Effect of Surface Roughness on Pitting Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Investigated by Electrochemical Noise Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Specimen Preparation
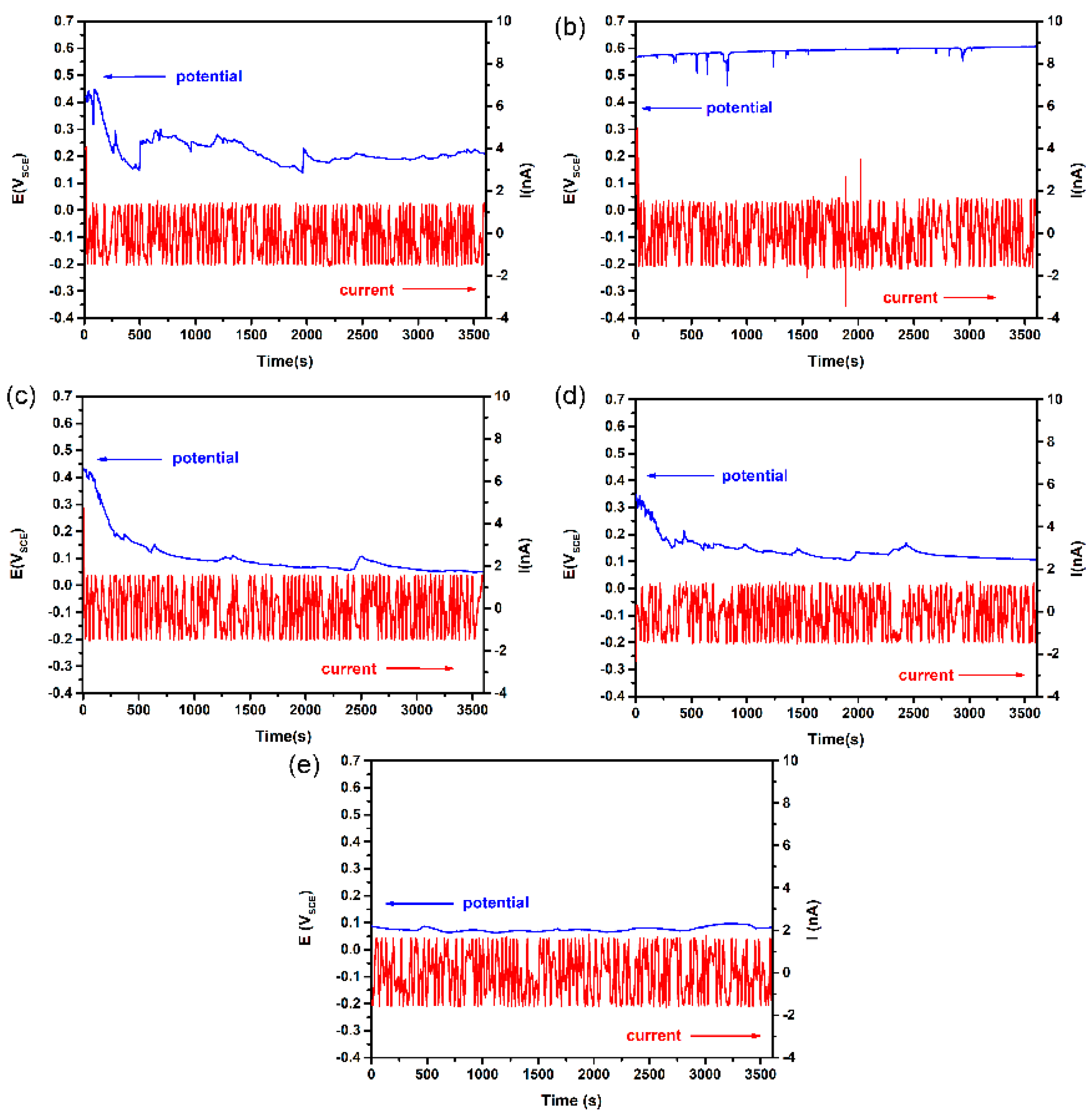
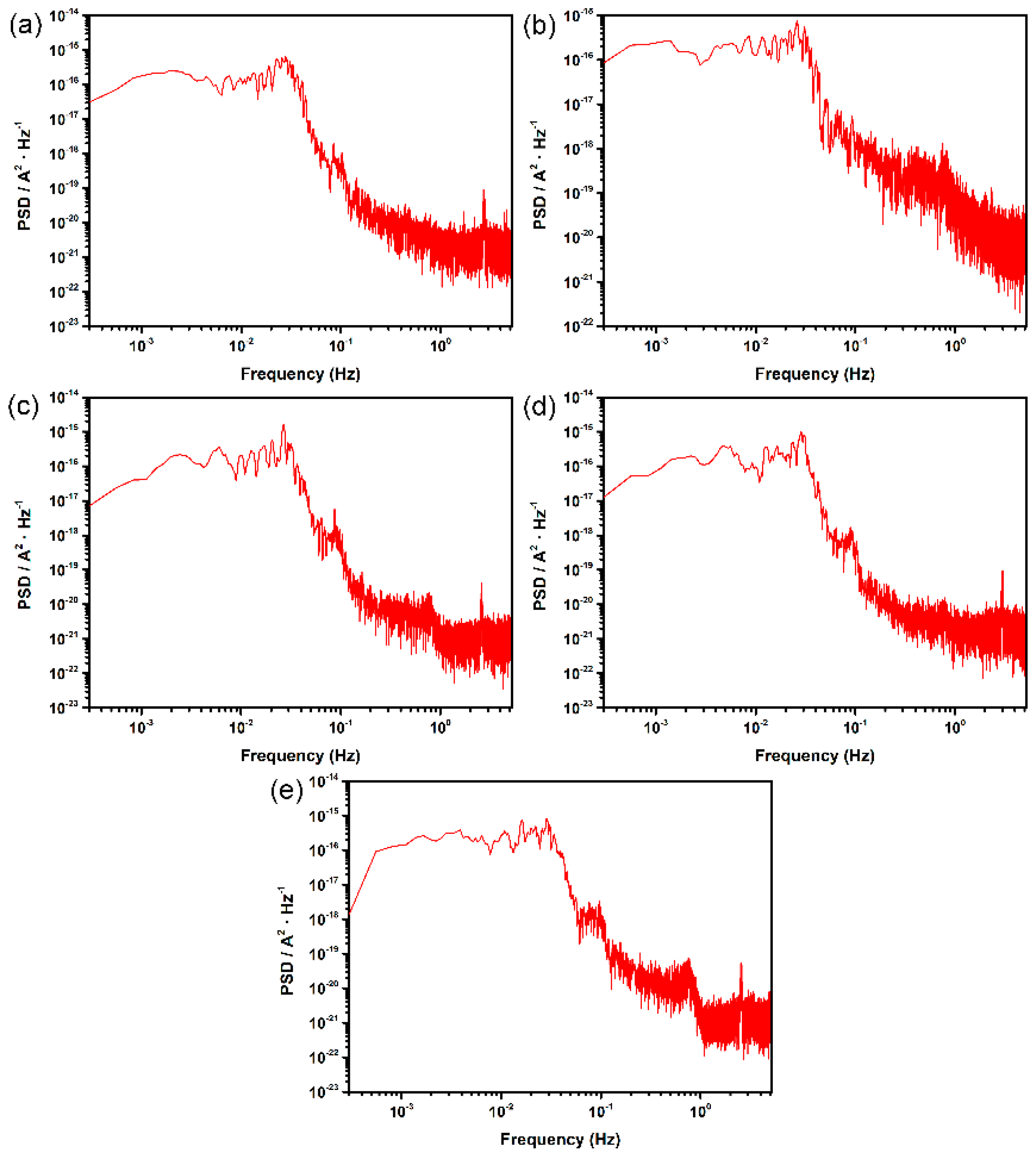
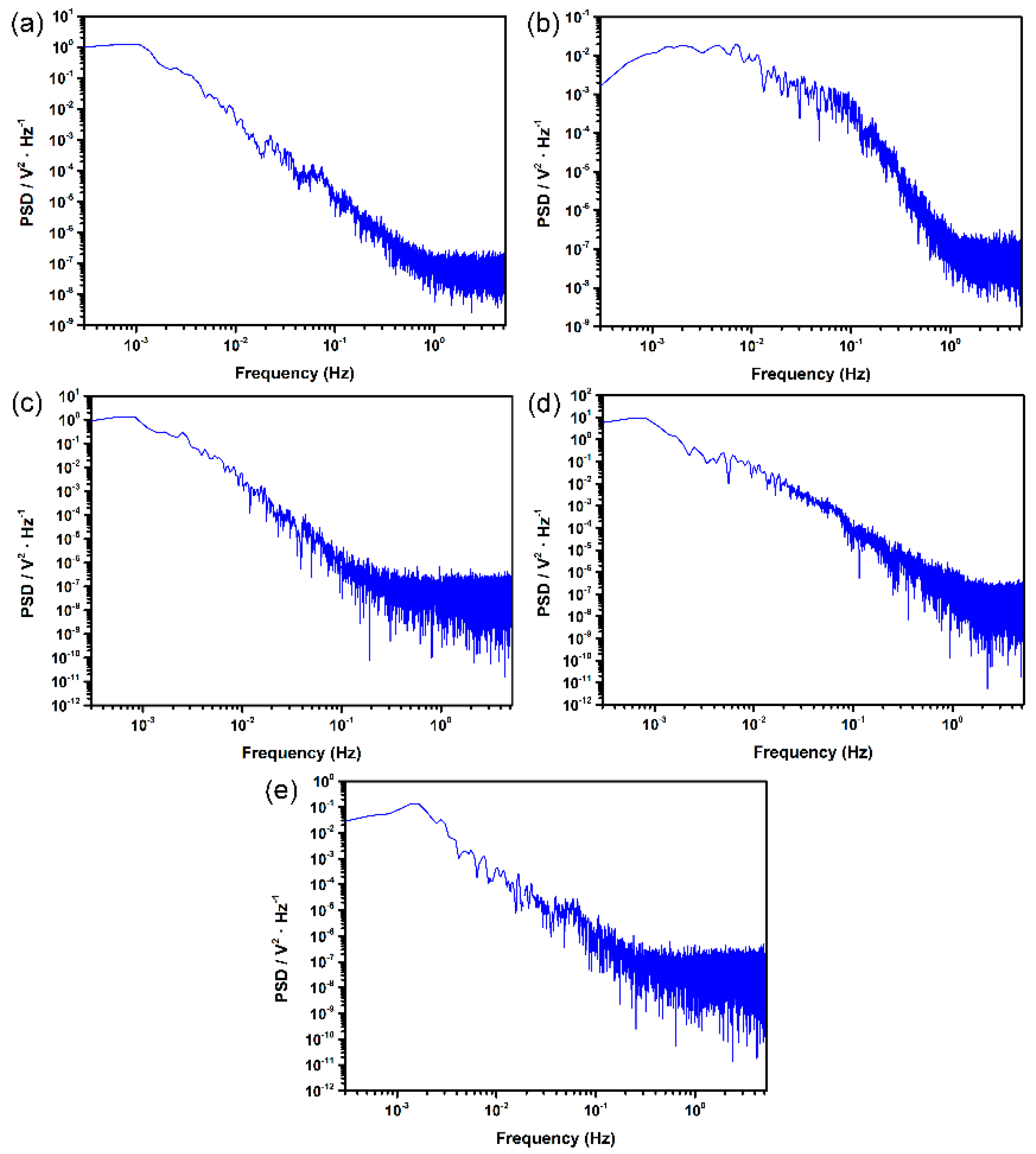
2.2. EN Experiments and Analysis
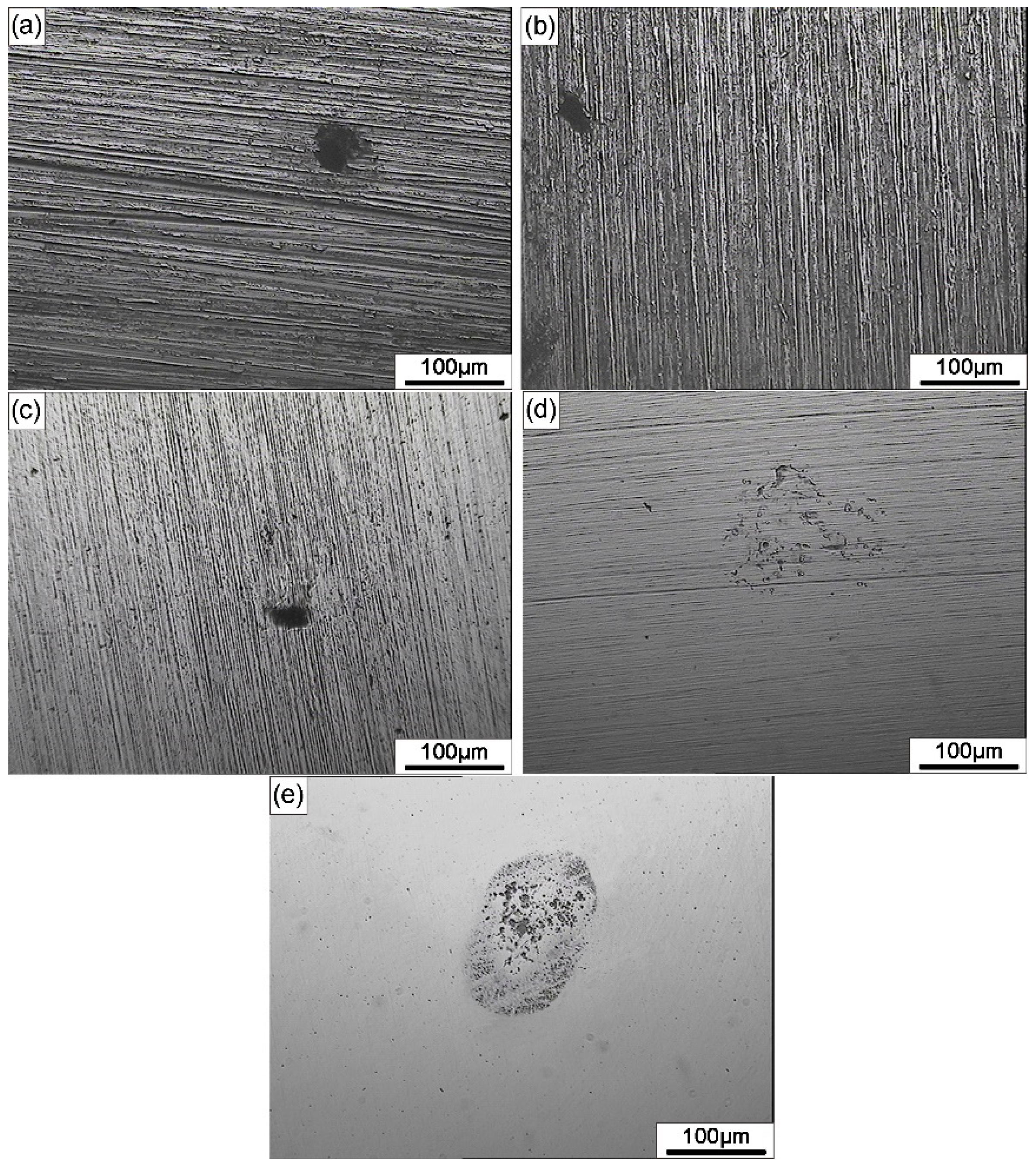
