Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
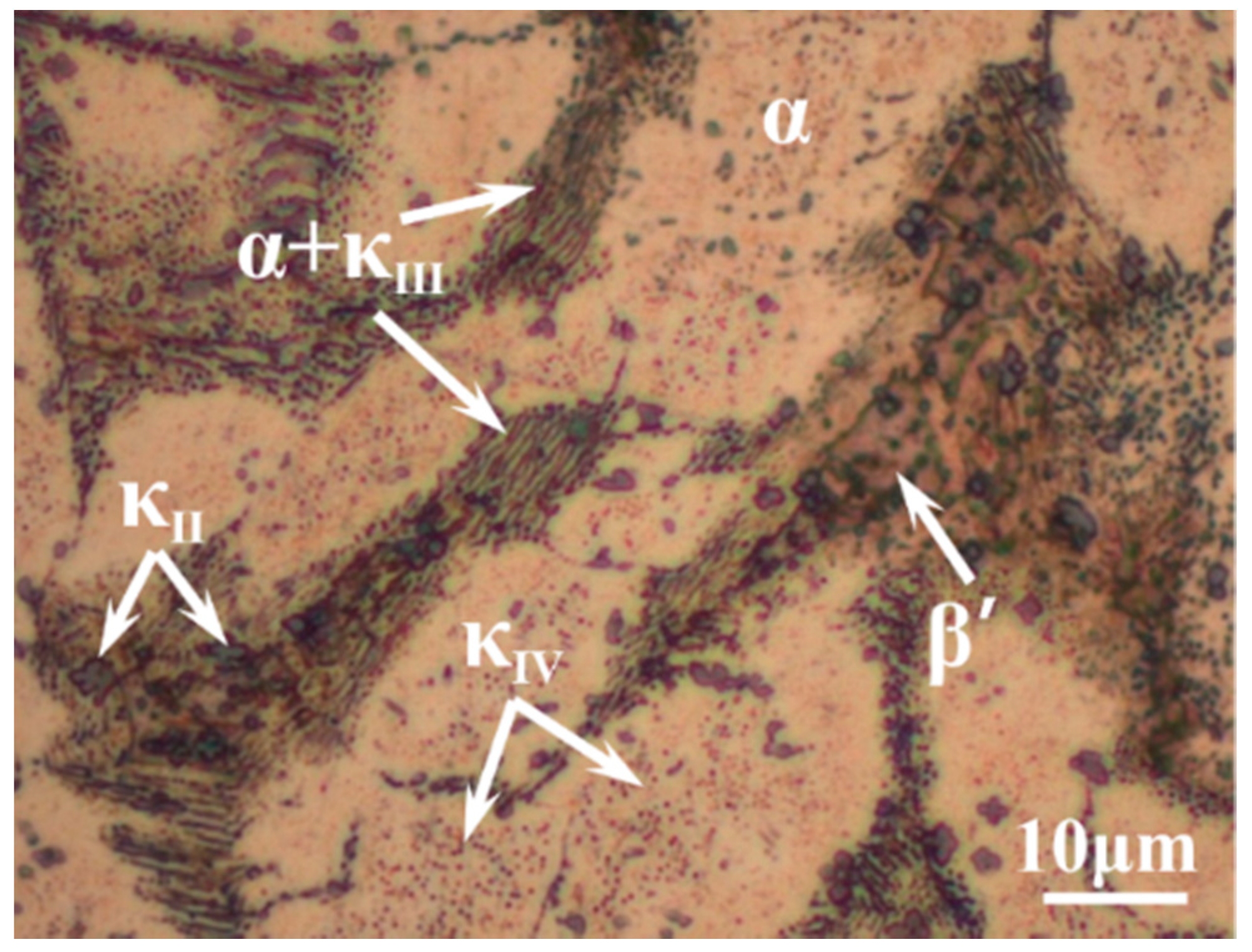
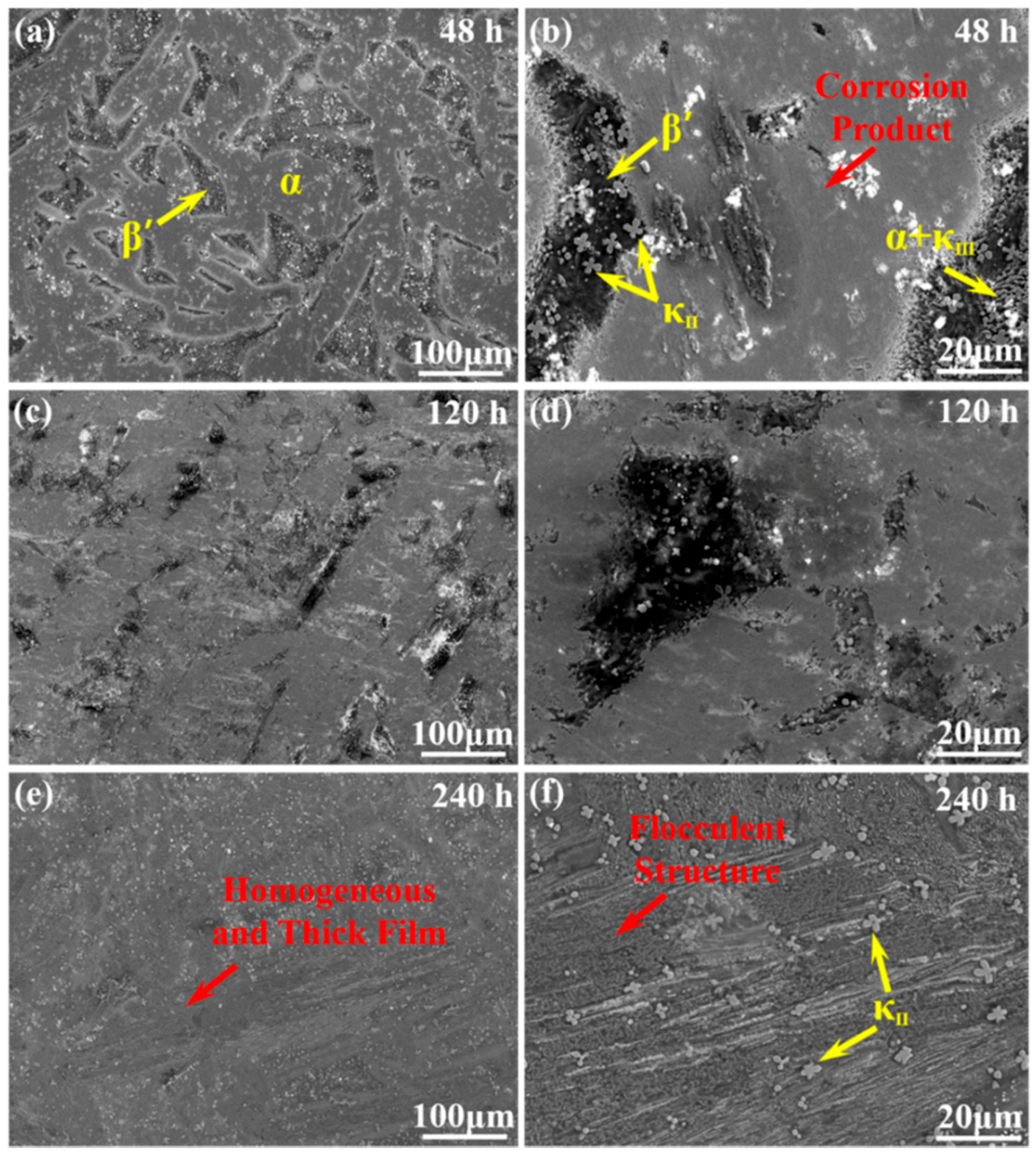
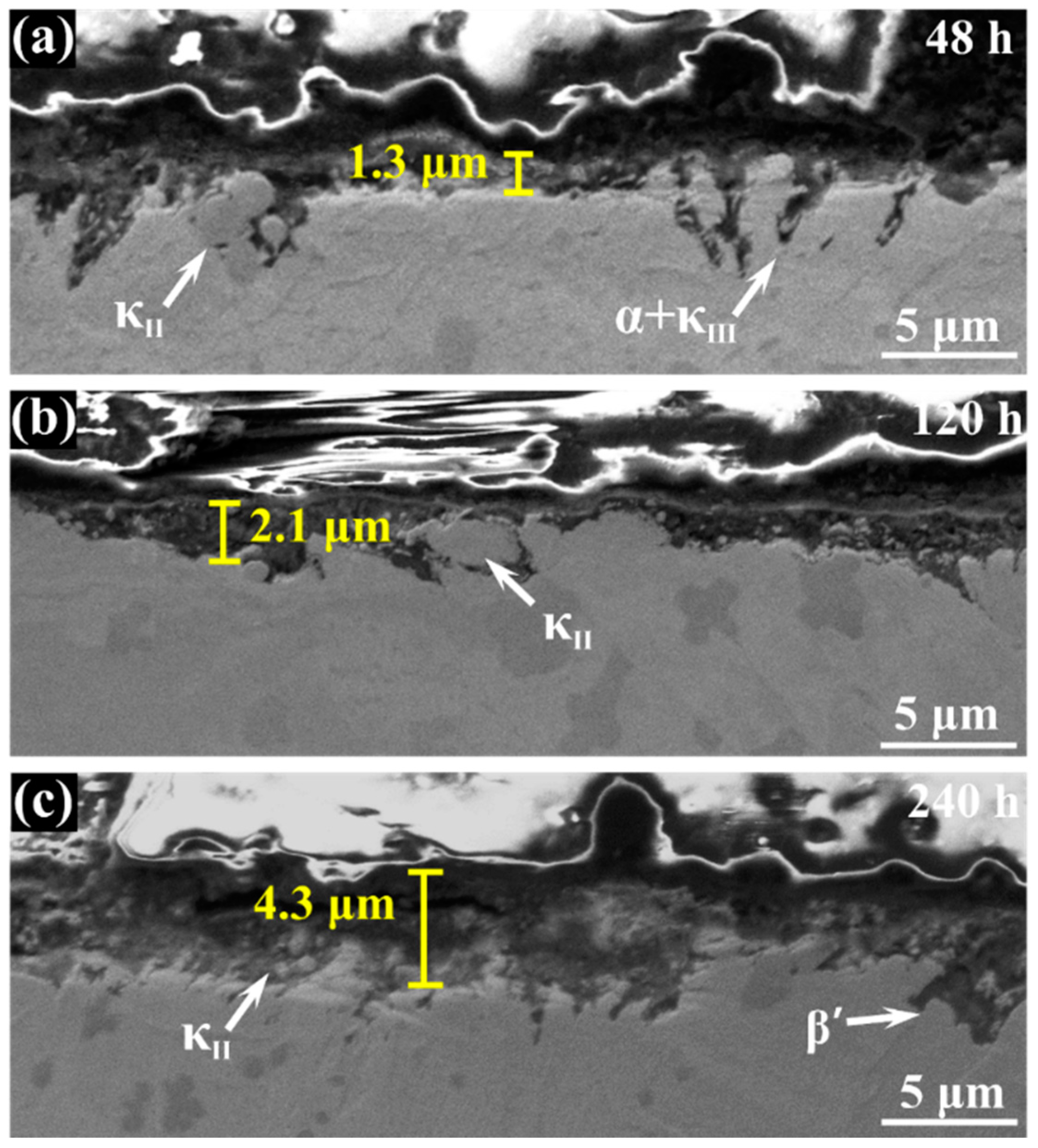
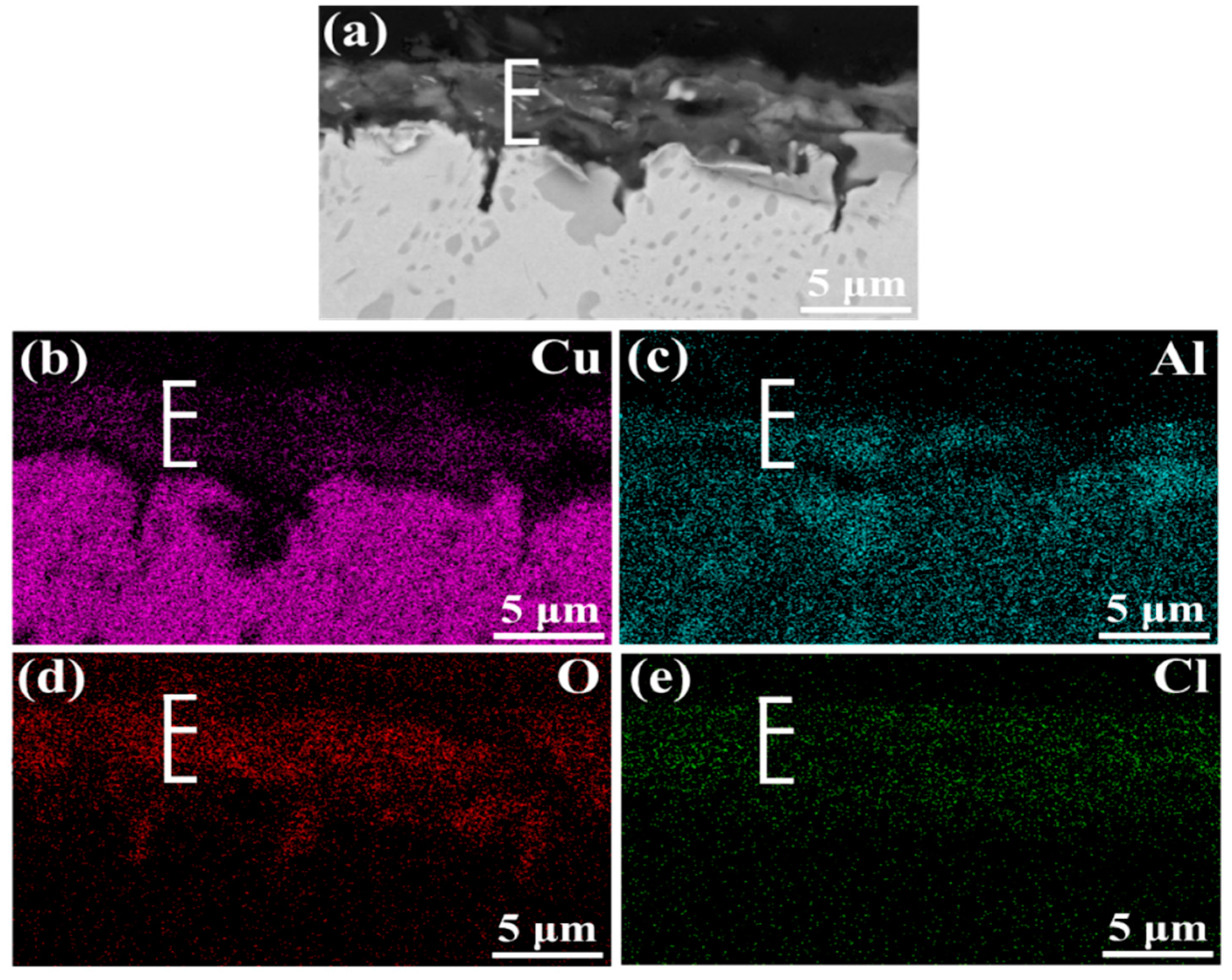
3.1. Morphology Observation
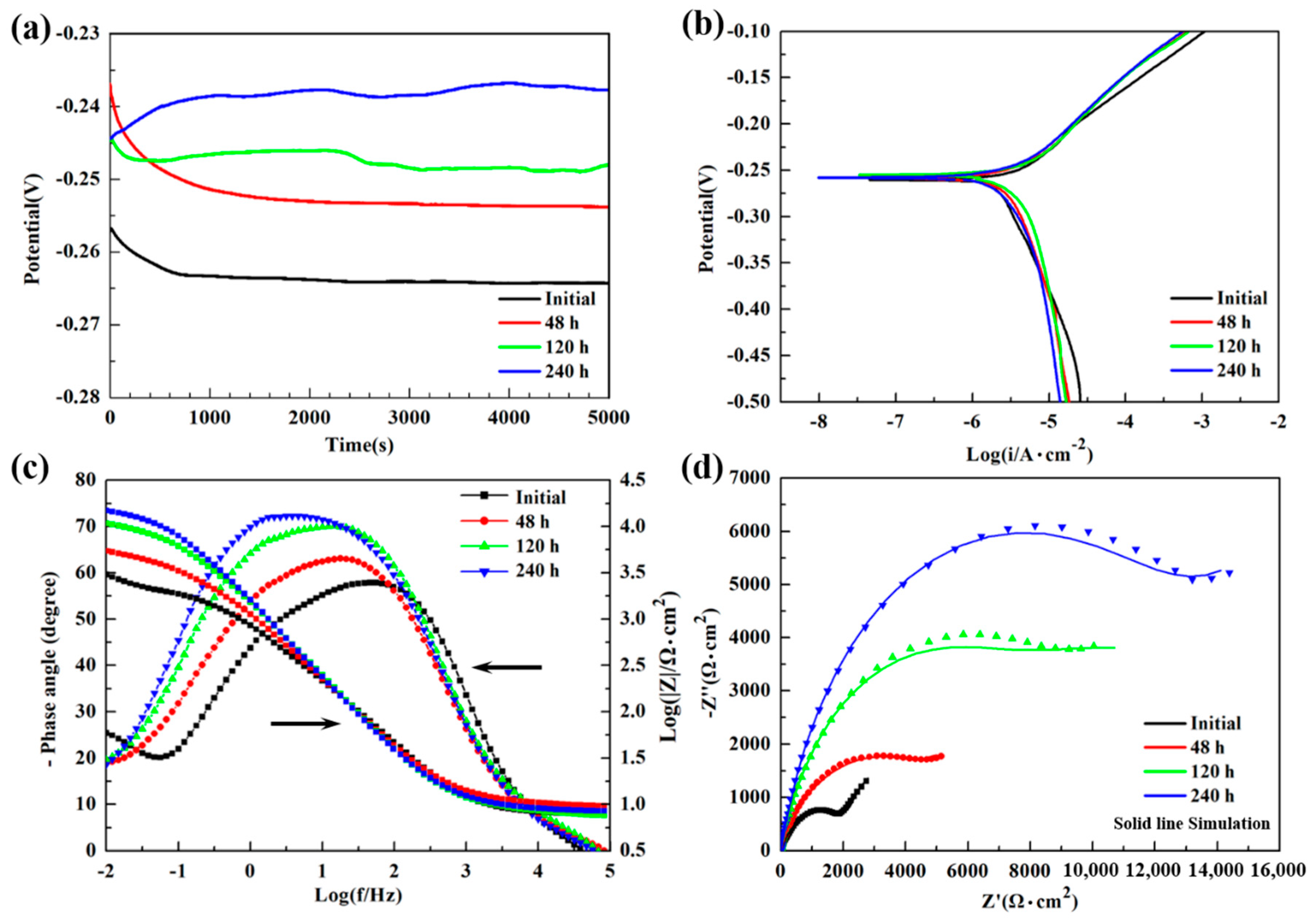
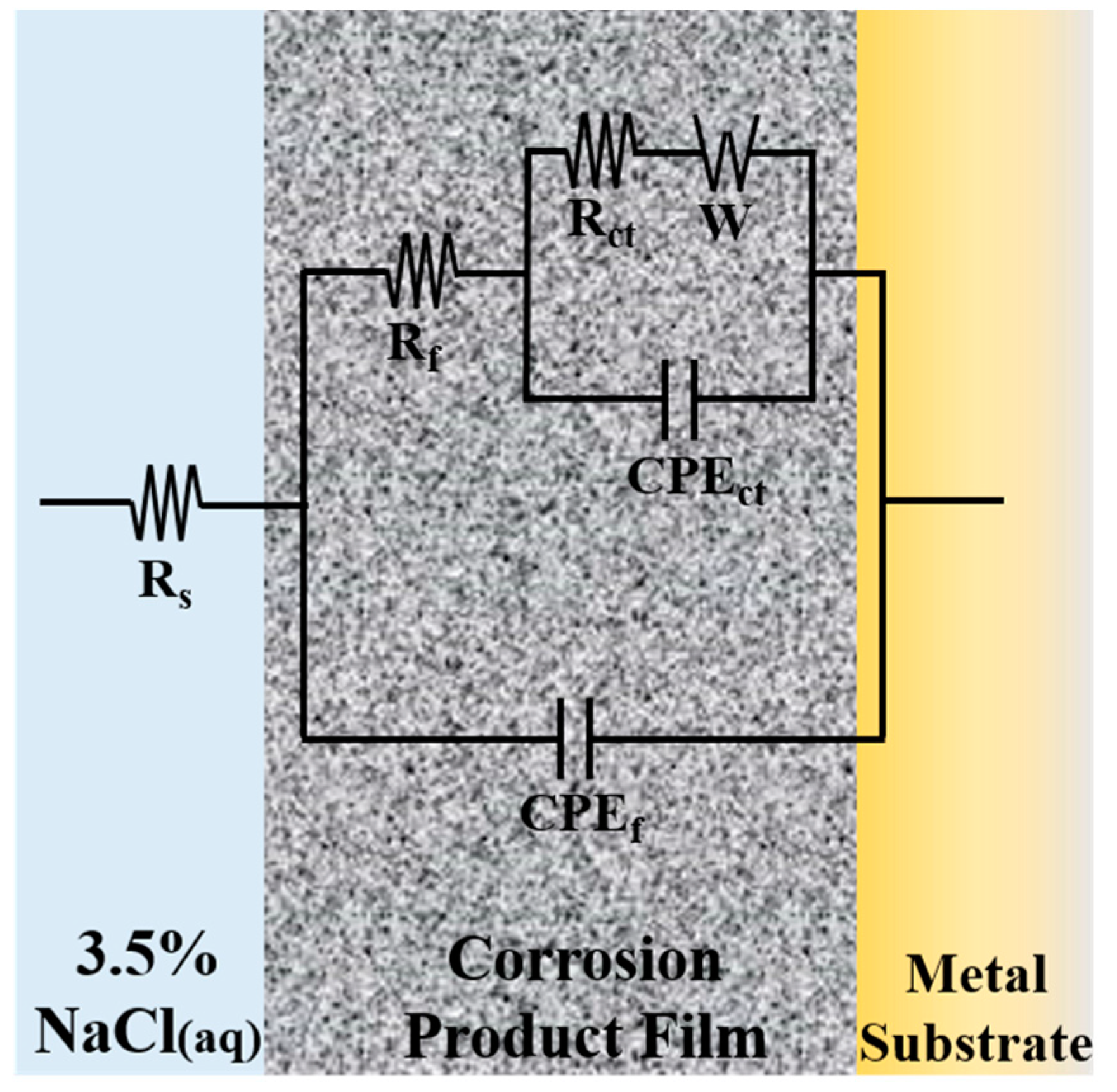
3.2. Electrochemical Measurements
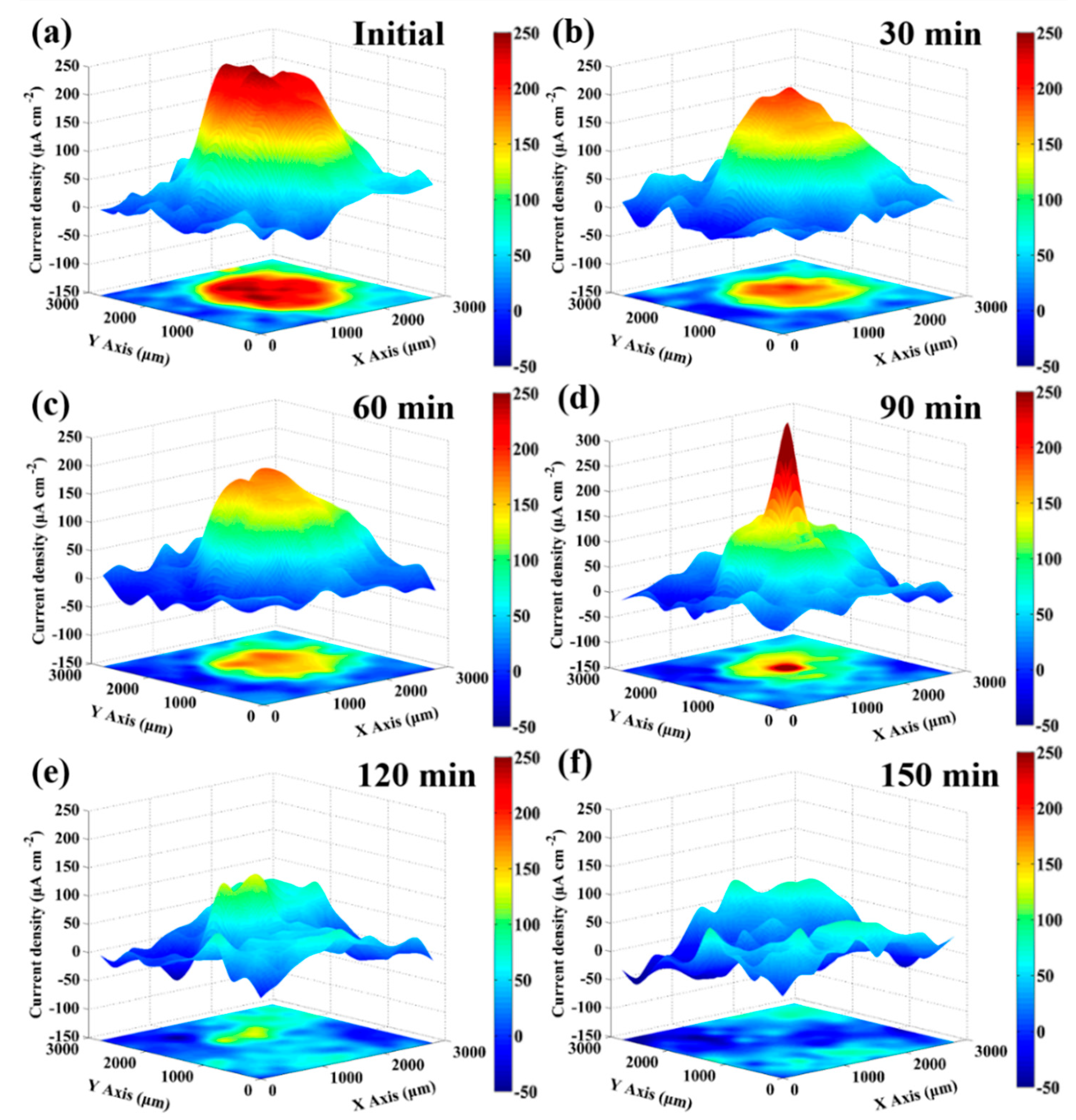
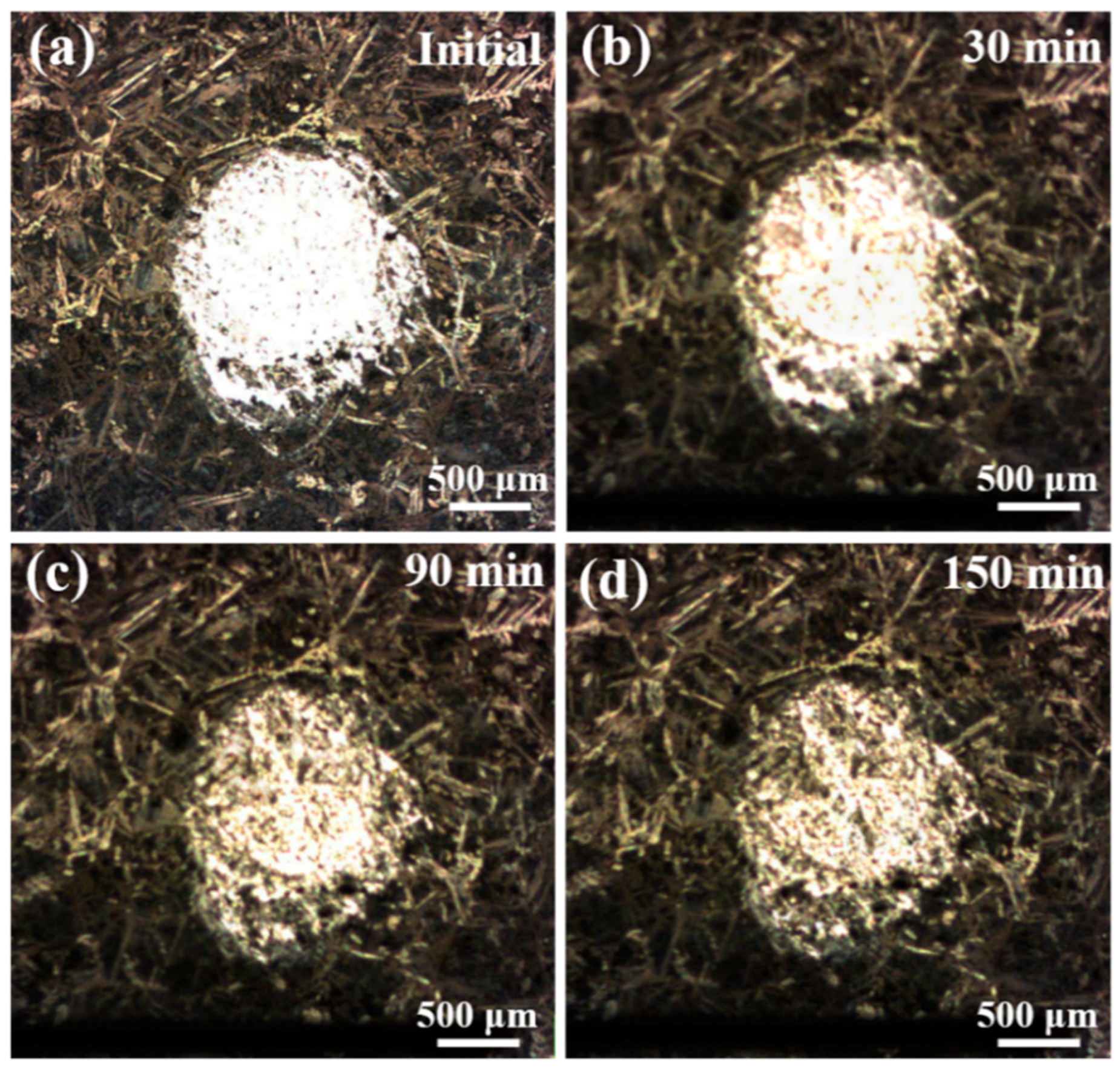
3.3. In-Situ SVET Measurements
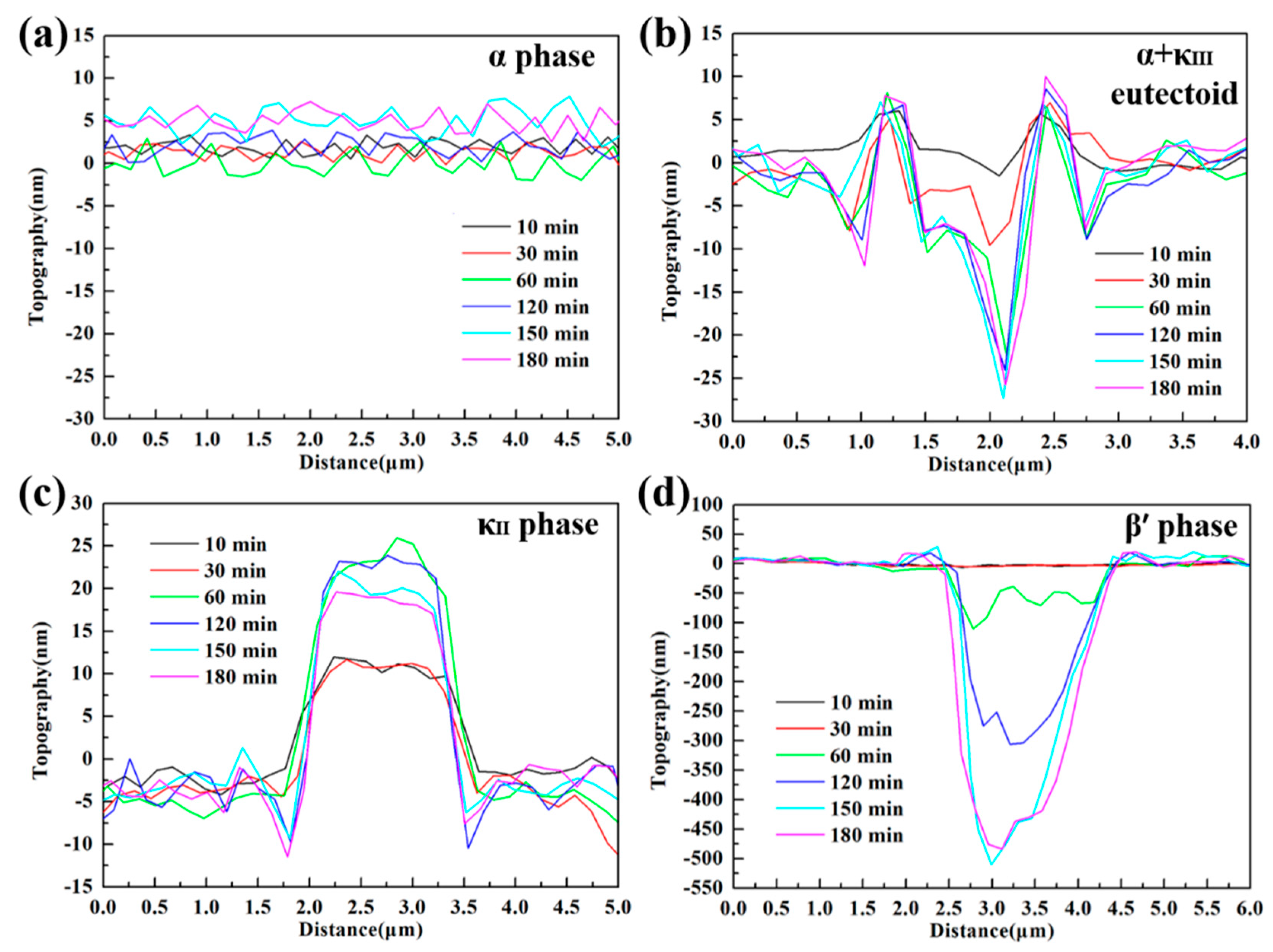
3.4. In-Situ AFM Measurements
4. Conclusions
- The corrosion resistance of NAB alloy is due to the protective film covered on the surface, avoiding the contact with corrosion medium and the transportation of ion and charge.
- Due to difference of location and chemical content, the lamellar α phase within the α + κIII eutectoid is corroded sharply, while the α phase far away from κ phases is well preserved.
- The κII and κIII phases present a remarkable corroded resistance as they form a stable and dense protective film within a short time when coming into contact with the corrosion medium. As a result of the metastable martensitic structure and the difficulty to form protective film, the β′ phase suffers the most serious corrosion damage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Culpan, E.A.; Rose, G. Microstructural characterization of cast nickel aluminium bronze. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanafrooz, A.; Hasan, F.; Lorimer, G.W.; Ridley, N. Microstructural development in complex nickel-aluminum bronzes. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1983, 14, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Jahanafrooz, A.; Lorimer, G.W.; Ridley, N. The morphology, crystallography, and chemistry of phases in as-cast nickel-aluminum bronze. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1982, 13, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantapong, J.; Uthaisangsuk, V.; Suranuntchai, S.; Manonukul, A. Effect of hot working on microstructure evolution of as-cast Nickel Aluminum Bronze alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.; Lorimer, G.; Ridley, N. Characterization of phases in a nickel-aluminium bronze. Met. Technol. 1980, 7, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorimer, G.; Hasan, F.; Iqbal, J.; Ridley, N. Observation of microstructure and corrosion behaviour of some aluminium bronzes. Br. Corros. J. 1986, 21, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Iqbal, J.; Ridley, N. Microstructure of as-cast aluminium bronze containing iron. Met. Sci. J. 1985, 1, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culpan, E.; Rose, G. Corrosion behaviour of cast nickel aluminium bronze in sea water. Br. Corros. J. 1979, 14, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, J.; Barik, R.; Kear, G.; Wood, R.; Stokes, K.; Walsh, F. The corrosion of nickel–aluminium bronze in seawater. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 3336–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.T.; Wang, L.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Han, Y.F.; Lu, W.J. Investigation of the microstructure and corrosion properties of friction stir processed cast NiAl bronze. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.N.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ni, D.R.; Ma, Z.Y. Characterization of the corrosion product films formed on the as-cast and friction-stir processed Ni-Al bronze in a 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Corrosion 2015, 71, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.N.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ni, D.R.; Ma, Z.Y. Studies of the nobility of phases using scanning Kelvin probe microscopy and its relationship to corrosion behaviour of Ni–Al bronze in chloride media. Corros. Sci. 2015, 92, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.B.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Shen, B.; Liu, L.; Hu, W.B. Microstructure design to improve the corrosion and cavitation corrosion resistance of a nickel-aluminum bronze. Corros. Sci. 2018, 138, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüssler, A.; Exner, H.E. The corrosion of nickel-aluminium bronzes in seawater—I. Protective layer formation and the passivation mechanism. Corros. Sci. 1993, 34, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wu, Z.; Qin, Z.B.; Liu, L.; Hu, W.B. Surface modification of nickel-aluminum bronze alloy with gradient Ni-Cu solid solution coating via thermal diffusion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, J.; Stokes, K. The influence of nickel–aluminium bronze microstructure and crevice solution on the initiation of crevice corrosion. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.B.; Wu, Z.; Zen, X.S.; Luo, Q.; Liu, L.; Lu, W.J.; Hu, W.B. Improving corrosion resistance of a nickel-aluminum bronze alloy via nickel ion implantation. Corrosion 2016, 72, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbaghzadeh, B.; Parvizi, R.; Davoodi, A.; Moayed, M. Corrosion evaluation of multi-pass welded nickel-aluminum bronze alloy in 3.5% sodium chloride solution: A restorative application of gas tungsten arc welding process. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, H.; Helal, N.; El-Rabiee, M.; Badawy, W. The role of Ni content on the stability of Cu–Al–Ni ternary alloy in neutral chloride solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Lv, Y.T.; Chen, K.; Zhao, B.J.; Han, Y.F.; Wang, L.Q.; Lu, W.J. Effects of Microstructure on the Stress Corrosion Cracking Behavior of Nickel-Aluminum Bronze Alloy in 3.5% NaCl Solution. Mat. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. 