Easy, Quick, and Reproducible Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
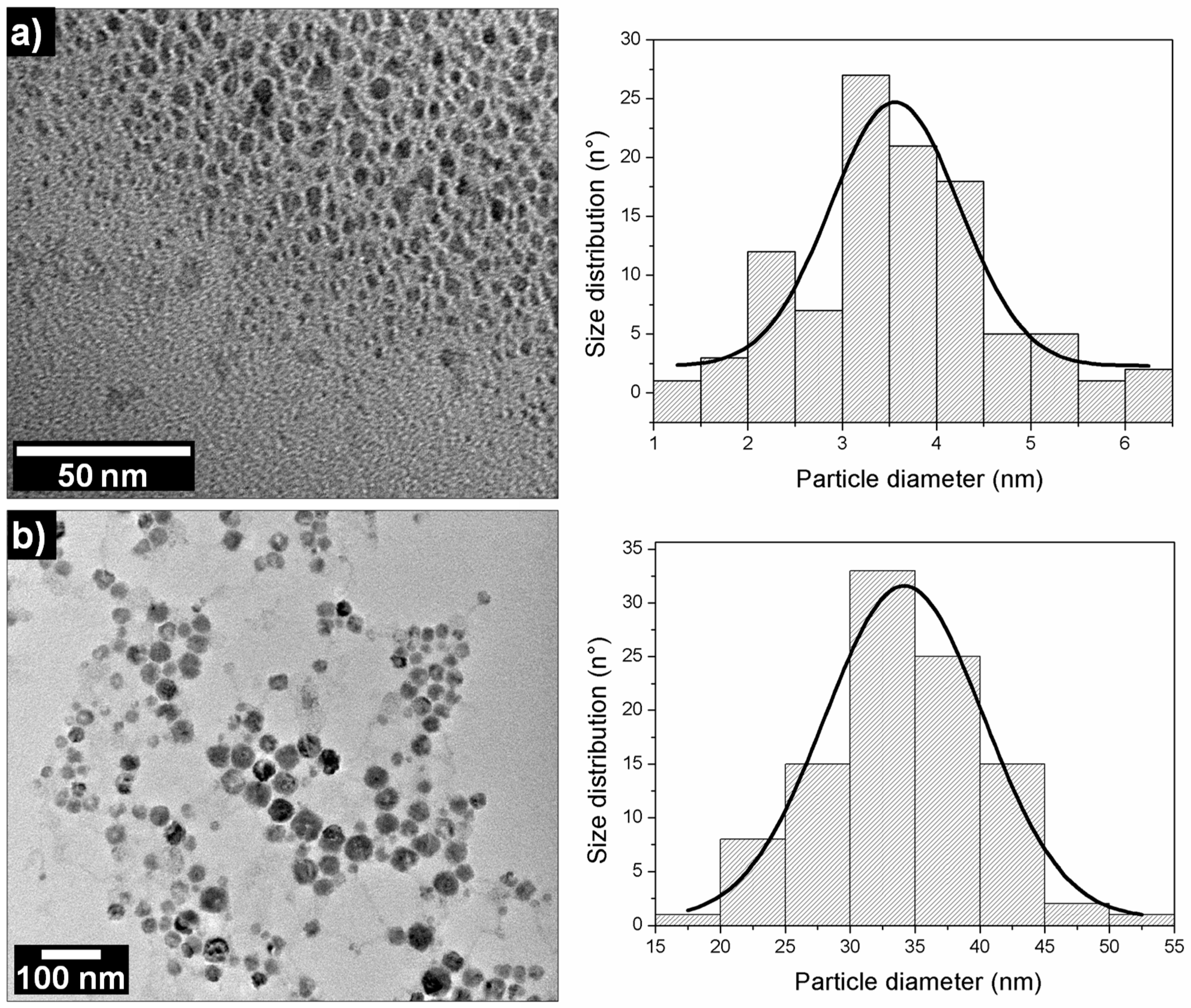
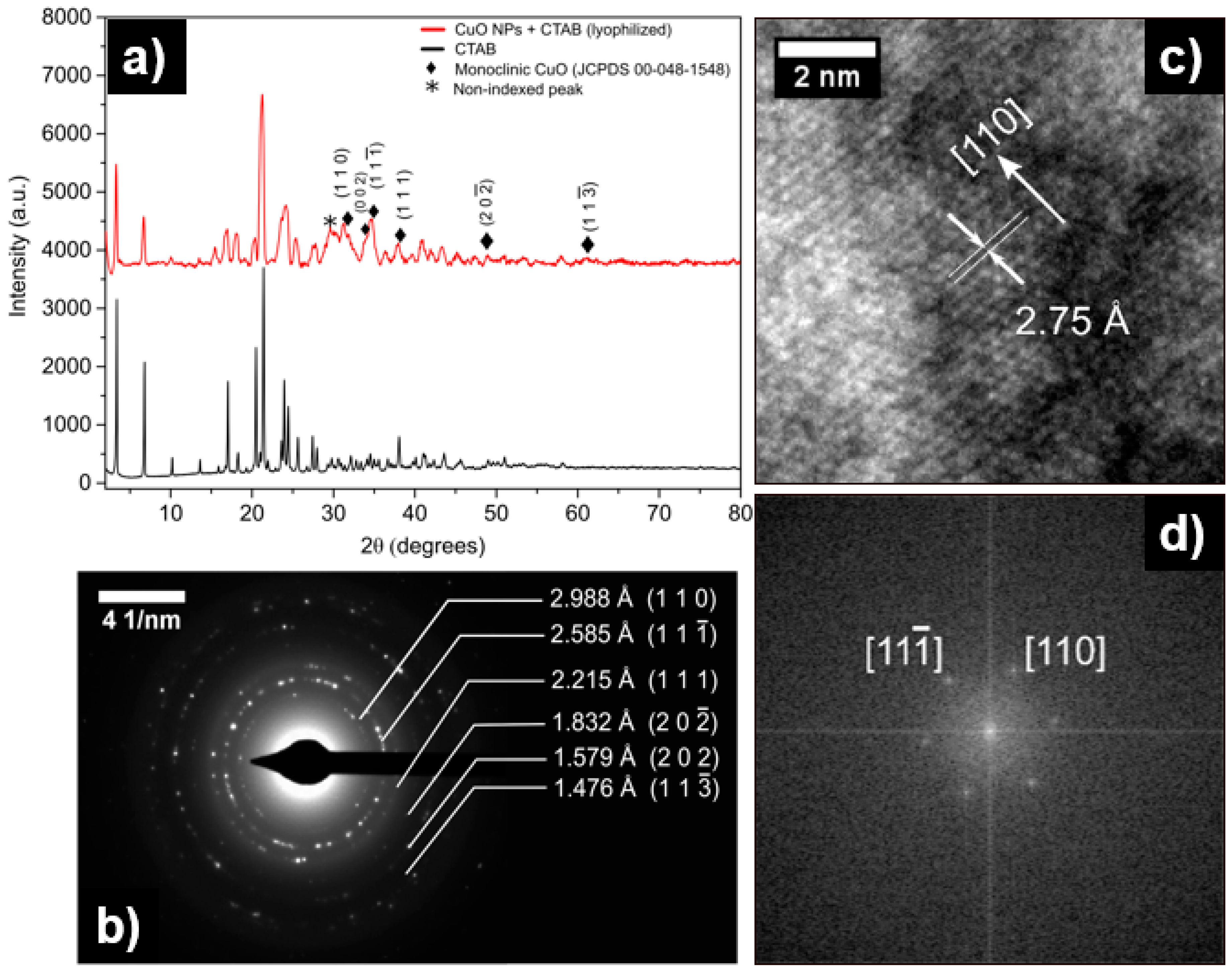
3. Results and Discussion
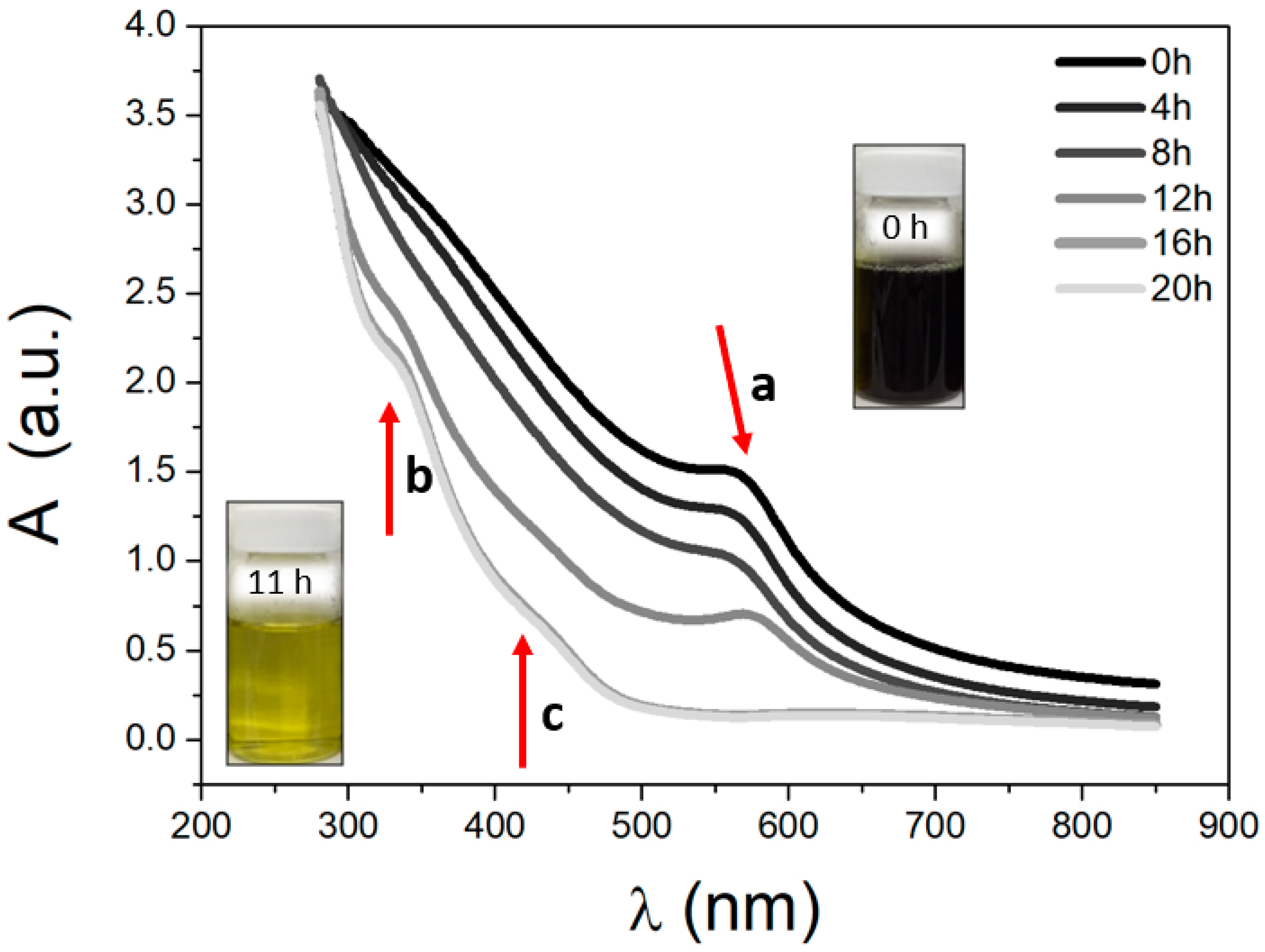
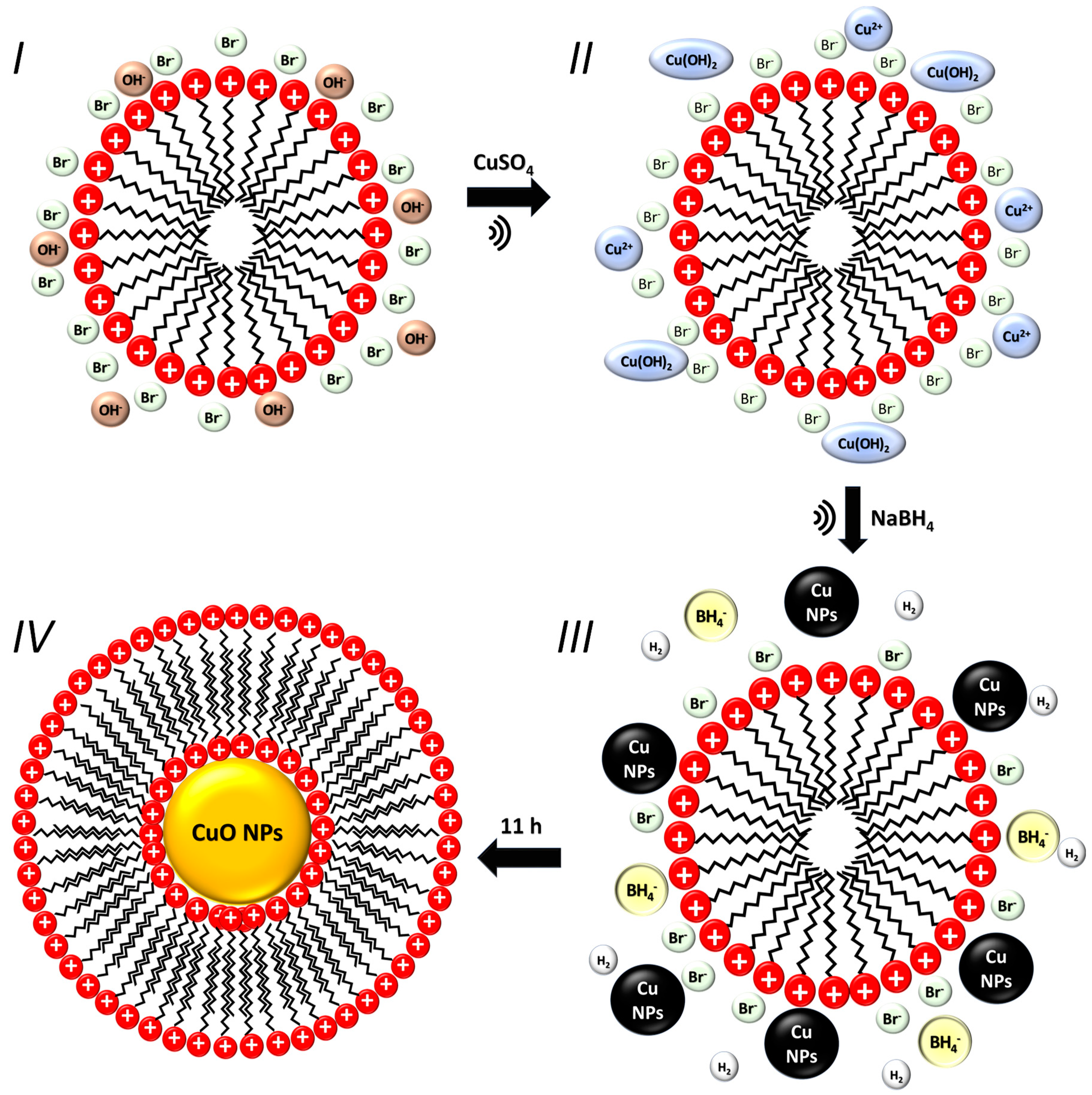
The Sonochemical Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Din, M.I.; Rehan, R. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Copper Nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavente, E.; Lozano, H.; Gonzalez, G. Fabrication of Copper Nanoparticles: Advances in Synthesis, Morphology Control, and Chemical Stability. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 7, 108–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodashenas, B.; Ghorbani, H.R. Synthesis of copper nanoparticles: An overview of the various methods. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Copper Nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Santos, C.G.; Paixão, M.W.; Soares, L.C.; De Souza, D.; Rodrigues, O.E.D.; Braga, A.L. CuO Nanoparticles: An Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst for Cross-Coupling Reactions of Organic Diselenides with Aryl Boronic Acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 6635–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendi, A.A.; Rashad, M. Photo-Induced Changes in Nano-Copper Oxide for Optoelectronic Applications. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 2018, 538, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, K.; Kido, Y.; Akaishi, Y.; Quitain, A.; Kida, T. Synthesis of Cu2O/CuO Nanocrystals and Their. Sensors 2019, 19, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M. Optimized Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of an Alginate—Cupric Oxide Bionanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, M.E.; Biscu, E.R.; Holban, A.M.; Gestal, M.C.; Grumezescu, A.M. Methods of Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Applications of CuO Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaweeteerawat, C.; Chang, C.H.; Roy, K.R.; Liu, R.; Li, R.; Toso, D.; Fischer, H.; Ivask, A.; Ji, Z.; Zink, J.I.; et al. Cu Nanoparticles Have Different Impacts in Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus brevis than Their Microsized and Ionic Analogues. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7215–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, O.V.; Godymchuk, A.Y.; Gusev, A.A.; Gulchenko, S.I.; Vasyukova, I.A.; Kuznetsov, D.V. Considerable Variation of Antibacterial Activity of Cu Nanoparticles Suspensions Depending on the Storage Time, Dispersive Medium, and Particle Sizes. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 412530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, E.; Ahmed, R.A. Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles with Various Sizes and Shapes: Application as a Superior Non-Enzymatic Sensor and Antibacterial Agent. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 4712–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, R.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Properties of CuO Nanocrystals with Various Shapes. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3939–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, S.P.; Adhyapak, P.V.; Mulik, U.P.; Amalnerkar, D.P. Facile Synthesis of CuO Nanomorphs and Their Morphology Dependent Sunlight Driven Photocatalytic Properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204–206, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yin, J.; Du, W.; Gao, F.; Fan, Y.; Lu, Q. Monodisperse CuO Hard and Hollow Nanospheres as Visible-Light Photocatalysts. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgohain, K.; Singh, J. Quantum Size Effects in CuO Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2000, 61, 11093–11096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y. Applied Surface Science Microwave-Assistant Synthesis of Ordered CuO Micro-Structures on Cu Substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Long, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Lu, P. Controlled Growth and Characteristics of Single-Phase Cu2O and CuO Films by Pulsed Laser Deposition. Vaccum 2009, 83, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G. Ultrasonochemical-Assisted Synthesis of CuO Nanorods with High Hydrogen Storage Ability. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 439162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Elgamiel, R.; Diamant, Y.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical Preparation and Characterization of Nanocrystalline Copper Oxide Embedded in Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Its Effect on Crystal Growth of Copper Oxide. Langmuir 2001, 17, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, D. One-Pot Low-Temperature Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanostructures and Their Electrochemical Properties. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19454–19460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, C.; Manikandan, G.; Gomathisankar, P. Microwave, Sonochemical and Combustion Synthesized CuO Nanostructures and Their Electrical and Bactericidal Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 580, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Karimi, R.; Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Aslani, A.; Kaviani, K. Sonochemical Synthesis, Characterization and Thermal and Optical Analysis of CuO Nanoparticles. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 3096–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Z. Sonochemistry-Synthesized CuO Nanoparticles as Polymer Solar Cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28786–28793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpisutpaisan, N.; Charoonsuk, P. Sonochemical Synthesis and Characterization of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. Energy Procedia 2011, 9, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, D. Detergents: An Overview. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 463, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, S.; Mandal, S. Surfactant-Assisted Shape Control of Copper Nanostructures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 421, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biçer, M.; Şişman, I. Controlled Synthesis of Copper Nano/Microstructures Using Ascorbic Acid in Aqueous CTAB Solution. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, J.; Du, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, G.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Facile Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with High Concentration via a CTAB-Induced Silver Mirror Reaction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 400, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelczak, M.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Shape Control in Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.; Anandan, S.; Suresh, S.; Asiri, A.M.; Wu, J.J. Surfactant Assisted Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue in the Presence of Visible Light. Energy Environ. Focus 2015, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, V.D.; Tran, N.Q.; Nguyen, T.P.P. Synergistic Effect of Citrate Dispersant and Capping Polymers on Controlling Size Growth of Ultrafine Copper Nanoparticles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2013, 10, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, U.S.; Shetty, A.N. Simple Glucose Reduction Route for One-Step Synthesis of Copper Nanofluids. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 4, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Q.; Wu, X. Synthesis of Highly Stable Dispersions of Nanosized Copper Particles Using L-Ascorbic Acid. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Chen, D. Synthesis of High-Concentration Cu Nanoparticles in Aqueous CTAB Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.M.; Zhou, D.B.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ichino, R.; Okido, M. Preparation of Cu Nanoparticles with NaBH4 by Aqueous Reduction Method. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Yu, S.; Shi, T.; Jiang, S. Template-Free Synthesis of Cu2O Hollow Nanospheres and Their Conversion into Cu Hollow Nanospheres. Powder Technol. 2009, 193, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litmanovich, O.E.; Tatarinov, V.S.; Litmanovich, A.A. Why the Size of Copper Nanoparticles Depends on the Nature of the Reducing Agent in the Preparation of Sols in a Cationic Polyelectrolyte Solution 1. