Antibacterial Activity and Biodegradation of Cellulose Fiber Blends with Incorporated ZnO
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy
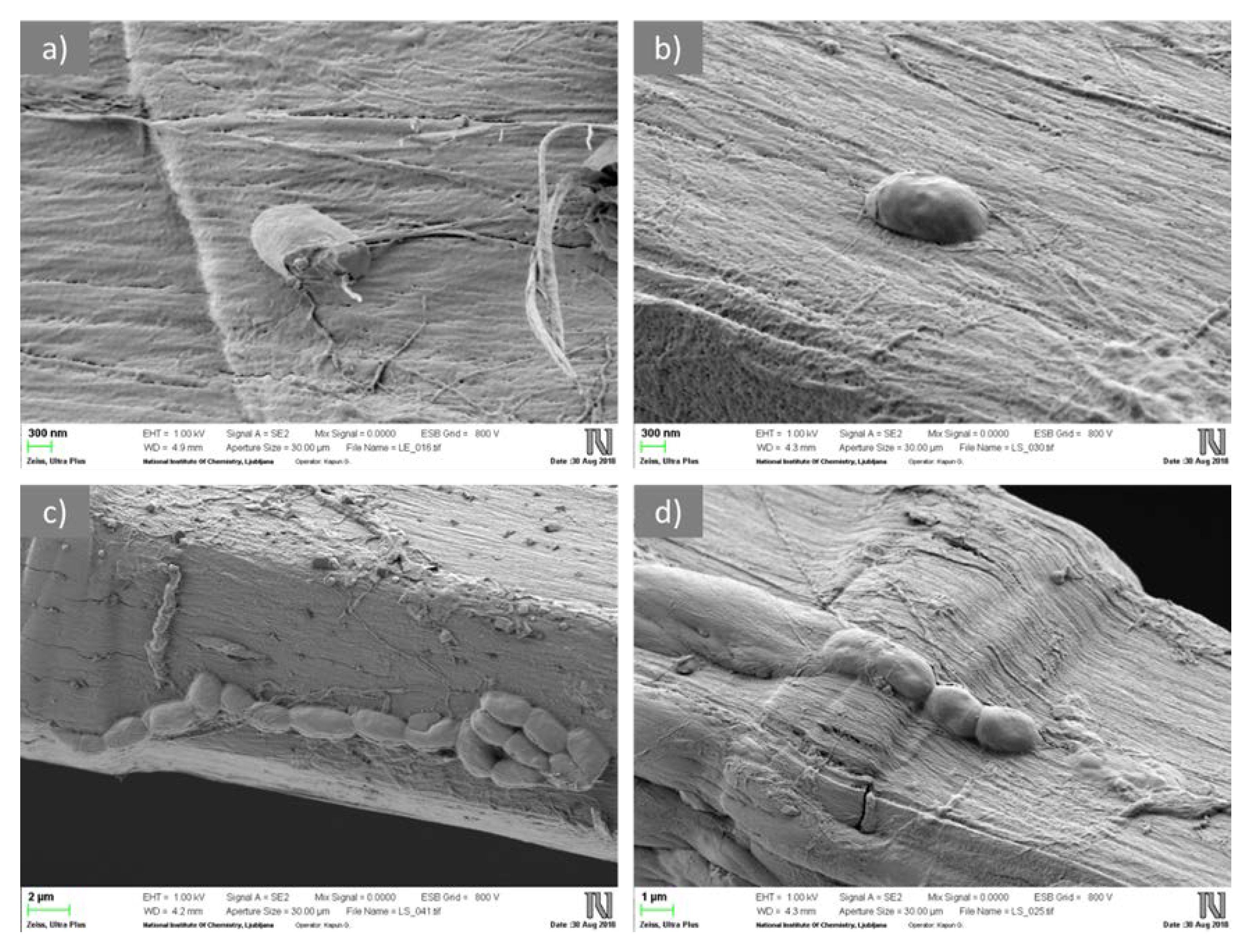
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
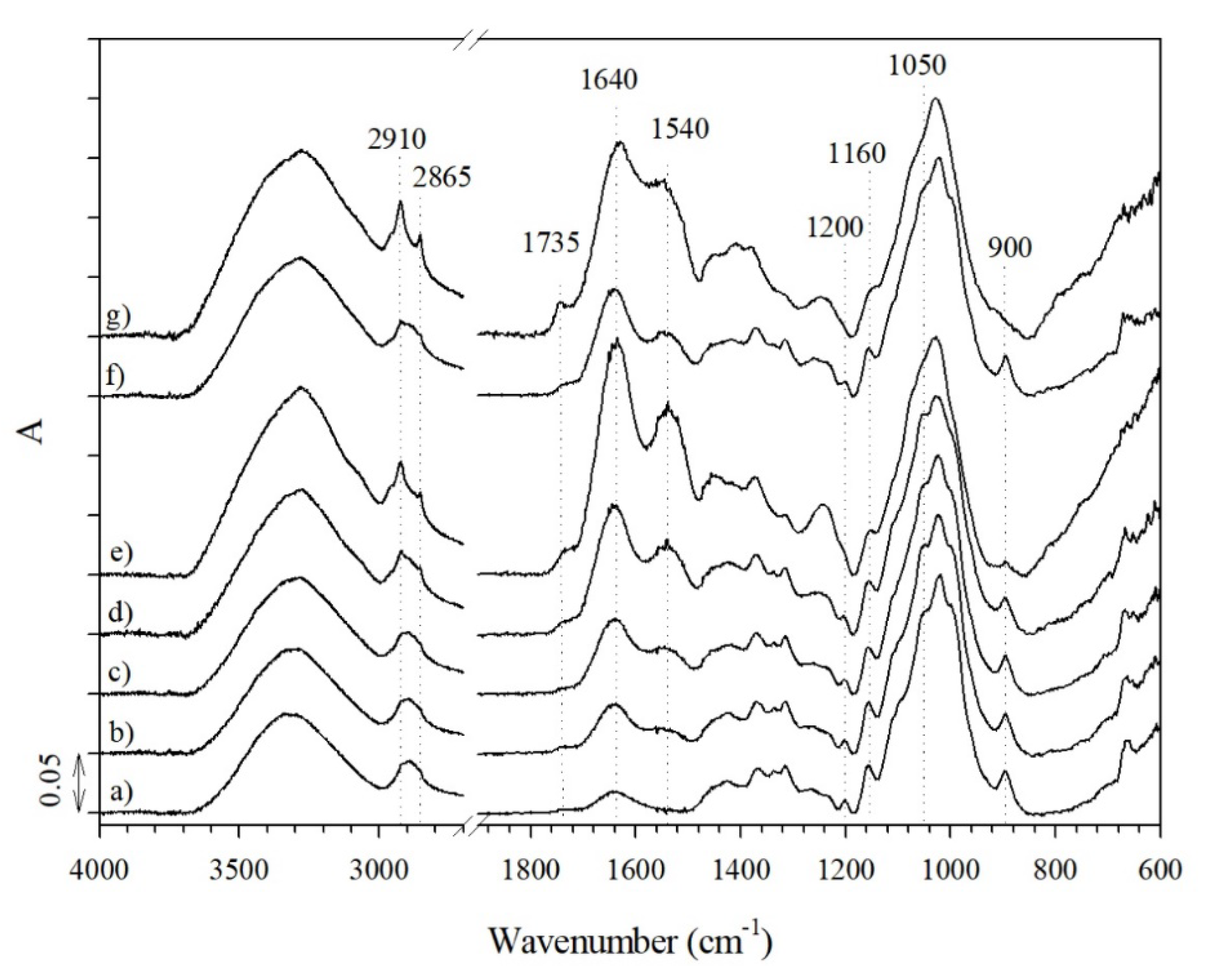
2.2.3. Fourier Transform-Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.2.4. Antibacterial Activity
2.2.5. Soil Burial Test
2.2.6. Soil Contamination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CLY Fibers
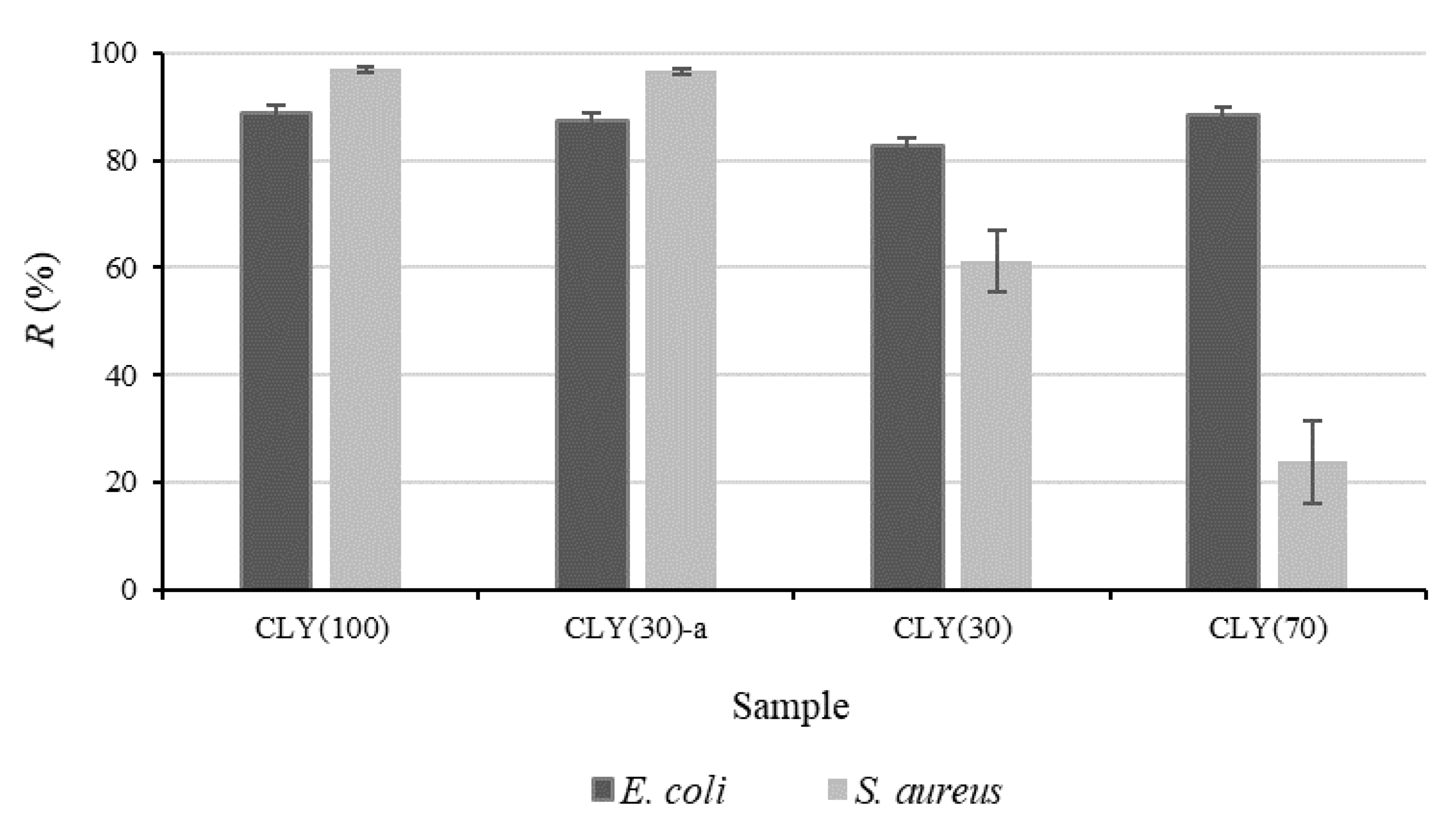
3.2. Antibacterial Activity
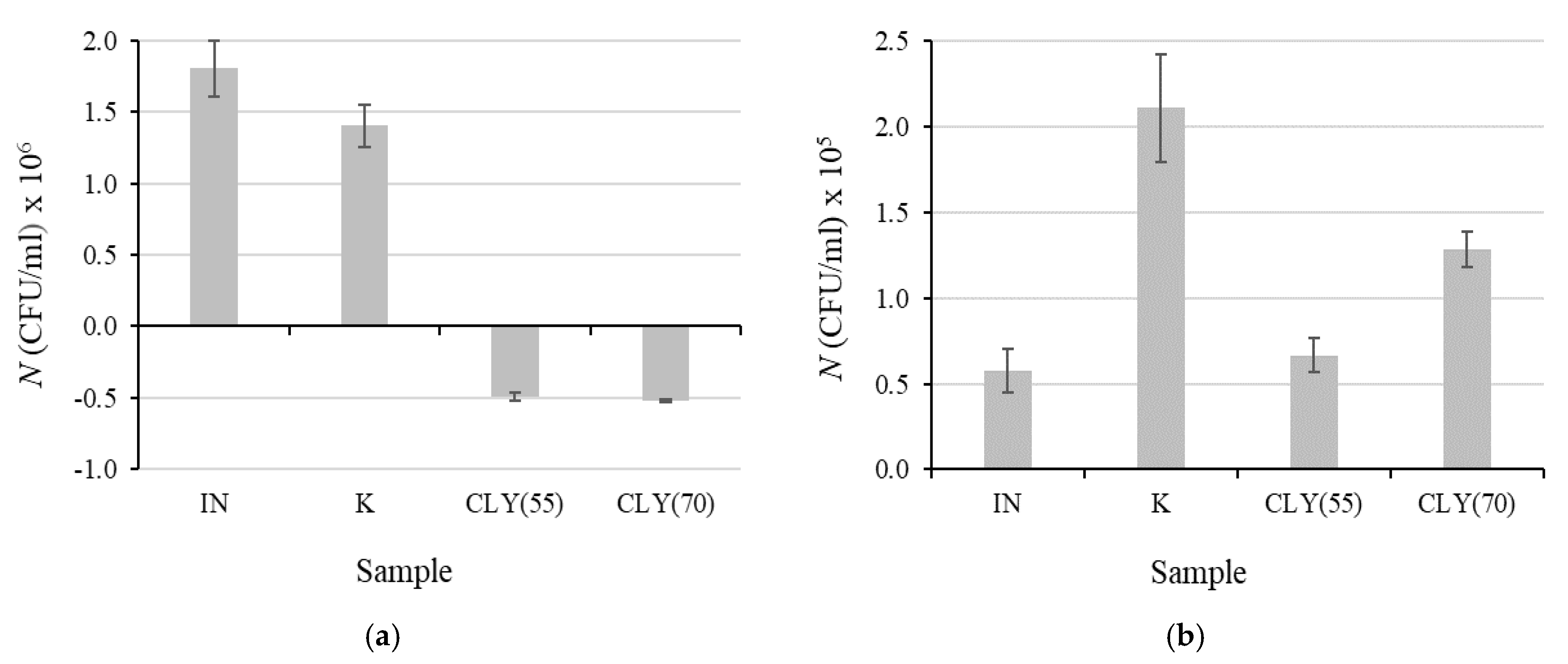
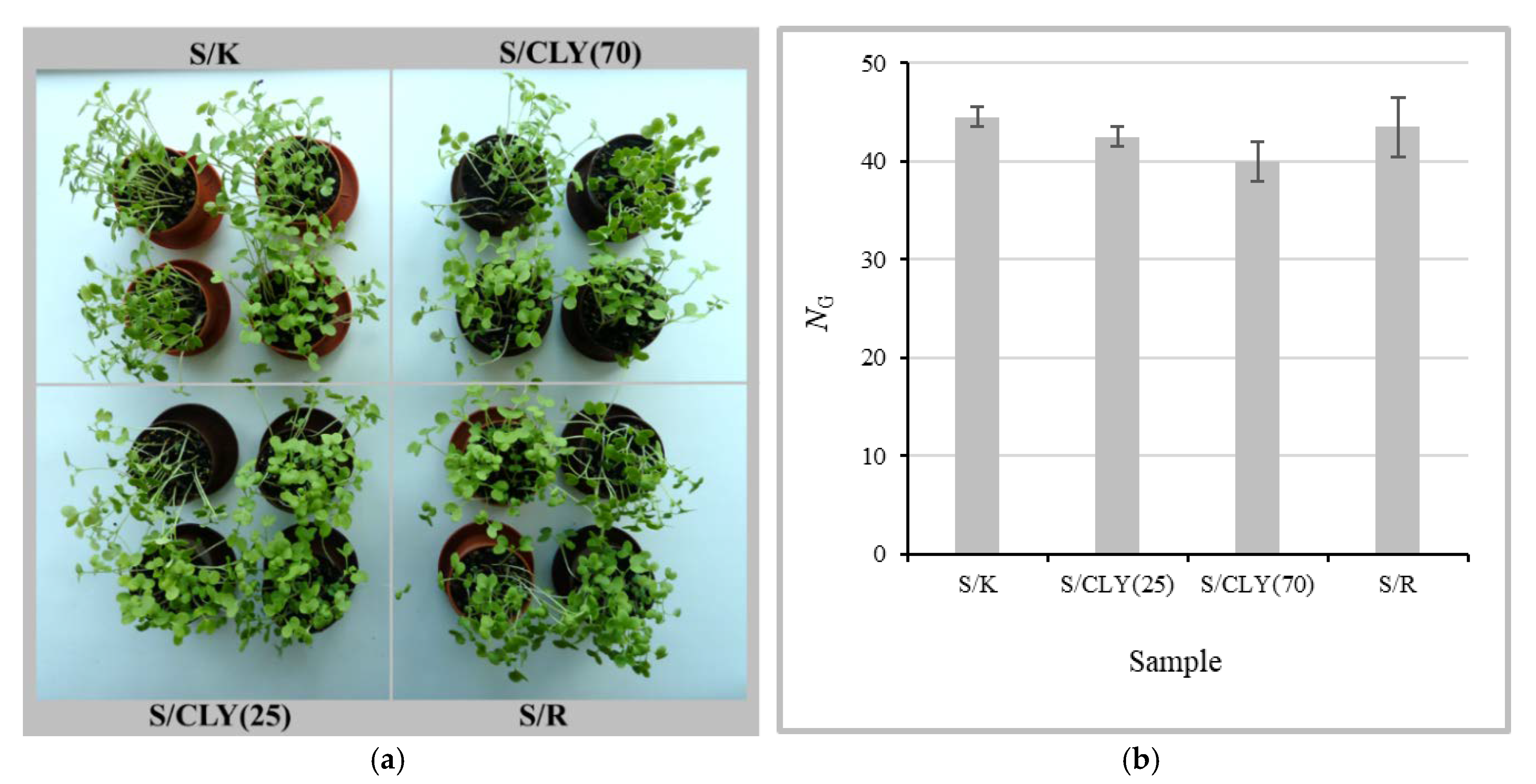
3.3. Biodegradation of Fiber Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szostak-Kotowa, J. Biodeterioration of textiles. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 53, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, T.L. Protection of Textiles from Biological Attack. In Functional Finishes, Part A, Handbook of Fibre Science and Technology; Lewin, M., Sello, S.B., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, INC.: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 367–426. ISBN 0-8247-1716-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J. Antimicrobial Finishes. In Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodgead Publishing Limited: Camridge, UK, 2004; pp. 165–174. ISBN 1-85573-905-4. [Google Scholar]
