Determination of Construction Temperatures of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Mixture Based on CRMB Mastic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Bitumen Mastic
2.3. Research Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination Based on the CRMB Binder
3.2. Determination Based on the CRMB Mastic
3.2.1. The Relationship between Viscosity and Temperature of the CRMB Mastic
3.2.2. Demarcating the Viscosity Ranges of the CRMB Mastic
3.2.3. Determination of Construction Temperatures Using Viscosity of the CRMB Mastic
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szydlo, A.; Mackiewicz, P. Asphalt mixes deformation sensitivity to change in rheological parameters. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2005, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzinauskas, V. Filler in asphalt mixtures. In The Asphalt Institute Research Report; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tunnicliff, D.G. Binding effects of mineral filler. In Proceedings of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, Washington, DC, USA; 1967; 2, p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.S.; Shu, X.; Chen, X.W. Effects of mineral fillers on hot-mix asphalt laboratory-measured properties. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2007, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H. Effect of mineral powder content on the performance of asphalt mastic. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2008, 9, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.S.; Mohammad, L.N.; Graves, P.S.; Abadie, C. Louisiana experience with crumb rubber-modified hot-mix asphalt pavement. In Bituminous Paving Mixtures 2002: Materials and Construction; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouranian, M.R.; Shishehbor, M. Sustainability Assessment of Green Asphalt Mixtures: A Review. Environments 2019, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ma, T.; Huang, X.M.; Guan, Y.S.; Zhang, Z.X.; Tang, F.L. The performance of hot-recycling asphalt binder containing crumb rubber modified asphalt based on physiochemical and rheological measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.R.; Weinberg, K. A review on split Hopkinson bar experiments on the dynamic characterisation of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 1264–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, Z.; Hasan, M.R.M.; Diab, A.; Shao, H.; Chen, S.; Ge, D. Environmental and mechanical performance of crumb rubber modified warm mix asphalt using Evotherm. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Y.; Solaimanian, M.; Kennedy, T.W. Mixing and Compaction Temperatures for Hot Mix Asphalt Concrete; University of Texas at Austin. Center for Transportation Research: Austin, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bahia, H.U.; Hanson, D.; Zeng, M.; Zhai, H.; Khatri, M.; Anderson, R. Characterization of Modified Asphalt Binders in Superpave Mix Design; Transportation Reaserch Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Reinke, G. Determination of Mixing and Compaction Temperature of PG Binders Using a Steady Shear Flow Test; Superpave Binder Expert Task Group, AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Akisetty, C.K.; Lee, S.-J.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Effects of Compaction Temperature on Volumetric Properties of Rubberized Mixes Containing Warm-Mix Additives. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2009, 21, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.C.; Watson, D.E.; Turner, P.A.; Casola, J.R. NCHRP Report 648: Mixing and Compaction Temperatures of Asphalt Binders in Hot-Mix Asphalt; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Ge, Z.; Yuan, J. Determining on construction temperature of warm rubberized asphalt mixture. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2011, 11, 1386–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, H.I.; Kamran, F. Laboratory evaluation of dry process crumb rubber modified mixtures containing Warm Mix Asphalt Additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Research Institue of Highway Ministry of Transport. M.O.T. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixture for Highway Engineering; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, T.W.; Huber, G.A.; Harrigan, E.T.; Cominsky, R.J.; Hughes, C.S.; Von Quintus, H.; Moulthrop, J.S. Superior Performing Asphalt Pavements (Superpave): The Product of the SHRP Asphalt Research Program; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D4402. Standard Test Method for Viscosity Determination of Asphalt at Elevated Temperatures using a Rotational Viscometer; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.L. Experimental study on compaction temperature of organic viscosity of CRMA. Chin. Foreign Highw. 2013, 32, 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, N.; Chen, H.X. Determining method of mixing and compaction temperatures for modified asphalt mixture. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2007, 7, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.Z. Investigation of the mixing construction temperature of SBS modified asphalt. Shanxi Traffic Sci. Technol. 2008, 9, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, W.H. Research on the determination method of the construction temperature of SBS modified asphalt. Highw. Automot. Appl. 2013, 11, 92–96. [Google Scholar]

