Effect of Nanobainite Content on the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al-Alloyed High Carbon Steel with Nanobainitic Microstructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
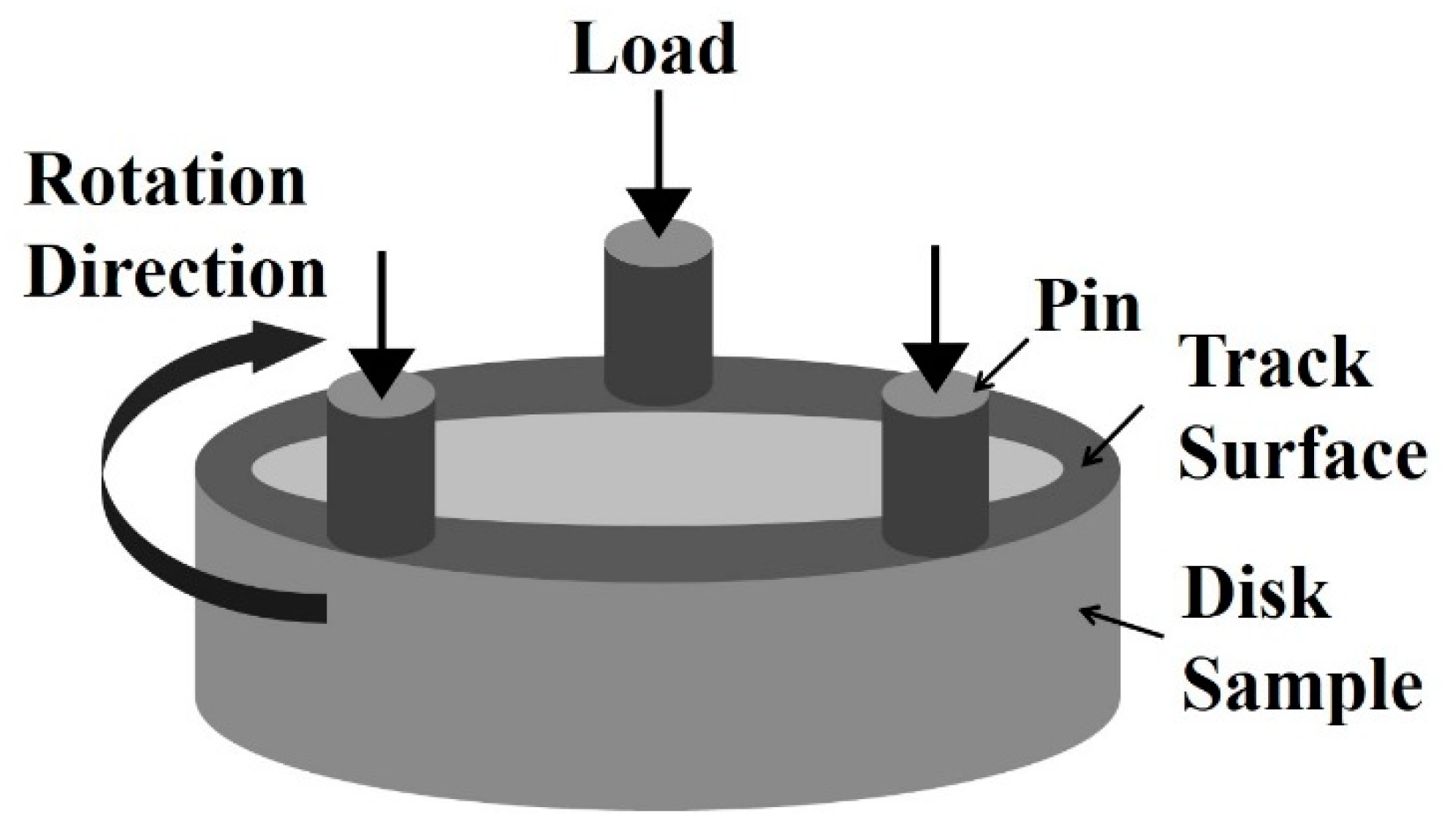
2.2. Wear Tests
2.3. Microstructural Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
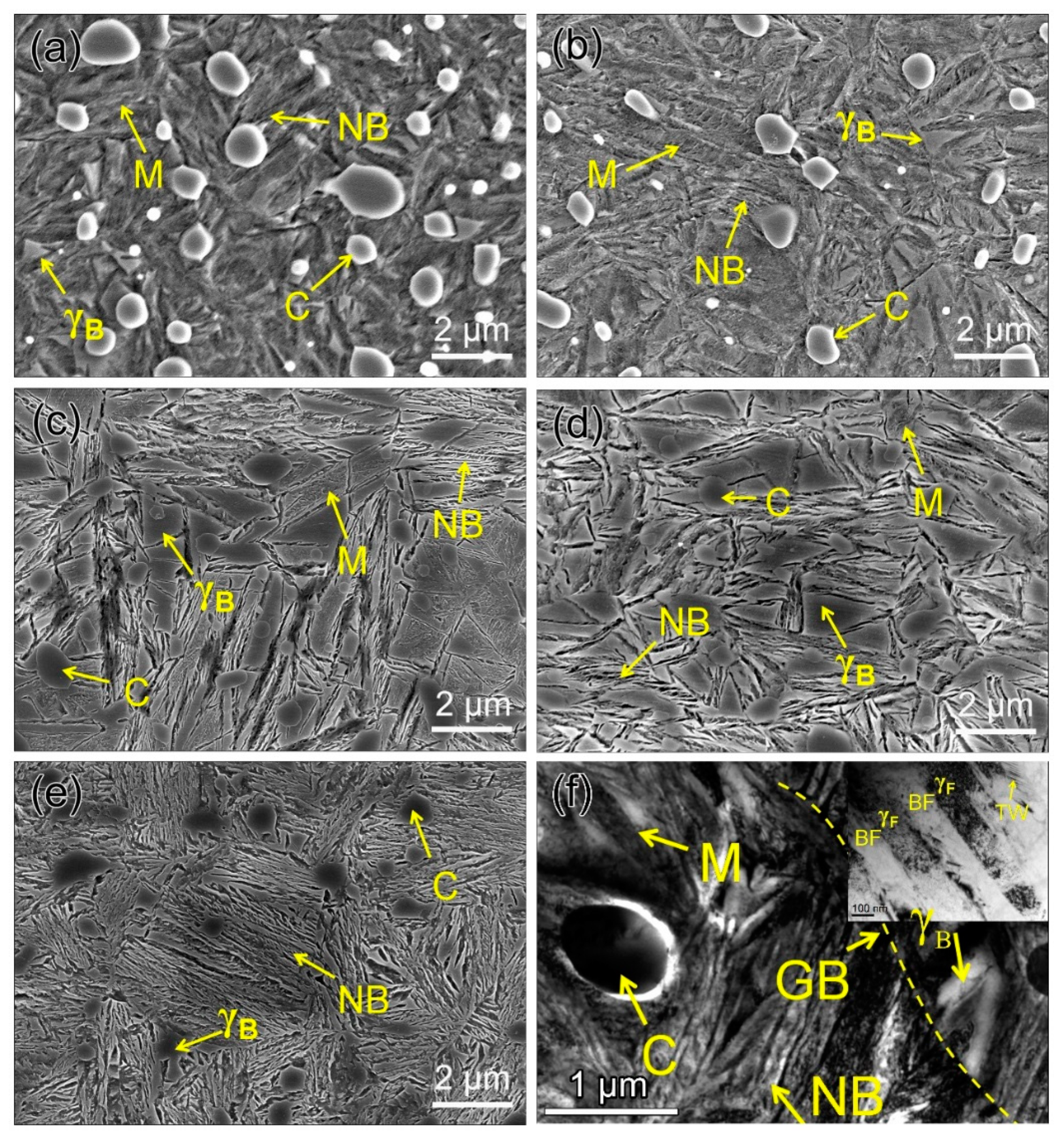
3.1. Microstructure Characterization
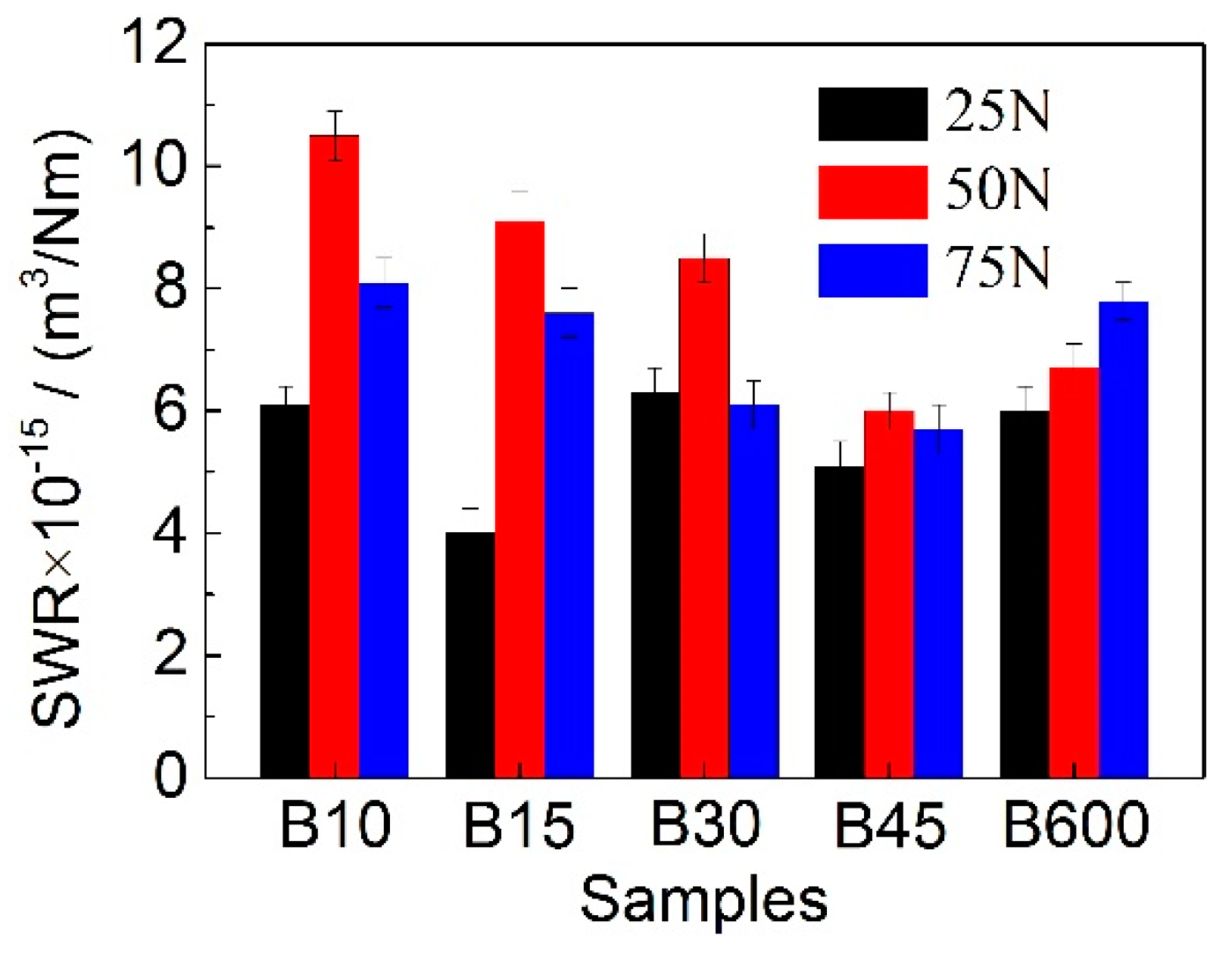
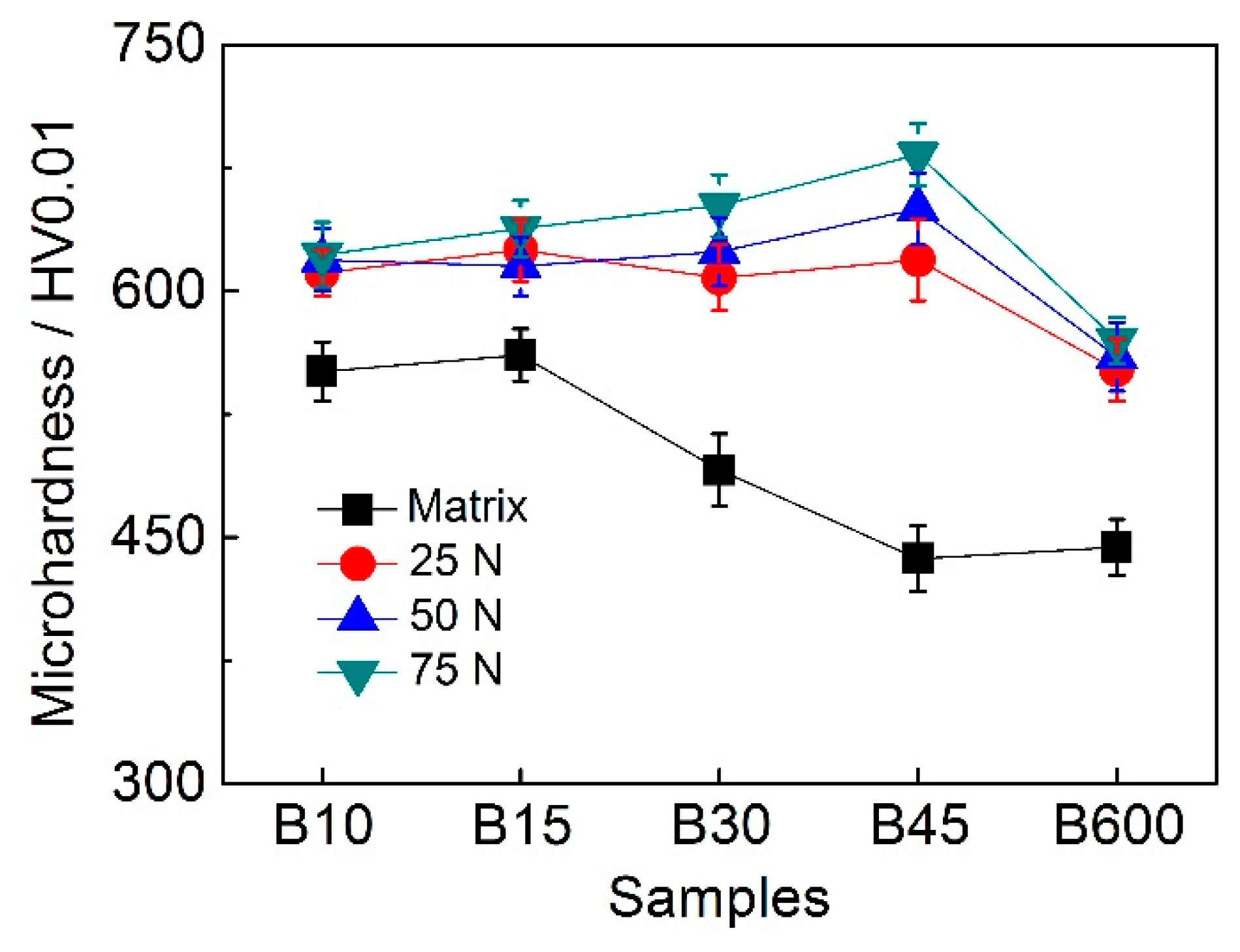
3.2. Wear Behavior
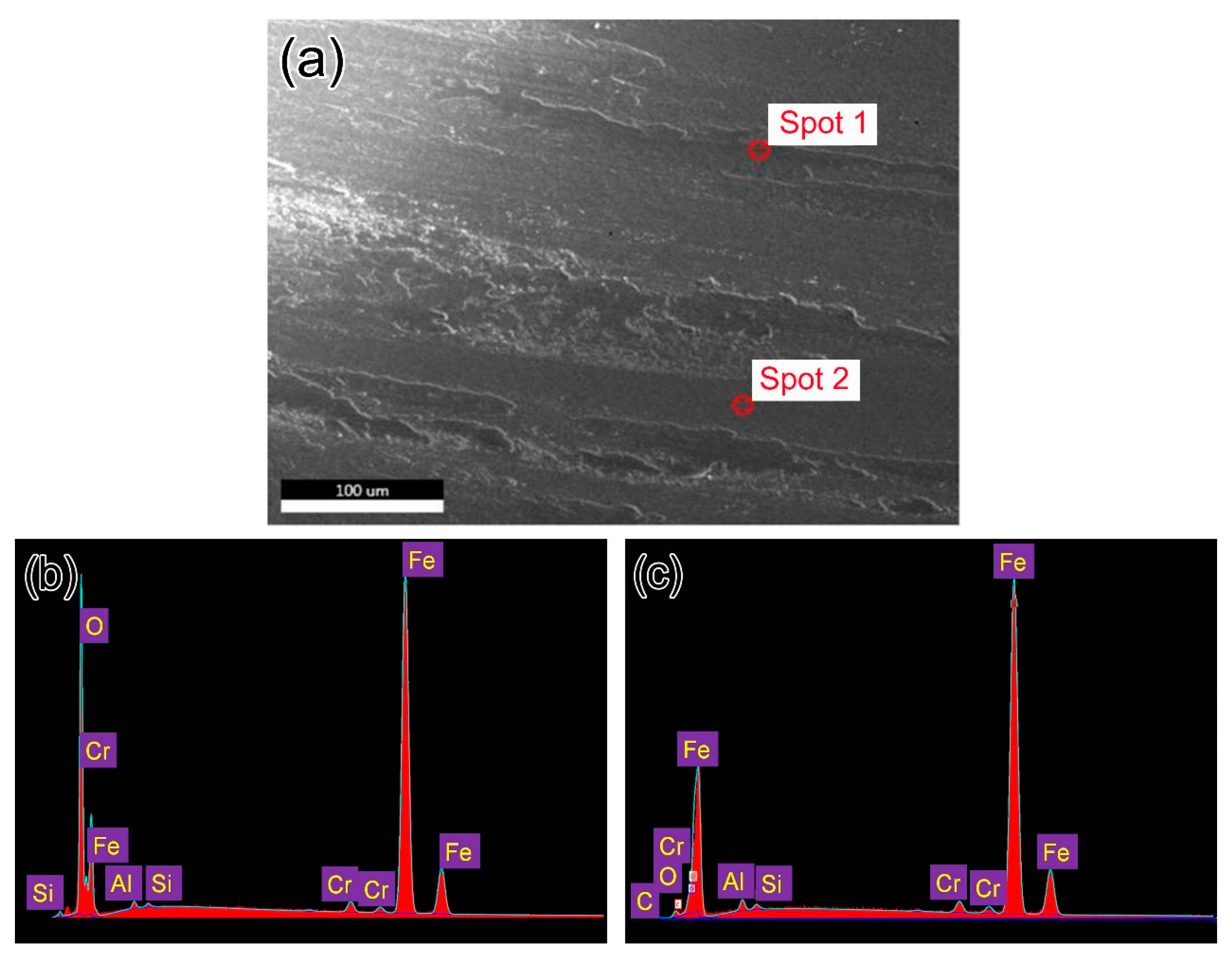
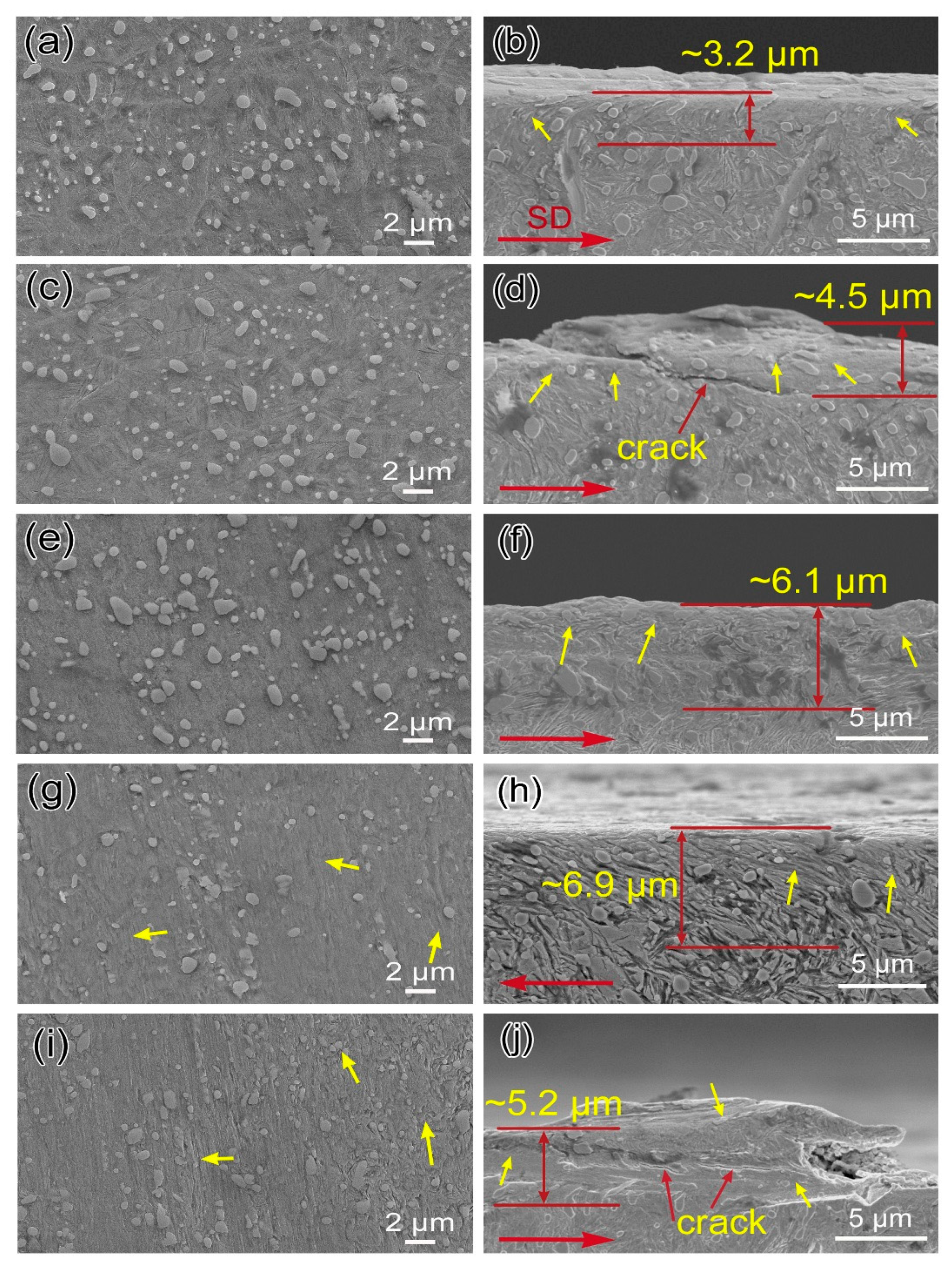
3.3. Morphologies of Worn Surfaces and Cross-Section
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Effect of Hardness on Wear Resistance
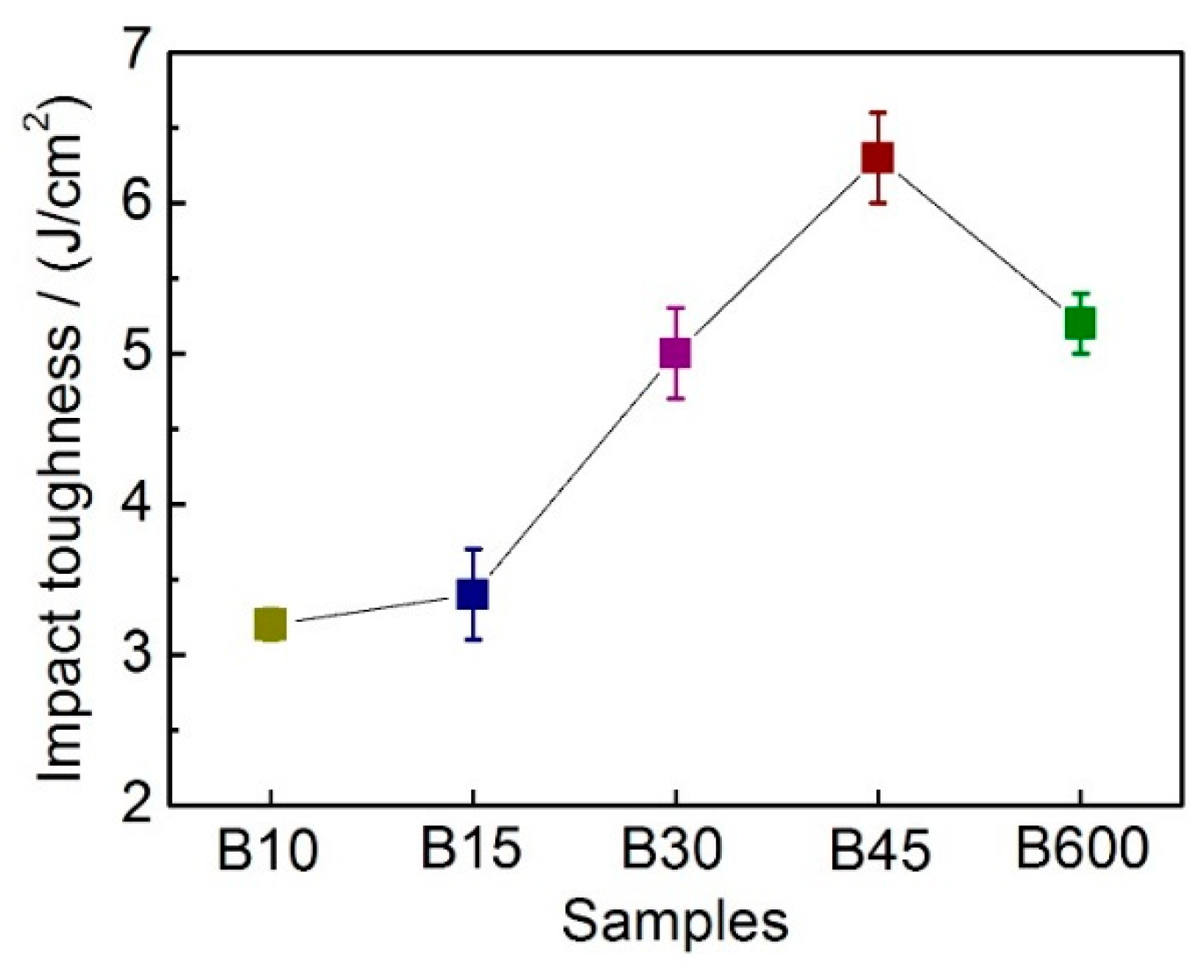
3.4.2. Effect of Toughness on Wear Resistance
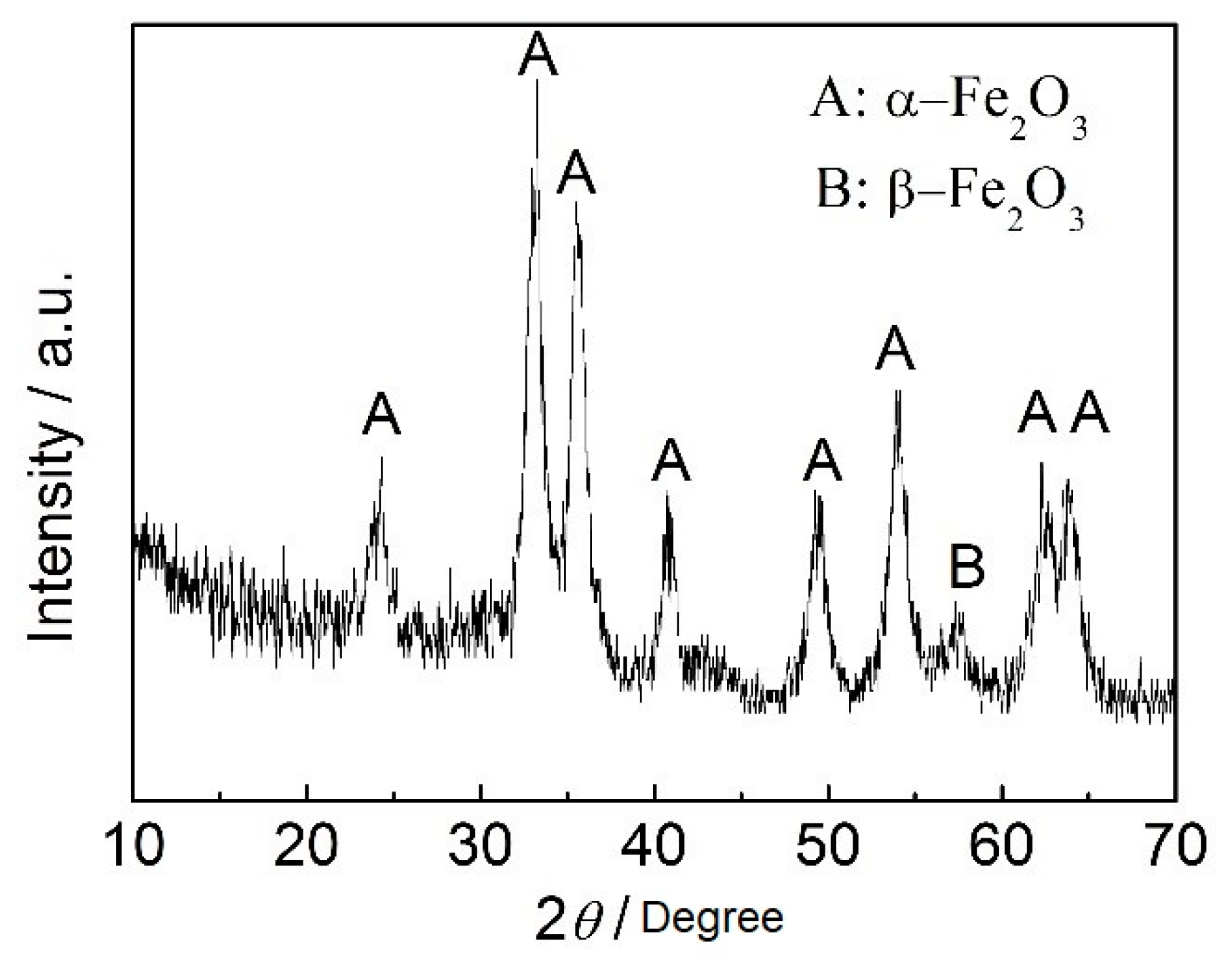
3.4.3. Wear Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A multiphase microstructure composed of nanobainite, martensite, blocky retained austenite, and undissolved carbides has been prepared in Al-alloyed high carbon steel via austempering followed by quenching heat treatments. The varying nanobainite content can be obtained through changing austempering duration.
- (2)
