Luminescent Properties of (004) Highly Oriented Cubic Zinc Blende ZnO Thin Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, K.S.; Chang, S.P. Effect of structure morphologies on hydrogen gas sensing by ZnO Nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2018, 230, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonker, R.K.; Sikarwar, S.; Sabhajeet, S.R.; Yadav, B.C. Spherical growth of nanostructures ZnO based optical sensing and photovoltaic application. Opt. Mater. 2018, 83, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.L.; Vanalakar, S.A.; Patil, P.S.; Kim, J.H. Fabrication of nanostructured ZnO thin films based NO2 gas sensor via SILAR technnique. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 239, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunge, Y.M.; Yadav, A.A.; Kulkarni, S.B.; Mathe, V.L. A multifunctional ZnO thin film based devices for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of terephthalic acid and CO2 gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 274, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, T. An overview: Facet-dependent metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 277, 604–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairose, S.; Ernest, S.; Daniel, S. Effect of Oxygen Sputter Pressure on the Structural, Morphological and Optical Properties of ZnO Thin Films for Gas Sensing Application. Sens. Imaging 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Pérez, L.; Aguilar, M.; Zelaya-Angel, O.; Muñoz-Aguirre, N. Improved electrical, optical, and structural properties of undoped ZnO thin films grown by water-mist-assisted spray pyrolysis. Phys. Stat. Solidi A 2006, 203, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Aurutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, A.; Jagadish, C. Review of zincblende ZnO: Stability of metastable ZnO phases. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Córdova, A.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Sanchez-Aké, C. Zinc blende phase detection in ZnO thin films grown with low doping Mn concentration by double-beam pulsed laser deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 18971–18977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.Q.; Ren, F.; Chen, X.H.; Zhan, H.H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Kang, J.Y. Cubic ZnO films obtained at low pressure by molecular beam epitaxy. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 097106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, L.; Muñoz-Aguirre, N.; Muñoz-Aguirre, S.; Zelaya-Angel, O. Nanometric structures of highly oriented zinc blende ZnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 2015, 139, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Tan, Y.; Liu, X. Blue Luminescent Center in ZnO Film Deposited on Silicon Substrates. Opt. Mater. 2004, 26, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Dai, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, J. Evolutions of defects and blue-green emissions in ZnO microwhiskers fabricated by vapor-phase transport. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2012, 73, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Duan, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, X.; Cai, W. Blue Luminescence of ZnO Nanoparticles Based on Non-Equilibrium Processes: Defect Origins and Emission Controls. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micro Concentrated Cleaning Solution, International Products, Burlington, N.J. Available online: https://www.ipcol.com/cleaners/micro-90 (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide—From Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiojiri, M.; Kaito, C. Structure and growth of ZnO smoke particles prepared by gas evaporation technique. J. Cryst. Growth 1981, 52, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morkoç, H.; Özgür, Ü. Zinc Oxide: Fundamentals, Materials and Device Technology; Wiley VCH Verlag GmbH&Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, F. Zinc oxide light-emitting diodes: A review. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Zhao, Q.X.; Yang, L.L.; Lorenz, M.; Cao, B.Q.; Zuñiga-Perez, J.; Czekalla, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Grundmann, M.; et al. Zinc oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growth, light emitting diodes and lasers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.I.; Kwon, B.W.; Park, D.H.; Seo, W.-S.; Yi, Y.; Angadi, B.; Lee, C.-L.; Choi, W.K. Emissive ZnO-graphene quantum dots for white-light-emitting diodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.J.; Im, S.; Lee, S.Y. Violet and UV luminescence emitted from ZnO thin films grown on sapphire by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 2000, 366, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Valencia, J.R.; Alcaire, M.; Romero-Gómez, P.; Macias-Montero, M.; Aparicio, F.J.