Effects of Microwave Sintering Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
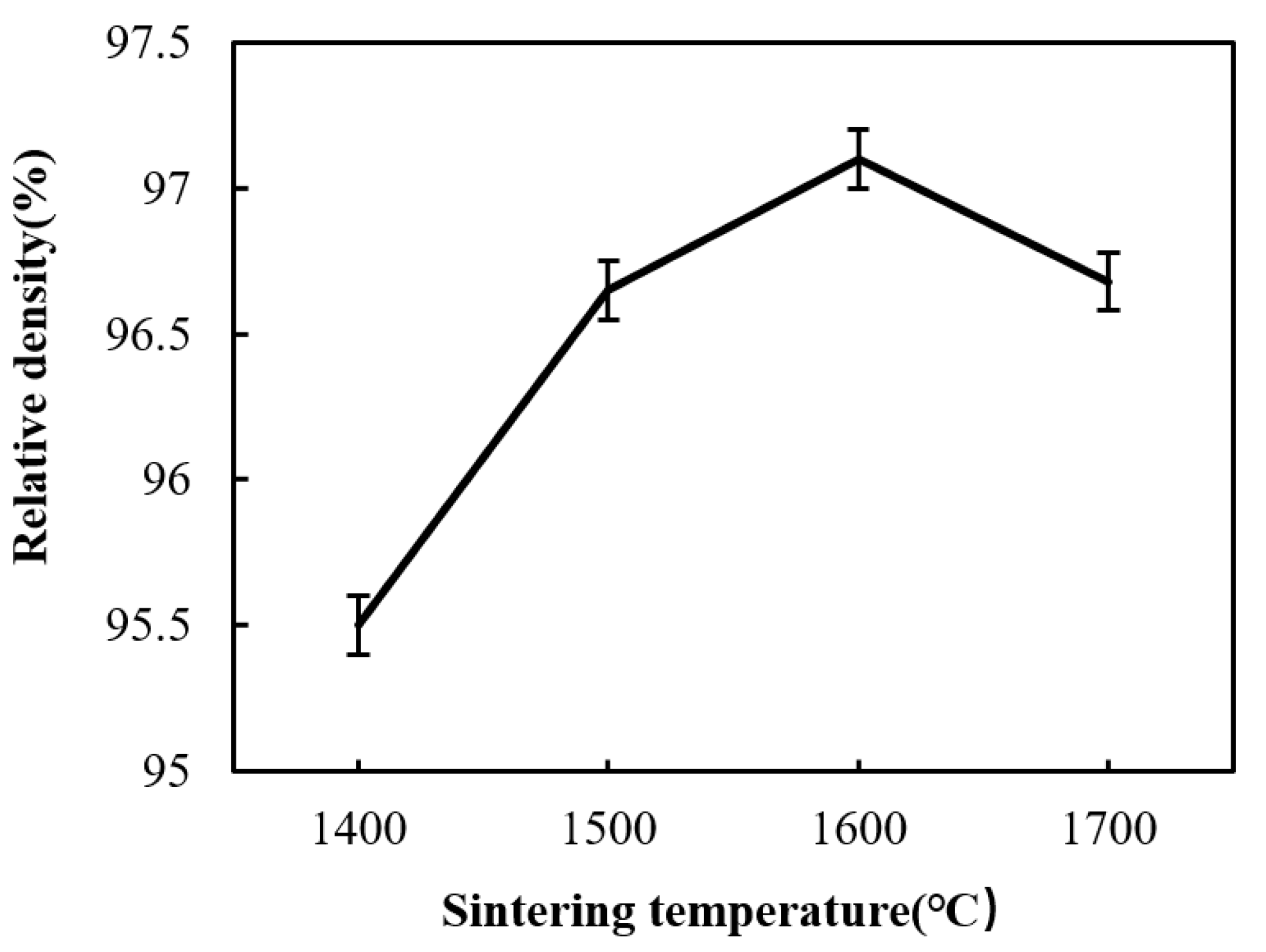
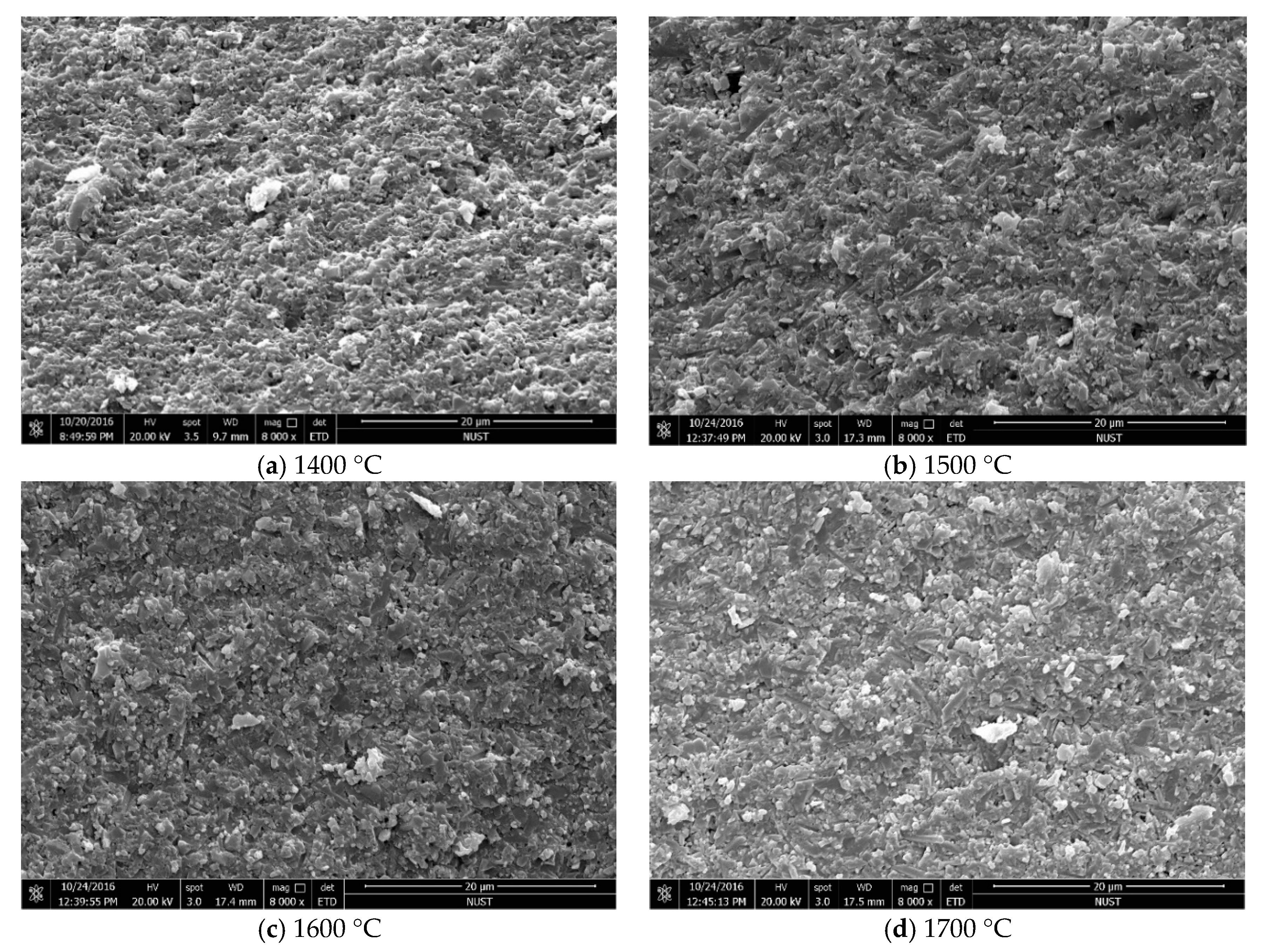
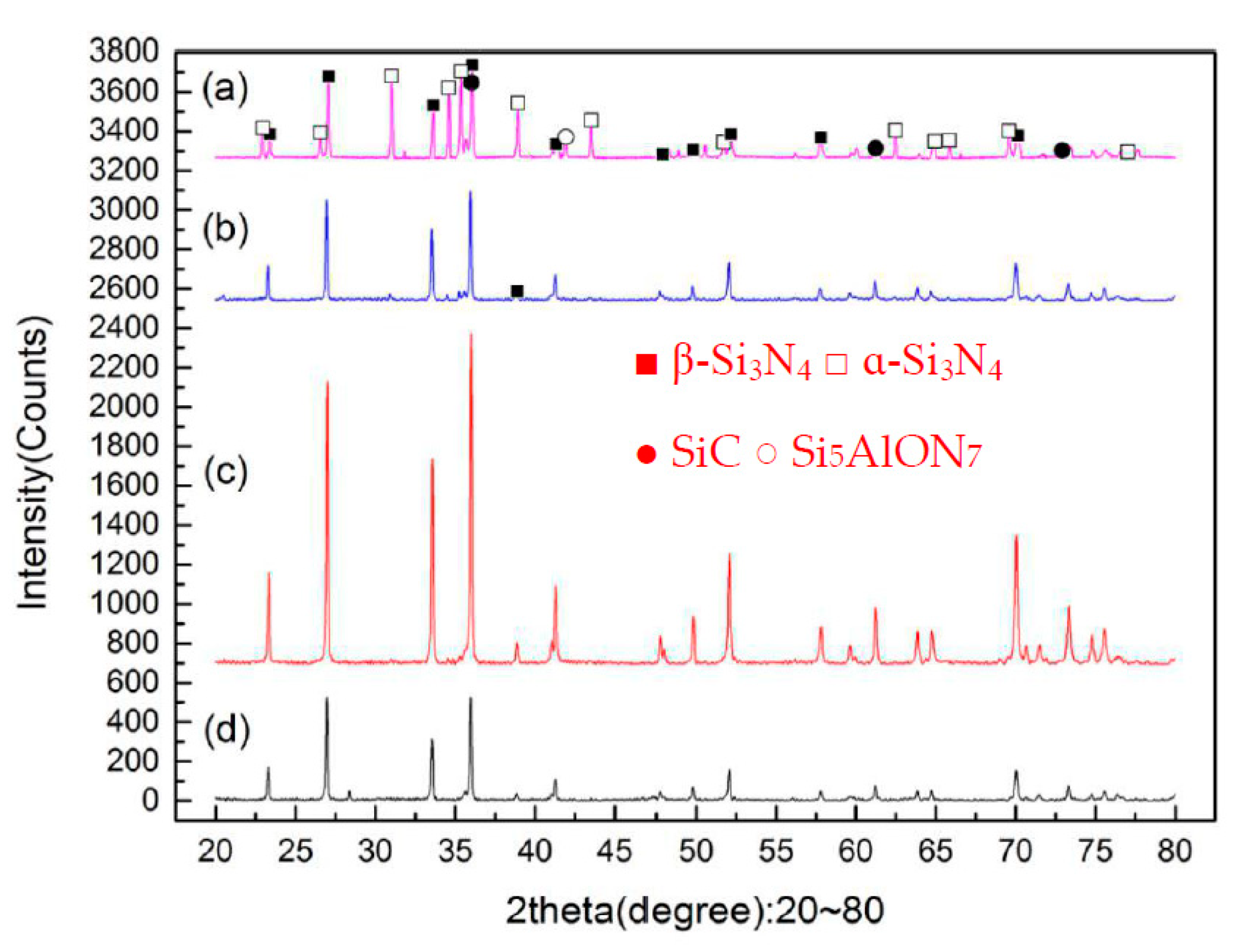
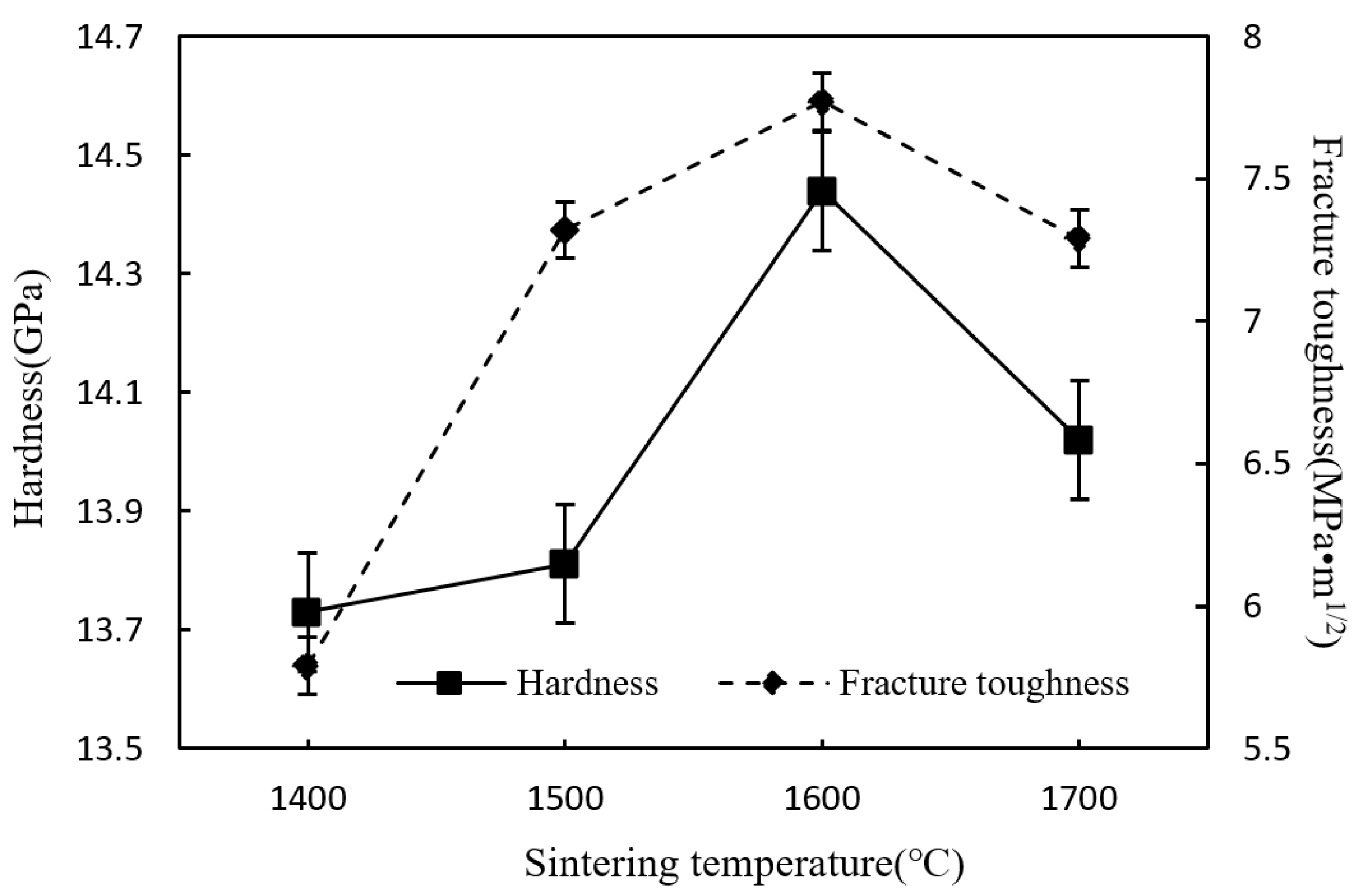
3.1. Effect of Sintering Temperature
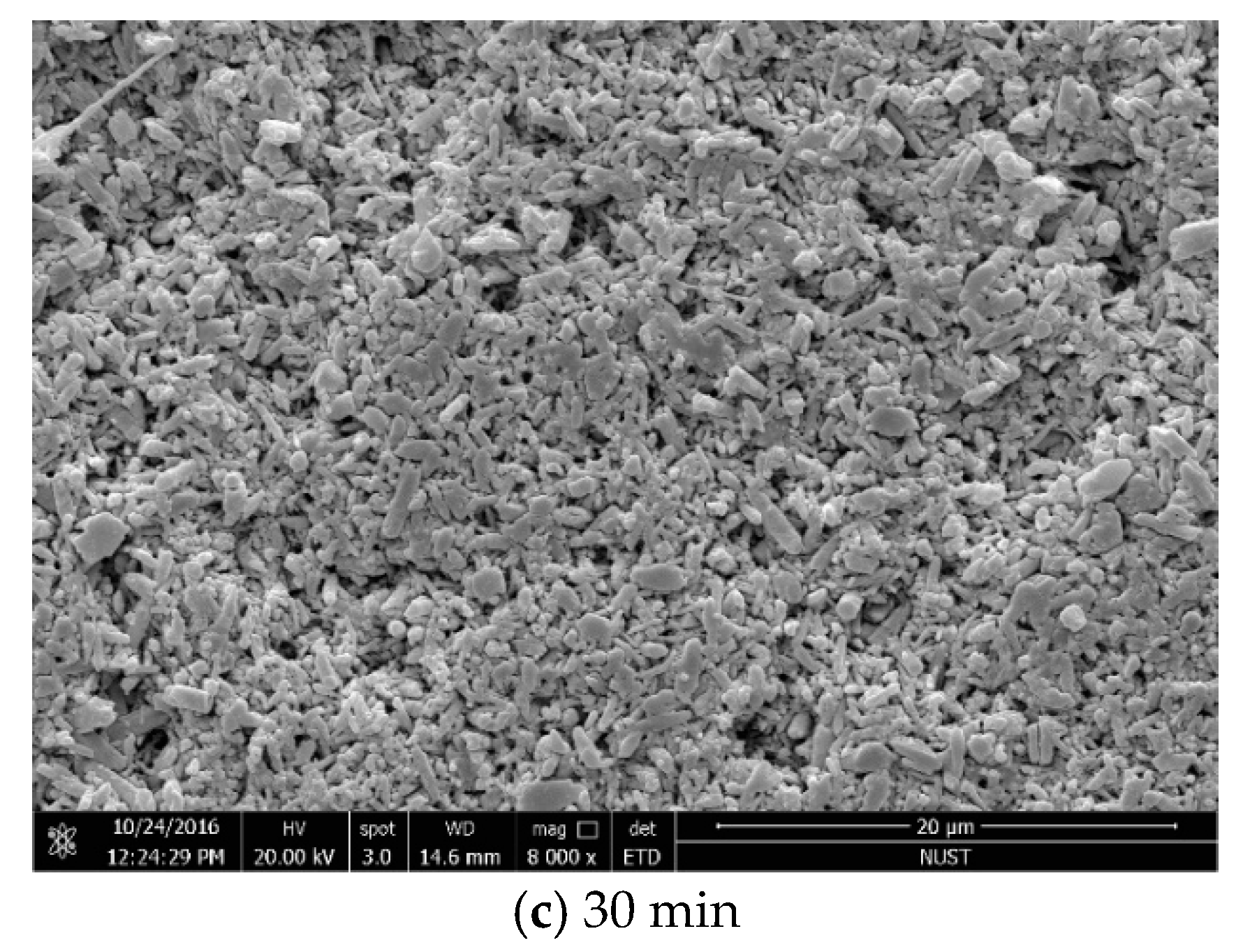
