Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Hollow MgO Spheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
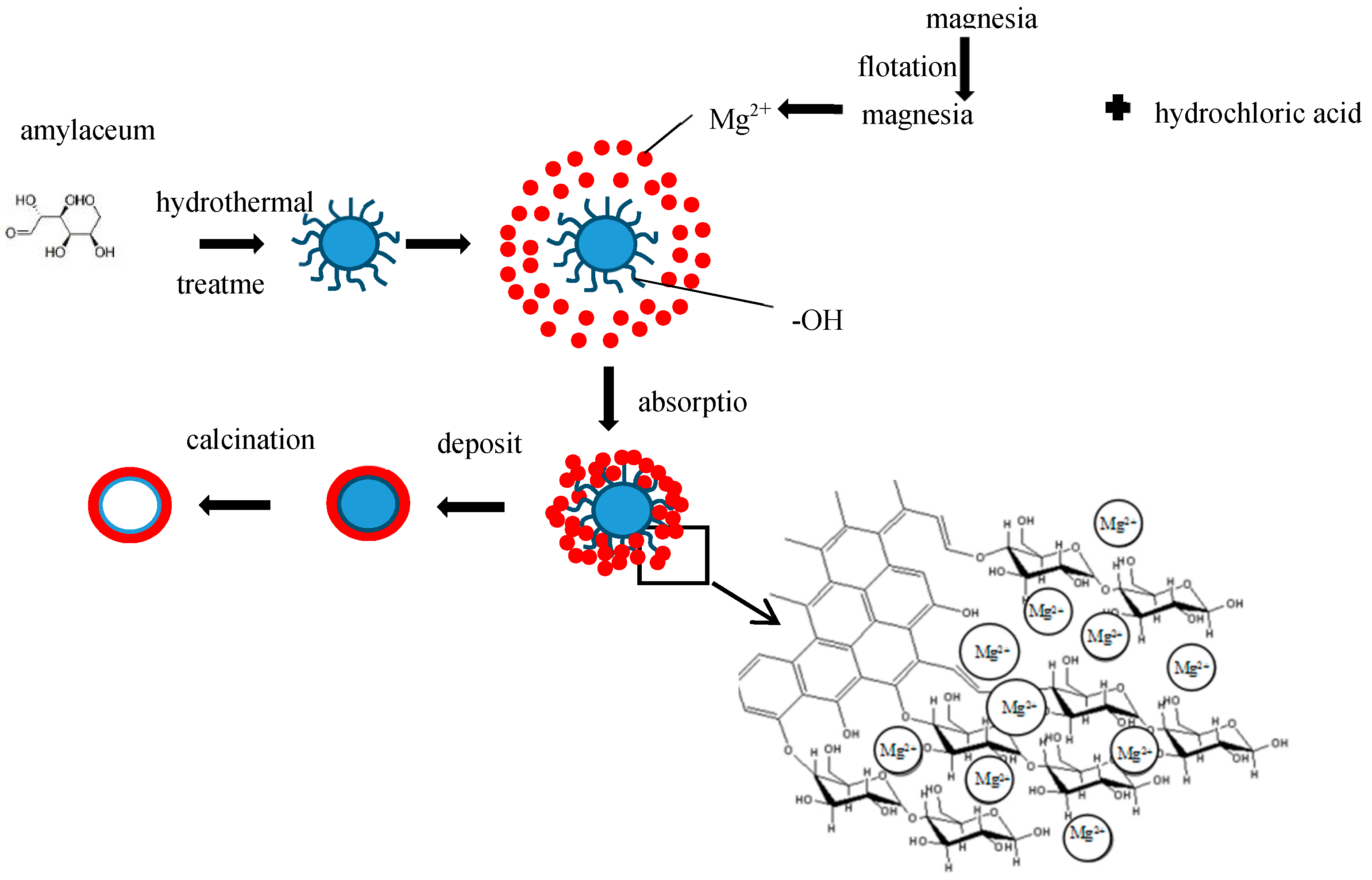
2.2. Methods