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2011, 53, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, I.; Noh, W.; Kwon, J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Kang, D.H. Preparation of Copper Nanoparticles in Cellulose Acetate Polymer and the Reaction Chemistry of Copper Complexes in the Polymer. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2002, 23, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavee, G.N.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sorensen, C.M.; Hadjapanayis, G.C. Borohydride Reductions of Metal Ions. A New Understanding of the Chemistry Leading to Nanoscale Particles of Metals, Borides, and Metal Borates. Langmuir 1992, 8, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavee, G.N.; Klabunde, K.J.; Sorensen, C.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Borohydride Reduction of Nickel and Copper Ions in Aqueous and Nonaqueous Media. Controllable Chemistry Leading to Nanoscale Metal and Metal Boride Particles. Langmuir 1994, 10, 4726–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulfinger, L.; Solomon, S.D.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.V.; Rutkowsky, S.A.; Boritz, C. Synthesis and Study of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, G.W.; Waller, M.C.; Hohnstedt, L.F. Aqueous Sodium Borohydride Chemistry: Lead, Barium, Mercury, Cadmium, and Zinc. Anal. Chem. 1961, 33, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, Internet Version 2005; CRC Press: Boca Ratón, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Andal, V.; Buvaneswari, G. Preparation of Cu2O Nano-Colloid and Its Application as Selective Colorimetric Sensor for Ag+ ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suramwar, N.V.; Thakare, S.R.; Khaty, N.T. One pot Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles at Room Temperature and Its Catalytic Activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1807–S1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Yusof, N.S.; Ashokkumar, M. Ultrasonic Modification of Micelle Nanostructures. In Handbook of Ultrasonics and Sonochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 491–524. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Zhu, J.J.; Lu, D.J.; Chen, H.Y. Hollow PbWO4 Nanospindles via a Facile Sonochemical Route. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 8403–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonofragmentation of Molecular Crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14530–14533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text, 4th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Cheng, S.; Shi, T.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Liao, G.; Tang, Z. Size Distribution Control of Copper Nanoparticles and Oxides: Effect of Wet-Chemical Redox Cycling. Inorg. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.M.D.; Le, T.T.T.; Fribourg-Blanc, E.; Dang, M.C. Synthesis and Optical Properties of Copper Nanoparticles Prepared by a Chemical Reduction Method. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 015009–015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andal, V.; Buvaneswari, G. Effect of Reducing Agents in the Conversion of Cu2O Nanocolloid to Cu Nanocolloid. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshchenko, O.A.; Dmitruk, I.M.; Dmytruk, A.M.; Alexeenko, A.A. Influence of Annealing Conditions on Size and Optical Properties of Copper Nanoparticles Embedded in Silica Matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2007, 137, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestryakov, A.N.; Petranovskii, V.P.; Kryazhov, A.; Ozhereliev, O.; Pfänder, N.; Knop-Gericke, A. Study of Copper Nanoparticles Formation on Supports of Different Nature by UV-Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 385, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhineshbabu, N.R.; Rajendran, V.; Nithyavathy, N.; Vetumperumal, R. Study of Structural and Optical Properties of Cupric Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I.; Louër, D. High-Resolution Powder Diffraction Studies of Copper(II) Oxide. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1991, 24, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Song, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, S. CuO Nanowire Growth on Cu2O by in Situ Thermal Oxidation in Air. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 8559–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cu2+ | CTAB | NaBH4 | Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 42 ± 9.3 | 0.401 | 29 ± 2.5 |