2.3. Surface Observation and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Noise Analysis at OCP
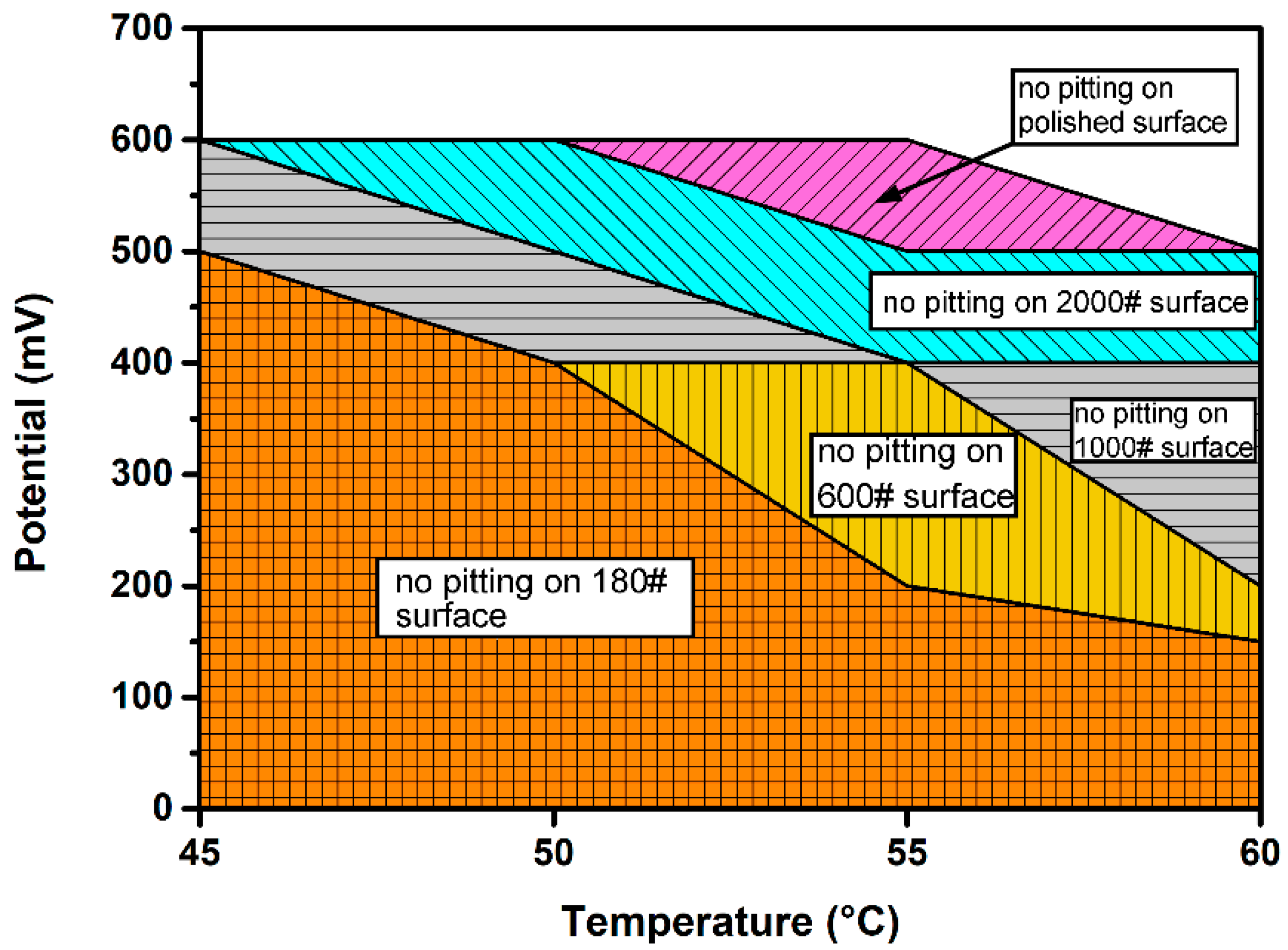
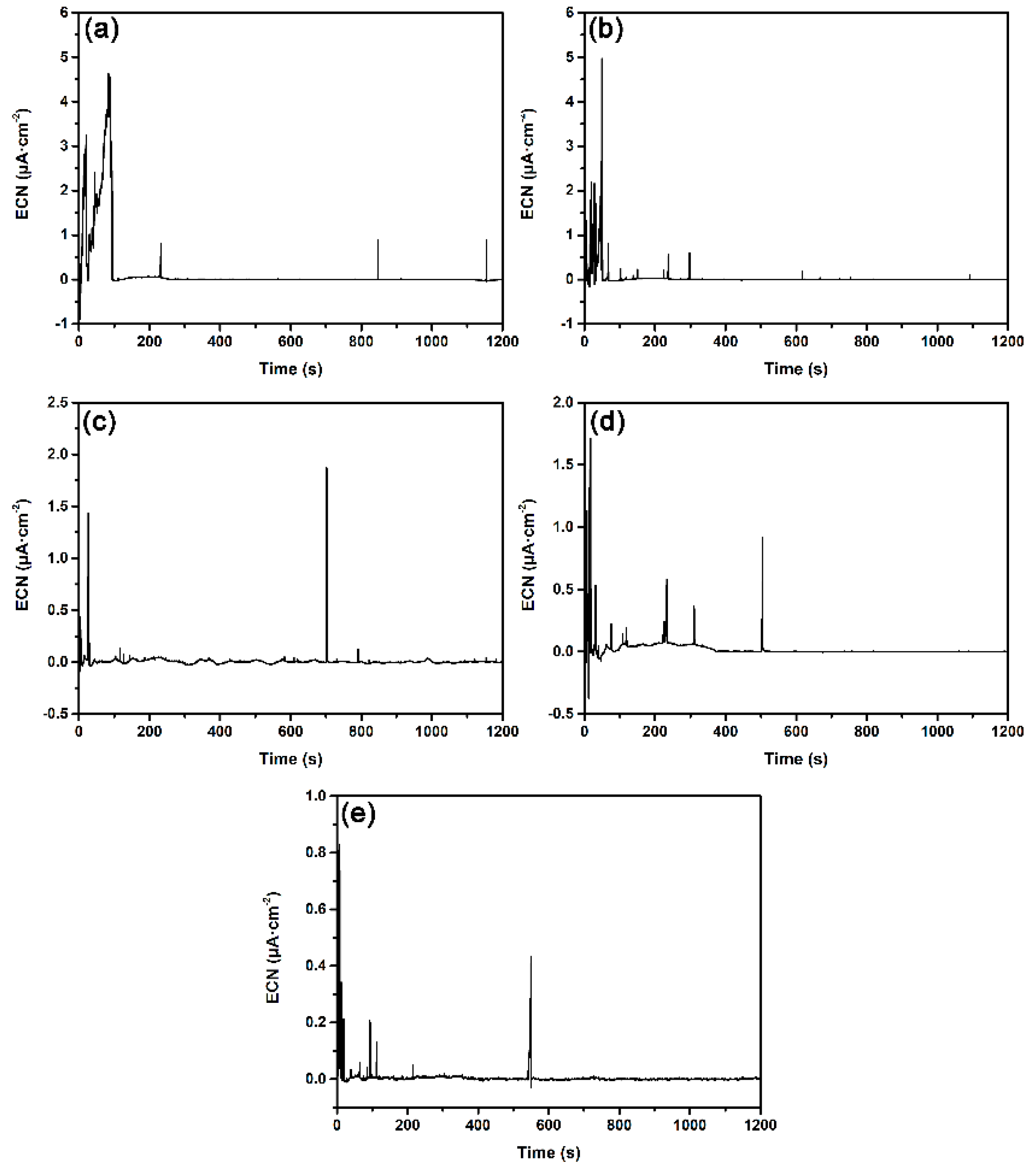
3.2. Potentiostatic Electrochemical Current Noise Analysis
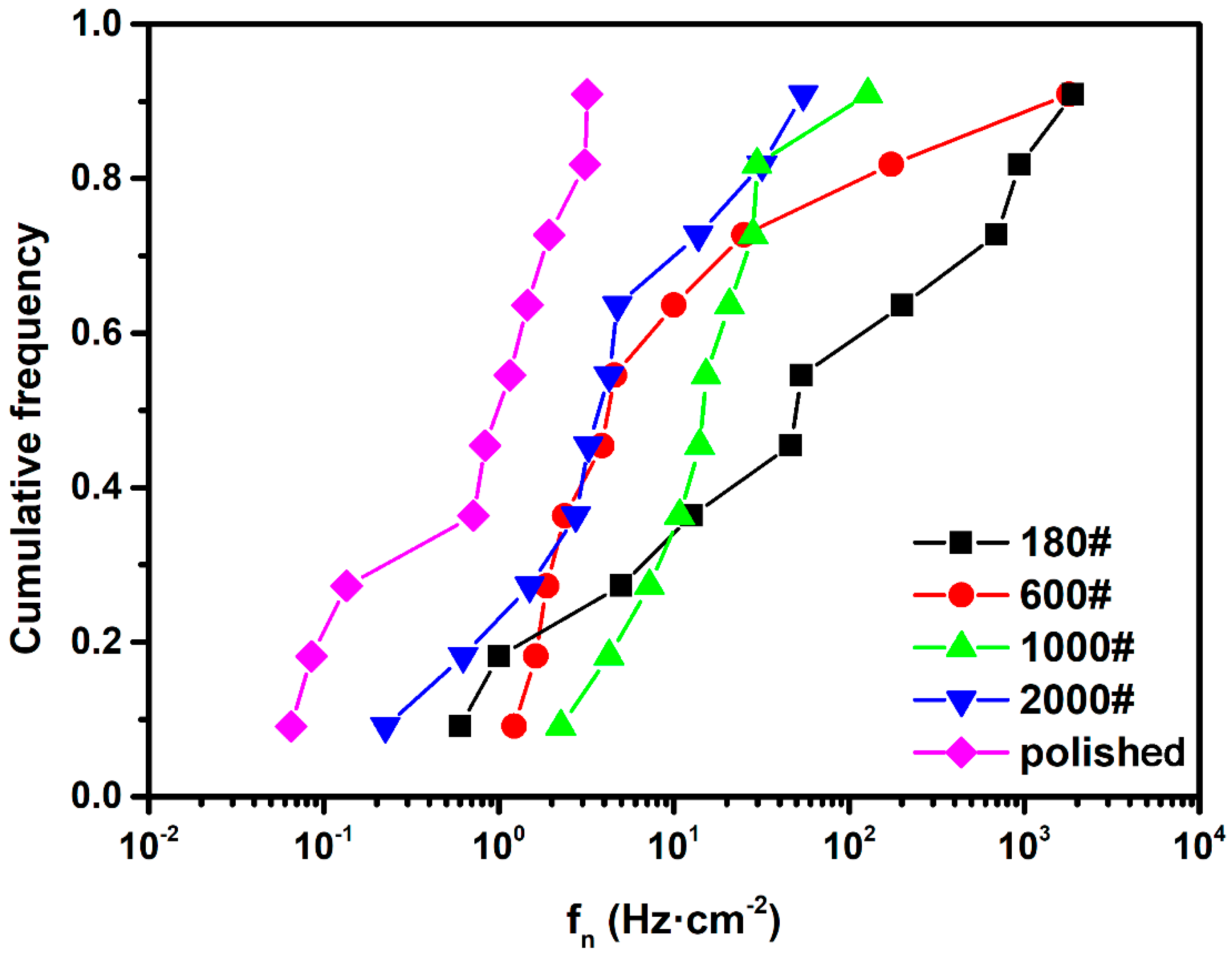
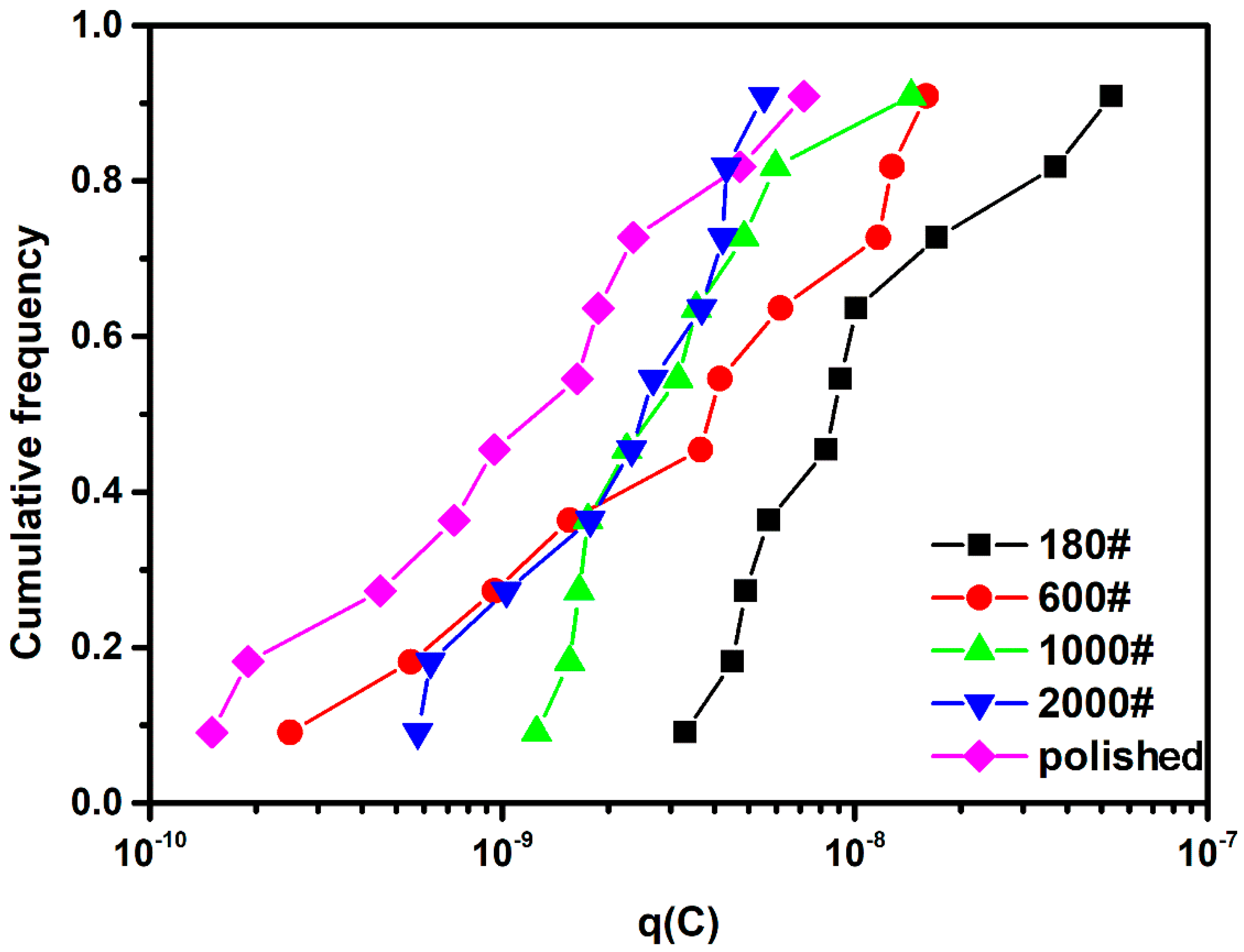
3.2.1. Influence of Surface Roughness on Metastable Pit Nucleation
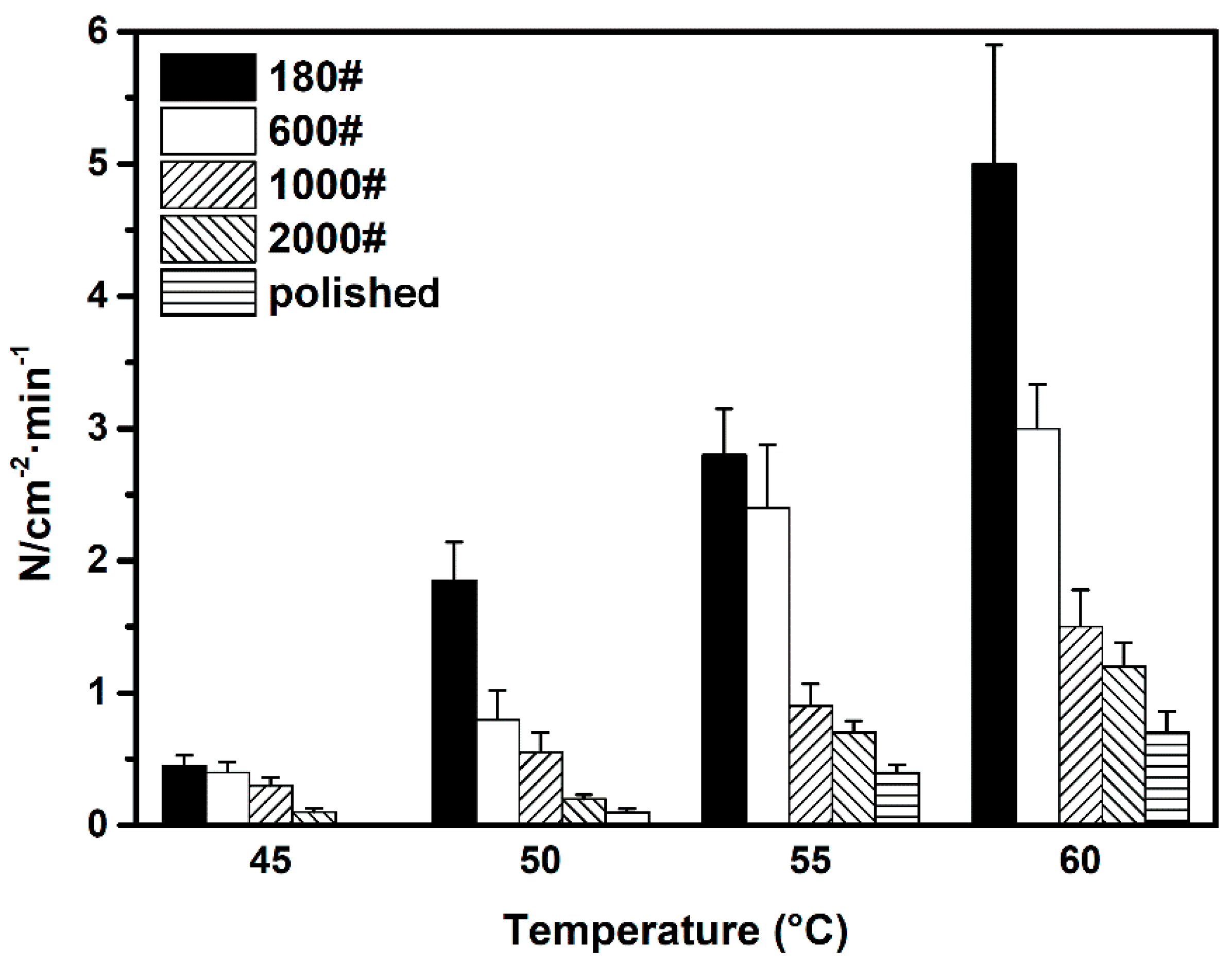