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Barranco, A. Oxygen Optical Sensing in Gas and Liquids with Nanostructured ZnO Thin Films Based on Exciton Emission Detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 9852–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumbul, A.; Aslan, F.; Demirozu, S.; Goktas, A.; Kilic, A.; Durgun, M.; Zarbali1, M.Z. Solution processed boron doped ZnO thin films: Influence of different boron complexes. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 035903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, A.M.; Taha, S.; Said, G.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Yakuphanoglu, F. Structural and optical properties of spin coated Zn1−xCrxO nanostructures. Superlattices Microstruct. 2013, 60, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, C. Blue light emission from the heterostructured ZnO/InGaN/GaN. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamé, S.; Navarro Quezada, A.; Skuridina, D.; Reich, C.; Henning, D.; Frentrup, M.; Wernicke, T.; Koslow, I.; Kneissl, M.; Esser, N.; et al. Preparation and structure of ultra-thin Ga(0001) layers on In0.11Ga0.89N-single quantum Wells. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2016, 55, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ali, T.; Siddique, M.N.; Ahmad, A.; Tripathi, P. Enhanced room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped SnO2 nanoparticles: A comprehensive study. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 083906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Khan, S. Effect of (Mn-Co) co-doping on the structural, morphological, optical, photoluminescence and electrical properties of SnO2. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 720, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, S.; Yang, C.; Yu, P.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; Wong, G.K.L. Highly monodisperse polymer-capped ZnO nanoparticles: Preparation and optical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 2901–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, H.-J. Origin of green luminescence of ZnO powders reacted with carbon black. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 124902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, D.; Huso, J.; Morrison, J.L.; Corolewski, C.D.; McCluskey, M.D.; Bergman, L. Achieving highly-enhanced UV photoluminescence and its origin in ZnO nanocrystalline films. Opt. Mater. 2016, 58, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Jin, H.; Xi, L.; Wang, Y.; Townsend, P.D. Photoluminescence identification of surface contaminants on zinc oxide from their phase transitions. Spectrosc. Lett. 2018, 51, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davood, R. Synthesis and photoluminescence characterization of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 2013, 134, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthirakumar, P.; Hong, C.H. Effect