Weibull Statistical Analysis of Strength Fluctuation for Failure Prediction and Structural Durability of Friction Stir Welded Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints Correlated to Metallurgical Bonded Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
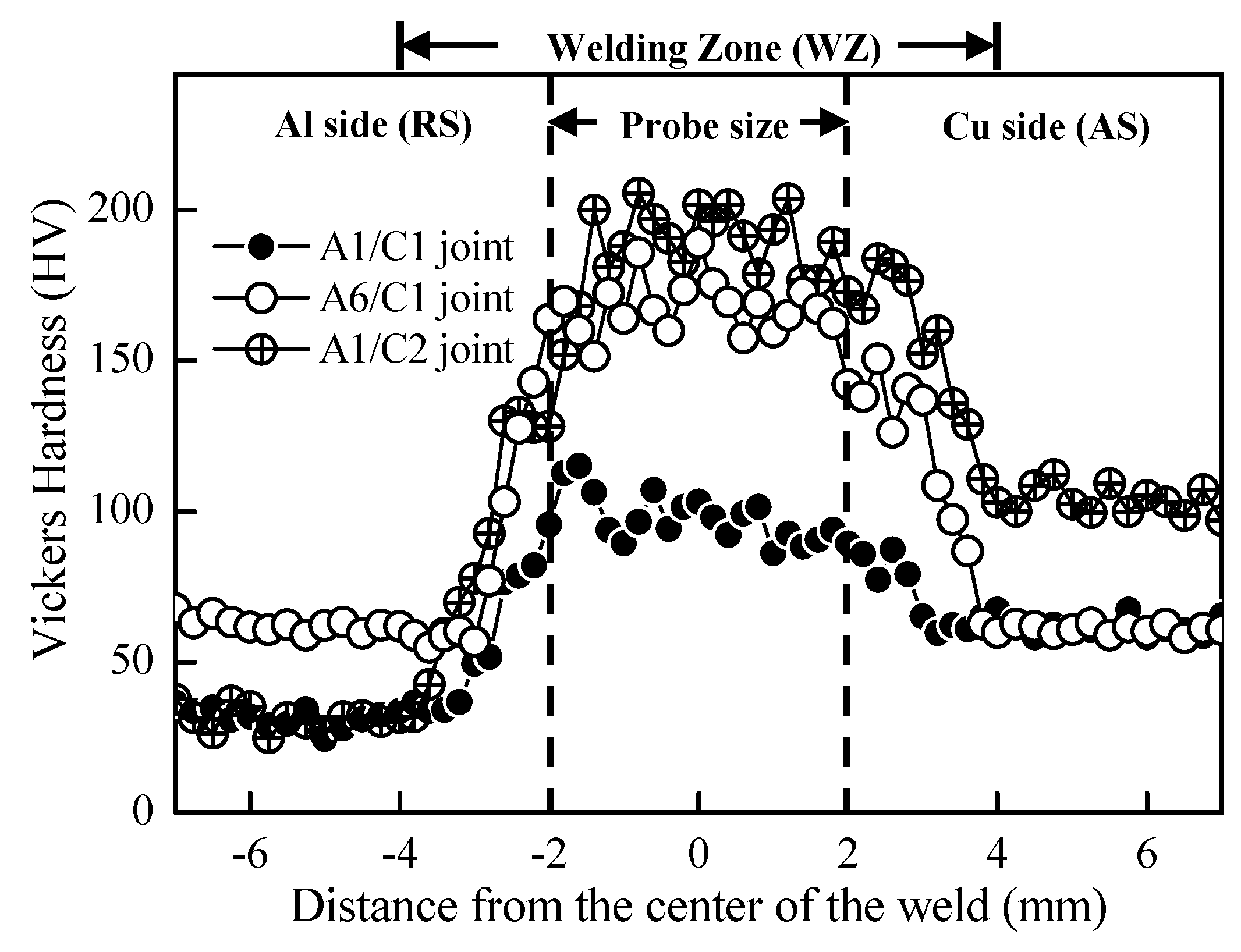
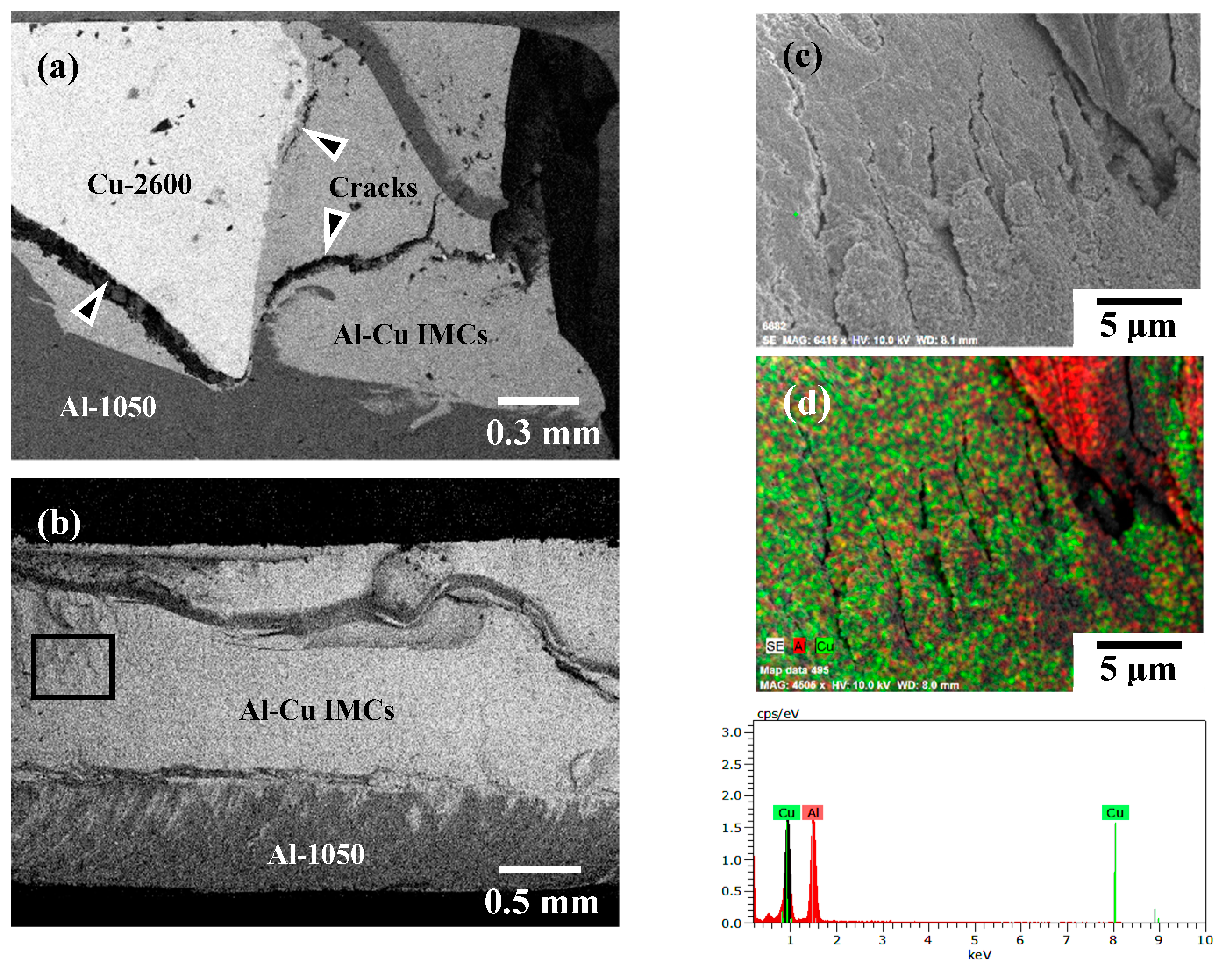
3.1. Microstructures and Microhardness Variation of FSW Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints
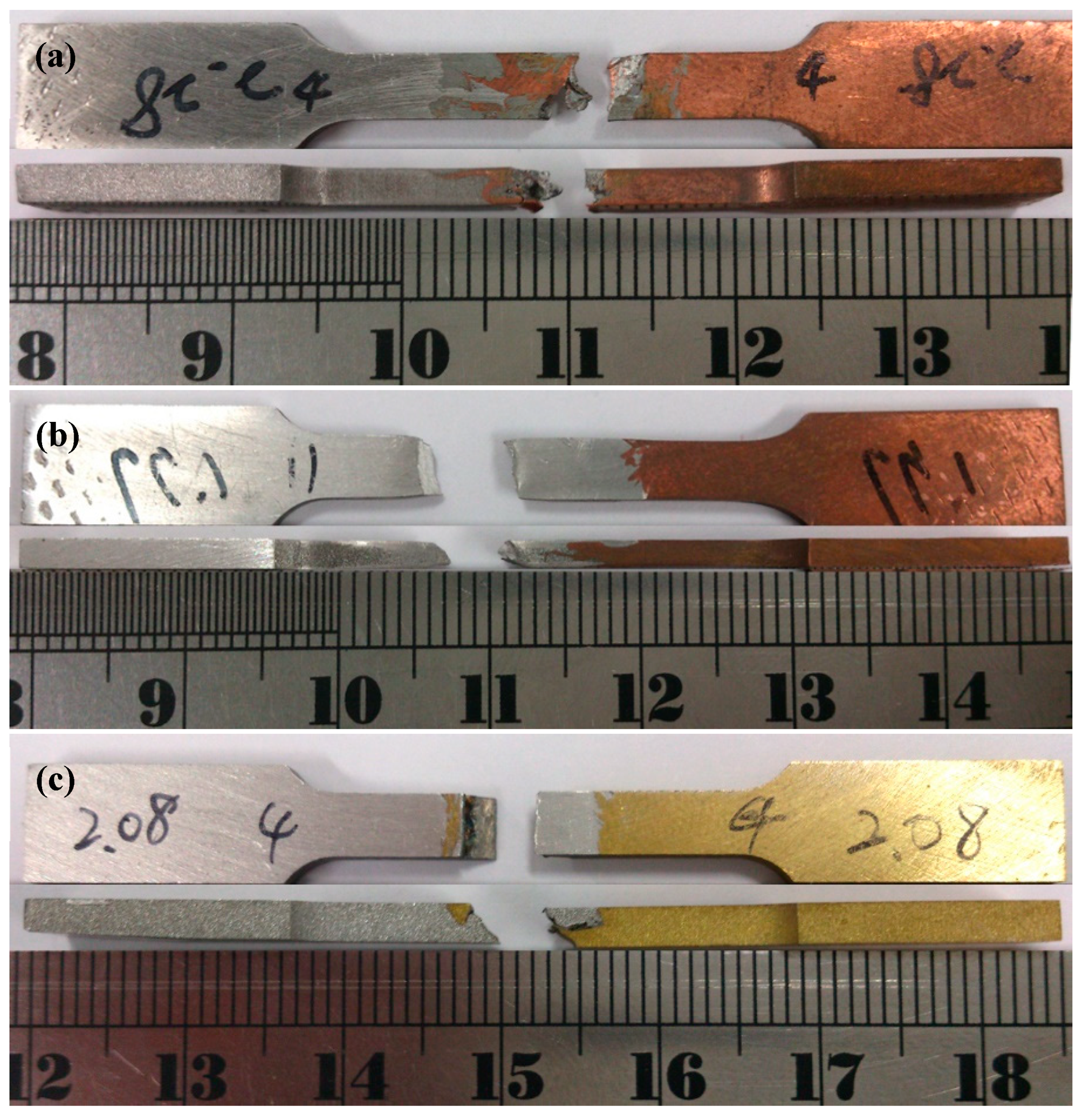
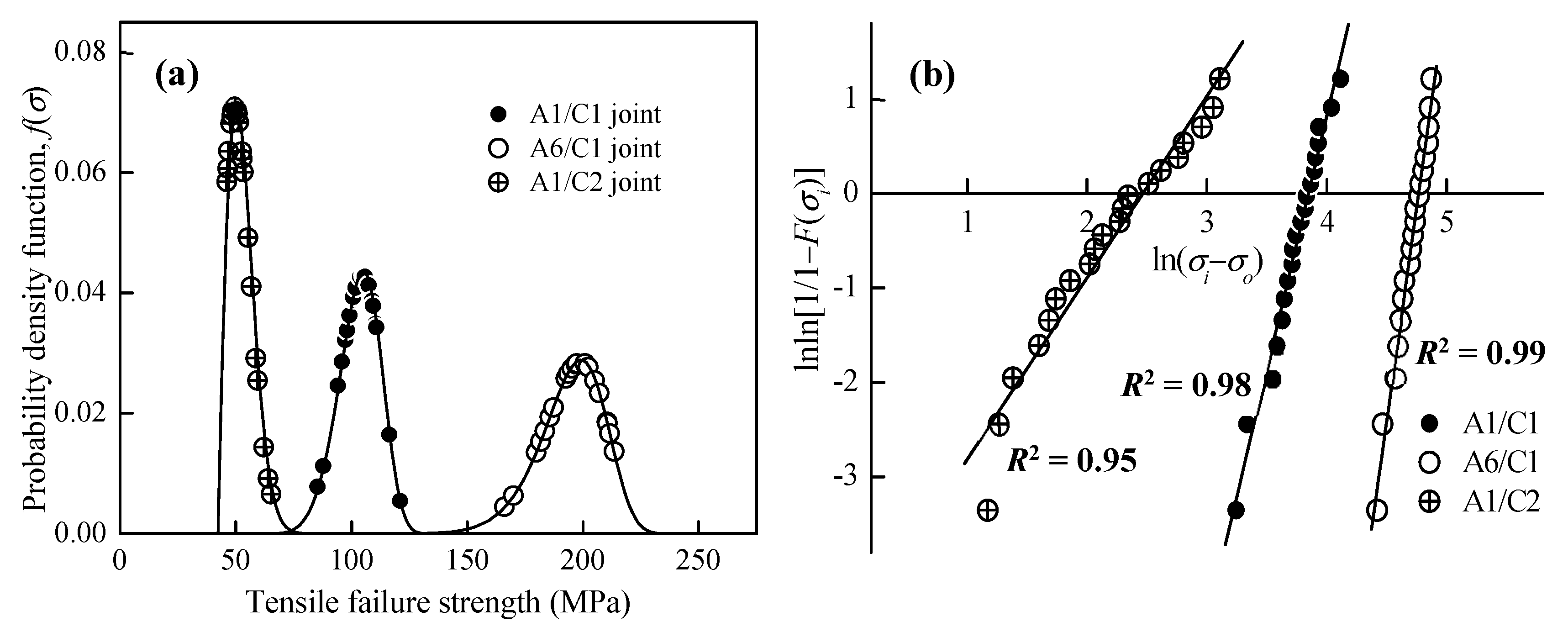