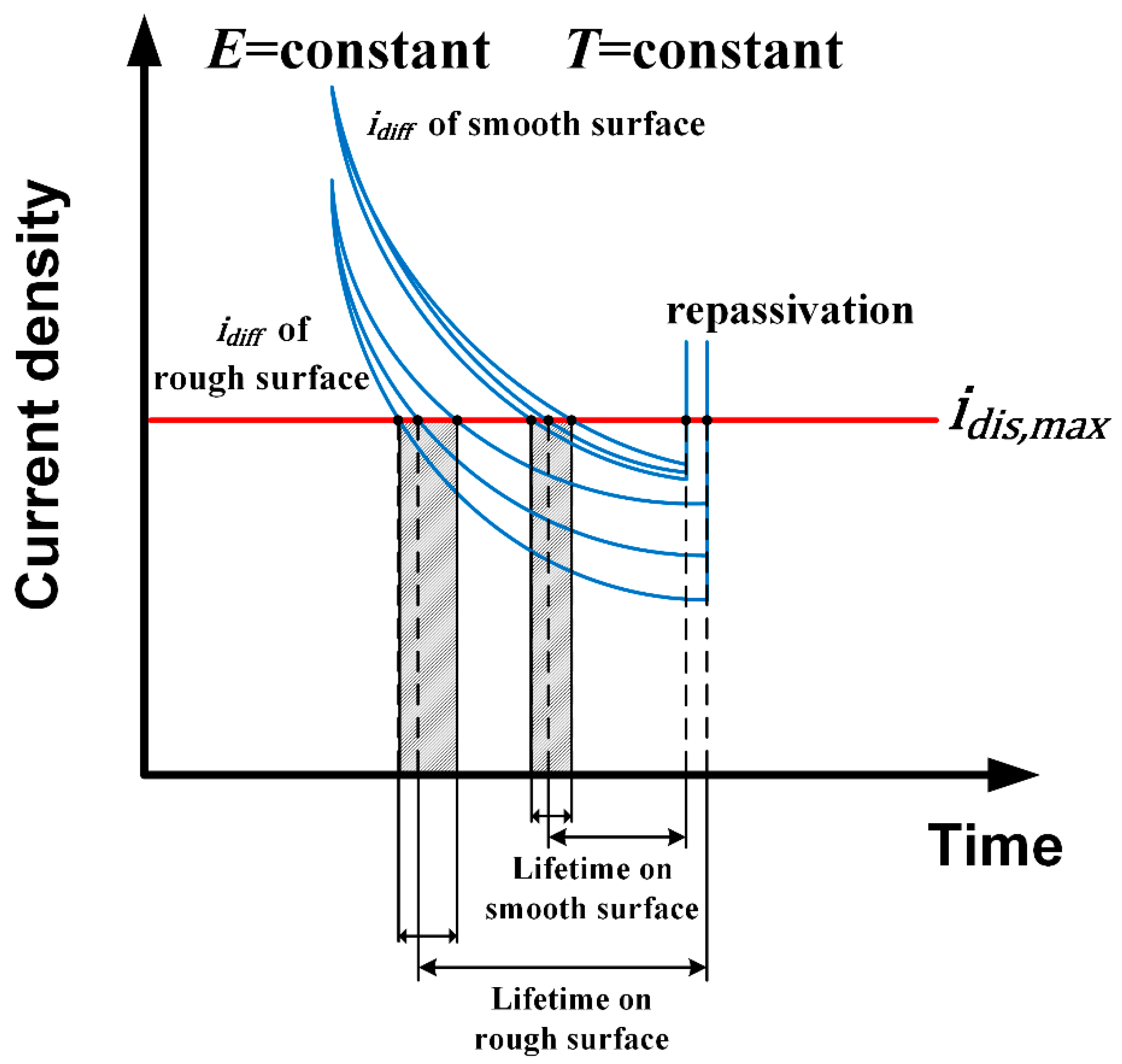
3.2.2. Influence of Surface Roughness on Metastable Pit Growth Rate
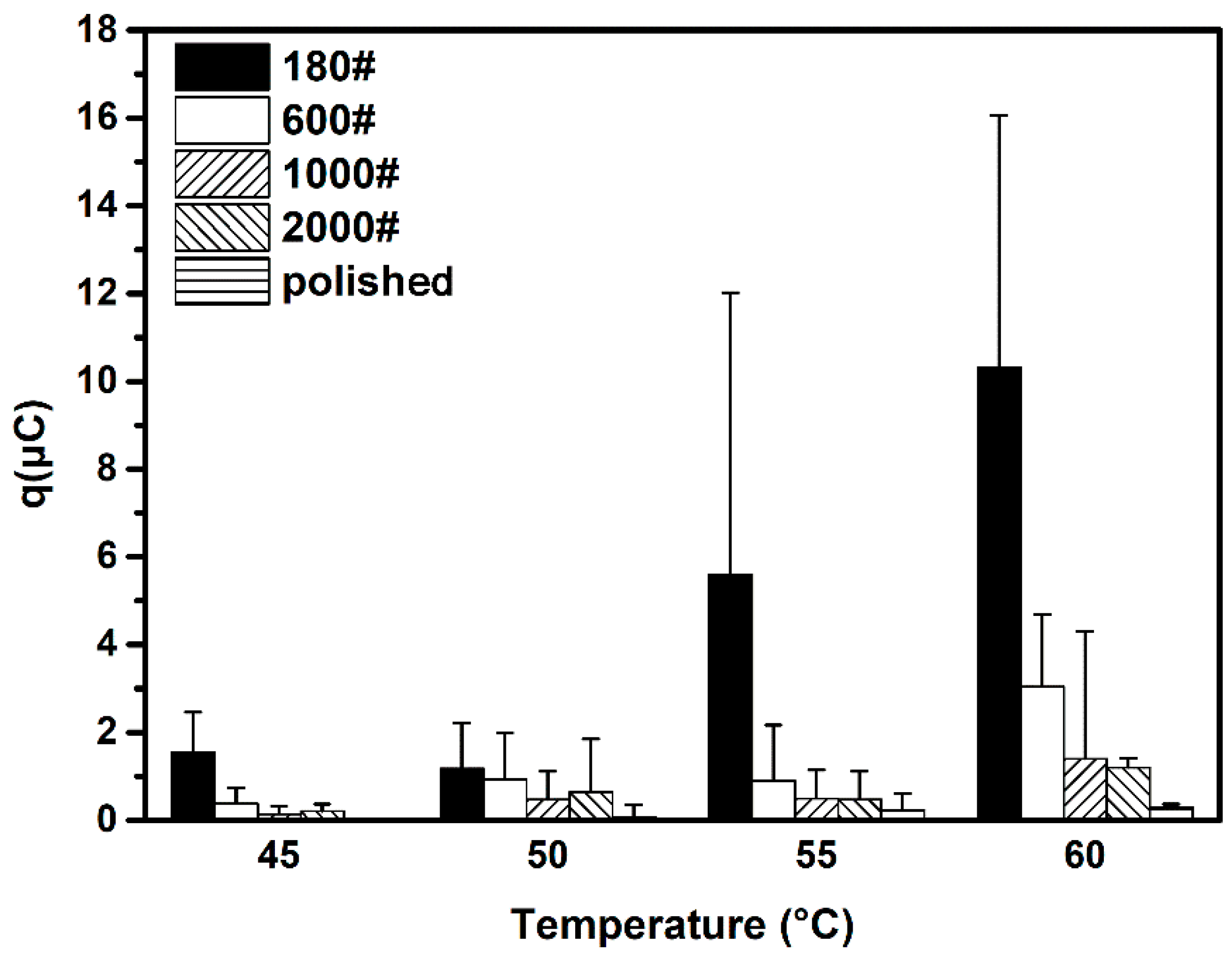
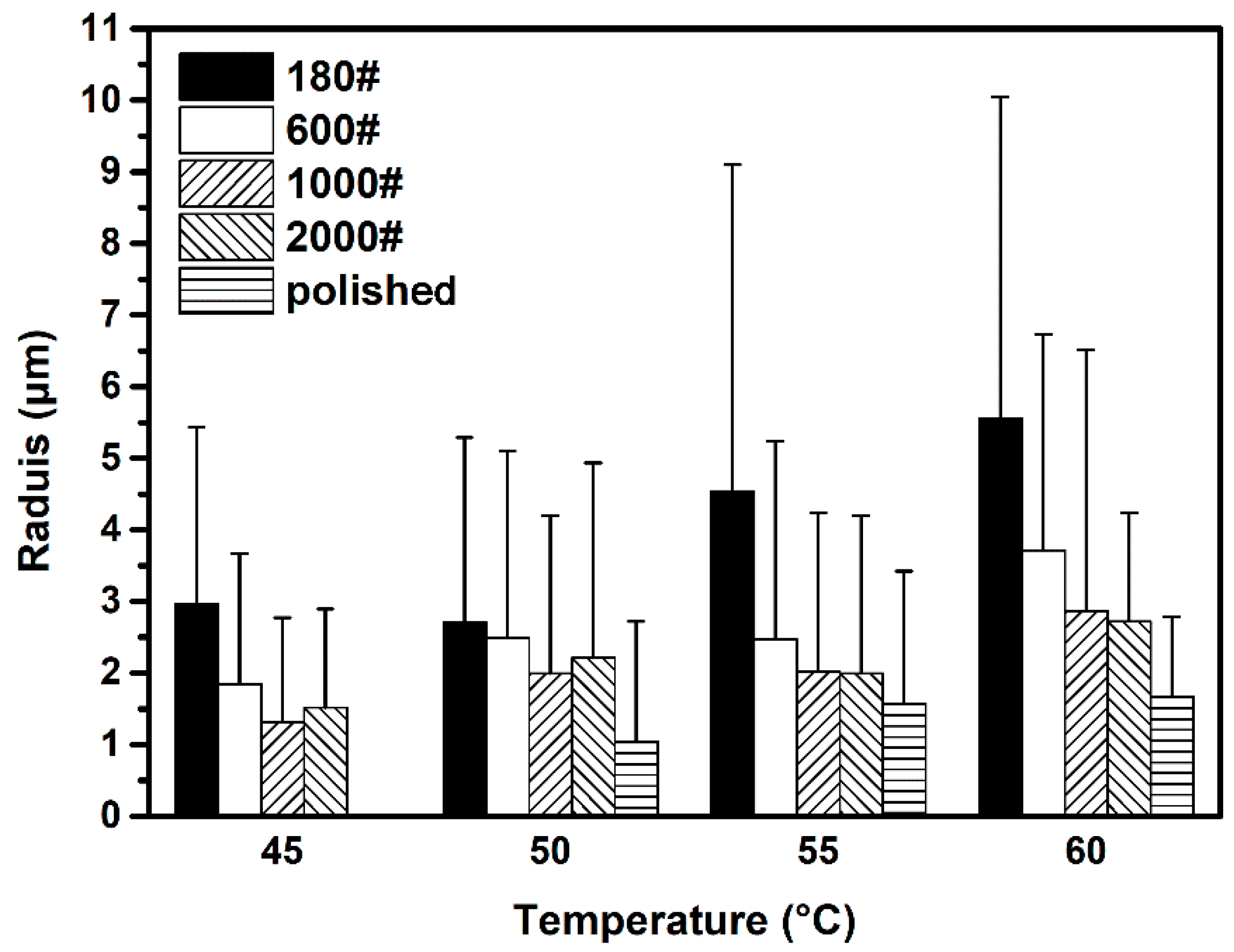
3.2.3. Influence of Surface Roughness on Metastable Pit Size
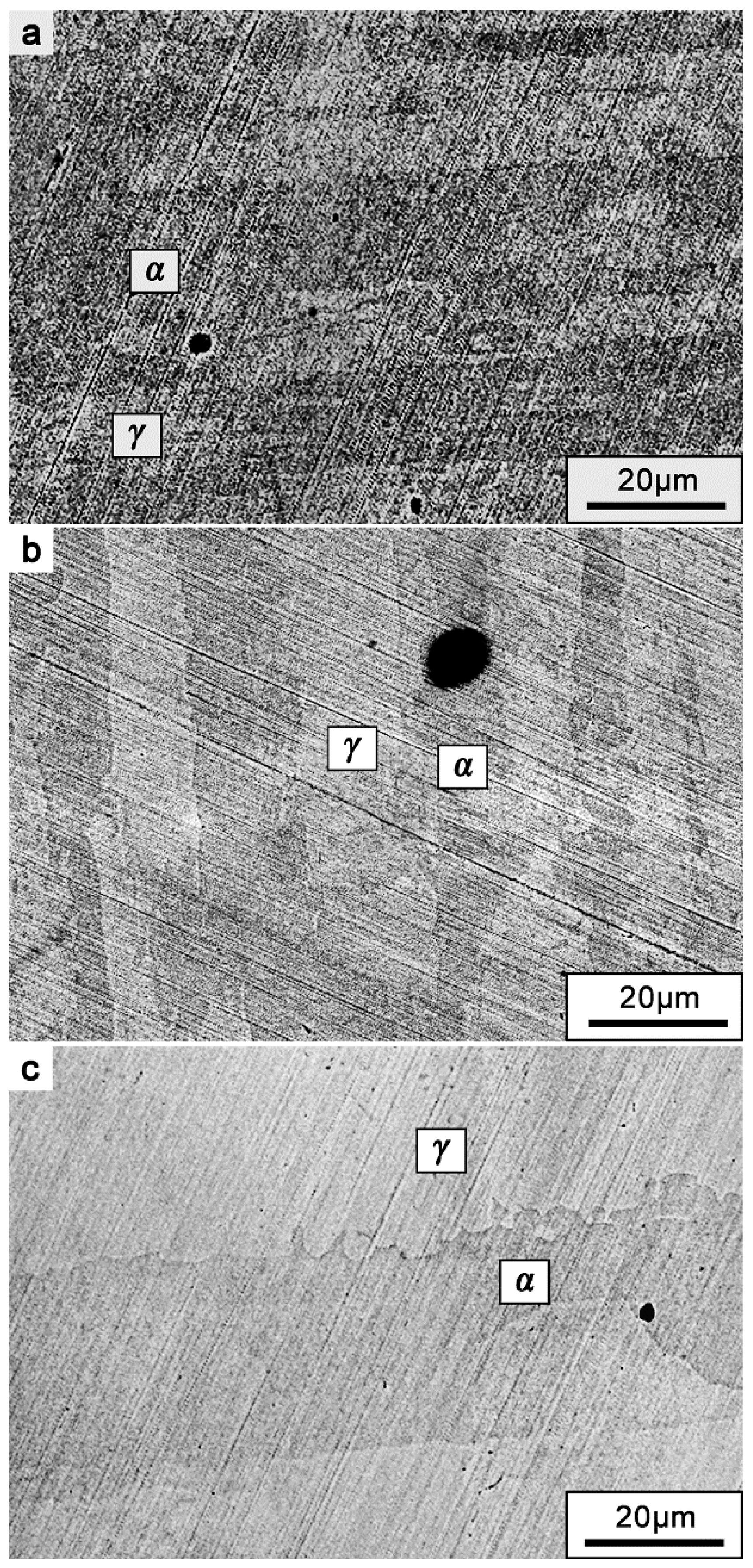
3.2.4. Influence of Surface Roughness on Metastable Pit Position
4. Conclusions