- Simončič, B.; Tomšič, B. Recent Concepts of Antimicrobial Textile Finishes. In Textile Finishing: Recent Developments and Future Trends; Mital, K.L., Bahners, T., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Part 1; pp. 3–68. ISBN 978-1-119-42676-9. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Kang, Y.K.; Im, S.S. Biodegradability of cellulose fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Functional responses of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to metal oxide nanoparticles in vitro. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.R.N.; Srividya, L. Evaluation of in vitro cytotoxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using human cell lines. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbič, A.; Šala, M.; Gorjanc, M. The influence of in situ synthesis parameters on the formation of ZnO nanoparticles and the UPF value of cotton fabric. Tekstilec 2018, 61, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Umar, A.; Kumar, G.; Nalwa, H.S. Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: A review. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3940–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Rahman, A.U.; Husen, A. Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Activity Against Microbes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Mishra, H.; Ekielski, A.; Talegaonkar, S.; Vaidya, B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, A.; Park, S.-H.; Shim, K.-D.; Kim, D.-J.; Jhee, K.-H.; Lee, H.-W.; Heo, C.-H.; Kim, H.-M.; Jang, E.-S. Antibacterial mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles under dark conditions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimniewska, M.; Goslinska-Kuzniarek, O. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Flax Fibres Against the Staphylococcus aureus Bacteria Strain. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 24, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L. Antimicrobial Properties of Flax Fibers in the Enzyme Retting Process. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 24, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Warner, P.; Wang, H. Antibacterial Properties of Hemp and Other Natural Fibre Plants: A Review. BioResources 2014, 9, 3642–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ASTM. ASTM E2149–01, Standard Test Method for Determining the Antimicrobial Activity of Immobilized Antimicrobial Agents under Dynamic Contact Conditions; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Klančnik, A.; Toplak, N.; Kovač, M.; Marquis, H.; Jeršek, B. Quantification of Listeria monocytogenes cells with digital PCR and their biofilm cells with real-time PCR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 118, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 11721-1:2001, Textiles—Determination of Resistance of Cellulose-Containing Textiles to Micro-Organisms—Soil Burial Test—Part 1: Assessment of Rot-Retardant Finishing; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 1172-1:2003, Textiles—Determination of the Resistance of Cellulose-Containing Textiles to Micro-Organisms—Soil Burial Test—Part 2: Identification of Long-Term Resistance of a Rot Retardant Finish; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, S.; Siva, P.; Balu, K.S.; Suriyaprabha, R.; Rajendran, V.; Maaza, M. Acalypha