3.2. Tensile Failure Strength of FSW Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints
4. Discussion
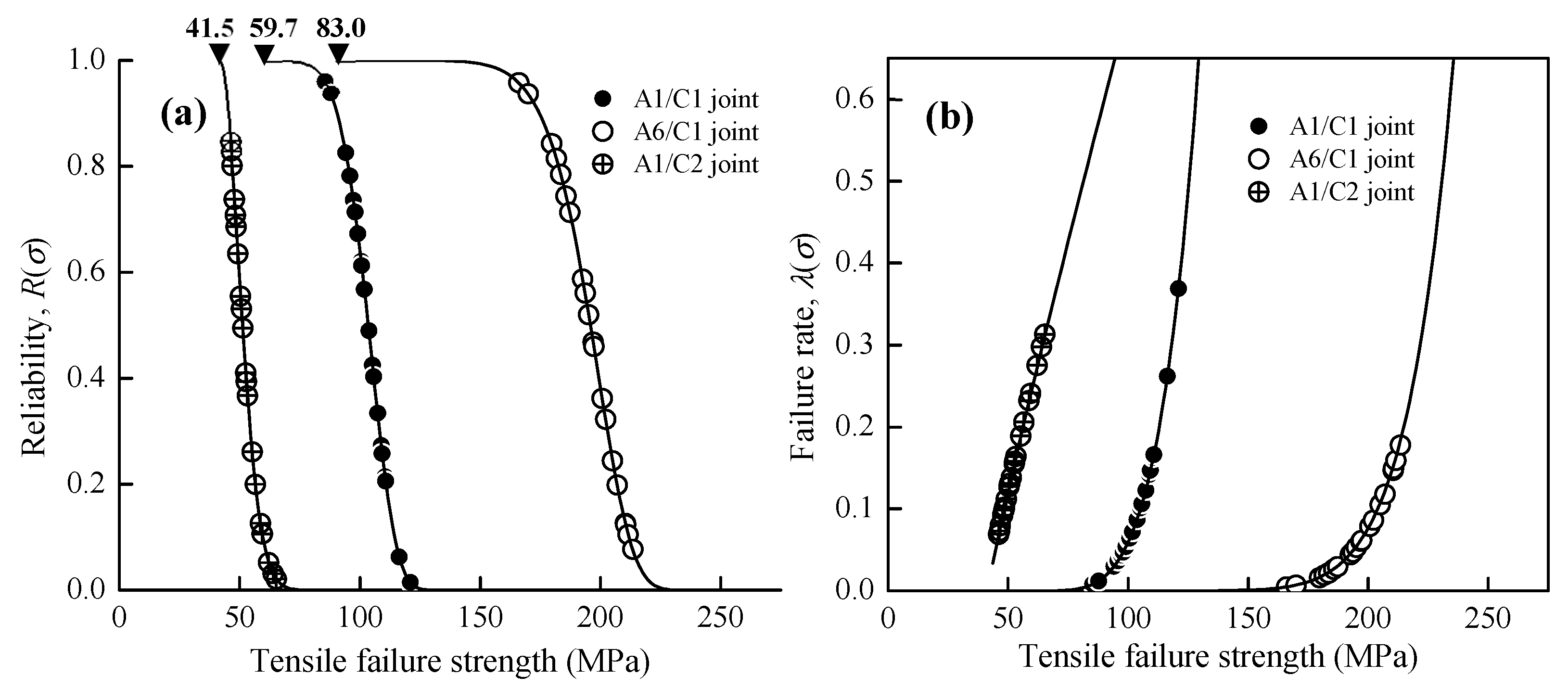
4.1. The Weibull Statistical Analysis on the Failure Probability of Al–Cu Joints
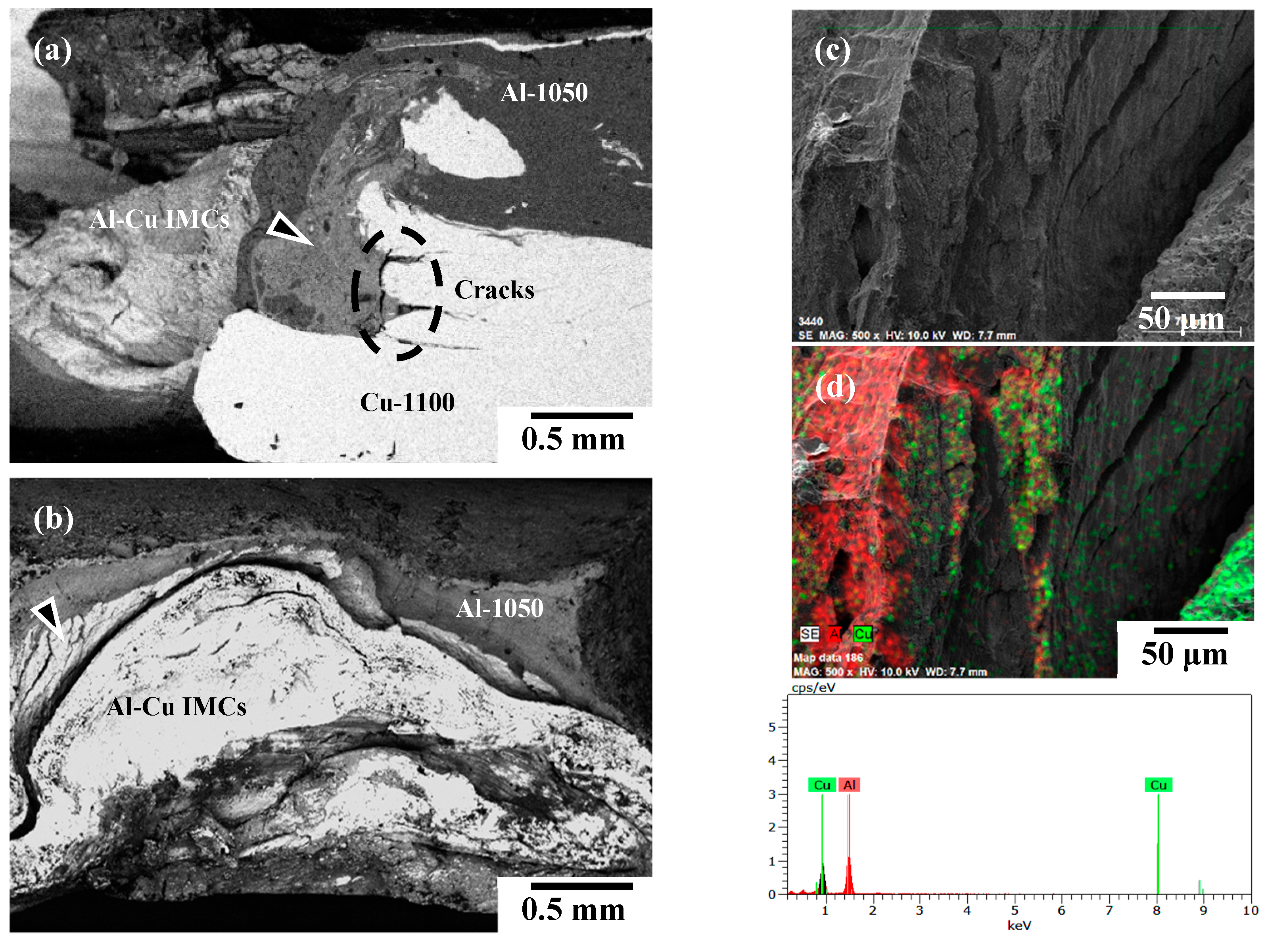
4.2. Microstructural Variations Affect Data Fluctuation and Failure Behaviors
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Dissimilar Al–Cu joints of AA1050H/C1100-Cu (A1/C1), AA6061-T6/C1100-Cu (A6/C1), and AA1050H/C2600-brass (A1/C2) couples are successfully joined without typical cavity defects in the welding zone (WZ) by the friction stir welding process (FSW).
- (2)
- Al2Cu and Al4Cu9 are the major intermetallic compounds (IMCs) formed in the metallurgical bonded welding zone of FSW Al–Cu dissimilar joints, and γ-Cu5Zn8 is another reacted IMC observed in the WZ of the AA1050H/C2600-brass joint.
- (3)
- The microhardness of FSW Al–Cu joints in the WZ is increased as a result of the formation of Al–Cu IMCs and intense plastic deformation during FSW.
- (4)
- The AA6061-T6/C1100-Cu joint exhibits a significant metallurgical bonded zone with onion rings in the WZ region, whereas the AA1050H/C2600-brass joint usually displays a mechanical kissing bonded boundary at the Al–Cu joining interface.
- (5)
- Through the powerful statistical analysis of the Weibull model, FSW Al–Cu dissimilar joints, which display a wear-out failure model, can be recognized as reliable joints for further engineering applications.
- (6)
- Better welding reliability and a higher tensile strength with ductile dimpled ruptures can be obtained for those FSW Al–Cu joints with IMCs particles uniformly dispersed in a large area fraction of the metallurgical bonded WZ region.
