Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
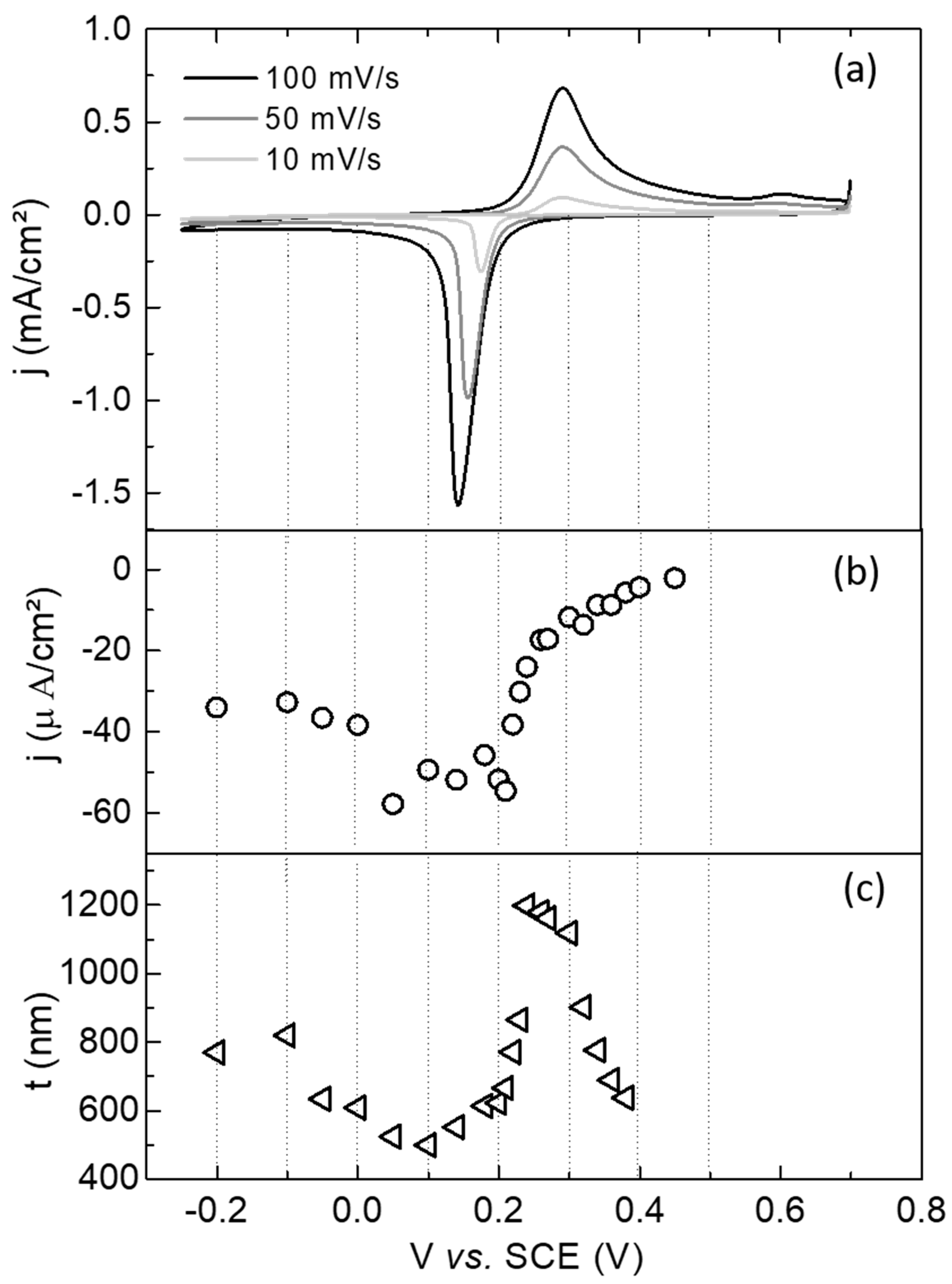
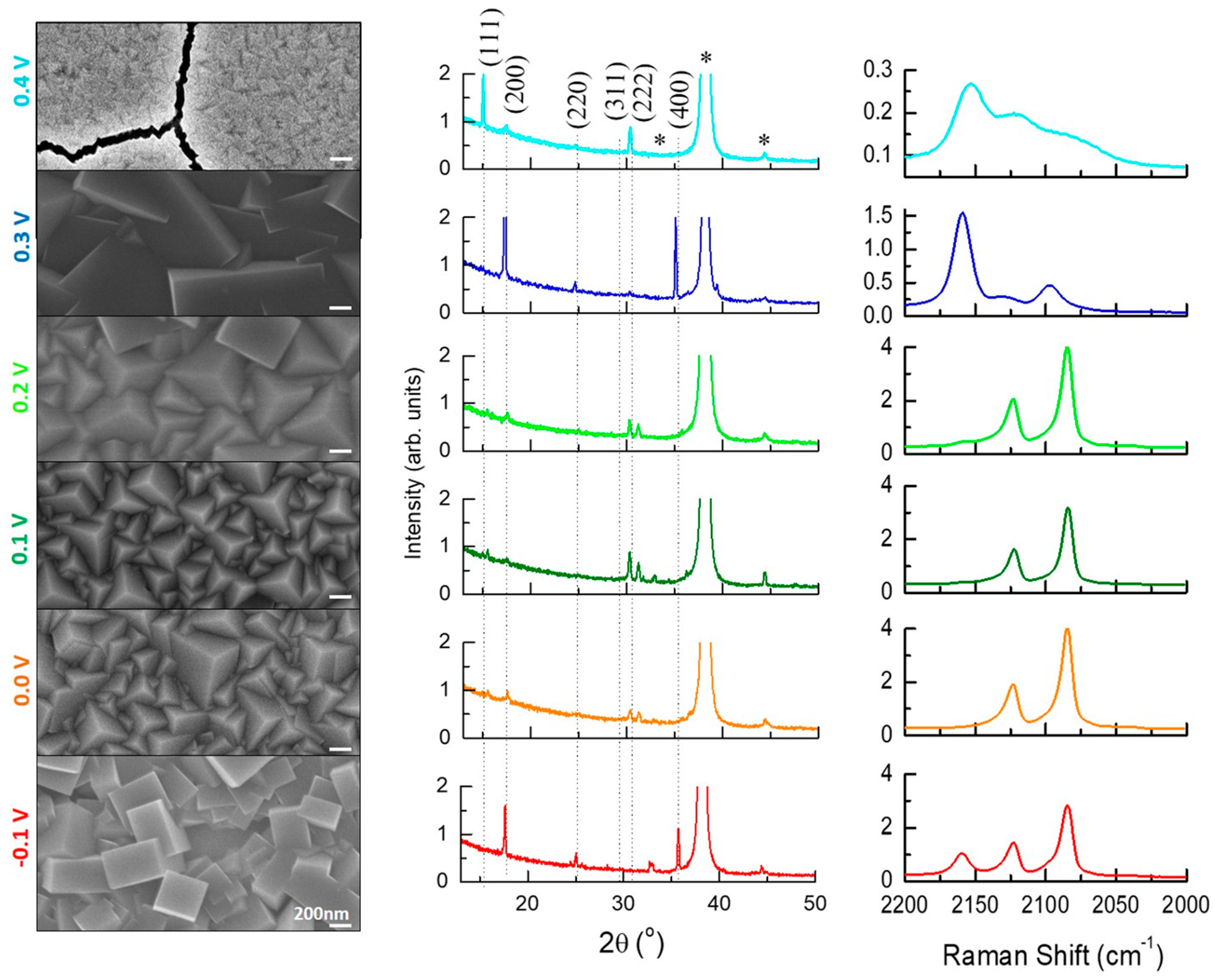
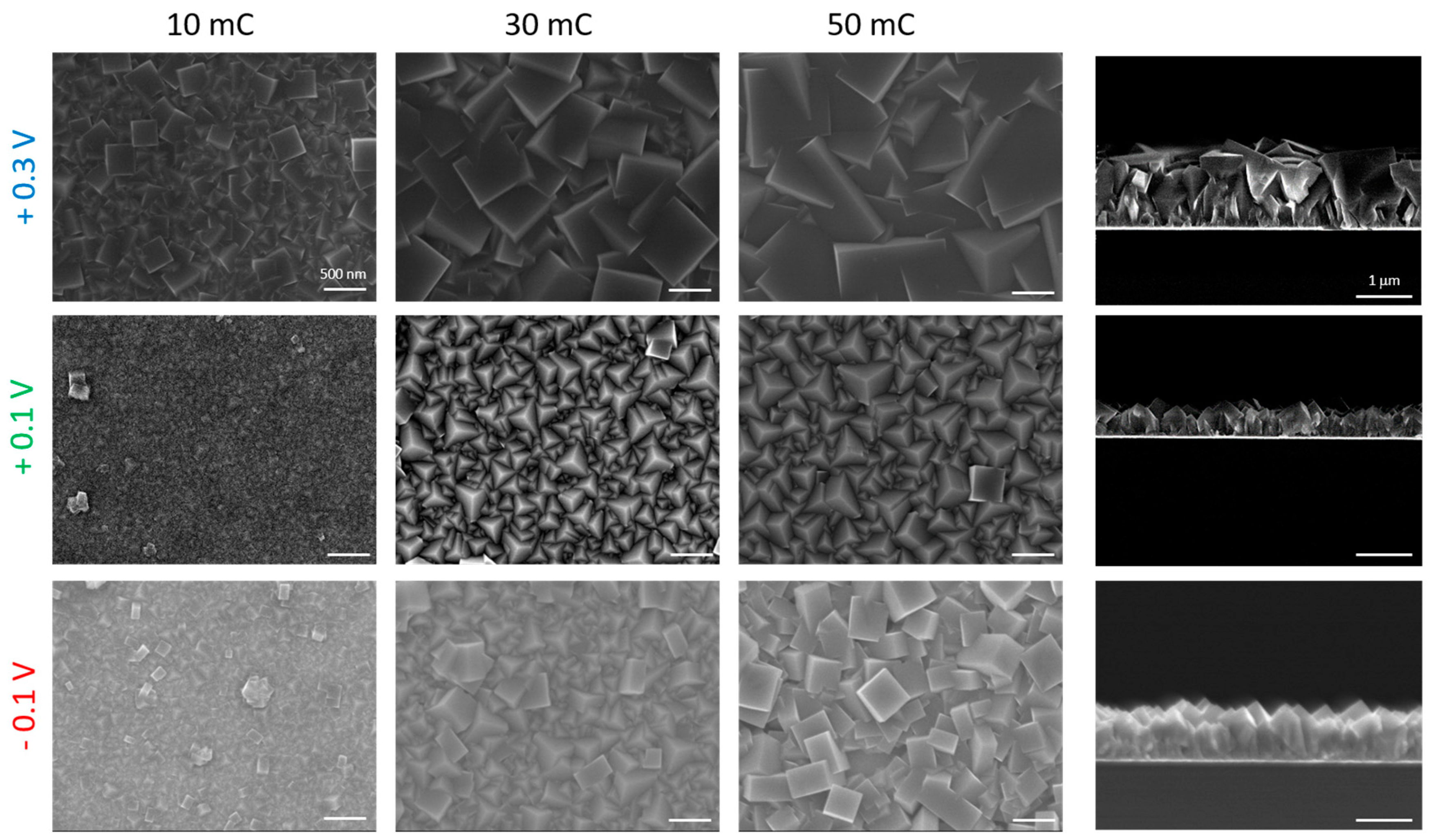
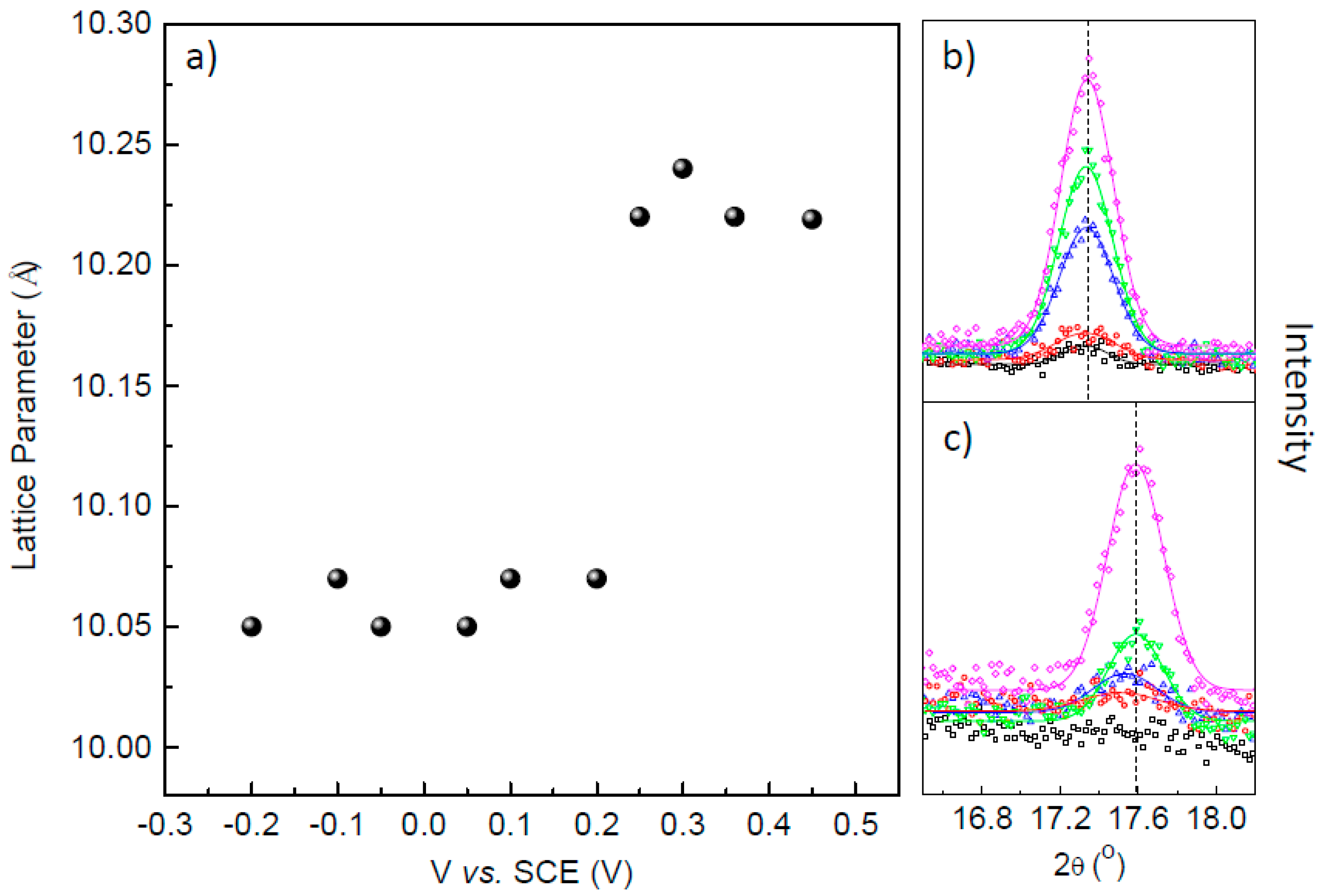
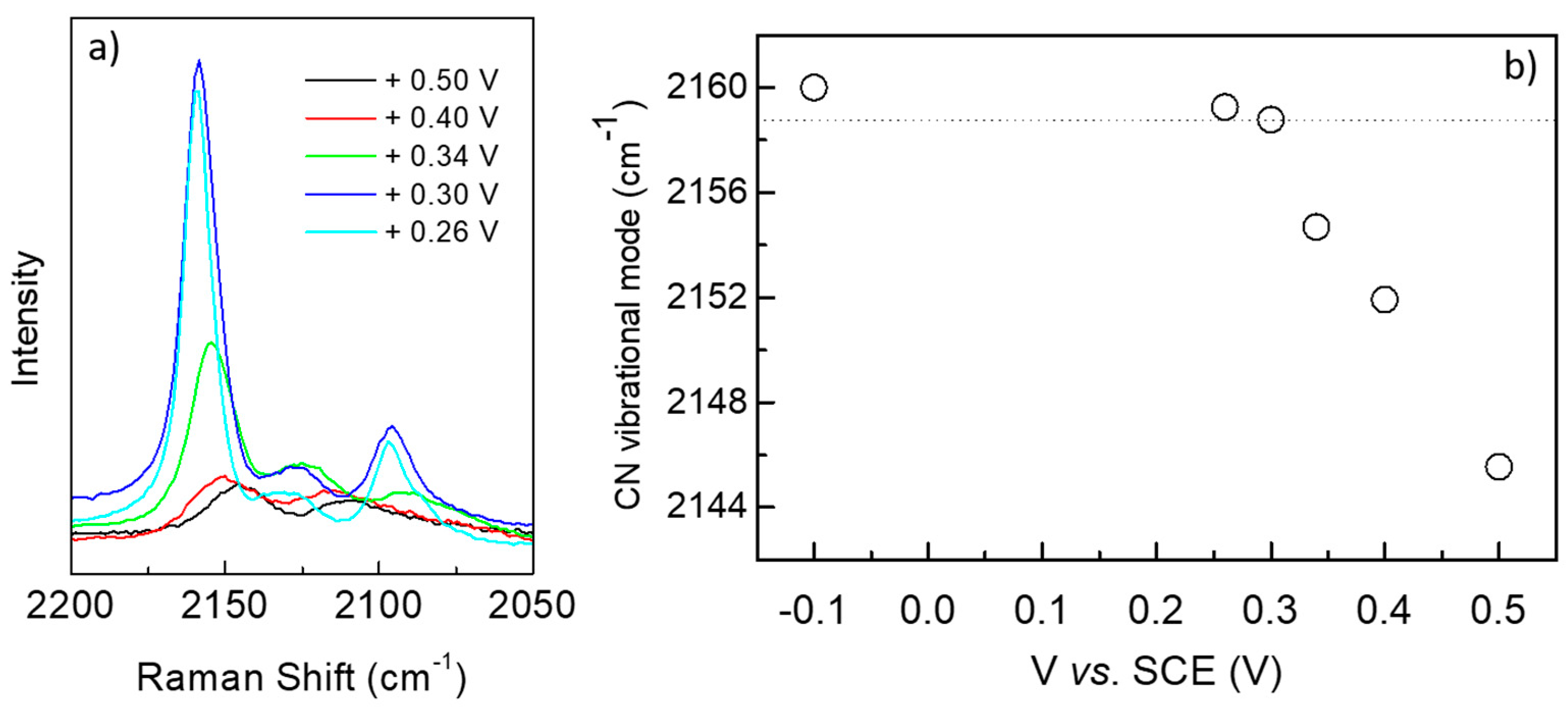
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keggin, J.F.; Miles, F.D. Structures and Formulae of the Prussian Blues and Related Compounds. Nature 1936, 137, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.; Welo, L.A. The Nature of Prussian Blue. J. Phys. Chem. 1928, 32, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, A. Electrochromism: A fascinating branch of electrochemistry. ChemTexts 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chu, Y.; Ai, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, F. Graphene oxide with in-situ grown Prussian Blue as an electrochemical probe for microRNA-122. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarnath, C.A.; Sawant, S.N. Tailoring synthesis strategies for polyaniline-prussian blue composite in view of energy storage and H2O2 sensing application. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, C.D.; Peddada, S.V.; Huggins, R.A.; Cui, Y. Nickel hexacyanoferrate nanoparticle electrodes for aqueous sodium and potassium ion batteries. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5421–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, R.; Lu, G.; Li, Y. Cobalt Hexacyanoferrate Nanoparticles as a High-Rate and Ultra-Stable Supercapacitor Electrode Material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11007–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Wu, X.L.; Yin, Y.X.; Guo, Y.G. High-quality