Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol–A Nanoadsorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Materials Preparation
2.2.1. Graphite Oxide (GO) Preparation
2.2.2. Preparation of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4)
2.2.3. Synthesis of Graphite Oxide/Cross-Linked Chitosan (GO–CS) and Graphite Oxide/Cross-Linked Chitosan/Magnetite (GO–CSm) Composites
2.2.4. Synthesis of Graphite Oxide/Polystyrene (GO-PS) and Graphite Oxide/Polystyrene/Magnetite (GO-PSm) Composites
2.2.5. Synthesis of Graphite Oxide/Polyaniline (GO–PANI) and Graphite Oxide/Polyaniline/Magnetite (GO–PANIm) Composites
2.3. Characterization Techniques—Instrumentation
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Effect of pH and Ionic Strength on BPA Adsorption
2.4.2. Effect of Contact Time
2.4.3. Desorption Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Sorbent Characterization
3.1.1. XRD Measurements
3.1.2. Surface Properties—Morphology
3.1.3. Magnetization Measurements (VSM and 57Fe Mössbauer)
3.2. Adsorption Results
3.2.1. Effect of pH
3.2.2. Effect of Ionic Strength
3.2.3. Effect of Contact Time
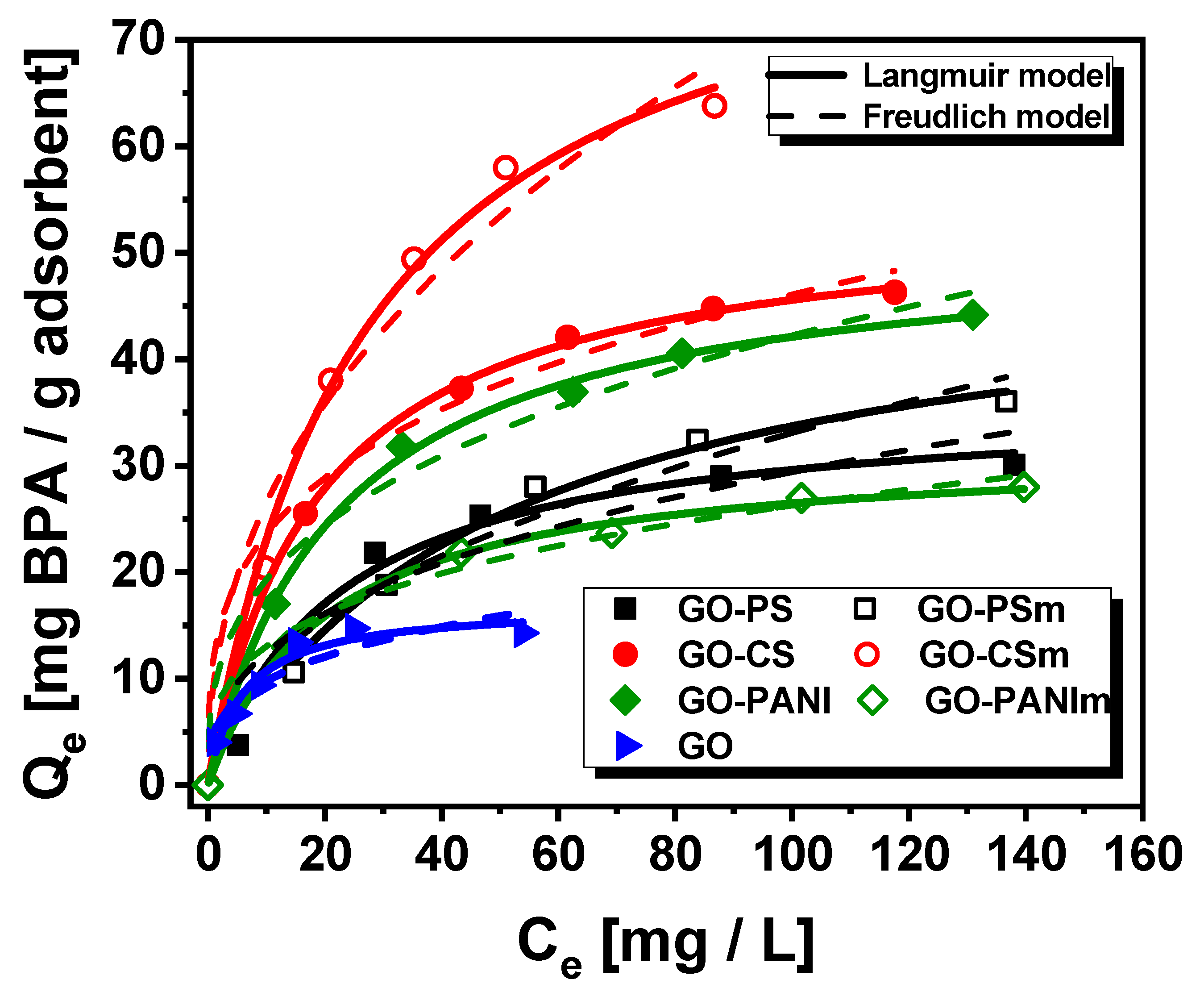
3.2.4. Effect of Initial Concentration
3.2.5. Desorption
3.3. FTIR Measurements
3.4. Mechanism of Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.; Tang, P.; Si, S.; Liu, L. Adsorption and removal of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution by p -phenylenediamine-modified magnetic graphene oxide. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Choo, K.; Lee, B.; Choi, S. The methods of identification, analysis, and removal of endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bele, S.; Samanidou, V.; Deliyanni, E. Effect of the reduction degree of graphene oxide on the adsorption of Bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzidou, A.C.; Deliyanni, E.A. Comparison of activation media and pyrolysis temperature for activated carbons development by pyrolysis of potato peels for effective adsorption of endocrine disruptor Bisphenol-A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.; Lue-Hing, C.; Cotruvo, J.; Drewes, J.E.; Eaton, A.; Pleus, R.C.; Schlenk, D. Pharmaceuticals in the Water Environment; National Association of Clean Water Agencies: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Filippou, O.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Samanidou, V.F. Fabrication and evaluation of magnetic activated carbon as adsorbent for ultrasonic assisted magnetic solid phase dispersive extraction of Bisphenol A from milk prior to high performance liquid chromatographic analysis with ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1479, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwak, S.Y. Rapid adsorption of Bisphenol A from wastewater by β-cyclodextrin-functionalized mesoporous magnetic clusters. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Ni, X.J.; Cao, Y.H.; Cao, G.Q. Adsorption behavior of Bisphenol A on CTAB-modified graphite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassouane, F.; Aït-Amar, H.; Amrani, S.; Rodriguez-Couto, S. A promising laccase immobilization approach for Bisphenol A removal from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Bele, S.; Saroyan, H.S.; Samanidou, V.F.; Bandosz, T.J. Degradation of endocrine disruptor, Bisphenol-A, on an mixed oxidation state manganese oxide/modified graphite oxide composite: A role of carbonaceous phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 539, 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L.; Aziz, H.A. Application of ozone for the removal of Bisphenol A from water and wastewater—A review. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Johansson, E.M.J. Photocatalytic activity and mechanism of Bisphenol a removal over TiO2−x/rGO nanocomposite driven by visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Yusoff, A.R.M.; Shuo, C.W.; Buang, N.A.; Gohari, R.J.; Zahari, A.M.; Yusop, Z.; Gu, F.L.; Lau, W.-J.; Sathishkumar, P. A reusable electrospun PVDF-PVP-MnO2 nanocomposite membrane for Bisphenol A removal from drinking water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5801–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Chen, B. Enhanced Bisphenol A removal from stormwater in biochar-amended biofilters: Combined with batch sorption and fixed-bed column studies. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y. Adsorption of Bisphenol A from water by surfactant-modified zeolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.; Ye, C. Fabrication of three functionalized silica adsorbents: Impact of co-immobilization of imidazole, phenyl and long-chain alkyl groups on Bisphenol A adsorption from high salt aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Sun, Z.; Park, Y.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Removal of Bisphenol A from wastewater by Ca-montmorillonite modified with selected surfactants. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Cao, R.; Sun, H. Analytica chimica acta molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres prepared by Pickering emulsion polymerization for selective solid-phase extraction of eight bisphenols from human urine samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 872, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Czech, B.; Wójcik, G.; Naebe, M. The light enhanced removal of Bisphenol A from wastewater using cotton waste derived carbon microtubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 539, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions with untreated coffee residues as potential low-cost adsorbents: Equilibrium, reuse and thermodynamic approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, A.R.; Rahaman, M.S. Removal of Bisphenol A by electrochemical carbon-nanotube filter: Influential factors and degradation pathway. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Ye, N. Magnetite-graphene oxide composites as a magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of trace sulfonamides in water samples. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9725–9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Tian, S.; Zhu, J.; Lu, M. Fe3O4 nanoparticles as the adsorbent of magnetic solid-phase extraction for clean and preconcentration of maltol and ethyl maltol in food samples followed by HPLC Analysis. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X. Recent advances of adsorbents in solid phase extraction for environmental samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 96, 407–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Chang, Q.; Hou, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Analytical methods graphene grafted magnetic microspheres for solid phase extraction of Bisphenol A and triclosan from water samples followed by gas chromatography- mass spectrometric analysis. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Fan, H. Adsorption and removal of Bisphenol A, α-naphthol and β-naphthol from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@polyaniline core-shell nanomaterials. Synth. Met. 2016, 212, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, C.T.; Yavuz, C.T.; Mayo, J.T.; Yu, W.W.; Prakash, A.; Falkner, J.C.; Yean, S.; Cong, L.; Shipley, H.J.; Kan, A.; et al. Low-field magnetic separation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals. Science 2006, 341, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonidis, K.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Kaprara, E.; Mitrakas, M.; Polavarapu, L. Inorganic engineered nanoparticles in drinking water treatment: A critical review. Environ. Sci Water Res. Tech. 2016, 2, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Journal of colloid and interface science magnetic modification of microporous carbon for dye adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Graphite oxide/chitosan composite for reactive dye removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Deliyanni, E.A. Functionalization of graphite oxide with magnetic chitosan for the preparation of a nanocomposite dye adsorbent. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelgund, G.M.; Bliznyuk, V.N.; Oki, A. Photocatalytic activity and NIR laser response of polyaniline conjugated graphene nanocomposite prepared by a novel acid-less method. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 187, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matko, V.; Jezernik, K. Greatly improved small inductance measurement using quartz crystal parasitic capacitance compensation. Sensors 2010, 10, 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matko, V. Next generation AT-cut quartz crystal sensing devices. Sensors 2011, 11, 4474–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Deliyanni, E.A. Desulfurization of diesel fuels: Adsorption of 4,6-DMDBT on different origin and surface chemistry nanoporous activated carbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore- and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Kinetics of reaction in pure and mixed systems. In Soil Physical Chemistry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahid, M.K.; Phearom, S.; Choi, Y.-G. Evaluation of arsenate adsorption efficiency of mill-scale derived magnetite particles with column and plug flow reactors. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 28, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; He, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, L. Polystyrene/graphene oxide nanocomposites synthesized via Pickering polymerization. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 99, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.A.; Choi, H.J.; Shin, Y.R.; Chang, D.W.; Dai, L.; Baek, J.B. Polyaniline-grafted reduced graphene oxide for efficient electrochemical supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Preparation of activated carbon from date stones by microwave induced chemical activation: Application for methylene blue adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 170, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Arafat, H.A.; Pinto, N.G. Effect of chemical surface heterogeneity on the adsorption mechanism of dissolved aromatics on activated carbon. Carbon 2000, 38, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Toledo, I.