- (7)
- FSW Al–Cu joints with a mechanical kissing bonded boundary and a thick continuous interfacial IMC layer results in a rapid increase in the failure probability and the deterioration of tensile strength with a brittle fracture at the WZ region of the joints.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.T.; Wang, G.Z.; Xuan, F.Z.; Liu, C.J.; Tu, S.T. Local mechanical properties of a dissimilar metal welded joint in nuclear power systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 568, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feistauer, E.E.; Bergmann, L.A.; Barreto, L.S.; Dos Santos, J.F. Mechanical behaviour of dissimilar friction stir welded tailor welded blanks in Al-Mg alloys for Marine applications. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Liu, L. Interface microstructure and mechanical properties of arc spot welding Mg-steel dissimilar joint with Cu interlayer. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Robson, J.D.; Ciuca, O.; Prangnell, P.B. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of high power ultrasonic spot welded aluminum alloy AA6111-Ti6Al4V dissimilar joints. Mater.Charact. 2014, 97, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesha, C.B. Dissimilar friction stir welding between aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy at a low rotational speed. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yang, F. Microstructures and mechanical behavior of aluminum-copper lap joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 705, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, W.; Dong, L.; Shi, Y.; Jiu, J.; Fu, Y.Q. Interfacial bonding mechanism and annealing effect on Cu-Al joint produced by solid-liquid compound casting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, B.; Yang, J.W.; Liu, J. Modeling of resistance heat assisted ultrasonic welding of Cu-Al joint. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 256, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarwitz, M.; Fetzer, F.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Weld seam geometry and electrical resistance of laser-welded aluminum-copper dissimilar joints produced with spatial beam oscillation. Metals 2018, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Li, X.G.; Wang, C.G. Influence of diffusion brazing parameters on microstructure and properties of Cu/Al joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 35, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Friction stir welding of dissimilar alloys—A perspective. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D.; Needham, J.C.; Murch, M.G.; Templesmith, P.; Dawes, C.J. Friction Welding. Patent Application No. 9125978.8, 6 December 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Anouma, M.; Nakata, K. Dissimilar metal joining of ZK60 magnesium alloy and titanium by friction stir welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yan, K.; Huang, L. Microstructural characterizations and mechanical properties in under water friction stir welding of aluminum and magnesium dissimilar alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidy, M.; Baharudin, B.H.T.; Paslar, S.; Matori, K.A.; Sulaiman, S.; Fadaeifard, F. Multi-objective optimization of friction stir welding