of annealing temperature and pH on morphology and optical property of highly dispersible ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repp, S.; Erdem, E. Controlling the exciton energy of zinc oxide (ZnO) quantum dots by changing the confinement conditions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 152, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repp, S.; Weber, S.; Erdem, E. Defect Evolution of Nonstoichiometric ZnO Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 25124–25130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.C.; Look, D.C.; Jogai, B.; Litton, C.W.; Collins, T.C.; Harsch, W.; Cantwell, G. Neutral-donor–bound-exciton complexes in ZnO crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 57, 12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Rana Sadaf, J.; Israr Qadir, M.; Zaman, S.; Zainelabdin, A.; Bano, N.; Ijaz, H. Luminescence from Zinc Oxide Nanostructures and Polymersand their Hybrid Devices. Materials 2010, 3, 2643–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaci, F.; Vempati, S.; Donmez, I.; Biyikliab, N.; Uyar, T. Role of zinc interstitials and oxygen vacancies of ZnO in photocatalysis: A bottom-up approach to control defect density. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10224–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, D.R.T.; Maierhofer, C.; Winter, A.; Reckzügel, M.; Srama, R.; Rossow, U.; Thomas, A.; Horn, K.; Richter, W. In situ monitoring of heterostructure growth by optical spectroscopies: CdS on InP (110). Appl. Surf. Sci. 1992, 