2.3. Theoretical Design
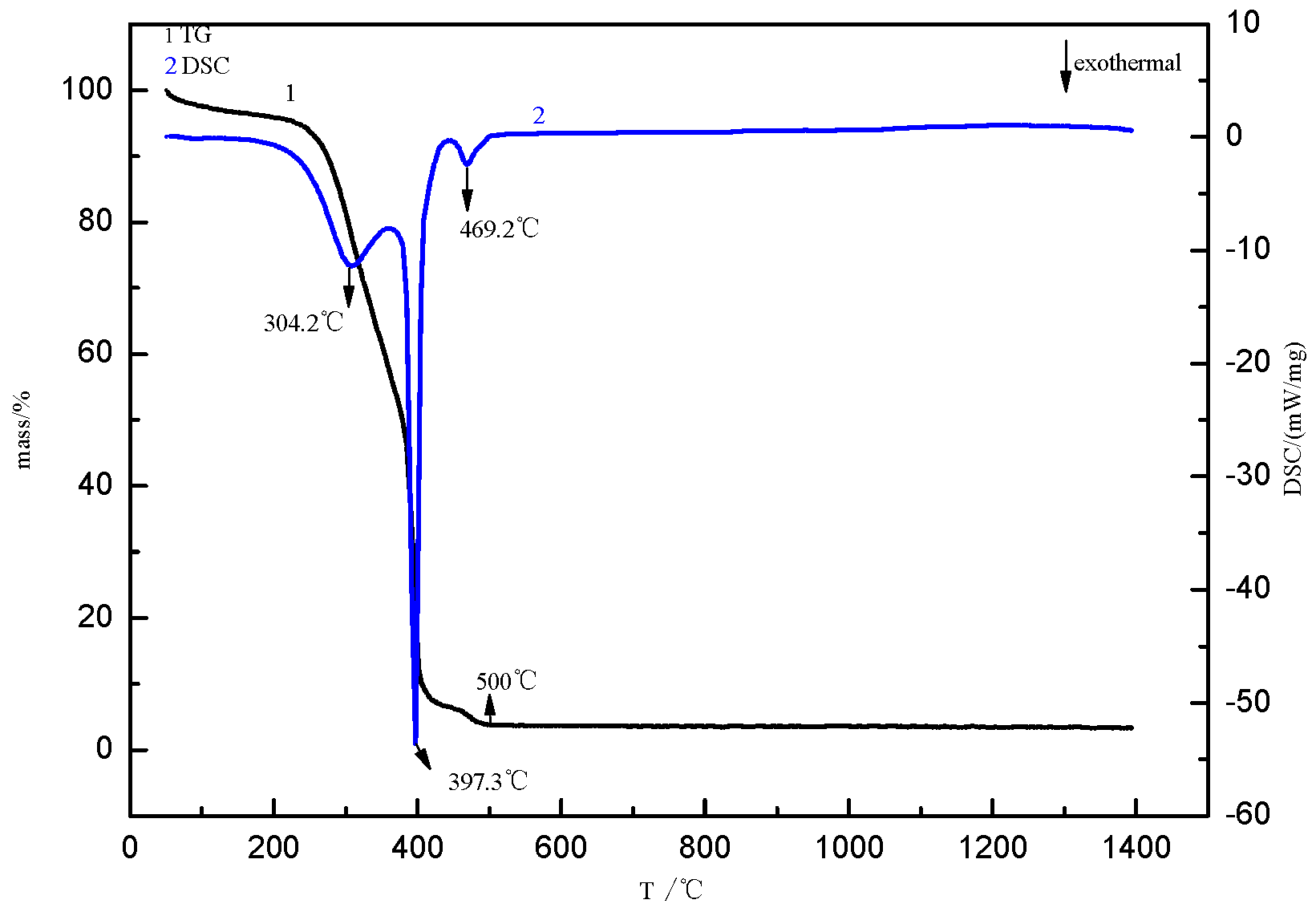
2.4. Determination of Decarbonization Temperature
2.5. Characterization
3. Results
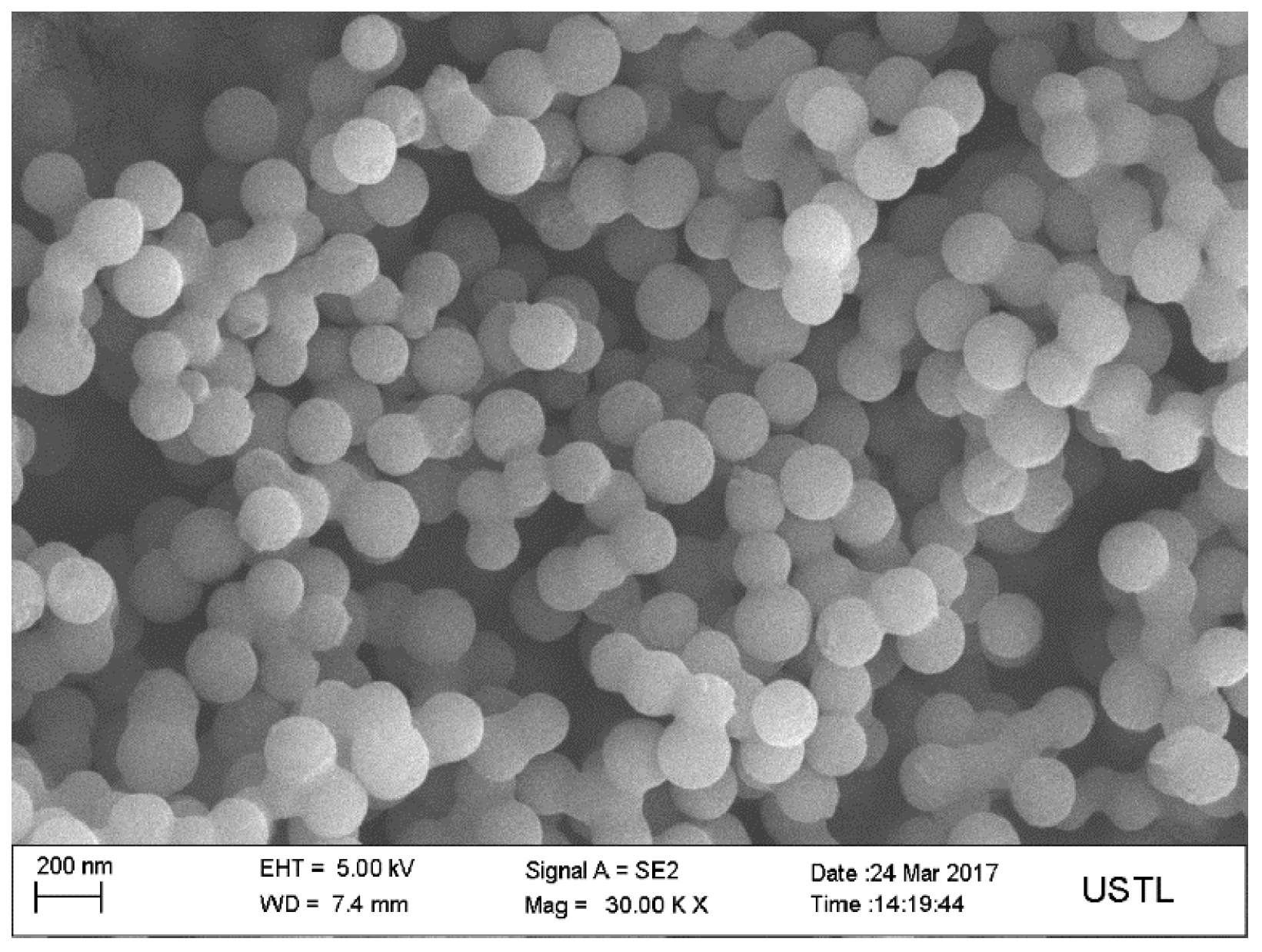
