Production and Heat Properties of an X-ray Reflective Anode Based on a Diamond Heat Buffer Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
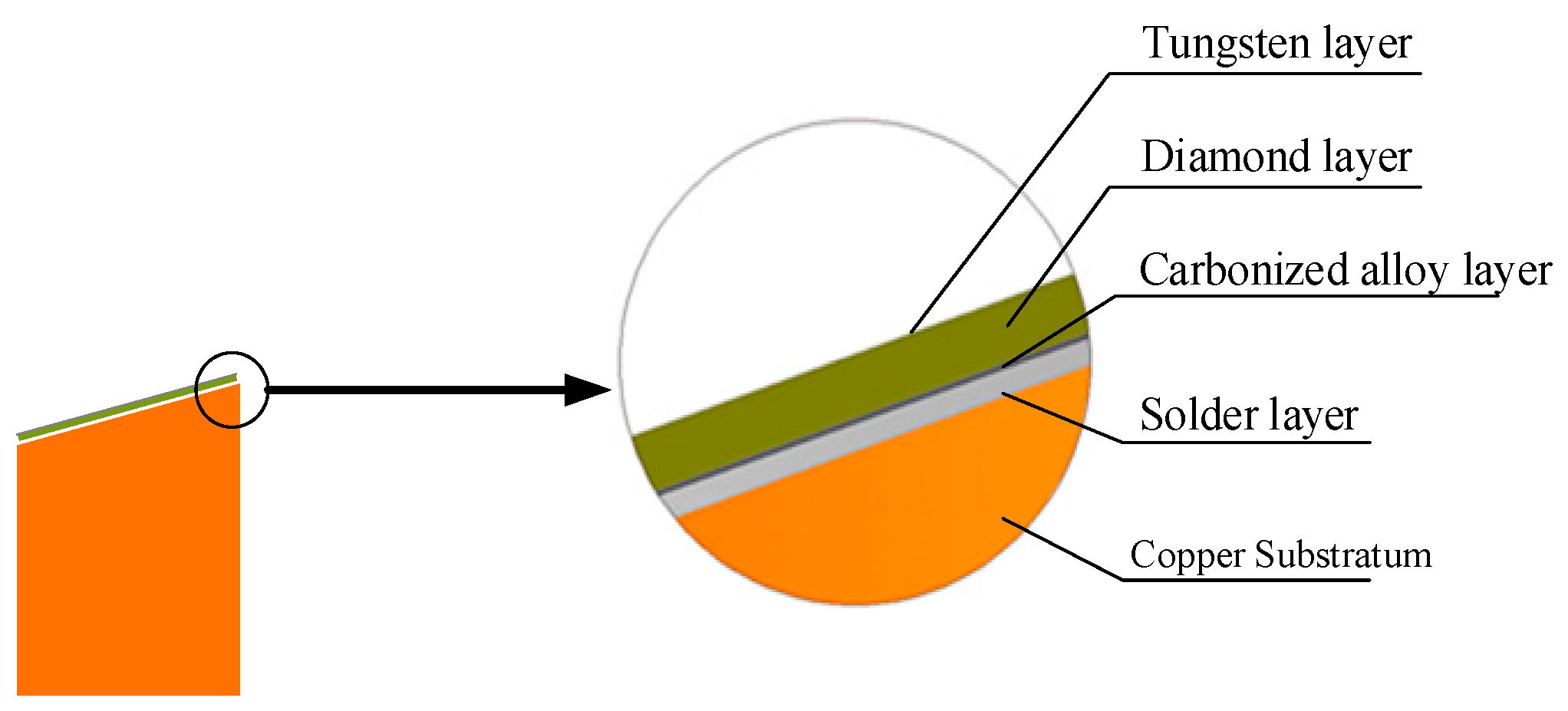
2.1. Production Process of the Diamond Composite Anode
2.2. Property Test of the Diamond Composite Anode
3. Results and Discussion
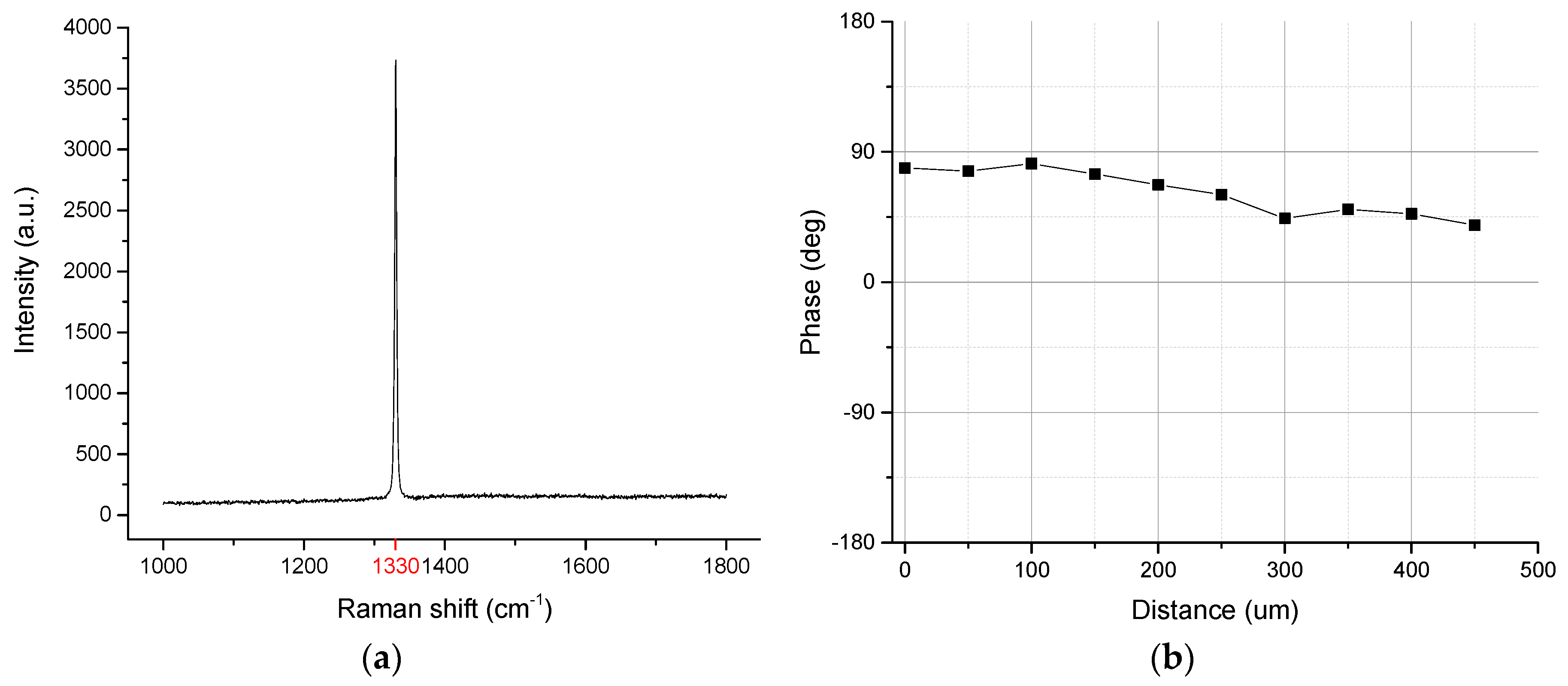
3.1. Results of and Discussion on Inter-Layer Bonding Strength Tests
