Interaction of a Ti–Cu Alloy with Carbon: Synthesis of Composites and Model Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
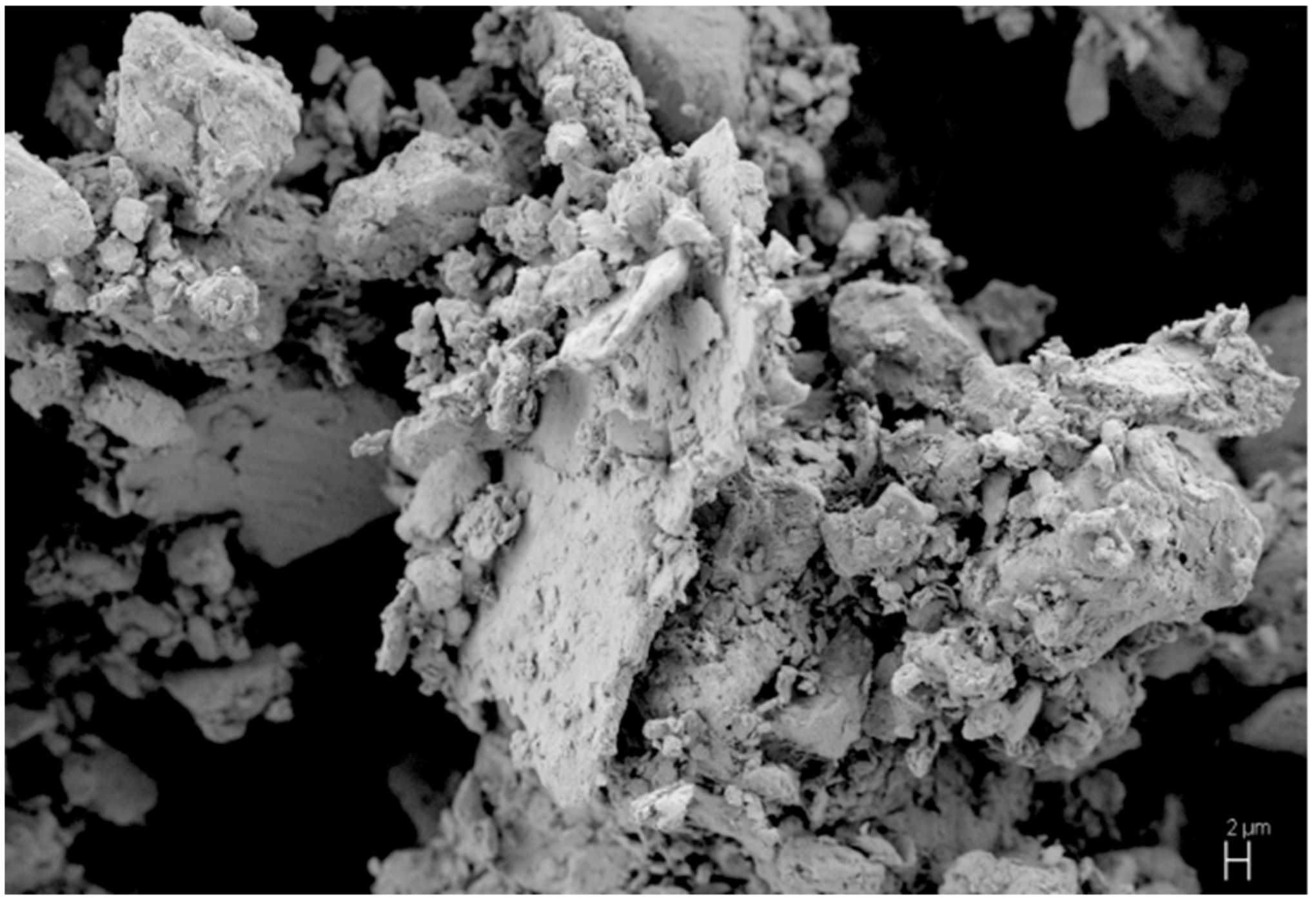
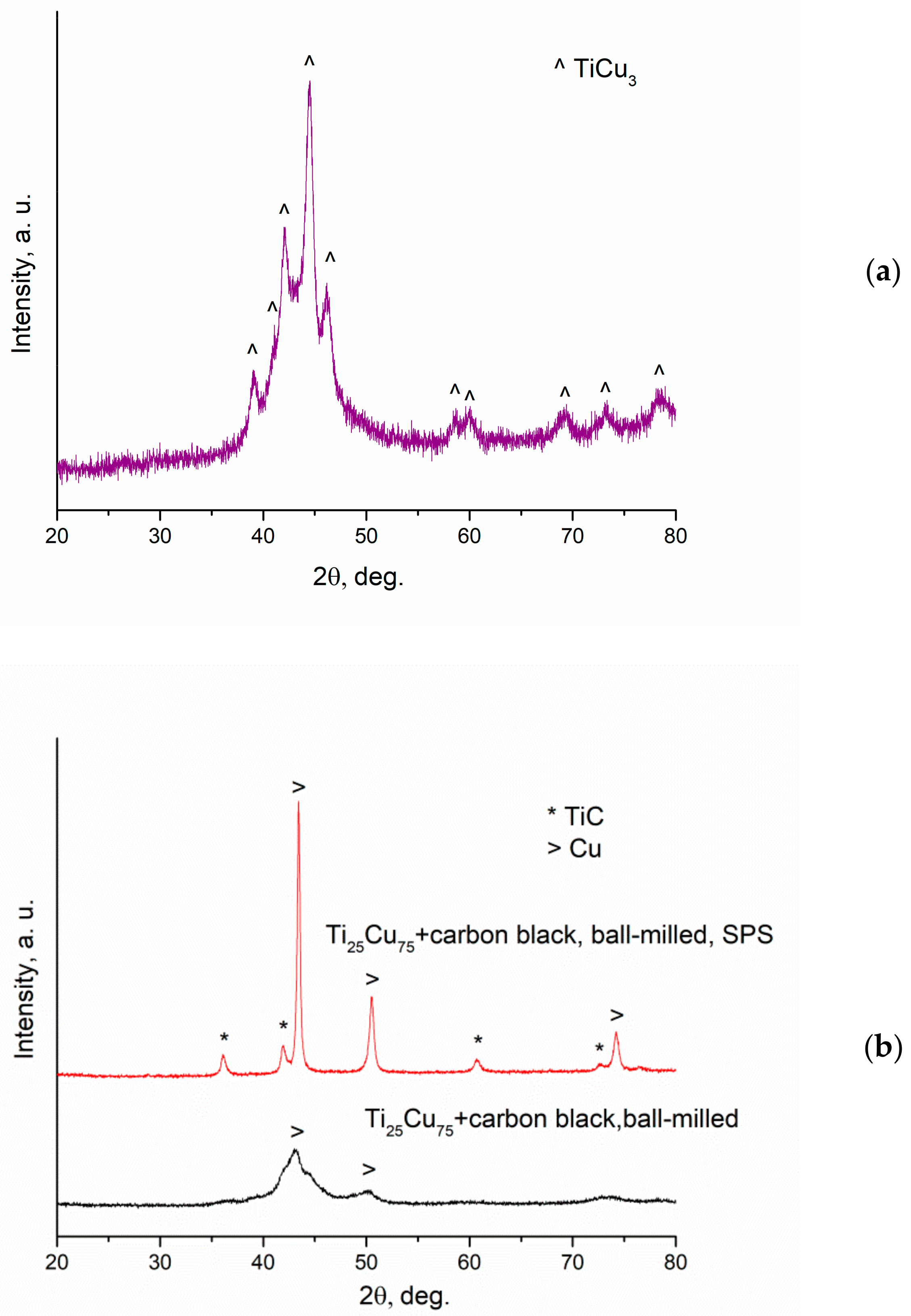
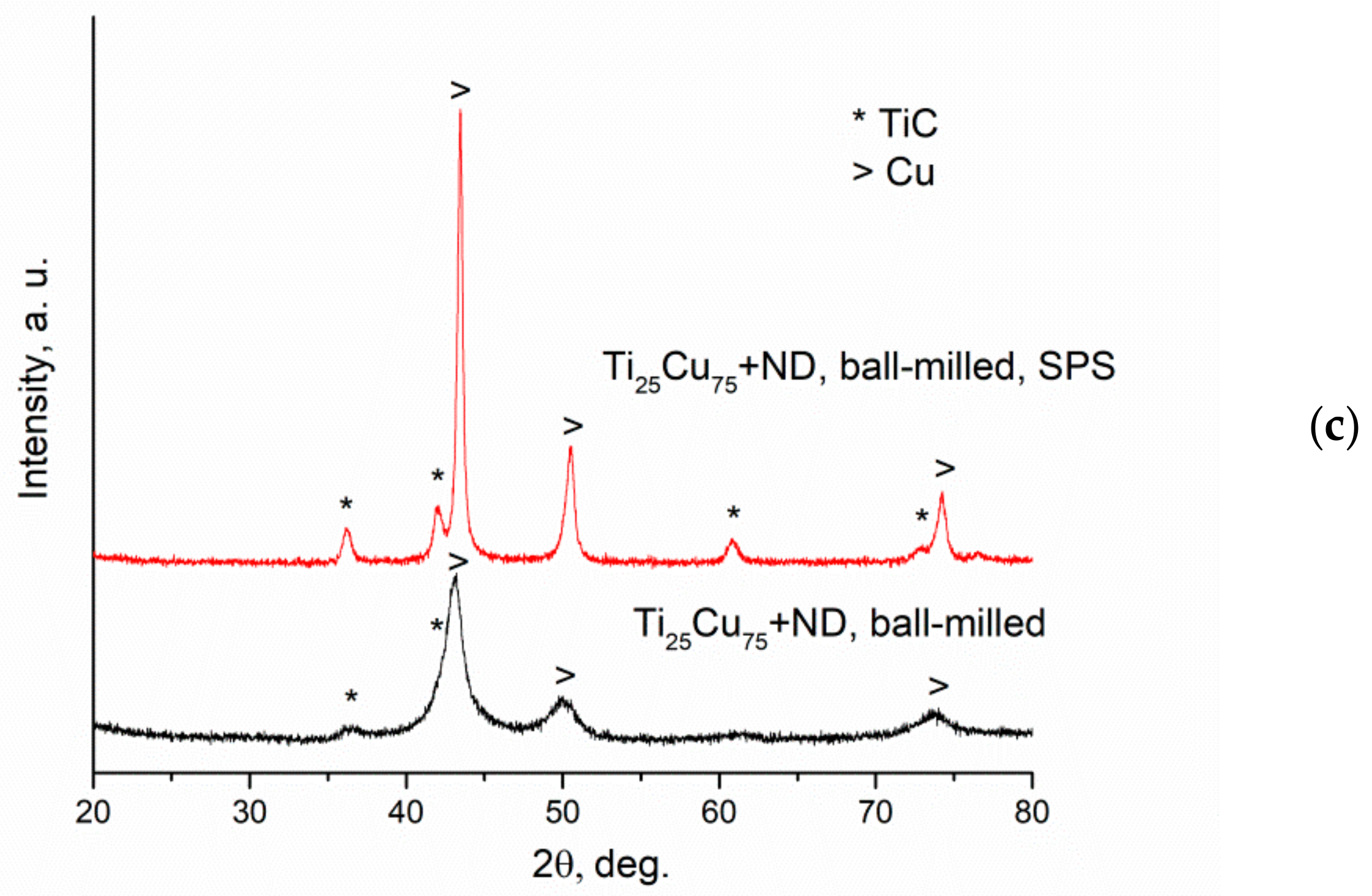
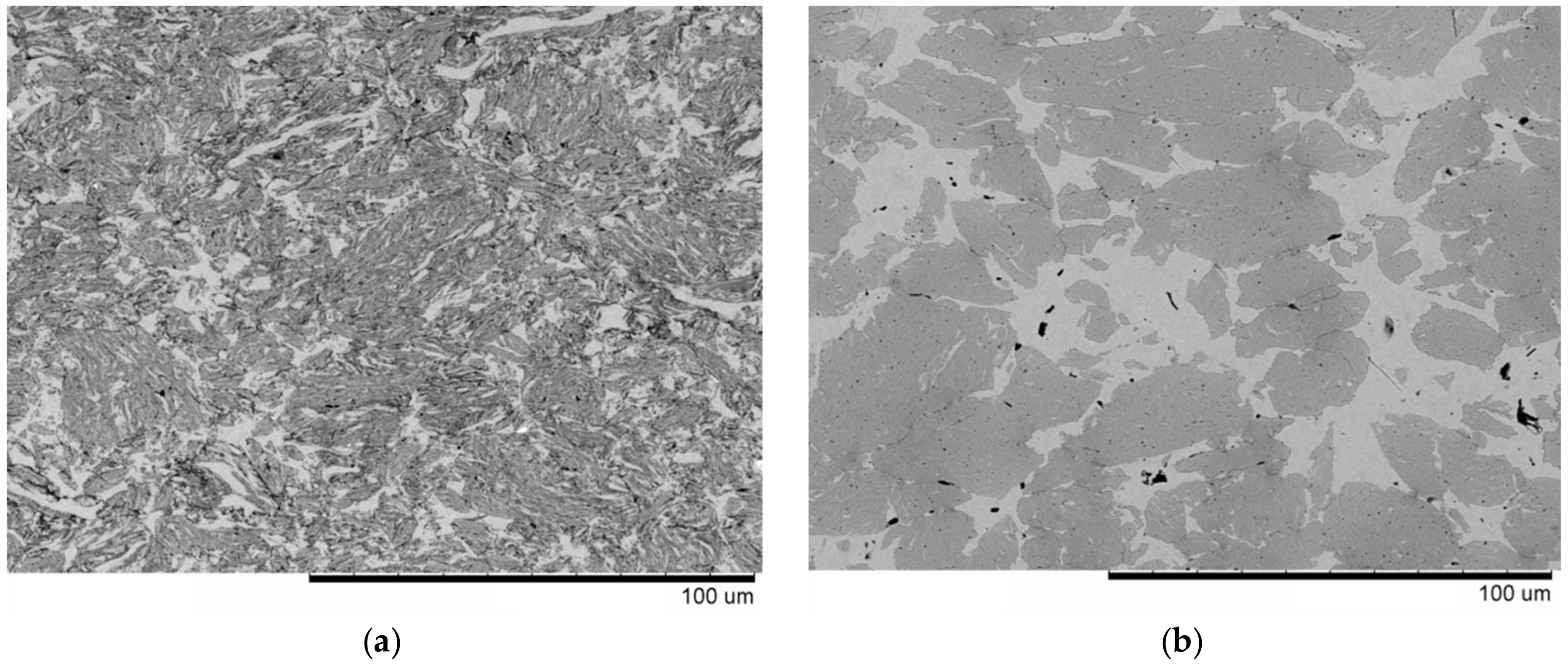
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The ball milling outcome of mixtures of Ti25Cu75 ribbon with C depends on the nature of the carbon source; mixing is more efficient in the case of carbon black than in the case of nanodiamonds;
- (2)
- During sintering, at Ti–Cu alloy/carbon contacts, titanium atoms diffuse to the alloy/graphite interface and react with carbon to form a titanium carbide layer; no evidence of carbon diffusion into the alloy was obtained;
- (3)
- The distribution of TiC particles in the composite structures obtained via reactive solid-state processing of Ti25Cu75+C follows the distribution of carbon particles in the reaction mixtures; in order to obtain a uniform distribution of nanoparticles of TiC in the copper matrix, carbon source nanoparticles should be thoroughly mixed with the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tjong, S.C.; Ma, Z.Y. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2000, 29, 49–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Metal matrix composites reinforced by nano-particles—A review. Metals 2014, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinfar, N.; Kennedy, A.R.; Shipway, P.H. Reaction synthesis of Cu–TiCx master-alloys for the production of copper-based composites. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Jiang, Q.C. Evolution process of the synthesis of TiC in the Cu–Ti–C system. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 452, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakanth, R.G.; Rajkumar, K.; Aravindan, S. Fabrication of copper–TiC–graphite hybrid metal matrix composites through microwave processing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 48, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Koizumi, Y.; Kenta, Y.; Chiba, A. In-situ fabrication and characterization of ultrafine structured Cu-TiC composites with high strength and high conductivity by mechanical milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 657, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, G.H.A. The effect of reinforcement percentages on properties of copper matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 676, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.O.; Nguyen, H.V.; Kim, J.S.; Dudina, D.V. Structural investigations of TiC–Cu nanocomposites prepared by ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Metals 2017, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.O.; Nguyen, H.V.; Kim, J.S.; Moreira, J.A., Jr. Characterization of in-situ Cu–TiH2–C and Cu–Ti–C nanocomposites produced by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. Metals 2017, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, H.; Qi, F.; Liu, Q.; Fan, X.; Shi, Y. Mechanism of in situ synthesis of TiC in Cu melts and its microstructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 3410–3418. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, N.; Aghajani, H.; Akbarpour, M.R. Microstructure and tribological properties of in-situ TiC-C/Cu nanocomposites synthesized using different carbon sources (graphite, carbon nanotube and graphene) in the Cu-Ti-C system. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 22059–22067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Krzystyniak, M.; Glandut, N.; Li, C. Effects of boron addition on the microstructure and properties of in situ synthesis TiC reinforced Cu-Ti-C composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 766, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchagin, M.A.; Gabdrashova, S.E.; Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Bulina, N.V.; Kuznetsov, V.L.; Ishchenko, A.V. Combustion characteristics and structure of carbon nanotube/titanium composites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J. Al-Ti-C master alloy with nano-sized TiC particles dispersed in the matrix prepared by using carbon nanotubes as C source. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Shen, P.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, Q. Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of nano-TiCx particles with different shapes by using carbon nano-tube as C source. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.A.; Shelekhov, E.V.; Prosviryakov, A.S.; Presniakov, M.Y.; Senatulin, B.R.; Kotov, A.D.; Khomutov, M.G.; Khodos, I.I. Application of nanodiamonds for in situ synthesis of TiC reinforcing nanoparticles inside aluminium matrix during mechanical alloying. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 75, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Dudina, D.V. Field-Assisted Sintering: Science and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; p. 425. ISBN 978-3-319-76031-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dudina, D.V.; Korchagin, M.A.; Gavrilov, A.I.; Bulina, N.V.; Batraev, I.S.; Esikov, M.A.; Georgarakis, K.; Kato, H. Formation of TiC-Cu nanocomposites by a reaction between Ti25Cu75 melt-spun alloy and carbon. Mater. Lett. 2019, 235, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Georgarakis, K.; Nakayama, K.; Li, Y.; Tsarkov, A.; Xie, G.; Dudina, D.; Louzguine, D.; Yavari, A.R. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of metallic glass fiber-reinforced Al alloy matrix composites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarfors, A.E.W. The influence of carbon on the phases in the copper-titanium system and their precipitation. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 4533–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W. Powder Cell for Windows, V.2.4; Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing: Berlin, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ukhina, A.V.; Dudina, D.V.; Anisimov, A.G.; Mali, V.I.; Bulina, N.V.; Bataev, I.A.; Skovorodin, I.N.; Bokhonov, B.B. Porous electrically conductive materials produced by spark plasma sintering and hot pressing of nanodiamonds. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12459–12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukhina, A.