56–58, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Q. First-principles study of negative thermal expansion in zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 063508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, P.S.; Baranov, A.N.; Dobrokhotov, Z.V.; Solozhenko, V.L. Solozhenko, Synthesis and Thermal Stability of Cubic ZnO in the Salt Nanocomposites. Russ. Chem. Bulletin 2010, 19, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.F.; Vasilevskiy, M.I.; Oliveira, F.; Rolo, A.G.; Viseu, T.; Ayres de Campos, J.; Alves, E.; Correia, R. Resonant Raman scattering in ZnO:Mn and ZnO:Mn:Al thin films grown by RF sputtering. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 334205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, E.A.; Mel’nikA, N.N.; TsurkanL, E.; Kicherman, V. Raman spectra of ZnO single cristal. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1977, 26, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitenko, V.A.; Plekhanov, V.G.; Mukhin, S.V. Raman spectra of oxide zinc powders and single crystals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1996, 63, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
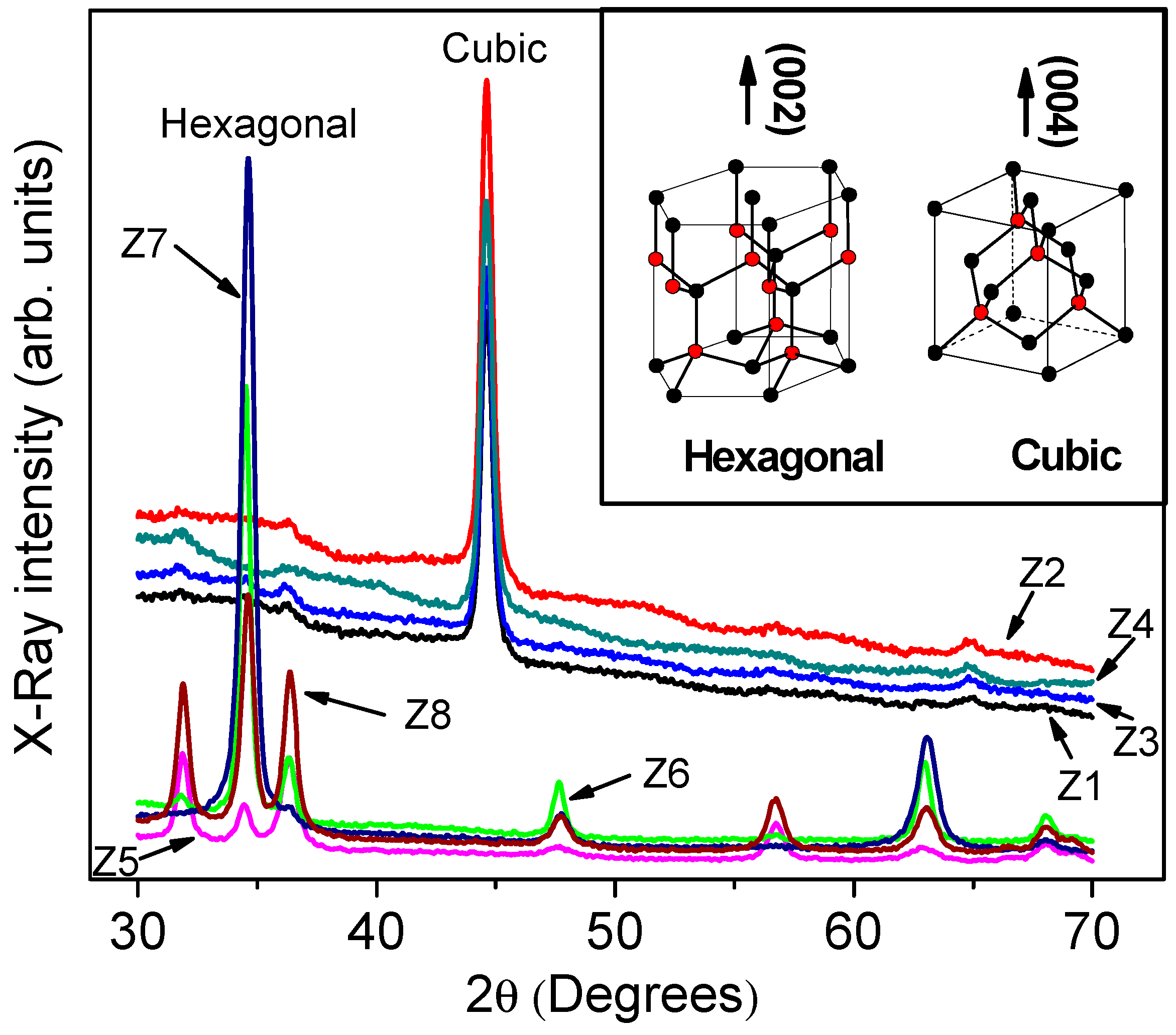
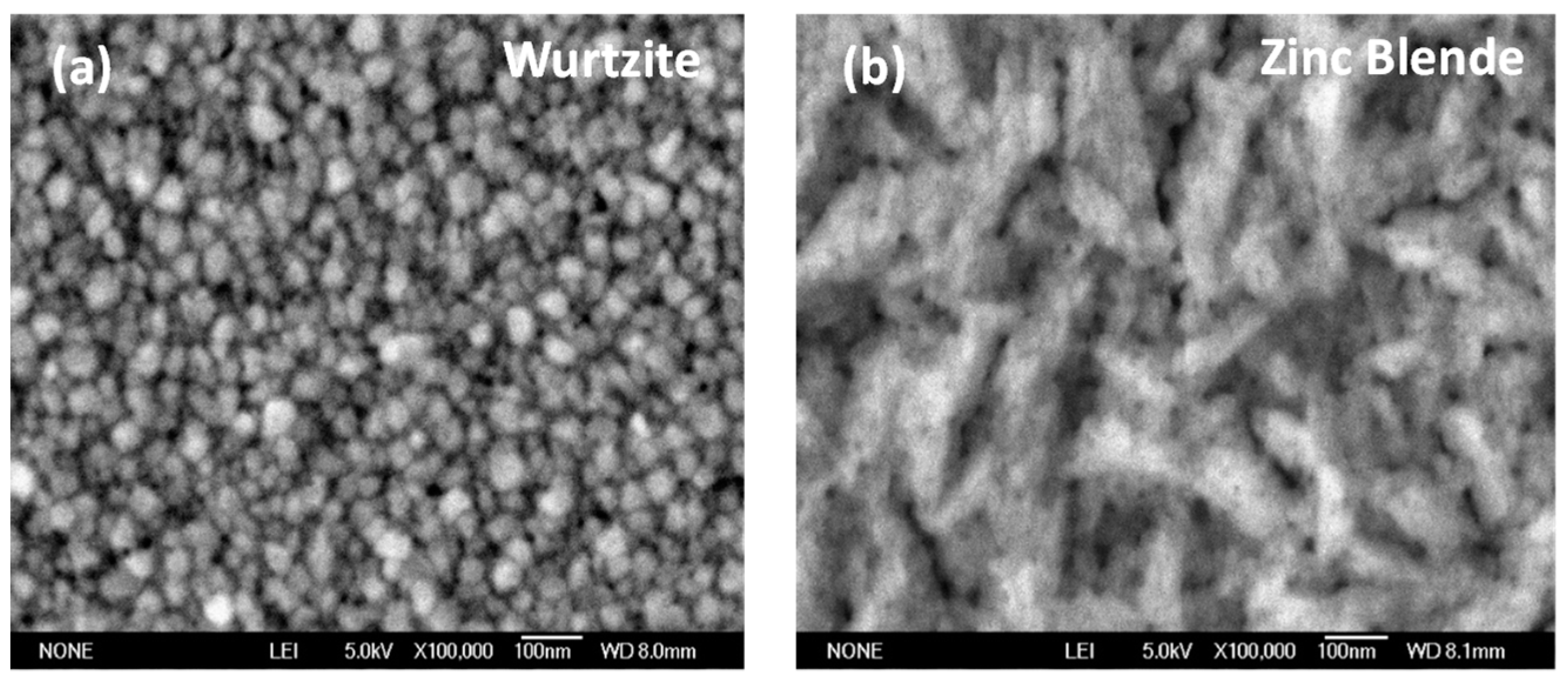

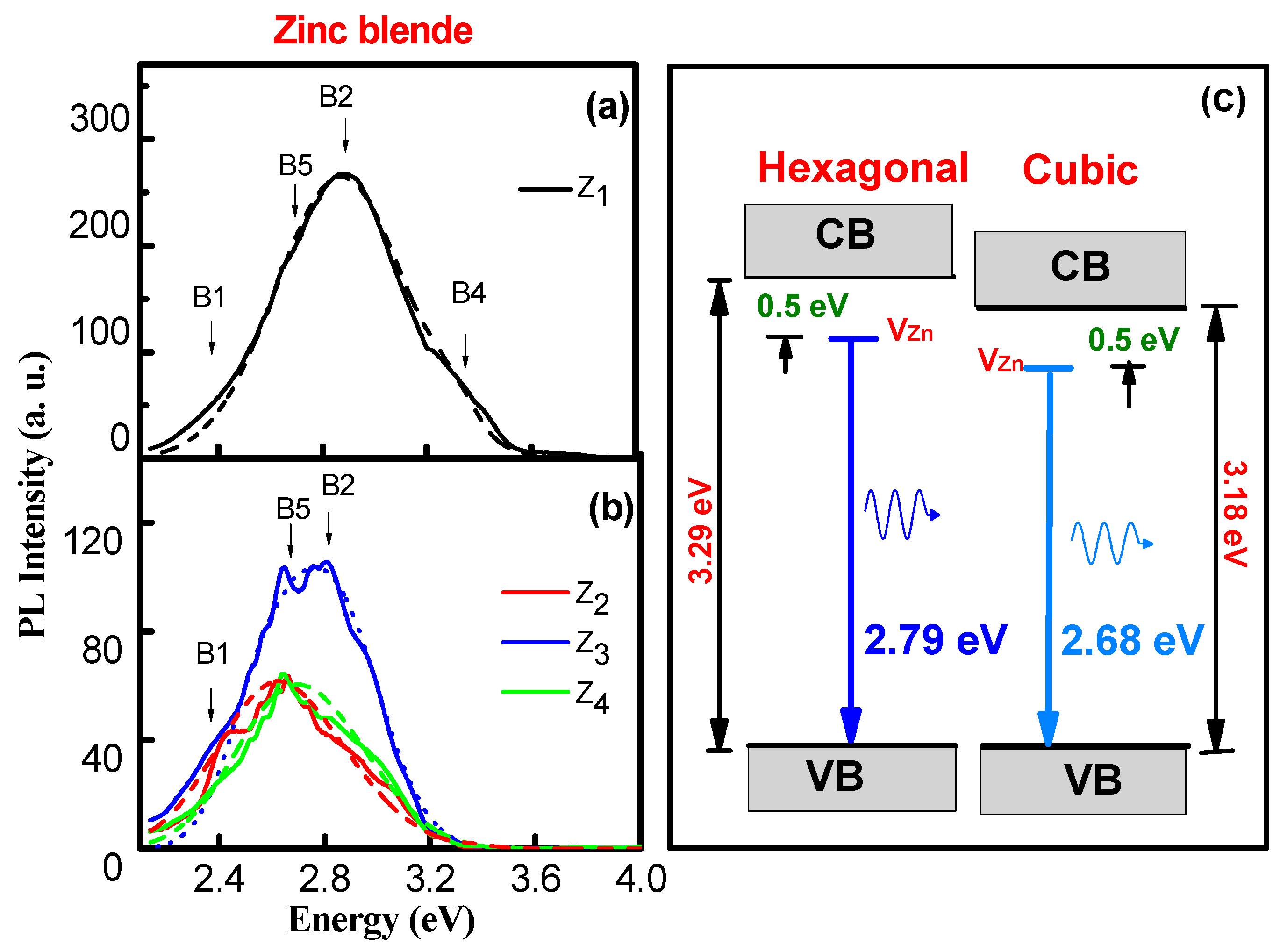
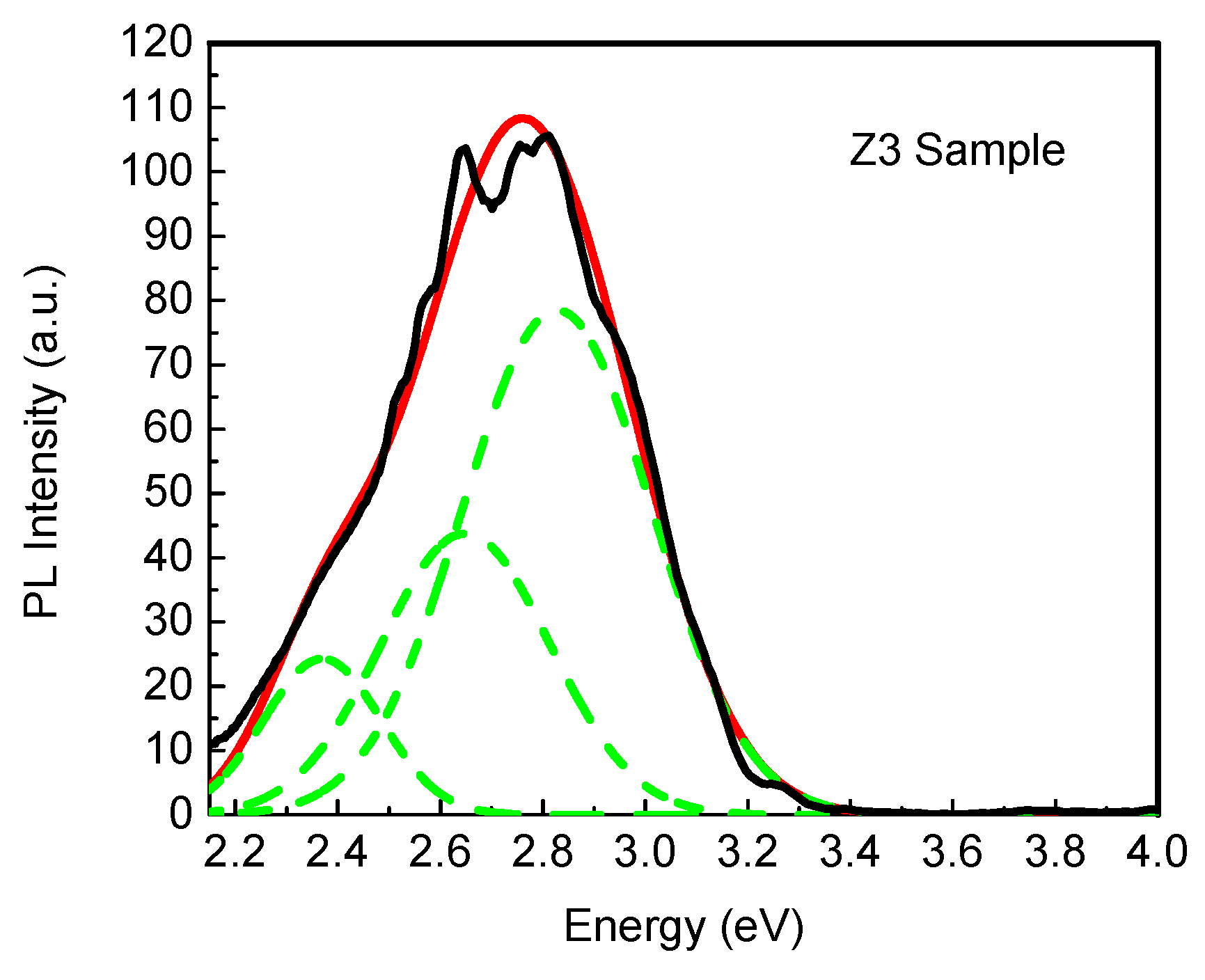
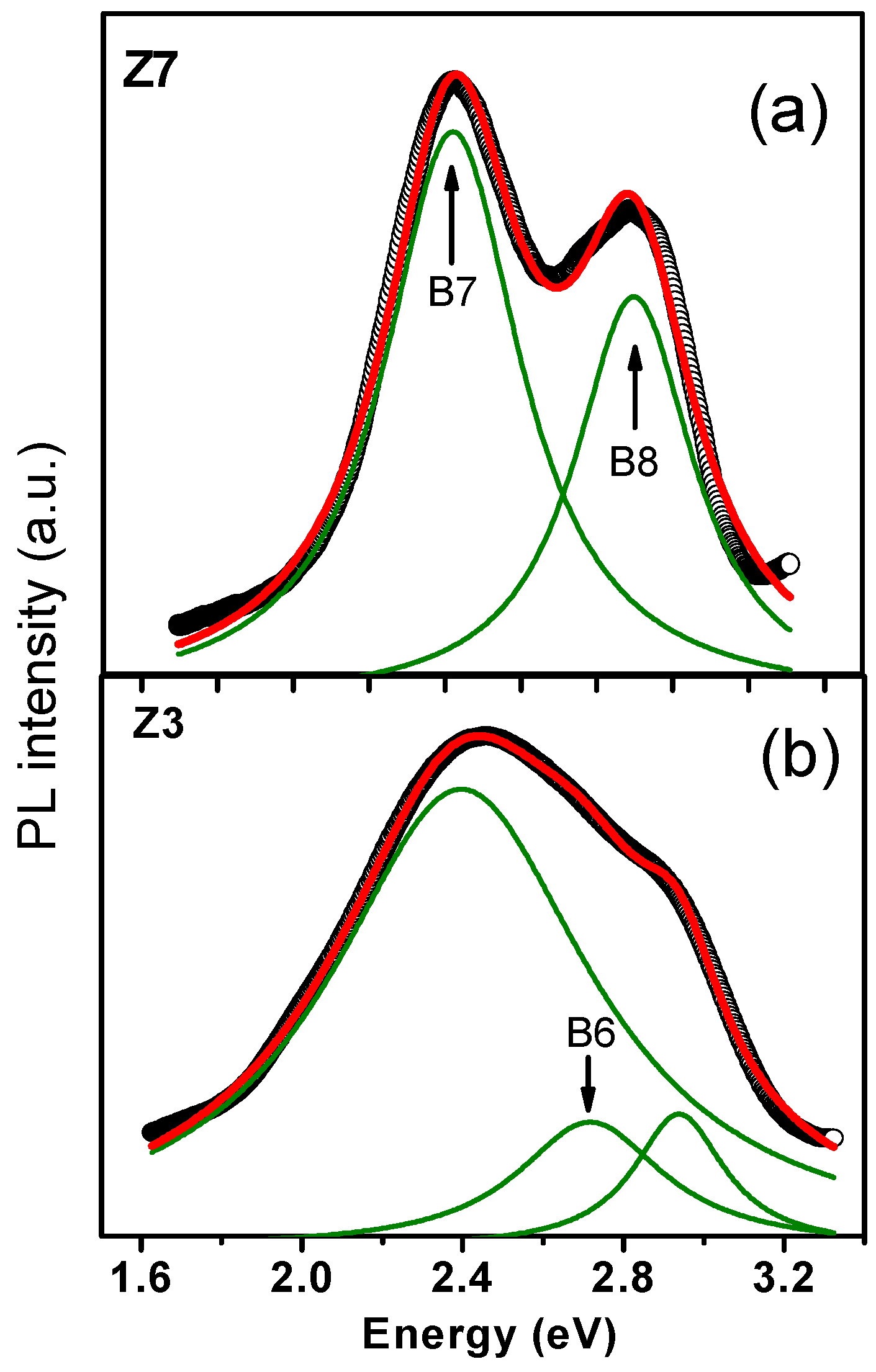
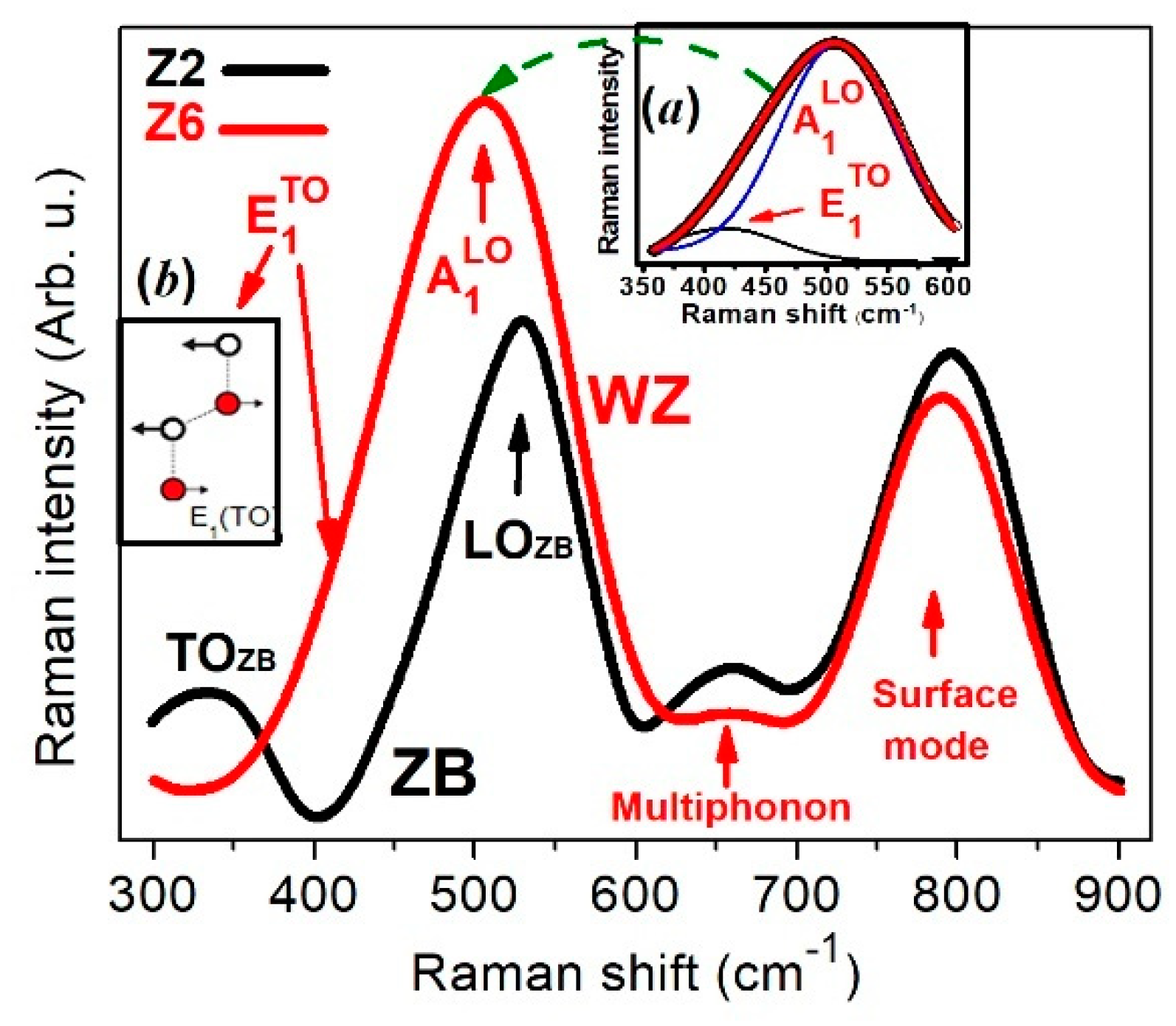
| Phase | Sample | Full-Width at Half-Maximum (°) | d (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hexagonal | Z5 | 0.6160 | 34.6200 | 13.362 ± 0.24 |