indica– mediated green synthesis of ZnO nanostructures under differential thermal treatment: Effect on textile coating, hydrophobicity, UV resistance, and antibacterial activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3184–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Salem, S.S.; Shaheen, T.I. In-Vitro cytotoxicity, antibacterial, and UV protection properties of the biosynthesized Zinc oxide nanoparticles for medical textile applications. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.A.R.; Gusatti, M.; Ternus, R.Z.; Fiori, M.A.; Riella, H.G. In Situ Growth of ZnO Nanostructures on Cotton Fabric by Solochemical Process for Antibacterial Purposes. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 9082191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedot, M.; Maliszewska, I.; Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Suchorska-Woźniak, P.; Lewińska, A.; Teterycz, H. The Relationship between the Mechanism of Zinc Oxide Crystallization and Its Antimicrobial Properties for the Surface Modification of Surgical Meshes. Materials 2017, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedot-Toboła, M.; Ciesielska, M.; Maliszewska, I.; Rac-Rumijowska, O.; Suchorska-Woźniak, P.; Teterycz, H.; Bryjak, M. Deposition of Zinc Oxide on Different Polymer Textiles and Their Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduraru, A.; Ghitulica, C.; Trusca, R.; Surdu, V.A.; Neacsu, I.A.; Holban, A.M.; Birca, A.C.; Iordache, F.; Vasile, B.S. Antimicrobial Wound Dressings