Optimization on Reducing Slag Entrapment in 150 × 1270 mm Slab Continuous Casting Mold
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
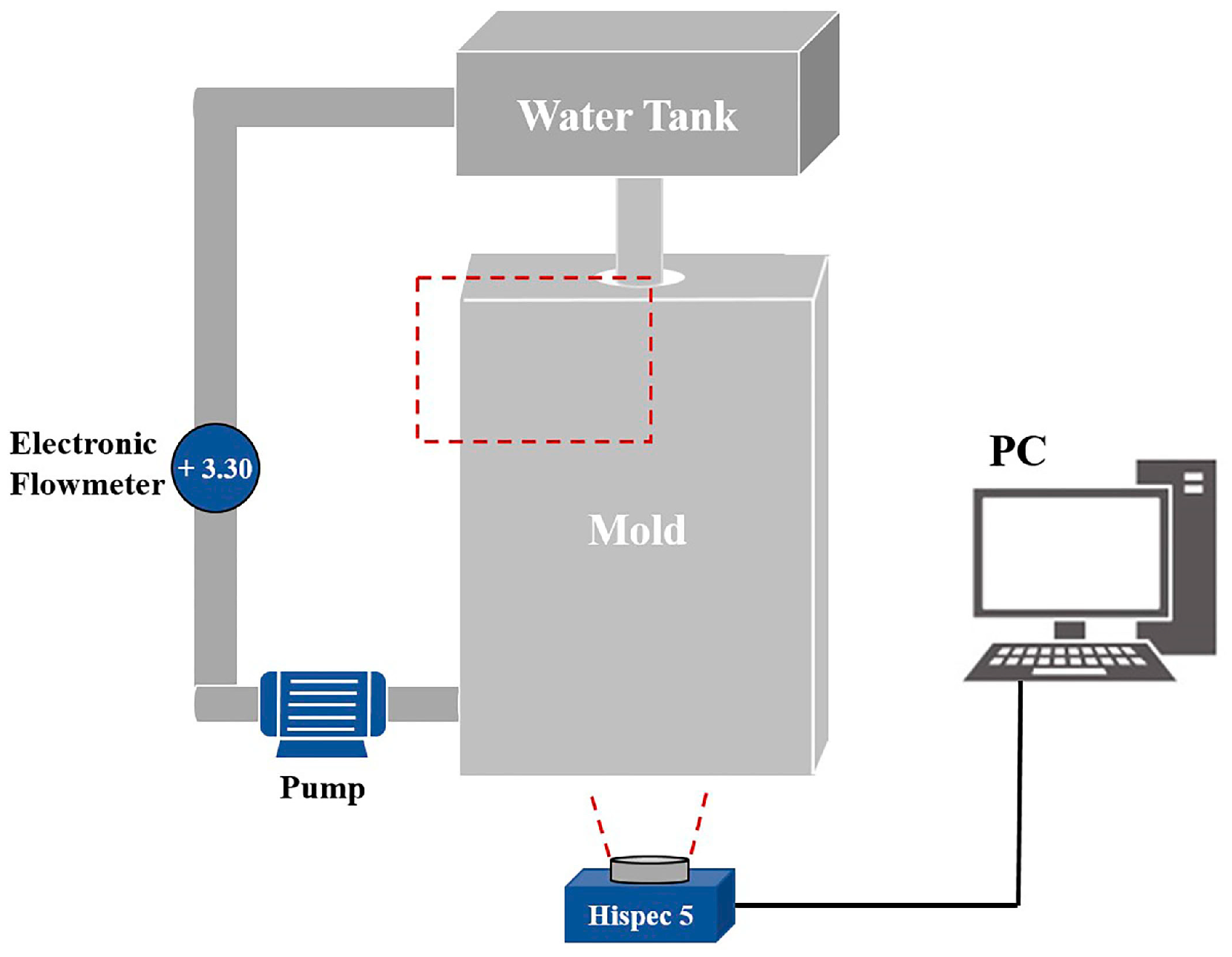
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Similarity