- Rougher surface conditions decreased the EN resistance Rn of DSS 2205 and consequently increasesd the probability of stable pit occurrence.
- Based on the frequency domain analysis of EN, the pit nucleation was more frequent and the difference in pit initiation morphology was much larger on rougher-surfaced DSS 2205. Besides, the short noise analysis of the EN record showed that the pit growth process was more stable and the probability of metastable-to-stable transition was higher on rougher surfaces. However, the resolution of EN measurement was not sufficient to distinguish clearly the differences between specimens of different surface roughness.
- Potentiostatic EN measurement represents more obviously the effect of surface roughness on pitting corrosion of DSS. On rougher surfaces, the frequency of metastable pit initiation increases because pit sites on a rough surface are more likely to reach Ccirit. The dispersity of the metastable pitting rate is also greater due to the more significant differences in initial pit sites on a rough surface.
- According to potentiosatic EN measurement, rougher surface increasd the growth rate of metastable pit propagation on DSS, as well as its SD. A model representing the relationship between effective diffusion length of a pit site and the diffusion rate of a metastable pit has been proposed to explain the variation of growth rate with surface roughness.
- The increase in surface roughness also enlarged the final size of a metastable pit on DSS. The SD of this parameter increased likewise. The final size of the metastable pit is attributed to the decrease in diffusion current density associated with the surface roughness.
