Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties Through the Use of Segregate Carbon Nanotube Networks
Abstract
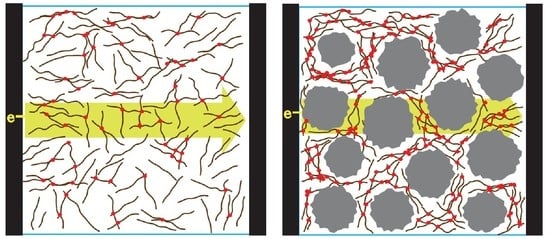
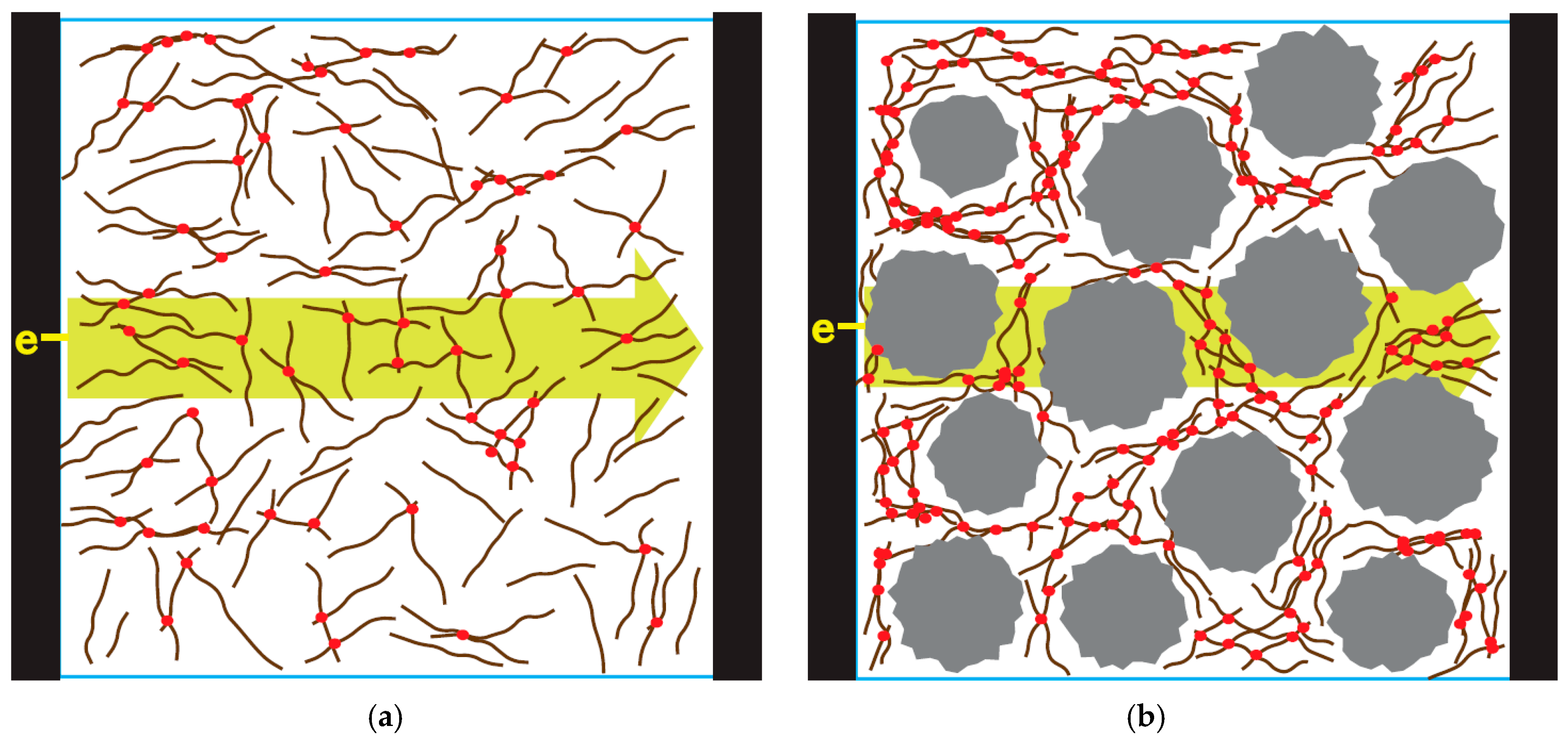
1. Introduction
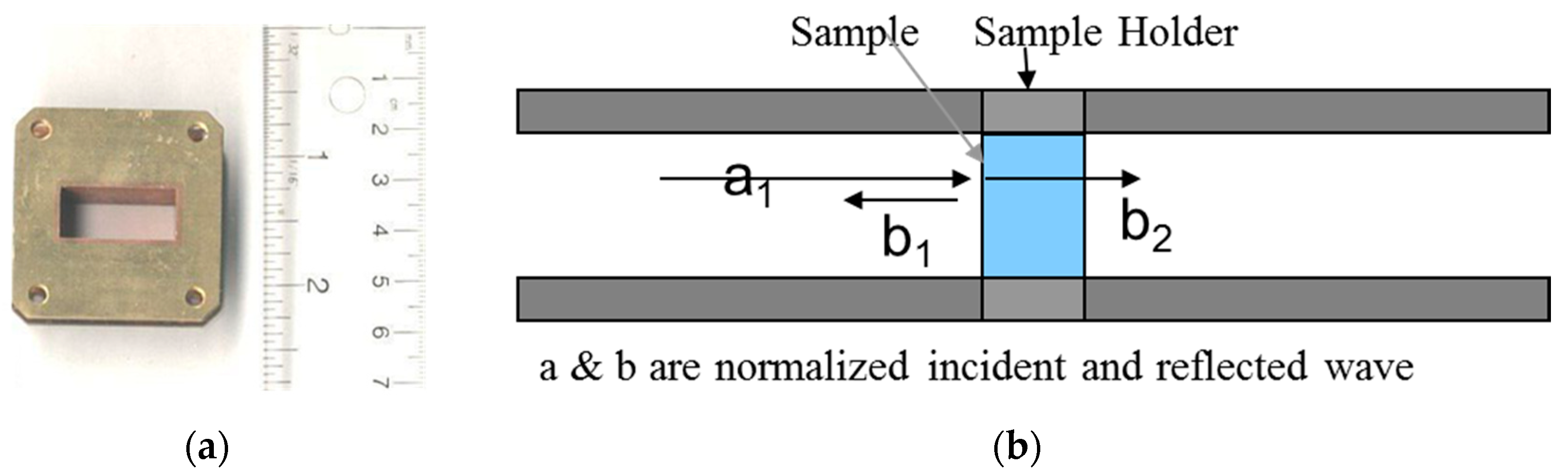
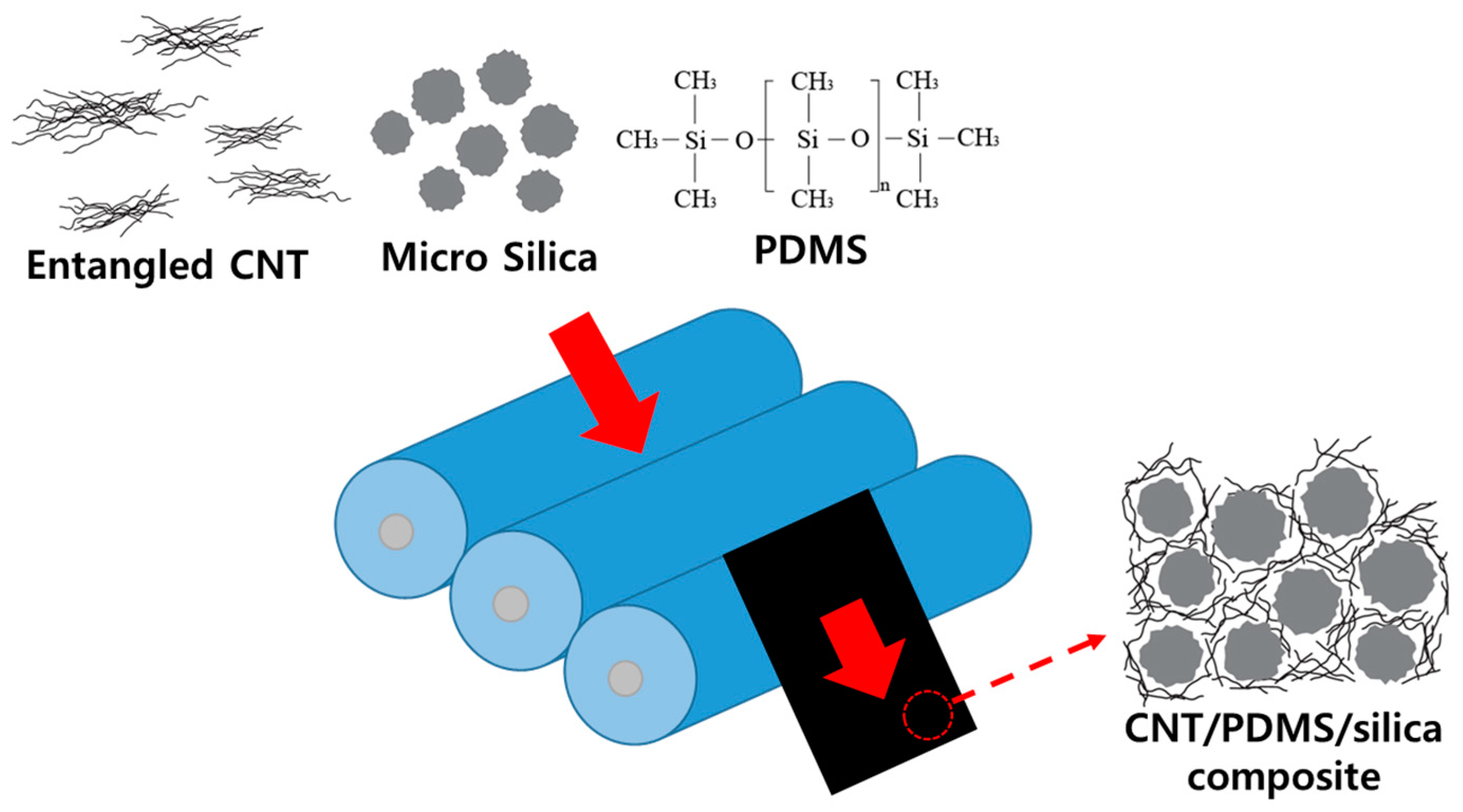
2. Materials and Methods
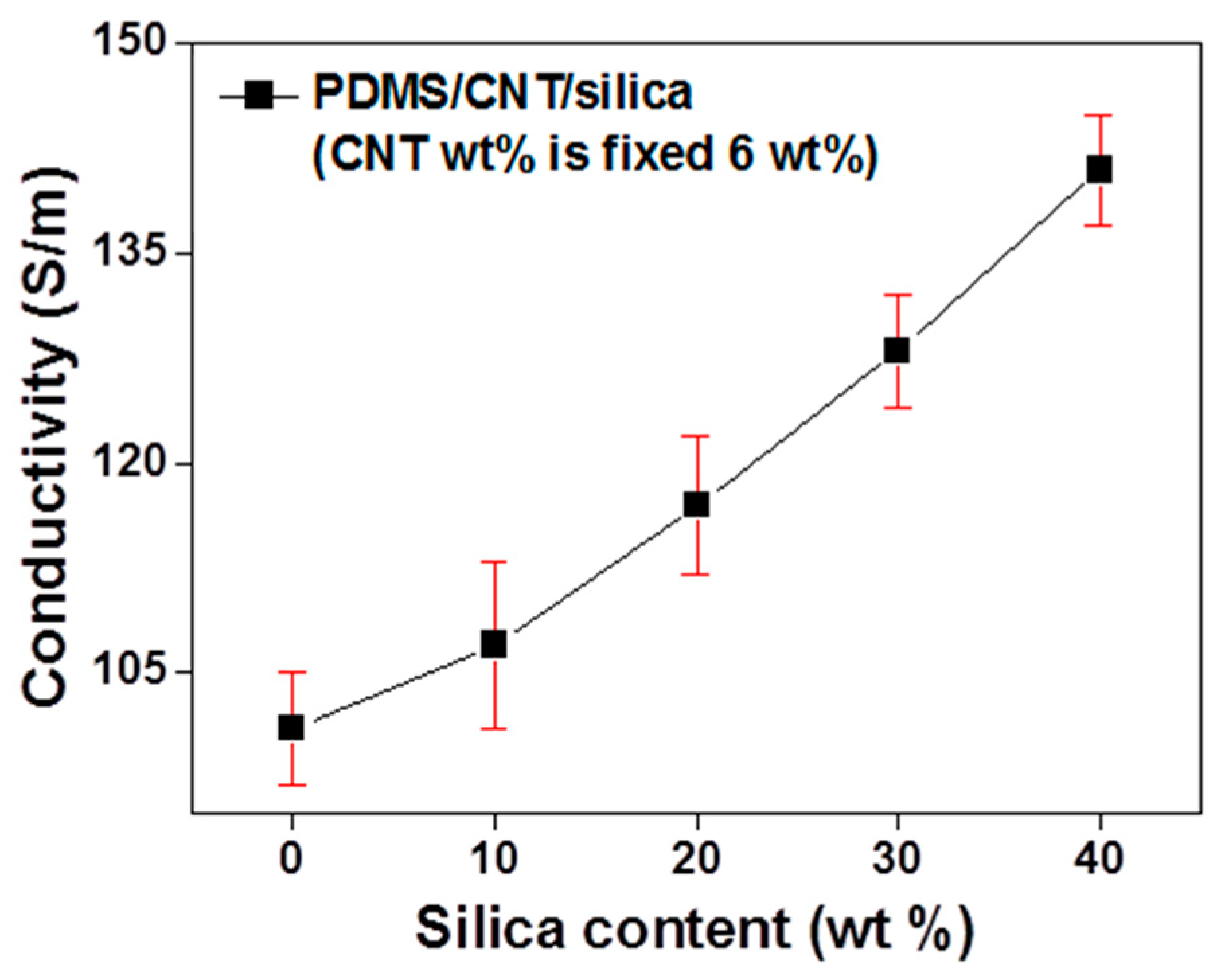
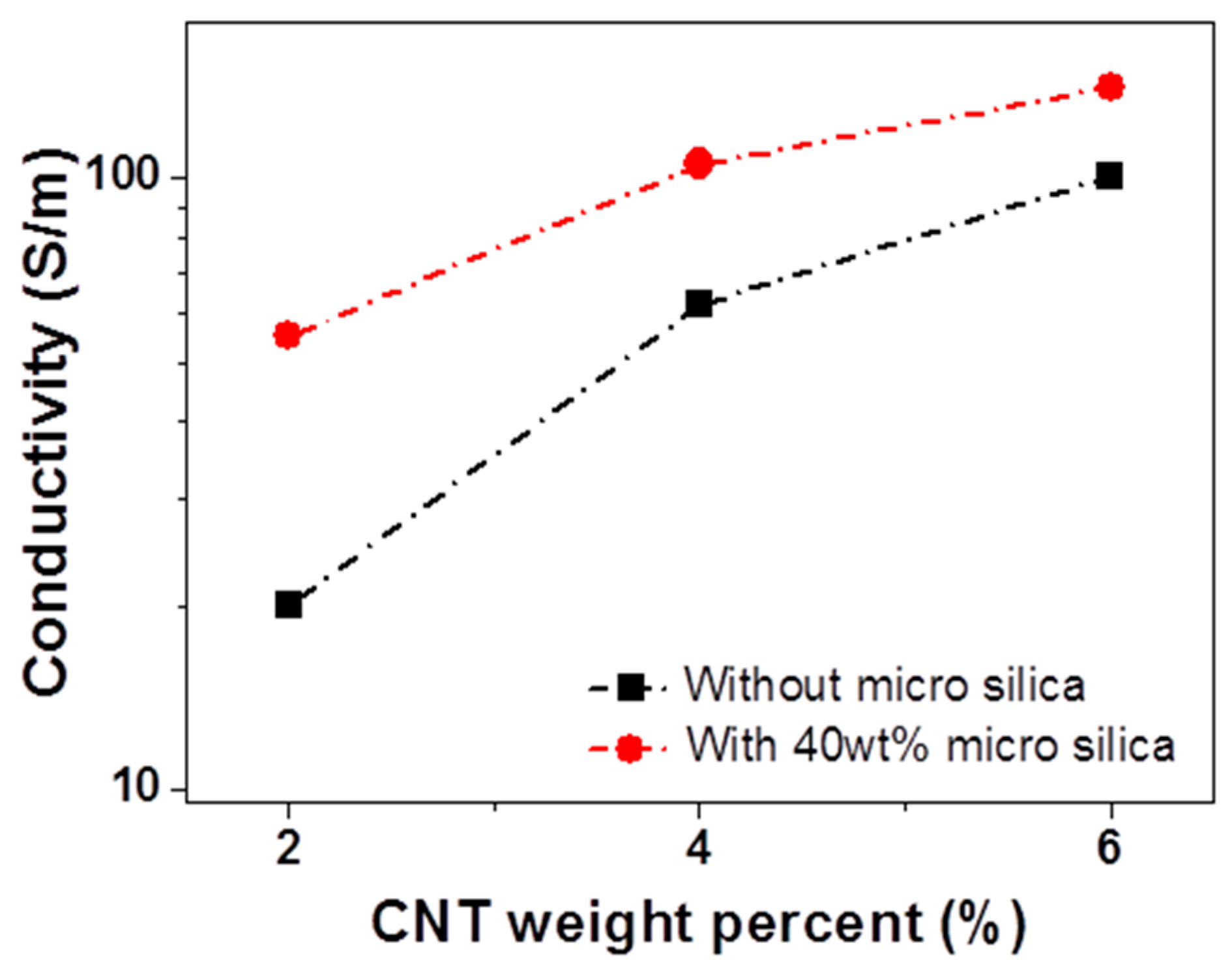
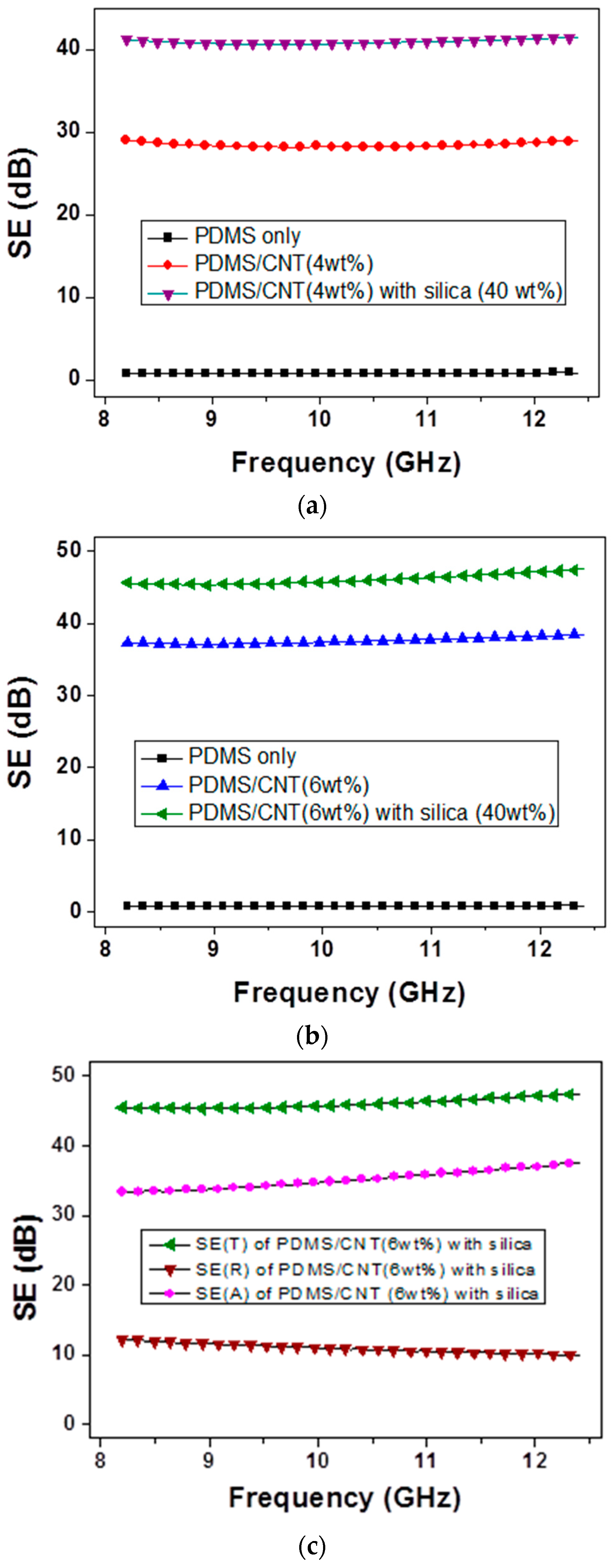
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, S.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.W.; Theilmann, P.; Park, S.H. Enhanced thermal and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube composites through the use of functionalized CNT-reactive polymer linkages and three-roll milling. Compos. Part A 2015, 77, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Moon, C.; Park, S.H. Smart conducting polymer composites having zero temperature coefficient of resistance. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Theilmann, P.; Asbeck, P.; Bandaru, P.R. Enhanced dielectric constants and shielding effectiveness of uniformly dispersed functionalized carbon nanotube composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 