Criterion and Dimensional Analysis
2.3. Experiment Schemes and Materials
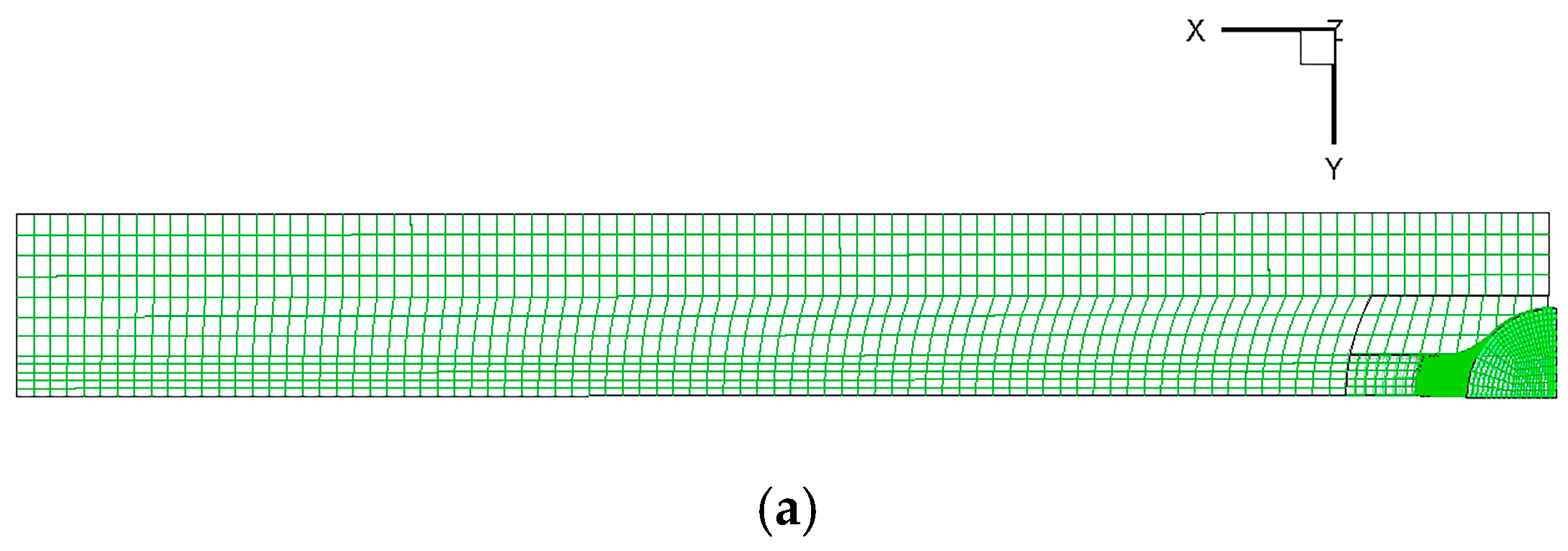
2.4. Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions
3. Results and Discussions