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Dudina, D.V.; Yubuta, K.; Kato, H. Structural characterization of carbon-based materials obtained by spark plasma sintering of non-graphitic carbon with nickel and iron as catalysts and space holders. In Ceramic Transactions Processing, Properties, and Design of Advanced Ceramics and Composites II—Proceedings of 2016 Materials Science and Technology (MS&T’16); Bansal, N.P., Ed.; John Willey and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrinfar, N.; Shipway, P.H.; Kennedy, A.R.; Saidi, A. Carbide stoichiometry in TiCx and Cu–TiCx produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Scr. Mater. 2002, 46, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Hirano, K. Diffusion of titanium in copper. Metall. Trans. A 1997, 8, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woychik, C.G.; Lowndes, D.H.; Massalski, T.B. Solidification structures in melt-spun and pulsed laser-quenched Cu-Ti alloys. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Matsuura, K.; Ohno, M. TiC coating on titanium by carbonization reaction using spark plasma sintering. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 2098–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; McKittrick, J.; Ivanov, E.; Olevsky, E.A. Densification mechanism and mechanical properties of tungsten powder consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Int. J. Refr. Metals Hard Mater. 2016, 61, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V.; Dudina, D.V.; Anisimov, A. G.; Mali, V.I.; Batraev, I.S. Carbon uptake during spark plasma sintering: Investigation through the analysis of the carbide “footprint” in a Ni–W alloy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 80228–80237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B.; Ukhina, A.V.; Anisimov, A.G.; Mali, V.I.; Esikov, M.A.; Batraev, I.S.; Kuznechik, O.O.; Pilinevich, L.P. Reactivity of materials towards carbon of graphite foil during spark plasma sintering: A case study using Ni–W powders. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, J.C.; Neubauer, E.; Barcena, J.; Clegg, W.J. Effect of titanium on copper–titanium/carbon nanofibre composite materials. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

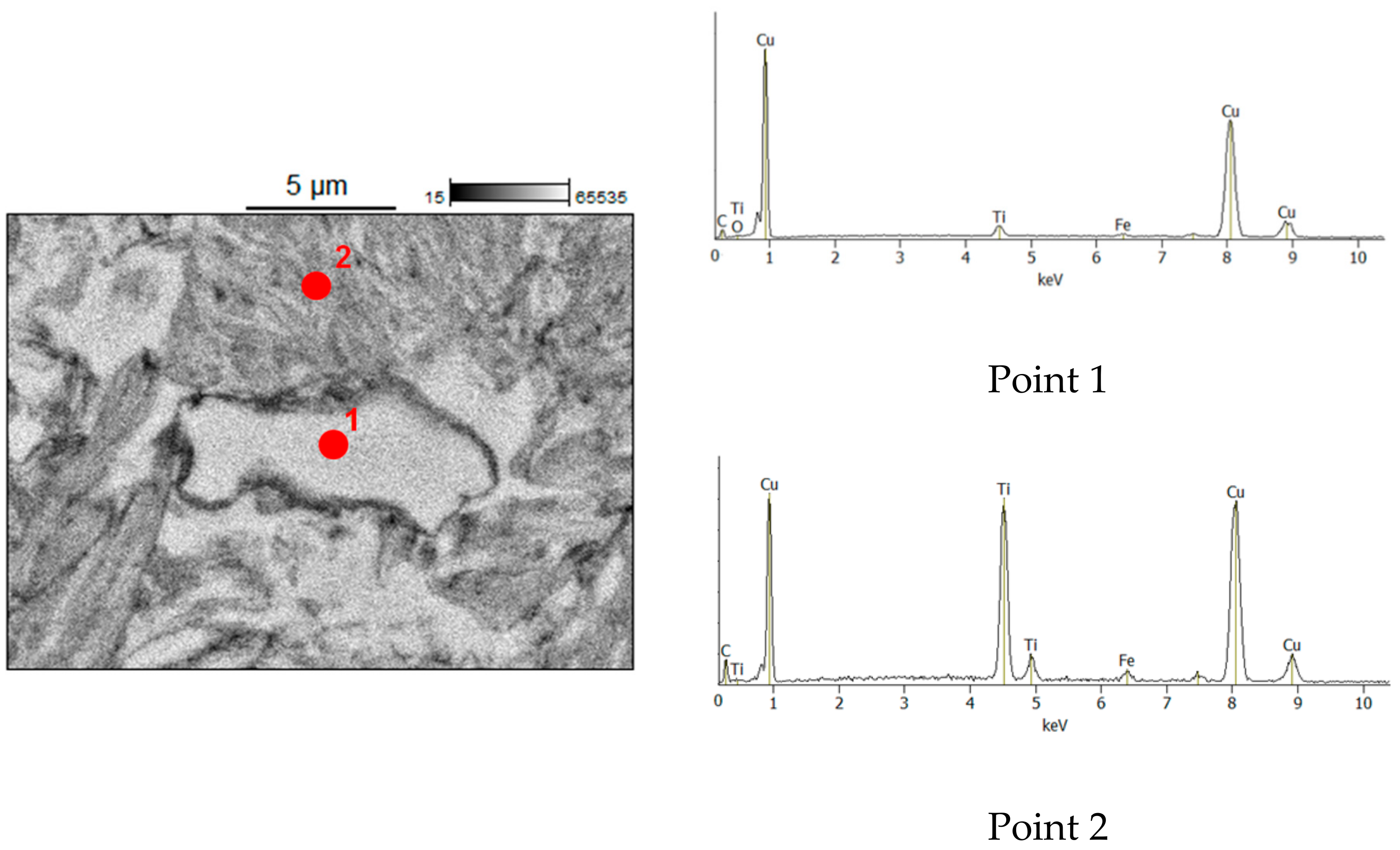
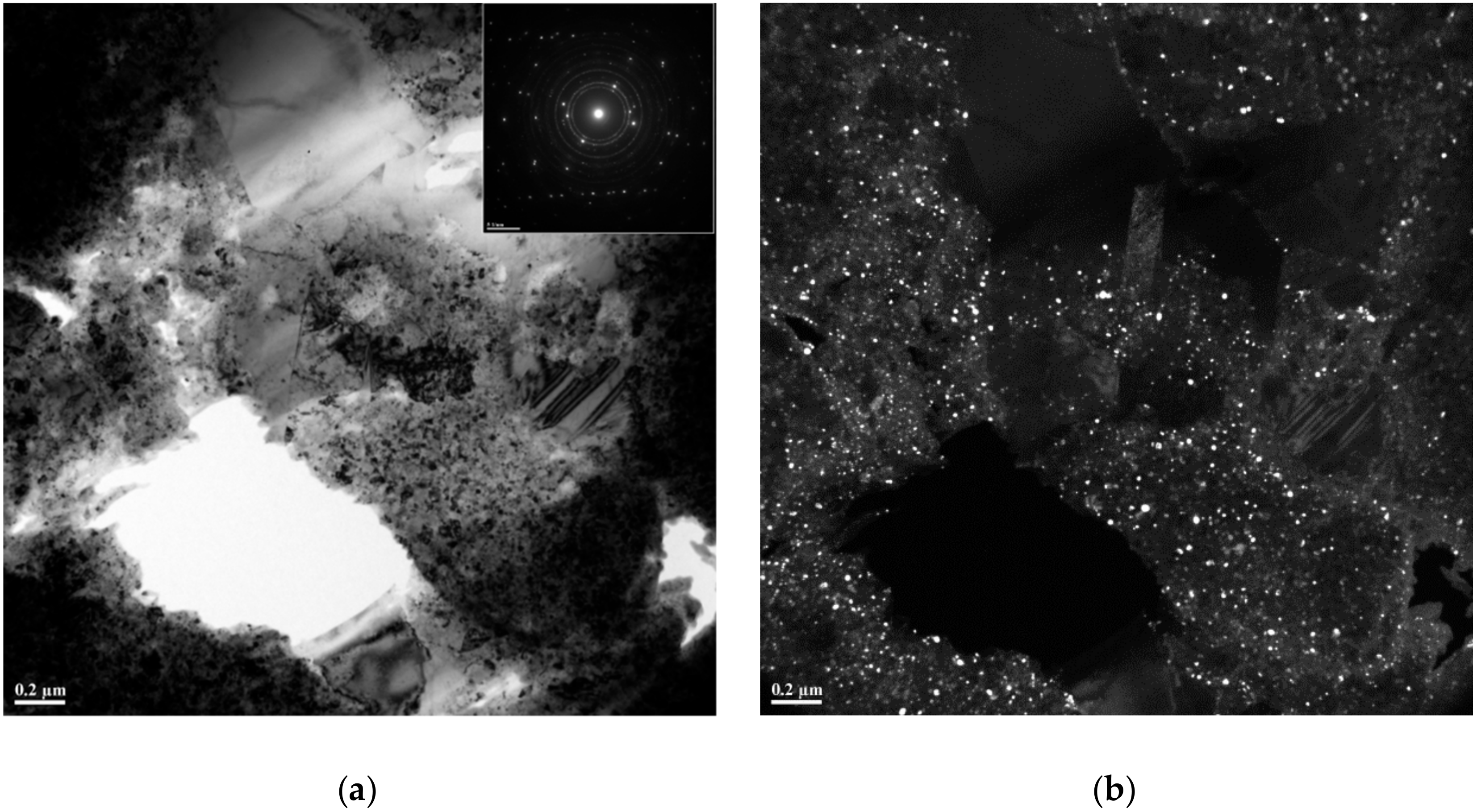
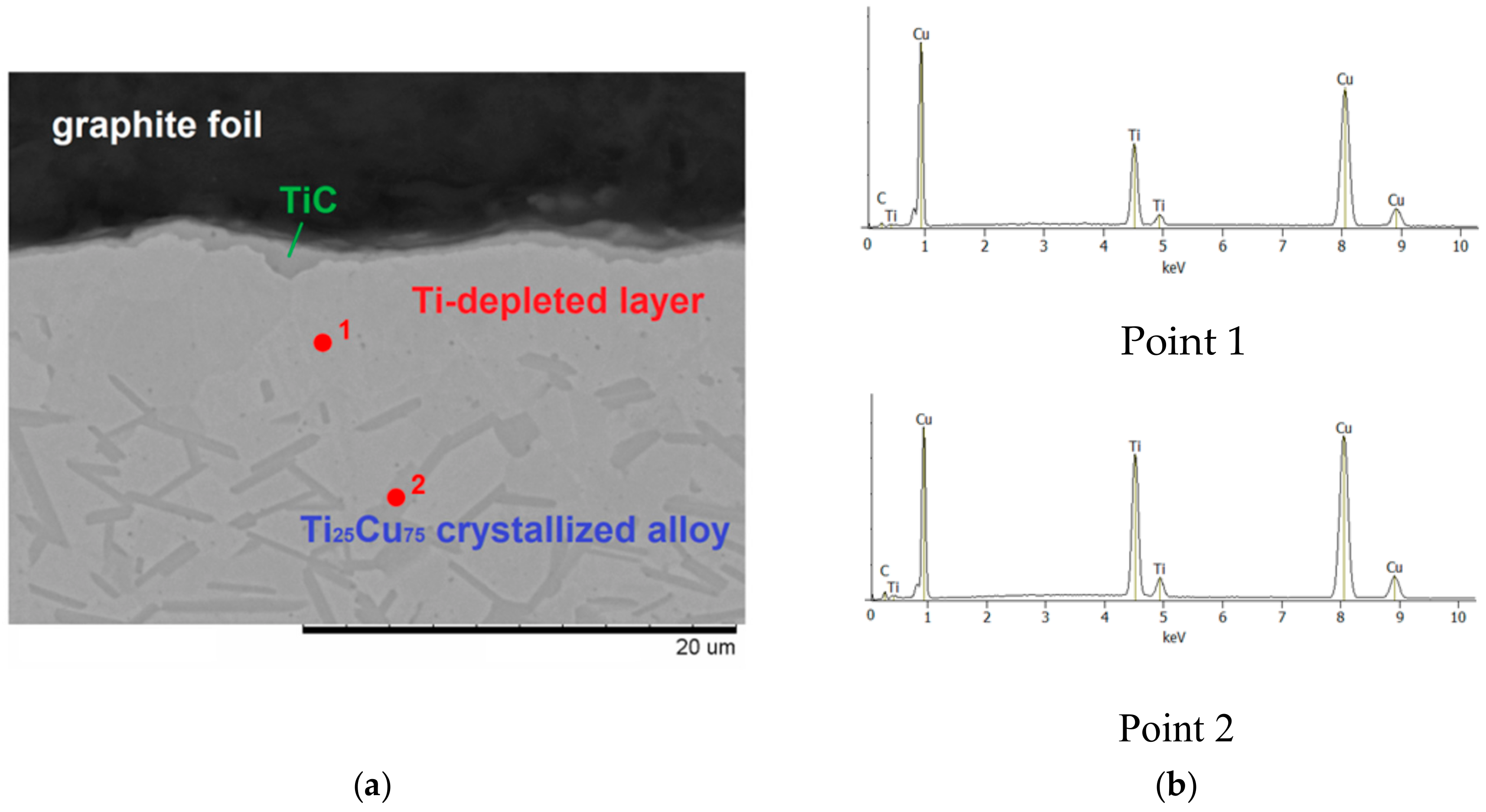

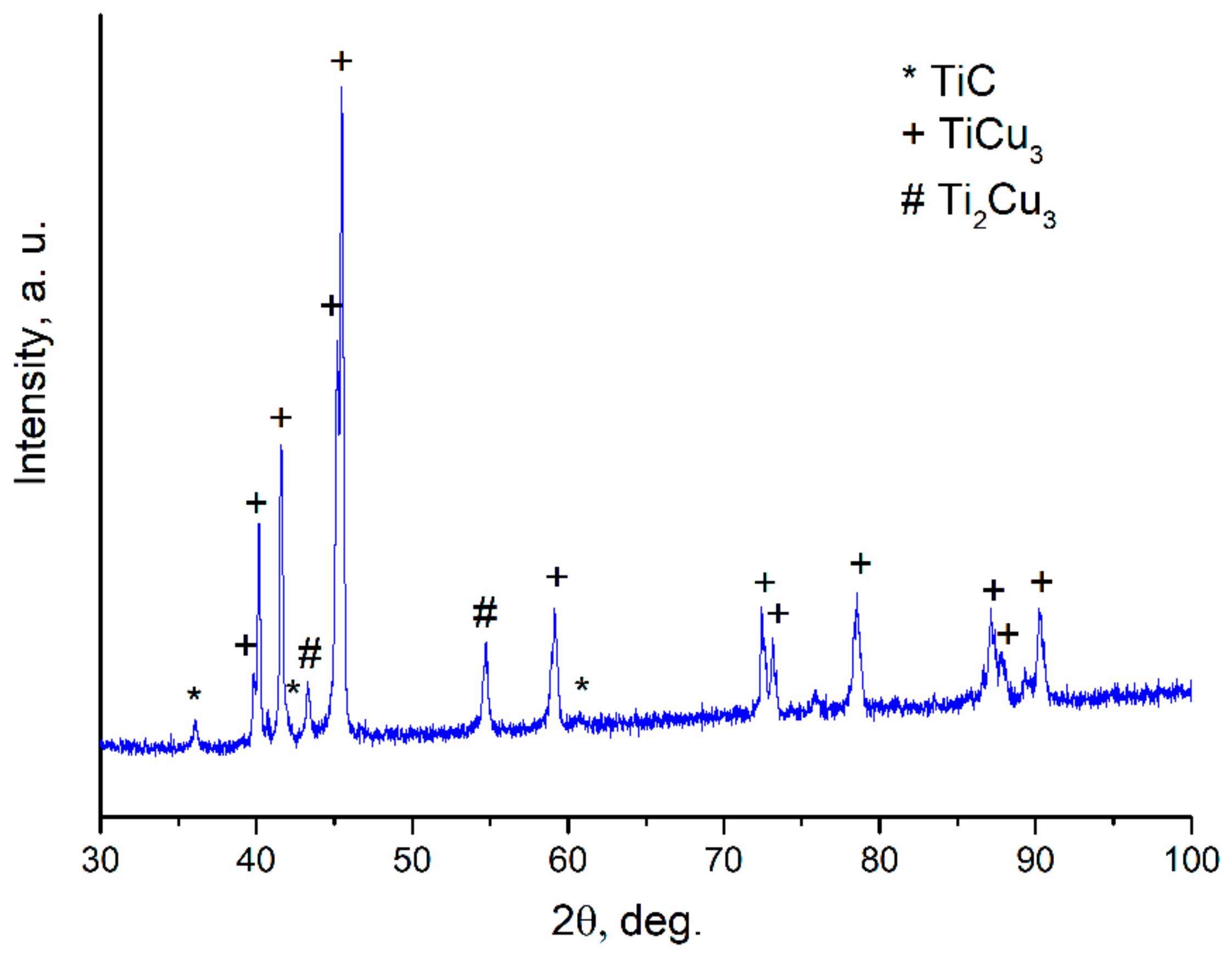
| Reaction Mixture Processed by Ball Milling and SPS | Cu Lattice Parameter 1, Å | TiC Lattice Parameter 2, Å |
|---|---|---|
| Ti25Cu75+carbon black | 3.620 | 4.321 |
