Passive Q-Switching by Cr4+:YAG Saturable Absorber of Buried Depressed-Cladding Waveguides Obtained in Nd-Doped Media by Femtosecond Laser Beam Writing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Waveguides Description
3. Results
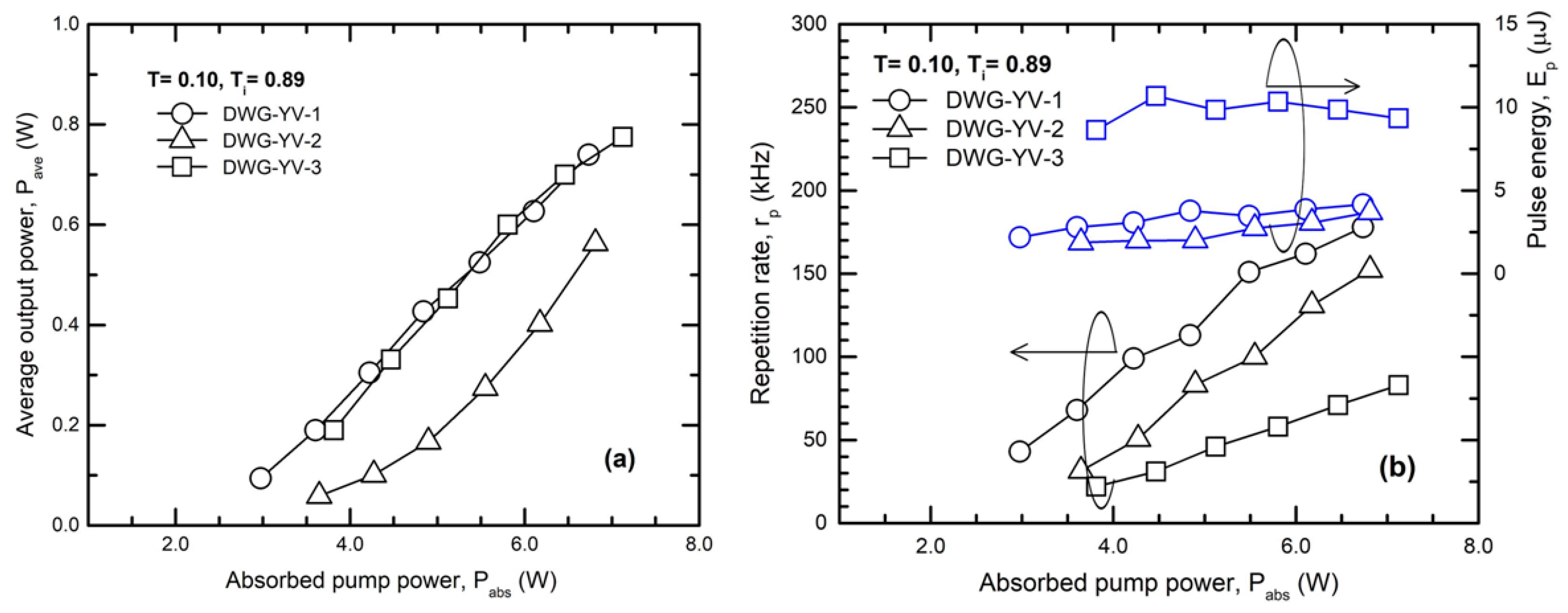
Laser Emission Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, K.M.; Miura, K.; Sugimoto, N.; Hirao, K. Writing waveguides in glass with a femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, S.; Will, M.; Burghoff, J.; Tuennermann, A. Femtosecond waveguide writing: a new avenue to three-dimensional integrated optics. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ródenas, A.; Torchia, G.A.; Lifante, G.; Cantelar, E.; Lamela, J.; Jaque, F.; Roso, L.; Jaque, D. Refractive index change mechanisms in femtosecond laser written ceramic Nd:YAG waveguides: micro-spectroscopy experiments and beam propagation calculations. Appl. Phys. B 2009, 95, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenmorgen, J.; Petermann, K.; Huber, G.; Rademaker, K.; Nolte, S.; Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond laser written stress-induced Nd:Y3Al5O12 (Nd:YAG) channel waveguide laser. Appl. Phys. B 2009, 97, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Rodenas, A.; Chen, F.; Thomson, R.R.; Kar, A.K.; Jaque, D.; Lu, Q. 70% slope efficiency from an ultrafast laser-written Nd:GdVO4 channel waveguide laser. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24994–24999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okhrimchuk, A.G.; Shestakov, A.V.; Khrushchev, I.; Mitchell, J. Depressed cladding, buried waveguide laser formed in a YAG:Nd3+ crystal by femtosecond laser writing. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 2248–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R. Optical waveguides in crystalline dielectric materials produced by femtosecond-laser micromachining. Laser Photonics Rev. 2014, 8, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, D.; Macdonald, J.R.; Kar, A.K. Ultrafast laser inscription: perspectives on future integrated applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2014, 8, 827–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meany, T.; Gräfe, M.; Heilmann, R.; Perez-Leija, A.; Gross, S.; Steel, M.J.; Withford, M.J.; Szameit, A. Laser written circuits for quantum photonics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2015, 9, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamu, G.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M.; Pavel, N. Watt-level output power operation from diode-laser pumped circular buried depressed-cladding waveguides inscribed in Nd:YAG by direct femtosecond-laser writing. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 500209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamu, G.; Pavel, N. Power scaling from buried depressed-cladding waveguides realized in Nd:YVO4 by femtosecond-laser beam writing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 84, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, S.; Thorburn, F.; Lancaster, A.; Stites, R.; Cook, G.; Kar, A. Operation of Ho:YAG ultrafast laser inscribed waveguide lasers. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Luo, S.; Xu, B.; Xu, H.; Cai, Z.; Hong, M.; Wu, P. Femtosecond-laser micromachined Pr:YLF depressed cladding waveguide: Raman, fluorescence, and laser performance. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 3990–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifle, E.; Loiko, P.; Mateos, X.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Ródenas, A.; Griebner, U.; Petrov, V.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F. Femtosecond-laser-written hexagonal cladding waveguide in Tm:KLu(WO4)2: µ-Raman study and laser operation. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 4258–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhrimchuk, A. Femtosecond fabrication of waveguides in ion-doped laser crystals. In Coherence and Ultrashort Pulse Laser Emission; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Calmano, T.; Paschke, A.