Curing Kinetic Parameters of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Mallow Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Conclusions
- Kinetic parameters, such as the activation energies (58.971 kJ/mol and 44.536 kJ/mol), the pre-exponential factors Z (1.08 × 108 min−1 and 8.04 × 105 min−1), and the times to reach 50% of the curing reaction (t½), for temperatures ranging from 25 to 100 °C were calculated.
- Particularly for the commonly used room temperature (25 °C), the values of t½ 138.68 and 55.26 min for curing were found for epoxy resin and the composite reinforced with 20 vol % mallow fibers, respectively.
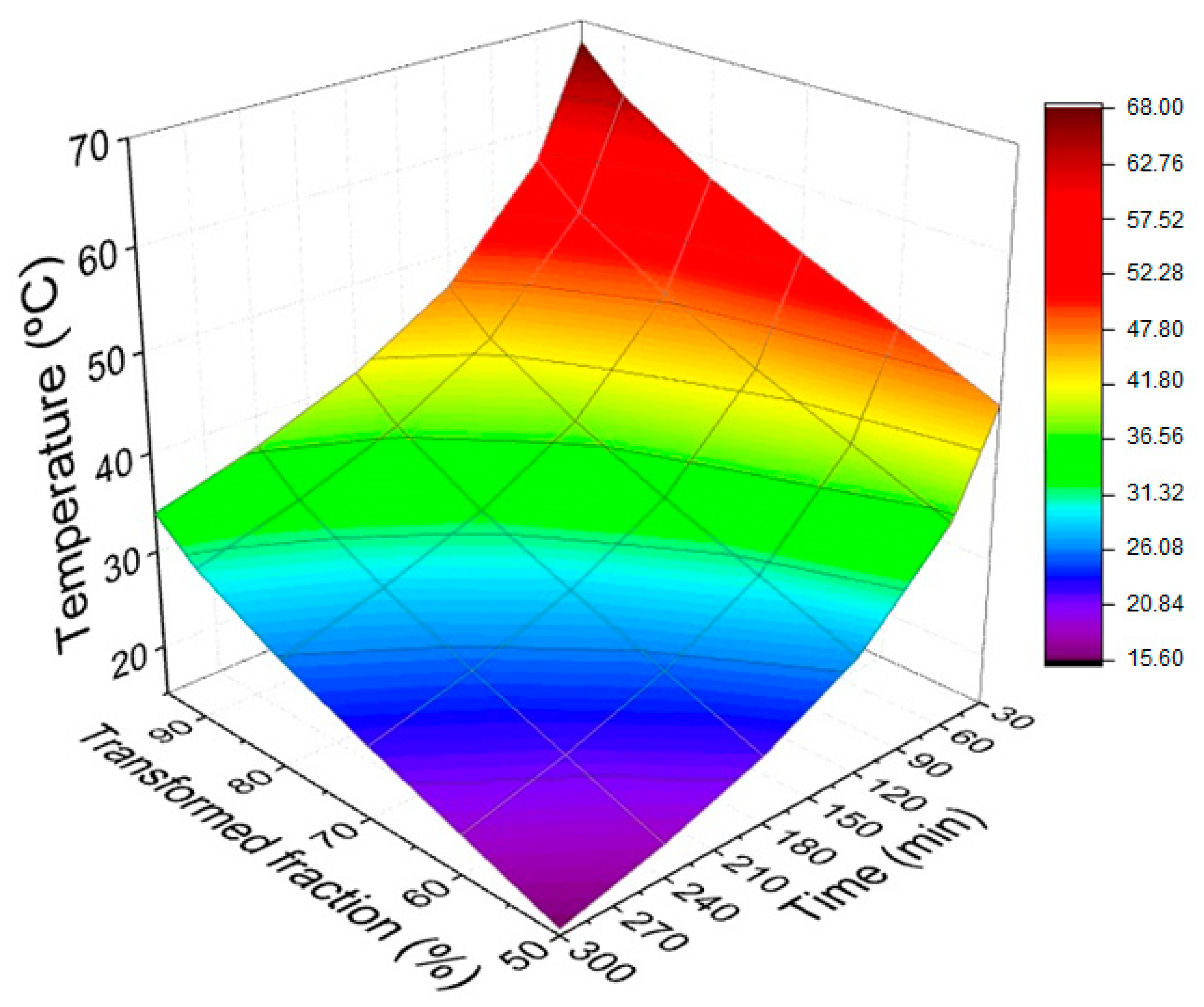
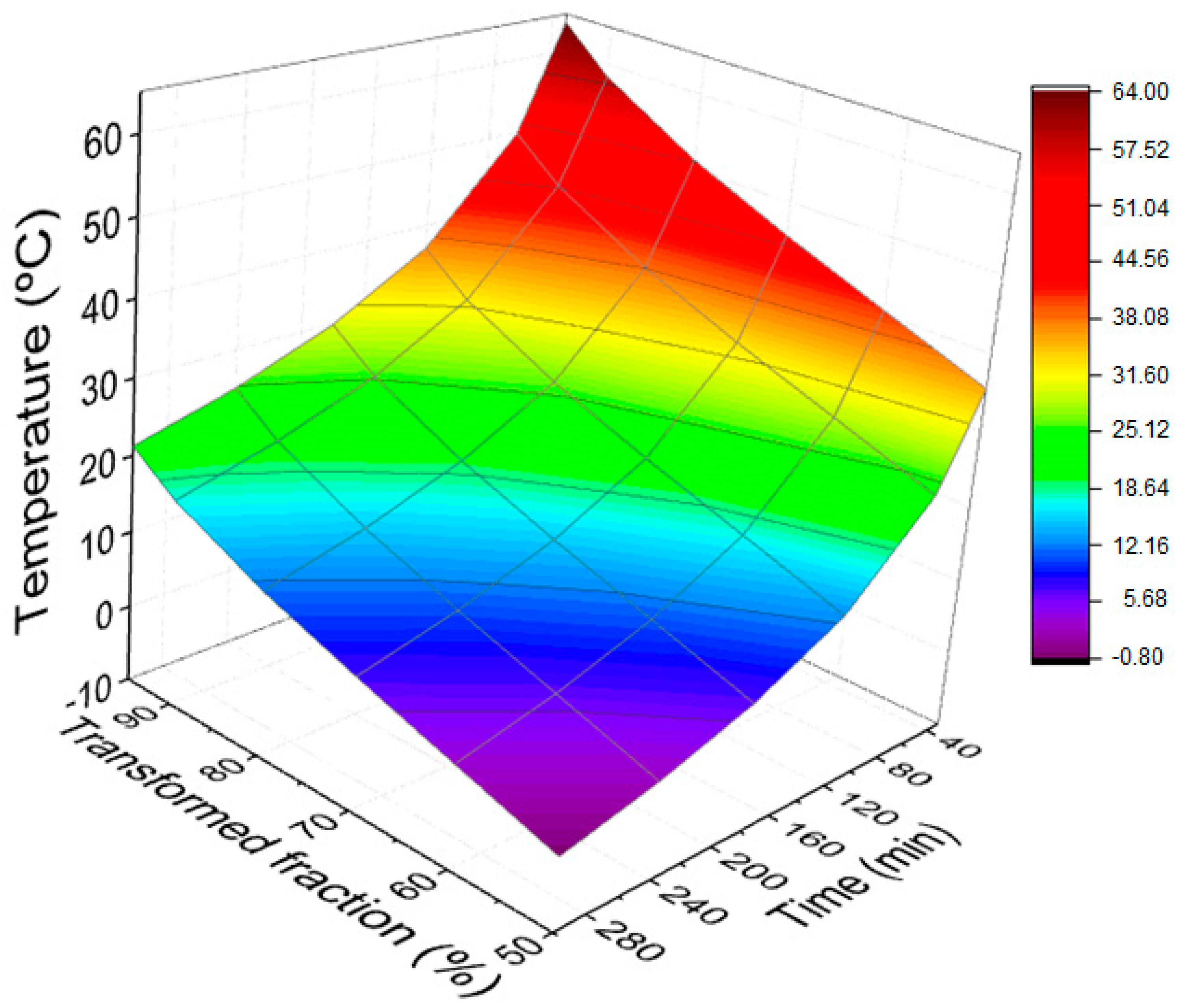
- The curves’ response surfaces obtained for both plain epoxy and 20 vol % mallow fiber-reinforced composites have practical application in the determination of the appropriate combination of time, transformed fraction, and temperature, according to the actual case.
