Influence of Nano-SiO2, Nano-CaCO3 and Nano-Al2O3 on Rheological Properties of Cement–Fly Ash Paste
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Admixture Proportion
2.2. Rheology Test
2.3. Rheological Parameters Analysis
τ = τ0 + Kγn, τ ≥ τ0
3. Results
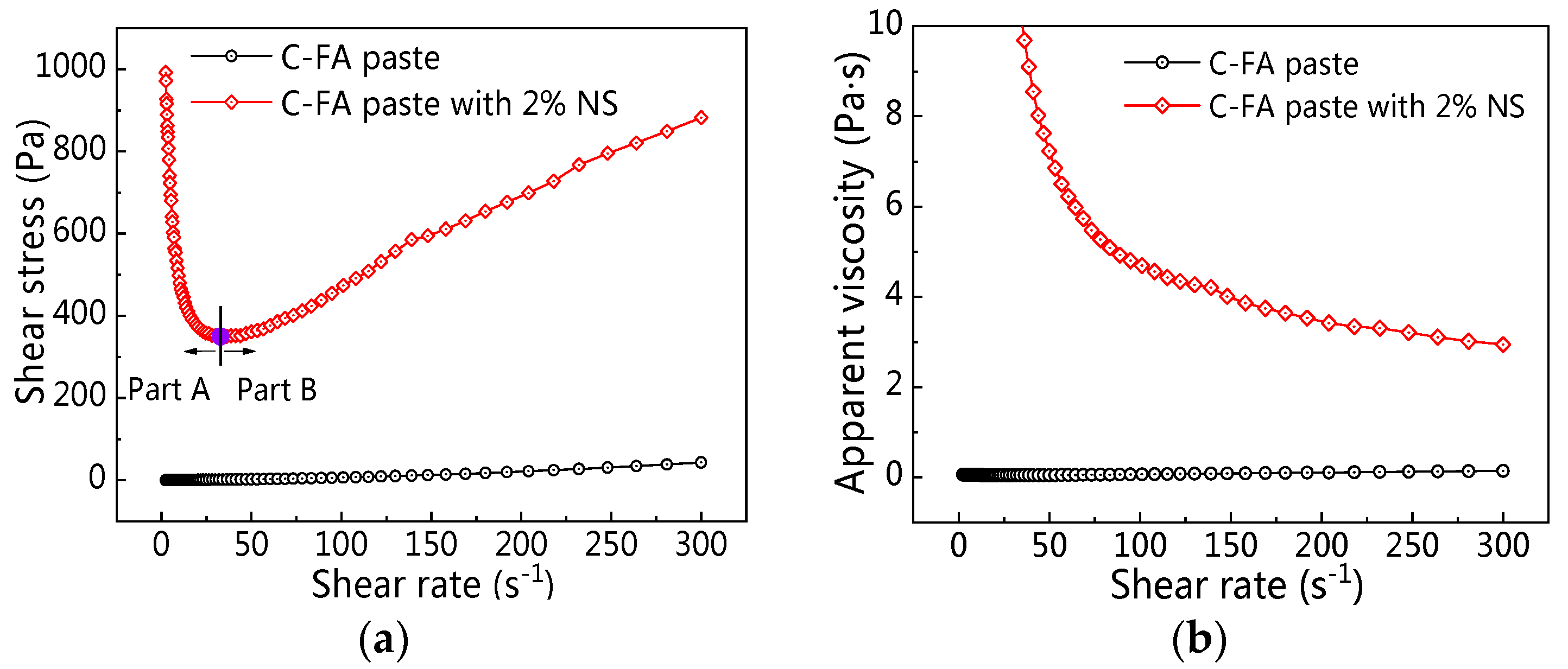
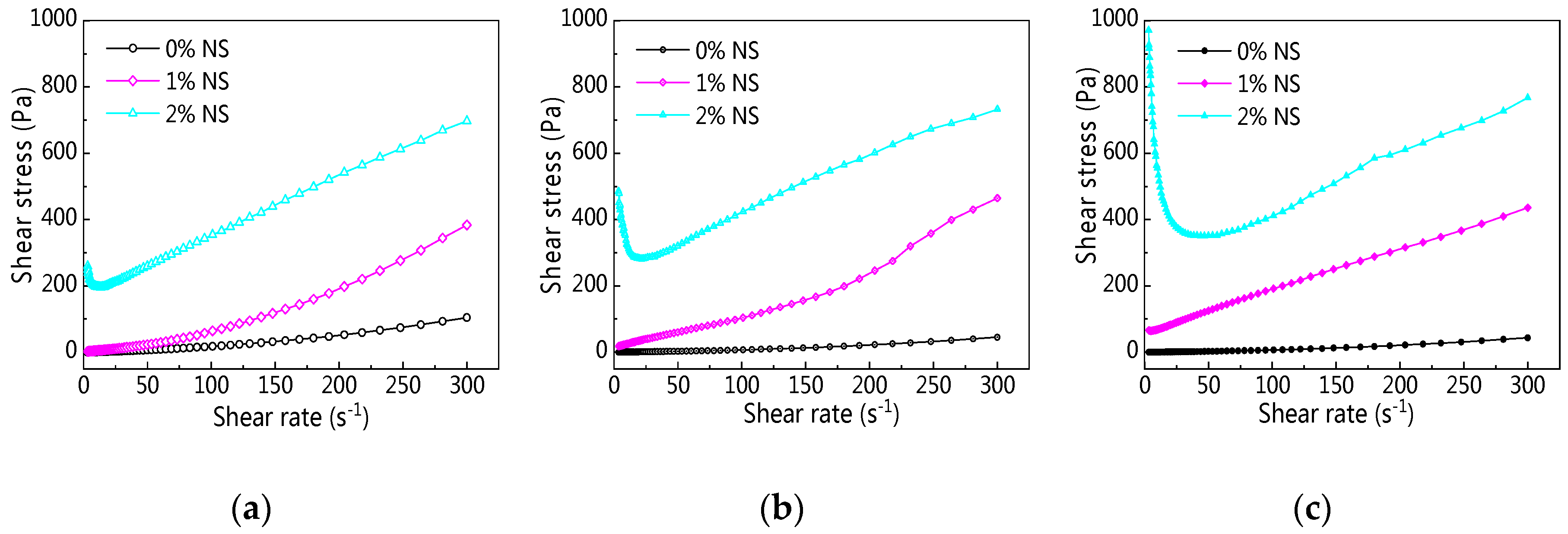
3.1. Influence of NS on C–FA Paste Rheology
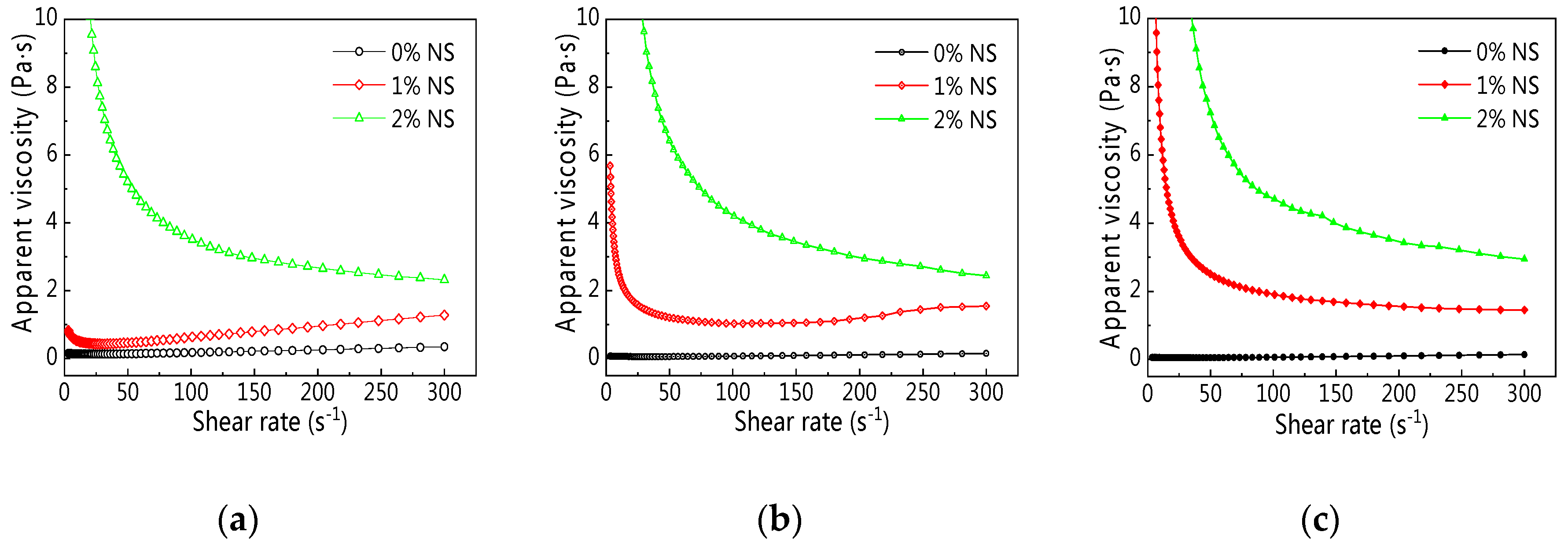
3.1.1. Rheological Curve
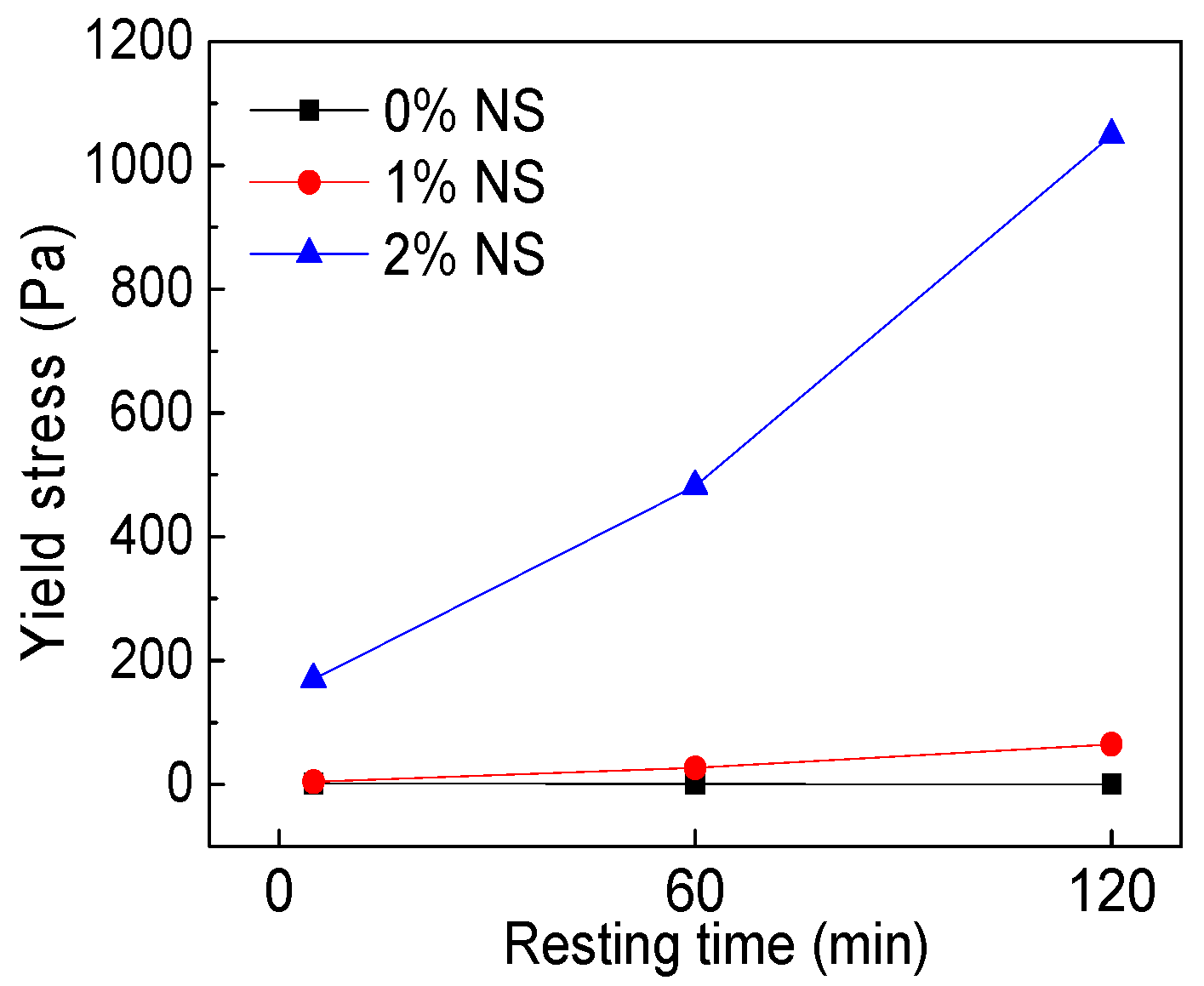
3.1.2. Yield Stress
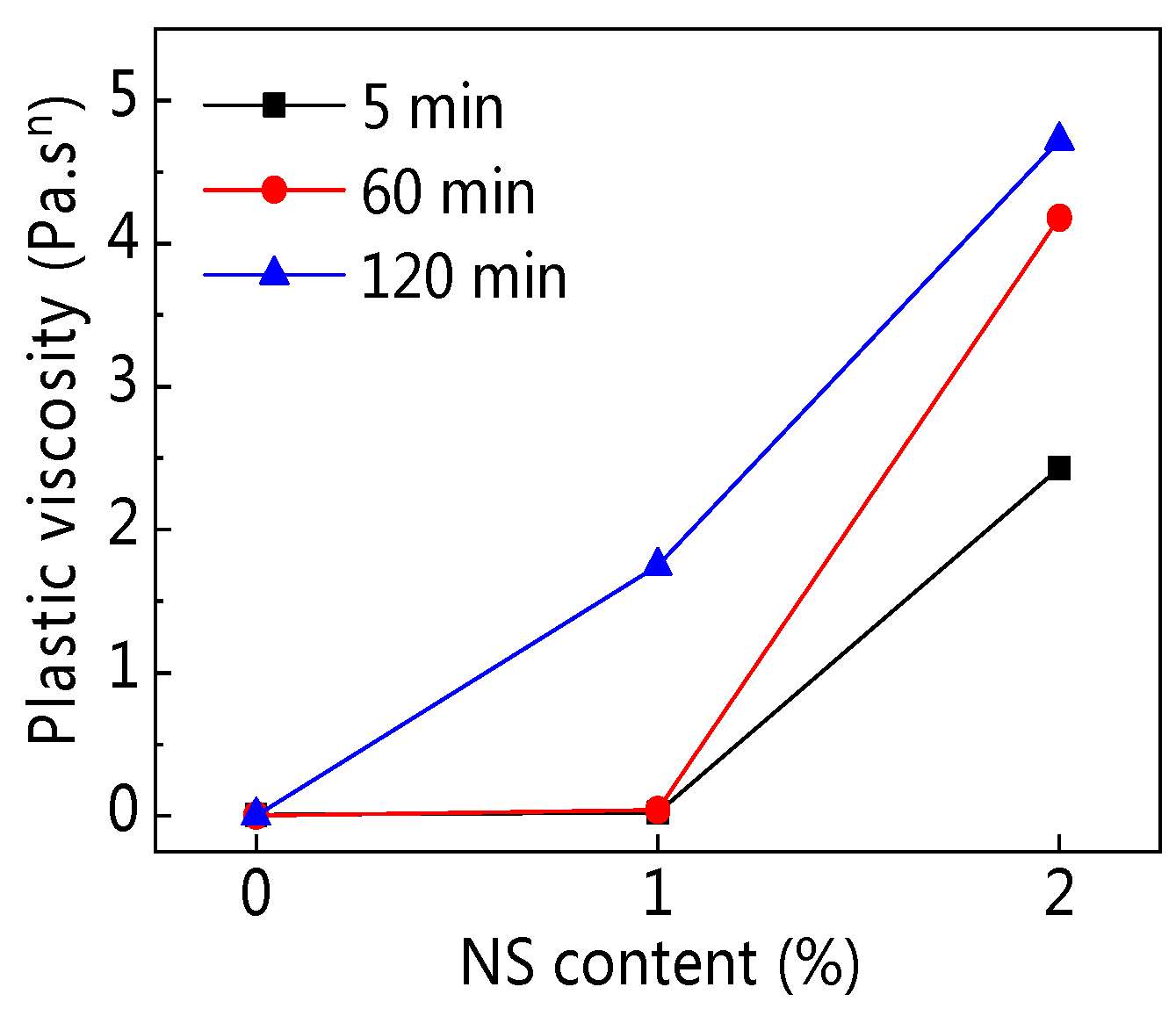
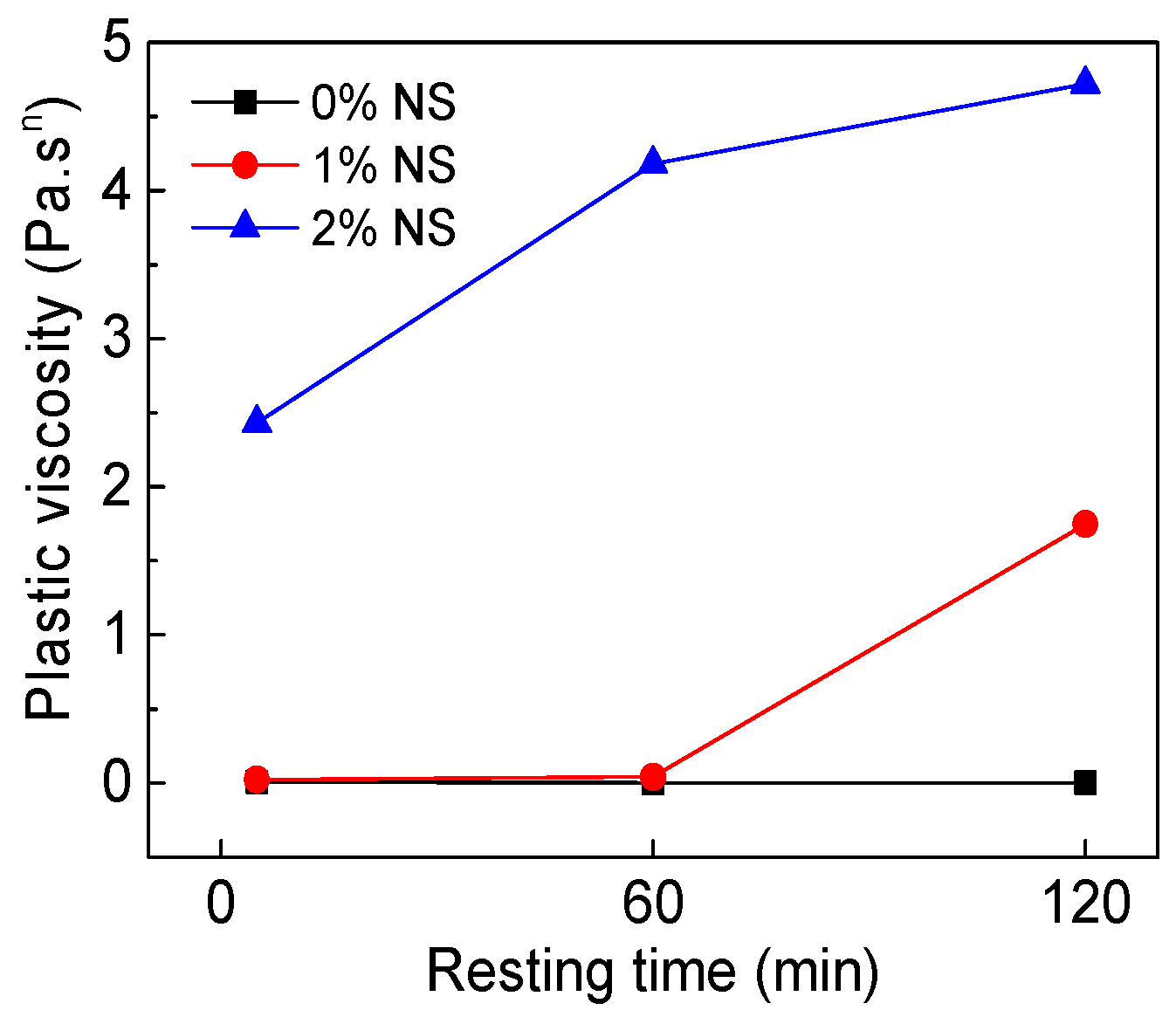
3.1.3. Plastic Viscosity
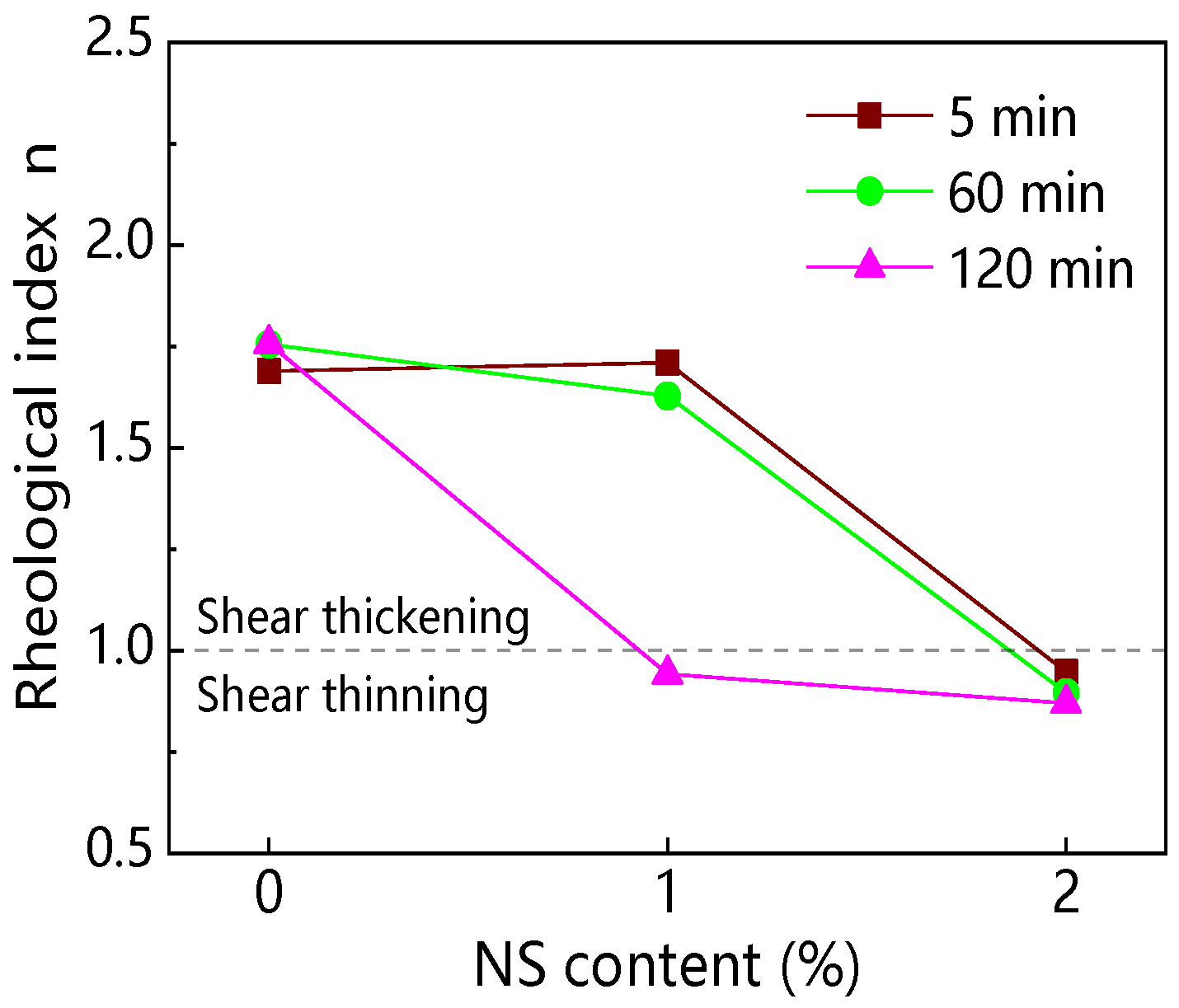
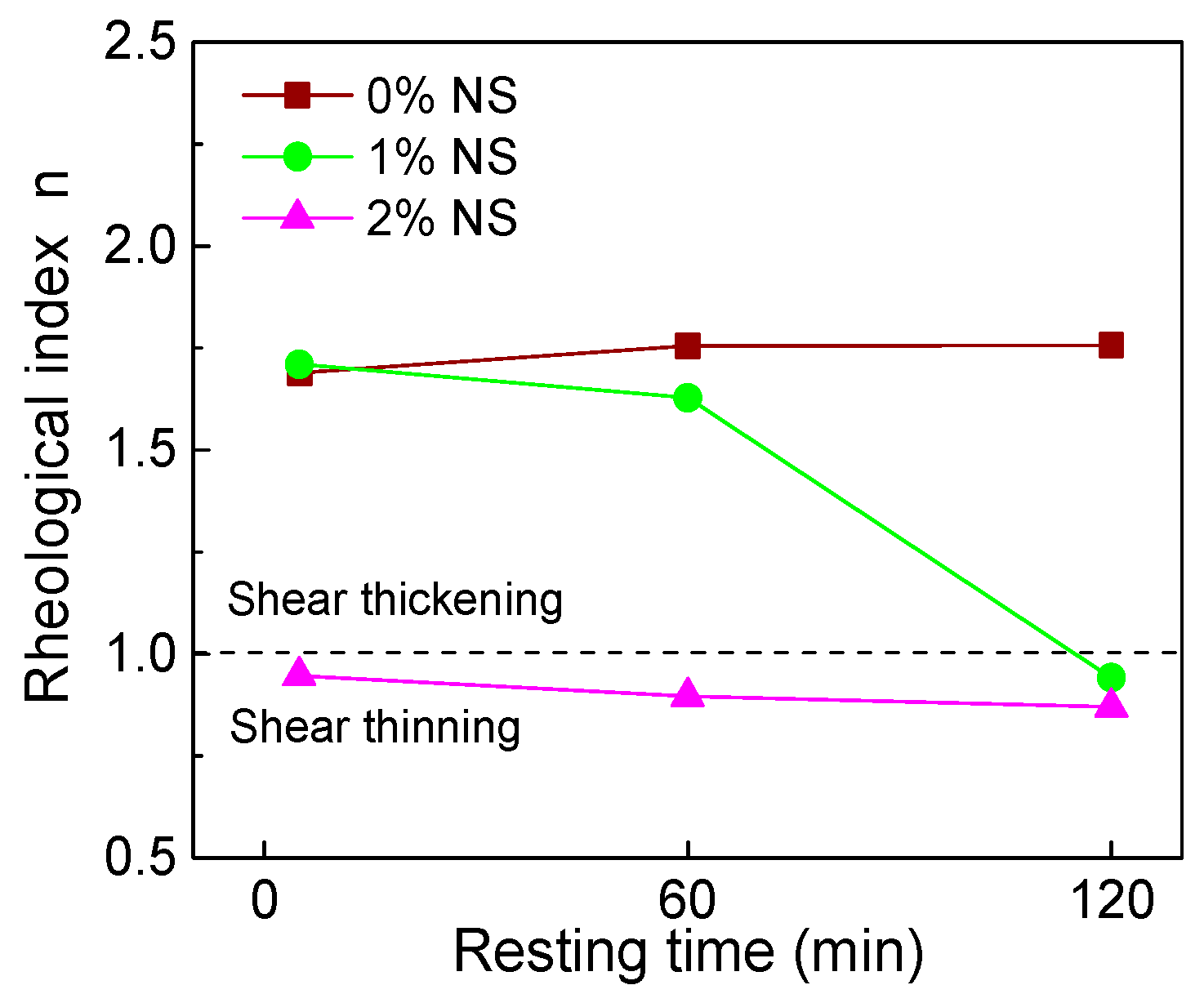
3.1.4. Rheological Index
3.2. Influence of NC on C–FA Paste Rheology
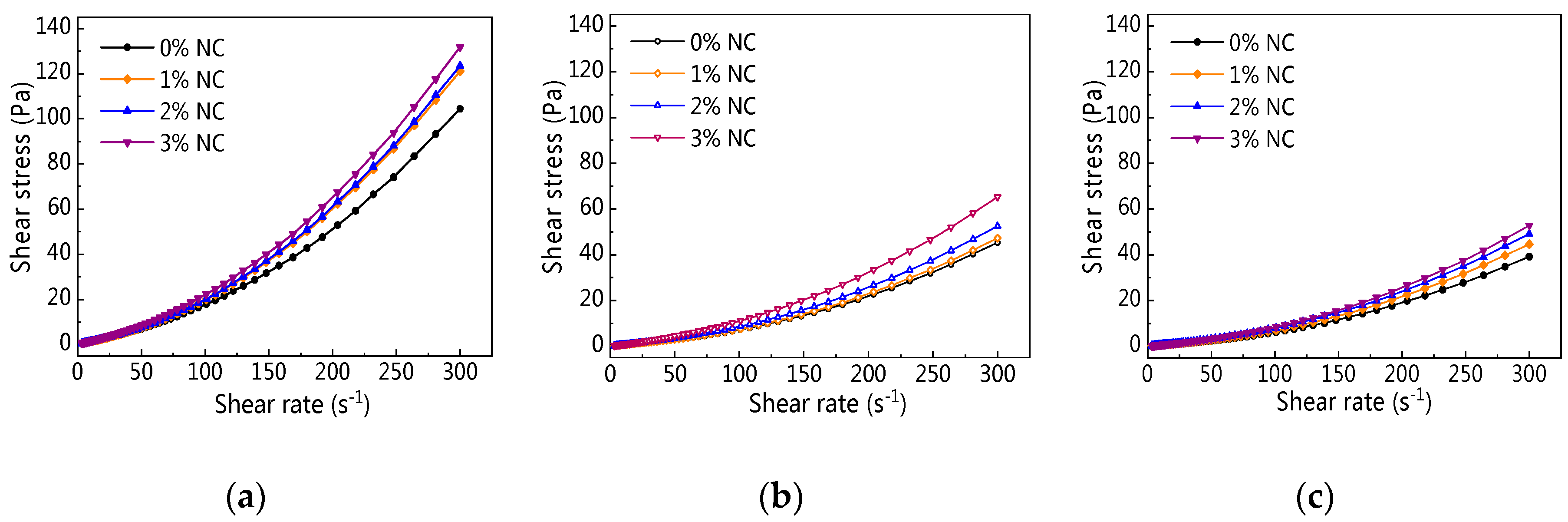
3.2.1. Rheological Curve
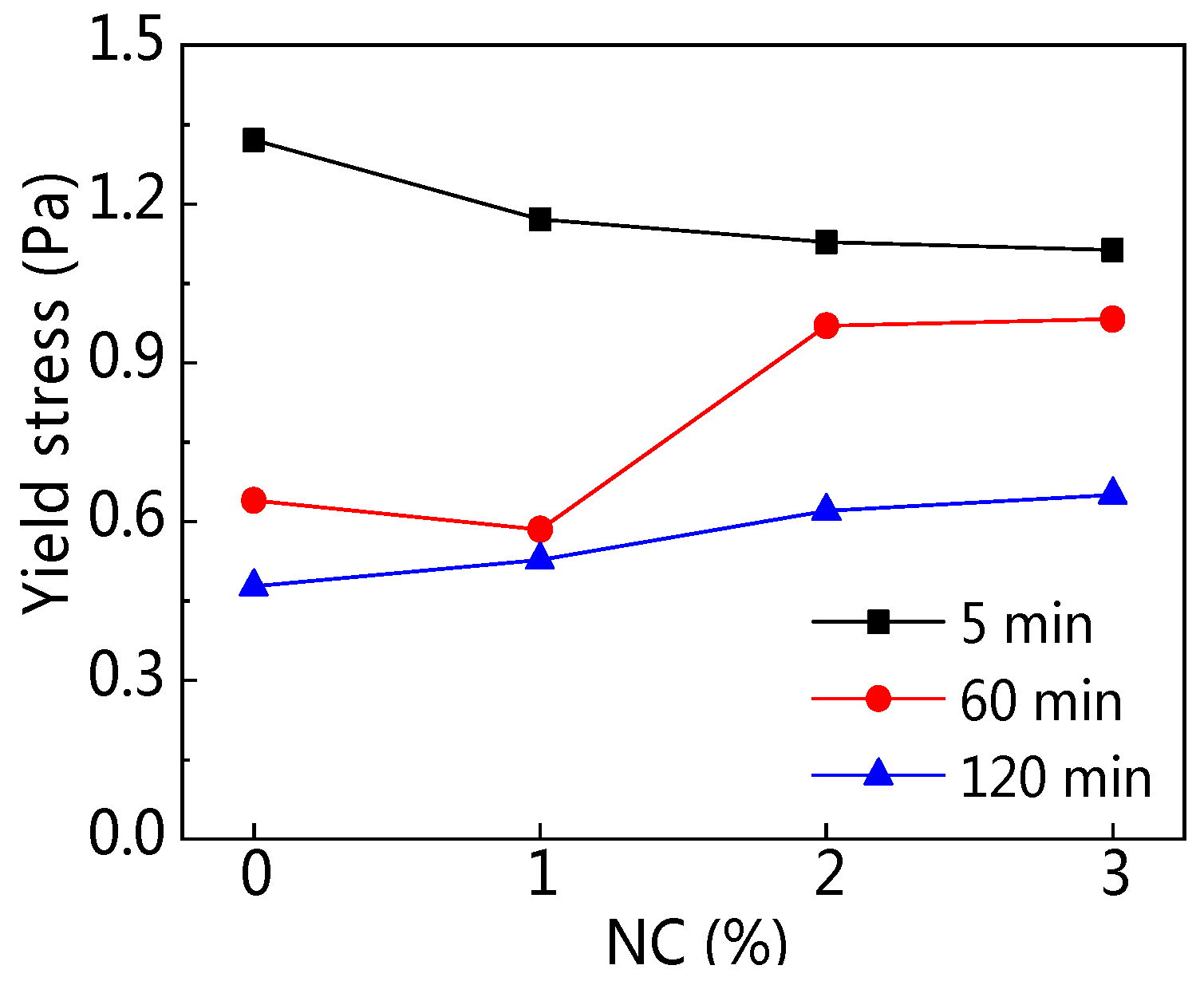
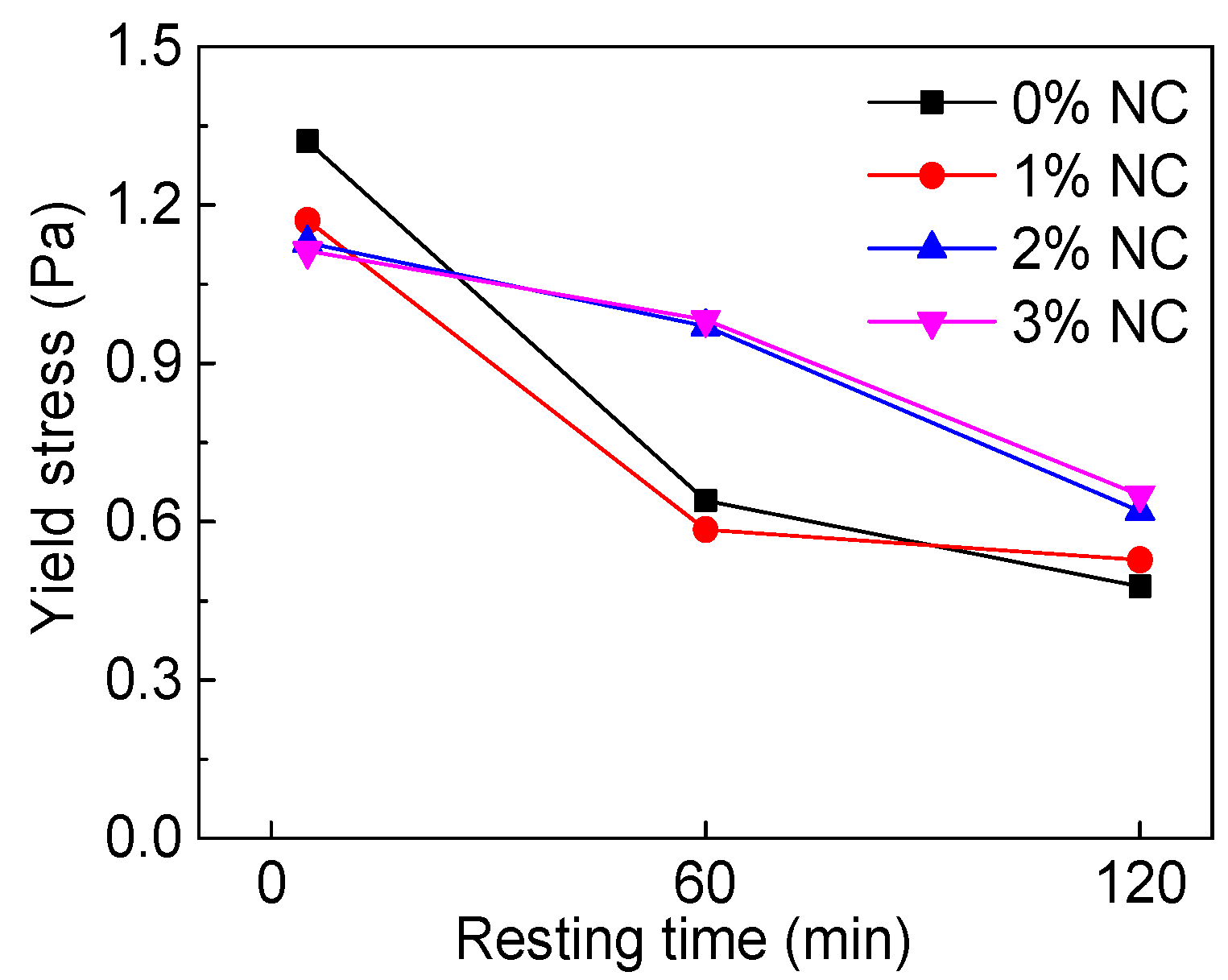
3.2.2. Yield Stress
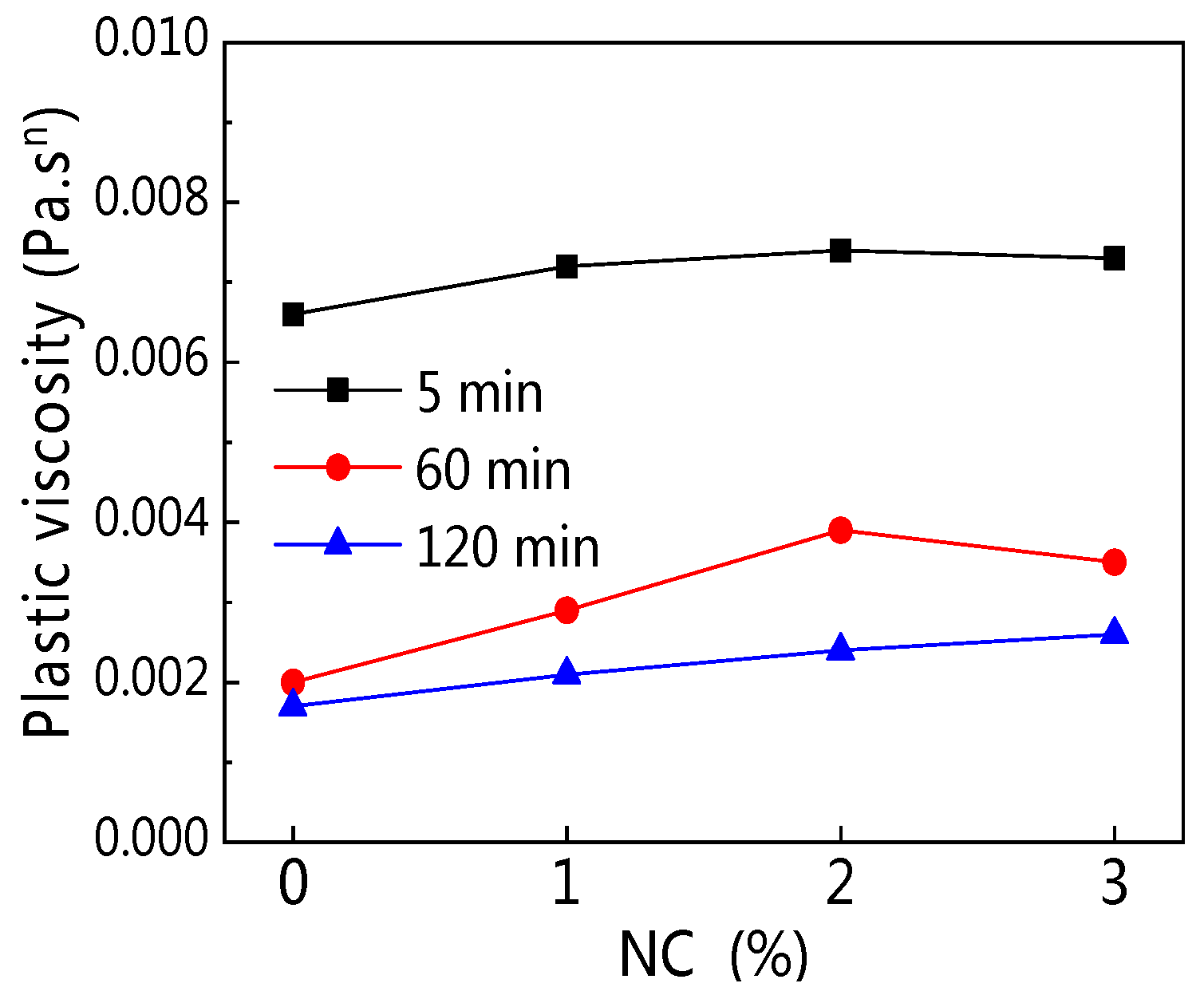
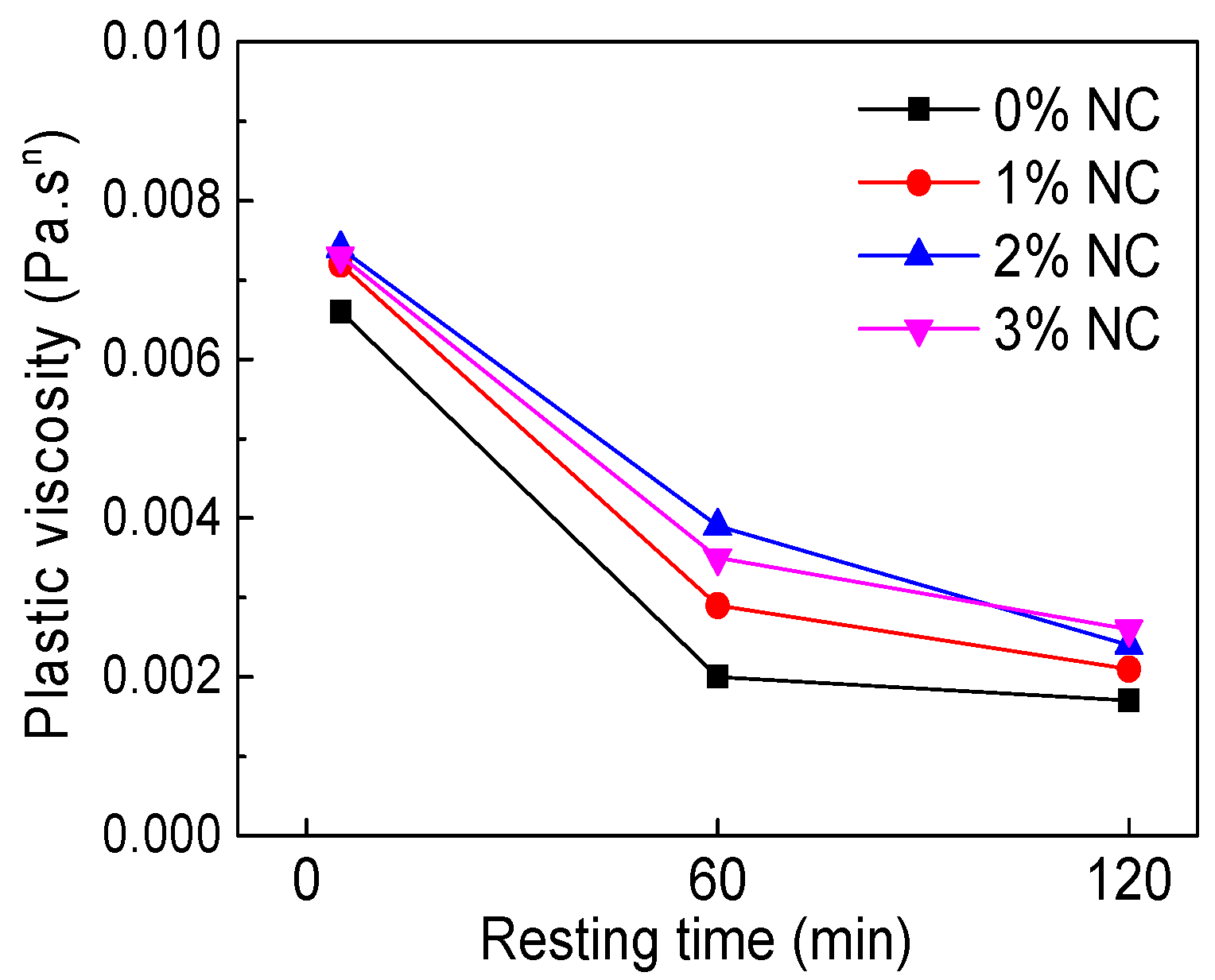
3.2.3. Plastic Viscosity
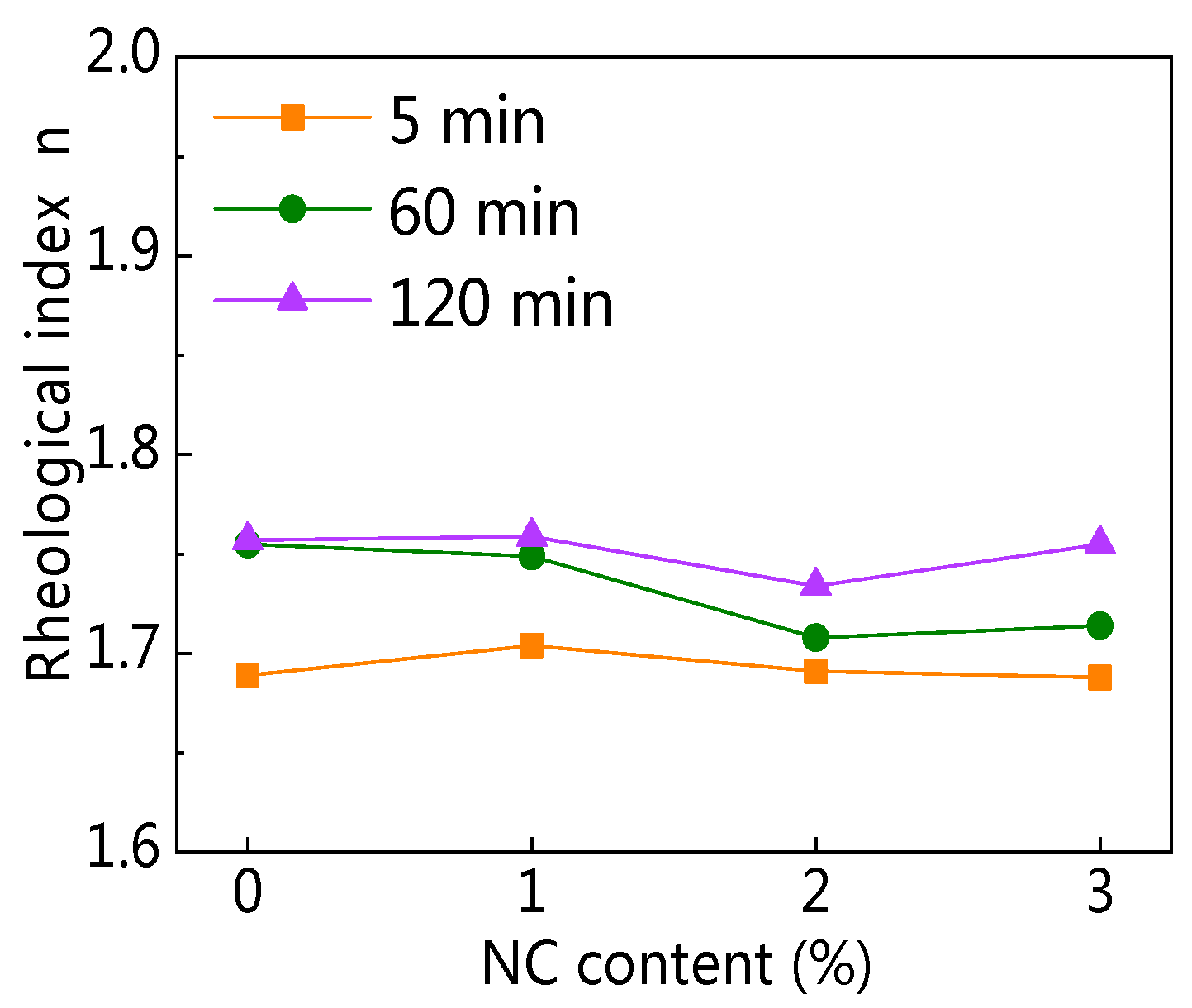
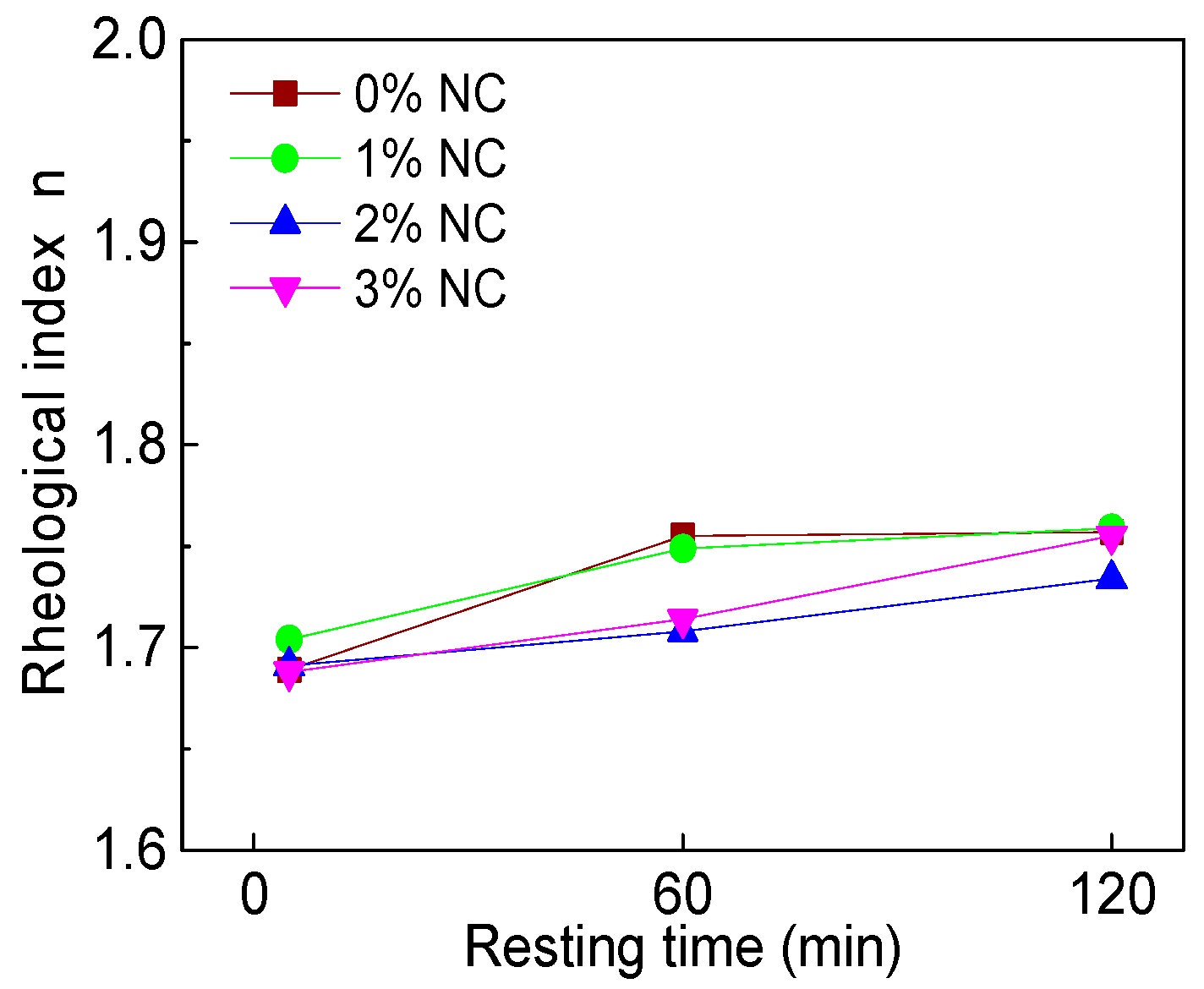
3.2.4. Rheological Index
3.3. Influence of NA on C–FA Paste Rheology
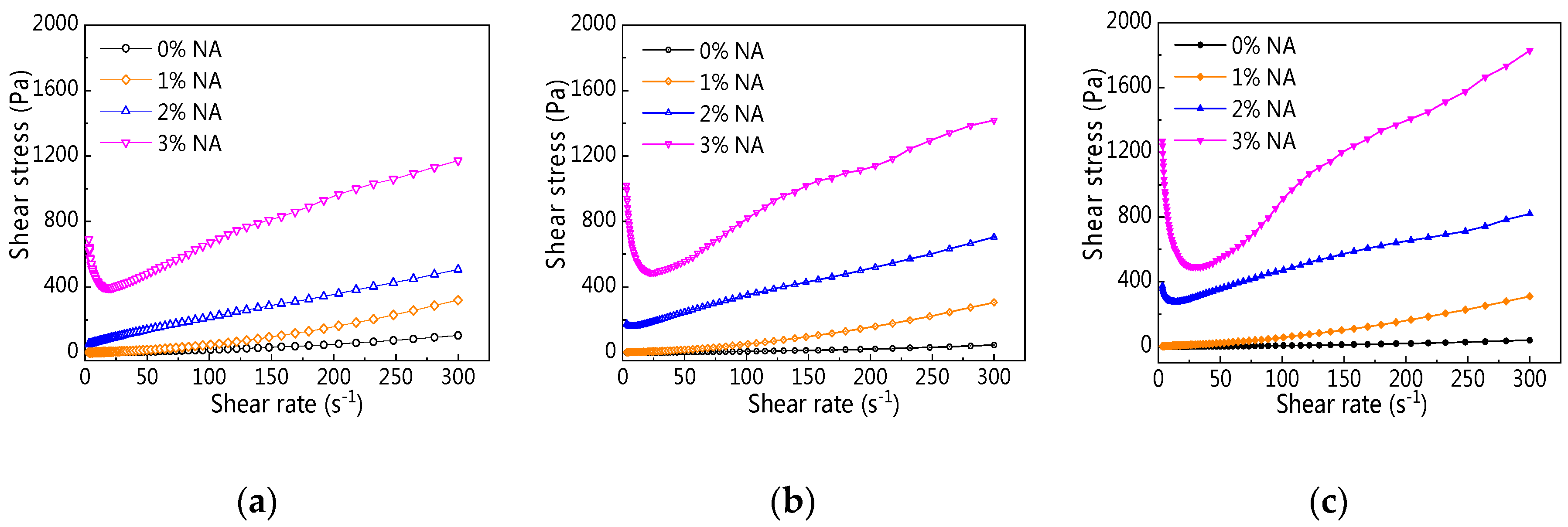
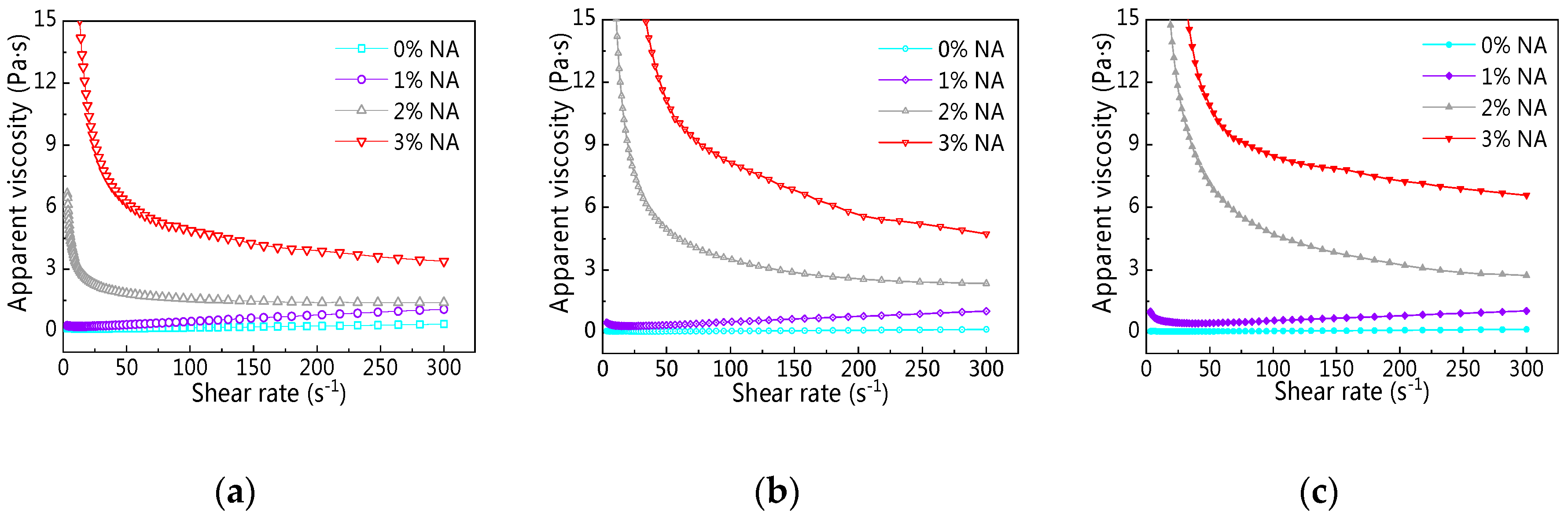
3.3.1. Rheological Curve
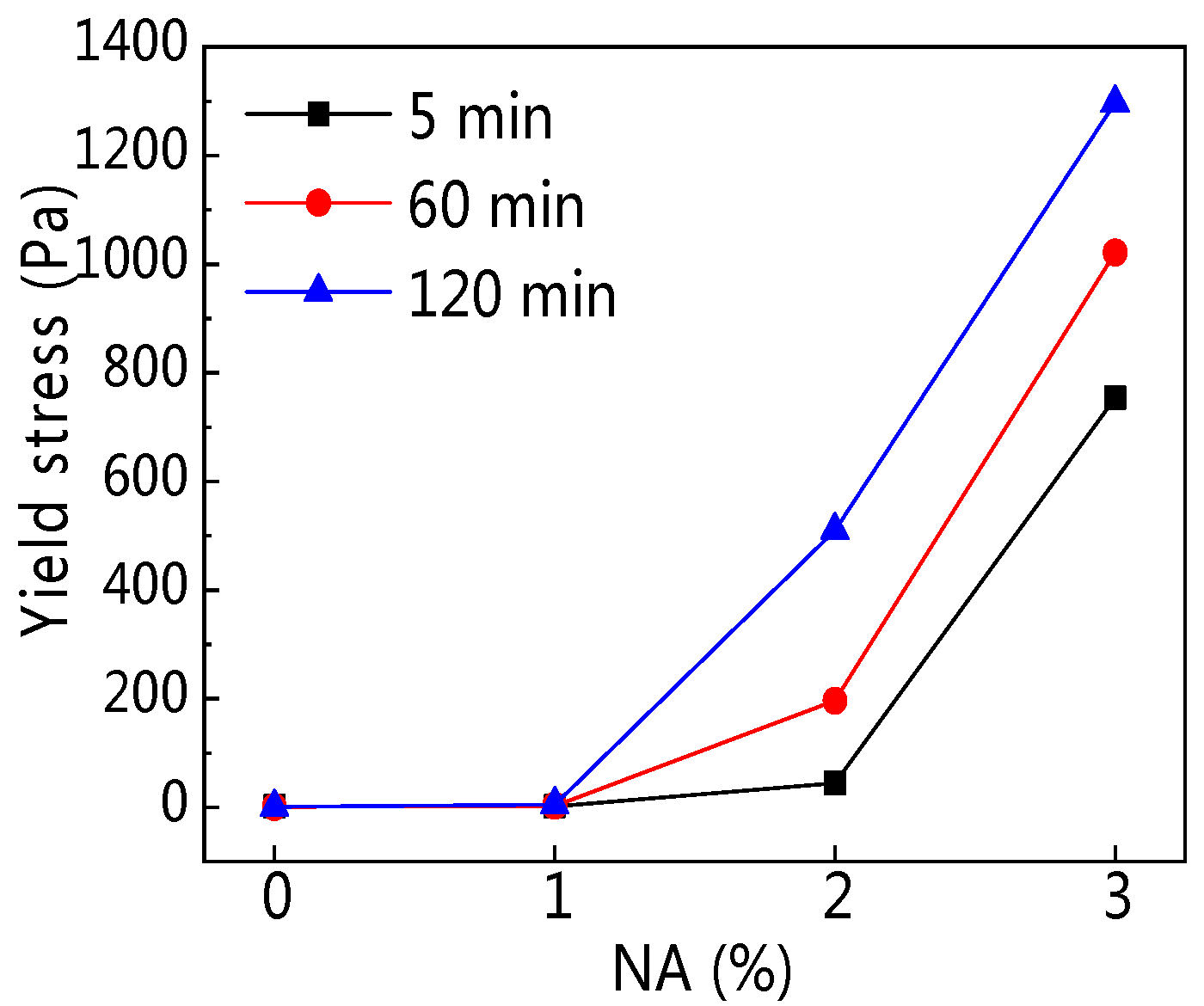
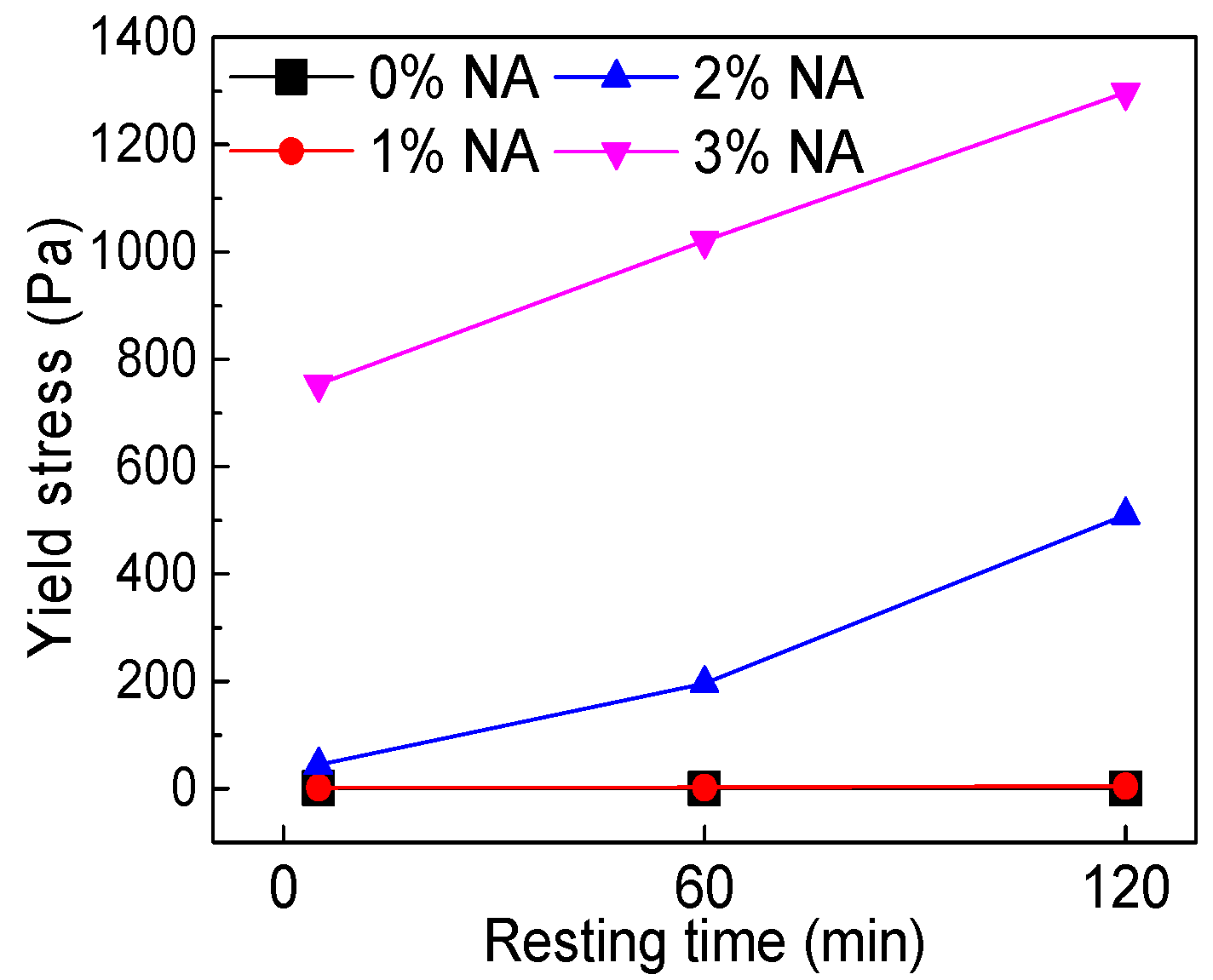
3.3.2. Yield Stress
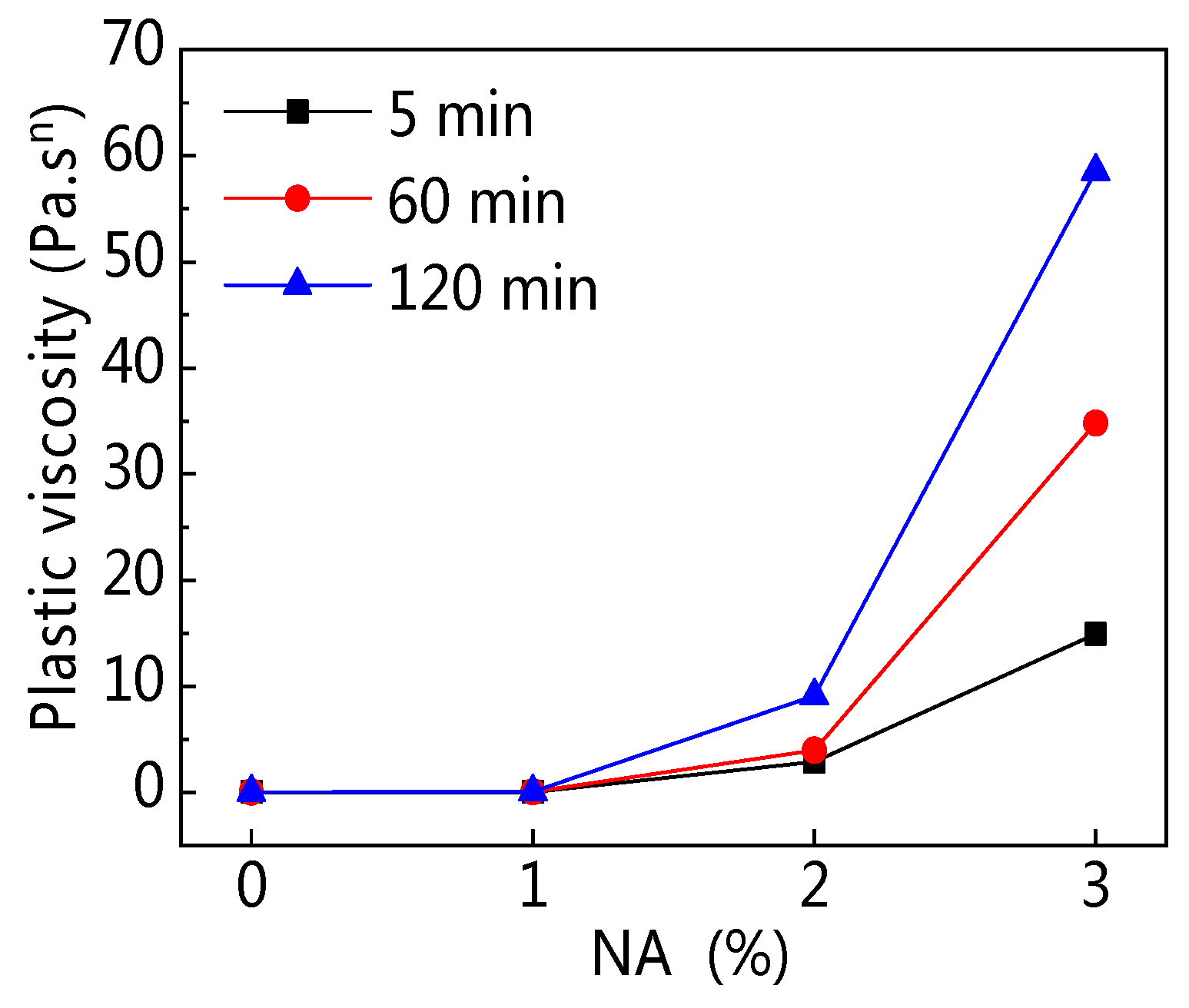
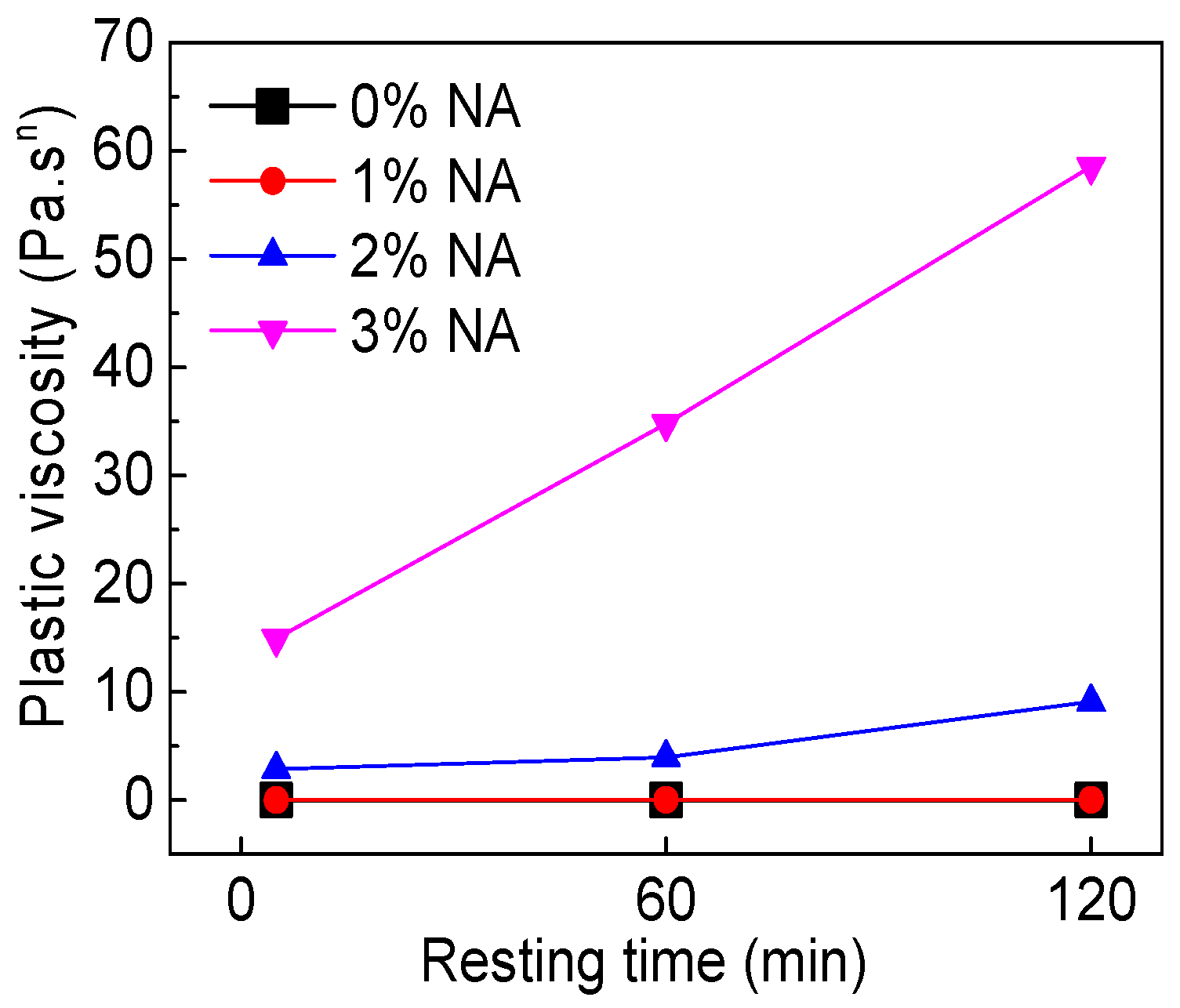
3.3.3. Plastic Viscosity
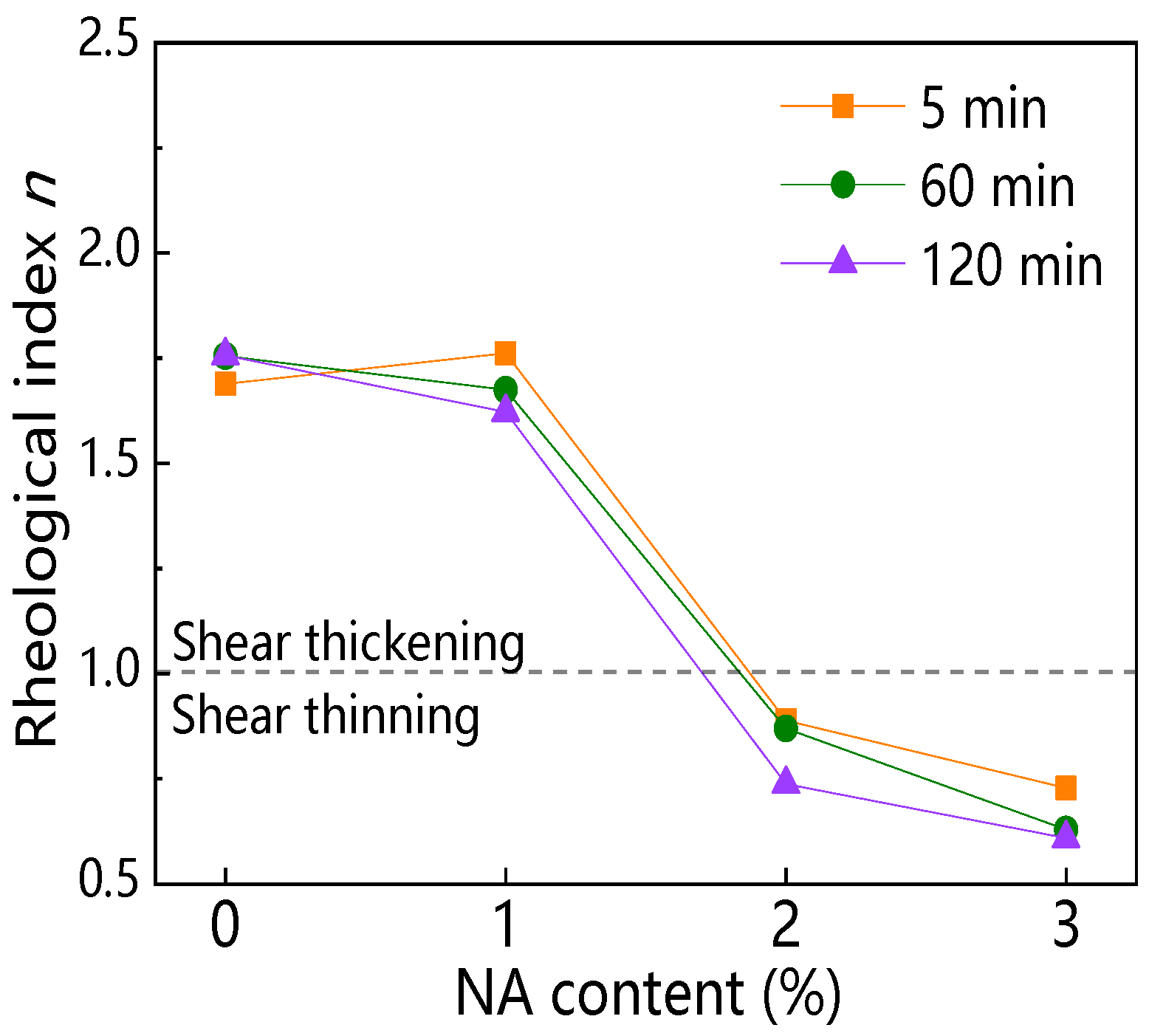
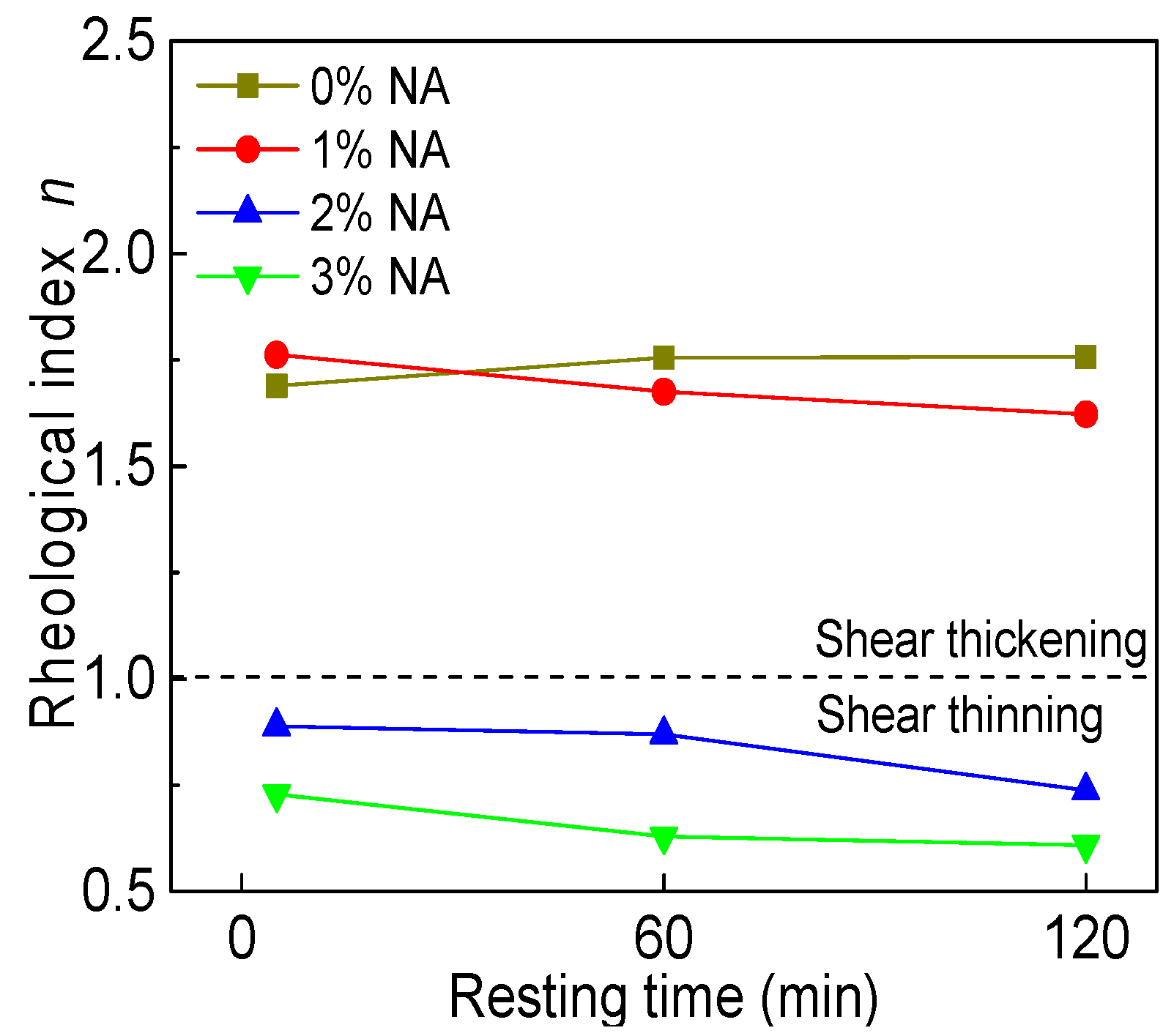
3.3.4. Rheological Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Rheological Properties of C–FA Paste
4.2. Effect of Nanomaterials on C–FA Paste Rheology
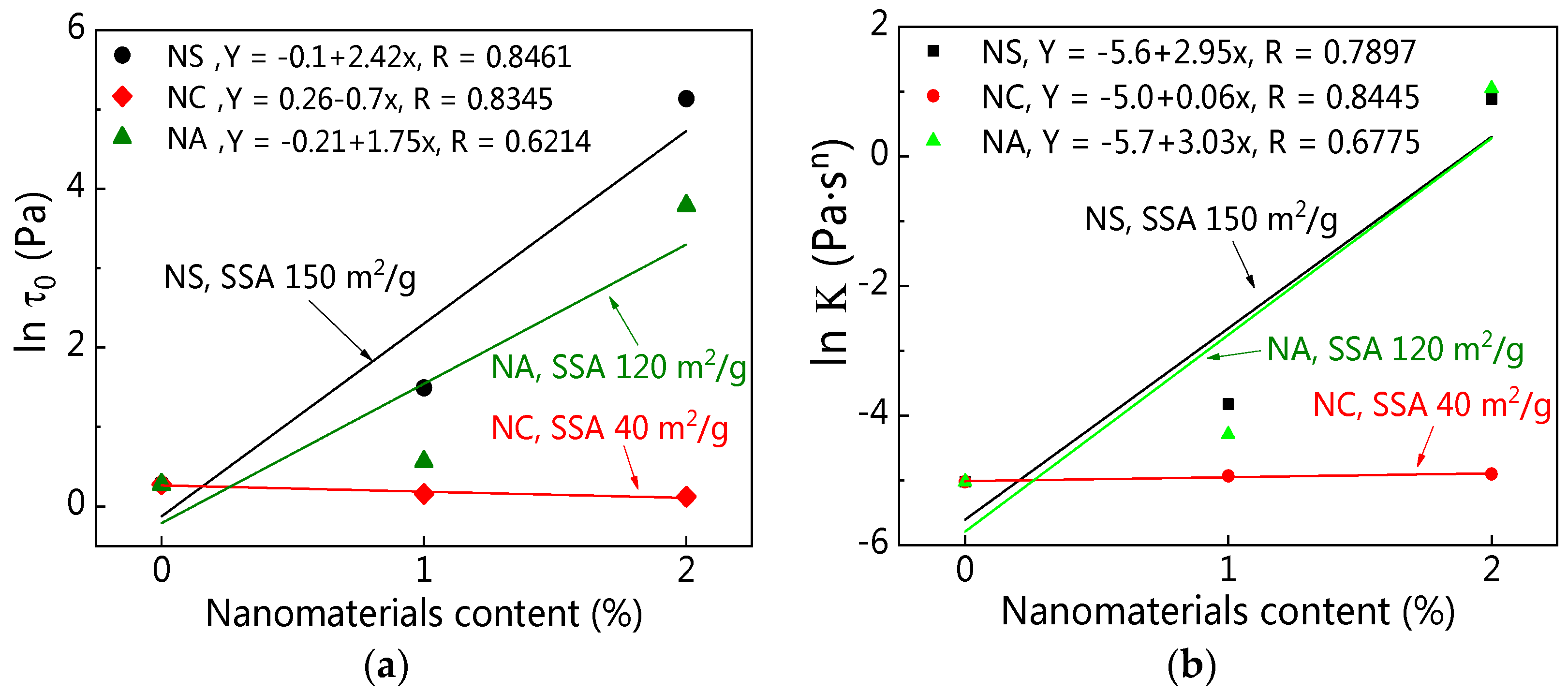
4.2.1. Specific Surface Area
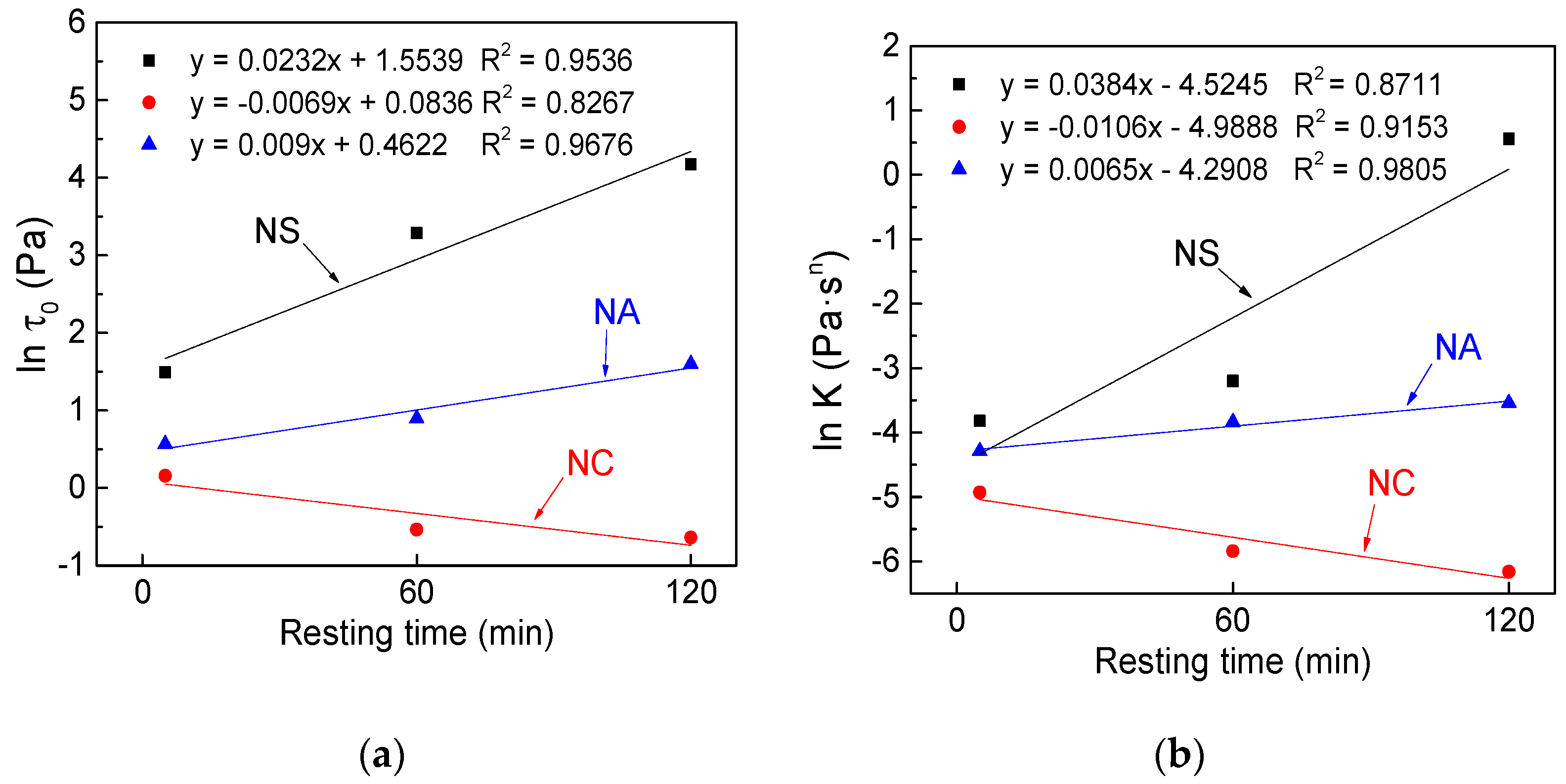
4.2.2. Resting Time
4.2.3. Rheological Characteristic