- The variation of surface roughness did not affect the pit nucleation site preference on DSS 2205. The effects of surface roughness on the both phases of DSS are identical, and the pit location was determined mainly by other factors, such as the chemical content of the phases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Igual Muñoz, A.; García Antón, J.; Guiñón, J.L.; Pérez Herranz, V. The effect of chromate in the corrosion behavior of duplex stainless steel in LiBr solutions. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4127–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhong, C.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Critical pitting and repassivation temperatures for duplex stainless steel in chloride solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5220–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, R.A.; Suter, T.A.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Weber, L.; Magdowski, R.; Bo, H. Corrosion resistance of super duplex stainless steels in chloride ion containing environments: Investigations by means of a new microelectrochemical method I. Precipitation-free states. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 707–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, R.A.; Suter, T.; Solenthaler, C.; Gullo, G.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Bo, H. Corrosion resistance of super duplex stainless steels in chloride ion containing environments: Investigations by means of a new microelectrochemical method II. Influence of precipitates. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, G.T.; Pistorius, P.C. Surface Roughness and the Metastable Pitting of Stainless Steel in Chloride Solutions. Corrosion 1995, 51, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Burstein, G.T. The generation of surface roughness during slurry erosion-corrosion and its effect on the pitting potential. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, W.P. Transient Voltage Changes Produced in Corroding Metals and Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1968, 115, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyn, A.; Goellner, J.; Bierwirth, M.; Klapper, H. Recent applications of electrochemical noise for corrosion testing-Benefits and restrictions. In Corrosion NACE Expo2007, Nashville: Paper, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 March 2007; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H.S.; Goellner, J.; Burkert, A.; Heyn, A. Environmental factors affecting pitting corrosion of type 304 stainless steel investigated by electrochemical noise measurements under potentiostatic control. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladky, K.; Dawson, J.L. The measurement of localized corrosion using electrochemical noise. Corros. Sci. 1981, 21, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legat, A.; Doleček, V. Corrosion Monitoring System Based on Measurement and Analysis of Electrochemical Noise. Corrosion 1995, 51, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottis, R.A.; Al-Awadhi, M.A.A.; Al-Mazeedi, H.; Turgoose, S. Measures for the detection of localized corrosion with electrochemical noise. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-J.; Kwon, H.-S. Electrochemical noise analysis of localized corrosion of duplex stainless steel aged at 475 °C. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 91, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J. Wavelet analysis of potentiostatic electrochemical noise. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4000–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, H.S.; Goellner, J.; Heyn, A. The influence of the cathodic process on the interpretation of electrochemical noise signals arising from pitting corrosion of stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, M.; Moayed, M.H. Investigation of the effect of solution annealing temperature on critical pitting temperature of 2205 duplex stainless steel by measuring pit solution chemistry. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Hoseinpoor, M.; Moayed, M.H. A statistical study on the effect of annealing temperature on pitting corrosion resistance of 2205 duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Huet, F.; Nogueira, R.P.; Rousseau, P. Drift Removal Procedures in the Analysis of Electrochemical Noise. Corrosion 2002, 58, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F.; Han, L.T.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H. Analysis of electrochemical impedance and noise data for polymer coated metals. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U. Noise Resistance Applied to Corrosion Measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1997, 144, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottis, R.A. Interpretation of Electrochemical Noise Data. Corrosion 2001, 57, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocci, U.; Huet, F.; Jaoul, B.; Rousseau, P. Computer Simulations in the Analysis of Electrochemical Noise; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cottis, R.A.; Turgoose, S. Electrochemical Noise Measurements—A Theoretical Basis. Mater. Sci. Forum 1995, 192–194, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Meng, G.; Wang, F. Electrochemical noise analysis on the pit corrosion susceptibility of Mg–10Gd–2Y–0.5Zr, AZ91D alloy and pure magnesium using stochastic model. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 3500–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Amaya, J.M.; Cottis, R.A.; Botana, F.J. Shot noise and statistical parameters for the estimation of corrosion mechanisms. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 3280–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mazeedi, H.A.; Cottis, R. A practical evaluation of electrochemical noise parameters as indicators of corrosion type. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2787–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayed, M.H.; Laycock, N.J.; Newman, R.C. Dependence of the Critical Pitting Temperature on surface roughness. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Momeni, M.; Moayed, M.H.; Davoodi, A. Correlation between critical pitting temperature and degree of sensitisation on alloy 2205 duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Jiang, Y.M.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Effect of annealing treatment on microstructure evolution and the associated corrosion behavior of a super-duplex stainless steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Scully, J.R.; Frankel, G.S. Localized Corrosion: Passive Film Breakdown vs. Pit Growth Stability: Part II. A Model for Critical Pitting Temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, C484–C491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, G.T.; Mo, W.T.; Hatton, T.A.; Tester, J.W.; Tilly, J.; Isaacs, H.S.; Newman, R.C. Mass transfer and electrochemical kinetic interactions in localized pitting corrosion. AIChE J. 1986, 32, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Zhang, B.; Yong, X.P.; Wang, J.Q.; Han, E.-H.; Ke, W. Effects of cyclic stress on the metastable pitting characteristic for 304 stainless steel under potentiostatic polarization. Corros. Sci. 2015, 93, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Du, N.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q. Metastable pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2014, 85, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, G.T.; Liu, C.; Souto, R.M.; Vines, S.P. Origins of pitting corrosion. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 39, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistorius, P.C.; Burstein, G.T. Growth of corrosion pits on stainless steel in chloride solution containing dilute sulphate. Corros. Sci. 1992, 33, 1885–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Scully, J.R.; Frankel, G.S. Localized Corrosion: Passive Film Breakdown vs. Pit Growth Stability: Part III. A Unifying Set of Principal Parameters and Criteria for Pit Stabilization and Salt Film Formation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, C762–C770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BROWN, B.F. Concept of the Occluded Corrosion Cell. Corrosion 1970, 26, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.J. Proceedings of CORROSION/2002 Research Topical Symposium: Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion; NACE International: Houston, TX, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1-57590-130-5. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, G.S.; Stockert, L.; Hunkeler, F.; Boehni, H. Metastable Pitting of Stainless Steel. Corrosion 1987, 43, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistorius, P.C.; Burstein, G.T. Metastable pitting corrosion of stainless steel and the transition to stability. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1992, 341, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Effect of annealing temperature on the pitting corrosion resistance of super duplex stainless steel UNS S32750. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | N | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt % | 0.026 | 0.047 | 1.37 | 0.023 | 0.001 | 22.27 | 3.10 | 5.46 | 0.15 | 0.15 | Bal. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Dai, N.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J. Effect of Surface Roughness on Pitting Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Investigated by Electrochemical Noise Measurements. Materials 2019, 12, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050738
Tang Y, Dai N, Wu J, Jiang Y, Li J. Effect of Surface Roughness on Pitting Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Investigated by Electrochemical Noise Measurements. Materials. 2019; 12(5):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050738
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yiwei, Nianwei Dai, Jun Wu, Yiming Jiang, and Jin Li. 2019. "Effect of Surface Roughness on Pitting Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Investigated by Electrochemical Noise Measurements" Materials 12, no. 5: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050738
APA StyleTang, Y., Dai, N., Wu, J., Jiang, Y., & Li, J. (2019). Effect of Surface Roughness on Pitting Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Investigated by Electrochemical Noise Measurements. Materials, 12(5), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050738




