Quantitative Description of External Force Induced Phase Transformation in Silicon–Manganese (Si–Mn) Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation of The TRIP Stress–Strain Curves
3. Experimental Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
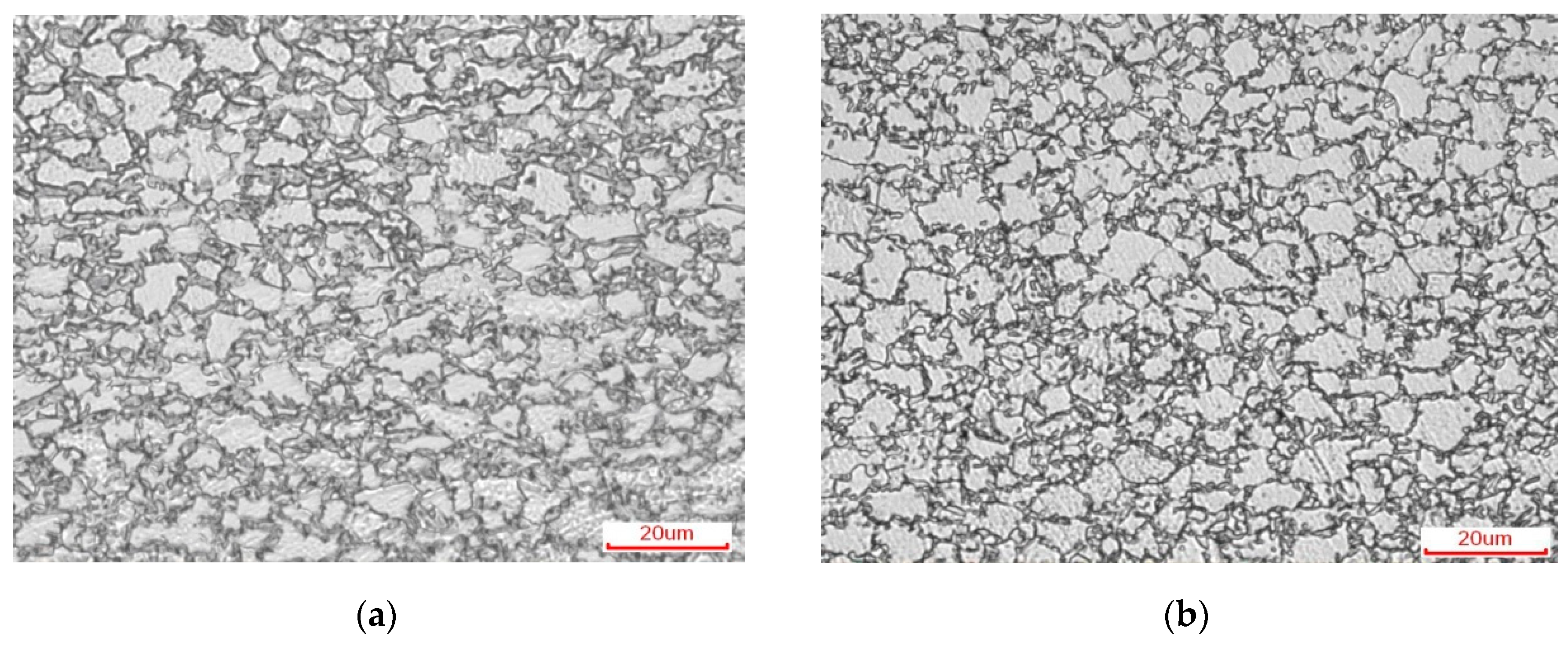
4.1. Microstructure
4.2. Calculation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guarnieri, G.; Kanter, J. Some characteristics of the metastable austenite of 4-percent to 6-percent chromium +1/2-percent molybdenum cast steel. Trans. ASM 1948, 40, 1147–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, R.; Cohen, M. Austenite transformation above and within the martensite range. Trans. AIME 1948, 176, 384–387. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, M.; Thompson, F. The acceleration of the rate of isothermal transformation of austenite. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1949, 162, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, T. The formation of bainite in an en-21 steel. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 175, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zackay, V.F.; Parker, E.R.; Fahr, D.; Busch, R. The enhancement of ductility in high-strength steels. Trans. ASM 1967, 60, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zrník, J.; Stejskal, O.; Nový, Z.; Hornak, P.; Fujda, M. Structure dependence of the TRIP phenomenon in Si–Mn bulk steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Di, W.; Lv, H.-s.; Fang, S.-r. Continuous cooling transformation behaviour of C-Si-Mn TRIP steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2007, 14, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Jha, G.; Gope, N.; Singh, S. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of cold rolled C–Mn–Si TRIP-aided steel. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-y.; Zhang, Z.-c.; Zhu, F.-x.; Li, Y.-m.; Manabe, K.-i. Effect of cooling method on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled C-Si-Mn TRIP steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of Warm Deformation on Mechanical Properties of TRIP Aided Fe-C-Mn-Si Multiphase Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.I.; Tanino, H.; Kobayashi, J. Warm Ductility of 0.2% C–1.5% Si–5% Mn TRIP-aided Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Melero, E.; Dijk, N.H.V.; Zhao, L.; Sietsma, J.; Offerman, S.E.; Wright, J.P.; Zwaag, S.V.D. The effect of aluminium and phosphorus on the stability of individual austenite grains in TRIP steels. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Han, M.; Wu, C.L.; Yin, Y.Q.; Zhu, K.; Shen, R.H.; Chen, J.H. A high-performance TRIP steel enhanced by ultrafine grains and hardening precipitates. Mater. Des. 2017, 127, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, H.D.; Van, C.N.; Ngoc, T.T.; Manh, T.S. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of a CMnSi TRIP steel using design of experiment. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 24664–24674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloui, M.; Militzer, M. Phase field modeling of the simultaneous formation of bainite and ferrite in TRIP steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 144, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Chao, Q.; Rolfe, B.; Beladi, H. One-step quenching and partitioning treatment of a tailor welded blank of boron and TRIP steels for automotive applications. Mater. Des. 2019, 174, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wibowo, M.K.; Hermans, M.J.M.; Bohemen, S.M.C.V.; Sietsma, J. Retention of austenite in the welded microstructure of a 0.16C-1.6Mn-1.5Si (wt.%) TRIP steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 5286–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, B.L.; Jimenez-Melero, E.; Atzema, E.H.; Krugla, M.; Azeem, M.A.; Rowley, D.; Lee, P.D. Metastable austenite driven work-hardening behaviour in a TRIP-assisted dual phase steel. Int. J. Plast. 