- The SWR firstly decreases and then increases with the nanobainite content increases in samples. The optimum wear resistance is achieved by B45 containing 60 ± 1.8 vol.% nanobainite.
- (3)
- The main reason for the improved wear resistance of B45 is the peak hardness increase due to deformation-induced transformation of retained austenite to martensite, work hardening, along with grain nanocrystallization and amorphization of the deformed layer. And the high toughness of the matrix is also thought to contribute to the improvement of wear resistance.
- (4)
- The wear mechanism is proved to be oxidation wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean Michel Martin, A.E. Superlubricity: Friction’s vanishing act. Phys. Today 2018, 71, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.; Bhadeshia, H.; Mawella, K.; Jones, D.; Brown, P. Design of novel high strength bainitic steels: Part 1. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2001, 17, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel-Farzad, H.; Faridi, H.R.; Rajabpour, F.; Abolhasani, A.; Kazemi, S.; Khaledzadeh, Y. Developing very hard nanostructured bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y. Effect of Austenite Grain Size on Transformation of Nanobainite and Its Mechanical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Mateo, C.; Caballero, F.G.; Sourmail, T.; Kuntz, M.; Cornide, J.; Smanio, V.; Elvira, R. Tensile behaviour of a nanocrystalline bainitic steel containing 3 wt.