- Curing temperatures for the composite reinforced with 20 vol % mallow fibers are lower than that for pure epoxy resin, for a particular time. This possibly means that natural fibers act as catalysts for the curing reaction, a finding which is reported for the first time for a natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brydson, J.A. Plastics Materials, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Askeland, D.R.; Phulé, P.P. The Science and Engineering of Materials; Brooks/Cole: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Montserrat, S.; Málek, J. A kinetic analysis of the curing reaction of an epoxy resin. Thermochim. Acta 1993, 228, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Rezende, M.C.; Pardini, L.C. Methods of study of curing kinetics of epoxy resins (in Portuguese, Brazil). Polímeros 1999, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, G.W.; Monteiro, S.N.; D’almeida, J.R.M.; Neto, H.S.N. Thermal analysis of DGEBA / TETA epoxy resin for different formulations of stoichiometric ratio (in Portuguese). ABM 2004, 1, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, A.A.A.; Emad, M. Cure Kinetics of Epoxy Resin Studied by Dynamics and Isothermal DSC Data. Eng. Technol. J. A 2016, 34, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, A.A.A.; Emad, M. The Rheological Properties of Isothermal Curing of DGEBA/TETA Epoxy System. Eng. Technol. J. A 2015, 3, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdosian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Anderson, M.; Xu, C.C. Curing kinetics and mechanical properties of bio-based epoxy composites comprising lignin-based epoxy resins. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenojar, J.; del Real, J.C.; Ballesteros, Y.; Martinez, M.A. Kinetics of curing process in carbon/epoxy nano-composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 369, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibres, Biodegradable Polymers and Bio-composites: An overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2000, 276–277, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahed, D.N.; Jog, J.P. Natural fiber polymer composites: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 1999, 18, 351–363. [Google Scholar]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Lopes, F.P.D.; Barbosa, A.P.; Bevitori, A.B.; Da Silva, I.L.A.; Da Costa, L.L. Natural lignocellulosic fibers as engineering materials—An overview. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42A, 2963–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, Y.M.; Ribeiro, C.G.D.; Ferreira, C.L.; Lima, E.S.; Margem, J.I.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Monteiro, S.N. Mechanical behavior of mallow fabric reinforced polyester matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L.; Luz, F.S.; Santos, J.L.; Braga, F.O.; Marçal, R.L.S.B. Charpy impact test of epoxy composites reinforced with untreated and mercerized mallow fibers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Holanda, L.I.F.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Gomes, A.V.; Júnior, E.P.L. Natural Mallow Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composite for Ballistic Armor Against Class III-A Ammunition. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 4425–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Assis, F.S.; Margem, F.M.; Luz, F.S.; Braga, F.O. Charpy impact tenacity of epoxy matrix composites reinforced with aligned jute fibers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Junior, E.P.L.; Luz, F.S. Mallow Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites in Multilayered Armor for Personal Ballistic Protection. JOM 2017, 69, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, N.O.R.; Ferreira, J.B.; Vieira, J.S.; Ribeiro, C.G.D.; Lopes, F.P.D.; Margem, F.M.; Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Silva, L.C. Comparative tensile strength analysis between epoxy composites reinforced with curaua fiber and glass fiber. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.O.; Milanezi, T.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Louro, L.H.L.; Gomes, A.V.; Lima, J.R.E.P. Ballistic comparison between epoxy-ramie and epoxy-aramid composites in Multilayered Armor Systems. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.F.C.; Louro, L.H.L.; Monteiro, S.N.; Gomes, A.V.; Marçal, R.L.S.B.; Lima, J.R.E.P.; Margem, J.I. Ballistic Performance of Mallow and Jute Natural Fabrics Reinforced Epoxy Composites in Multilayered Armor. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. 2017, 20, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margem, J.I.; Gomes, V.A.; Margem, F.M.; Ribeiro, C.G.D.; Braga, F.O.; Monteiro, S.N. Flexural Behavior of Epoxy Matrix Composites Reinforced with Malva Fiber. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. 2015, 18, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Assis, F.S.; Ferreira, C.L.; Simonassi, N.T.; Weber, R.P.; Souza, M.O.; Colorado, H.; Pereira, A.C. Fique Fabric: A Promising Reinforcement for Polymer Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, F.S.; Tommasini, F.J.; Nascimento, L.F.C.; Figueiredo, A.B.S.; Monteiro, S.N. Critical length and interfacial strength of PALF and coir fiber incorporated in epoxy resin matrix. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwish, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering—An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- D’Almeida, J.R.M.; Menezes, G.W.; Monteiro, S.N. Ageing of the DGEBA/TETA epoxy system with off-stoichiometric compositions. Mater. Res.-Ibero-Am. J. 2003, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of Phase Change. I General Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
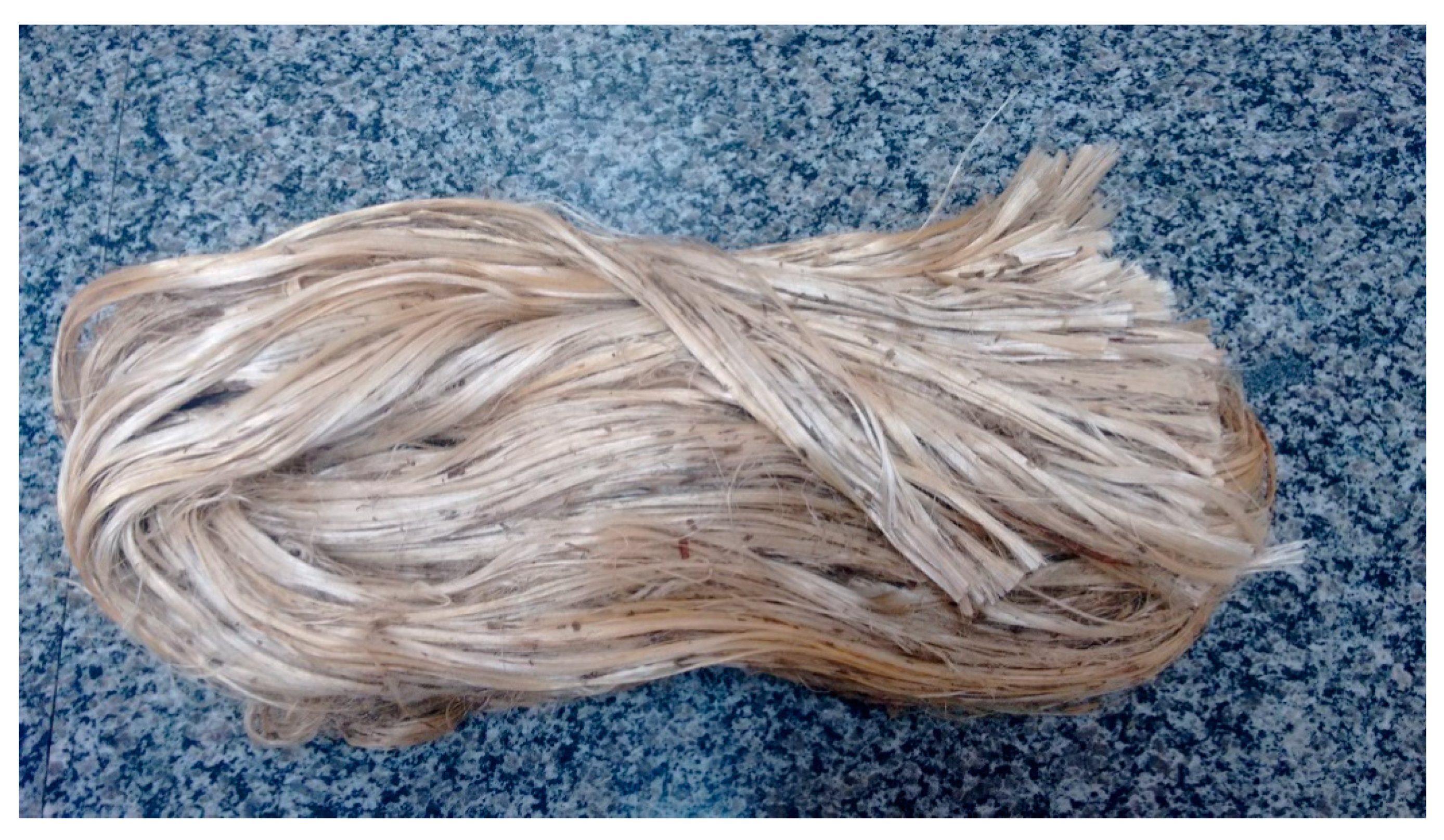
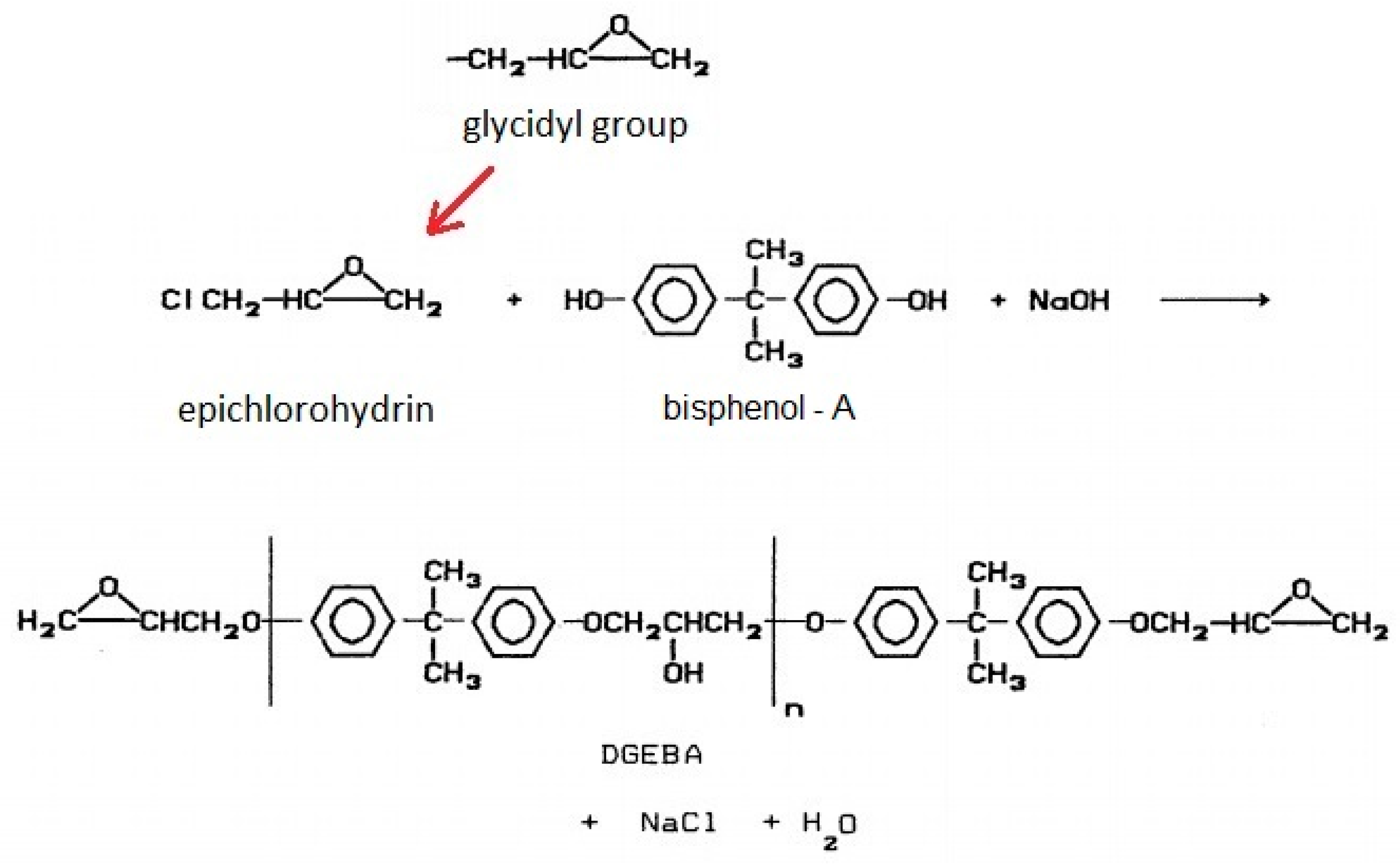

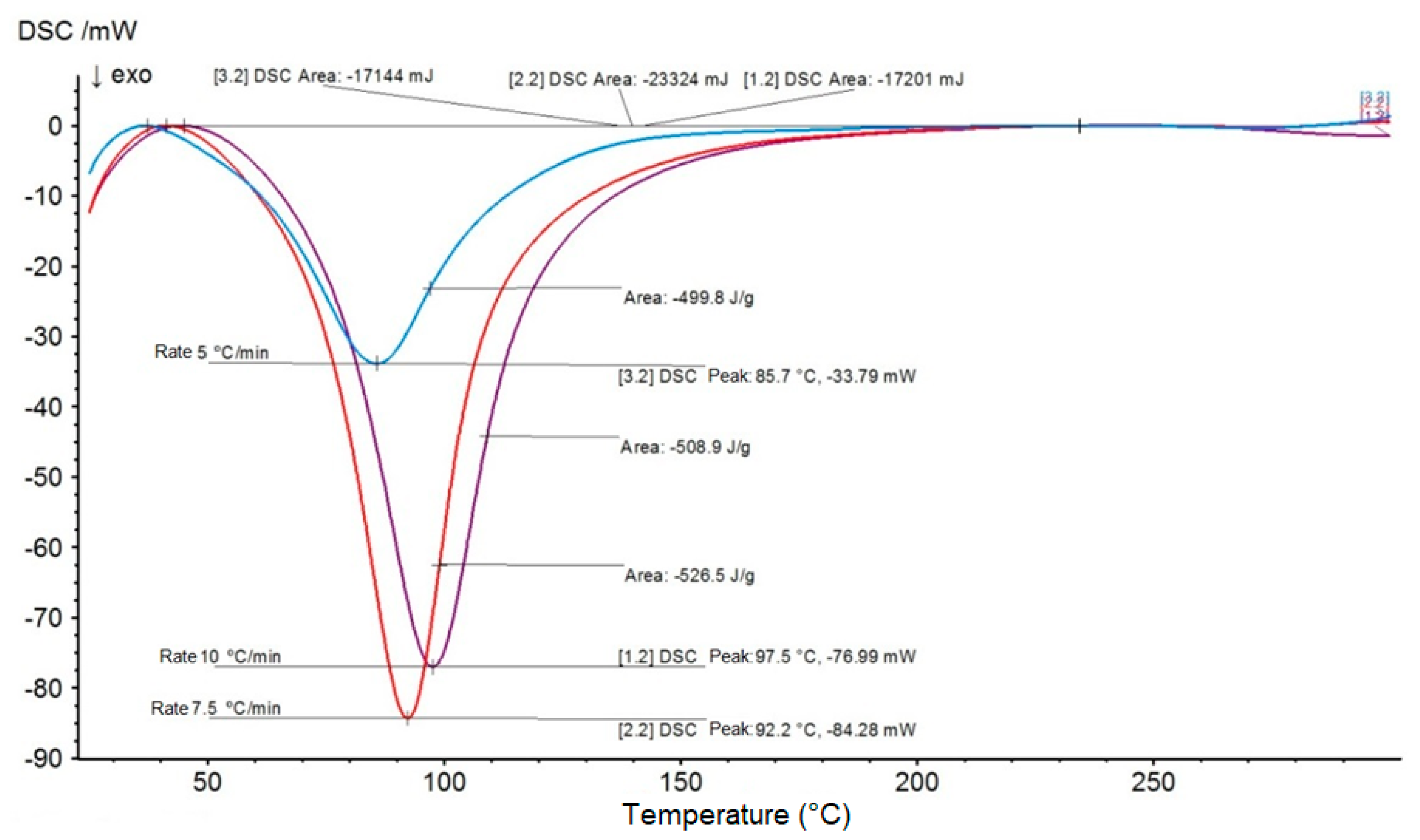