2017, 88, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.P.; Saleh, A.A.; Marceau, R.K.W.; Taylor, A.S.; Stanford, N.E.; Kostryzhev, A.G.; Pereloma, E.V. Site-specific atomic-scale characterisation of retained austenite in a strip cast TRIP steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 134, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, P.; Kermanidis, A.; Krizan, D. Fatigue behavior and retained austenite transformation of Al-containing TRIP steels. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 91, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Tomota, Y.; Arakaki, Y.; Harjo, S.; Sueyoshi, H. Evaluation of austenite volume fraction in TRIP steel sheets using neutron diffraction. Mater. Charact. 2017, 127, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tang, Z.; Ding, H.; Misra, R. The significant impact of phase fraction and austenite stability on the mechanical properties of a low-alloyed TRIP-aided steel: An insight into experimental analysis and predictions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlade, A.; Bouaziz, O.; Furnémont, Q. A physically based model for TRIP-aided carbon steels behaviour. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 356, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquerel, J.; Verbeken, K.; Decooman, B.C. Microstructure-based model for the static mechanical behaviour of multiphase steels. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Liu, W.N.; Sun, X.; Khaleel, M.A. Microstructure-based constitutive modeling of TRIP steel: Prediction of ductility and failure modes under different loading conditions. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2592–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollomon, J.H.; Member, J. Tensile Deformation. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1945, 162, 268–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.; Tyson, W.R. Tensile properties of fibre-reinforced metals: Copper/tungsten and copper/molybdenum. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1965, 13, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.G. Influence of martensite composition and content on the properties of dual phase steels. Metall. Trans. A 1978, 9, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y. Investigation on Transformation-Induced Plasticity Behavior in Complex Strain State for TRIP Steels and Its Application to Autobody Panels. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.T. Physical and Mechanical Metallurgy of Dual-Phase Steel; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Samek, L.; De Moor, E.; Penning, J.; De Cooman, B.C. Influence of alloying elements on the kinetics of strain-induced martensitic nucleation in low-alloy, multiphase high-strength steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomota, Y.; Umemoto, M.; Komatsubara, N.; Hiramatsu, A.; Nakajima, N.; Moriya, A.; Miyahara, M. Prediction of mechanical properties of multi-phase steels based on stress-strain curves. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, I.; Altuna, M.A. Work-hardening of ferrite and microstructure-based modelling of its mechanical behaviour under tension. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 4682–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.-M.; Gutiérrez, I. Unified Formulation to Predict the Tensile Curves of Steels with Different Microstructures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 426, 4525–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.I.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, K.T.; Chong, S.L.; Dong, H.S. Ultrafine grained ferrite–martensite dual phase steels fabricated via equal channel angular pressing: Microstructure and tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3125–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüper, T.; Endo, S.; Ishikawa, N.; Osawa, K. Effect of Volume Fraction of Constituent Phases on the Stress-Strain Relationship of Dual Phase Steels. ISIJ Int. 2007, 39, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Furnémont, Q.; Mertens, A.; Delannay, F. On the sources of work hardening in multiphase steels assisted by transformation-induced plasticity. Philos. Mag. A 2001, 81, 1789–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Furnémont, Q.; Pardoen, T.; Delannay, F. On the role of martensitic transformation on damage and cracking resistance in TRIP-assisted multiphase steels. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, P.; Cornet, X.; Harlet, Ph. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of a low-carbon, low-sillicon steel by formation of a multiphased microstructure containing retained austenite. Metall. Trans. A 1998, 29, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.G.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, T.H. Effects of volume fraction and stability of retained austenite on formability in a 0.1C-1.5Si-1.5Mn-0.5Cu TRIP-aided cold-rolled steel sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 371, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Usui, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Hashimoto, S. Effects of Volume Fraction and Stability of Retained Austenite on Ductility of TRIP-aided Dual-phase Steels. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X. X-ray Metallography; Mechanical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D. Fundamentals of Materials Science; Mechanical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.P.; He, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Fu, R.Y.; Huang, S. Research on mechanical stability of retained austenite in low-silicon, non-aluminum and medium-carbon TRIP steels. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2011, 32, 5. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.P.; He, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Ling, Y.T.; Lu, X.G. Thermodynamic calculation of Ms temperature for martensitic transformation in Fe-C-Mn-Si alloys. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2011, 32, 6. [Google Scholar]








| Steel | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | N | Heat Treatment Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformation of Induced Plasticity (TRIP) | 0.11 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 0.005 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.0035 | 1058 K × 3 min + 698 K × 3 min |
| Dual Process (DP) | 0.11 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.01 | 0.005 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.0035 | 1058 K × 3 min |
| C | Si | Mn | Vol (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite | 0.0075 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 60 |
| Austenite (Martensite) | 0.262 | 1.12 | 2.32 | 40 |
| C | Si | Mn | Vol (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrite | 0.0075 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 60 |
| Bainite | 0.0525 | 1.12 | 2.32 | 30 |
| Retained austenite | 0.95 | 1.12 | 2.32 | 10 |
| Martensite | 0.95 | 1.12 | 2.32 | – |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, W.; He, Y.; Li, L. Quantitative Description of External Force Induced Phase Transformation in Silicon–Manganese (Si–Mn) Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels. Materials 2019, 12, 3781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223781
He Z, Liu H, Zhu Z, Zheng W, He Y, Li L. Quantitative Description of External Force Induced Phase Transformation in Silicon–Manganese (Si–Mn) Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels. Materials. 2019; 12(22):3781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223781
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhongping, Huachu Liu, Zhenyu Zhu, Weisen Zheng, Yanlin He, and Lin Li. 2019. "Quantitative Description of External Force Induced Phase Transformation in Silicon–Manganese (Si–Mn) Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels" Materials 12, no. 22: 3781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223781
APA StyleHe, Z., Liu, H., Zhu, Z., Zheng, W., He, Y., & Li, L. (2019). Quantitative Description of External Force Induced Phase Transformation in Silicon–Manganese (Si–Mn) Transformation Induced Plasticity (TRIP) Steels. Materials, 12(22), 3781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223781