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Fernández, F.J.V. Bisphenol A removal from water by activated carbon. Effects of carbon characteristics and solution chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6246–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Toledo, M.I.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Sánchez-Polo, M. Cooperative adsorption of Bisphenol-A and chromium(III) ions from water on activated carbons prepared from olive-mill waste. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 73, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gong, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, C.; Hu, L.; Zhu, L.; Sun, L.; Shu, D. Recyclable CNTs/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites as adsorbents to remove Bisphenol A from water and their regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yao, H.; Li, X.X.; Wang, B.; Huo, P.; Xu, W.; Ou, H.; Yan, Y. Synthesis of chitosan/γ-Fe2O3/fly-ash-cenospheres composites for the fast removal of Bisphenol A and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, T.; Oikawa, K.; Kawata, K.; Ishihara, S.; Iyobe, T.; Yamada, A. Study of removal effect of Bisphenol A and β-estradiol by porous carbon. J. Heal. Sci. 2004, 50, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y. Comparison with as-grown and microwave modified carbon nanotubes to removal aqueous Bisphenol A. Desalination 2009, 249, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Pan, F.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Xia, D.; Li, A. Enhanced adsorption of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution with 2-vinylpyridine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Tan, P.; Li, H. A novel magnesium ascorbyl phosphate graphene-based monolith and its superior adsorption capability for Bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Mitchell, J.K.; Bandosz, T.J. Reactive adsorption of mustard gas surrogate on zirconium (hydr)oxide/graphite oxide composites: The role of surface and chemical features. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies, Tables and Charts; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0471852988. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bandosz, T.J. Zinc (hydr)oxide/graphite oxide/AuNPs composites: Role of surface features in H2S reactive adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 436, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Khezri, K. A grafting from approach to graft polystyrene chains at the surface of graphene nanolayers by RAFT polymerization: Various graft densities from hydroxyl groups. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Xu, W.Z.; Charpentier, P.A. Synthesis of graphene-polystyrene nanocomposites via RAFT polymerization. Polymer 2014, 55, 5322–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Morimoto, M.; Sashiwa, H.; Saimoto, H.; Shigemasa, Y. Preparation and characterization of water-soluble chitin and chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 36, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H.; Sun, M. Fabrication of novel magnetic chitosan grafted with graphene oxide to enhance adsorption properties for methyl blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tu, Y.; Li, L.; Shang, S.; Tao, X.M. Well-dispersed chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divandari, H.