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malhotra, V.M. Durability of concrete incorporating high-volume of low-calcium (ASTM Class F) fly ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1990, 12, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M. A review on the utilization of fly ash. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 327–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirboga, R.; Gul, R. Thermal conductivity and compressive strength of expanded perlite aggregate concrete with mineral admixtures. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, L.; Wong, Y.L.; Poon, C.S. Degree of hydration and gel/space ratio of high-volume fly ash/cement systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wu, X.Z. Influence of fly ash and its mean particle size on certain engineering properties of cement composite mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felekoglu, B.; Tosun, K.; Baradan, B.; Altun, A.; Uyulgan, B. The effect of fly ash and limestone fillers on the viscosity and compressive strength of self-compacting repair mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.L.; Ortega, J.M.; Flor, M.; Lopez, M.P.; Sanchez, I.; Climent, M.A. Microstructure and durability of fly ash cement grouts for micropiles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 117, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Malhotra, V.M. Effect of curing on the compressive strength, resistance to chloride-ion penetration and porosity of concretes incorporating slag, fly ash or silica fume. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1995, 17, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.M.O.; Perez, M.D.E.; Escribano, R.R.R.; Navarro, J.L.P.; Martin, I.S. Microstructural Effects of Sulphate Attack in Sustainable Grouts for Micropiles. Materials 2016, 9, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.L.; Feng, J.; Long, G.C.; Xie, Y.J. Effects of mineral admixtures on shear thickening of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.H.; Chaouche, M. Rheology and stability of self-compacting concrete cement pastes. Appl. Rheol. 