Droplet Impact on the Super-Hydrophobic Surface with Micro-Pillar Arrays Fabricated by Hybrid Laser Ablation and Silanization Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Micro-Pillar Arrays
2.3. Chemical Modification with FAS
2.4. Measurement and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
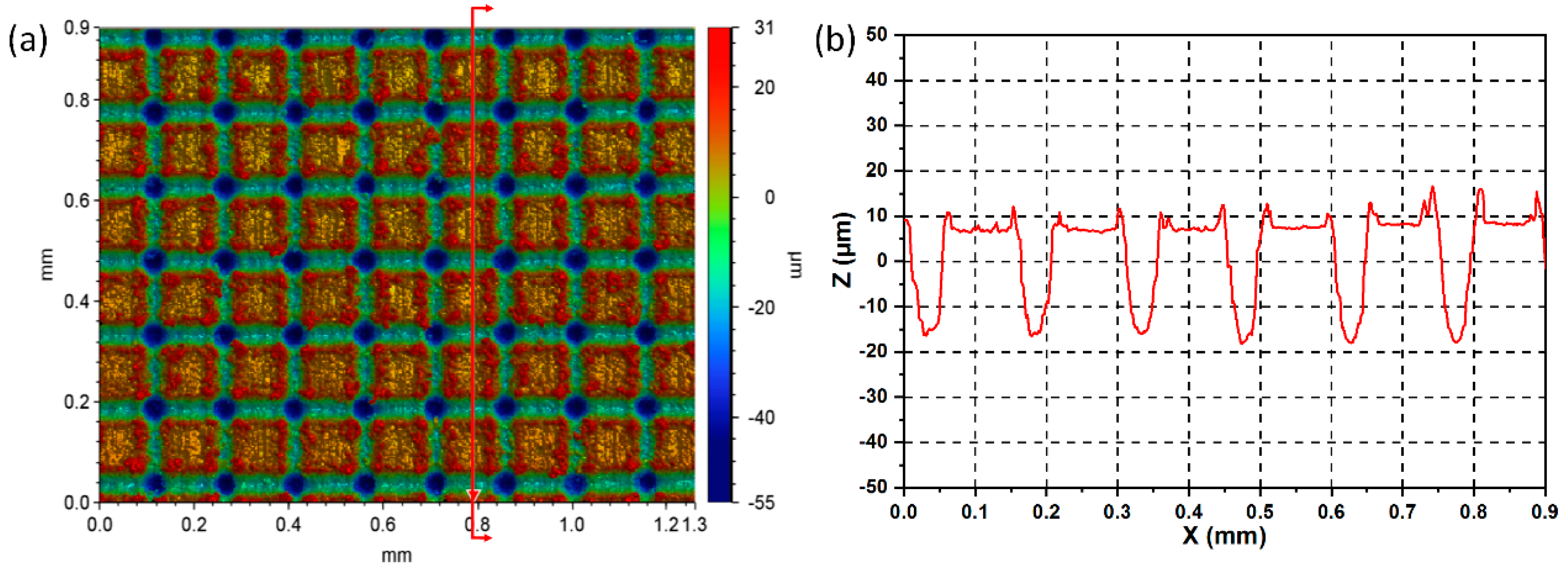
3.1. Surface Microstructures
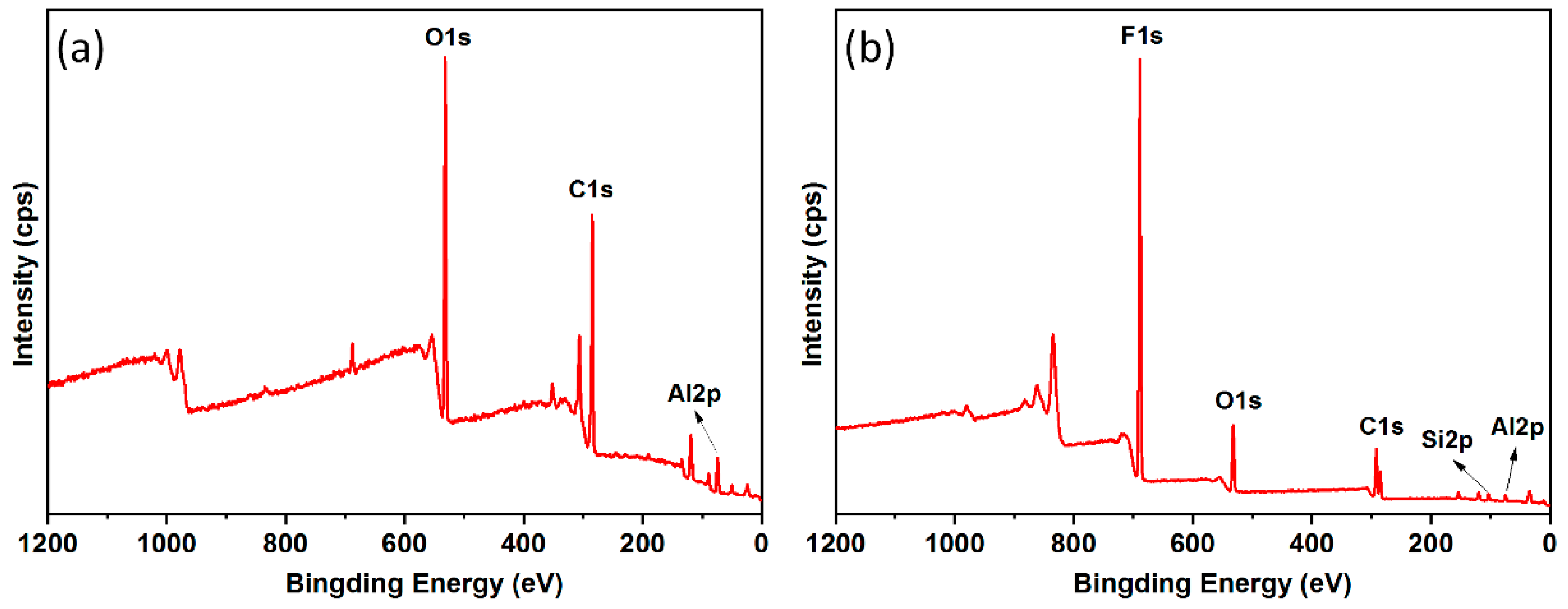
3.2. Surface Chemistry
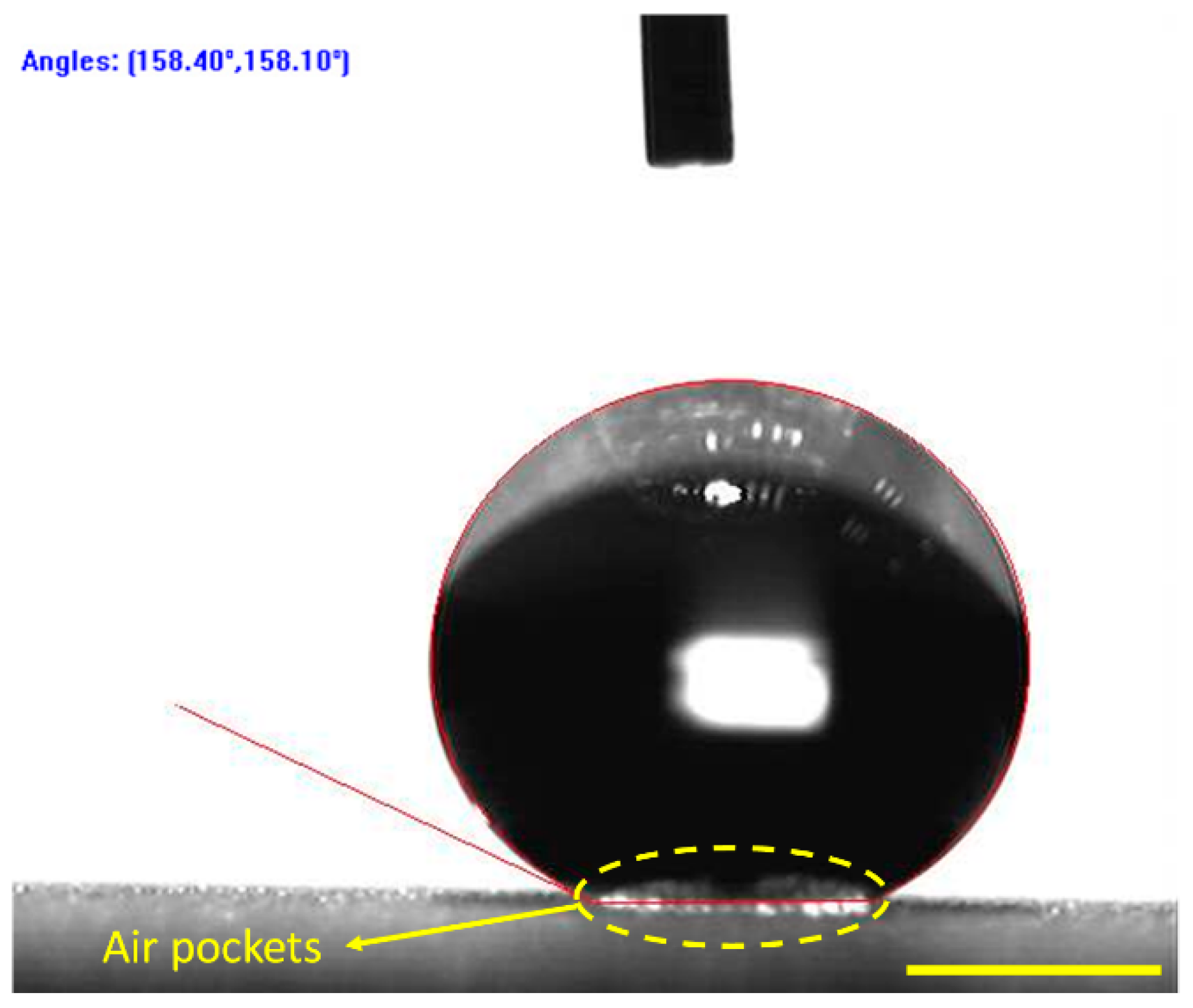
3.3. Wettability
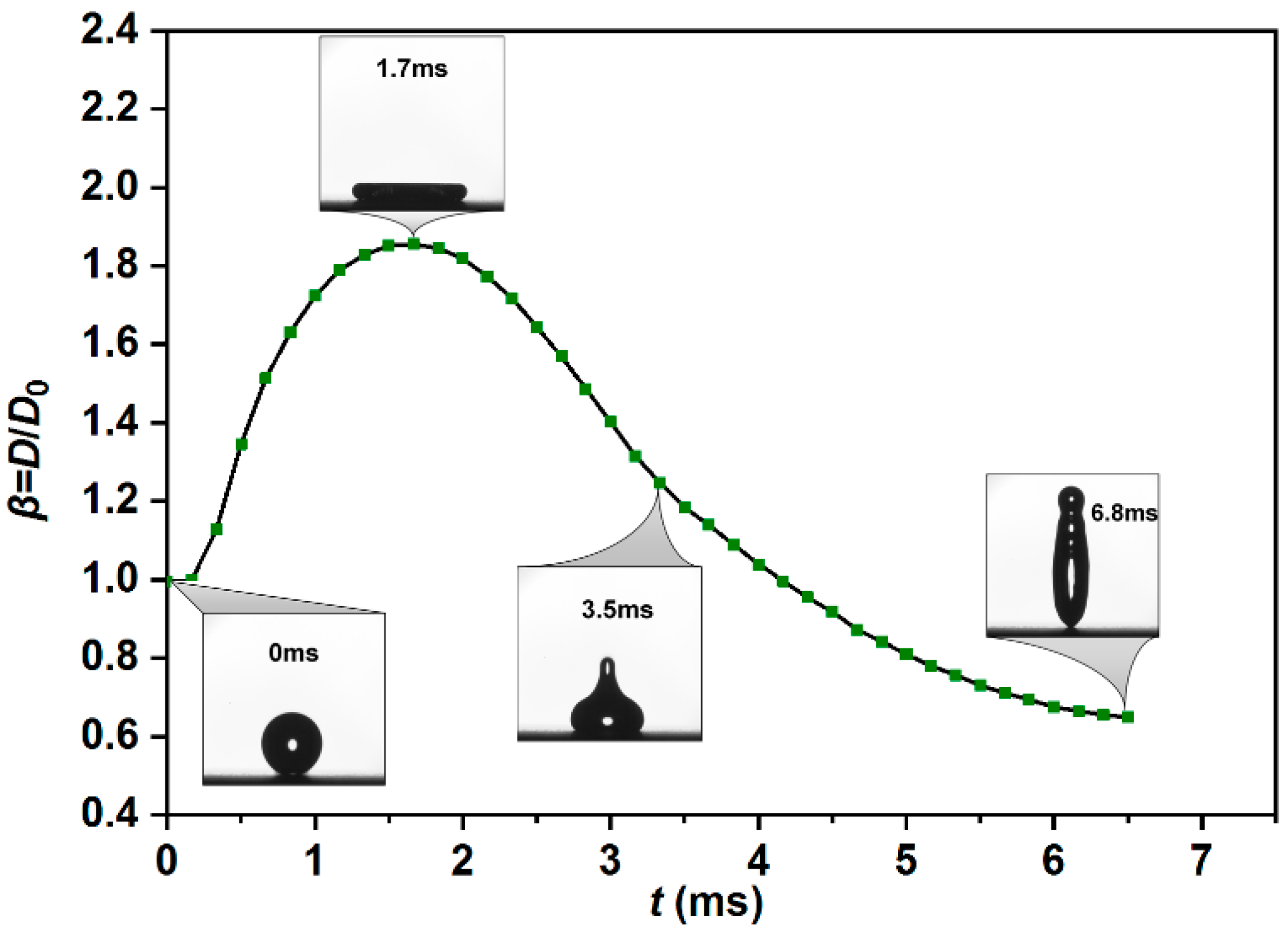
3.4. Droplet Impacting Behavior
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huhtamäki, T.; Tian, X.L.; Korhonen, J.T.; Ras, R.H.A. Surface-wetting characterization using contact-angle measurements. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Nosonovsky, M. The rose petal effect and the modes of superhydrophobicity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 4713–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Directional adhesion of super-hydrophobic butterfly wings. Soft Matter 2007, 3, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.H.; Li, Y.S.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.L.; Liu, B.Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D.B. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Tserepi, A.; Gogolides, E. From superamphiphobic to amphiphilic polymeric surfaces with ordered hierarchical roughness fabricated with colloidal lithography and plasma nanotexturing. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3960–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.P.; Tian, Y.L. Insights into the wettability transition of nanosecond laser ablated surface under ambient air exposure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 533, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.J.; Zeng, W.G.; Liao, G.F.; Yi, C.F.; Xu, Z.S. Thermally and chemically stable candle soot superhydrophobic surface with excellent self-cleaning properties in air and oil. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagdheesh, R.; García-Ballesteros, J.J.; Ocaña, J.L. One-step fabrication of near superhydrophobic aluminum surface by nanosecond laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Mei, X.S.; Tian, Y.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.P. Modification of wettability property of titanium by laser texturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Zuo, Z.; Guo, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, A. Fabrication of superhydrophobic surface on aluminum by continuous chemical etching and its anti-icing property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 317, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C. Natural and biomimetic artificial surfaces for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning, low adhesion, and drag reduction. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 1–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.P.; Tian, Y.L. Hybrid laser ablation and chemical modification for fast fabrication of bio-inspired super-hydrophobic surface with excellent self-cleaning, stability and corrosion resistance. J. Bionic Eng. 2019, 16, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chik, N.; Zain, W.S.W.M.; Mohamad, A.J.; Sidek, M.Z.; Ibrahim, W.H.W.; Reif, A.; Rakebrandt, J.H.; Pfleging, W.; Liu, X. Bacterial adhesion on the titanium and stainless-steel surfaces undergone two different treatment methods: Polishing and ultrafast laser treatment. IOP Conf. Ser.-Mater. Sci. 2018, 358, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdan, U.; Hočevar, M.; Gregorčič, P. Transition from superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic state of laser textured stainless steel surface and its effect on corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2017, 123, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosi, S.F.; Moradi, S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G. Microfabrication of polymeric surfaces with extreme wettability using hot embossing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 378, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Fabrication of an anti-reflective and super-hydrophobic structure by vacuum ultraviolet light-assisted bonding and nanoscale pattern transfer. Micromachines 2018, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaki, T.; Hieda, J.; Saito, N.; Saito, N.; Takai, O. Corrosion resistance and chemical stability of super-hydrophobic film deposited on magnesium alloy AZ31 by microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7094–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xin, J.H. Super-hydrophobic surfaces from a simple coating method: A bionic nanoengineering approach. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.; Palumbo, G.; Erb, U. Recent advances in superhydrophobic electrodeposits. Materials 2016, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.P.; Tian, Y.L. Fabrication of super-hydrophobic nickel film on copper substrate with improved corrosion inhibition by electrodeposition process. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 560, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.T.; Garcia-Girón, A.; Romano, J.M.; Huerta-Murillo, D.; Jagdheesh, R.; Walker, M.; Dimov, S.S.; Ocaña, J.L. Influence of ambient conditions on the evolution of wettability properties of an IR-, ns-laser textured aluminium alloy. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39617–39627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; He, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xie, X.; Zhou, C.; Hong, W.; Hu, W. Low-cost fabrication of large-area broccoli-like multiscale micro- and nanostructures for metallic super-hydrophobic surfaces with ultralow water adhesion and superior anti-frost ability. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Tian, Y.L.; Wang, F.J.; Liu, X.P.; Jing, X.B. Fabrication and stability investigation of bio-inspired superhydrophobic surface on nitinol alloy. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 567, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, F.J.; Liu, X.P.; Jing, X.B. Fabrication of bio-inspired nitinol alloy surface with tunable anisotropic wetting and high adhesive ability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 527, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tian, Y.L.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, F.J.; Liu, X.P. Modification of wetting property of Inconel 718 surface by nanosecond laser texturing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Y.; Zhong, M.L.; Fan, P.X.; Gong, D.W.; Zhang, H.J. Wettability conversion of ultrafast laser structured copper surface. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, S29107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.P.; Rashid, M.R.; Khew, S.Y.; Li, F.P.; Hong, M.H. Wettability transition of laser textured brass surfaces inside different mediums. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L. Drop impact dynamics: Splashing, spreading, receding, bouncing…. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2006, 38, 159–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, H. Droplet impact and LFP on wettability and nanostructured surface. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 99, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, J.C.; Dhiman, R.; Kwon, H.M.; Varanasi, K.K. Reducing the contact time of a bouncing drop. Nature 2013, 503, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wu, L.; Yu, C.; Dai, H.; Wang, T.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, L. Ballistic jumping drops on superhydrophobic surfaces via electrostatic manipulation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josserand, C.; Thoroddsen, S.T. Drop impact on a solid surface. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2016, 48, 365–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukiwe, C.; Kwok, D.Y. On the maximum spreading diameter of impacting droplets on well-prepared solid surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, A.; Shioya, M.; Hirasawa, J.; Okazaki, T. Impact of an ink drop on paper. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 1993, 37, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Mao, L.Q.; Ma, X.H. Dynamic behavior of water droplet impact on microtextured surfaces: The effect of geometrical parameters on anisotropic wetting and the maximum spreading diameter. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, B.L.; Bousfield, D.W. Newtonian drop impact with a solid surface. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoon, S.S. Empirical model for the maximum spreading diameter of low-viscosity droplets on a dry wall. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 61, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Avedisian, C.T. On the collision of a droplet with a solid surface. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1991, 432, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PasandidehFard, M.; Qiao, Y.M.; Chandra, S.; Mostaghimi, J. Capillary effects during droplet impact on a solid surface. Phys. Fluids 1996, 8, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Kuhn, D.C.S.; Tran, H. Spread and rebound of liquid droplets upon impact on flat surfaces. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, L.K.; Patil, N.D.; Bhardwaj, R.; Neild, A. Droplet bouncing and breakup during impact on a microgrooved surface. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9620–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Nam, Y.; Lastakowski, H.; Hur, J.I.; Shin, S.; Biance, A.L.; Pirat, C.; Kim, C.J.; Ybert, C. Two types of cassie-to-wenzel wetting transitions on superhydrophobic surfaces during drop impact. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4592–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y. Droplet impact on anisotropic superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2018, 34, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippig, F.; Holländer, A. Fluram labeling of high density NH2 surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 6817–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Y.; Zhong, M.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Fan, P.X. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser microstructured aluminum in ambient air. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, C. Study on the fabrication of super-hydrophobic surface on Inconel alloy via nanosecond laser ablation. Materials 2019, 12, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulinich, S.A.; Honda, M.; Zhu, A.L.; Rozhin, A.G.; Du, X.W. The icephobic performance of alkyl-grafted aluminum surfaces. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioboo, R.; Marengo, M.; Tropea, C. Time evolution of liquid drop impact onto solid, dry surfaces. Exp. Fluids 2002, 33, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.B.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, T.G. Maximum spread of droplet impacting onto solid surfaces with different wettabilities: Adopting a rim-lamella shape. Langmuir 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishino, C.; Reyssat, M.; Reyssat, E.; Okumura, K.; Quéré, D. Wicking within forests of micropillars. EPL 2007, 79, 56005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, D.; Bouamrirene, F.; Verneuil, É.; Buguin, A.; Silberzan, P.; Moulinet, S. Bouncing or sticky droplets: Impalement transitions on superhydrophobic micropatterned surfaces. EPL 2006, 74, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyssat, M.; Yeomans, J.M.; Quéré, D. Impalement of fakir drops. EPL 2008, 81, 26006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.; Skurtys, O.; Osorio, F. Experimental study of drop impacts and spreading on epicarps: Effect of fluid properties. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roisman, I.V. Inertia dominated drop collisions. II. An analytical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations for a spreading viscous film. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 052104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