process parameters of AA6061-T6 and AA7075-T6 using a biogeography based optimization algorithm. Materials 2017, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Li, T.; Yu, J.; Liu, L. A review of bonding immiscible Mg/steel dissimilar metals. Materials 2018, 11, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, C. Microstructure evolution during dissimilar friction stir welding of AA7003-T4 and AA6060-T4. Materials 2018, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, N.; Harms, A.; Deringer, J.; Fricke, A.; Böhm, S. Dissimilar friction stir butt welding of aluminum and copper with cross-section adjustment for current-carrying components. Metals 2018, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Givi, M.K.B.; Rajani, H.R.Z. A metallurgical and mechanical study on dissimilar friction stir welding of aluminum 1050 to brass (CuZn30). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7093–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, I.; Loureiro, A.; Verdera, D.; Gesto, D.; Rodrigues, D.M. Influence of tool offsetting on the structure and morphology of dissimilar aluminum to copper friction-stir welds. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 5096–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisadi, H.; Tavakoli, A.; Sangsaraki, M.T.; Sangsarki, K.T. The influences of rotational and welding speeds on microstructures and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al5083 and commercially pure copper sheets lap joints. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Pal, S.; Pal, S.K.; Jain, R. Influence of plate position, tool offset and tool rotational speed on mechanical properties and microstructures of dissimilar Al/Cu friction stir welding joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 235, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei Zoeram, A.; Mousavi Anijdan, S.H.; Jafarian, H.R.; Bhattacharjee, T. Welding parameters analysis and microstructural evolution of dissimilar joints in Al/Bronze processed by friction stir welding and their effect on engineering tensile behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 687, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regensburg, A.; Schürer, R.; Weigl, M.; Bergmann, J.P. Influence of pin length and electrochemical platings on the mechanical strength and macroscopic defect formation in stationary shoulder friction stir welding of aluminum to copper. Metals 2018, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, R. Dissimilar friction stir welding of 6061 Al to T2 pure Cu adopting tooth-shaped joint configuration: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 690, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, G.H.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhou, W.L.; He, W.X.; Huang, Y.X.; Song, X.G. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir spot welded dissimilar aluminum-copper joint. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Yarrapareddy, E.; Kovacevic, R. Microstructural evolution in the friction stir welded 6061 aluminum alloy (T6-temper condition) to copper. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 172, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Xiao, B.L.; Ni, D.R.; Ma, Z.Y. Enhanced mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar Al-Cu joint by intermetallic compounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 5723–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Shen, J.J.