% silicon. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, F.C.; Yan, Z.G.; Wang, T.S.; Qian, L.H. Wear property of low-temperature bainite in the surface layer of a carburized low carbon steel. Wear 2011, 271, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiro, A.; Vuorinen, E.; Sundin, K.G.; Prakash, B.; Sourmail, T.; Smanio, V.; Caballero, F.G.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Elvira, R. Wear of nano-structured carbide-free bainitic steels under dry rolling–sliding conditions. Wear 2013, 298–299, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Jiang, T.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y. Improved rolling contact fatigue life for an ultrahigh-carbon steel with nanobainitic microstructure. Scr. Mater. 2014, 90–91, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C. The rolling/sliding wear performance of high silicon carbide-free bainitic steels. Wear 2005, 258, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Bakshi, S.; Shipway, P.H.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Three-body abrasive wear of fine pearlite, nanostructured bainite and martensite. Wear 2013, 308, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gola, A.M.; Ghadamgahi, M.; Ooi, S.W. Microstructure evolution of carbide-free bainitic steels under abrasive wear conditions. Wear 2017, 376–377, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, E.; Ojala, N.; Heino, V.; Rau, C.; Gahm, C. Erosive and abrasive wear performance of carbide free bainitic steels – comparison of field and laboratory experiments. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, A.; Zhi, C.; Ding, R.; Wang, J. Two-body abrasion wear mechanism of super bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourmail, T.; Caballero, F.G.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Smanio, V.; Ziegler, C.; Kuntz, M.; Elvira, R.; Leiro, A.; Vuorinen, E.; Teeri, T. Evaluation of potential of high Si high C steel nanostructured bainite for wear and fatigue applications. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, T.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.C. Sliding wear resistance and worn surface microstructure of nanostructured bainitic steel. Wear 2012, 282–283, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rementeria, R.; García, I.; Aranda, M.M.; Caballero, F.G. Reciprocating-sliding wear behavior of nanostructured and ultra-fine high-silicon bainitic steels. Wear 