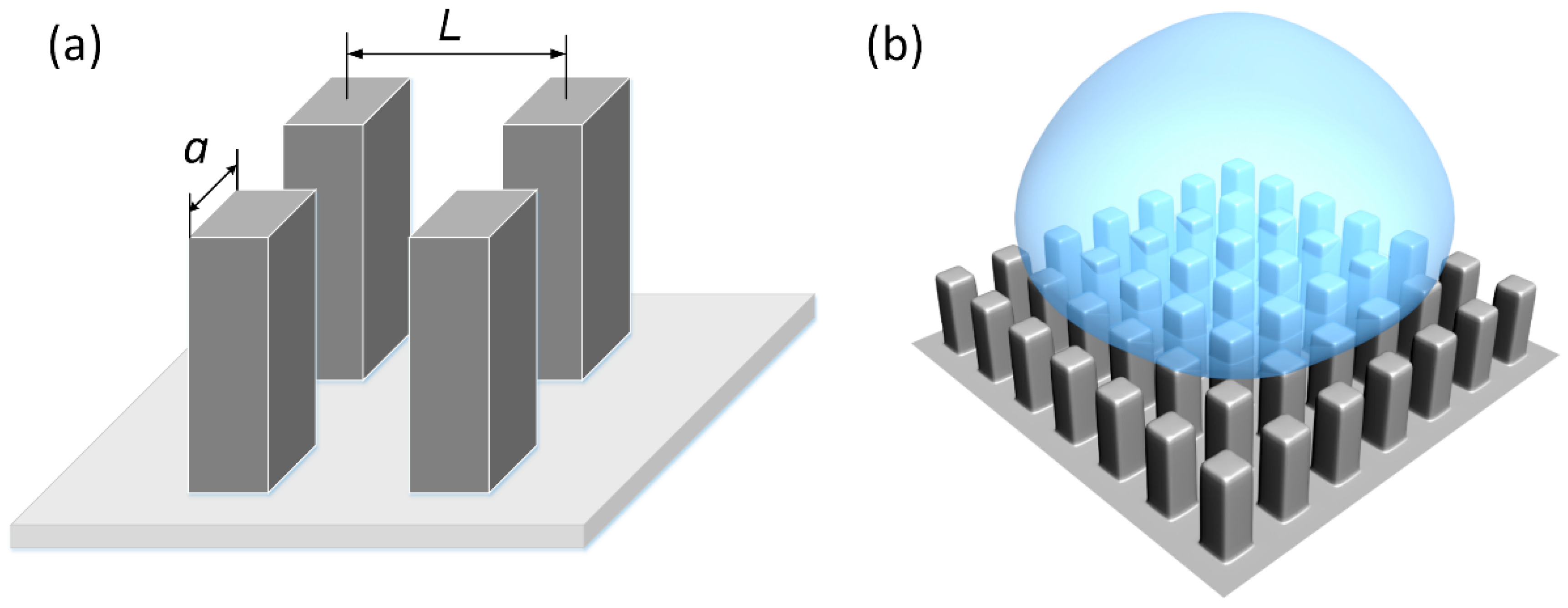
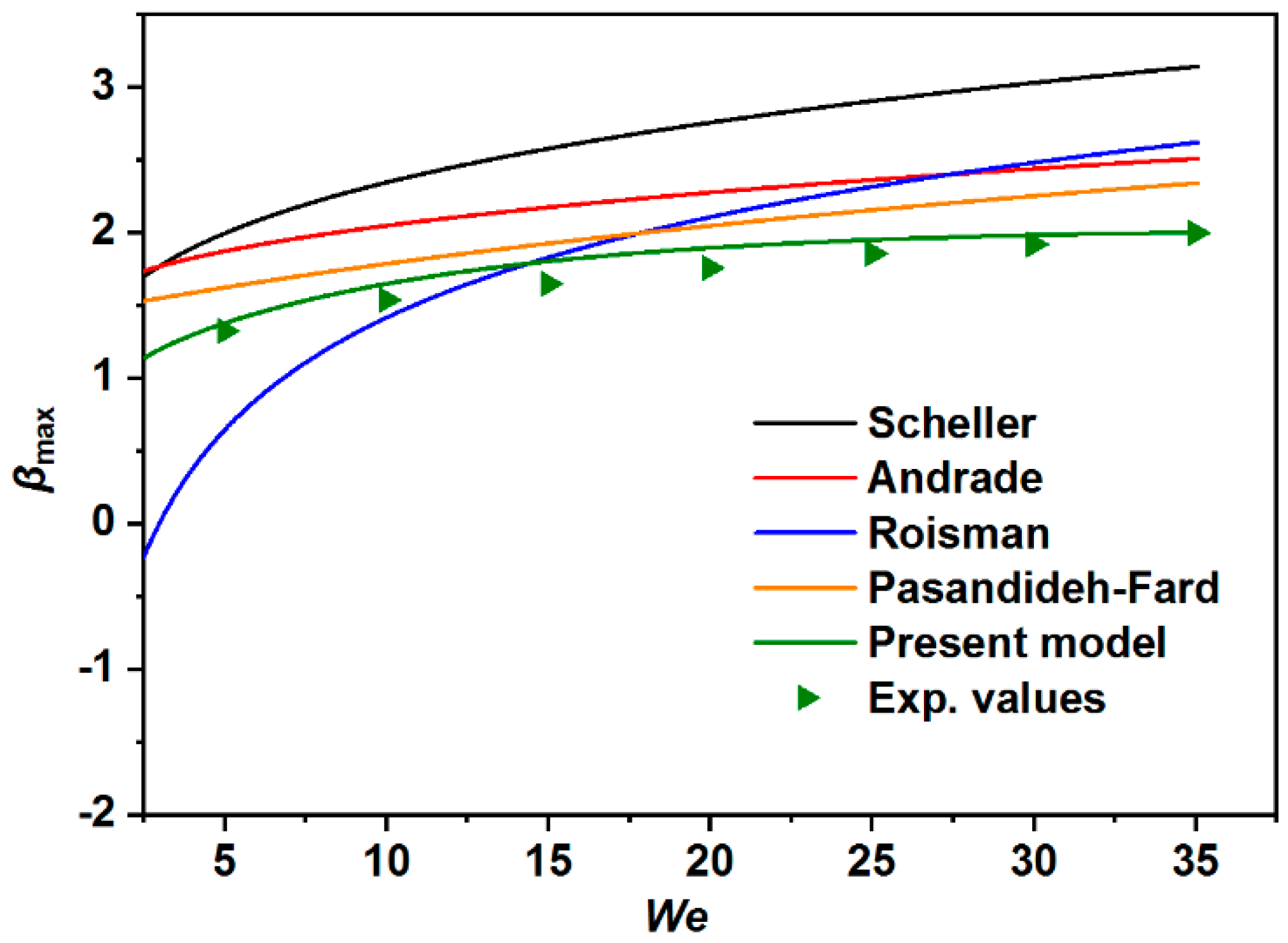
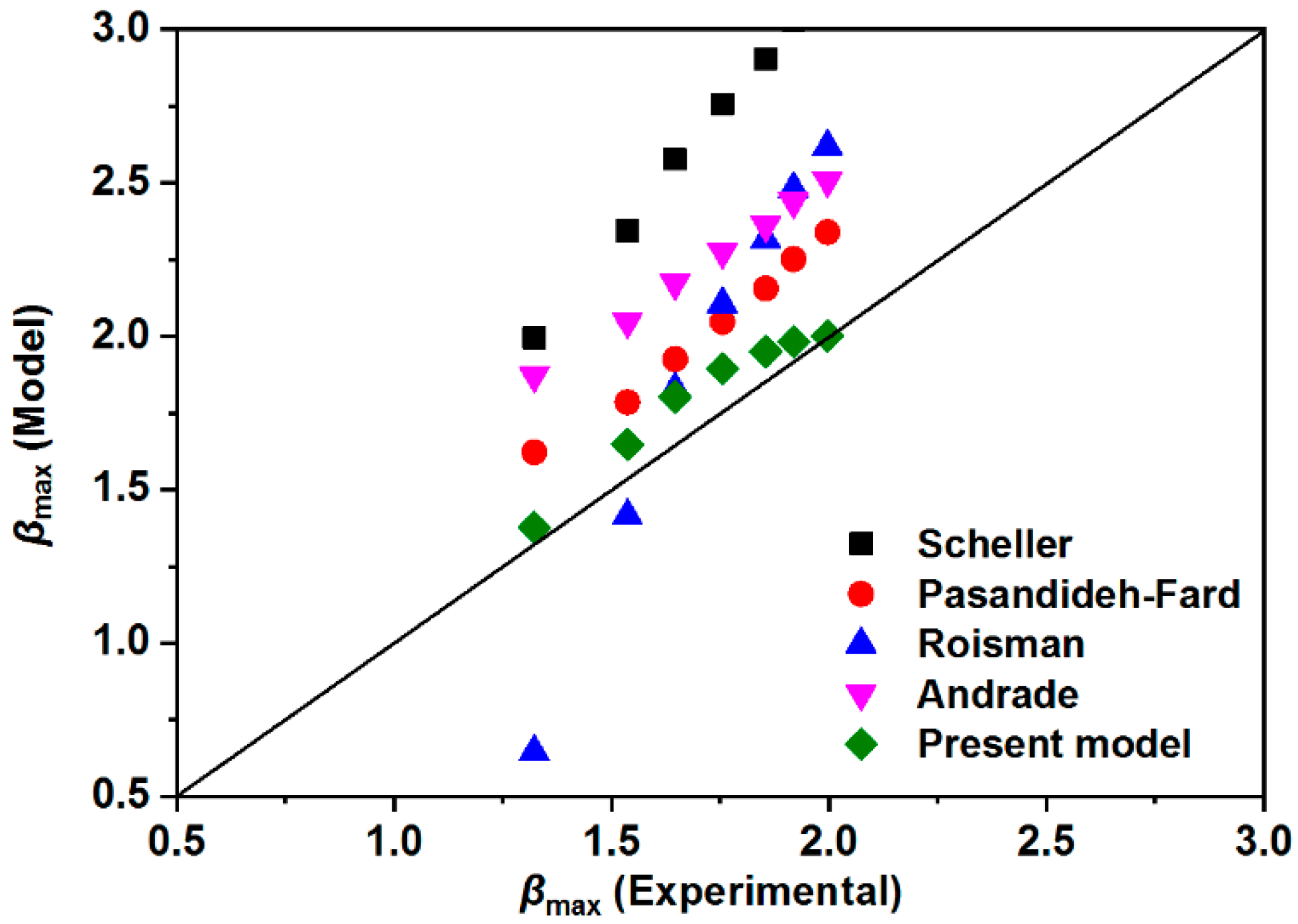
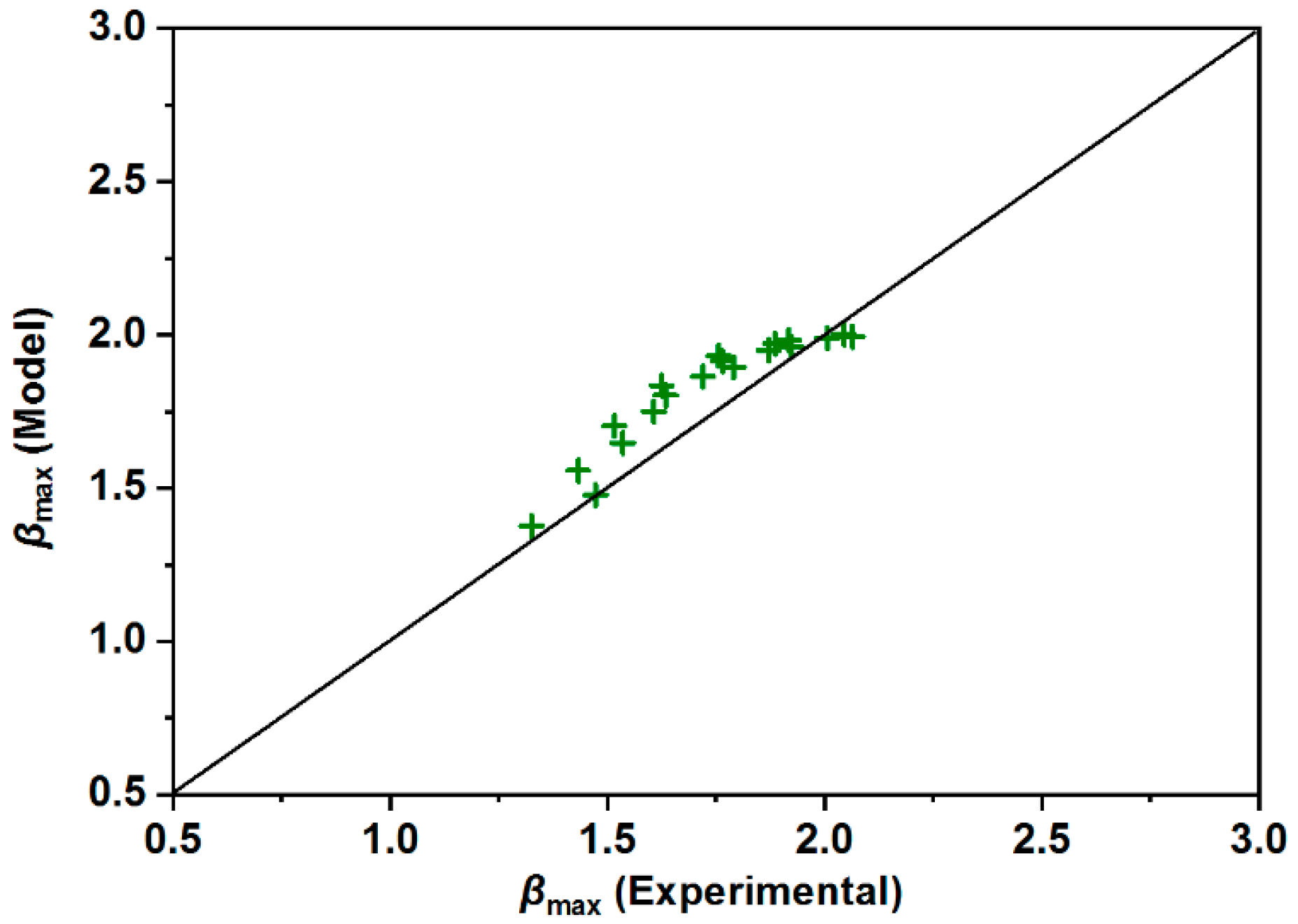
| Models | Equation |
|---|---|
| Scheller [37] | |
| Andrade [54] | |
| Roisman [55] | |
| Pasandideh-Fard [40] 1 | |
| Present model |
| Model | Mean Error (%) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Scheller | 47.76 | 0.89 |
| Andrade | 24.35 | 0.43 |
| Roisman | 22.09 | 0.44 |
| Pasandideh-Fard | 11.72 | 0.22 |
| Present model | 4.99 | 0.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. Droplet Impact on the Super-Hydrophobic Surface with Micro-Pillar Arrays Fabricated by Hybrid Laser Ablation and Silanization Process. Materials 2019, 12, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050765
Xia Z, Xiao Y, Yang Z, Li L, Wang S, Liu X, Tian Y. Droplet Impact on the Super-Hydrophobic Surface with Micro-Pillar Arrays Fabricated by Hybrid Laser Ablation and Silanization Process. Materials. 2019; 12(5):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050765
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Zhenyan, Yuhe Xiao, Zhen Yang, Linan Li, Shibin Wang, Xianping Liu, and Yanling Tian. 2019. "Droplet Impact on the Super-Hydrophobic Surface with Micro-Pillar Arrays Fabricated by Hybrid Laser Ablation and Silanization Process" Materials 12, no. 5: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050765
APA StyleXia, Z., Xiao, Y., Yang, Z., Li, L., Wang, S., Liu, X., & Tian, Y. (2019). Droplet Impact on the Super-Hydrophobic Surface with Micro-Pillar Arrays Fabricated by Hybrid Laser Ablation and Silanization Process. Materials, 12(5), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050765