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Schaffie, M.; Ranjbar, M. Integrating synthesized citric acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles with magnetic fields for enhanced oil recovery: Experimental study and mechanistic understanding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooss, V.A.; Athawale, A.A. Polyaniline–graphene oxide nanocomposites: Influence of nonconducting graphene oxide on the conductivity and oxidation-reduction mechanism of polyaniline. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 3778–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwer, S. Graphene oxide-polyaniline nanocomposites for high performance supercapacitor and their optical, electrical and electrochemical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, D.; Liu, C.; Chen, F.; Liu, J. Preparation of polyaniline/graphene oxide nanocomposite for the application of supercapacitor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 307, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ruan, X. Shell-free three-dimensional graphene-based monoliths for the aqueous adsorption of organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Ye, H.; Li, M.M.; Zhao, B.X. Efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.F. Elimination of Bisphenol A from water via graphene oxide adsorption. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2013, 29, 829–836. [Google Scholar]
- Marzougui, Z.; Chaabouni, A.; Elleuch, B.; Elaissari, A. Removal of Bisphenol A and some heavy metal ions by polydivinylbenzene magnetic latex particles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15807–15819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Shen, S.L.; Zhao, B.X. A novel water treatment magnetic nanomaterial for removal of anionic and cationic dyes under severe condition. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xing, B. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by carbon nanotubes: Role of aromaticity and substitution of hydroxyl groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7254–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Pignatello, J.J. Characterization of aromatic compound sorptive interactions with black carbon (charcoal) assisted by graphite as a model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Ghadermazi, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sadighara, P.; Jahed-Khaniki, G.; Heibati, B.; McKay, G. Adsorptive removal of endocrine disrupting Bisphenol A from aqueous solution using chitosan. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Tang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, C.; Xu, P.; Cheng, M.; Wan, J.; Wang, R. Fabrication of water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer based on β-cyclodextrin modified magnetic chitosan and its application for selective removal of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 77, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chi, B.; Li, M.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D. Synthesis of sulfonated polystyrene sphere based magnesium silicate and its selective removal for Bisphenol A. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 14, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
