.; El-Desoky, M.M. Effect of iron doping on the characterization and transport properties of calcium phosphate glassy semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, S. Universal low-frequency behaviour in the a.c. hopping conductivity of disordered systems. Philos. Mag. B 1985, 52, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, S.; Butcher, P. Universal behaviour of AC hopping conductivity in disordered systems. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1985, 77, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklepić, K.; Banhatti, R.D.; Tricot, G.; Mosner, P.; Koudelka, L.; Moguš-Milanković, A. Insights from local network structures and localized diffusion on the ease of lithium ion transport in two mixed glass-former systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 17641–17657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šantić, A.; Nikolić, J.; Pavić, L.; Banhatti, R.D.; Mosner, P.; Koudelka, L.; Moguš-Milanković, A. Scaling features of conductivity spectra reveal complexities in ionic, polaronic and mixed ionic-polaronic conduction in phosphate glasses. Acta Mater. 2019, 175, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roling, B.; Happe, A.; Funke, K.; Ingram, M.D. Carrier concentrations and relaxation spectroscopy: New information from scaling properties of conductivity spectra in ionically conducting glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roling, B. Scaling properties of the conductivity spectra of glasses and supercooled melts. Solid State Ionics 1998, 105, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidebottom, D.L. Universal approach for scaling the ac conductivity in ionic glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 3653–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidebottom, D.L.; Roling, B.; Funke, K. Ionic conduction in solids: Comparing conductivity and modulus representations with regard to scaling properties. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 63, 024301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, R57–R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhatti, R.D.; Cramer, C.; Zielniok, D.; Robertson, A.H.J.; Ingram, M.D. Insights into ion-network interactions and ion transport in glass. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 2009, 223, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, V.N.; Mirlin, D.N. Optical absorption by polarons in rutile (TiO2) single crystals. Phys. Status Solidi B 1968, 27, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrøder, T.B.; Dyre, J.C. Scaling and universality of ac conduction in disordered solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Glass | Batch Composition (mol.%) | Measured Composition a (mol.%) | Molar O/P Ratio | Density b (g cm−3) | Fe2+/Fetot Ratio b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-2 | 2B2O3-39.2Fe2O3-58.8P2O5 | 2.3B2O3-42.8Fe2O3-54.9P2O5 | 3.73 | 3.06 | 0.22 |
| B-4 | 4B2O3-38.4Fe2O3-57.6P2O5 | 3.9B2O3-39.4Fe2O3-56.7P2O5 | 3.65 | 2.97 | nm |
| B-6 | 6B2O3-37.6Fe2O3-56.4P2O5 | 6.2B2O3-40.2Fe2O3-53.6P2O5 | 3.80 | 2.94 | nm |
| B-8 | 8B2O3-36.8Fe2O3-55.2P2O5 | 7.4B2O3-37.7Fe2O3-54.9P2O5 | 3.73 | 2.95 | 0.16 |
| B-10 | 10B2O3-36.0Fe2O3-54P2O5 | 8.8B2O3-36.6Fe2O3-54.6P2O5 | 3.75 | 2.93 | nm |
| B-12 | 12B2O3-35.2Fe2O3-52.8P2O5 | 10.6B2O3-37.4Fe2O3-52.1P2O5 | 3.88 | 3.01 | nm |
| B-14 | 14B2O3-34.4Fe2O3-51.6P2O5 | 12.7B2O3-35.0Fe2O3-52.2P2O5 | 3.87 | 2.89 | nm |
| B-18 | 18B2O3-32.8Fe2O3-49.2P2O5 | 15.0B2O3-33.9Fe2O3-51.1P2O5 | 3.94 | 2.91 | nm |
| B-20 | 20B2O3-32Fe2O3-48P2O5 | 17.7B2O3-32.5Fe2O3-49.8P2O5 | 4.01 | 2.86 | nm |
| Glass | σDCa/(Ω cm)−1 ± 0.5% | EDC/eV ± 0.5% | log (σ0/(Ω cm)−1 K) ± 0.5% |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-2 | 3.08 × 10−10 | 0.63 | 3.43 |
| B-4 | 8.56 × 10−11 | 0.66 | 3.26 |
| B-6 | 1.19 × 10−10 | 0.65 | 3.27 |
| B-8 | 4.49 × 10−11 | 0.67 | 3.19 |
| B-10 | 2.21 × 10−11 | 0.69 | 3.14 |
| B-12 | 4.36 × 10−11 | 0.67 | 3.13 |
| B-14 | 1.57 × 10−11 | 0.69 | 2.99 |
| B-18 | 1.33 × 10−11 | 0.69 | 2.92 |
| B-20 | 8.97 × 10−12 | 0.69 | 2.71 |
| Glass | N (Fe ions) × 10−21/cm−3 | Nv (Polarons) × 10−21/cm−3 | R = N−1/3/Å | rp/Å | (Δε∙T)/K | <rLOC2(∞)>1/2 /Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-2 | 10.7 | 2.03 | 4.54 | 1.93 | 4937 | 2.64 |
| B-4 | 9.65 | 1.83 | 4.70 | 1.89 | 4098 | 2.53 |
| B-6 | 9.84 | 1.87 | 4.67 | 1.88 | 4476 | 2.61 |
| B-8 | 9.35 | 1.78 | 4.75 | 1.91 | 4767 | 2.84 |
| B-10 | 9.09 | 1.73 | 4.79 | 1.93 | 4165 | 2.62 |
| B-12 | 9.62 | 1.83 | 4.70 | 1.89 | 4828 | 2.75 |
| B-14 | 8.77 | 1.67 | 4.85 | 1.95 | 4338 | 2.73 |
| B-18 | 8.67 | 1.65 | 4.87 | 1.96 | 4365 | 2.75 |
| B-20 | 8.30 | 1.58 | 4.94 | 1.99 | 5060 | 3.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavić, L.; Fazinić, S.; Ertap, H.; Karabulut, M.; Moguš-Milanković, A.; Šantić, A. Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3. Materials 2020, 13, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112505
Pavić L, Fazinić S, Ertap H, Karabulut M, Moguš-Milanković A, Šantić A. Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3. Materials. 2020; 13(11):2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112505
Chicago/Turabian StylePavić, Luka, Stjepko Fazinić, Hüseyin Ertap, Mevlüt Karabulut, Andrea Moguš-Milanković, and Ana Šantić. 2020. "Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3" Materials 13, no. 11: 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112505
APA StylePavić, L., Fazinić, S., Ertap, H., Karabulut, M., Moguš-Milanković, A., & Šantić, A. (2020). Polaronic Conductivity in Iron Phosphate Glasses Containing B2O3. Materials, 13(11), 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13112505






