Ferromagnetic ε-Fe2MnN: High-Pressure Synthesis, Hardness and Magnetic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allain, S.; Chateau, J.-P.; Bouaziz, O.; Migot, S.; Guelton, N. Correlations between the calculated stacking fault energy and the plasticity mechanisms in Fe-Mn-C alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 387–389, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.; Allain, S.; Faral, M.; Guelton, N. The development of a new Fe-Mn-C austenitic steel for automotive applications. Rev. Metall. Int. J. Metall. 2006, 103, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-E.; Lee, Y.-K. Strain hardening behavior of a Fe-18Mn-0.6C-1.5Al TWIP steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 527, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed-Akbari, A.; Imlau, J.; Prahl, U.; Bleck, W. Derivation and Variation in Composition-Dependent Stacking Fault Energy Maps Based on Subregular Solution Model in High-Manganese Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40A, 3076–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grässel, O.; Krüger, L.; Frommeyer, G.; Meyer, L.W. High strength Fe-Mn-(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP steels development-properties-application. Int. J. Plast. 2000, 16, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, A.S.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Somani, M.C. The influence of aluminum on hot deformation behavior and tensile properties of high-Mn TWIP steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 467, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, H.J.; Liedtke, D. Wärmebehandlung von Eisenwerkstoffen II: Nitrieren und Nitrocarburieren; Kontakt & Studium Band 686; Expert Verlag: Tübingen, Germany, 2014; ISBN 978-3-8169-3282-6. [Google Scholar]