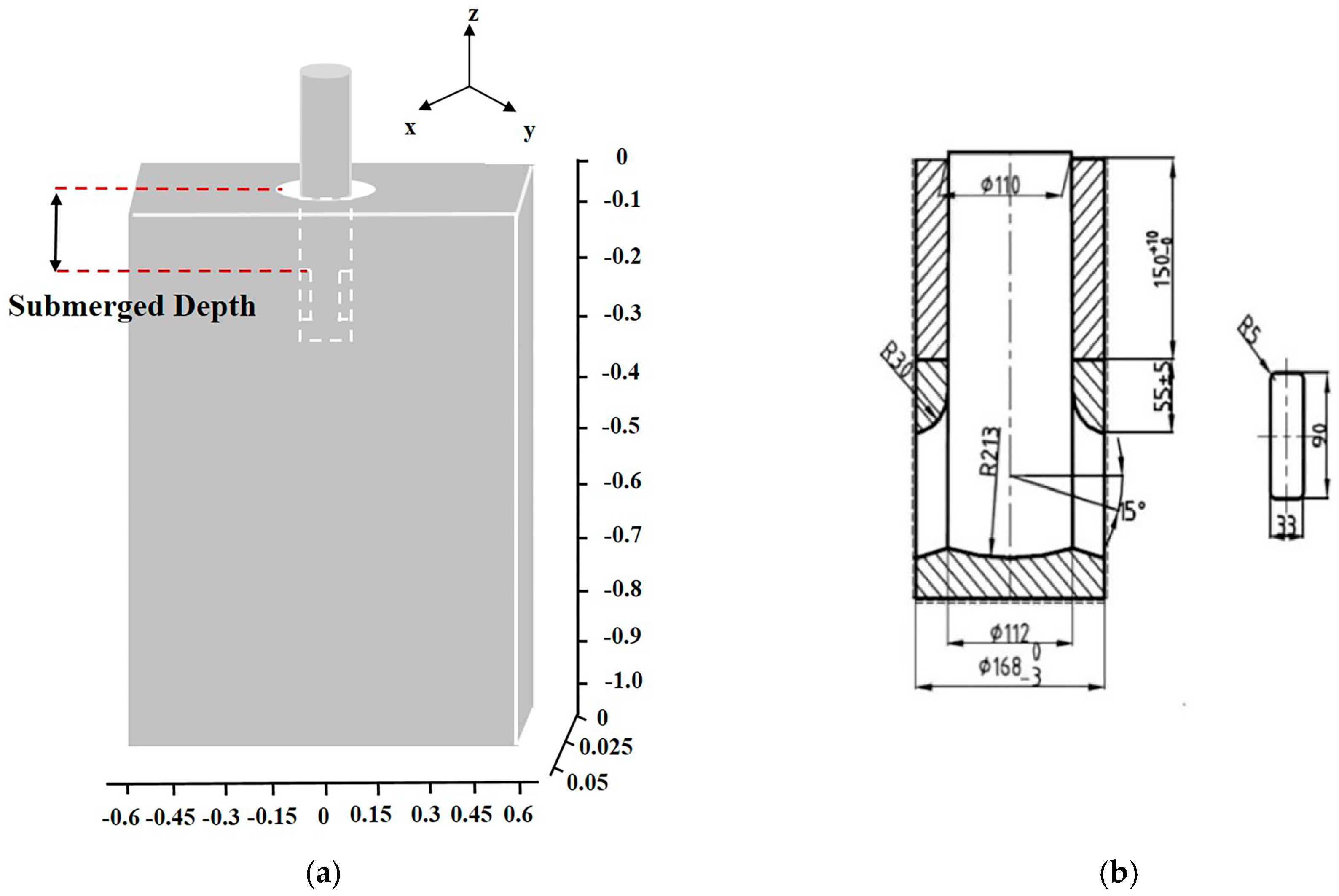
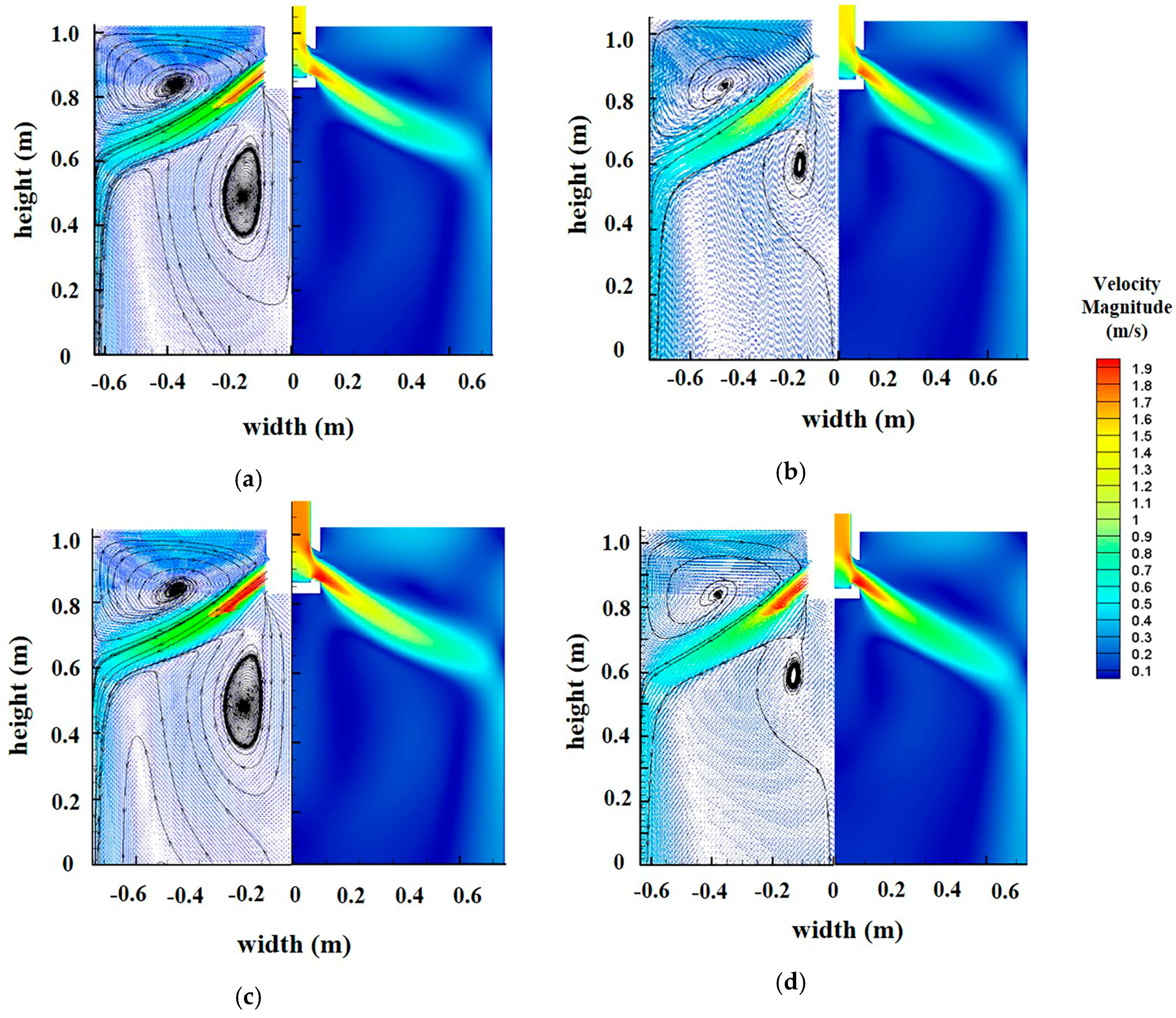
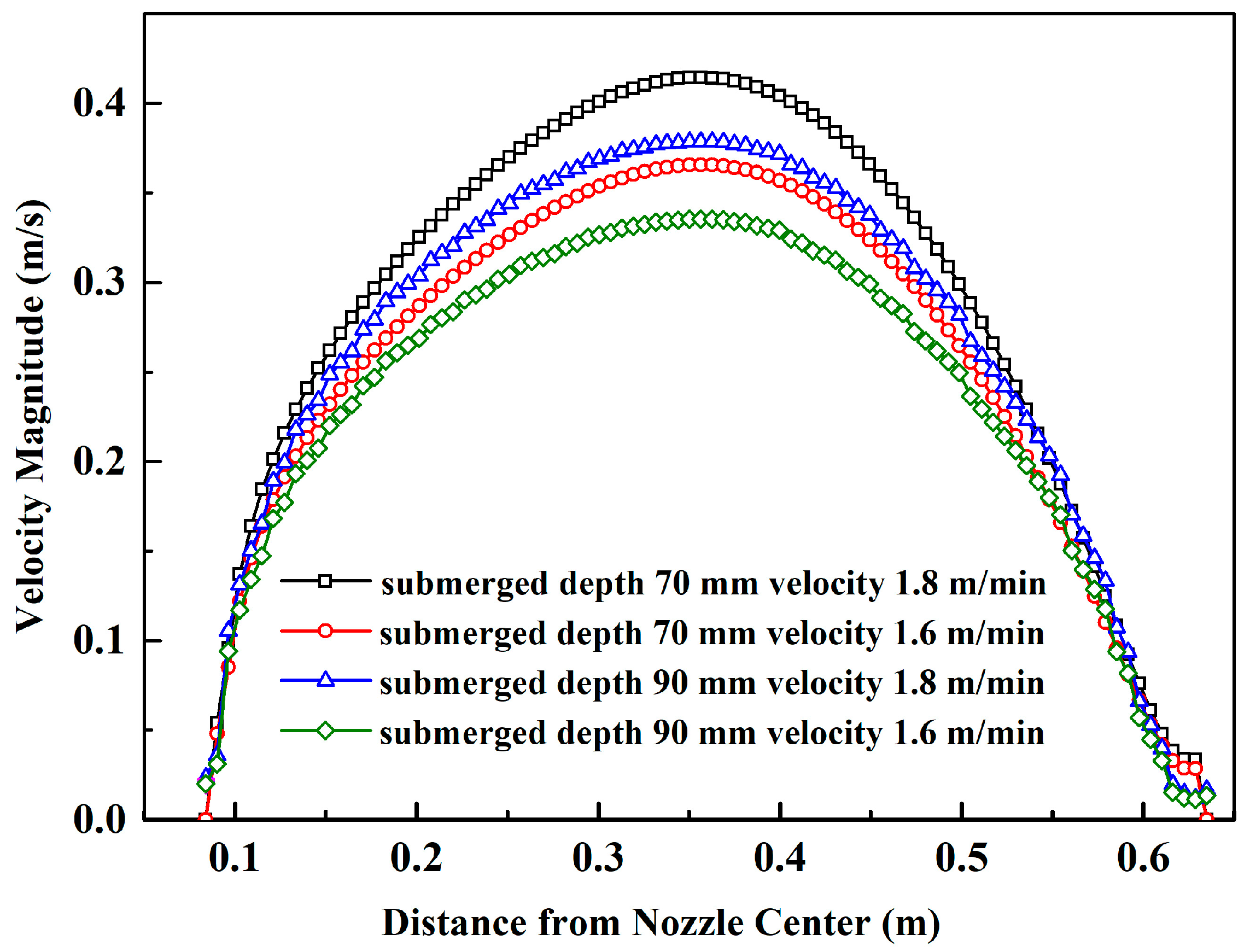
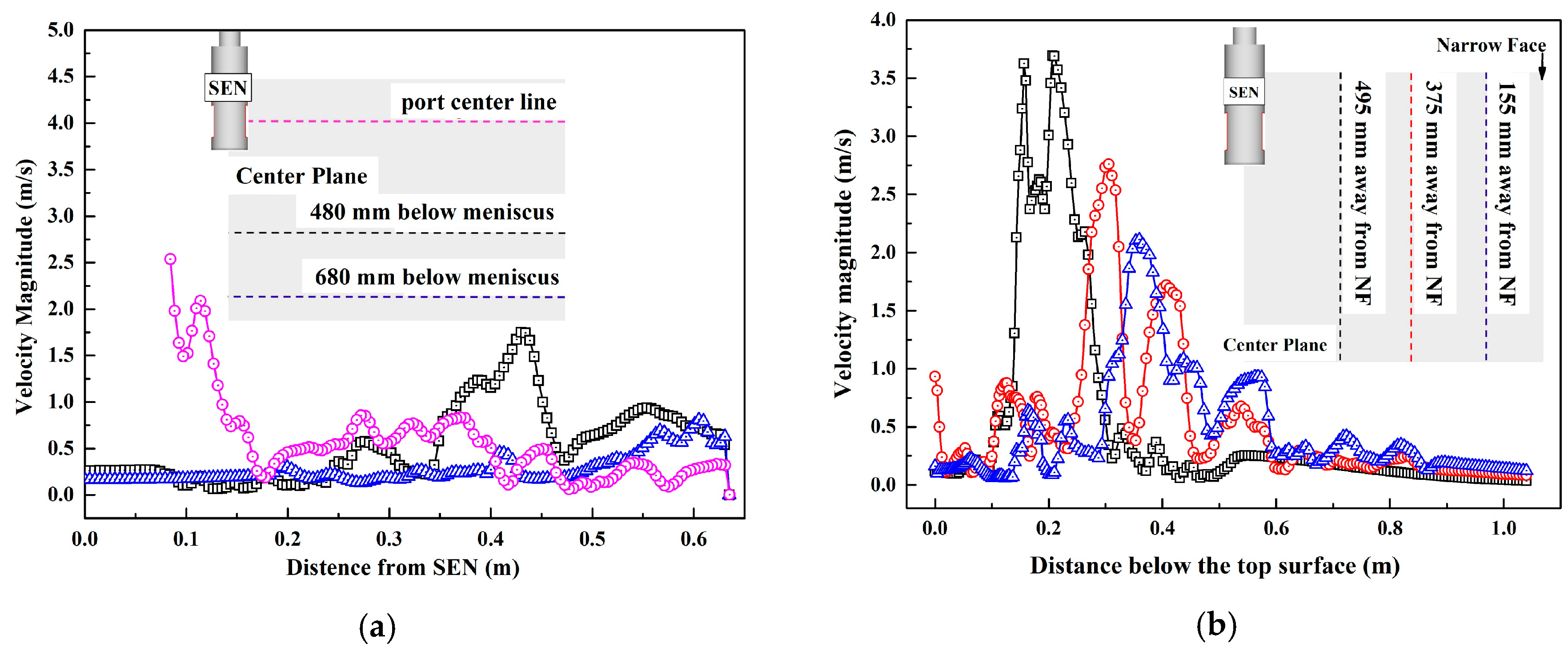
3.1. Submerged Depth and Casting Speed
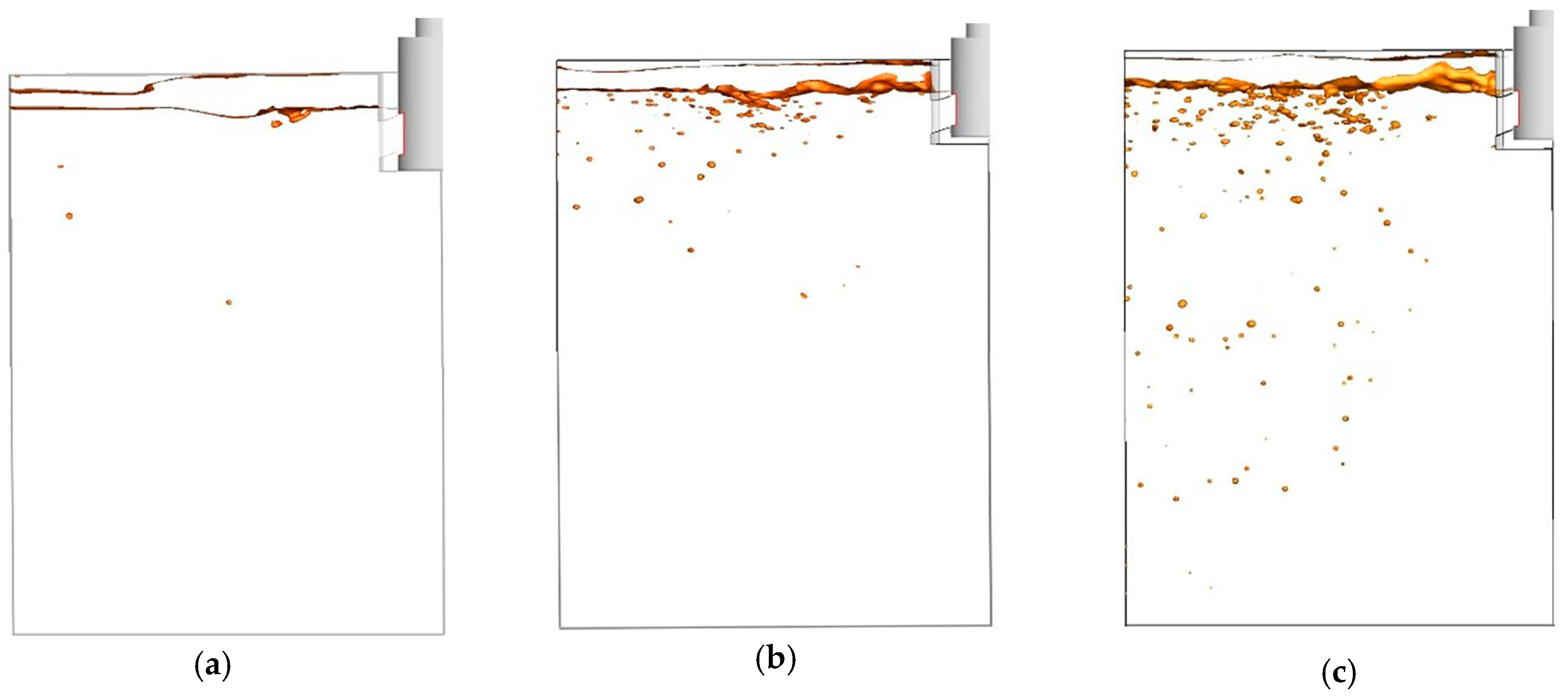
