Nanocellulose-Block Copolymer Films for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Composite Films
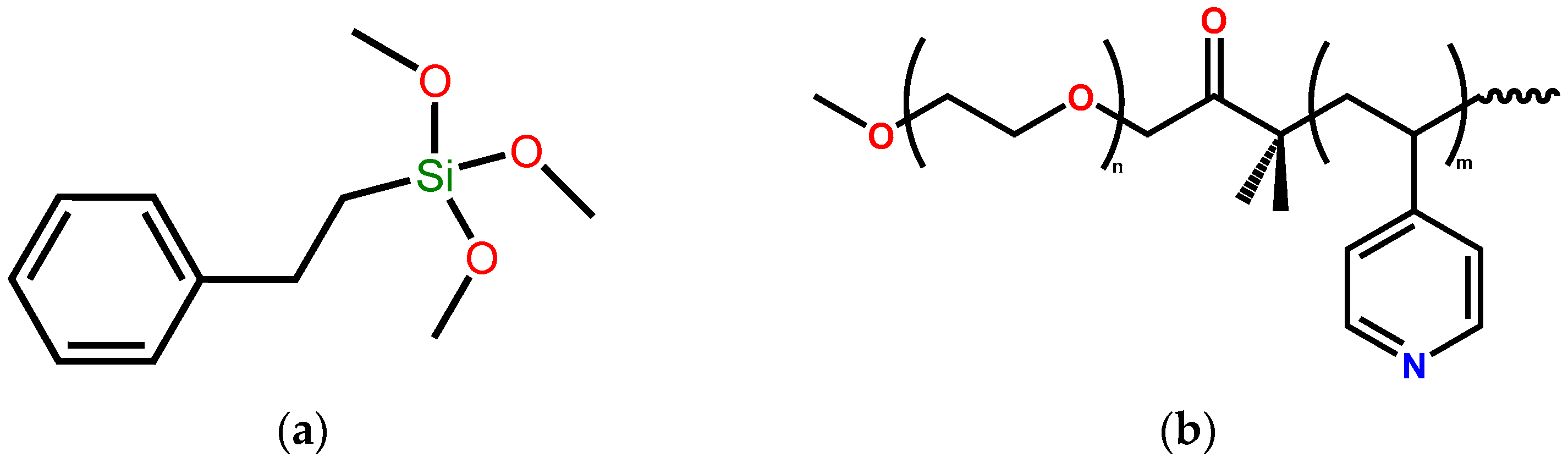
2.2.1. Modification of CNFs with TMPES and P4VP-PEO
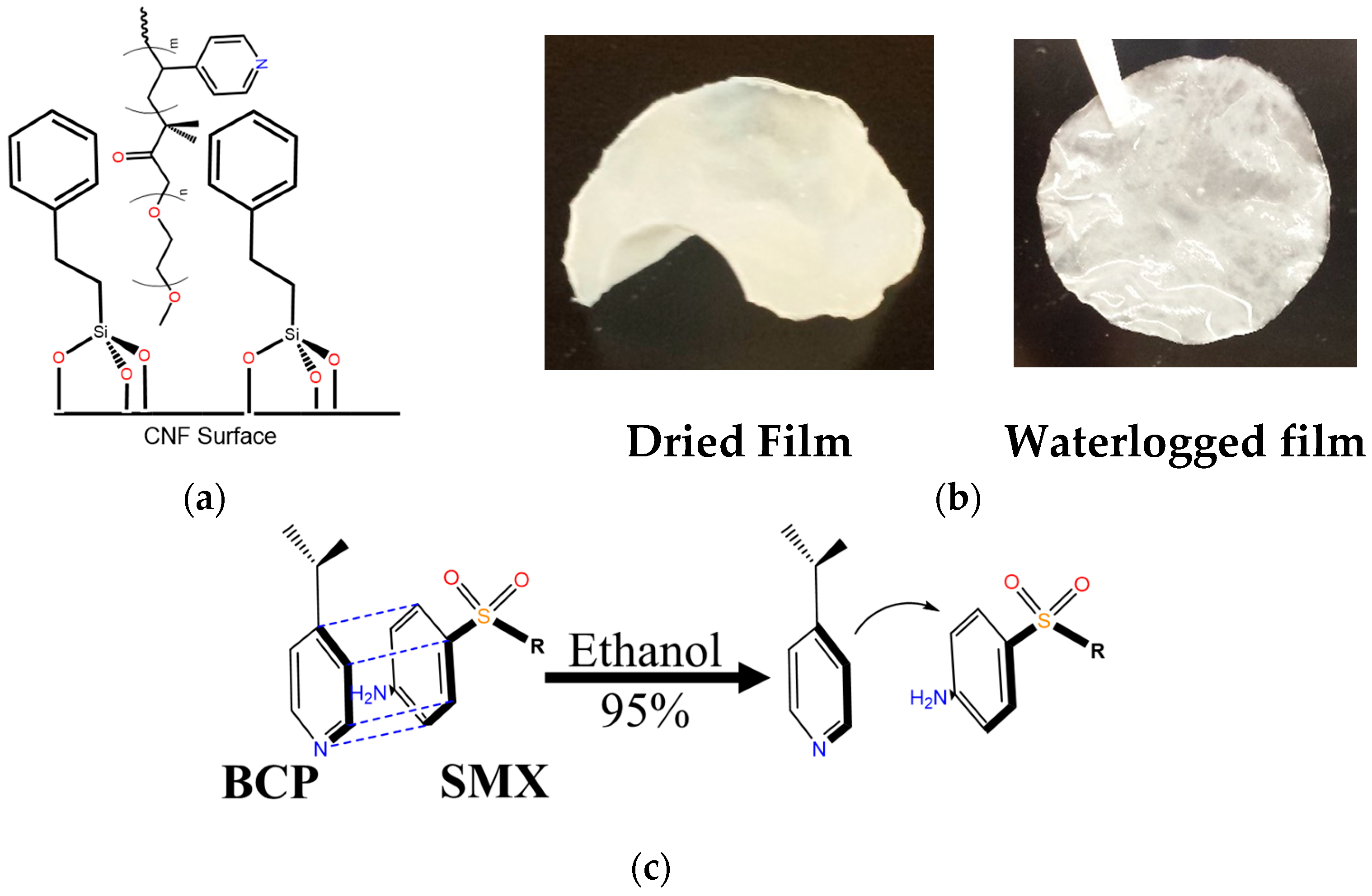
2.2.2. Preparation of TMPES-Modified CNFs Films and TMPES and P4VP-PEO-Modified CNFs Films
2.2.3. Preparation of CNFs Films without Modifications
2.3. Characterization of Modified CNFs Films
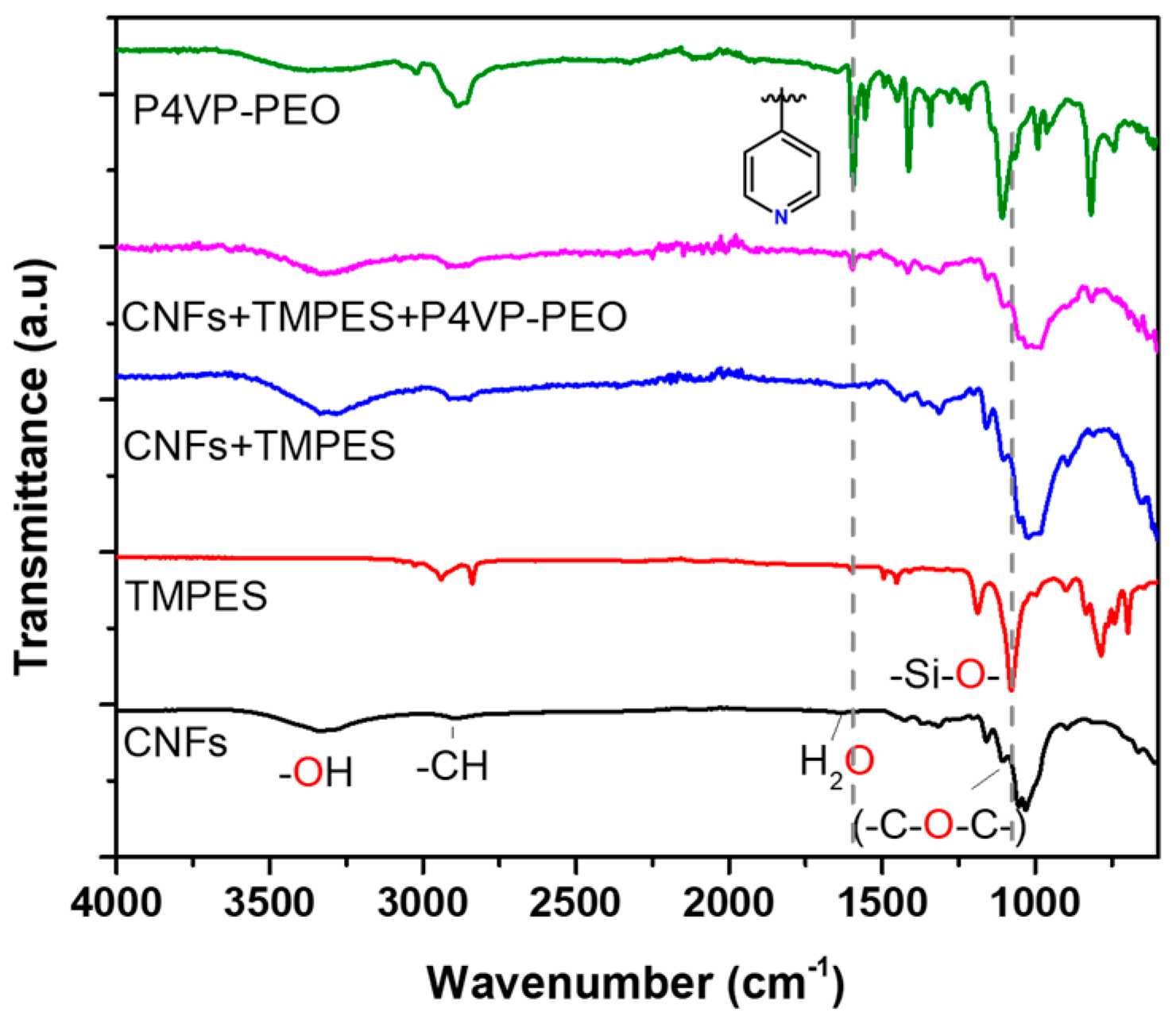
2.3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
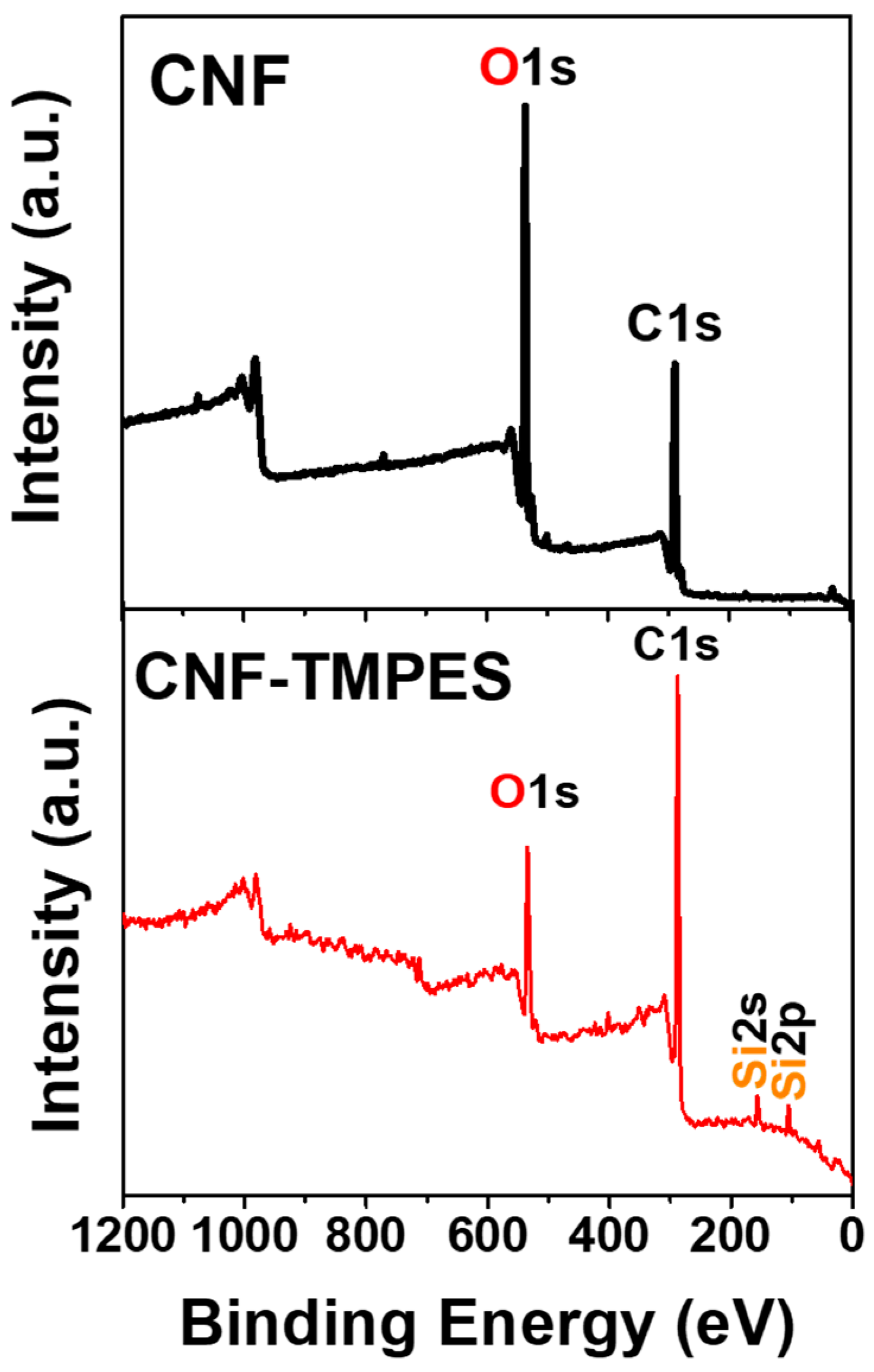
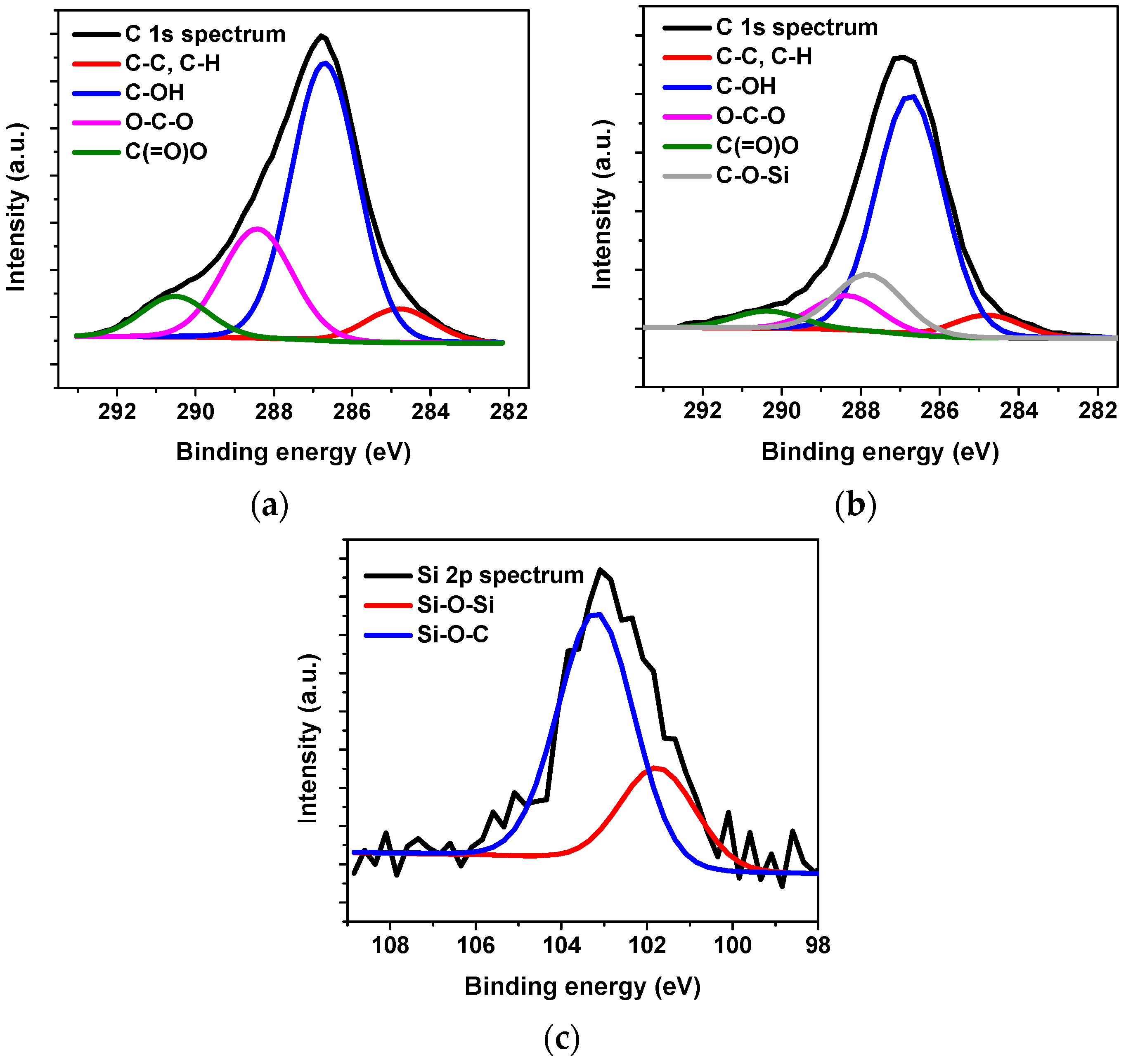
2.3.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
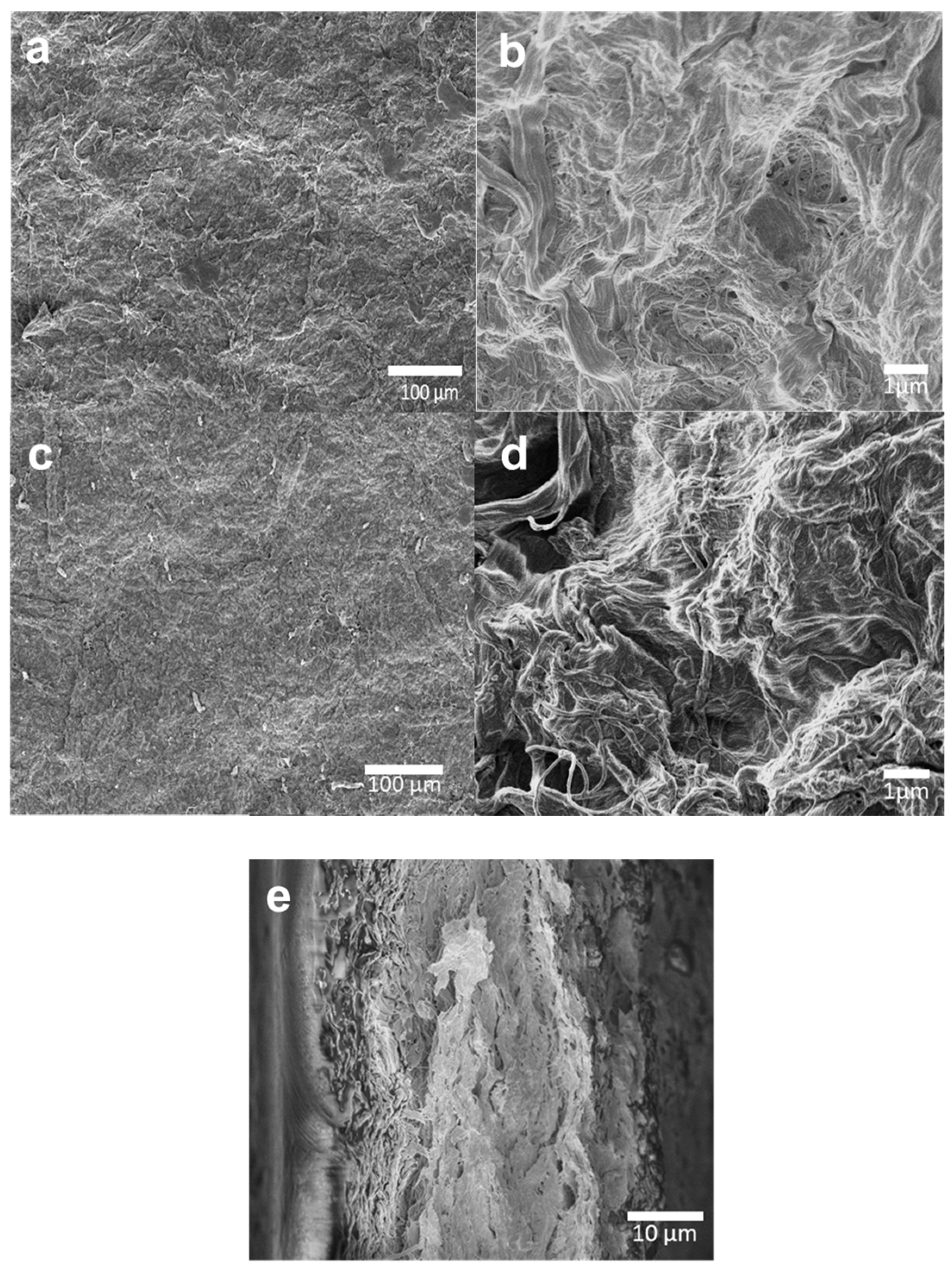
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
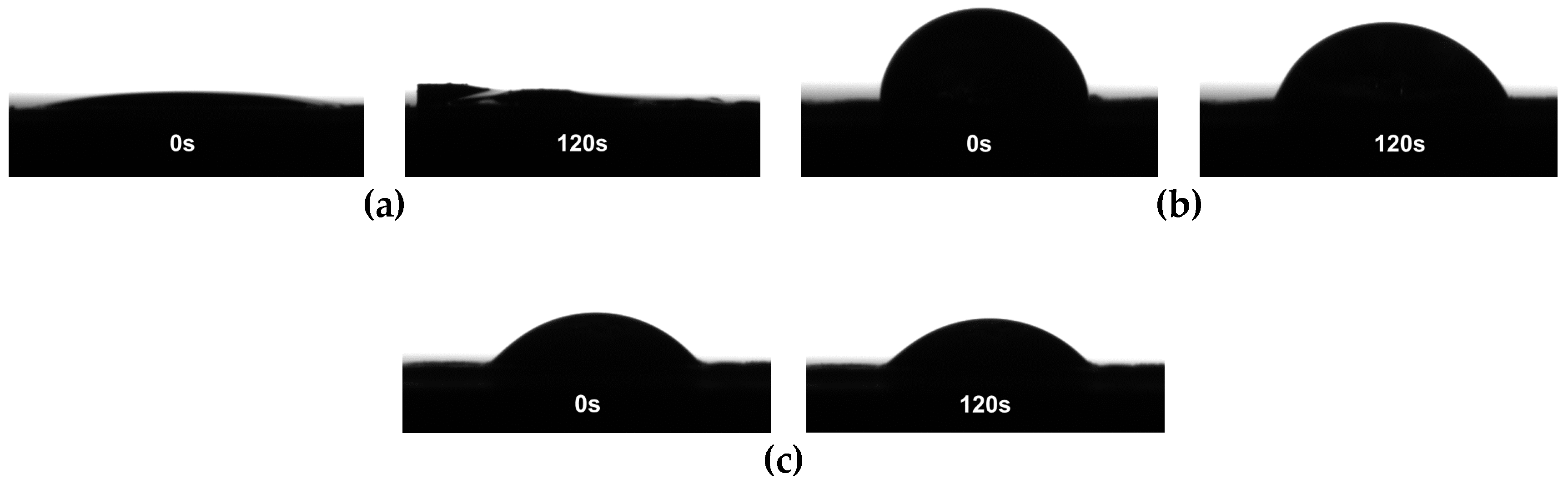
2.3.4. Contact Angle Measurements
2.4. Adsorption Batch Experiments of SMX using TMPES-Modified CNFs Films and TMPES and P4VP-PEO-Modified CNFs Films
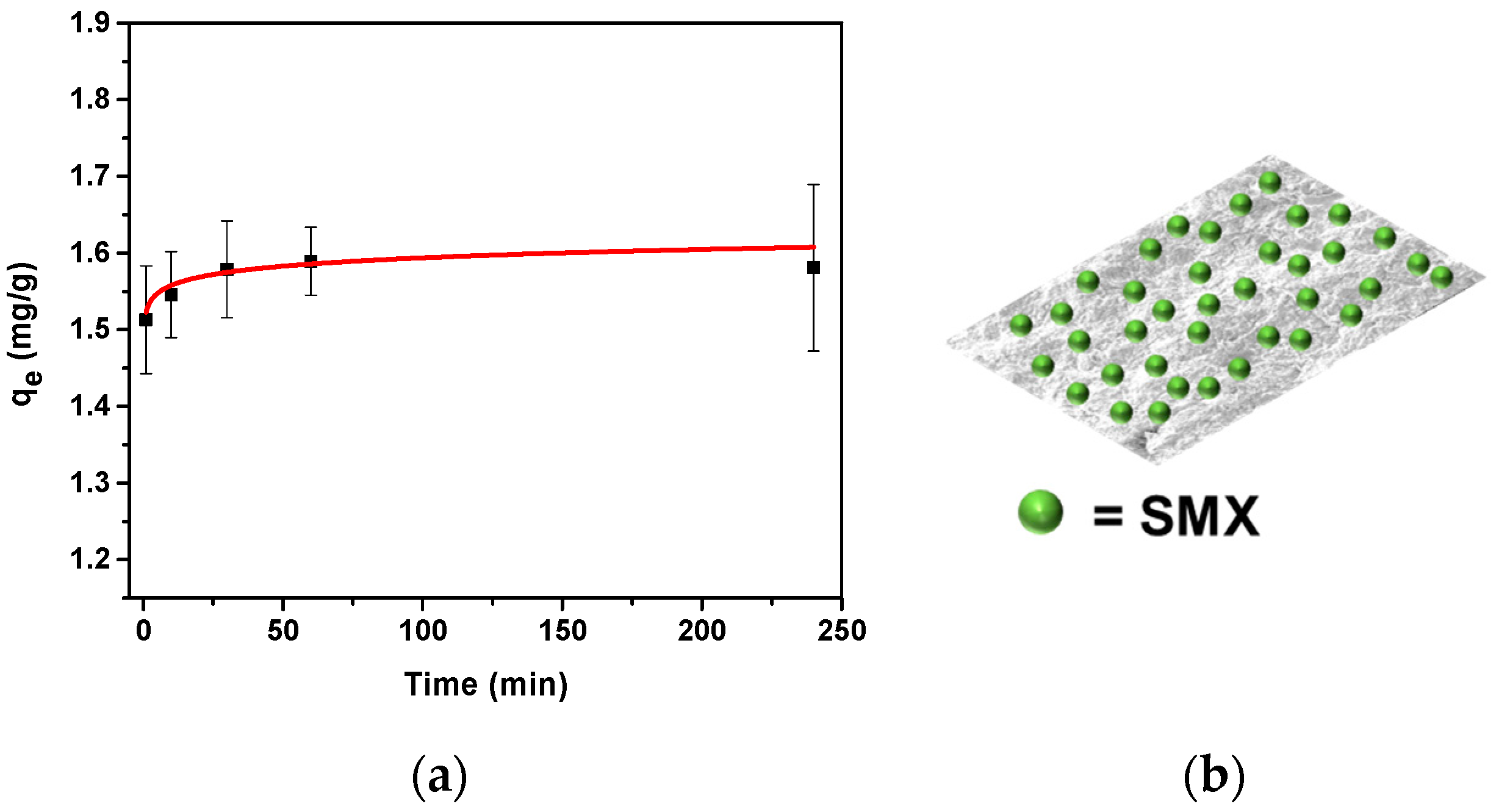
2.4.1. Adsorption as a Function of Time
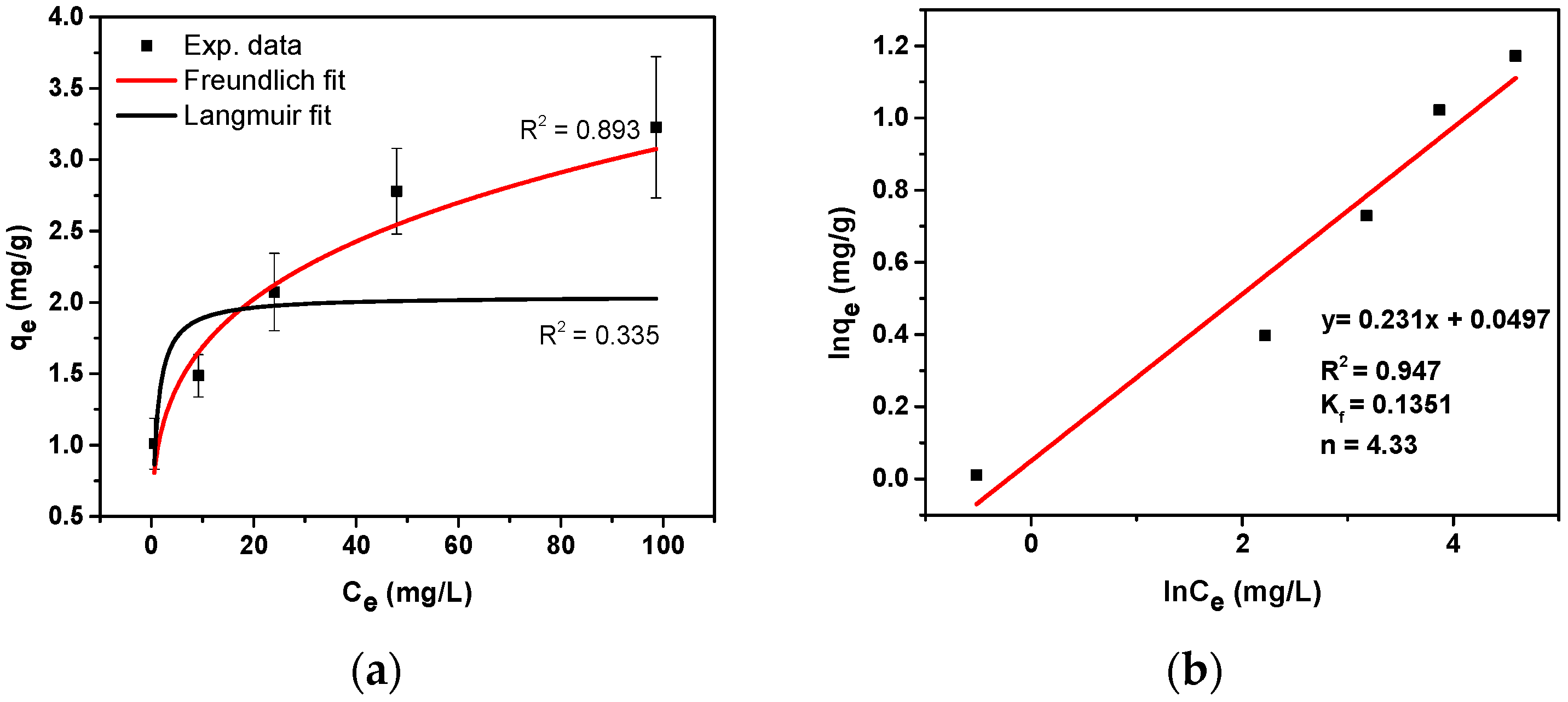
2.4.2. Adsorption Isotherm Experiments
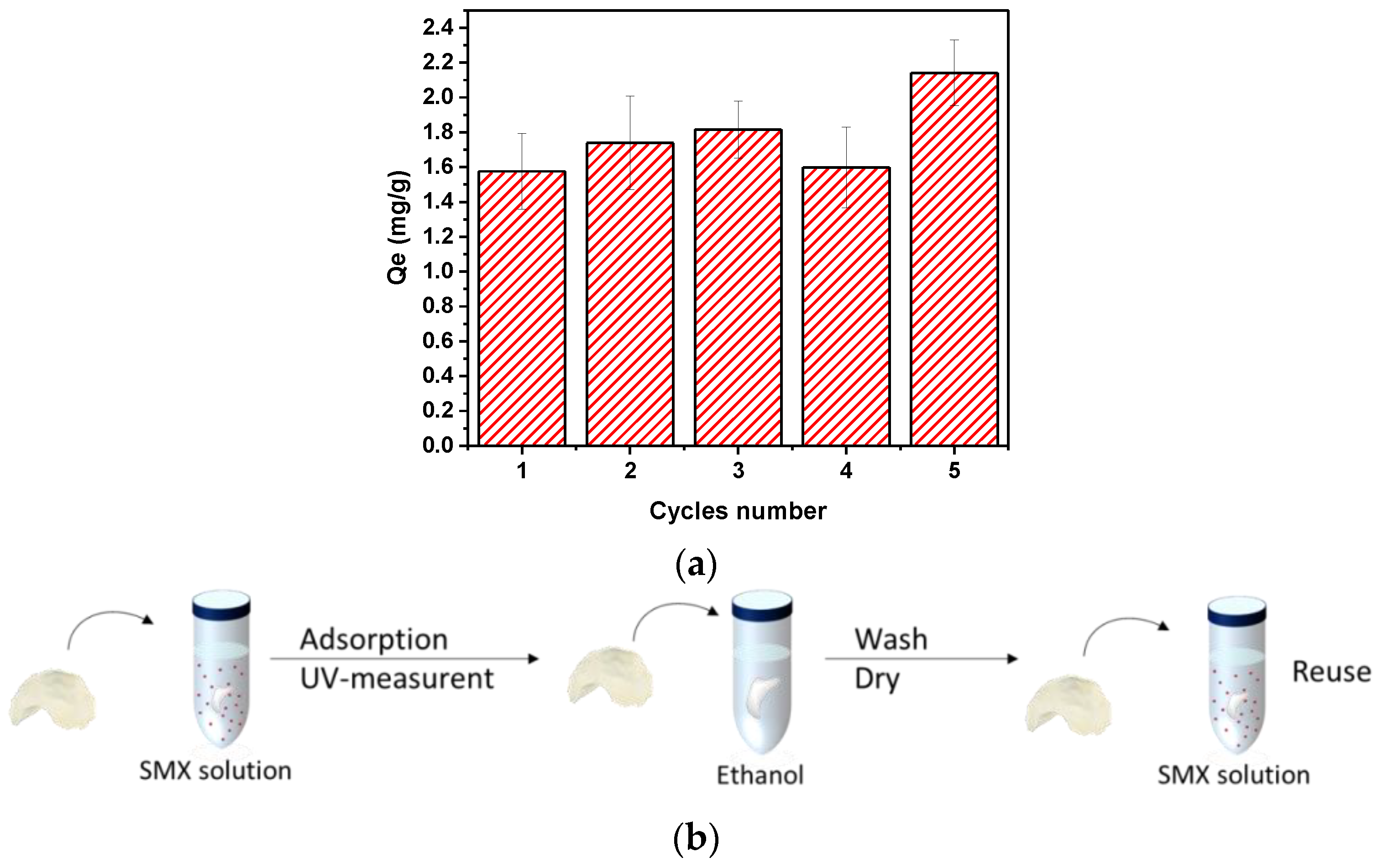
2.4.3. Reusability Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Modification of CNFs with TMPES and P4VP-PEO
3.2. Characterization of the Modified CNFs Films
3.3. Adsorption Batch Experiments with SMX