| 1 | 3 | 10 | 35 ± 1.3 | 0.542 | 32 ± 3.1 |
| 1 | 6 | 10 | 36 ± 1.3 | 0.150 | 37 ± 1.5 |
| 1 | 8 | 10 | 36 ± 2.9 | 0.181 | 39 ± 1.7 |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 38 ± 1.9 | 0.264 | 42 ± 2.0 |
| 1 | 6 | 1 | 84 ± 5.9 | 0.141 | 39± 0.8 |
| 1 | 6 | 5 | 30 ± 1.2 | 0.184 | 31 ± 1.0 |
| 1 | 6 | 10 | 36 ± 1.3 | 0.150 | 37 ± 1.5 |
| 1 | 6 | 15 | 34 ± 3.1 | 0.299 | 36 ± 1.7 |
| 1 | 6 | 20 | 40 ± 0.9 | 0.224 | 39 ± 2.0 |
| 1 | 6 | 50 | 79 ± 8.7 | 0.204 | 44 ± 1.8 |
| 1 | 6 | 100 | 77 ± 6.5 | 0.349 | 37 ± 3.2 |
| Miller Index (h k l) | Interplanar Distance dhkl (Å) | Intensity of Signal (%) |
|---|---|---|
| (1 1 0) | 2.75201 | 13 |
| (1 1 −1) | 2.52367 | 100 |
| (1 1 1) | 2.32429 | 99 |
| (2 0 -2) | 1.86764 | 30 |
| (2 0 2) | 1.58227 | 10 |
| (1 1 -3) | 1.50660 | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, N.; Ramírez, S.; Díaz, I.; Garcia, A.; Hassan, N. Easy, Quick, and Reproducible Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles. Materials 2019, 12, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050804
Silva N, Ramírez S, Díaz I, Garcia A, Hassan N. Easy, Quick, and Reproducible Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles. Materials. 2019; 12(5):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050804
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Nataly, Sara Ramírez, Isaac Díaz, Andreina Garcia, and Natalia Hassan. 2019. "Easy, Quick, and Reproducible Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles" Materials 12, no. 5: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050804
APA StyleSilva, N., Ramírez, S., Díaz, I., Garcia, A., & Hassan, N. (2019). Easy, Quick, and Reproducible Sonochemical Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles. Materials, 12(5), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050804