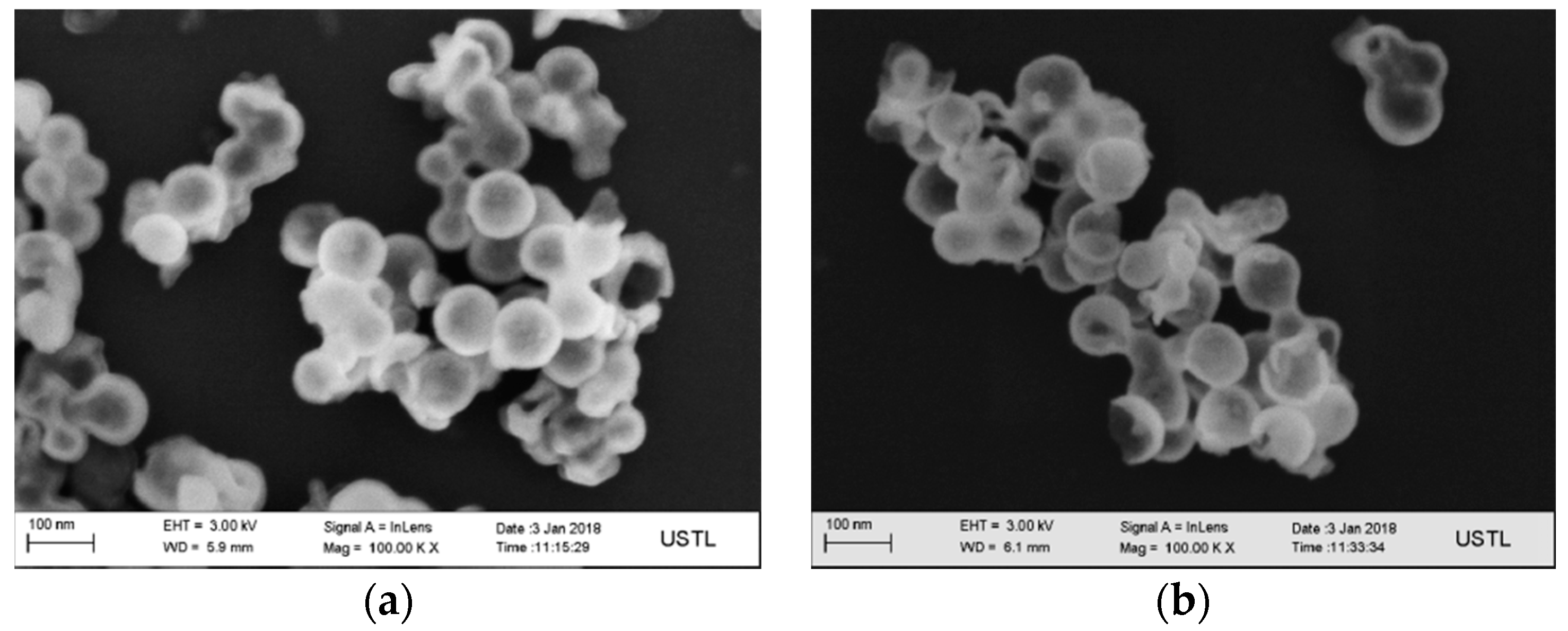
3.1. Structures of Carbon-Based Adsorbent Microspheres
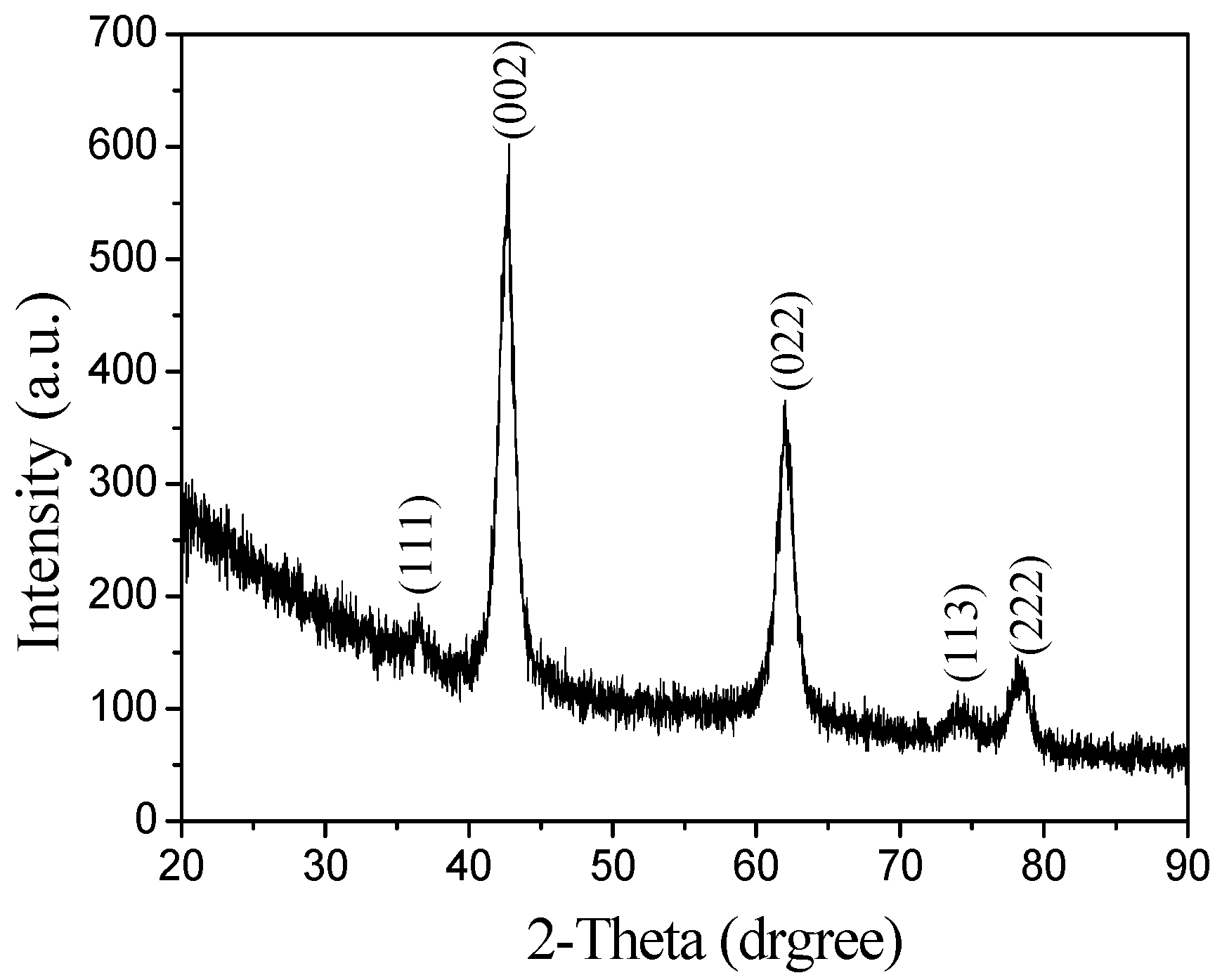
3.2. Structures of the MgO Hollow Microspheres
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The calcination temperature of the samples is determined to be 550 °C by thermogravimetry-differential scanning calorimetry.
- (2)
- The surface of the carbon microspheres is smooth; the size is uniform and the particle size distribution is concentrated in the range of 100–200 nm.