2005, 15, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, B.; Unluer, C.; Tan, M.J. Investigation of the rheology and strength of geopolymer mixtures for extrusion-based 3D printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 94, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.L.; Chen, Z.M.; Jiao, Z.; Xiao, G.M.; Shao, L. Study on microstructure, rheology and thermal stability of cement epoxy asphalt mortar multiphase materials. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Wu, Q.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Lee, S. Rheology, curing temperature and mechanical performance of oil well cement: Combined effect of cellulose nanofibers and graphene nano-platelets. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Z.; Liu, J.P.; Han, F.Y.; Lin, W. Effect of Superplasticizers on Apparent Viscosity of Cement-Based Material with a Low Water-Binder Ratio. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, A. Effect of solid concentration and shear rate on shear-thickening response of high-performance cement suspensions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Kong, X.M. Correlations of the dispersing capability of NSF and PCE types of superplasticizer and their impacts on cement hydration with the adsorption in fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Montes, O.; Palacios, M.; Rivilla, P.; Puertas, F. Compatibility between superplasticizer admixtures and cements with mineral additions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, D.P.; Ferraris, C.F.; Galler, M.A.; Hansen, A.S.; Guynn, J.M. Influence of particle size distributions on yield stress and viscosity of cement-fly ash pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M. A synopsis about the effect of nano-Al2O3, nano-Fe2O3, nano-Fe3O4 and nano-clay on some properties of cementitious materials—A short guide for Civil Engineer. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Q.; Jiang, L.H.; Jiang, S.B.; Yan, X.C.; Xu, N. The mechanical properties and electrochemical behavior of cement paste containing nano-MgO at different curing temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Ahalawat, S. Preparation of Size Controlled Silica Nano Particles and Its Functional Role in Cementitious System. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2012, 10, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, H.; Bagheri, A.; Parhizkar, T. The pozzolanic reactivity of monodispersed nanosilica hydrosols and their influence on the hydration characteristics of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornstrom, J.; Martinelli, A.; Matic, A.; Borjesson, L.; Panas, I. Accelerating effects of colloidal nano-silica for beneficial calcium-silicate-hydrate formation in cement. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 392, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Riahi, S. The effects of SiO2 nanoparticles on physical and mechanical properties of high strength compacting concrete. Compos. Pt. B Eng. 2011, 42, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.K.; Kawashima, S.; Kong, D.Y.; Corr, D.J.; Qian, J.S.; Shah, S.P. Modification effects of colloidal nanoSiO(2) on cement hydration and its gel property. Compos. Pt. B Eng. 2013, 45, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, N.; Ozkul, M.H. The fresh properties of nano silica incorporating polymer-modified cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balapour, M.; Joshaghani, A.; Althoey, F. Nano-SiO2 contribution to mechanical, durability, fresh and microstructural characteristics of concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Han, B.G.; Chen, G.Z.; Zhao, L.Z.; Ou, J.P. A viscosity prediction model for cement paste with nano-SiO2 particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 185, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltulu, M.; Sahin, R. Effect of nano-SiO2, nano-Al2O3 and nano-Fe2O3 powders on compressive strengths and capillary water absorption of cement mortar containing fly ash: A comparative study. Energy Build. 