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Liu, C.; Kuang, L.Y. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of friction stir welded joints of aluminum alloy to copper. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, I.; Oliveira, J.C.; Loureiro, A.; Rodrigues, D.M. Formation and distribution of brittle structures in friction stir welding of aluminum and copper: Influence of process parameters. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, I.; Oliveira, J.C.; Loureiro, A.; Rodrigues, D.M. Formation and distribution of brittle structures in friction stir welding of aluminum and copper: Influence of shoulder geometry. Intermetallics 2012, 22, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, H.L.; Huang, W.S. Influence of interfacial structure development on the fracture mechanism and bond strength of aluminum/copper bimetal plate. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.; Kleyner, A. Practical Reliability Engineering, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 78–140. ISBN 978-0-470-97981-5. [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, W. A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. J. Appl. Mech. 1951, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.W. Development of hydrothermally synthesized hydroxyapatite coatings on metallic substrates and Weibull’s reliability analysis of its strength. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2015, 12, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effertz, P.S.; Infante, V.; Quintino, L.; Suhuddin, U.; Hanke, S.; Dos Santos, J.F. Fatigue life assessment of friction spot welded 7075-T76 aluminum alloy using Weibull distribution. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 87, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacha, L.; Karolczuk, A. Validation of the weakest link approach and the proposed Weibull based probability distribution of failure for fatigue design of steel welded joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 67, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérot, N.; Bousquet, N. Functional Weibull-based models of steel fracture toughness for structural risk analysis: Estimation and selection. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 165, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C.; Tang, A. Mechanical behavior and Weibull statistics based failure analysis of vanadium flow battery stacks. J. Power Sources 2019, 412, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.G.; Dai, J.Y.; Tong, H.Y.; Ding, B.Z.; Song, Q.H.; Hu, Z.Q. Interfacial reactions on annealing Cu/Al multilayer thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 6165–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, B.; Nolan, D. Reliability Engineering Handbook (Quality and Reliability), 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 33–63. ISBN 978-0-824-70364-6. [Google Scholar]