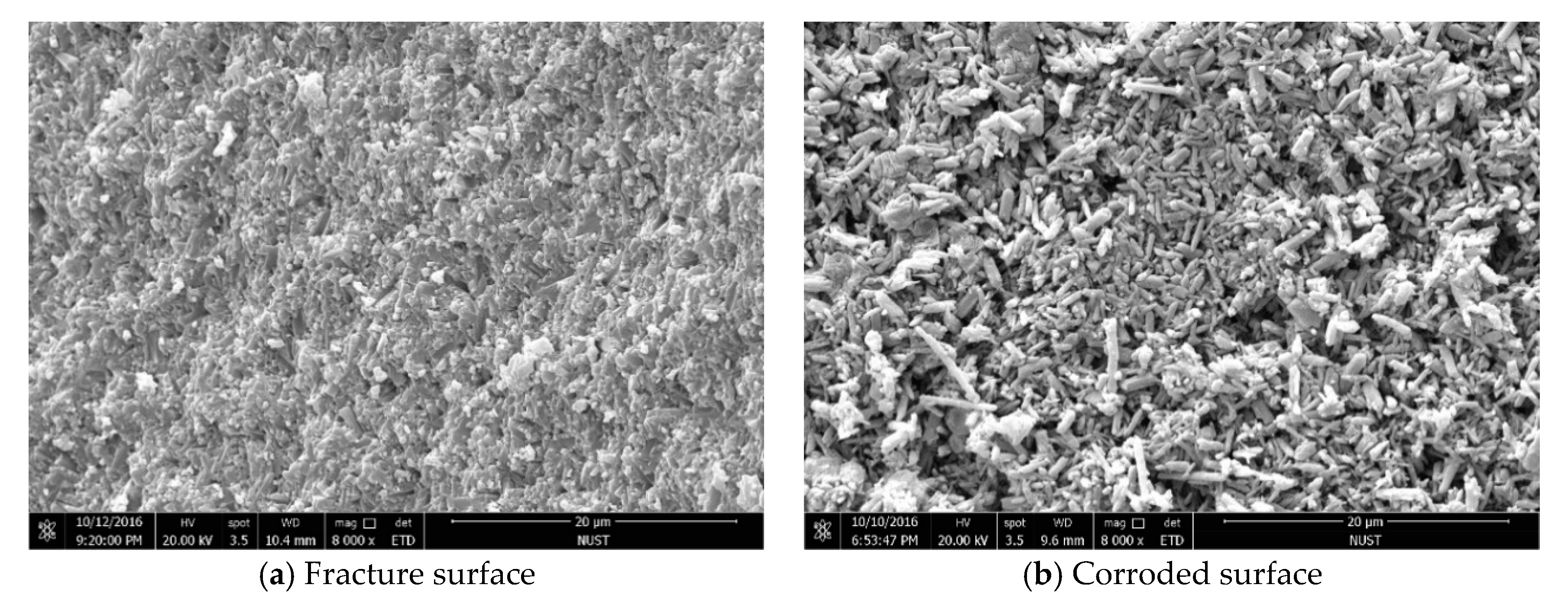
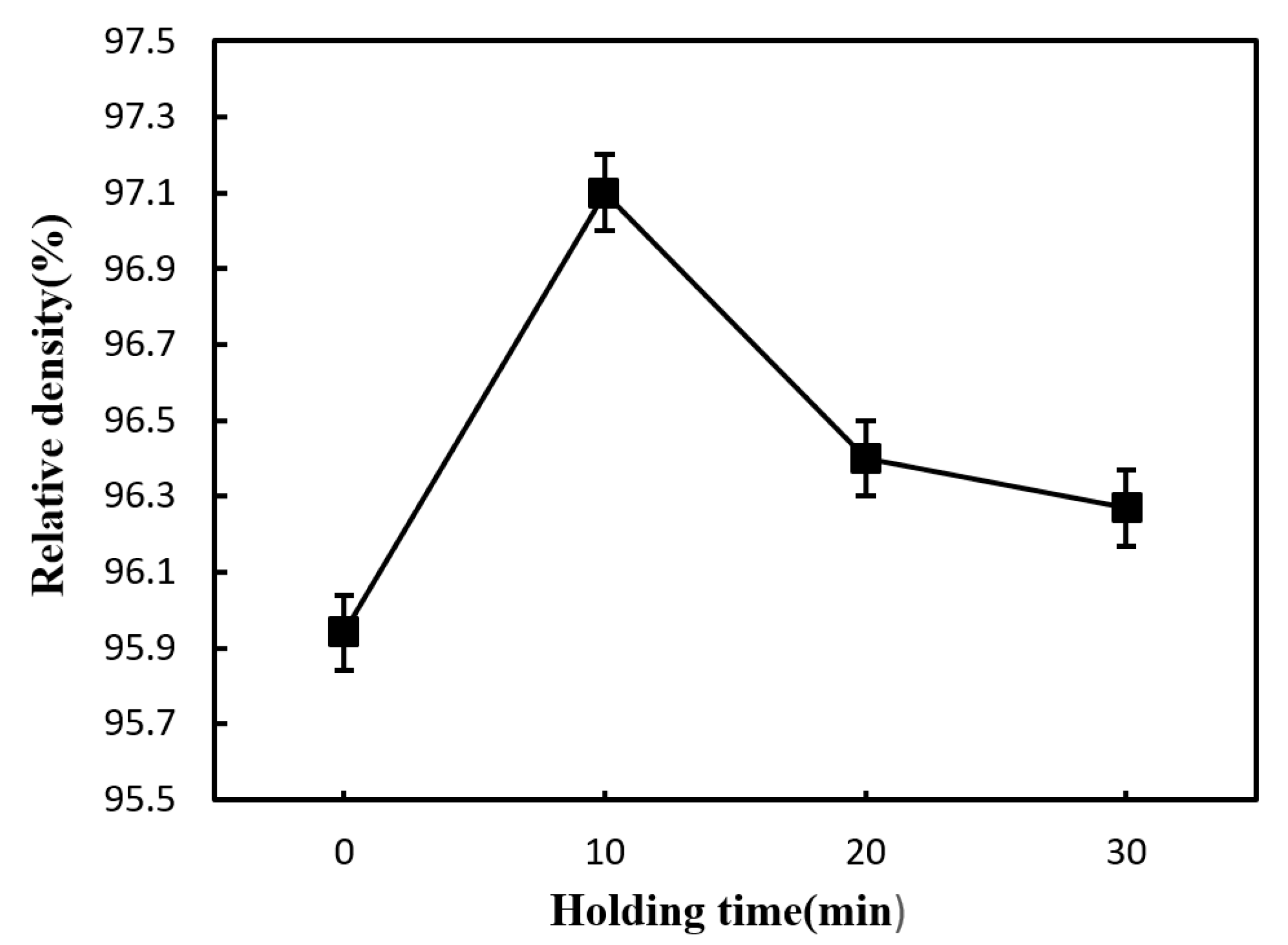
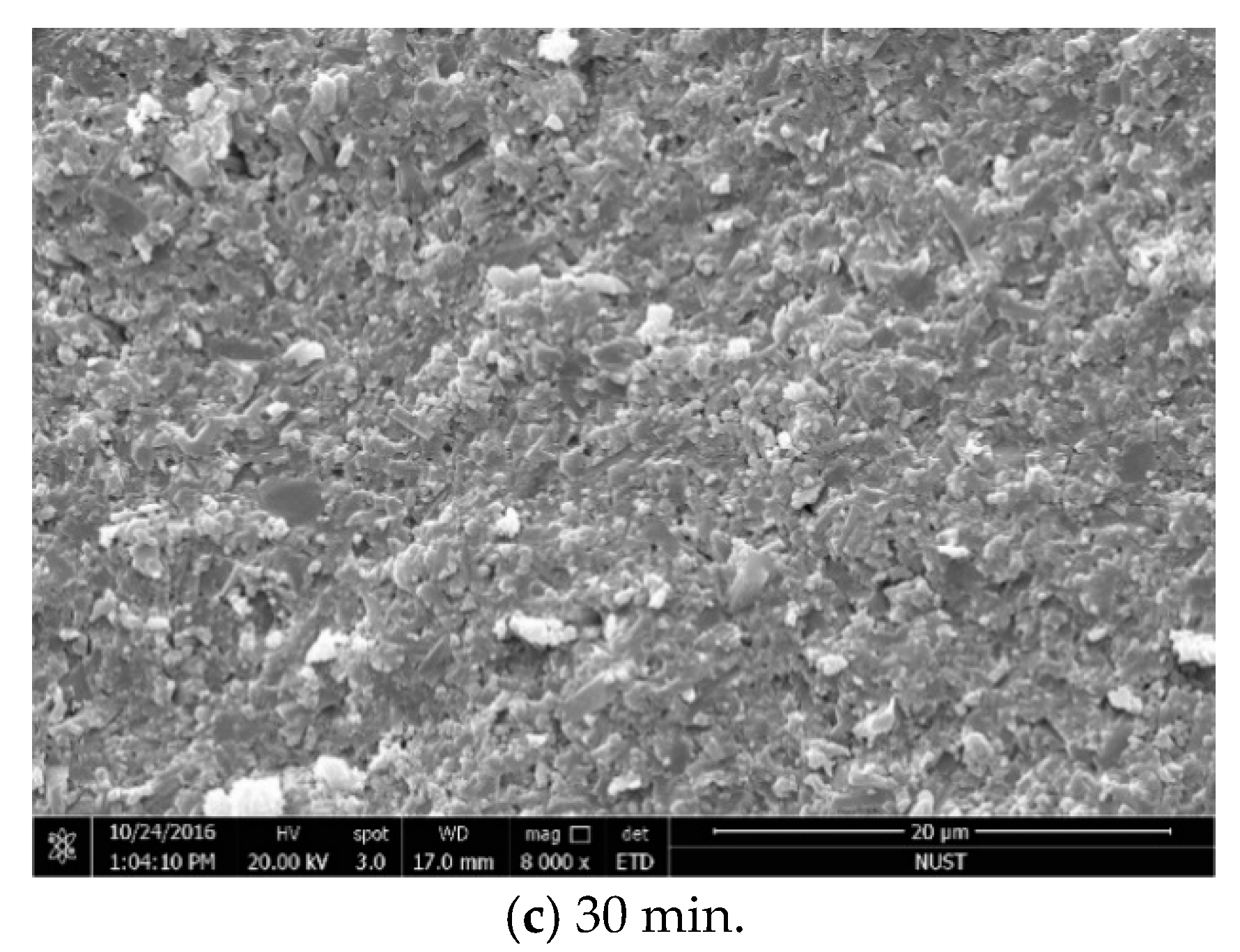
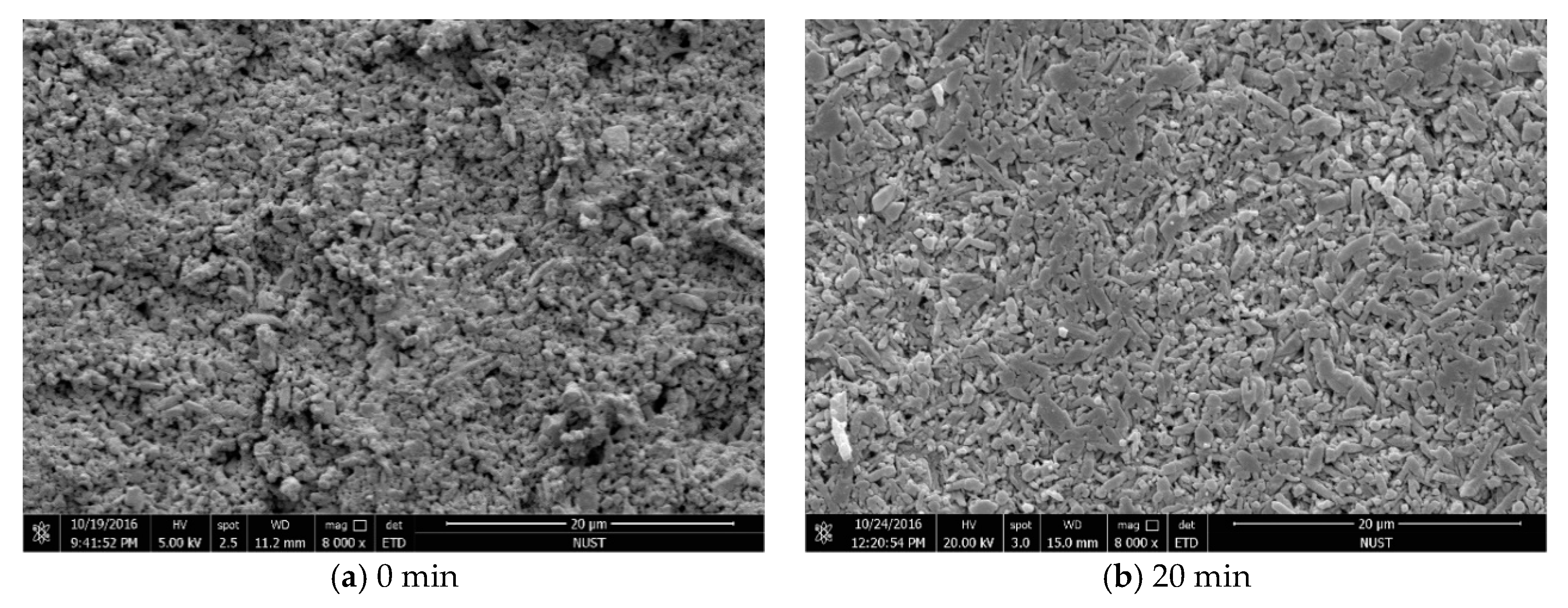
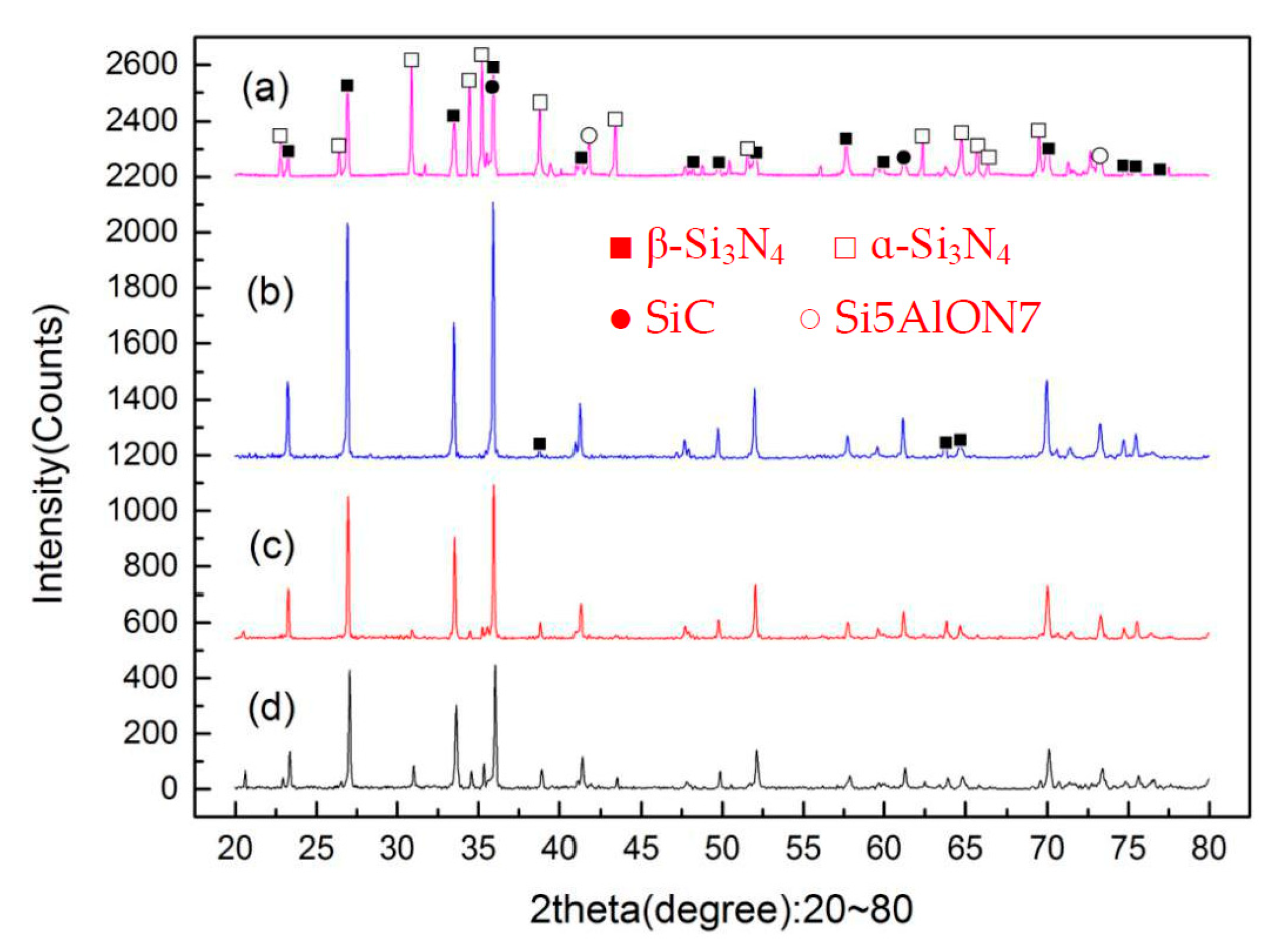
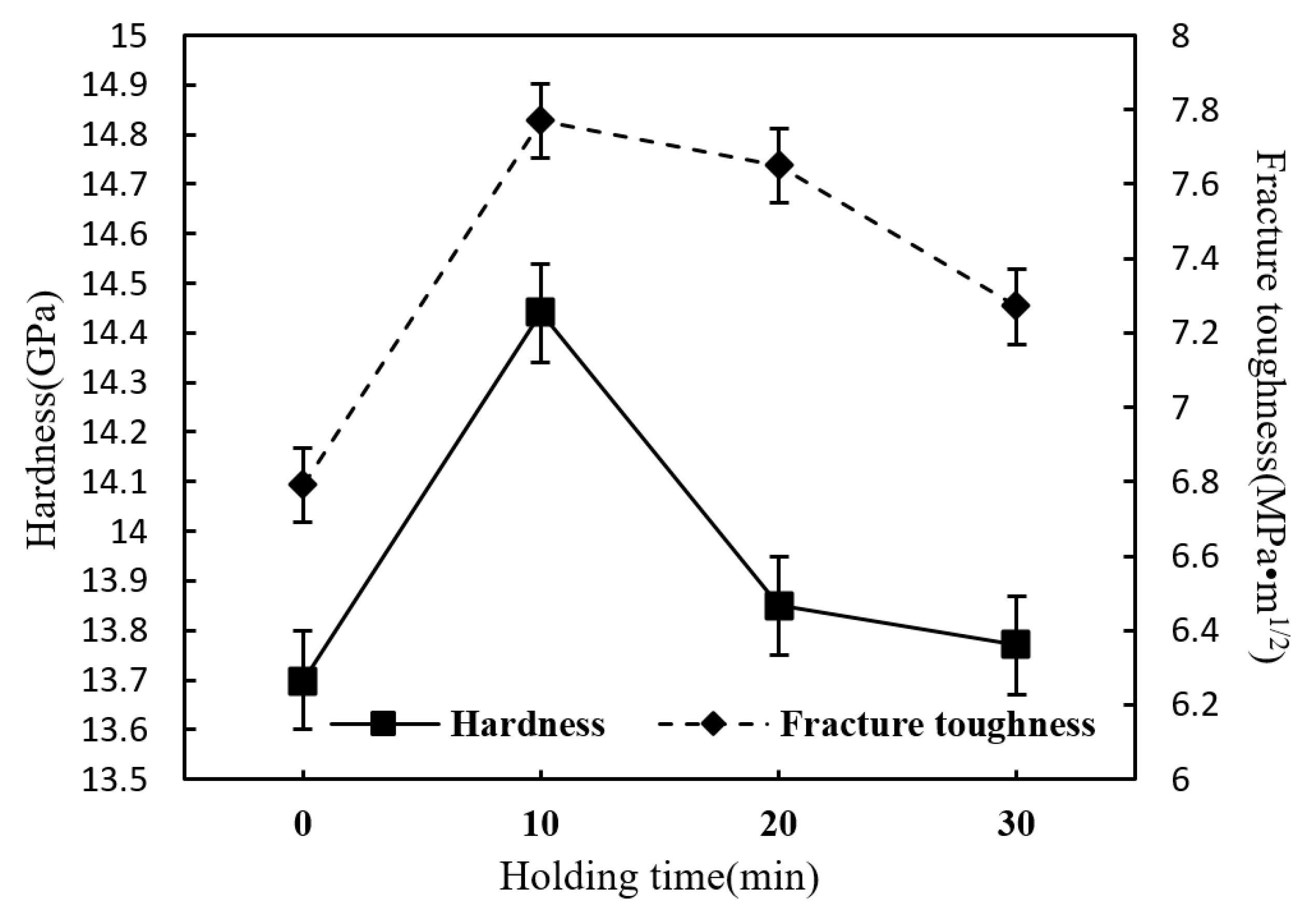
3.2. Influence of Holding Time on the Properties of Si3N4/n-SiC Ceramics
4. Conclusions