3.2. Results of and Discussion on Temperature Measurements at Focal Spot Region
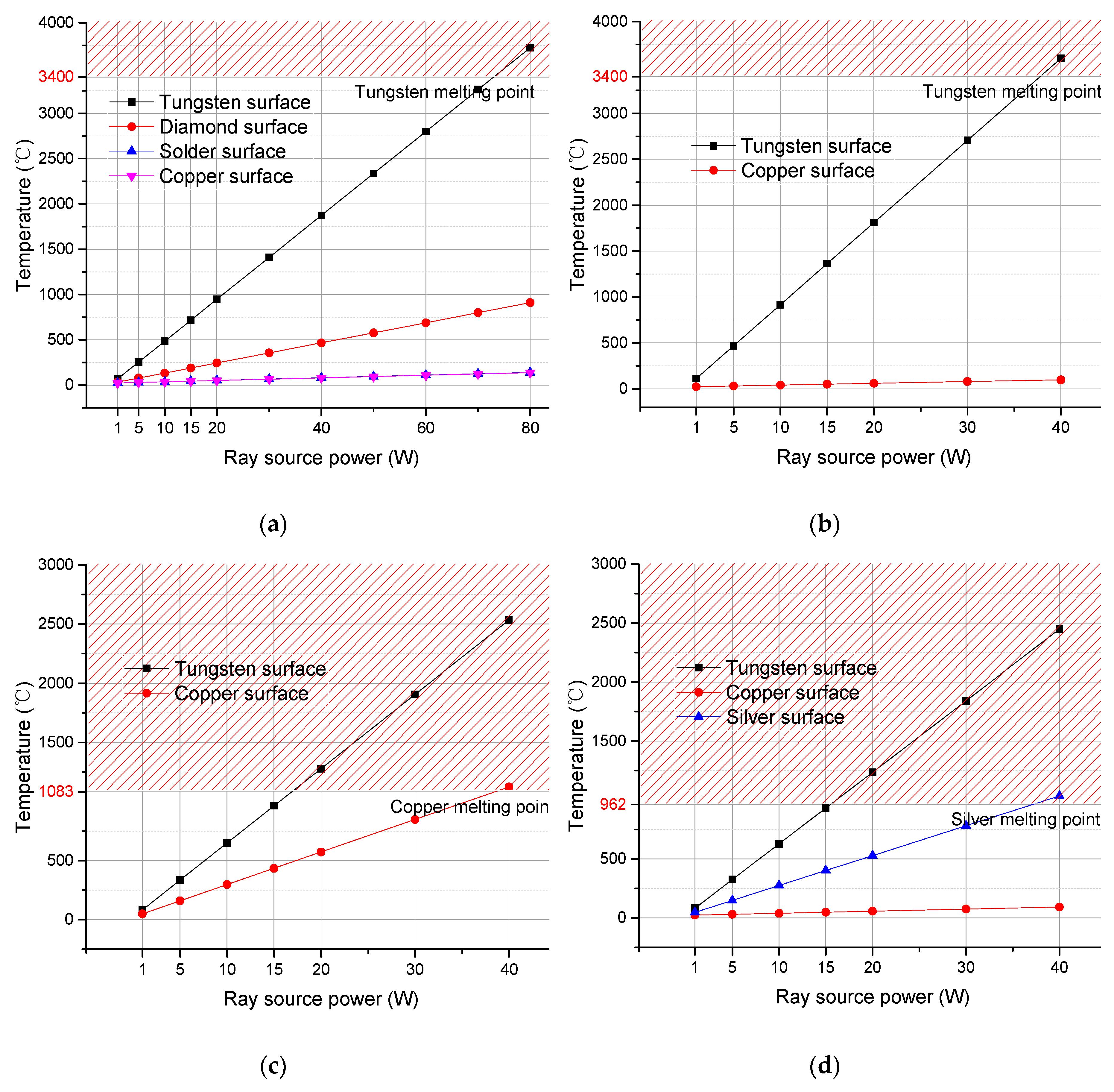
3.2.1. Surface Temperatures at Focal Spot Region
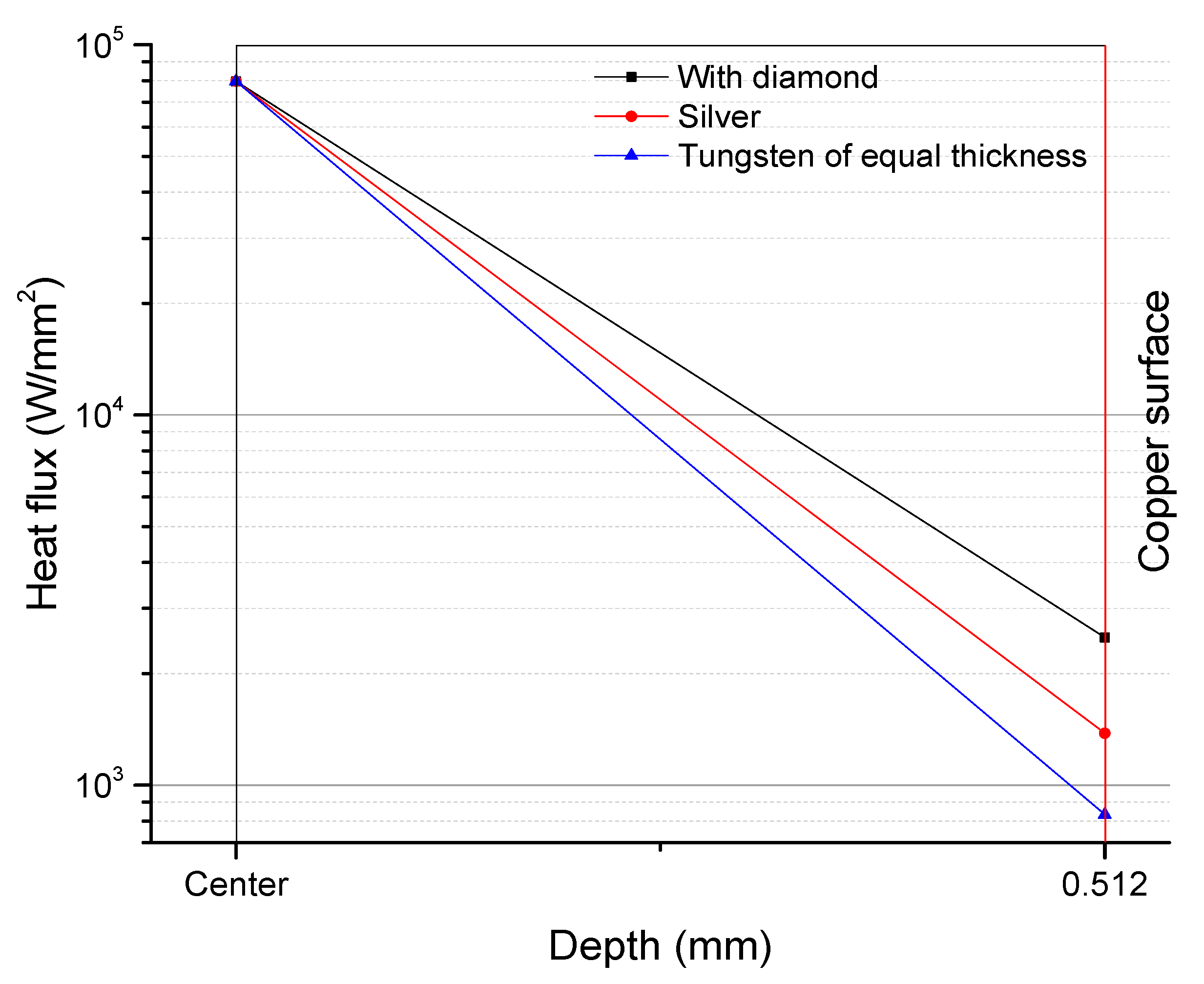
3.2.2. Comparison of Vertical Temperature Distribution of Each Layer in the Focal Spot Region
3.2.3. Comparison on Power Limit Temperatures
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The inter-layer bonding results of the composite anode were smooth, and no obvious gap or crack was found in each layer. This showed that the diamond buffer layer and copper substratum can be combined by brazing.
- (2)
- For the problem of precise temperature measurement at the focal spot on the surface of an X-ray anode, an analytical measurement and processing method based on infrared radiation spectra was proposed in this paper. The highest temperature value corresponding to the spectral peak of the micro-focus area was calculated by the infrared radiation spectrum which measured in the relevant area indirectly. This method was specifically designed for small-focus area temperature measurements.
- (3)
- For the vertical temperature measurement through the cross section of an X-ray composite anode, a method based on finite element was presented in this paper, which was proven reliable by verifying the simulation result with experimental measurements that resulted in surface temperature determination of an anode.