- Komuro, M.; Kozono, Y.; Hanazono, M.; Sugita, Y. Epitaxial growth and magnetic properties of Fe16N2 films with high saturation magnetic-flux density. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 5126–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Smith, P.A.I. Magnetic nitrides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, B.C. Magnetic structure of Fe4N. Phys. Rev. 1958, 112, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirba, I.; Schwöbel, C.A.; Diop, L.V.B.; Duerrschnabel, M.; Molina-Luna, L.; Hofmann, K.; Komissinskiy, P.; Kleebe, H.J.; Gutfleisch, O. Synthesis, morphology, thermal stability and magnetic properties of α″-Fe16N2 nanoparticles obtained by hydrogen reduction of γ-Fe2O3 and subsequent nitrogenation. Acta Mater. 2017, 123, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leineweber, A.; Jacobs, H.; Hüning, F.; Lueken, H.; Kockelmann, W. Nitrogen ordering and ferromagnetic properties of ε-Fe3N1+x (0.10 ≤ x ≤ 0.39) and ε-Fe3(N0.80C0.20)1.38. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 316, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenmeyer, M.; Shlyk, L.; Senyshyn, A.; Mönig, R.; Niewa, R. Structural and Magnetic Characterization of Single-phase Sponge-like Bulk α″-Fe16N2. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2015, 641, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer y Blancá, E.L.; Desimoni, J.; Christensen, N.E.; Emmerich, H.; Cottenier, S. The magnetization of γ’-Fe4N: Theory vs. experiment. Phys. Status Solidi B 2009, 246, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, A. Self-consistent calculations for the electronic structures of iron nitrides, Fe3N, Fe4N and Fe16N2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 102, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Harima, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Katayama-Yoshida, H.; Nakata, Y.; Hirotsu, Y. Electronic band structure and magnetism of Fe16N2 calculated by the FLAPW method. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 15042–15046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, S.; Siberchicot, B.; Pénicaud, M.; Demazeau, G. The electronic and magnetic properties of Fe3N. J. Phys. I Fr. 1992, 2, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xue, D.; Li, F.; Yang, J.; Kong, Y.; Gao, M. Effects of substitutional atoms on the properties of γ’-(Fe1-xTMx)4N (TM = Co, Ni) compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1997, 172, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnen, C.A.; de Figueiredo, R.S.; dos Santos, A.V. Mössbauer spectroscopy, crystallographic, magnetic and electronic structure of ZnFe3N and InFe3N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 219, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, A.; Müller, P.; von Appen, J.; Lueken, H.; Niewa, R.; Dronskowski, R. Synthesis, crystal structure, and magnetic properties of the semihard itinerant ferromagnet RhFe3N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7212–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, A.; Burghaus, J.; Dronskowski, R. The Ternary Nitrides GaFe3N and AlFe3N: Improved Synthesis and Magnetic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4332–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghaus, J.; Kleemann, J.; Dronskowski, R. The Ternary Nitrides InxFe4-xN (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.8): Synthesis, Magnetic Properties, and Theoretical Considerations. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2011, 637, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriedt, H.A.; Gokcen, N.A.; Nafziger, R.H. The Fe-N (Iron-Nitrogen) System. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1987, 8, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewa, R.; Rau, D.; Wosylus, A.; Meier, K.; Hanfland, M.; Wessel, M.; Dronskowski, R.; Dzivenko, D.A.; Riedel, R.; Schwarz, U. High-Pressure, High-Temperature Single-Crystal Growth, Ab initio Electronic Structure Calculations, and Equation of State of epsilon-Fe3N1+x. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, K.H. The Iron–Nitrogen System: The Crystal Structures of ε-Phase Iron Nitrides. Acta Crystallogr. 1952, 5, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.; Rechenbach, D.; Zachwieja, U. Structure determination of γ’-Fe4N and ε-Fe3N. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 227, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leineweber, A.; Jacobs, H.; Hüning, F.; Lueken, H.; Schilder, H.; Kockelmann, W. ε-Fe3N: Magnetic structure, magnetization and temperature dependent disorder of nitrogen. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 288, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Magnetic properties of Co and Ni substituted ε-Fe3N nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 2005, 164, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Spin-glass-like ordering in ε-Fe3-xNixN (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sharma, S. Observation of exchange bias and spin-glass-like ordering in ε-Fe2.8Cr0.2N nanoparticles. PRAMANA J. Phys. 2008, 70, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.P.; Raja, M.M.; Panda, R.N. Enhancement of magnetic moment in Co substituted nanocrystalline ε-CoxFe3–xN (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) synthesized by modified citrate precursor route. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 75, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Mössbauer and magnetic studies for the coexistence of ε-Fe3–xNixN and γ’-Fe4–yNiyN phases in Fe-Ni-N nanoparticles. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2007, 45, 834–838. [Google Scholar]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Ningthoujam, R.S.; Weissmuller, J. Mössbauer Study of Nanocrystalline ε-Fe3–xCoxN System. Hyperfine Interact. 2004, 156, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Mössbauer studies of ε-Fe3–xNixN and γ’-Fe4–yNiyN nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 2005, 165, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, N.S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Synthesis and structural investigation of ε-Fe3–xNixN (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) nanoparticles. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. 2006, 52, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningthoujam, R.S.; Gajbhiye, N.S. Magnetization studies on ε-Fe2.4Co0.6N nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010, 45, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y.Q. Effects of nitriding temperature on the structure and magnetic properties of CoFe2 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 29, 20071–20080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, H. (Fe1–xNix)3N nanoparticles: The structure, magnetic and photocatalytic properties for water splitting. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44641–44645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S.; Hu, Q.; Fang, L.; Chen, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.; Ohfuji, H.; Kojima, Y.; et al. Neutron diffraction study of structural and magnetic properties of ε-Fe3N1.098 and ε-Fe2.322Co0.678N0.888. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 752, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, S.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Q.; Qi, L.; Feng, L.; Lei, L. Synthesis and characterization of spherical-bulk ε-Fe3–xCoxN (x = 0.0, 0.25, 1.95). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 197, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Ye, Z.; Qie, Y.; Fan, Z.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Yang, H. The synthesis, morphology and magnetic properties of (Fe1–xMnx)3N nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 30, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Pan, X.; Ye, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Yang, H. Synthesis, Structure and Properties Comparison of Fe3N Doped with Ni, Mn and Co. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5945–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Rau, D.; Toffoletti, L.; Müller, C.; Burkhardt, U.; Schnelle, W.; Niewa, R.; Schwarz, U. Ternary Metastable Nitrides ε-Fe2TMN (TM = Co, Ni): High-Pressure, High-Temperature Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Thermal Stability, and Magnetic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 4600–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Rau, D.; Schnelle, W.; Burkhardt, U.; Niewa, R.; Schwarz, U. High-Pressure High-Temperature Synthesis of ε-Fe2IrN0.24. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akselrud, L.; Grin, Y. WinCSD: Software package for crystallographic calculations (Version 4). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapina, T.; Leineweber, A.; Mittemeijer, E.J.; Kockelmann, W. The lattice parameters of ε-iron nitrides: Lattice strains due to a varying degree of nitrogen ordering. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Brook, G.B. Smithells Metals Reference Book, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 9780080517308. [Google Scholar]