| Properties | Requirements | Test Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C; 0.1 mm) | 60–80 | 68.9 | |
| Ductility (15 °C; cm) | ≥40 | 68 | |
| Softening point (°C) | ≥46 | 48.3 | |
| Flash point (°C) | ≥230 | 263 | |
| Wax content (%) | ≤3 | 1.84 | |
| Density (g/cm3) | report | 1.032 | |
| Solubility (trichloroethylene; %) | ≥99.5 | 99.7 | |
| RTFOT (163 °C, 75 min) | Mass change (%) | ≤0.8 | 0.3 |
| Retained penetration (%) | ≥58 | 78 | |
| Ductility (15 °C; cm) | ≥15 | 44 | |
| PG grade | 64–22 | ||
| Testing Items | Relative Densities | Water Ratio (%) | Metal Content (%) | Fiber Content (%) | Screenings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test results | 1.16 | 0.6 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 8.3 |
| Requirements | 1.10–1.30 | <1 | <0.05 | <1 | <10 |
| Testing Items | Ash Content (%) | Acetone Extract (%) | Carbon Black Content (%) | Rubber Hydrocarbon Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test results | 7.2 | 4.9 | 31.3 | 55.2 |
| Requirements | ≤8 | ≤22 | ≥28 | ≥42 |
| Kinds of Filling | Apparent Density (g/cm3) | Hydrophilic Coefficient | <0.075 mm Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral powder | 2.71 | 0.89 (<1) | 90.4 |
| Cement | 2.80 | 0.78 (<1) | 92.3 |
| Screen Size (mm) | Passing percent (%) |
|---|---|
| 0.075 | 83.4 |
| 0.15 | 91.2 |
| 0.3 | 97.3 |
| 0.6 | 100 |
| Aggregate Properties | #1 (9.5–16 mm) | #2 (4.75–9.5 mm) | #3 (2.36–4.75 mm) | #4 (0–2.36 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent density (g/cm3) | 2.868 | 2.857 | 2.839 | 2.865 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 2.797 | 2.766 | 2.757 | 2.749 |
