Preparation of Reswellable Amorphous Porous Celluloses through Hydrogelation from Ionic Liquid Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
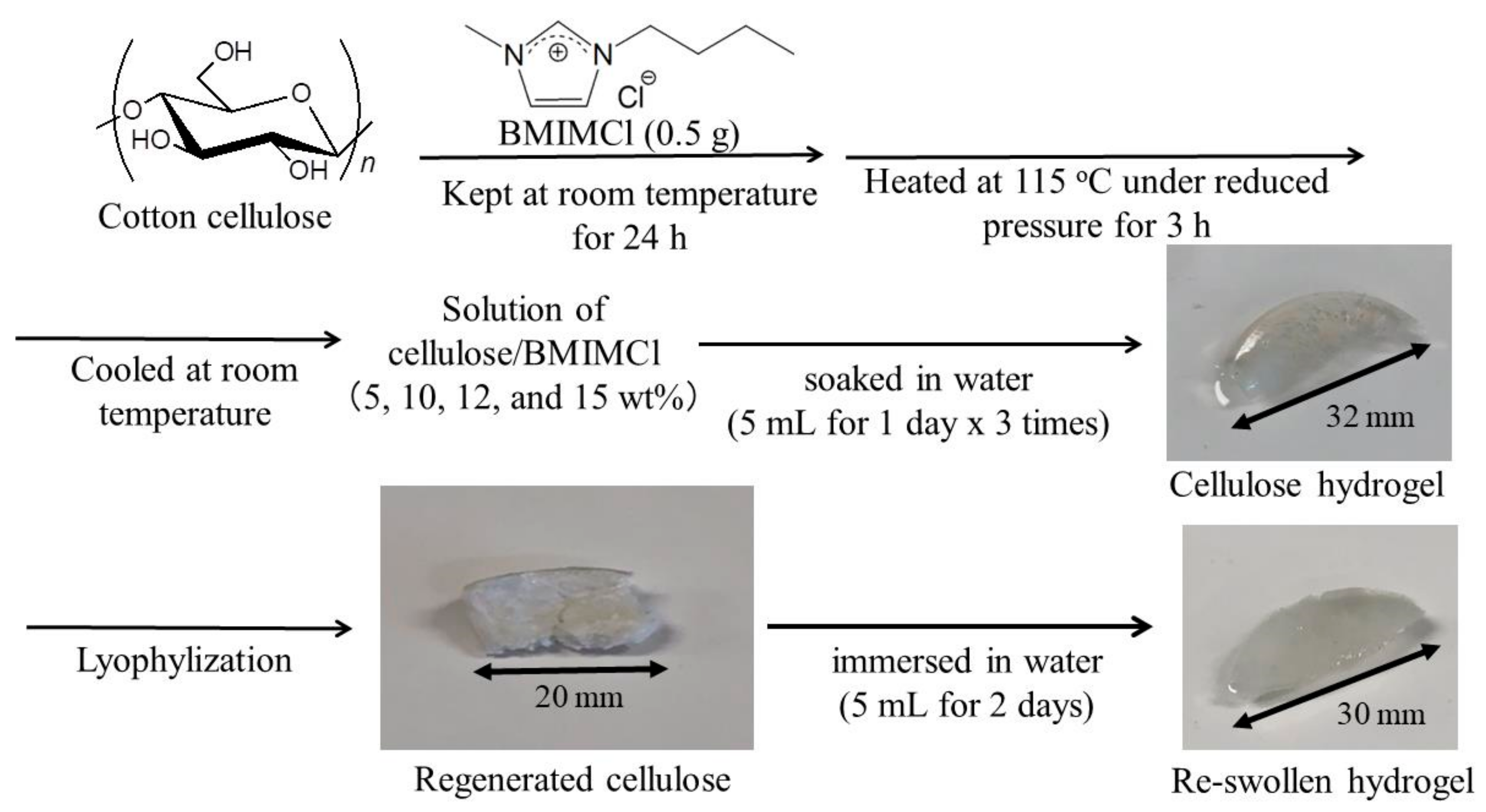
2.2. Preparation of Cellulose Hydrogels
2.3. Preparation of Porous Celluloses and Their Reswelling Experiment
2.4. Regeneration from Cellulose/BMIMCl Solutions Using Acetonitrile
2.5. Measurement
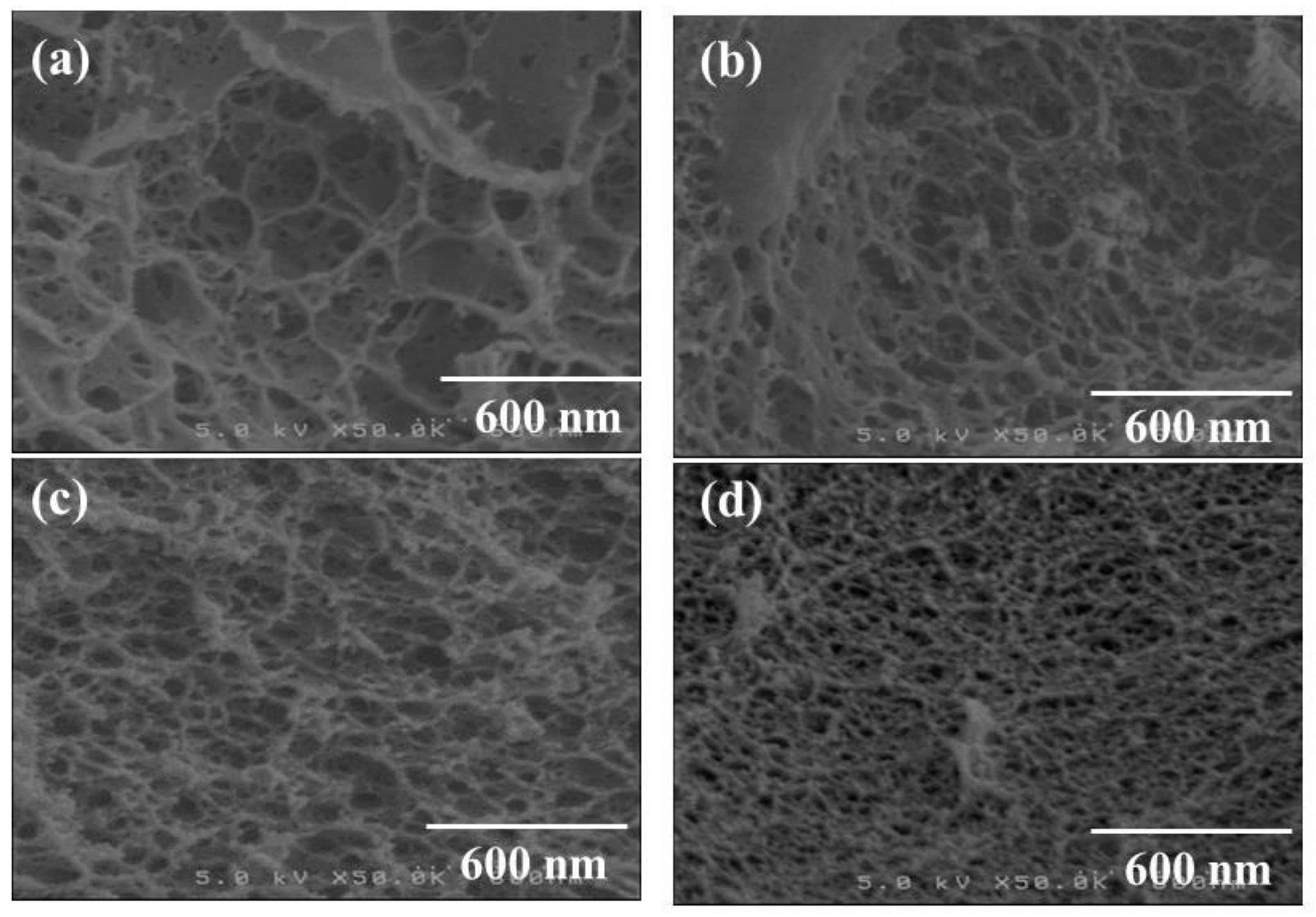
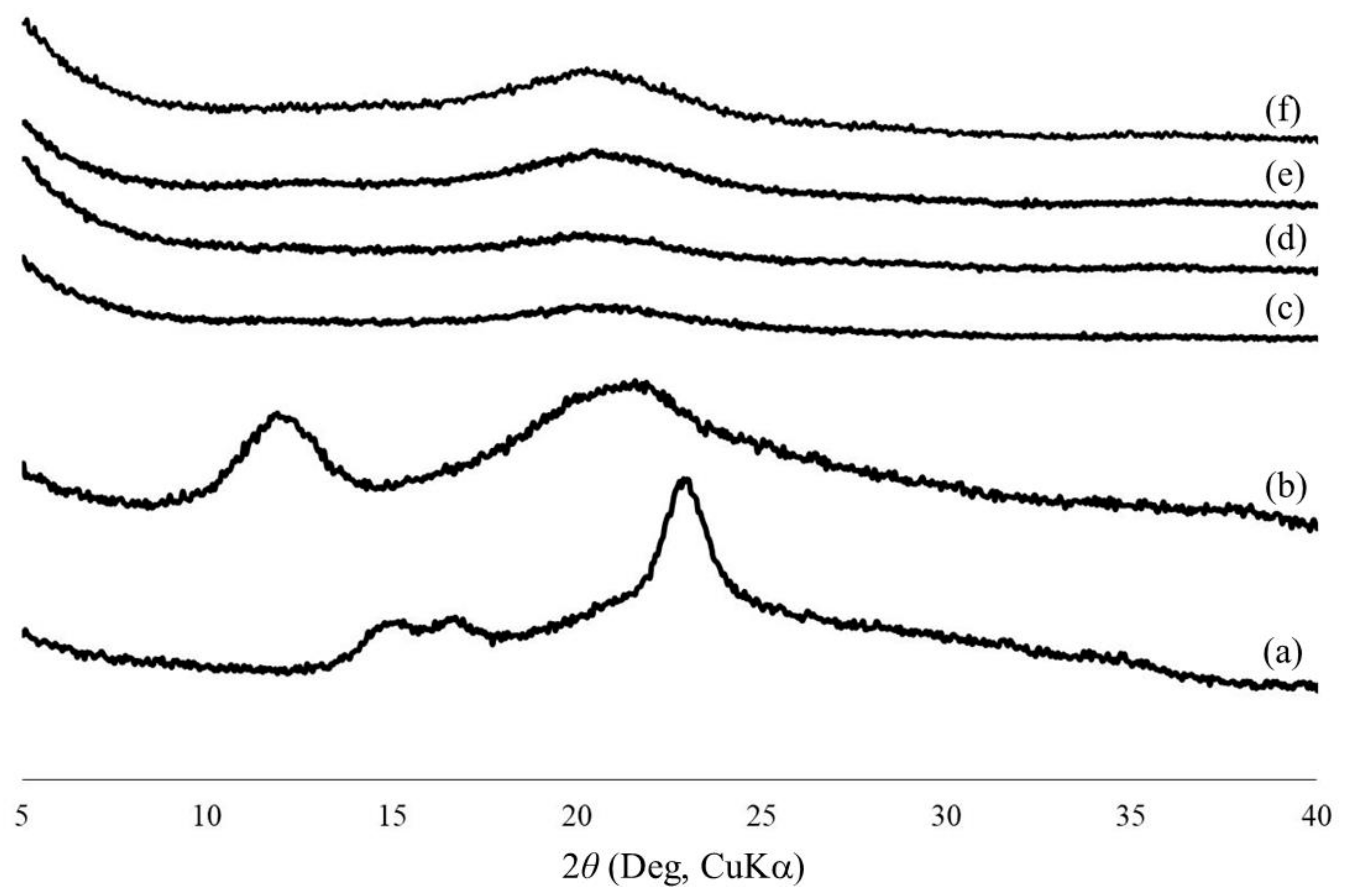
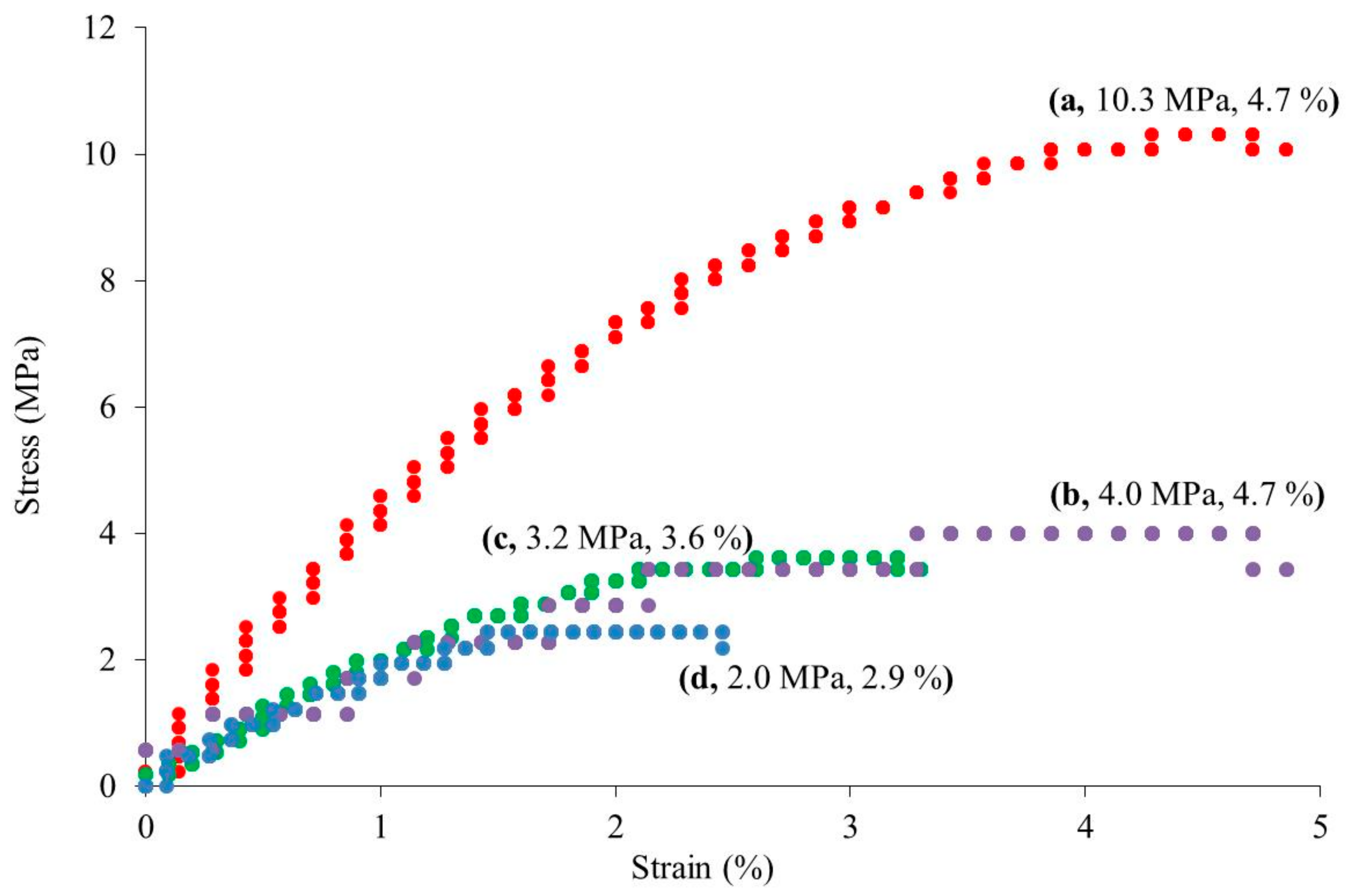
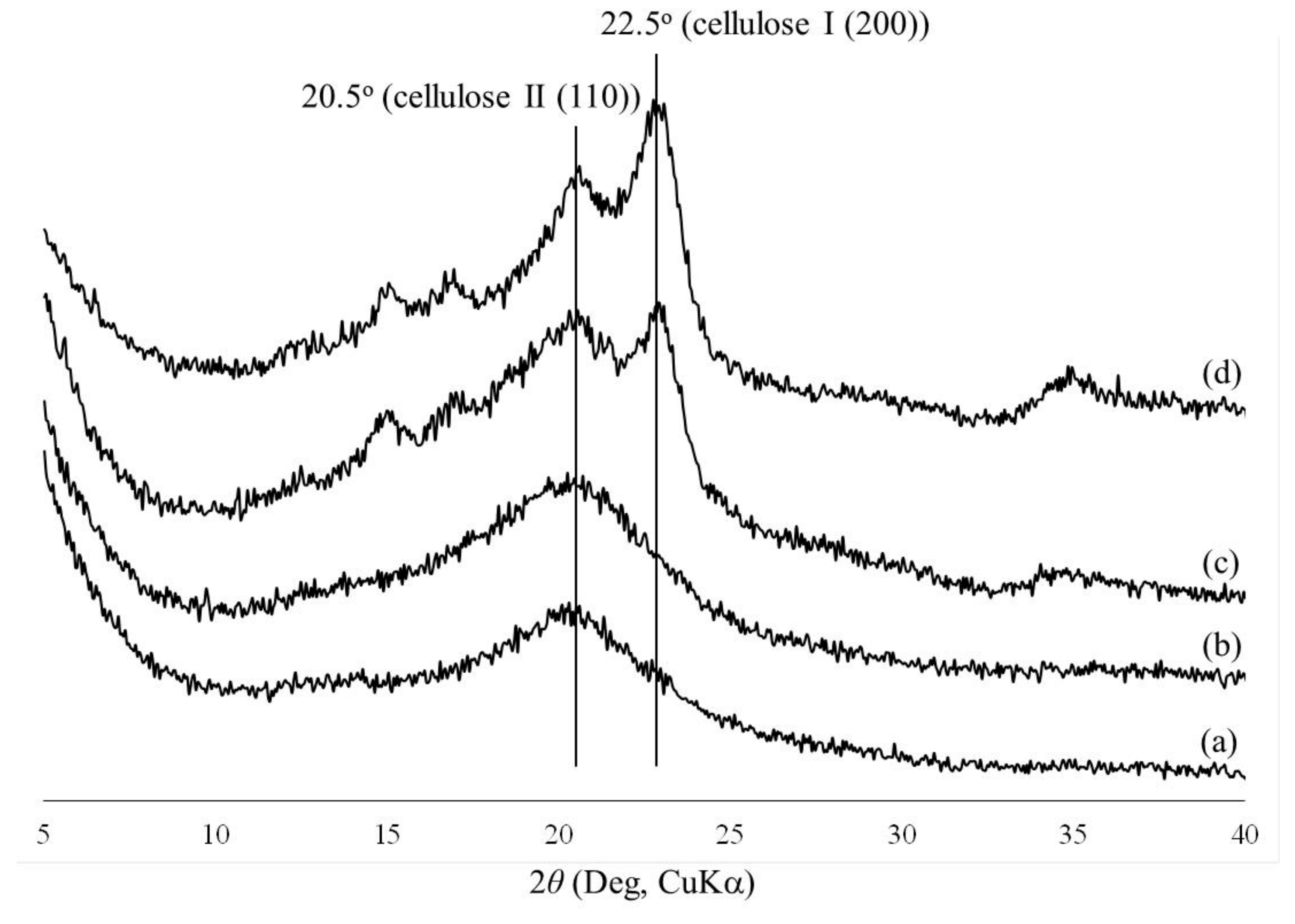
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L. Properties of regenerated cellulose films plasticized with α-monoglycerides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 3500–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Wang, L.; Yu, I.K.M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hunt, A.J.; Jérôme, F.; Zhang, S.; Ok, Y.S.; Poon, C.S. Valorization of lignocellulosic fibres of paper waste into levulinic acid using solid and aqueous Brønsted acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Phuong, H.A.; Izzati Ayob, N.A.; Blanford, C.F.; Mohammad Rawi, N.F.; Szekely, G. Nonwoven membrane supports from renewable resources: Bamboo fiber reinforced poly (lactic