- Oberg, E.; Jones, F.D.; Horton, H.L.; Ryffel, H.H. Machinery’s Handbook, 27th ed.; Industrial Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, T.; de Wit, L.; Saris, F.W.; Königer, A.; Rauschenbach, B.; Wolff, G.K.; Krauss, S. Hardness and corrosion resistance of single-phase nitride and carbide on iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1995, A199, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guemmaz, M.; Mosser, A.; Grob, J.J.; Stuck, R. Sub-surface modifications induced by nitrogen ion implantation in stainless steel (SS316L). Correlation between microstructure and nanoindentation results. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998, 100, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauling, L. The nature of the interatomic forces in metals. Phys. Rev. 1938, 54, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.C. Electronic structure of alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1937, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
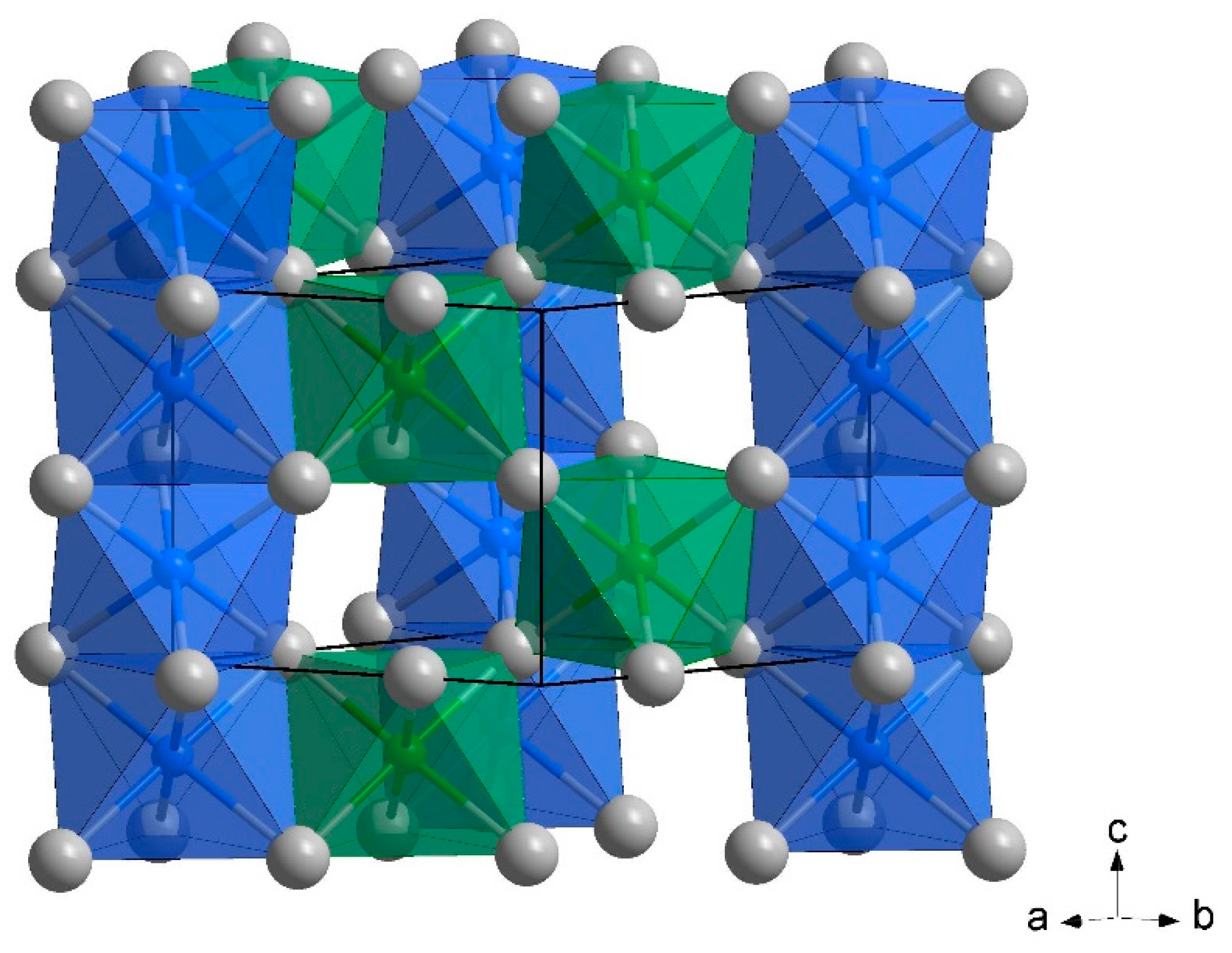
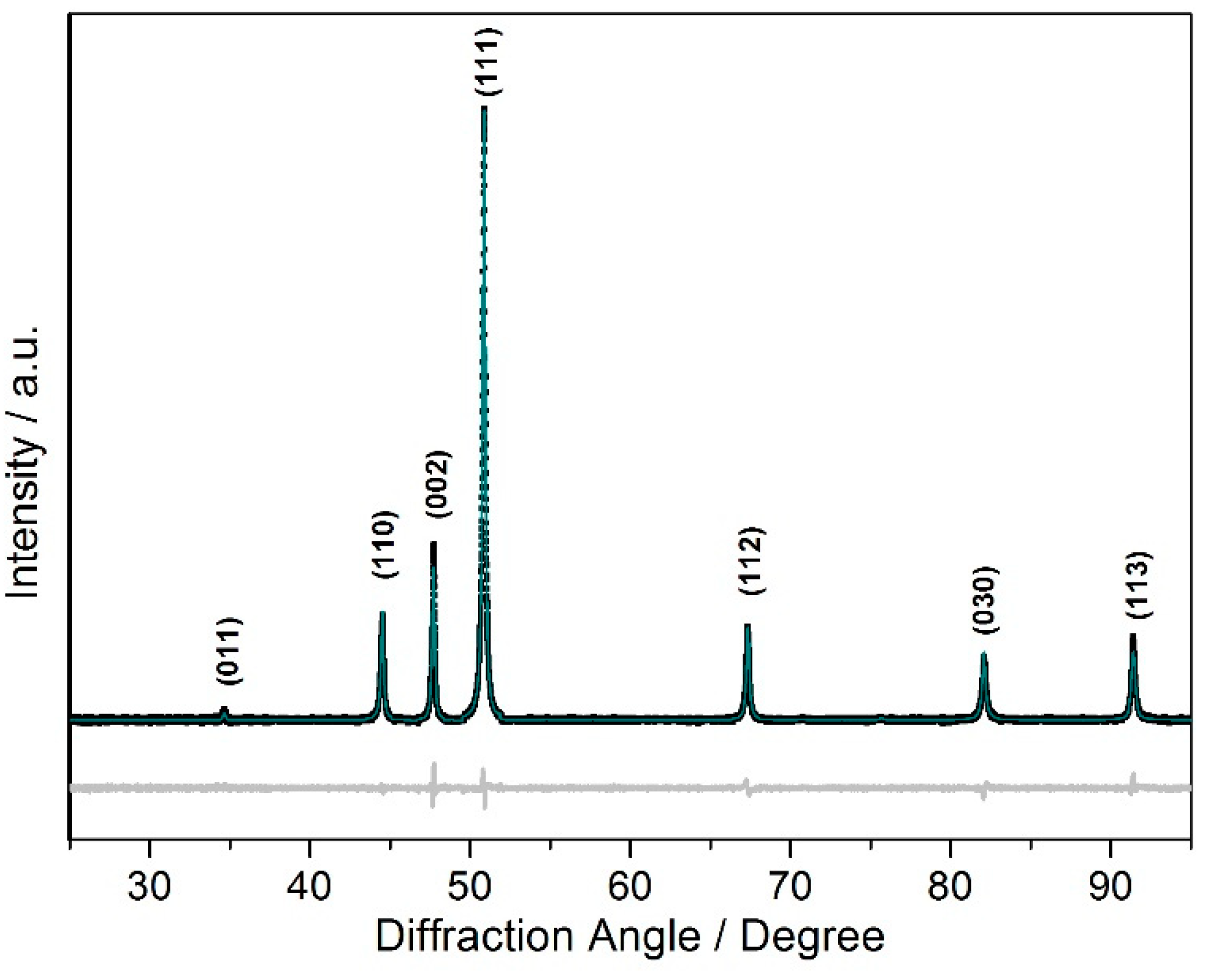
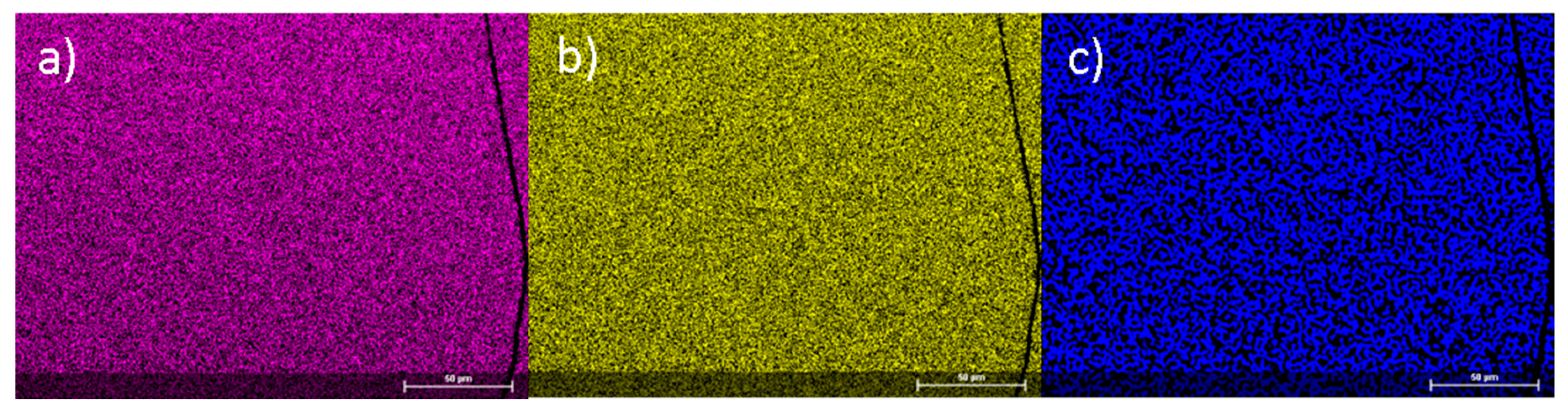
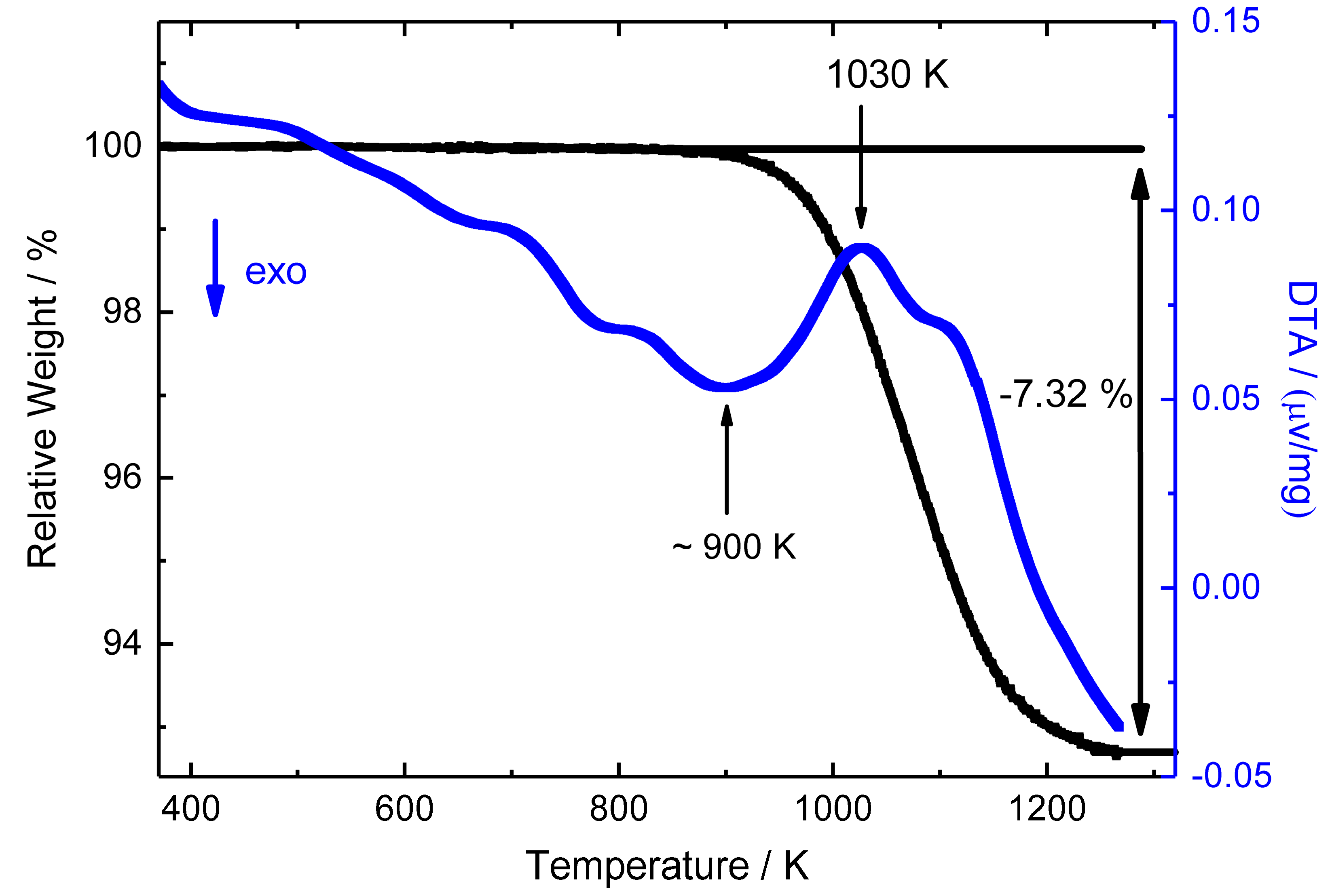
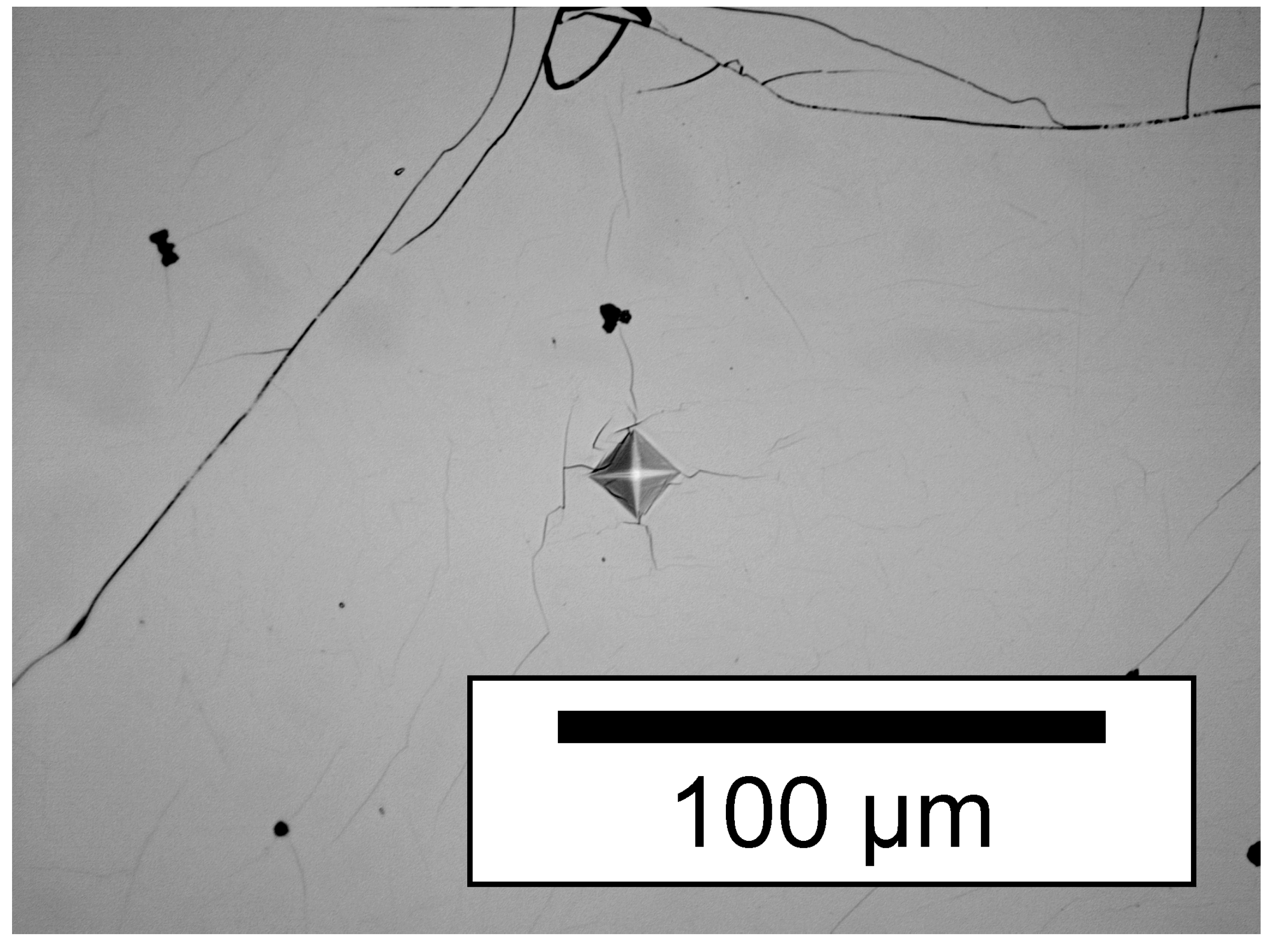
| Composition | Fe2MnN |
|---|---|
| Space group | P6322 (No. 182) |
| Structure type | ε-Fe3N |
| Unit cell | |
| a/Å | 4.71875(5) |
| c/Å | 4.41981(7) |
| Volume/Å3 | 85.229(3) |
| Formula units, Z | 2 |
| Radiation 1 | CoKα1 |
| Measurement range, deg. | 3.5 ≤ 2θ ≤ 95.465 |
| Measured points | 18394 |
| Measured reflections | 17 |
| Refined parameters | 8 |