| Z6 | 0.4276 | 34.5014 | 19.452 ± 0.53 | |
| Z7 | 0.5491 | 34.6088 | 15.152 ± 0.27 | |
| Z8 | 0.6062 | 34.6200 | 13.762 ± 0.35 | |
| Cubic | Z1 | 0.5163 | 44.6148 | 16.629 ± 0.30 |
| Z2 | 0.5118 | 44.6186 | 16.777 ± 0.55 | |
| Z3 | 0.5500 | 44.6200 | 15.613 ± 0.11 | |
| Z4 | 0.5742 | 44.6000 | 14.953 ± 0.18 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Aguirre, N.; Martínez-Pérez, L.; Muñoz-Aguirre, S.; Flores-Herrera, L.A.; Vergara Hernández, E.; Zelaya-Angel, O. Luminescent Properties of (004) Highly Oriented Cubic Zinc Blende ZnO Thin Films. Materials 2019, 12, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203314
Muñoz-Aguirre N, Martínez-Pérez L, Muñoz-Aguirre S, Flores-Herrera LA, Vergara Hernández E, Zelaya-Angel O. Luminescent Properties of (004) Highly Oriented Cubic Zinc Blende ZnO Thin Films. Materials. 2019; 12(20):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203314
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Aguirre, Narcizo, Lilia Martínez-Pérez, Severino Muñoz-Aguirre, Luis Armando Flores-Herrera, Erasto Vergara Hernández, and Orlando Zelaya-Angel. 2019. "Luminescent Properties of (004) Highly Oriented Cubic Zinc Blende ZnO Thin Films" Materials 12, no. 20: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203314
APA StyleMuñoz-Aguirre, N., Martínez-Pérez, L., Muñoz-Aguirre, S., Flores-Herrera, L. A., Vergara Hernández, E., & Zelaya-Angel, O. (2019). Luminescent Properties of (004) Highly Oriented Cubic Zinc Blende ZnO Thin Films. Materials, 12(20), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203314