acid) composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11885–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Luo, Y.; Gu, X.; Dou, H.; Wang, J. Diffusion mechanism of aqueous solutions and swelling of cellulosic fibers in silicone non-aqueous dyeing system. Polymers 2019, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curvello, R.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Garnier, G. Engineering nanocellulose hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 267, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doelker, E. Cellulose Derivatives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 199–265. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, M.A.; Habu, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Takada, A.; Kadokawa, J.I. Ionic liquid induces flexibility and thermoplasticity in cellulose film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hadi, A.; Schnabel, R.; Straube, E.; Müller, G.; Henning, S. Correlation between degree of crystallinity, morphology, glass temperature, mechanical properties and biodegradation of poly (3-hydroxyalkanoate) PHAs and their blends. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, T.; Heinze, T. Interaction of ionic liquids with polysaccharides 5. Solvents and reaction media for the modification of cellulose. Bioresources 2008, 3, 576–601. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Chen, Z.I. Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 142, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkert, A.; Marsh, K.N.; Pang, S.S.; Staiger, M.P. Ionic liquids and their interaction with cellulose. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6712–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gericke, M.; Fardim, P.; Heinze, T. Ionic liquids-Promising but challenging solvents for homogeneous derivatization of cellulose. Molecules 2012, 17, 7458–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isik, M.; Sardon, H.; Mecerreyes, D. Ionic liquids and cellulose: Dissolution, chemical modification and preparation of new cellulosic materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11922–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Application of ionic liquids for dissolving cellulose and fabricating cellulose-based materials: State of the art and future trends. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanutz, F.; Vocht, M.P.; Panzier, N.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Processing of cellulose using ionic liquids. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Mishra, A.; Chauhan, S.; Verma, P.