| R(P)/R(wP) | 0.034/0.0056 |
| Atom | Site | SOF 1 | x | y | z | Biso |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe, Mn | 6g | 2/3, 1/3 | 0.3413(3) | 0 | 1/2 | 1.0(2) |
| N | 2c | 0.571(8) | 2/3 | 1/3 | 3/4 | 1 |
| N | 2b | 0.429 | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 1 |
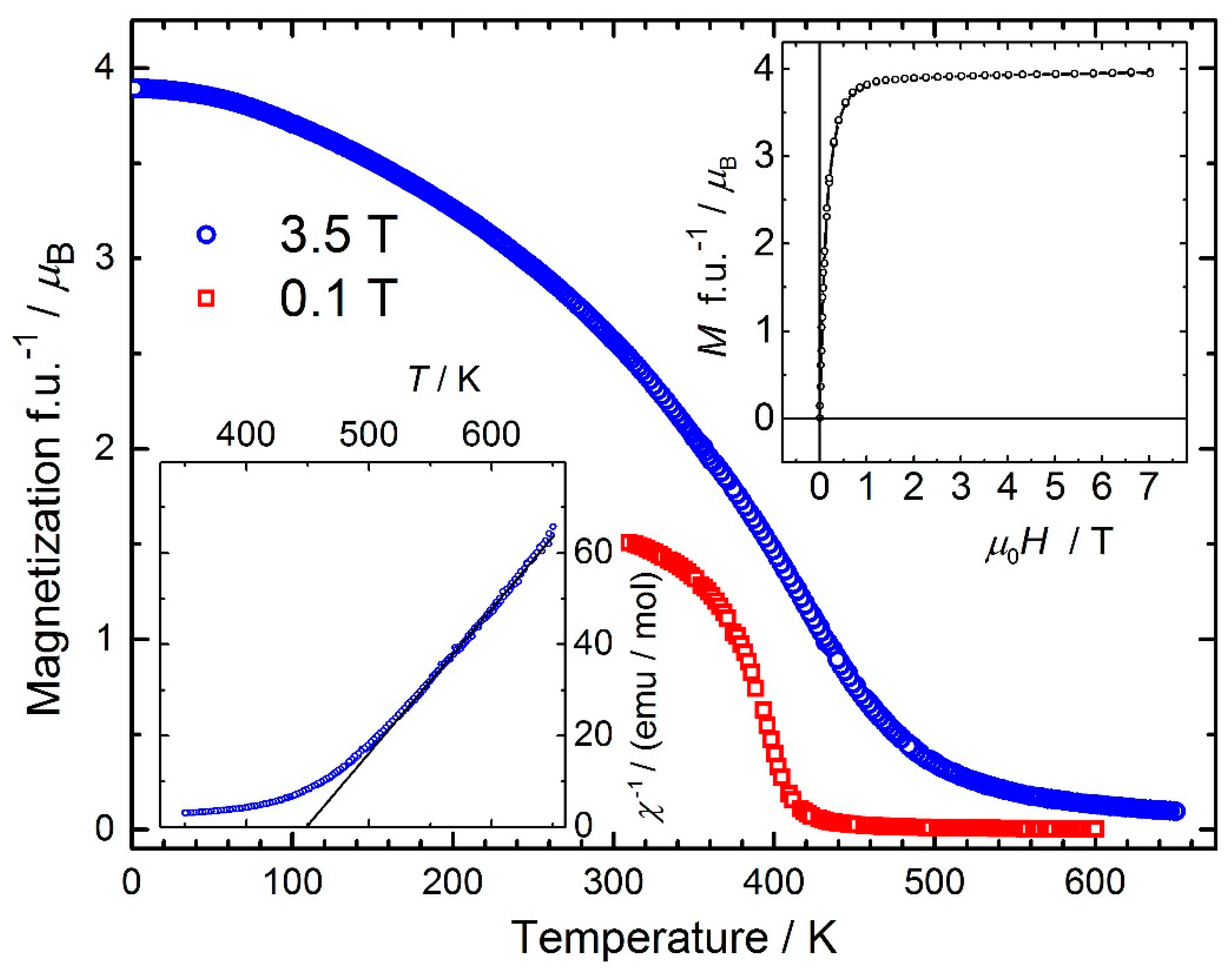
| M | Msp/µB | TC/K | a/Å | c/Å | TD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 3.88 | 402 | 4.71875(5) | 4.41981(7) | 900 | this work |
| Fe | 6.0 | 575 | 4.6982(3) | 4.3789(4) | 750 | [24,26] |
| Co | 4.3 | 488 | 4.6759(5) | 4.3776(5) | 750 | [43] |
| Ni | 3.1 | 234 | 4.6698(4) | 4.3699(4) | 750 | [43] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwarz, U.; Guo, K.; Clark, W.P.; Burkhardt, U.; Bobnar, M.; Castillo, R.; Akselrud, L.; Niewa, R. Ferromagnetic ε-Fe2MnN: High-Pressure Synthesis, Hardness and Magnetic Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121993
Schwarz U, Guo K, Clark WP, Burkhardt U, Bobnar M, Castillo R, Akselrud L, Niewa R. Ferromagnetic ε-Fe2MnN: High-Pressure Synthesis, Hardness and Magnetic Properties. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121993
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwarz, Ulrich, Kai Guo, William P. Clark, Ulrich Burkhardt, Matej Bobnar, Rodrigo Castillo, Lev Akselrud, and Rainer Niewa. 2019. "Ferromagnetic ε-Fe2MnN: High-Pressure Synthesis, Hardness and Magnetic Properties" Materials 12, no. 12: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121993
APA StyleSchwarz, U., Guo, K., Clark, W. P., Burkhardt, U., Bobnar, M., Castillo, R., Akselrud, L., & Niewa, R. (2019). Ferromagnetic ε-Fe2MnN: High-Pressure Synthesis, Hardness and Magnetic Properties. Materials, 12(12), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121993