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.H.; Lin, A.Y.C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: Review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackelberg, P.E.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Zaugg, S.D.; Henderson, A.K.; Reissman, D.B. Persistence of pharmaceutical compounds and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 329, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolar, D.; Gros, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Moreno, J.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Barceló, D. Removal of emerging contaminants from municipal wastewater with an integrated membrane system, MBR–RO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239–240, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, K.C.; Seema, H.; Saleh, M.; Le, N.H.; Mahesh, K.; Chandra, V.; Kim, K.S. Environmental applications using graphene composites: Water remediation and gas adsorption. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3149–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, C.K.; Liu, Z.; Vijwani, H.; Nadagouda, M.; Mukhopadhyay, M.S.; Tsige, M. Carbon nanotube based groundwater remediation: The case of trichloroethylene. Molecules 2016, 21, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Baun, A.; Birkedal, R.; Kühnel, D.; Jensen, K.A.; Vogel, U.; Wallin, H. Bioaccumulation and ecotoxicity of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.; Luo, L.; Huang, C. Toxicity of graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes against human cells and zebrafish. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.; Grishkewich, N.; Tam, K.C. Cellulose nanomaterials: Promising sustainable nanomaterials for application in water/wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 623–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Bhattacharyya, R. Cellulose Nanofibers: Synthesis, Properties and Applications, Polymer Nanocomposites Based on Inorganic and Organic Nanomaterials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stenstad, P.; Andresen, M.; Tanem, B.S.; Stenius, P. Chemical surface modifications of microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 2008, 15, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Borrell, P.F.; Božič, M.; Kokol, V.; Oksman, K.; Mathew, A.P. Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardam, A.; Raj, K.R.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M.M. Nanocellulose fibers for biosorption of cadmium, nickel, and lead ions from aqueous solution. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, A.; Safari, S.; Yang, H.; van de Ven, T.G.M. Copper removal using electrosterically stabilized nanocrystalline cellulose. ACS App. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11301–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Deepa, J.R.; Christa, J. Nanocellulose/nanobentonite composite anchored with multi-carboxyl functional groups as an adsorbent for the effective removal of Cobalt(II) from nuclear industry wastewater samples. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 467, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Male, K.B.