| Water absorption (%) | 0.89 | 1.15 | 1.05 | 1.47 |
| Screen Size (mm) | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passing-percent (%) | #1 | 100 | 83.2 | 10.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| #2 | 100 | 100 | 98.5 | 12.1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| #3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 85.3 | 25.7 | 14.0 | 8.1 | 4.0 | 2.9 | 1.9 | |
| #4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 86.3 | 64.1 | 39.2 | 18.5 | 10 | 7.6 | |
| Test Parameters | Rotor | Revolving Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|
| CRMB binder | 27# | 20 |
| CRMB mastic | 27# | 30 |
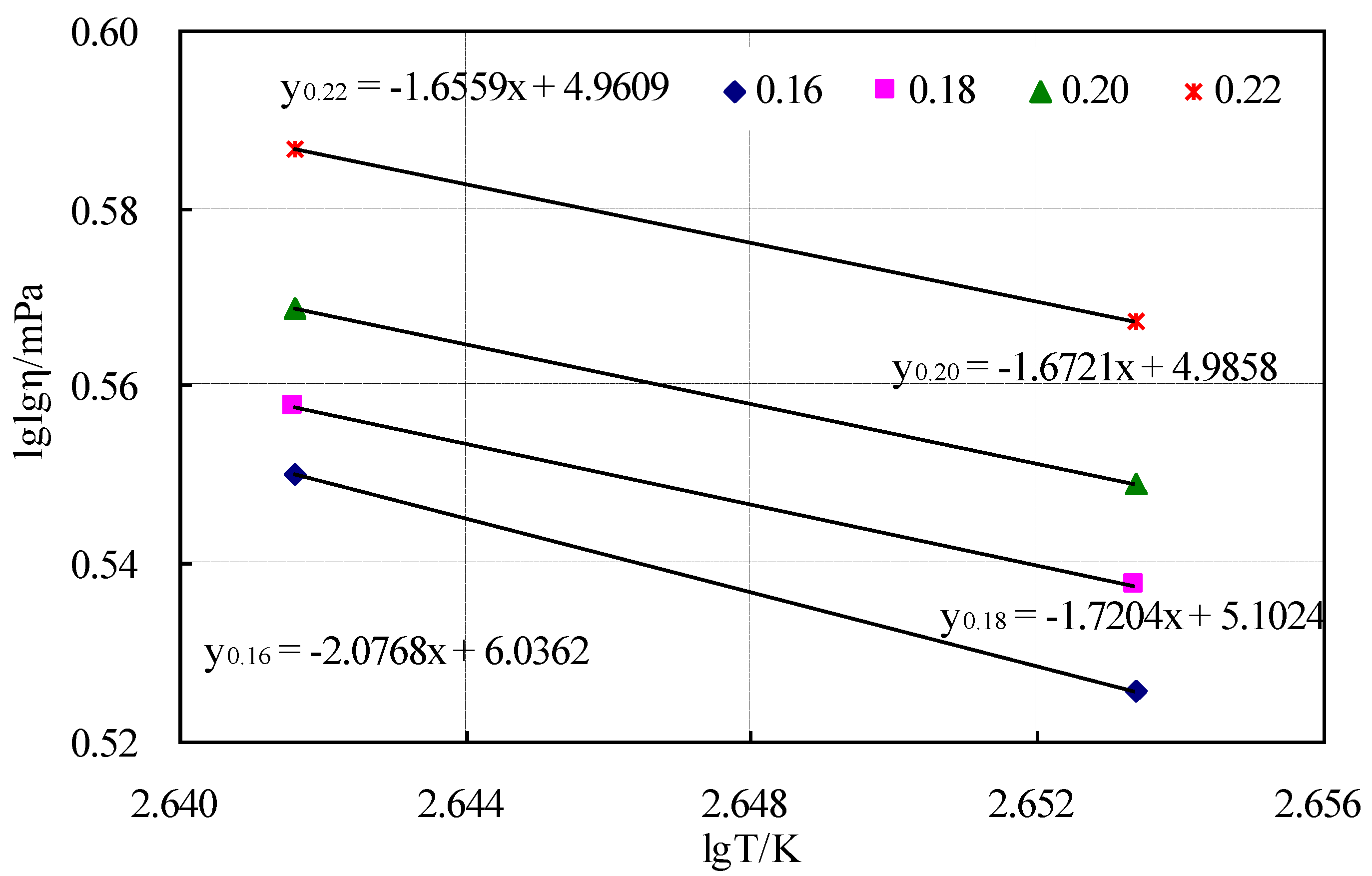
| Generalized Filler–Bitumen Ratio | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing temperature (°C) | 269–281 | 299–315 | 313–329 | 329–346 |
| Compaction temperature (°C) | 246–256 | 270–283 | 282–295 | 298–311 |
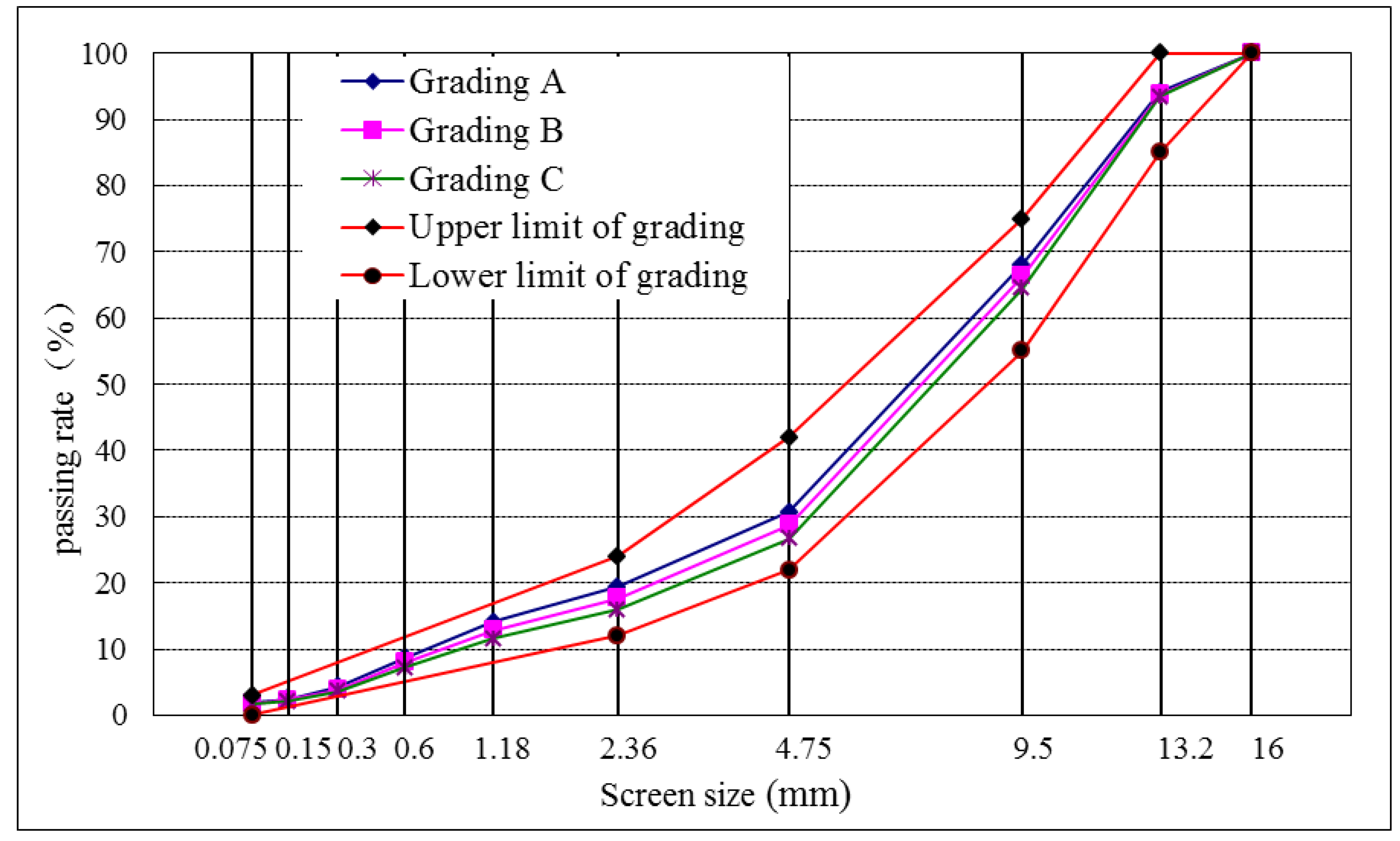
| Types of Gradation #1:#2:#3:#4 | Screen Size (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.0 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| A (35:38:7:20) | 100.0 | 94.1 | 68.1 | 30.7 | 19.4 | 14.1 | 8.7 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 2.0 |
| B (37:38:7:18) | 100.0 | 93.8 | 66.3 | 28.7 | 17.7 | 12.9 | 8.0 | 3.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 |
| C (39:38:7:16) | 100.0 | 93.4 | 64.5 | 26.7 | 16.0 | 11.6 | 7.2 | 3.6 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
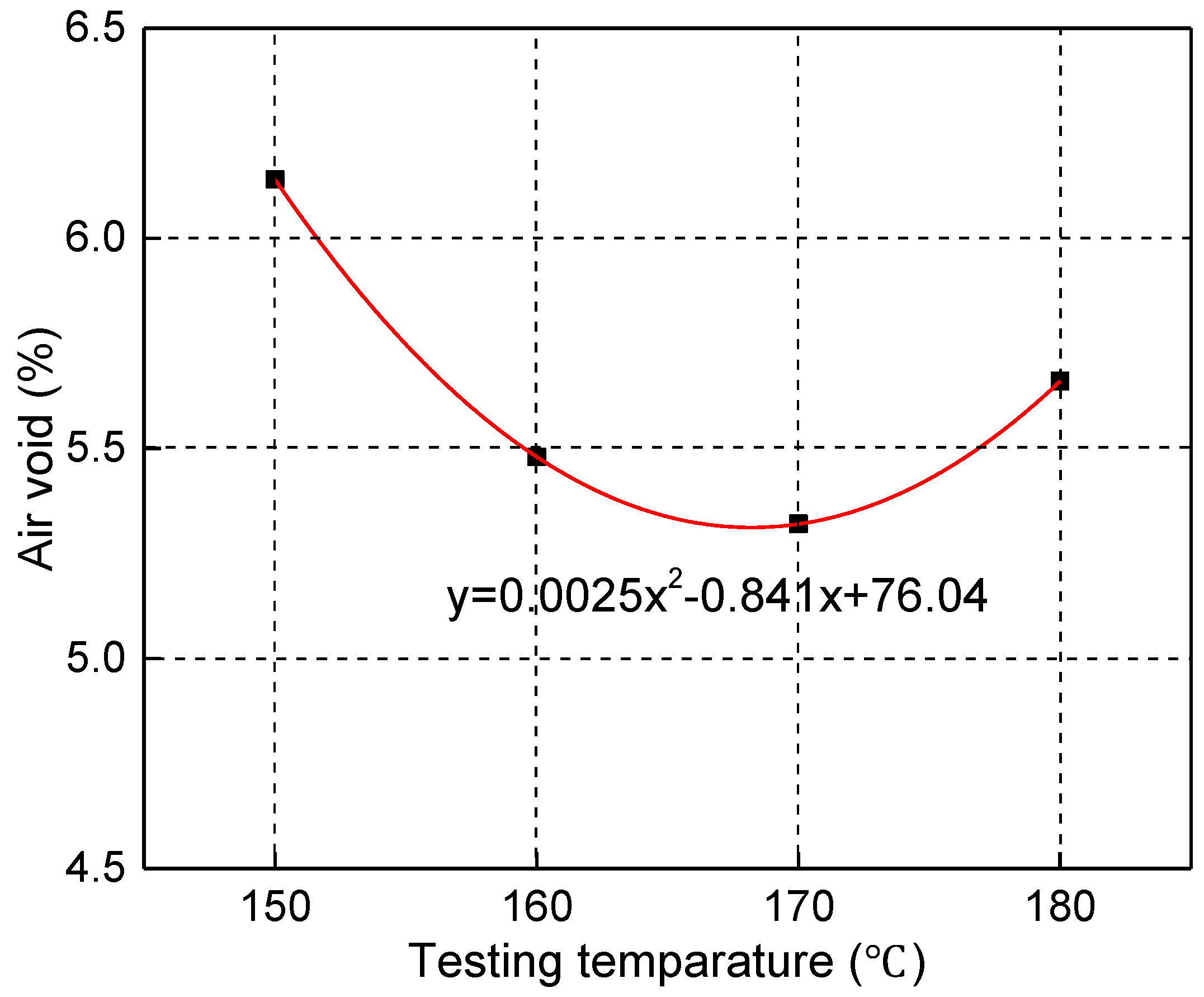
| Types of Gradation | Bitumen Aggregate Ratio (%) | Air Void (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gradation A | 8.2 | 3.1 |
| Gradation B | 8.2 | 4.8 |
| Gradation C | 8.2 | 5.2 |