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E. Dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids and their mixed cosolvents: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 13, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadokawa, J.; Murakami, M.; Kaneko, Y. A facile preparation of gel materials from a solution of cellulose in ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hu, K.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H. Hydrogels prepared from pineapple peel cellulose using ionic liquid and their characterization and primary sodium salicylate release study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Impacts of some macromolecules on the characteristics of hydrogels prepared from pineapple peel cellulose using ionic liquid. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Li, L.; Lin, Z.; Cui, S. Formation mechanism of ionic liquid-reconstituted cellulose hydrogels and their application in gel electrophoresis. Acta Polym. Sin. 2011, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Qu, B.; Li, J.; Xiao, H.; He, B.; Qian, L. Preparation of cellulose-based conductive hydrogels with ionic liquid. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shamshina, J.L.; Berton, P.; Bandomir, J.; Wang, H.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Comparison of hydrogels prepared with ionic-liquid-isolated vs commercial chitin and cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Dai, G. Preparations, properties, and formation mechanism of novel cellulose hydrogel membrane based on ionic liquid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.; Martin, A., Jr.; Conrad, C. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A.; Usuda, M. Crystallinity indexes of cellulosic materials. Sen-i Gakkaishi 1989, 46, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ling, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Takabe, K.; Xu, F. Unraveling variations of crystalline cellulose induced by ionic liquid and their effects on enzymatic hydrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Dwiatmoko, A.A.; Choi, J.W.; Suh, Y.-W.; Suh, D.J.; Oh, M. Cellulose pretreatment with 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride for solid acid-catalyzed hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8273–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Entry | Cellulose Concentration in BMIMCl Solution (wt.%) | Water Content of Primary Hydrogel (wt.%) (a) | Residual BMIMCl in Porous Cellulose (wt.%) (b) | Water Content of Reswollen Hydrogel (wt.%) (a) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 94.8 | 0.52 | 90.8 |