243111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddubskaya, A.; Demidenko, M.; Batrakov, K.; Valušis, G.; Kaplas, T.; Svirko, Y.; Kuzhir, P. Tunable perfect THz absorber based on a stretchable ultrathin carbon-polymer bilayer. Materials 2019, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Bandaru, P.R. Improved mechanical properties of carbon nanotube/polymer composites through the use of carboxyl-epoxide functional group linkages. Polymer 2010, 51, 5071–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Park, S.H. Electrical heating behavior of flexible carbon nanotube composites with different aspect ratios. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Theilmann, P.; Asbeck, P.; Bandaru, P.R. Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding through the use of functionalized carbon nanotube-reactive polymer composites. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2010, 9, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lln, J.C. Cataracts and cell-phone radiation. IEEE Antennas. 2003, 45, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigg, D.M. Plastic composites for electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Polym. Compos. 1983, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, P.B.; Mallick, A.K.; SK, D. Electromagnetic interference shielding by carbon fibre filled polychloroprene rubber composites. Composites 1991, 22, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Chung, D.D.L. Partial replacement of carbon fiber by carbon black in multifunctional cement–matrix composites. Carbon 2007, 45, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Electrically conductive cement-based materials. Adv. Cem. Res. 2004, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilmann, P.; Yun, D.J.; Asbeck, P.; Park, S.H. Superior electromagnetic interference shielding and dielectric properties of carbon nanotube composites through the use of high aspect ratio CNTs and three-roll milling. Org. Electron. 2013, 14, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Novel carbon nanotube-polystyrene foam composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; He, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Eklund, P.C. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, X. Intrinsically conducting polymers for electromagnetic interference shielding. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2005, 16, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigney, A.; Laurent, C.; Flahaut, E.; Basca, R.R.; Rousset, A. Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2001, 39, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Grunlan, J.C. Clay assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes in conductive epoxy nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svab, I.; Musil, V.; Smit, I.; Makarovic, M. Mechanical properties of wollastonite-reinforced polypropylene composites modified with SEBS and SEBS-g-MA elastomers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunlan, J.C.; Mehrabi, A.R.; Bannon, M.V.; Bahr, J.L. Water-based single-walled-nanotube-filled polymer composite with an exceptionally low percolation threshold. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.D.; Guo, Z.X.; Yu, J. Effect of electrically inert particulate filler on electrical resistivity of polymer/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Polymer 2008, 49, 3826–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Grunlan, J.C.; Yu, C. Improved thermoelectric behavior of nanotube-filled polymer composites with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) poly(styrenesulfonate). ACS Nano 2010, 4, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, M.; Kamal, M.R. Estimation of the volume resistivity of electrically conductive composites. Polym. Compos. 1997, 18, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Materials for electromagnetic interference shielding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2000, 9, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, M.; Apperley, T.; Okoniewski, M.; Sundararaj, U. Comparative study of electromagnetic interference shielding properties of injection molded versus compression molded multi-walled carbon nanotube/polystyrene composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 5126–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Gelves, G.A.; Park, S.; Sundararaj, U. Electrical and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of flow-induced oriented carbon nanotubes in polycarbonate. Carbon 2011, 49, 3430–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, D.; Pastore, R.; Vricella, A.; Marchetti, M. Matter’s Electromagnetic Signature Reproduction by Graded-Dielectric Multilayer Assembly. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 2801–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, D.; Pastore, R.; Delfini, A.; Giusti, A.; Vricella, A.; Santoni, F.; Marchetti, M.; Tolochko, O.; Vasilyeva, E. Electromagnetic characterization of advanced nanostructured materials and multilayer design optimization for metrological and low radar observability applications. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 134, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-H.; Ha, J.-H. Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties Through the Use of Segregate Carbon Nanotube Networks. Materials 2019, 12, 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091395
Park S-H, Ha J-H. Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties Through the Use of Segregate Carbon Nanotube Networks. Materials. 2019; 12(9):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091395
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sung-Hoon, and Ji-Hwan Ha. 2019. "Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties Through the Use of Segregate Carbon Nanotube Networks" Materials 12, no. 9: 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091395
APA StylePark, S.-H., & Ha, J.-H. (2019). Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties Through the Use of Segregate Carbon Nanotube Networks. Materials, 12(9), 1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12091395