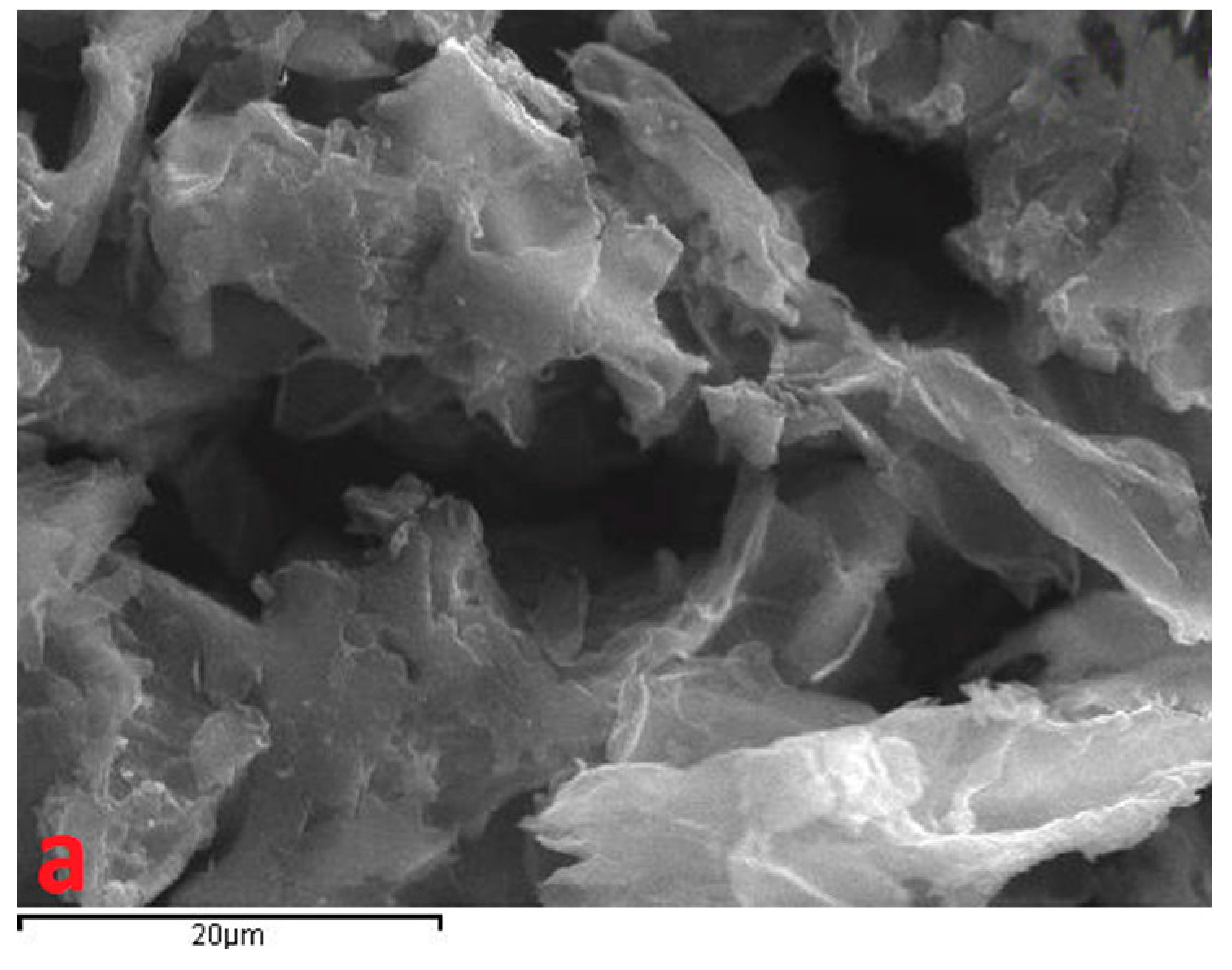













| Adsorbent | SSA m2/g | Vtot (cm3/g) | Vmic (cm3/g) | Vmes (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | 20.93 | 0.088 | 0.064 | 0.024 |
| GO–PS | 8.35 | 0.061 | 0 | 0.061 |
| GO–PSm | 10.00 | 0.059 | 0 | 0.059 |
| GO–CS | 0.89 | 0.099 | 0 | 0.099 |
| GO–CSm | 5.32 | 0.034 | 0 | 0.034 |
| GO–PANI | 27.02 | 0.260 | 0 | 0.260 |
| GO–PANIm | 35.78 | 0.300 | 0 | 0.300 |
| Adsorbent | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| GO–PS | 0.0991 | 19.20 | 0.947 | 0.0083 | 20.49 | 0.997 |
| GO–PSm | 0.1951 | 32.95 | 0.936 | 0.0083 | 36.04 | 0.976 |
| GO–CS | 0.0486 | 46.28 | 0.968 | 0.0011 | 52.66 | 0.992 |
| GO–CSm | 0.0320 | 69.12 | 0.934 | 0.0004 | 81.26 | 0.976 |
| GO–PANI | 0.1260 | 44.91 | 0.948 | 0.0039 | 48.49 | 0.980 |
| GO–PANIm | 0.0161 | 25.15 | 0.912 | 0.0003 | 34.71 | 0.895 |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir Model | Freudlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| GO | 17.27 | 0.172 | 0.934 | 5.03 | 0.299 | 0.772 |
| GO–PS | 36.27 | 0.044 | 0.972 | 5.24 | 0.374 | 0.853 |
| GO–PSm | 50.25 | 0.020 | 0.990 | 3.82 | 0.468 | 0.942 |
| GO–CS | 54.18 | 0.053 | 0.997 | 12.07 | 0.291 | 0.952 |
| GO–CSm | 86.22 | 0.037 | 0.989 | 9.70 | 0.436 | 0.931 |
| GO–PANI | 51.56 | 0.045 | 0.995 | 8.81 | 0.340 | 0.944 |
| GO–PANIm | 31.76 | 0.050 | 0.991 | 6.49 | 0.303 | 0.961 |
| Adsorbent | Qmax (mg/g) | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetite (Fe3O4) | 5.1 | 2.8–8.5 | [49] |
| GO | 17.3 | 3 | [3] |
| Magnetic chitosan fly-ash-cenospheres | 31.9 | 7 | [50] |
| Porous carbon produced at 1000 °C from Moso bamboo | 41.8 | – | [51] |
| Magnetic carbon nanotubes | 45.3 | 6.2 | [49] |
| Modified carbon nanotubes | 70 | 6 | [52] |
| Reduced GO (RGO) | 80.8 | 3 | [3] |
| Graphene | 94.1 | 3 | [3] |
| Magnetic–polydivinylbenzene | 115.9 | 6–7 | [53] |
| Potato peels derived activated carbon (KOH activation) | 190.7 | 3 | [4] |
| MAP–GBM | 324.0 | 7 | [54] |
| Potato peels derived activated carbon (H3PO4 activation) | 445.9 | 3 | [4] |
| GO–CSm | 86.2 | 3 | This study |
| GO–PSm | 50.25 | 3 | This study |
| GO–PANIm | 31.8 | 3 | This study |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rekos, K.; Kampouraki, Z.-C.; Sarafidis, C.; Samanidou, V.; Deliyanni, E. Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol–A Nanoadsorbents. Materials 2019, 12, 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121987
Rekos K, Kampouraki Z-C, Sarafidis C, Samanidou V, Deliyanni E. Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol–A Nanoadsorbents. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121987
Chicago/Turabian StyleRekos, Kyriazis, Zoi-Christina Kampouraki, Charalampos Sarafidis, Victoria Samanidou, and Eleni Deliyanni. 2019. "Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol–A Nanoadsorbents" Materials 12, no. 12: 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121987
APA StyleRekos, K., Kampouraki, Z.-C., Sarafidis, C., Samanidou, V., & Deliyanni, E. (2019). Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol–A Nanoadsorbents. Materials, 12(12), 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121987