2018, 733, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateya, B.; Ashour, E.; Sayed, S. Corrosion of α-Al bronze in saline water. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfeld, F.; Liu, G.; Xiao, H.; Tsai, C.; Little, B. The corrosion behavior of copper alloys, stainless steels and titanium in seawater. Corros. Sci. 1994, 36, 2063–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, Y.F.; Liu, L.; Lv, W.J.; Hu, W.B. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution and erosion–corrosion behavior of a nickel–aluminum bronze alloy in chloride solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Lv, Y.T.; Zhao, B.J.; Han, Y.F.; Wang, L.Q.; Lu, W.J. Response relationship between loading condition and corrosion fatigue behavior of nickel-aluminum bronze alloy and its crack tip damage mechanism. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, J.; Stokes, K. Analysis of nickel–aluminium bronze crevice solution chemistry using capillary electrophoresis. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüssler, A.; Exner, H. The corrosion of nickel-aluminium bronzes in seawater—II. The corrosion mechanism in the presence of sulphide pollution. Corros. Sci. 1993, 34, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, L.; Fernandes, J.; Belo, M.D.; Ferreira, M.; Rosa, L.G. Anodising of Al 2024-T3 in a modified sulphuric acid/boric acid bath for aeronautical applications. Corros. Sci. 2003, 45, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.; Ismail, K.; Fathi, A. Effect of Ni content on the corrosion behavior of Cu–Ni alloys in neutral chloride solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 3603–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguzie, E.E.; Li, J.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, D.M.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, F.H. The effect of Cu addition on the electrochemical corrosion and passivation behavior of stainless steels. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5028–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.L.; Luo, H.Y.; Liang, T.X.; Guo, W.L. The effects of grain refinement and deformation on corrosion resistance of passive film formed on the surface of 304 stainless steels. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 896–907. [Google Scholar]
- Neodo, S.; Carugo, D.; Wharton, J.; Stokes, K. Electrochemical behaviour of nickel–aluminium bronze in chloride media: Influence of pH and benzotriazole. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 695, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Qiao, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.G. Corrosion properties of friction–stir processed cast NiAl bronze. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, M.; Balan, K. Failure of a nickel aluminium bronze (NAB) canned motor pump impeller working under polluted sea water–Influence of material selection, section thickness dependent microstructure and temper annealing heat treatment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 70, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.T.; Chen, R.P.; Zhang, W.W.; Luo, Z.Q.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of microstructure on the mechanical and corrosion behaviors of a hot-extruded nickel aluminum bronze. Acta Metall. Sin.-Engl. 2010, 23, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.B.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Shen, B.; Hu, W.B. Improving corrosion resistance of nickel-aluminum bronzes by surface modification with chromium ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 334, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, D.; Bayley, C.; Noren, B. Electrochemical monitoring of selective phase corrosion of nickel aluminum bronze in seawater. Corrosion 2008, 64, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phase | Cu | Al | Fe | Ni | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 85.4 | 8.2 | 2.9 | 2.4 | 1.1 |
| β′ | 84.5 | 8.6 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 1.0 |
| κII | 24.1 | 18.4 | 32.8 | 22.8 | 1.8 |
| κIII | 30.6 | 17.9 | 19.2 | 31.2 | 1.1 |
| Immersion Time | EOCP (V) | Ecorr (V) | icorr (μA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | −0.264 | −0.260 | 11.35 |
| 48 h | −0.253 | −0.258 | 5.32 |
| 120 h | −0.248 | −0.255 | 5.04 |
| 240 h | −0.237 | −0.257 | 3.78 |
| Immersion Time (h) | Rs (Ω·cm2) | CPEf (μF·cm−2) | nf | Rf (Ω·cm2) | CPEct (μF·cm−2) | nct | Rct (Ω·cm2) | W (Ω·s−1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7.924 | 163.12 | 0.6761 | 1761 | 121.27 | 0.8043 | 317.6 | 2660 |
| 48 | 9.901 | 620.98 | 0.7693 | 1943 | 187.72 | 0.7614 | 3698 | 5391 |
| 120 | 8.072 | 168.15 | 0.8384 | 6946 | 941.58 | 0.7048 | 10,362 | 6242 |
| 240 | 8.640 | 148.08 | 0.8712 | 11,976 | 1234.8 | 0.6466 | 35,939 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Zhao, R.; Qin, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, W. Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020209
Ding Y, Zhao R, Qin Z, Wu Z, Wang L, Liu L, Lu W. Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution. Materials. 2019; 12(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yang, Rong Zhao, Zhenbo Qin, Zhong Wu, Liqiang Wang, Lei Liu, and Weijie Lu. 2019. "Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution" Materials 12, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020209
APA StyleDing, Y., Zhao, R., Qin, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, L., Liu, L., & Lu, W. (2019). Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution. Materials, 12(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020209