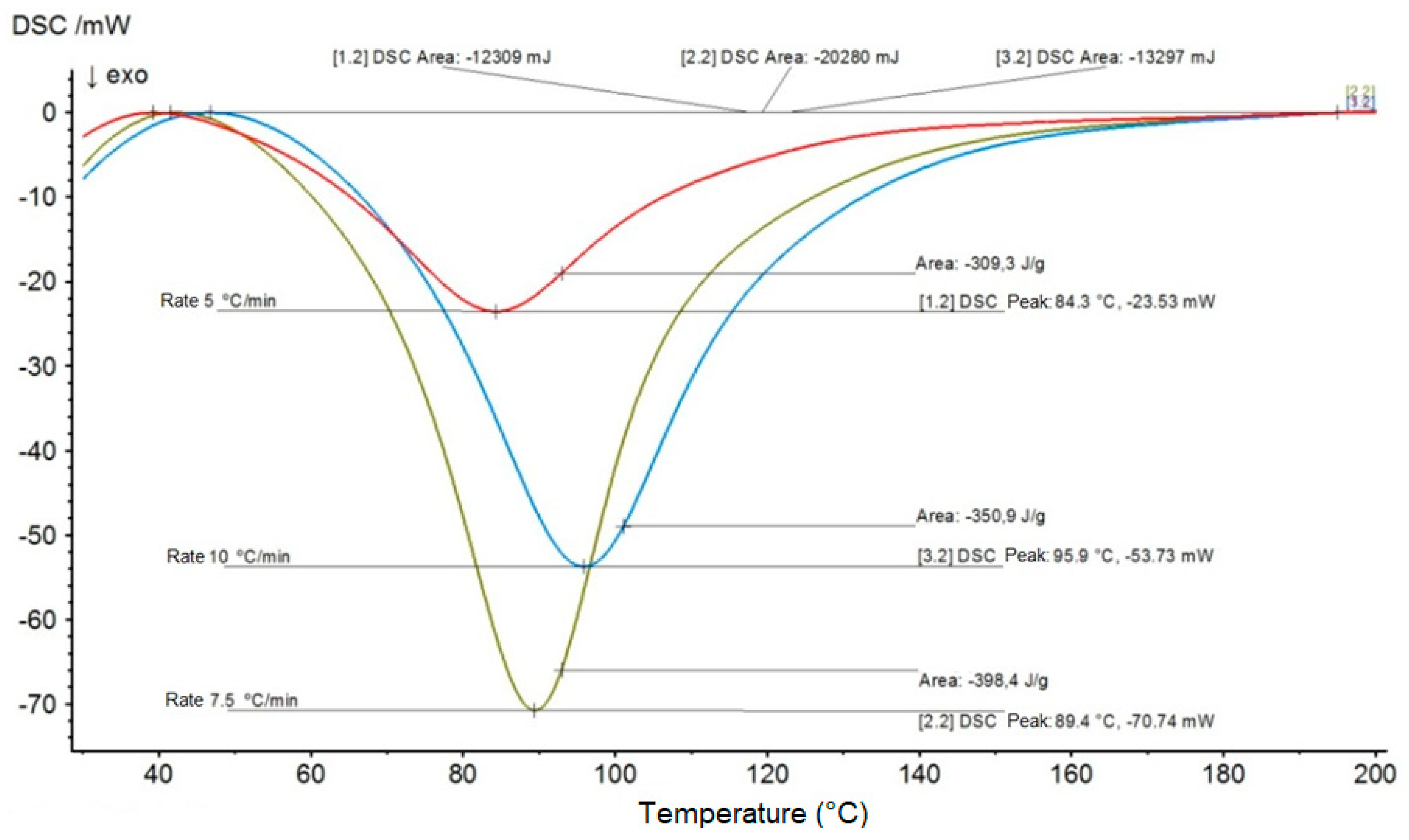
| Test Materials | Activation Energy (kJ/mol) | Pre-exponential Factor “Z” (min−1) × 105 | Temperatures (°C) | Constant Rate “k” (min−1) | Mean Time to Reach 50% Cure “t½” (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain epoxy resin | 58.97 | 1.080 | 25 | 0.0050 | 138.68 |
| 50 | 0.0316 | 21.98 | |||
| 80 | 0.2039 | 3.40 | |||
| 100 | 0.5987 | 1.16 | |||
| Epoxy composite reinforced with 20 vol % of mallow fibers | 44.54 | 8.036 | 25 | 0.0125 | 55.26 |
| 50 | 0.0504 | 13.75 | |||
| 80 | 0.2064 | 3.36 | |||
| 100 | 0.4656 | 1.49 |
| Transformed Fraction (%) | Time (min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 60 | 120 | 180 | 240 | 300 | |
| 50 | 45.49 °C | 35.87 °C | 26.82 °C | 21.77 °C | 18.29 °C | 15.64 °C |
| 60 | 49.53 °C | 39.67 °C | 30.40 °C | 25.23 °C | 21.67 °C | 18.96 °C |
| 70 | 53.58 °C | 43.48 °C | 33.99 °C | 28.69 °C | 25.05 °C | 22.28 °C |
| 80 | 58.01 °C | 47.64 °C | 37.89 °C | 32.47 °C | 28.73 °C | 25.89 °C |
| 90 | 53.58 °C | 43.48 °C | 33.99 °C | 28.69 °C | 25.05 °C | 22.28 °C |
| 95 | 67.89 °C | 56.90 °C | 46.60 °C | 40.86 °C | 36.92 °C | 33.93 °C |
| Transformed Fraction (%) | Time (min) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 60 | 120 | 180 | 240 | 300 | |
| 50 | 35.49 °C | 23.65 °C | 12.68 °C | 6.63 °C | 2.50 °C | −0.63 °C |
| 60 | 40.53 °C | 28.30 °C | 17.00 °C | 10.77 °C | 6.51 °C | 3.29 °C |
| 70 | 45.62 °C | 33.00 °C | 21.35 °C | 14.93 °C | 10.55 °C | 7.24 °C |