2013, 58, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, K.R.; Liu, Z.Q.; He, F.Q. Chemical effect of nano-alumina on early-age hydration of Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 116, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Nikraz, H. Effects of nano-Al2O3 on early-age microstructural properties of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 52, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, A.H.; Wang, X.R. Effect of nano-CaCO3 on properties of cement paste. Energy Proc. 2012, 16, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołaszewski, J.; Kostrzanowska-Siedlarz, A.; Cygan, G.; Drewniok, M. Mortar as a model to predict self-compacting concrete rheological properties as a function of time and temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feys, D.; Verhoeven, R.; De Schutter, G. Evaluation of time independent rheological models applicable to fresh self-compacting concrete. Appl. Rheol. 2007, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, C.R.; Mei, G.X. Shear-Thickening Behavior of Cement Pastes under Combined Effects of Mineral Admixture and Time. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiad, I. Influence of time addition of superplasticizers on the rheological properties of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, F.; Belhadi, R.; Carriat, J.; Ben Fraj, A. Effect of nano-silica particles on the hydration, the rheology and the strength development of a blended cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Q.; Zhang, C.Z.; Sun, W. Fly ash effects: I. The morphological effect of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 2023–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Q.; Zhang, C.Z.; Sun, W. Fly ash effects—III. The microaggregate effect of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, A.; San Nicolas, R.; Qiao, G.G.