- (3)
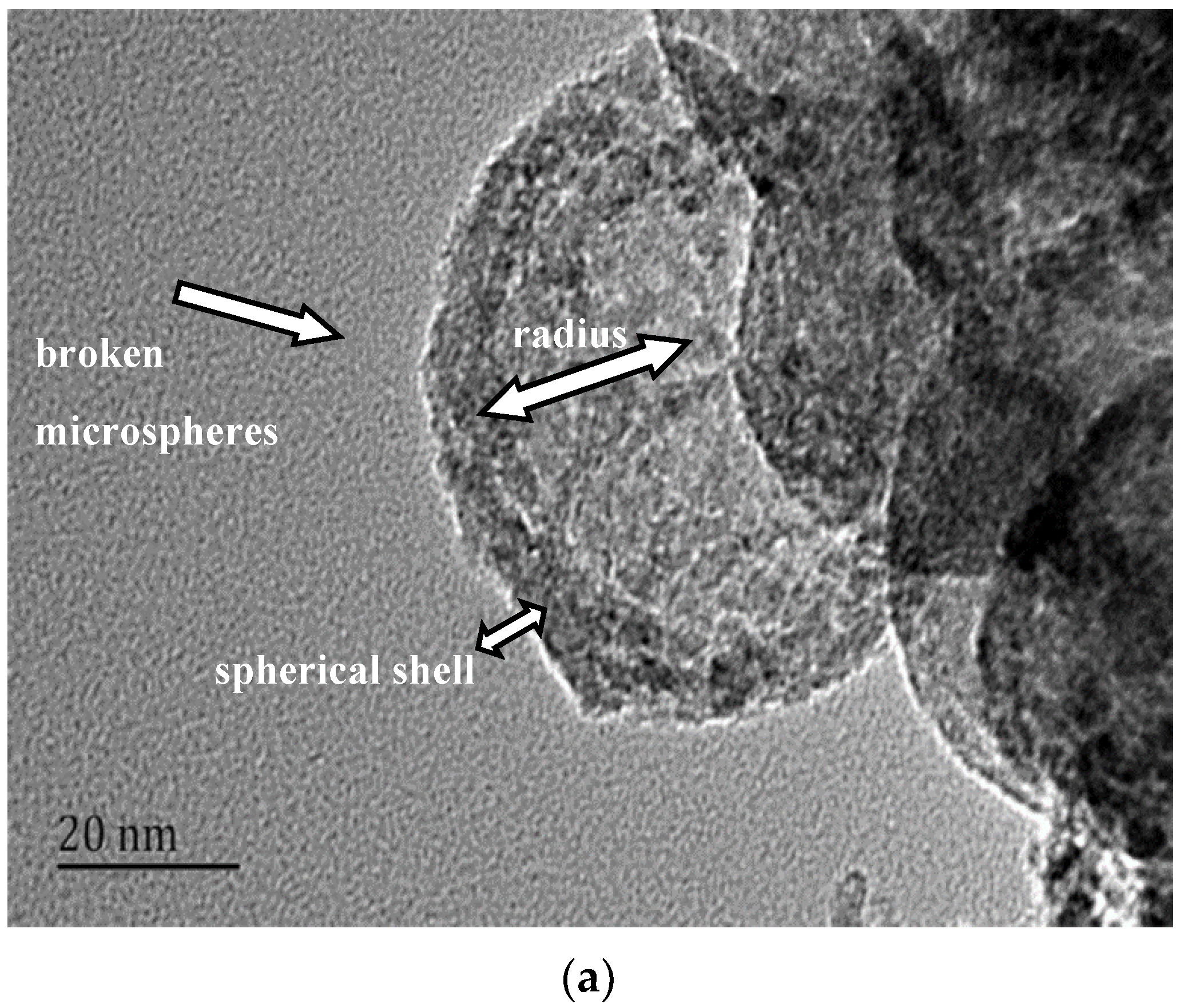
- The MgO microspheres have a hollow structure and periclase composition. The diameter of the sphere is concentrated in the range of 60–90 nm; the diameter of the hollow cavity is 50–60 nm; and the thickness of the spherical shell is 6–10 nm.