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Brabazon, D.; Paull, B.; Luong, J.H.T. Adsorption and desorption of methylene blue on porous carbon monoliths and nanocrystalline cellulose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8796–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, E.; Min, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pang, L.; Ma, T. Effective removal of cationic dyes using carboxylate-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chemosphere 2015, 141, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, A.; Butchosa, N.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Surface quaternized cellulose nanofibrils with high water absorbency and adsorption capacity for anionic dyes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De France, K.J.; Hoare, T.; Cranston, E.D. Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4609–4631. [Google Scholar]
- Maatar, W.; Alila, S.; Boufi, S. Cellulose based organogel as an adsorbent for dissolved organic compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.; Örmeci, B. Application of molecularly imprinted and non-imprinted polymers for removal of emerging contaminants in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3820–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoyo, H.A.; Wilson, D.L. Nano-sized cyclodextrin-based molecularly imprinted polymer adsorbents for perfluorinated compounds—A mini-review. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 981–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-W.; Baek, K.-Y.; Cho, K.-Y.; Shim, N.V.; Lee, S.-H. Amphiphilic block copolymer for adsorption of organic contaminants. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 1, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, F.S.; Fredrickson, G. Block copolymers—Designer soft materials. Phys. Today 1999, 52, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsen, M.W.; Schick, M. Stable and unstable phases of a diblock copolymer melt. Phys. Rev. Letter. 1994, 72, 2660–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Johir, M.A.H.; Sun, L.; Asadullah, M.; Belhaj, D. Sorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants on functionalized biochar: Protagonist role of π-π electron-donor-acceptor interactions and hydrogen bonds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, A.; Saito, T.; Fukuzumi, H. TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Nishino, T.; Shakeri, A.; Faezipour, M.; Ebrahimi, G.; Kotera, M. Water-repellent all-cellulose nanocomposite using silane coupling treatment. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, M.M.; Zhu, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Mitsuishi, M. Superhydrophobic surfaces with fluorinated cellulose nanofiber assemblies for oil—Water separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37168–37174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Boufi, S.; Celli, A.; Kango, S. Nanofibrillated cellulose: Surface modification and potential applications. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Morales, J.; Morales, K.; Ramos, D.; Ortiz-Quiles, E.O.; López-Encarnación, J.M.; Nicolau, E. Examining the use of nanocellulose composites for the sorption of contaminants of emerging concern: An experimental and computational study. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7714–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.; Gandini, A.; Fabbri, P.; Belgacem, M.N. Modification of cellulose fibres with organosilanes: Under what conditions does coupling occur? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salon, M.C.B.; Belgacem, M.N. Hydrolysis-condensation kinetics of different silane coupling agents. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2011, 186, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yin, J. Copolymer of poly(4-vinylpyridine)-g-poly(ethylene oxide) respond sharply to temperature, pH and ionic strength. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 4108–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Paul, U.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Liakos, I.; Marras, S.; Scarpellini, A.; Ayadi, F.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Transparent and flexible amorphous cellulose-acrylic hybrids. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souguir, Z.; Dupont, A.L.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Mortha, G.; Cheradame, H.; Ipert, S.; Lavédrine, B. Strengthening of degraded cellulosic material using a diamine alkylalkoxysilane. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7470–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, L.; Hao, S.; Chen, J. Surface modification of diamond and its effect on the mechanical properties of diamond/epoxy composites. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2017, 24, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhi, M.; Kunsta, S.R.; Beltrami, L.V.R.; Kerstner, E.K.; Filho, C.I.S.; Sarmento, V.H.V.; Malfatti, C. Effect of Tetraethoxy-silane (TEOS) amounts on the corrosion prevention properties of siloxane-PMMA hybrid coatings on galvanized steel substrates. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 1140–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xiao, H. Antibacterial/antiviral property and mechanism of dual-functional quaternized pyridinium-type copolymer. Polymers 2015, 7, 2290–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, B.; Liu, S. Reduction of the water wettability of cellulose film through controlled heterogeneous modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5726–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Zhou, Y.N.; Luo, Z.H. Smart fiber membrane for pH-induced oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19643–19650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; Taoufik, N.; García, A.M.; Korili, S.A. Comparative removal of emerging contaminants from aqueous solution by adsorption on an activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2018, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, M.B. Batch sorption experiments: Langmuir and freundlich isotherm studies for the adsorption of textile metal ions onto teff straw (eragrostis tef) agricultural waste. J. Thermodyn. 2013, 2013, 375830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.I.; Young, R.A.; Rowell, R.M. Swelling of compressed cellulose fiber webs in organic liquids. Cellulose 1995, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Morales, J.; Turley, T.A.; Betancourt-Ponce, M.; Nicolau, E. Nanocellulose-Block Copolymer Films for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2019, 12, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020230
Herrera-Morales J, Turley TA, Betancourt-Ponce M, Nicolau E. Nanocellulose-Block Copolymer Films for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. Materials. 2019; 12(2):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020230
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Morales, Jairo, Taylor A. Turley, Miguel Betancourt-Ponce, and Eduardo Nicolau. 2019. "Nanocellulose-Block Copolymer Films for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions" Materials 12, no. 2: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020230
APA StyleHerrera-Morales, J., Turley, T. A., Betancourt-Ponce, M., & Nicolau, E. (2019). Nanocellulose-Block Copolymer Films for the Removal of Emerging Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. Materials, 12(2), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020230