| Ti25Cu75+nanodiamonds | 3.623 | 4.315 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dudina, D.V.; Vidyuk, T.M.; Korchagin, M.A.; Gavrilov, A.I.; Bulina, N.V.; Esikov, M.A.; Datekyu, M.; Kato, H. Interaction of a Ti–Cu Alloy with Carbon: Synthesis of Composites and Model Experiments. Materials 2019, 12, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091482
Dudina DV, Vidyuk TM, Korchagin MA, Gavrilov AI, Bulina NV, Esikov MA, Datekyu M, Kato H. Interaction of a Ti–Cu Alloy with Carbon: Synthesis of Composites and Model Experiments. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091482
Chicago/Turabian StyleDudina, Dina V., Tomila M. Vidyuk, Michail A. Korchagin, Alexander I. Gavrilov, Natalia V. Bulina, Maksim A. Esikov, Masanari Datekyu, and Hidemi Kato. 2019. "Interaction of a Ti–Cu Alloy with Carbon: Synthesis of Composites and Model Experiments" Materials 12, no. 9: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091482
APA StyleDudina, D. V., Vidyuk, T. M., Korchagin, M. A., Gavrilov, A. I., Bulina, N. V., Esikov, M. A., Datekyu, M., & Kato, H. (2019). Interaction of a Ti–Cu Alloy with Carbon: Synthesis of Composites and Model Experiments. Materials, 12(9), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091482