as Potential Materials for Skin Tissue Regeneration. Materials 2019, 12, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.F.; Wei, Q.F. Microwave-Assisted Rapid Preparation of Nano-ZnO/Ag Composite Functionalized Polyester Nonwoven Membrane for Improving Its UV Shielding and Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Lyu, B.; Lyu, L.; Chen, S.; Ma, J. Construction of durable antibacterial and anti-mildew cotton fabric based on P(DMDAAC-AGE)/Ag/ZnO composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 204, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primc, G.; Tomšič, B.; Vesel, A.; Mozetič, M.; Ražić, S.E.; Gorjanc, M. Biodegradability of oxygen-plasma treated cellulose textile functionalized with ZnO nanoparticles as antibacterial treatment. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 324002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenčič, D.; Simončič, B.; Tomšič, B.; Orel, B. Biodegradation of silver functionalised cellulose fibres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomšič, B.; Simončič, B.; Orel, B.; Vilčnik, A.; Spreizer, H. Biodegradability of cellulose fabric modified by imidazolidinone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 347. [Google Scholar]



| Sample Code | wCLY (%) | wCV (%) | wLI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K | 0 | 70 | 30 |
| CLY(15) | 15 | 55 | 30 |
| CLY(20) | 20 | 50 | 30 |
| CLY(25) | 25 | 45 | 30 |
| CLY(30) | 30 | 40 | 30 |
| CLY(55) | 55 | 15 | 30 |
| CLY(70) | 70 | 0 | 30 |
| CLY(30)-a | 30 | 70 | 0 |