- A certain sintering temperature around 1600 °C is necessary for the densification and β-Si3N4 phase formation of the Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics. Held at a temperature below 1500 °C, the Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics cannot be completely sintered. However, a higher temperature over 1700 °C, can cause the decomposition of Si3N4 or Si3N4’s reacting with sintering aids (Al2O3 and Y2O3), which will lead to the decrease of density, Vickers hardness, and fracture toughness of the Si3N4/n-SiC.
- The density, hardness, and fracture toughness will all gradually degrade if the Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics are sintered with microwave exceeding 10 min. Although the long holding time makes some β-Si3N4 grains grow larger, it also causes the uneven size of the β-Si3N4 grain, and pores appear between the big grains at the same time. Accordingly, it can be concluded that the microwave sintered Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics should not be held for too long. In this paper, the optimum holding time of microwave sintered Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics is presented to be 10 min at 1600 °C.
- The microwave sintered Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics have the best mechanical performances at a sintering temperature of 1600 °C for 10 min, with the density being 97.1%, the Vickers hardness being 14.44 GPa, and the fracture toughness reaching 7.77 MPa·m1/2, which increases by 2.8%, 7.0%, and 13.1%, respectively, when compared with the microwave sintered Si3N4 ceramics (90 wt% Si3N4 + 5 wt% Al2O3 + 5 wt% Y2O3).