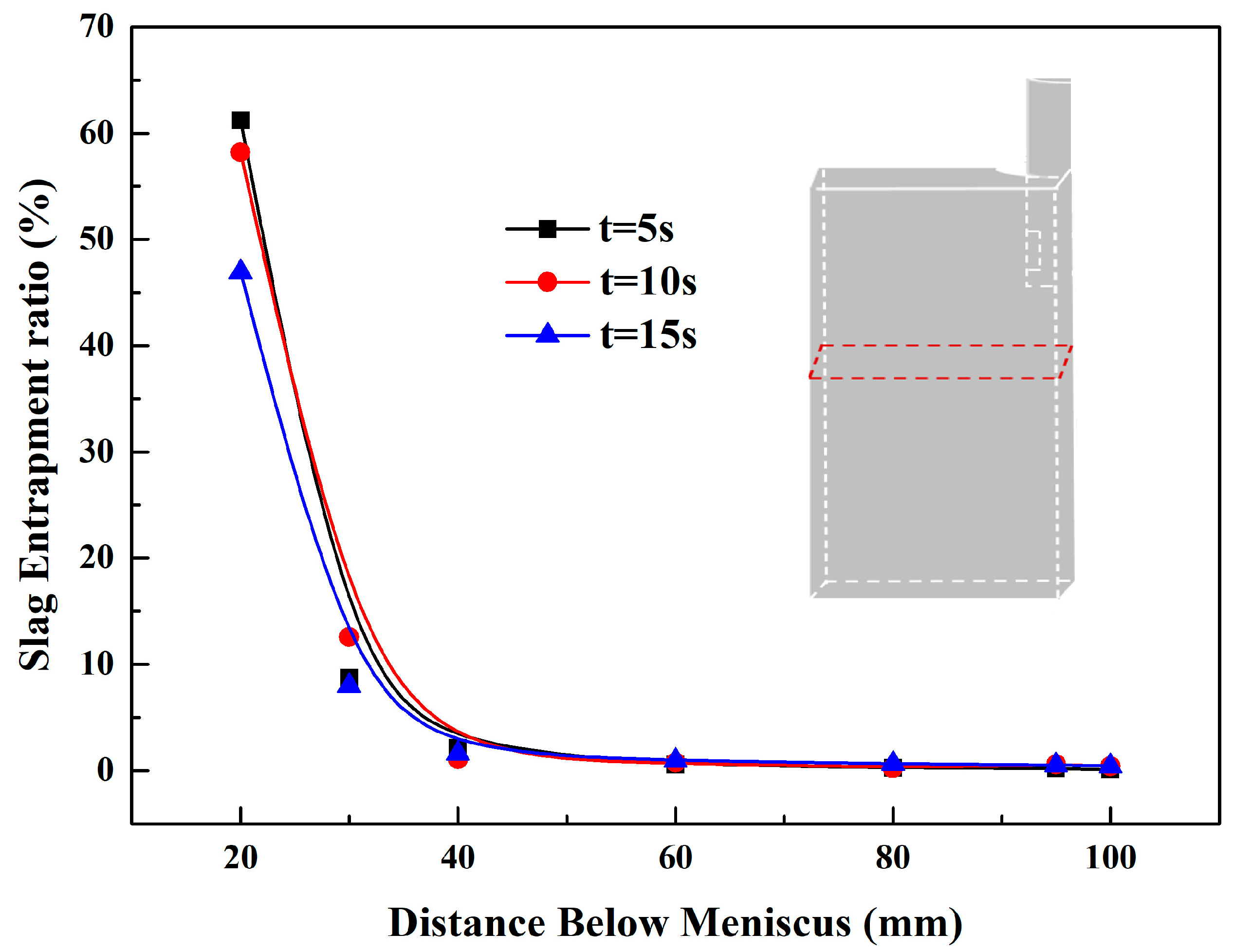
3.2. Slag Entrapment Ratio (SER)
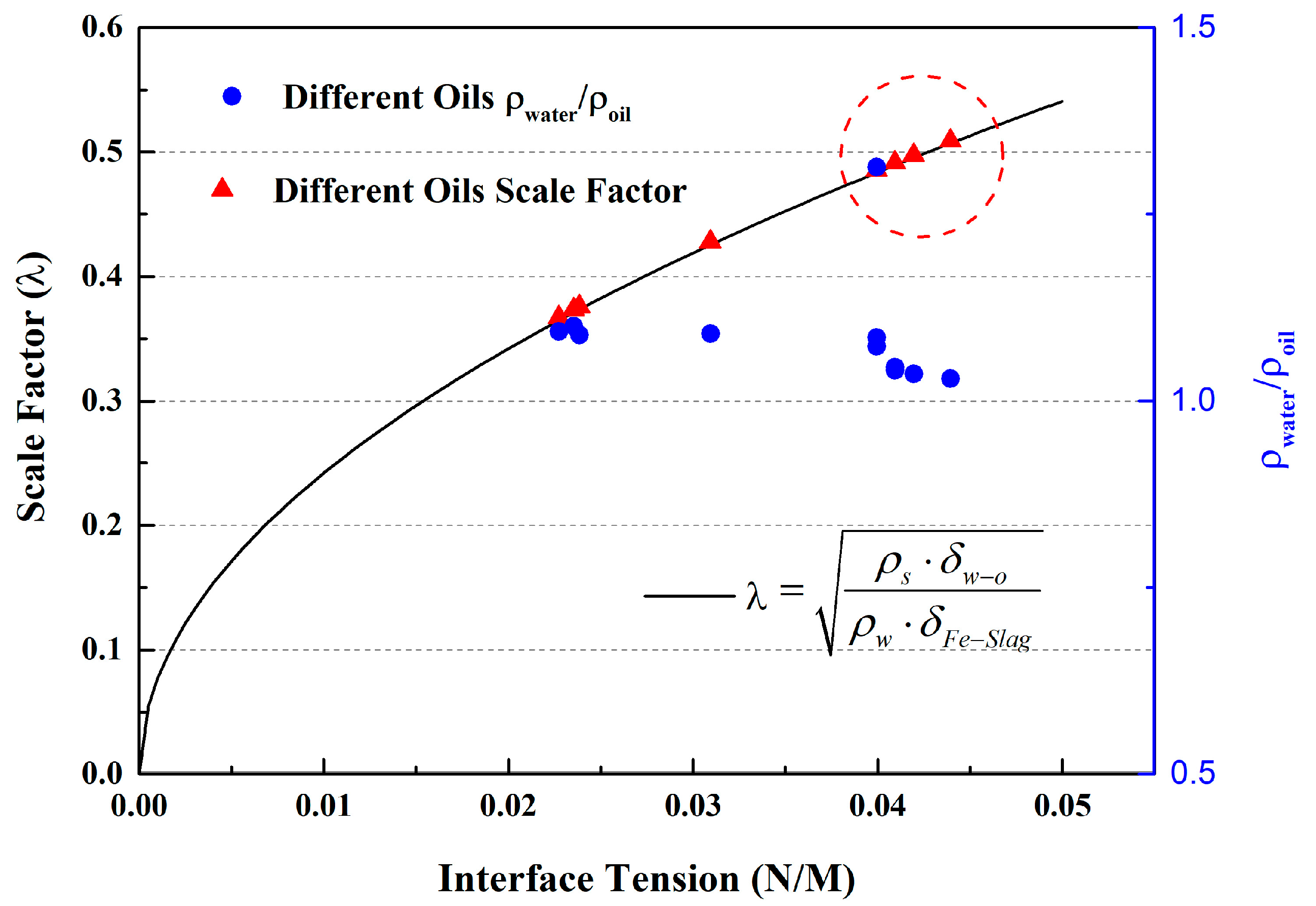
3.3. Effect of Oil Used on the Water Modelling Experiments
3.4. Model Validation
4. Conclusions
- The optimum scheme is SEN submerged depth is 90 mm and casting speed 1.6 m/min. The maximum surface velocity of the optimum scheme is the smallest (0.335 m/s), which is reduced by 19.1%, 11.4% and 8.3%, respectively, compared with the other three conditions.
- A new dimensionless parameter, the slag entrapment ratio (SER), was defined to explain the mixing of slag phase in each cross-plane. After 15 s, the maximum SER (0.44 %) appeared at the position of 0.1 m below the meniscus.