- (4)
- Analysis of heat distribution at the focal spot region of four types of X-ray anodes with different structures demonstrated that the X-ray reflective anode with a diamond heat buffer layer has much higher thermal stability and its working power limit is twice that of other anodes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jakubek, J.; Holy, T.; Jakubek, M.; Vavrik, D.; Vykydal, Z. Experimental system for high resolution X-ray transmission radiography. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2006, 563, 78–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, M.; Hanke, R.; Kruger, P.; Uhlmann, N.; Voland, V. Realization of a computed tomography setup to achieve resolutions below 1 μm. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2008, 591, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimmel, S.; Stephan, J.; Baumann, J. 3D computed tomography using a microfocus X-ray source: Analysis of artifact formation in the reconstructed images using simulated as well as experimental projection data. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2005, 542, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, S.; Sakai, Y.; Mizuta, Y.; Kita, S.; Okuyama, F. Superminiature X-ray tube. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5679–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, M.M. Determination of tungsten target parameters for transmission X-ray tube-A simulation study using Geant4. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2016, 48, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubin, M.L.; Yaskolko, A.A.; Chesnokov, D.A. Thermal Analysis of the Focal Spot of Anodes of Powerful X-ray Tubes. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 51, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podimsky, A.A.; Potrakhov, N.N. X-ray tubes for projection X-ray radiography of new Generation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 808, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemberg, O.; Otendal, M.; Hertz, H.M. Liquid-metal-jet anode electron-impact X-ray source. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espes, E.; Andersson, T.; Björnsson, F.; Gratorp, C.; Hansson, B.A.M.; Hemberg, O.; Johansson, G.; Kronstedt, J.; Otendal, M.; Tuohimaa, T.; et al. Liquid-Metal-Jet X-ray Tube Technology and Tomography Applications. Digital Imaging XVIII 2015, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.E.; Andrews, G.C.; Miller, R.S.; Campbell, A.C. A Dual Fluid Cooling System for High Power X-ray Tubes. U.S. Patent 6,519,317, 11 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- David, J. Stupple. Modeling of Heat Transfer in an Aluminum X-Ray Anode Employing Chemical Vapor Deposited Diamond Heat Spreader. J. Heat Transfer 2018, 140, 124501. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, X.; Xu, X. CVD diamond thin film for IR optics and X-ray optics. Thin Solid Films 2000, 368, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, G.A. Nonmetallic crystals with high thermal conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1973, 34, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfaure, C.; Mazellier, J.P.; Tranchant, N.; Bergonzo, P.; Ponard, P.; Saada, S. Nanofocus diamond X-ray windows: Thermal modeling of nano-sized heat source systems. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 59, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, G.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Che, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Kim, M.J.; Zhang, H. Regulated Interfacial Thermal Conductance between Cu and Diamond by a TiC Interlayer for Thermal Management Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 26507–26517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.Y.; Shu, S.L.; Feng, J.; Popp, A.; Schmidt, B.; Lu, H.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Tian, S.C.; Tong, C.Z.; Wang, L.J. High Power (>27 W) Semiconductor Disk Laser Based on Pre-Metalized Diamond Heat-Spreader. IEEE Photonics J. 2019, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Jin, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, G.; Zhang, J.; Fang, R. The deposition of diamond film with high thermal conductivity. Thin Solid Films 1997, 311, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Sano, T. Thermal properties of diamond particle-dispersed Cu composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 153, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, J.A.; Seibles, L. Growth and Characterization of PECVD Diamond Films. Mrs Proc. 1991, 250, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Qiu, W.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Z.; Dai, M.; Zhou, K. Effects of deposition parameters on microstructure and thermal conductivity of diamond films deposited by DC arc plasma jet chemical vapor deposition. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Morigami, H. Thermal properties of diamond/copper composite material. Microelectron. Reliab. 2004, 44, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Wong, N.B.; Li, G.; Lee, S.T. Metallization of CVD diamond films by ion beam assisted deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2000, 62, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msolli, S.; Alexis, J.; Kim, H. Mechanical Behavior and Adhesion of the Ti/Cr/Au Metallization Scheme on Diamond Substrate. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyzov, A.M.; Kruszewski, M.J.; Ciupiński, L.; Mazurkiewiz, M.; Michalski, A.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Diamond-tungsten based coating-copper composites with high thermal conductivity produced by Pulse Plasma Sintering. Mater. Des. 2015, 76, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.J.; Xu, F.; Zuo, D.W.; Lu, W.Z.; Wang, M. Parameters Optimization of Laser Processing CVD Diamond Film Based on FEM Simulation. Key Eng. Mater. 2010, 426–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelik, J.; Lux, B. Improved tool performance by application of heat-spreading diamond layers within a multilayer coating? Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 1999, 17, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Production and Heat Properties of an X-ray Reflective Anode Based on a Diamond Heat Buffer Layer. Materials 2020, 13, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010241
Li X, Wang X, Li Y, Liu Y. Production and Heat Properties of an X-ray Reflective Anode Based on a Diamond Heat Buffer Layer. Materials. 2020; 13(1):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010241
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinwei, Xin Wang, Ye Li, and Yanyang Liu. 2020. "Production and Heat Properties of an X-ray Reflective Anode Based on a Diamond Heat Buffer Layer" Materials 13, no. 1: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010241
APA StyleLi, X., Wang, X., Li, Y., & Liu, Y. (2020). Production and Heat Properties of an X-ray Reflective Anode Based on a Diamond Heat Buffer Layer. Materials, 13(1), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010241