2015, s338–339, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, B.; Hodgson, P.; Timokhina, I.; Beladi, H. The Impact of Retained Austenite Characteristics on the Two-Body Abrasive Wear Behavior of Ultrahigh Strength Bainitic Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, V.G.; Hesse, O.; Friedrich, T.; Kunert, M.; Brykov, M.N.; Shimizu, K.; Zurnadzhy, V.I.; Šuchmann, P. Two-body abrasion resistance of high-carbon high-silicon steel: Metastable austenite vs nanostructured bainite. Wear 2019, 418–419, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiro, A.; Kankanala, A.; Vuorinen, E.; Prakash, B. Tribological behaviour of carbide-free bainitic steel under dry rolling/sliding conditions. Wear 2011, 273, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Lv, B.; Yang, Z.N.; Zhang, F.C. Wear resistance of bainite steels that contain aluminium. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.G.; Miller, M.K.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Capdevila, C.; Babu, S.S. Redistribution of alloying elements during tempering of a nanocrystalline steel. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.G.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Very strong bainite. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnin, J.; Ridal, K.A. Determination of retained austenite in steel by X-ray diffraction. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1968, 206, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, D.; Holmes, B. Effect of alloying additions on the lattice parameter of austenite. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1970, 208, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Saha Podder, A.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Thermal stability of austenite retained in bainitic steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, M. Formation of a self-lubricating layer by oxidation and solid-state amorphization of nano-lamellar microstructures during dry sliding wear tests. Acta Mater. 2019, 166, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sangal, S.; Mondal, K. Reciprocating Sliding Wear Behavior of Newly Developed Bainitic Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5451–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Leiro, A.; Ripoll, M.R.; Vuorinen, E.; Sundin, K.G.; Prakash, B. High temperature three-body abrasive wear of 0.25C 1.42Si steel with carbide free bainitic (CFB) and martensitic microstructures. Wear 2016, 360–361, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.X.; Chen, K.M. Analysis for Wear Behaviors of Oxidative Wear. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.T.