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Provis, J.L. Modelling the yield stress of ternary cement-slag-fly ash pastes based on particle size distribution. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.J.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Huang, D.W.; Xin, G.F.; Wei, S.S.; Ge, Z. Effect of Fly Ash and Nano-CaCO3 on the Viscosity of Cement Paste. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 357–360, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artelt, C.; Garcia, E. Impact of superplasticizer concentration and of ultra-fine particles on the rheological behaviour of dense mortar suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, P.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Pajum, A.; Khodavirdi, M.M.; Izadi, H. Effect of nano-particles and aminosilane interaction on the performances of cement-based composites: An experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J. Towards a prediction of superplasticized concrete rheology. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Houst, Y.F. A simplified view on chemical effects perturbing the action of superplasticizers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Zhimin, D.; Keller, H.; Von Hossle, F.; Seidl, W. Fundamental mechanisms for polycarboxylate intercalation into C3A hydrate phases and the role of sulfate present in cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.C.; Shi, Y.; Ma, K.L.; Xie, Y.J. Reactive powder concrete reinforced by nanoparticles. Adv. Cem. Res. 2016, 28, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
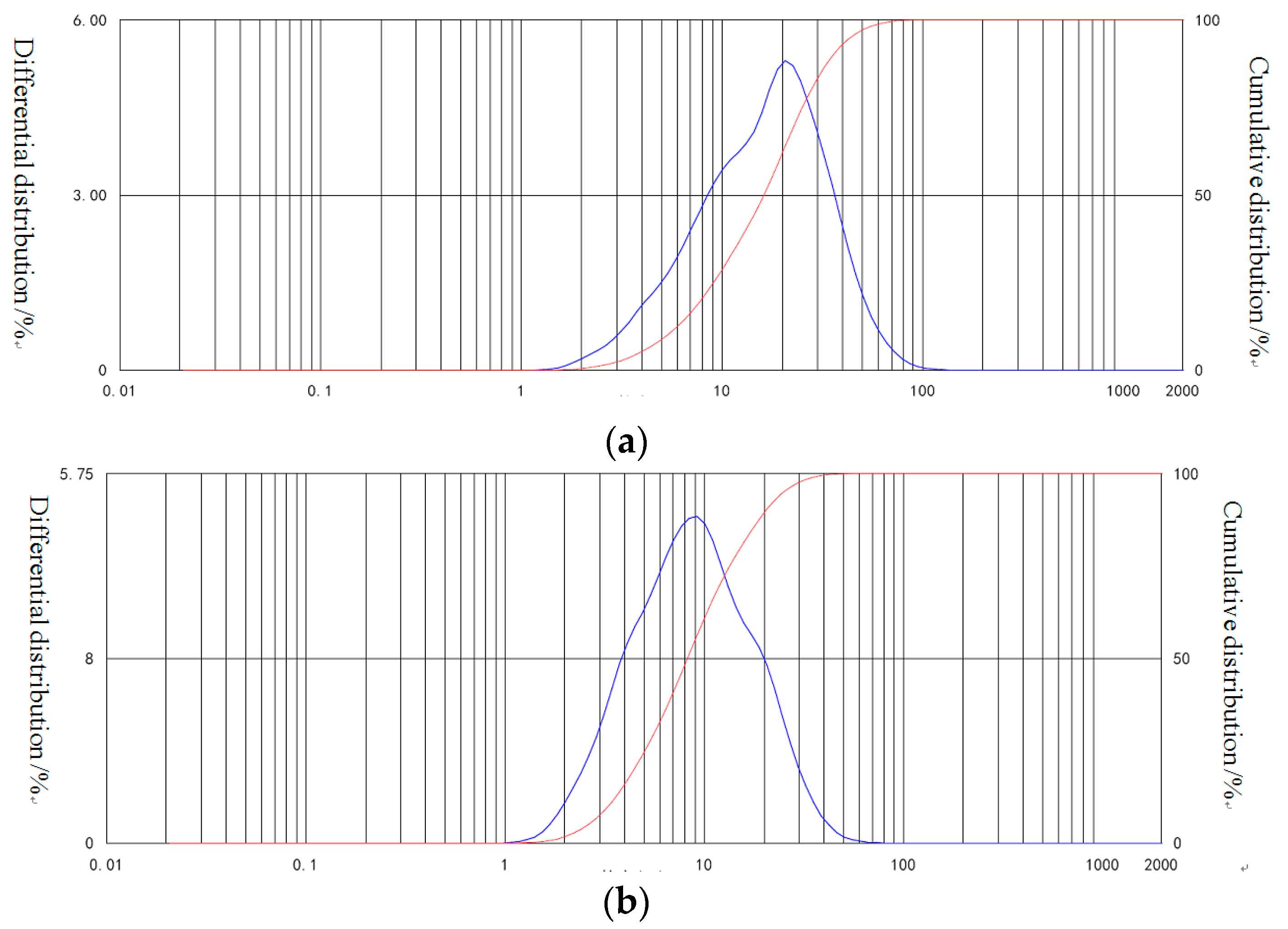

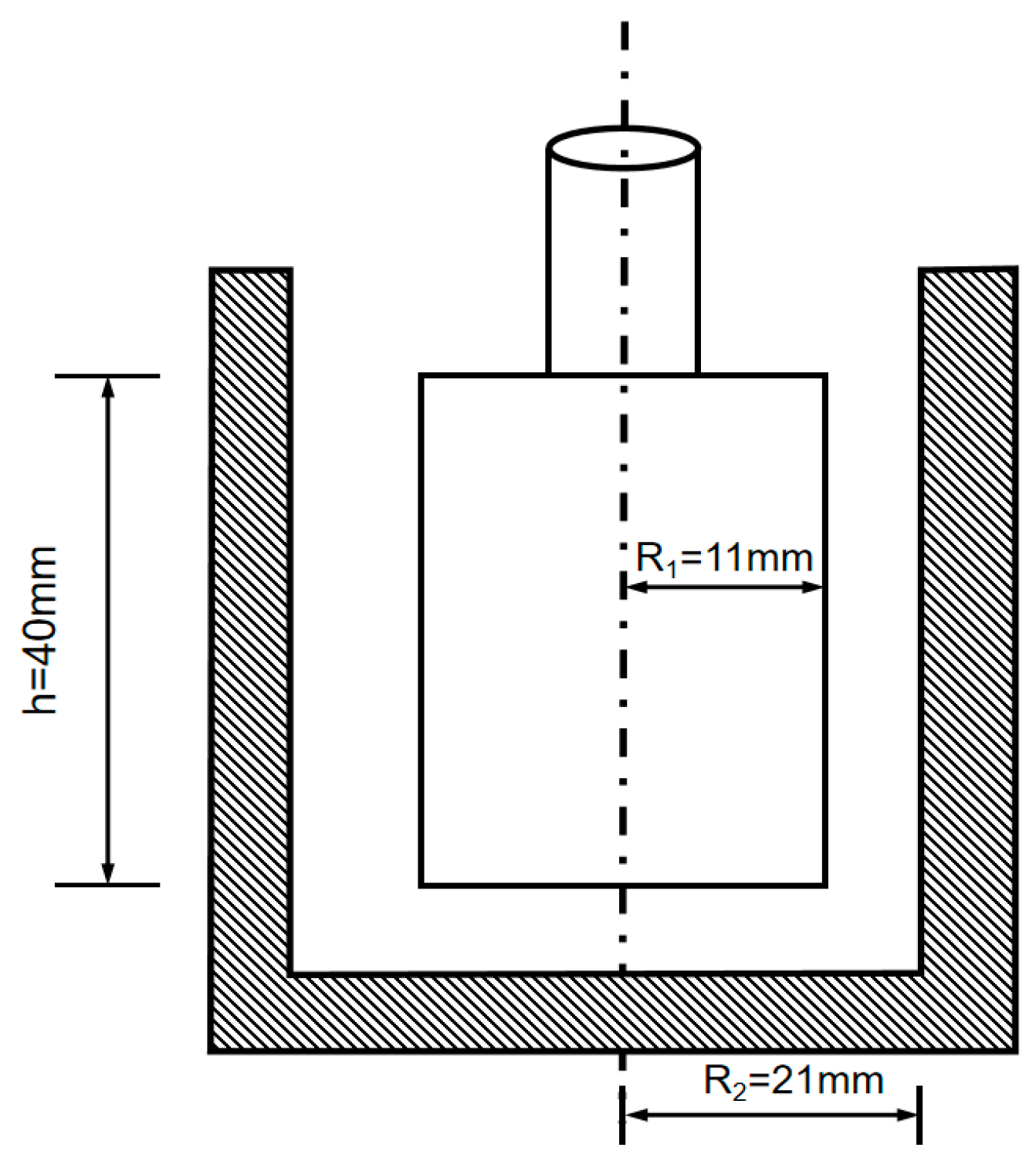




| No. | Cement (C) | Fly Ash (FA) |
|---|---|---|
| CaO | 63.5 | 4.3 |
| SiO2 | 20.6 | 52.3 |
| Al2O3 | 4.6 | 26.1 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.1 | 5.2 |
| MgO | 3.4 | 1.2 |
| SO3 | 2.21 | 0.72 |
| Loss on Ignition (%) | 3.34 | 2.10 |