Prussian blue crystals as superior cathode materials for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeerage, K.M.; Steen, W.A.; Schwartz, D.T. Correlating nanoscale structure with ion intercalation in electrodeposited nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.; Goodenough, J.B. A superior low-cost cathode for a Na-Ion battery. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 2018–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Sun, M.; Qian, J.; Cao, Y.; Ai, X.; Yang, H. Low-defect Prussian blue nanocubes as high capacity and long life cathodes for aqueous Na-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jian, Z.; Li, Z.; Ji, X. Prussian white analogues as promising cathode for non-aqueous potassium-ion batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 77, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, K.; Donohue, J.; Ramanna, N.; Cohn, A.P.; Muralidharan, N.; Eaves, J.; Pint, C.L. High-rate potassium ion and sodium ion batteries by co-intercalation anodes and open framework cathodes. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13335–13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xin, S.; Xue, L.; Goodenough, J.B. Stabilizing a High-Energy-Density Rechargeable Sodium Battery with a Solid Electrolyte. Chem 2018, 4, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zang, R.; Li, P.; Man, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, G. High Crystalline Prussian White Nanocubes as a Promising Cathode for Sodium-ion Batteries. Chem 2018, 13, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.J.; Schwarzenbach, D.; Petter, W.; Ludi, A. The