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.R. Mild-to-severe wear transition and transition region of oxidative wear in steels. Wear 2013, 306, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Austenizaiton | Austempering | Cooling | Tempering |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B10 | 880 °C/7 min | 270 °C/10 min | Cooling in oil | 160 °C/120 min |
| B15 | 270 °C/15 min | |||
| B30 | 270 °C/30 min | |||
| B45 | 270 °C/45 min | |||
| B600 | 270 °C/600 min | Ail cooled | non |
| Samples | Before Wear Testing | After Wear Testing | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VNB (vol.%) | Vγ (vol.%) | Cγ (wt.%) | Vγ (vol.%) | Cγ (wt.%) | |
| B10 | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 14.8 ± 0.1 | 1.09 ± 0.04 | 11.5 ± 1.8 | 0.92 ± 0.07 |
| B15 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | 16.6 ± 0.5 | 1.10 ± 0.05 | 11.6 ± 1.4 | 0.90 ± 0.03 |
| B30 | 39.4 ± 2.0 | 23.1 ± 2.2 | 1.59 ± 0.07 | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 1.05 ± 0.10 |
| B45 | 60 ± 1.8 | 17.8 ± 0.3 | 1.60 ± 0.05 | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 1.31 ± 0.03 |
| B600 | ~full | 9.9 ± 0.1 | 1.91 ± 0.08 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, T.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of Nanobainite Content on the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al-Alloyed High Carbon Steel with Nanobainitic Microstructure. Materials 2019, 12, 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12101618
Song Z, Zhao S, Jiang T, Sun J, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu H, Liu Y. Effect of Nanobainite Content on the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al-Alloyed High Carbon Steel with Nanobainitic Microstructure. Materials. 2019; 12(10):1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12101618
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhaohuan, Songhao Zhao, Tao Jiang, Junjie Sun, Yingjun Wang, Xiliang Zhang, Hongji Liu, and Yongning Liu. 2019. "Effect of Nanobainite Content on the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al-Alloyed High Carbon Steel with Nanobainitic Microstructure" Materials 12, no. 10: 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12101618
APA StyleSong, Z., Zhao, S., Jiang, T., Sun, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, H., & Liu, Y. (2019). Effect of Nanobainite Content on the Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of an Al-Alloyed High Carbon Steel with Nanobainitic Microstructure. Materials, 12(10), 1618. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12101618