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riley, F.L. Silicon nitride and related materials. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranzo, P.; González-Julián, J.; Osendi, M.I.; Belmonte, M. Enhanced particle rearrangement during liquid phase spark plasma sintering of silicon nitride-based ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.W.; Yin, Z.B.; Yuan, J.T.; Wang, Z.H.; Fang, Y.H. Effects of sintering additives on mechanical properties and microstructure of Si3N4 ceramics by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.W.; Yin, Z.B.; Yuan, J.T.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, Y. Preparation and characterization of Si3N4-based composite ceramic tool materials by microwave sintering. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16248–16257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.M.; Wu, L.X.; Ma, T.; Gu, S.X.; You, Y.; Lin, H.T.; Wu, S.H.; Zhang, G.J. Chemical reactivity of hot-pressed Si3N4-ZrB2 ceramics at 1500–1700 °C. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, H.; Hyuga, H.; Yoshizawa, Y.I.; Hirao, K.; Ohji, T. Correlation of wear behavior and indentation fracture resistance in silicon nitride ceramics hot-pressed with alumina and yttria. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapaszto, O.; Kun, P.; Weber, F.; Gergely, G.; Balazsi, K.; Pfeifer, J.; Arató, P.; Kidari, A.; Hampshire, S.; Balázsi, C. Silicon nitride based nanocomposites produced by two different sintering methods. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 3457–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Jiang, C.F.; Guo, W. Effect of CeO2 on low temperature pressureless sintering of porous Si3N4 ceramics. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alem, A.; Pugh, M.D.; Drew, R.A. Reaction bonded silicon nitride foams: The influence of iron disilicide on microstructure and mechanical strength. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 4966–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logesh, G.; Lodhe, M.; Balasubramanian, M. Effect of temperature and gaseous medium on the evolved microstructures of carbon fiber reinforced reaction bonded silicon nitride composites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6110–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajelakzay, M.; Bakhshi, S.R.; Borhani, G.H.; Ramazani, M. Synthesis and spark plasma sintering of the α-Si3N4 nanopowder. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14867–14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.H.; Li, X.G.; Liang, M.; Liang, Z.H.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.L. Spark plasma sintered high hardness β-Si3N4 composites with MgSiN2 as additives. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Yin, Z.B.; Liu, K.; Yuan, J.T. Investigation on mechanical properties and microstructure of silicon nitride ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, D.K. Effect of microwave heating on densification and α→β phase transformation of silicon nitride. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockalingam, S.; Earl, D.A. Mechanical properties of 2.45 GHz microwave sintered Si3N4–Y2O3–MgO–ZrO2 system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.I.; Valecillos, M.; Hirao, K. Densification behavior in microwave-sintered silicon nitride at 28 GHz. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 2424–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.I.; Valecillos, M.C.; Hirao, K.; Yamauchi, Y. Grain growth in microwave sintered Si3N4 ceramics sintered from different starting powders. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, W.B.; Zhou, W.; Long, L.; Deng, L.; Xiao, P.; Li, Y. Carbon fiber/Si3N4 composites with SiC nanofiber interphase for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 12328–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.; Seo, D.; Kim, S.; Hong, K.; Guahk, K.H.; Lee, K.S. Properties of silicon nitride for aluminum melts prepared by nitrided pressureless sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Kan, Y.; Wang, P. Silicon nitride/boron nitride ceramic composites fabricated by reactive pressureless sintering. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, F.; Qin, W.; Pan, H. Fabrication and mechanical properties of Si3N4/(W, Ti)C/Co graded nano-composite ceramic tool materials. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 3381–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yao, D.; Xia, Y.; Zuo, K.; Zeng, Y. Fabrication and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced reaction-bonded silicon nitride based ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 4739–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, F.; Hu, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B. A new way of fabricating Si3N4 ceramics by aqueous tape casting and gas pressure sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiegs, T.N.; Kiggans, J.O.; Kimrey, H.D. Microwave Sintering of Silicon Nitride. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 1991, 12, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Petzow, G. Grain growth studies of silicon nitride dispersed in an oxynitride glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.G.; Charles, E.A. Fracture toughness determinations by indentation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1976, 59, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzara, C.P.; Messier, D.R. Determination of Phase Content of Si3N4 by X-ray Diffraction Analysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1977, 56, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Suri, J.; Shaw, L.L. Liquid phase sintering of Si3N4/SiC nanopowders derived from silica fume. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 9179–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Ge, Q.M.; Sun, X.W.; Huang, L.P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of silicon nitride ceramics prepared by pressureless sintering with MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 as sintering additive. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockalingam, S.; Earl, D.A. Microwave sintering of Si3N4 with LiYO2 and ZrO2 as sintering additives. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1559–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Test No. | Compositions/wt% | Temperature/°C | Holding Time/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85% Si3N4 + 5% SiC + 5% Al2O3 + 5% Y2O3 | 1400, 1500, 1600, 1700 | 10 |
| 2 | 85% Si3N4 + 5% SiC + 5% Al2O3 + 5% Y2O3 | 1600 | 0,10,20,30 |
| 3 | 90% Si3N4 + 5% Al2O3 + 5% Y2O3 | 1600 | 10 |
| Number | n-SiC Content/wt% | Relative Densty/% | Hardness/GPa | Fracture Toughness/MPa·m1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 94.5 | 13.50 | 6.87 |
| 2 | 5 | 97.1 | 14.44 | 7.77 |
| Additives | Sintering Method | Sintering Temperature/°C | Holding Time/min | Relative Density/% | Hardness/GPa | Fracture Toughness/MPa·m1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% Y2O3 + 5 wt% MgO + 2 wt% Al2O3 [3] | Microwave | 1700 | 10 | 98.52 | 14.92 | 6.44 |
| 3 wt% MgO + 1.5 wt% Al2O3 + 3.5 wt% SiO2 [29] | Pressureless | 1780 | 180 | 99.70 | 14.20 | 6.40 |
| 5 wt% MgSiN2 + 3 wt% Y2O3 + 1 wt% CeO2 [13] | Spark plasma | 1650 | 6 | 99.40 | 16.53 | 6.89 |
| 10 wt% LiYO2 + 5 wt% ZrO2 [30] | Microwave | 1600 | 15 | 93.00 | 13.00 | 6.10 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, T.; Yuan, J. Effects of Microwave Sintering Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics. Materials 2019, 12, 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233837
Qiao L, Wang Z, Lu T, Yuan J. Effects of Microwave Sintering Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics. Materials. 2019; 12(23):3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233837
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Li, Zhenhua Wang, Taiyi Lu, and Juntang Yuan. 2019. "Effects of Microwave Sintering Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics" Materials 12, no. 23: 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233837
APA StyleQiao, L., Wang, Z., Lu, T., & Yuan, J. (2019). Effects of Microwave Sintering Temperature and Holding Time on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Si3N4/n-SiC ceramics. Materials, 12(23), 3837. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233837