| Requirements | - | 4.5–6.5 |
| Bitumen Aggregate Ratio (%) | Air Void (%) | VMA (%) | VFA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8.2 | 5.2 | 21.59 | 77.77 |
| Requirements | 5.5 ± 1 | ≥19 | — |
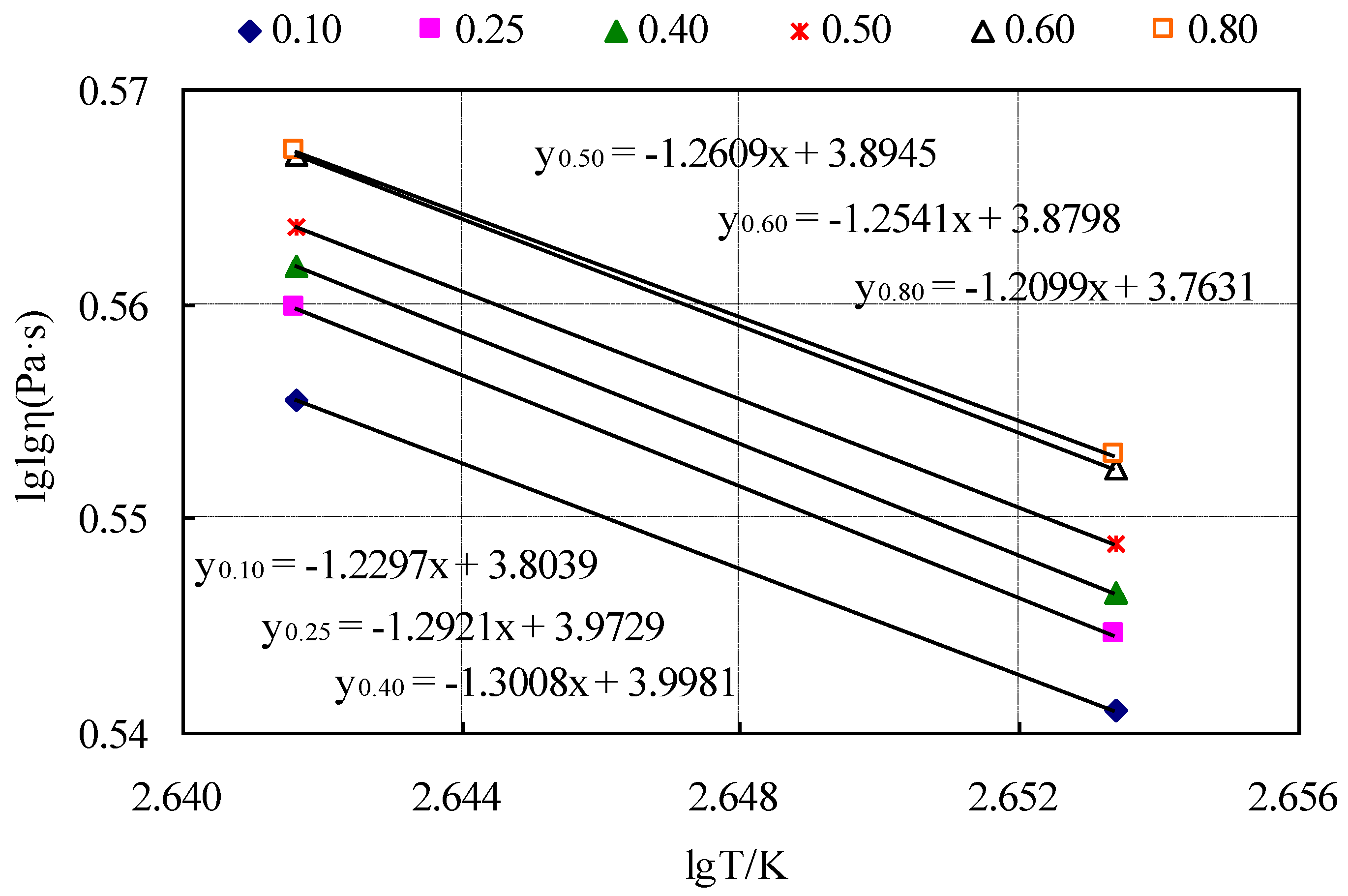
| Filler–Bitumen Ratio | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 0.80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing temperature (°C) | 178–185 | 181–188 | 183–189 | 185–192 | 188–195 | 189–196 |
| Compaction temperature (°C) | 162–169 | 165–172 | 167–174 | 169–180 | 171–178 | 171–179 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, M.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Y. Determination of Construction Temperatures of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Mixture Based on CRMB Mastic. Materials 2019, 12, 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233851
Li Y, Lyu Y, Xu M, Fan L, Zhang Y. Determination of Construction Temperatures of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Mixture Based on CRMB Mastic. Materials. 2019; 12(23):3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233851
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanan, Yuchao Lyu, Meng Xu, Liang Fan, and Yuzhen Zhang. 2019. "Determination of Construction Temperatures of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Mixture Based on CRMB Mastic" Materials 12, no. 23: 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233851
APA StyleLi, Y., Lyu, Y., Xu, M., Fan, L., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Determination of Construction Temperatures of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen Mixture Based on CRMB Mastic. Materials, 12(23), 3851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233851