| 2 | 10 | 90.7 | 0.60 | 85.2 |
| 3 | 12 | 89.3 | 0.68 | 82.2 |
| 4 | 15 | 85.4 | 0.38 | 69.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idenoue, S.; Oga, Y.; Hashimoto, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Kadokawa, J.-i. Preparation of Reswellable Amorphous Porous Celluloses through Hydrogelation from Ionic Liquid Solutions. Materials 2019, 12, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193249
Idenoue S, Oga Y, Hashimoto D, Yamamoto K, Kadokawa J-i. Preparation of Reswellable Amorphous Porous Celluloses through Hydrogelation from Ionic Liquid Solutions. Materials. 2019; 12(19):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193249
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdenoue, Satoshi, Yoshitaka Oga, Daichi Hashimoto, Kazuya Yamamoto, and Jun-ichi Kadokawa. 2019. "Preparation of Reswellable Amorphous Porous Celluloses through Hydrogelation from Ionic Liquid Solutions" Materials 12, no. 19: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193249
APA StyleIdenoue, S., Oga, Y., Hashimoto, D., Yamamoto, K., & Kadokawa, J.-i. (2019). Preparation of Reswellable Amorphous Porous Celluloses through Hydrogelation from Ionic Liquid Solutions. Materials, 12(19), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193249