- The dimensionless parameter density ratio was found to be an important factor. Furthermore, the density ratio of oil used (silicon oil AK 0.65) in the water modelling experiment to water is closer to the density ratio of slag and steel compared with other common oils.
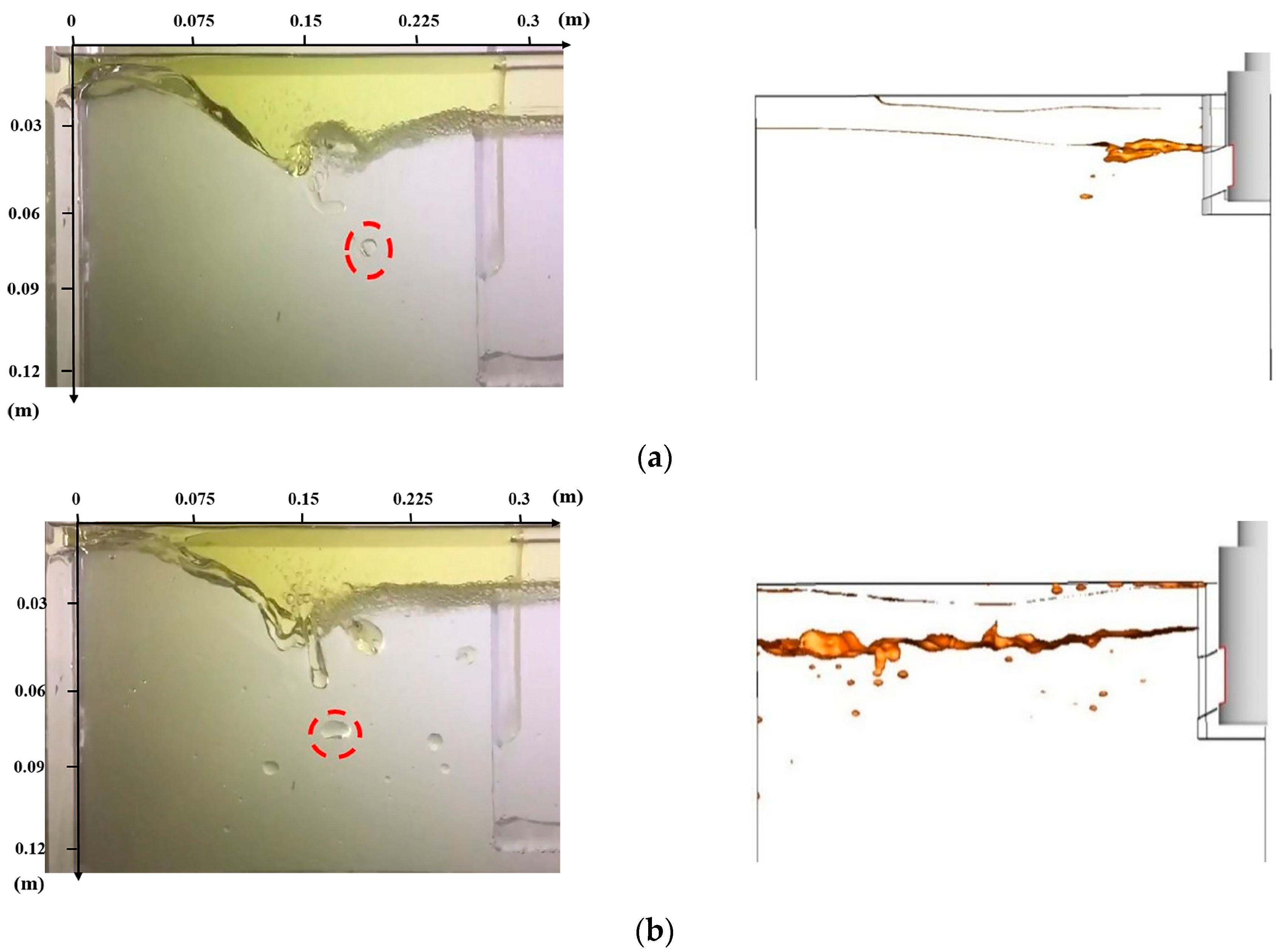
- The water modelling results were in good agreement with the numerical simulation results and the slag droplets observed in the experiment were found to be more likely to be entrapped in the area where the SER value is large.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Svensson, J.K.S.; Memarpour, A.; Brabie, V.; Jönsson, P.G. Studies of the decarburisation phenomena during preheating of submerged entry nozzles (SEN) in continuous casting processes. Ironmaking Steelmaking 2017, 44, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Cai, K.K.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Thomas, B.G. Investigation of fluid flow and steel cleanliness in the continuous casting strand. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.R.; Díaz, C.M.; Olivares, X.O.; Palafox, R.J. A physical model for the two-phase flow in a continuous casting mold. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Vanka, S.P.; Thomas, B.G.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Computational and experimental study of turbulent flow in a 0.4-scale water model of a continuous steel caster. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W. Water modeling of mold powder entrapment in slab continuous casting mold. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2007, 14, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q. Observations of vortex formation in the mould of a continuous slab caster. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhed, H.; Jonsson, L. An investigation of slag floatation and entrapment in a continuous-casting tundish using fluid-flow simulations, sampling and physical metallurgy. Scand. J. Metall. 2003, 32, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeler, L.C.; Thomas, B.G. Mold slag entrainment mechanisms in continuous casting molds. AISE Steel Technol. 2013, 10, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi, M.; Yoshida, J.; Shimizu, T.; Mizuno, Y. Model study on the entrapment of mold powder into molten steel. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmholtz, H.L.F. Über discontinuirliche Flüssigkeits-Bewegungen. Über die Erhaltung der Kraft 1868, 23, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ippen, A.T. Review: L. M. Milne-Thomson, Theoretical Hydrodynamics. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1941, 47, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savolainen, J.; Fabritius, T.; Mattila, O. Effect of fluid physical properties on the emulsification. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallison, J.M. The deformation of small viscous drops and bubbles in shear flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1984, 16, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthes-Biesel, D.; Acrivos, A. Deformation and burst of a liquid droplet freely suspended in a linear shear field. J. Fluid Mech. 1973, 61, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, H.; Rüdiger, S.; Heller, H.P.; Scheller, P.R. Model investigations on the stability of the steel-slag interface in continuous-casting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijn, R.A. Tipstreaming of drops in simple shear flows. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1993, 48, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristini, V.; Tan, Y.C. Theory and numerical simulation of droplet dynamics in complex flows—A review. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, G.F.; Anna, S.L. Microfluidic methods for generating continuous droplet streams. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, R319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, B.J.; Leal, L.G. An experimental investigation of drop deformation and breakup in steady, two-dimensional linear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 167, 241–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.J.; Lowengrub, J. A surfactant-conserving volume-of-fluid method for interfacial flows with insoluble surfactant. J. Comput. Phys. 2004, 201, 685–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yue, P.; Feng, J.J. Formation of simple and compound drops in microfluidic devices. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 092105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.A.; Stroock, A.D.; Ajdari, A. Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 381–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Espinosa, E.A.; Sánchez-Borroto, Y.; Errasti, M.; Piloto-Rodríguez, R.; Sierens, R.; Roger-Riba, J.; Christopher-Hansen, A. Surface tension prediction of vegetable oils using artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.; Ahmad, A. A study on viscosity, surface tension and volume flow rate of some edible and medicinal oils. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2013, 2, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Sahasrabudhe, S.N.; Rodriguez-Martinez, V.; O’Meara, M.; Farkas, B.E. Density, viscosity, and surface tension of five vegetable oils at elevated temperatures: Measurement and modeling. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1965–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, L.R.; Mitchell, E.E.; Parker, N.S. Interfacial tensions of commercial vegetable oils with water. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, A.G. Interfacial tensions of vegetable oil/water systems: Effect of oil purification. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 1090–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
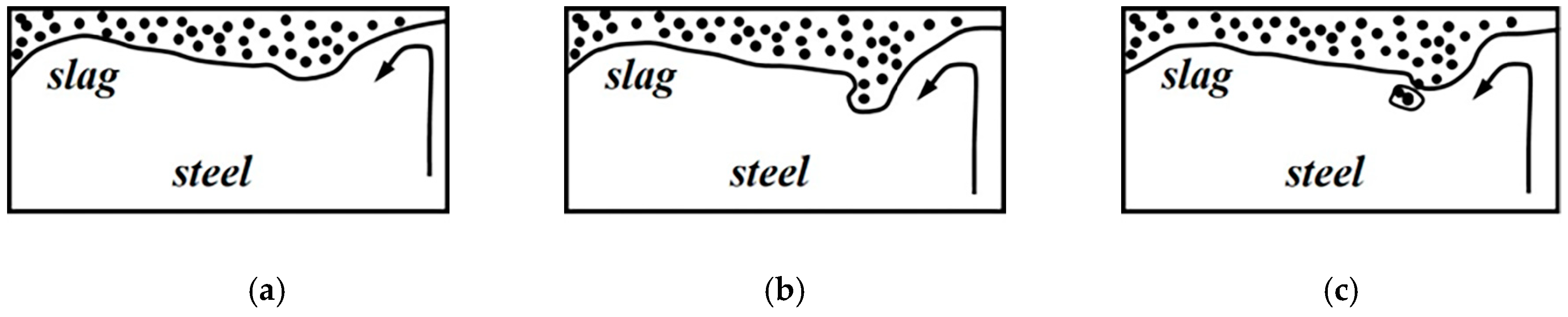


| 70 mm 1.8 m/min | 90 mm 1.8 m/min | 70 mm 1.6 m/min | 90 mm 1.6 m/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.414 | 0.379 | 0.366 | 0.335 |
| Oil | Density (kg/m3) | Interface Tension (N/m) | Density Ratio (ρwater/ρoil) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon oil AK 0.65 | 760 | 0.04 | 1.313 |
| Silicon oil AK5 | 920 | 0.04 | 1.085 |
| Silicon oil AK10 | 930 | 0.04 | 1.073 |
| Silicon oil AK35 | 955 | 0.041 | 1.045 |
| Silicon oil AK50 | 960 | 0.041 | 1.040 |
| Silicon oil AK100 | 963 | 0.042 | 1.036 |
| Silicon oil AK200 | 966 | 0.044 | 1.033 |
| Silicon oil AK500 | 969 | 0.044 | 1.030 |
| Peanut oil | 916 | 0.031 | 1.090 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Optimization on Reducing Slag Entrapment in 150 × 1270 mm Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Materials 2019, 12, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111774
Wang Y, Yang S, Wang F, Li J. Optimization on Reducing Slag Entrapment in 150 × 1270 mm Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Materials. 2019; 12(11):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111774
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Shufeng Yang, Feng Wang, and Jingshe Li. 2019. "Optimization on Reducing Slag Entrapment in 150 × 1270 mm Slab Continuous Casting Mold" Materials 12, no. 11: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111774
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, S., Wang, F., & Li, J. (2019). Optimization on Reducing Slag Entrapment in 150 × 1270 mm Slab Continuous Casting Mold. Materials, 12(11), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111774