| Alkali content (%) | 0.59 | 1.19 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.05 | 2.38 |
| Specific surface area (m2/kg) | 339 | 463 |
| 28 d compressive strength (MPa) | 50.3 | - |
| C3A | 7.4 | - |
| C3S | 56.7 | - |
| C2S | 15.1 | - |
| C4AF | 10.1 | - |
| Crystal Type | Purity (%) | Average Diameter (nm) | Specific Surface Area (m2·g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS | / | 99.5 | 30 | 150 |
| NC | / | 99.5 | 50 | 40 |
| NA | 99.9 | 20 | 120 |
| Sample | Mix Proportion (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | FA | NS | NC | NA | Water | Superplasticizer | |
| C–FA | 75 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–1%NS | 74 | 25 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–2%NS | 73 | 25 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–1%NC | 74 | 25 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–2%NC | 73 | 25 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–3%NC | 72 | 25 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–1%NA | 74 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–2%NA | 73 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 0.4 |
| C–FA–3%NA | 72 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 32 | 0.4 |
| No. | Resting Time (min) | τ0 (Pa) | K (Pa·sn) | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–FA | 5 | 1.321 | 0.0066 | 1.689 | 0.9991 |
| 60 | 0.6399 | 0.0020 | 1.755 | 0.9992 | |
| 120 | 0.4778 | 0.0017 | 1.757 | 0.9994 | |
| C–FA–1%NS | 5 | 4.449 | 0.0219 | 1.710 | 0.9998 |
| 60 | 26.72 | 0.0405 | 1.628 | 0.9935 | |
| 120 | 65.06 | 1.748 | 0.942 | 0.9995 | |
| C–FA–2%NS | 5 | 170 | 2.43 | 0.947 | 0.9997 |
| 60 | 482 | 4.18 | 0.896 | 0.9982 | |
| 120 | 1049 | 4.72 | 0.870 | 0.9955 |
| No. | Resting Time (min) | τ0 (Pa) | K (Pa·sn) | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–FA | 5 | 1.321 | 0.0066 | 1.689 | 0.9991 |
| 60 | 0.6399 | 0.0020 | 1.755 | 0.9992 | |
| 120 | 0.4778 | 0.0017 | 1.757 | 0.9994 | |
| C–FA–1%NC | 5 | 1.171 | 0.0072 | 1.704 | 0.9996 |
| 60 | 0.5851 | 0.0029 | 1.749 | 0.9993 | |