- Faucher, B.; Tyson, W.R. On the determination of Weibull parameters. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1988, 7, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, R.B. The New Weibull Handbook: Reliability and Statistical Analysis for Predicting Life, Safety, Survivability, Risk, Cost and Warranty Claims, 4th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing Books: North Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 3-1–3-9. ISBN 0-9653062-1-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.J.; Kao, P.W.; Ho, N.J. Ultrafine-grained Al-Al2Cu composite produced in situ by friction stir processing. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
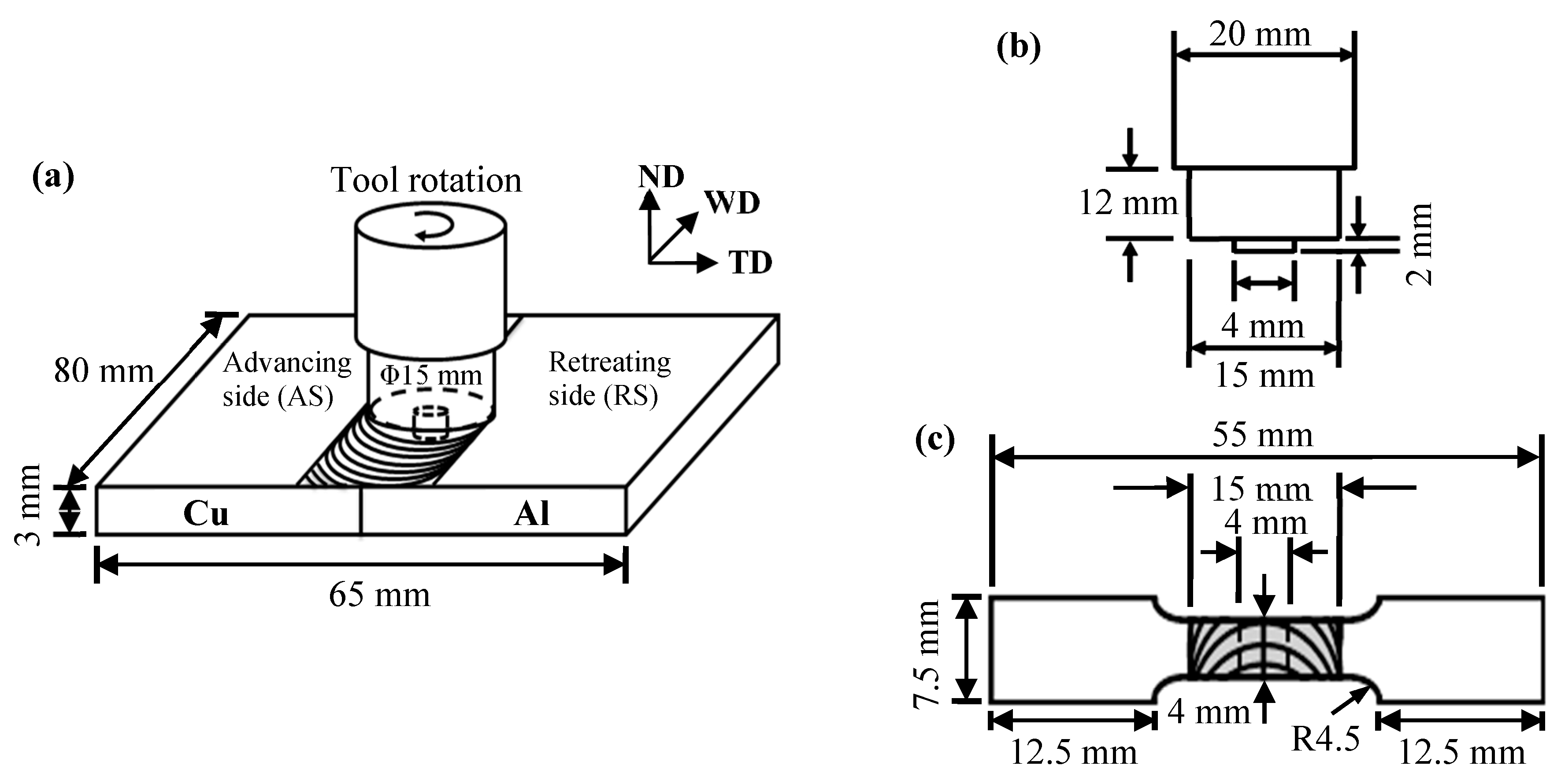
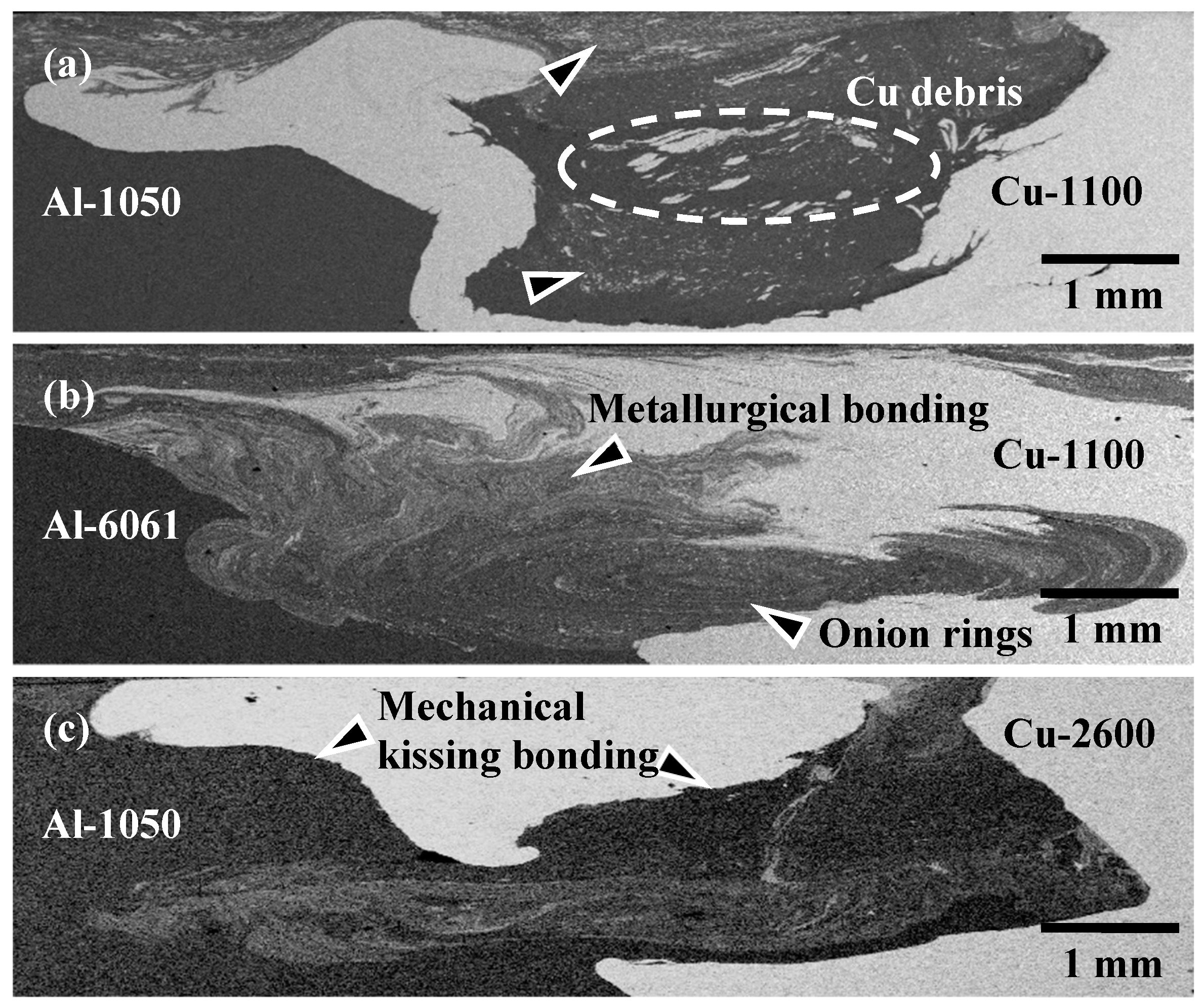
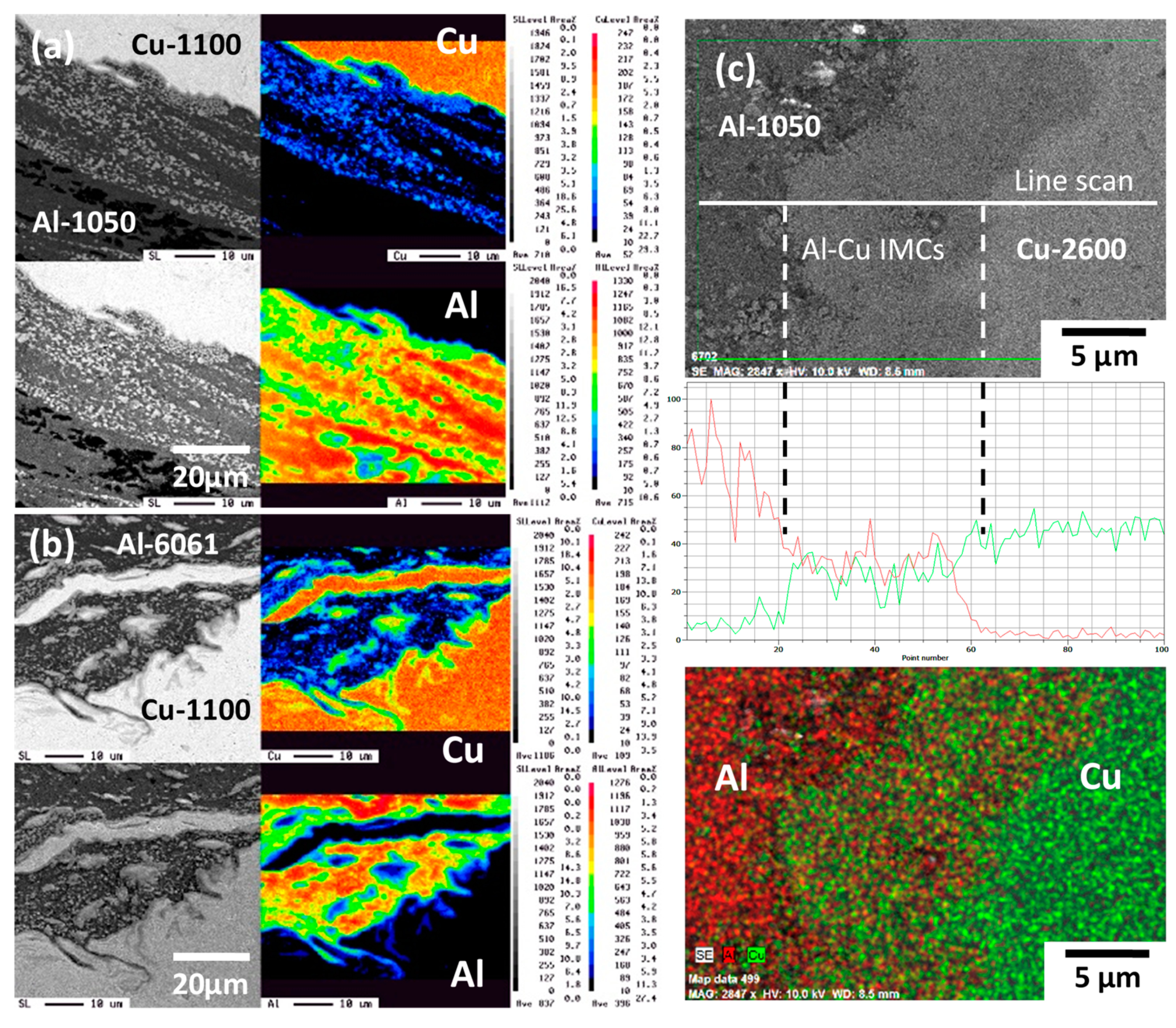
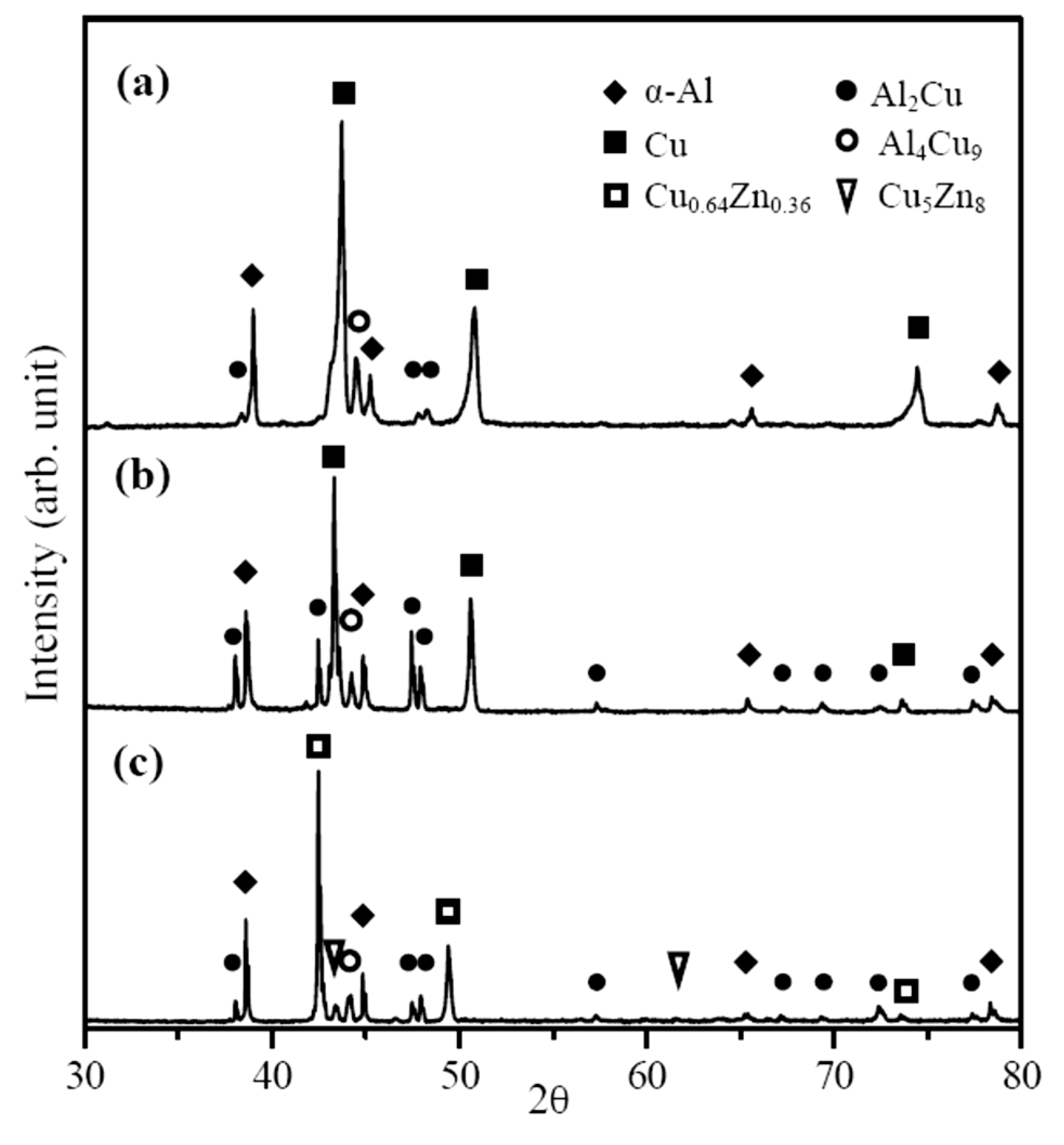


| Cu Base Metals | Cu | Zn | Pb | Fe | Si | Mg | Al | ||||
| C1100 (Pure Cu) | Bal. | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | - | 0.02 | ||||
| C2600 (brass) | 69.3 | Bal. | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.02 | ||||
| Al Base Metals | Al | Mg | Si | Fe | Mn | Cr | Cu | Zn | Ti | ||
| AA1050H | Bal. | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.05 | - | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | ||
| AA6061-T6 | Bal. | 1.03 | 0.66 | 0.35 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.02 | ||
| Samples | TensileStrength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AA1050H * | 121.8 ± 2.3 | 15.2±1.7 |
| AA6061-T6 * | 293.1 ± 2.6 | 12.8± 2.5 |
| C1100 Cu * | 227.9 ± 1.8 | 30.6 ± 1.8 |
| C2600 Brass * | 365.2 ± 1.5 | 27.7 ± 2.3 |
| A1/C1 Joint † | 108.6 ± 9.1 | 10.5 ± 3.3 |
| A6/C1 Joint † | 212.7 ± 8.5 | 22.3 ± 2.8 |
| A1/C2 Joint † | 53.2 ± 5.9 | 5.7 ± 0.9 |
| Samples | Weibull Modulus, m | Characteristics Strength (MPa), σc | Minimum Strength (MPa), σ0 | Coefficient of Determination, R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1/C1 Joint | 5.4 | 46.9 | 59.7 | 0.98 |
| A6/C1 Joint | 9.2 | 117.5 | 83.0 | 0.99 |
| A1/C2 Joint | 1.7 | 11.7 | 41.5 | 0.95 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.-W.; Jiang, S.-J. Weibull Statistical Analysis of Strength Fluctuation for Failure Prediction and Structural Durability of Friction Stir Welded Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints Correlated to Metallurgical Bonded Characteristics. Materials 2019, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020205
Yang C-W, Jiang S-J. Weibull Statistical Analysis of Strength Fluctuation for Failure Prediction and Structural Durability of Friction Stir Welded Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints Correlated to Metallurgical Bonded Characteristics. Materials. 2019; 12(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chung-Wei, and Shiau-Jiun Jiang. 2019. "Weibull Statistical Analysis of Strength Fluctuation for Failure Prediction and Structural Durability of Friction Stir Welded Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints Correlated to Metallurgical Bonded Characteristics" Materials 12, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020205
APA StyleYang, C.-W., & Jiang, S.-J. (2019). Weibull Statistical Analysis of Strength Fluctuation for Failure Prediction and Structural Durability of Friction Stir Welded Al–Cu Dissimilar Joints Correlated to Metallurgical Bonded Characteristics. Materials, 12(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020205





