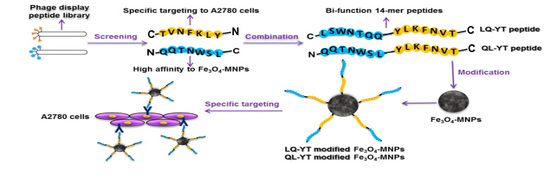
Novel Bi-Functional 14-mer Peptides with Both Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Targeting and Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Affinity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Cell Culture
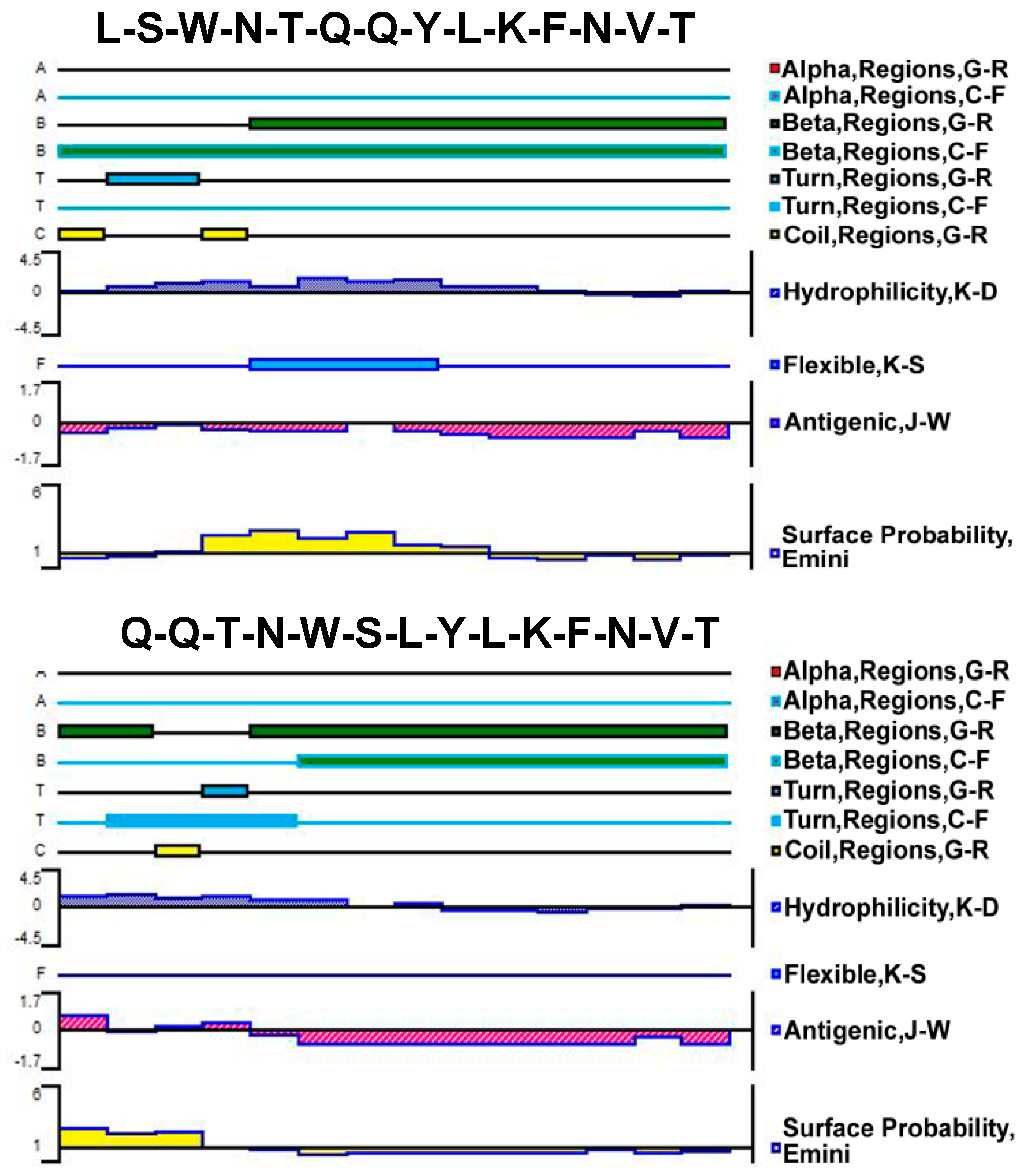
2.2. Design, Prediction, and Characterization of Bi-Functional Peptides
2.3. Characterization of Fe3O4-MNPs
2.4. Modification and Characterization of Fe3O4-MNPs
2.5. Identification of Cellular Affinity
2.6. MTT Assay and Scratch Wound Migration Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Composition and Secondary Structure of Synthesized 14-mer Peptides
3.2. Affinity of Synthesized 14-mer Peptides to Fe3O4-MNPs
3.3. Properties and Performances of Modified Fe3O4-MNPs
3.4. Specificity of Modified Fe3O4-MNPs Bound to A2780 Cells
3.5. Cytotoxicity of Polypeptide-Modified Fe3O4-MNPs
3.6. Discussion on Tumor Targeting of Related 14-mer Peptides
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coburn, S.B.; Bray, F.; Sherman, M.E.; Trabert, B. International patterns and trends in ovarian cancer incidence, overall and by histologic subtype. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oronsky, B.; Ray, C.M.; Spira, A.I.; Trepel, J.B.; Carter, C.A.; Cottrill, H.M. A brief review of the management of platinum-resistant-platinum-refractory ovarian cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opipari, A.W.; Tan, L.; Boitano, A.E.; Sorenson, D.R.; Aurora, A.; Liu, J.R. Resveratrol-induced Autophagocytosis in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guppy, A.E.; Nathan, P.D.; Rustin, G.J. Epithelial ovarian cancer: A review of current management. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 17, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Coleman, R.L.; Markman, M. Ovarian cancer. Lancet 2009, 374, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Yang, Y.; Kang, T.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, H.; Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Luo, F.; et al. Ovarian cancer therapy by VSVMP gene mediated by a paclitaxel-enhanced nanoparticle. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39152–39164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armijo, L.M.; Brandt, Y.I.; Mathew, D.; Yadav, S.; Maestas, S.; Rivera, A.C.; Cook, N.C.; Withers, N.J.; Smolyakov, G.A.; Adolphi, N.; et al. Iron Oxide Nanocrystals for Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2012, 2, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Dev. Res. 2010, 67, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serantes, D.; Simeonidis, K.; Angelakeris, M.; Chubykalofesenko, O.; Marciello, M.; Morales, M.D.P.; Baldomir, D.; Martinezboubeta, C. Multiplying Magnetic Hyperthermia Response by Nanoparticle Assembling. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 5927–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, I.; Shokrollahi, H.; Amiri, S. Ferrite-based magnetic nanofluids used in hyperthermia applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Schnorr, J.; Ludwig, A.; Stangl, V.; Ebert, M.; Hamm, B.; Taupitz, M. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of atherosclerosis using citrate-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Calcifying microvesicles as imaging target for plaque characterization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 767–779. [Google Scholar]
- Balivada, S.; Rachakatla, R.S.; Wang, H.; Samarakoon, T.N.; Dani, R.K.; Pyle, M.; Kroh, F.O.; Walker, B.; Leaym, X.; Koper, O.B.; et al. A/C magnetic hyperthermia of melanoma mediated by iron(0)/iron oxide core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: A mouse study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowford, S. Nanotechnology Introduction Series: The Energy Sector; HA Hessen Agentur GmbH: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.L. Morphology, surface layer evolution and structure-dye adsorption relationship of porous Fe3O4 MNPs prepared by solvothermal/gas generation process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullotti, E.; Yeo, Y. Extracellularly activated nanocarriers: A new paradigm of tumor targeted drug delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, D.L.; Gillies, R.J. Molecular imaging and targeted therapies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, J.P.; Kahn, M.L. Magnetism: Molecules to Materials: Models and Experiments. Magn. Mol. Mater. V 1999, 36, 161–187. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.K.; Lin, C.T.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, H.C. A novel peptide enhances therapeutic efficacy of liposomal anti-cancer drugs in mice models of human lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ma, H.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Yin, W.; Wang, H.; Xu, D. Targeted polymer-drug conjugates: Current progress and future perspective. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akita, N.; Maruta FSeymour, L.W.; Kerr, D.J.; Parker, A.L.; Asai, T.; Oku, N.; Nakayama, J.; Miyagawa, S. Identification of oligopeptides binding to peritoneal tumors of gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 97, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, R.J.; Egger, G.; Francas, M. TARPARE: A method for selecting target audiences for public health interventions. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2010, 23, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liang, S.; Hong, L.; Zhai, H.; Yuanyuan, L.U.; Han, Y.U.; et al. Inhibitory effects of a specific phage-displayed peptide on high peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Kuang, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Wu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, M. Targeted drug delivery to hepatocarcinoma in vivo by phage-displayed specific binding peptide. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.R.; Li, H.P.; Hao, H.J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Gu, J. Targeting of hepatoma cell and suppression of tumor growth by a novel 12mer peptide fused to superantigen TSST-1. Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pu, X.; Yin, G.; You, F. In Vivo Screening with Ph.D.-7™ and Identification of Ovarian Cancer A2780 Cell Targeted Heptapeptides. World J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 15628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Yin, G.; Pu, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liao, X.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X. Biopanning and characterization of peptides with Fe3O4 nanoparticles-binding capability via phage display random peptide library technique. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamluk, R.; Klagsbrun, M.; Detmar, M.; Bielenberg, D.R. Soluble neuropilin targeted to the skin inhibits vascular permeability. Angiogenesis 2005, 8, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yin, G.; Pu, X.; Chen, X.; Liao, X.; Huang, Z. Novel Bi-Functional 14-mer Peptides with Both Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Targeting and Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Affinity. Materials 2019, 12, 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050755
Li Y, Yin G, Pu X, Chen X, Liao X, Huang Z. Novel Bi-Functional 14-mer Peptides with Both Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Targeting and Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Affinity. Materials. 2019; 12(5):755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050755
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yueting, Guangfu Yin, Ximing Pu, Xianchun Chen, Xiaoming Liao, and Zhongbing Huang. 2019. "Novel Bi-Functional 14-mer Peptides with Both Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Targeting and Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Affinity" Materials 12, no. 5: 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050755
APA StyleLi, Y., Yin, G., Pu, X., Chen, X., Liao, X., & Huang, Z. (2019). Novel Bi-Functional 14-mer Peptides with Both Ovarian Carcinoma Cells Targeting and Magnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Affinity. Materials, 12(5), 755. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050755