| 80 | 51.22 °C | 38.16 °C | 26.12 °C | 19.50 °C | 14.97 °C | 11.56 °C |
| 90 | 58.40 °C | 44.77 °C | 32.22 °C | 25.33 °C | 20.63 °C | 17.08 °C |
| 95 | 63.88 °C | 49.81 °C | 36.87 °C | 29.77 °C | 24.92 °C | 21.27 °C |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nascimento, L.F.C.; da Luz, F.S.; Costa, U.O.; Braga, F.d.O.; Lima Júnior, É.P.; Monteiro, S.N. Curing Kinetic Parameters of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Mallow Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233939
Nascimento LFC, da Luz FS, Costa UO, Braga FdO, Lima Júnior ÉP, Monteiro SN. Curing Kinetic Parameters of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Mallow Fibers. Materials. 2019; 12(23):3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233939
Chicago/Turabian StyleNascimento, Lucio Fabio Cassiano, Fernanda Santos da Luz, Ulisses Oliveira Costa, Fábio de Oliveira Braga, Édio Pereira Lima Júnior, and Sergio Neves Monteiro. 2019. "Curing Kinetic Parameters of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Mallow Fibers" Materials 12, no. 23: 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233939
APA StyleNascimento, L. F. C., da Luz, F. S., Costa, U. O., Braga, F. d. O., Lima Júnior, É. P., & Monteiro, S. N. (2019). Curing Kinetic Parameters of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Mallow Fibers. Materials, 12(23), 3939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233939