| 120 | 0.5277 | 0.0021 | 1.759 | 0.9994 | |
| C–FA–2%NC | 5 | 1.128 | 0.0074 | 1.691 | 0.9996 |
| 60 | 0.97 | 0.0039 | 1.708 | 0.9992 | |
| 120 | 0.6201 | 0.0024 | 1.734 | 0.9993 | |
| C–FA–3%NC | 5 | 1.113 | 0.0073 | 1.688 | 0.9994 |
| 60 | 0.9827 | 0.0035 | 1.714 | 0.9992 | |
| 120 | 0.6506 | 0.0026 | 1.755 | 0.9993 |
| No. | Resting Time (min) | τ0 (Pa) | K (Pa·sn) | n | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–FA | 5 | 1.321 | 0.0066 | 1.689 | 0.9991 |
| 60 | 0.6399 | 0.0020 | 1.755 | 0.9992 | |
| 120 | 0.4778 | 0.0017 | 1.757 | 0.9994 | |
| C–FA–1%NA | 5 | 1.759 | 0.0137 | 1.762 | 0.9999 |
| 60 | 2.447 | 0.0214 | 1.675 | 0.9998 | |
| 120 | 4.976 | 0.0291 | 1.622 | 0.9997 | |
| C–FA–2%NA | 5 | 44.47 | 2.863 | 0.8885 | 0.9996 |
| 60 | 196 | 3.949 | 0.8694 | 0.9989 | |
| 120 | 510 | 9.082 | 0.7374 | 0.9991 | |
| C–FA–3%NA | 5 | 753.8 | 14.92 | 0.7281 | 0.9986 |
| 60 | 1021 | 34.79 | 0.6291 | 0.9937 | |
| 120 | 1297 | 58.55 | 0.6090 | 0.9897 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Ma, K.; Long, G.; Xie, Y. Influence of Nano-SiO2, Nano-CaCO3 and Nano-Al2O3 on Rheological Properties of Cement–Fly Ash Paste. Materials 2019, 12, 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162598
Peng Y, Ma K, Long G, Xie Y. Influence of Nano-SiO2, Nano-CaCO3 and Nano-Al2O3 on Rheological Properties of Cement–Fly Ash Paste. Materials. 2019; 12(16):2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162598
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yiming, Kunlin Ma, Guangcheng Long, and Youjun Xie. 2019. "Influence of Nano-SiO2, Nano-CaCO3 and Nano-Al2O3 on Rheological Properties of Cement–Fly Ash Paste" Materials 12, no. 16: 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162598
APA StylePeng, Y., Ma, K., Long, G., & Xie, Y. (2019). Influence of Nano-SiO2, Nano-CaCO3 and Nano-Al2O3 on Rheological Properties of Cement–Fly Ash Paste. Materials, 12(16), 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162598