| CLY(100) | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| CV(100) | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| LI(100) | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Bacterium | N (CFU/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t = 0 h | t = 2 h | t = 24 h, before Ultrasound | t = 24 h, after Ultrasound | |
| E. coli | 6.58 × 105 | 2.30 × 106 | 7.75 × 107 | 7.29 × 107 |
| S. aureus | 2.63 × 105 | 3.32 × 105 | 3.90 × 104 | 1.96 × 107 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malis, D.; Jeršek, B.; Tomšič, B.; Štular, D.; Golja, B.; Kapun, G.; Simončič, B. Antibacterial Activity and Biodegradation of Cellulose Fiber Blends with Incorporated ZnO. Materials 2019, 12, 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203399
Malis D, Jeršek B, Tomšič B, Štular D, Golja B, Kapun G, Simončič B. Antibacterial Activity and Biodegradation of Cellulose Fiber Blends with Incorporated ZnO. Materials. 2019; 12(20):3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalis, Domen, Barbka Jeršek, Brigita Tomšič, Danaja Štular, Barbara Golja, Gregor Kapun, and Barbara Simončič. 2019. "Antibacterial Activity and Biodegradation of Cellulose Fiber Blends with Incorporated ZnO" Materials 12, no. 20: 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203399
APA StyleMalis, D., Jeršek, B., Tomšič, B., Štular, D., Golja, B., Kapun, G., & Simončič, B. (2019). Antibacterial Activity and Biodegradation of Cellulose Fiber Blends with Incorporated ZnO. Materials, 12(20), 3399. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203399