Crystal Structure of Prussian Blue: Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3·xH2O. Inorg. Chem. 1977, 16, 2704–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, A.; Uchida, H.; Ishizaki, M.; Satoh, T.; Kaga, S.; Okamoto, S.; Ohta, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Simple synthesis of three primary colour nanoparticle inks of Prussian blue and its analogues. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 345609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Suenaga, M.; Ôno, K. Mössbauer Study of Soluble Prussian Blue, Insoluble Prussian Blue, and Turnbull’s Blue. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 3597–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, J.; Qiao, R.; Wray, L.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Chuang, Y.; Yang, W.; Lu, Y.; Evans, D.; Lee, J.; et al. Rhombohedral Prussian White as Cathode for Rechargeable Sodium-Ion Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessells, C.D.; Huggins, R.A.; Cui, Y. Copper hexacyanoferrate battery electrodes with long cycle life and high power. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, M.; Wessells, C.D.; Liu, N.; Nelson, J.; McDowell, M.T.; Huggins, R.A.; Toney, M.F.; Cui, Y. Full open-framework batteries for stationary energy storage. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itaya, K.; Akahoshi, H.; Toshima, S. Electrochemistry of Prussian Blue Modified Electrodes: An Electrochemical Preparation Method. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1982, 129, 1498–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaya, K.; Ataka, T.; Toshima, S. Spectroelectrochemistry and Electrochemical Preparation Method of Prussian Blue Modified Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 4767–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, C.A.; Murray, R.W. Observations on the Composition of Prussian Blue Films and Their Electrochemistry. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, P.R.; Ferreira, F.F.; Giménez-Romero, D.; Setti, G.O.; Faria, R.C.; Gabrielli, C.; Perrot, H.; Garcia-Jareño, J.J.; Vicente, F. Synchrotron structural characterization of electrochemically synthesized hexacyanoferrates containing K+: A revisited analysis of electrochemical redox. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13264–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadronecki, M.; Wrona, P.K.; Galus, Z. Study of Growth and the Electrochemical Behavior of Prussian Blue Films Using Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, E.W.; Kalwellis-Mohn, S. Hexacyanoferrate layers as electrodes for secondary cells. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1987, 17, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Okada, T. A secondary battery composed of multilayer Prussian Blue and its reaction characteristics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1988, 255, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Moritomo, Y. Thin film electrode of Prussian blue analogue for Li-ion battery. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 047101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwellis, S.; Grabner, E.W. A secondary cell based on thin layers of zeolite-like nickel hexacyanometallates. Electrochim. Acta 1989, 34, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzak, P.; Yun, J.; Dorsel, A.; Kriele, A.; Gilles, R.; Schneider, O.; Bandarenka, A.S. Electrodeposited Na2Ni[Fe(CN)6] Thin-Film Cathodes Exposed to Simulated Aqueous Na-Ion Battery Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8760–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeerage, K.M.; Schwartz, D.T. Characterization of cathodically deposited nickel hexacyanoferrate for electrochemically switched ion exchange. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, W.A.; Han, S.-W.; Yu, Q.; Gordon, R.A.; Cross, J.O.; Stern, E.A.; Seidler, G.T.; Jeerage, K.M.; Schwartz, D.T. Structure of Cathodically Deposited Nickel Hexacyanoferrate Thin Films Using XRD and EXAFS. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7714–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ropero, A.J.; Piernas-Muñoz, M.J.; Castillo-Martínez, E.; Rojo, T.; Casas-Cabanas, M. Electrochemical characterization of NaFe2(CN)6 Prussian Blue as positive electrode for aqueous sodium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 210, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamini, M.F.; da Silva, R.C.; Zoldan, V.C.; Isoppo, E.A.; Rodrigues Filho, U.P.; Aarão Reis, F.D.A.; Klein, A.N.; Pasa, A.A. Normal versus anomalous roughening in electrodeposited Prussian Blue layers. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritomo, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Kim, J. Doping-Induced Structural Phase Transition in Na1.6−xCo[Fe(CN)6]0.902.9H2O. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 78, 074602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, F.; Samain, L.; Long, G.J. Characterization and utilization of Prussian blue and its pigments. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 18018–18044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, O.; Einaga, Y.; Iyoda, T.; Fujishima, A.; Hashimoto, K. Reversible Photoinduced Magnetization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 144, L11–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguera, E.; Bertrán, J.F.; Diaz, C.; Blanco, J.; Rondón, S. Mössbauer and infrared spectroscopic studies of novel mixed valence states in cobaltous ferrocyanides and ferricyanides. Hyperfine Interact. 1990, 53, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleuzen, A.; Lomenech, C.; Escax, V.; Villain, F.; Varret, F.; Cartier Dit Moulin, C.; Verdaguer, M. Photoinduced ferrimagnetic systems in Prussian blue analogues CIxCo4[Fe(Cn)6]y (Ci = alkali cation). 1. Conditions to observe the phenomenon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 6648–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, S.F.A.; Diana, E.; Marchese, E.M.C.; Boccaleri, E.; Stanghellini, P.L. The vibrational spectra of the cyanide ligand revisited: The ν (CN) infrared and Raman spectroscopy of Prussian blue and its analogues. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossol, E.; Gorgatti Zarbin, A.J. Transparent films from carbon nanotubes/Prussian blue nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, and application as electrochemical sensors. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y.; Nam, K.W.; Guo, Y.G. Sodium iron hexacyanoferrate with high Na content as a Na-rich cathode material for Na-ion batteries. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, S.F.A.; Aschero, G.L.; Diana, E.; Rossetti, R.; Stanghellini, P.L. The Vibrational Spectra of the Cyanide Ligand Revisited: Terminal Cyanides. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 4928–4937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weidinger, D.; Sando, G.M.; Owrutsky, J.C. Vibrational dynamics of metal cyanides. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 489, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baggio, B.F.; Vicente, C.; Pelegrini, S.; Plá Cid, C.C.; Brandt, I.S.; Tumelero, M.A.; Pasa, A.A. Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films. Materials 2019, 12, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071103
Baggio BF, Vicente C, Pelegrini S, Plá Cid CC, Brandt IS, Tumelero MA, Pasa AA. Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071103
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaggio, Bruna F., Cristiano Vicente, Silvia Pelegrini, Cristiani Campos Plá Cid, Iuri Stefani Brandt, Milton André Tumelero, and André A. Pasa. 2019. "Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films" Materials 12, no. 7: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071103
APA StyleBaggio, B. F., Vicente, C., Pelegrini, S., Plá Cid, C. C., Brandt, I. S., Tumelero, M. A., & Pasa, A. A. (2019). Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films. Materials, 12(7), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071103