- (4)
- The surface of the spherical shell is composed of many crystallites and the microcrystalline gap in the surface of the spherical shell is 5–6 nm.
- (5)
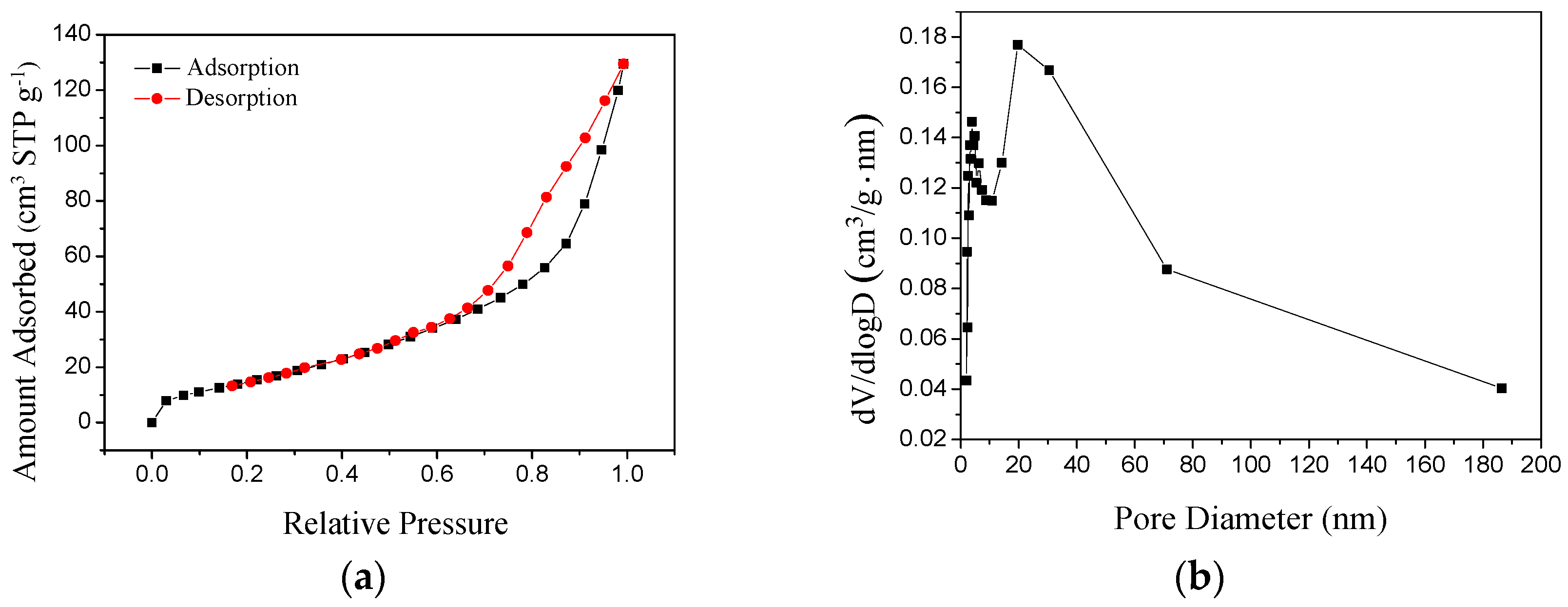
- The specific surface area is about 59.5 m²·g−1.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.-K.; Kang, Y.C. Three-Dimensional Porous Graphene-Metal Oxide Composite Microspheres: Preparation and Application in Li-ion Batteries. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.W.; Archer, L.A.; Yang, Z. Hollow micro-/nanostructures: Synthesis and applications. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3987–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, J. Facile fabrication of porous hollow CeO2 microspheres using polystyrene spheres as templates. J. Porous Mater. 2011, 19, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.Y.; Pawar, R.R.; Somani, R.S.; Bajaj, H.C. Facile hard template approach for synthetic hectorite hollow microspheres. Mater. Lett. 2014, 128, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Pang, W.; Yu, J.; Huo, Q.; Chen, J. Chemistry of Zeolites and Related Porous Materials: Synthesis and Structure; Wiley-Interscience Press: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.S.; Kang, Y.C.; Park, H.D.; Shul, Y.G. Morphology of particles prepared by spray pyrolysis from organic precursor solution. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Dai, J. Controlled synthesis of ZnO hollow microspheres via precursor-template method and its gas sensing property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8431–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Cao, S.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X. Synthesis of uniform hollow TiO2 and SiO2 microspheres via a freezing assisted reverse microemulsion-templated sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 151, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Yu, X. Preparation by Templating Method and Electrochemical Characteristics of Three-dimensional Multiporous LiMnPO4 as Cathode Material. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 45, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Yao, H.; Shi, J. Soft-to-hard templating to well-dispersed N-doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres via one-pot carbon/silica source copolymerization. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xiaolin, C.; Denghong, W.; Yuchuan, C.; Ge, B.; Jiankang, L.; Xinxing, L. Review of the Metallogenic Regularity of Magnesite Deposits in China. Acta. Geol. Sin-Engl. 2015, 89, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşkın, A.; Tatar, İ.; Kılınç, Ş.; Tezel, Ö. The Utilization of Waste Magnesite in the Production of the Cordierite Ceramic. Energy. Procedia. 2017, 107, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Xiangwei, C.; Yanlei, D. Influence of Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid on the Performance of Magnesia Supported Ru-based Catalysts for Ammonia Synthesis. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017, 46, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Preparation of zinc-doped silica gel materials and their adsorptive performance. J. Funct. Mater. 2011, 42, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Bao, R.; Busta, C.M.; Chrisey, D.B. Fabrication and formation mechanism of hollow MgO particles by pulsed excimer laser ablation of Mg in liquid. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 265610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Stetsyshyn, Y. Stability of Halloysite, Imogolite, and Boron Nitride Nanotubes in Solvent Media. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Lazzara, G. Halloysite Nanotubes Loaded with Calcium Hydroxide: Alkaline Fillers for the Deacidification of Waterlogged Archeological Woods. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27355–27364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, X.; Jiang, X.; Niu, D.; Yu, A.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.G. A Two-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis Approach to Monodispersed Colloidal Carbon Spheres. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.Q.; Liang, G.C.; Liang, J.S.; Xu, S.Z.; Zhao, X. LiFePO4 doped with magnesium prepared by hydrothermal reaction in glucose solution. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Han, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, X. Influences of the molecular structure of carbon sources on the structure, morphology and performances of the Li3V2(PO4)3–C cathode for lithium ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas Adsorption Characterization of Ordered Organic−Inorganic Nanocomposite Materials. Chem. Mater. 2011, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhong, L.; Wei, S. Preparation of nanostructured Mgo hollow microspheres and their adsorptive ability to Ni2+. J. Funct. Mater. 2011, 42, 328–331. [Google Scholar]


| Ingredient | MgO | CaO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | Calcination Reduction (IL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω | 47.69 | 0.49 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 51.22 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Li, G.; Yuan, L. Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Hollow MgO Spheres. Materials 2019, 12, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030537
Han J, Li G, Yuan L. Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Hollow MgO Spheres. Materials. 2019; 12(3):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030537
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jishuo, Guohua Li, and Lin Yuan. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Hollow MgO Spheres" Materials 12, no. 3: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030537
APA StyleHan, J., Li, G., & Yuan, L. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Nanostructured Hollow MgO Spheres. Materials, 12(3), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030537