-G.; Müller, S.; Kränkel, C.; Huber, G. Q-Switched operation of a fs-laser written Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG monolithic waveguide laser. In Proceedings of the Advances in Optical Materials 2012, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–3 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Calmano, T.; Müller, S.; Kränkel, C.; Huber, G. Multi-watt continuous wave output power and Q-switched laser operation of femtosecond-laser inscribed Yb:YAG based waveguides. In Proceedings of the 6th EPS-QEOD Europhoton Conference, Solid State, Fibre, and Waveguide Coherent Light Sources, Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 24–29 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Luan, Q.; Liu, F.; Chen, F.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R. Q-switched pulse laser generation from double-cladding Nd:YAG ceramics waveguides. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 18963–18968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakobyan, S.; Wittwer, V.J.; Hasse, K.; Kränkel, C.; Südmeyer, T.; Calmano, T. Highly efficient Q-switched Yb:YAG channel waveguide laser with 5.6 W of average output power. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4715–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Chen, F. Passively Q-switched Nd:YVO4 waveguide laser using graphene as a saturable absorber. Opt. Mat. 2015, 46, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Calmano, T.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Baek, I.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Yeom, D.-I.; Kränkel, C.; Rotermund, F. Monolayer graphene coated Yb:YAG channel waveguides for Q-switched laser operation. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, F.; Lancaster, A.; McDaniel, S.; Cook, G.; Kar, A.K. 5.9 GHz graphene based q-switched modelocked mid-infrared monolithic waveguide laser. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 26166–26174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Calmano, T.; Kim, M.H.; Yeom, D.-I.; Kränkel, C.; Huber, G.; Rotermund, F. Q-switched operation of a femtosecond-laser-inscribed Yb:YAG channel waveguide laser using carbon nanotubes. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 7999–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, H.; Shang, Z.; Nie, W.; Tan, Y.; Blanca del Rosal Rabes, J.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Jaque, D.; Chen, F. Femtosecond laser written waveguides with MoS2 as saturable absorber for passively Q-switched lasing. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, H.; Tan, Y.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Chen, F. Passively Q-switched waveguide lasers based on two-dimensional transition metal diselenide. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 10385–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, W.; Li, R.; Cheng, C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Romero, C.; Vázquez de Aldana, J.R.; Hao, X.; Chen, F. Room temperature subnanosecond waveguide lasers in Nd:YVO4 Q-switched by phase-change VO2: A comparison with 2D materials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croitoru, G.; Jipa, F.; Pavel, N. Passive Q-switch laser operation of circular, buried depressed-cladding waveguides realized by direct fs-laser beam writing in Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite media. Opt. Mat. Express 2017, 7, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, G.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M.; Pavel, N. Cladding waveguides realized in Nd:YAG ceramic by direct femtosecond-laser writing with a helical movement technique. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 790–797. [Google Scholar]
- Findlay, D.; Clay, R.A. The measurement of internal losses in 4-level lasers. Phys. Lett. 1966, 20, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, G.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M.; Pavel, N. Laser emission from diode-pumped Nd:YAG ceramic waveguide lasers realized by direct femtosecond-laser writing technique. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 5177–5182. [Google Scholar]
- Pavel, N.; Croitoru, G.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M. Diode-laser pumping into the emitting level for efficient lasing of depressed cladding waveguides realized in Nd:YVO4 by the direct femtosecond-laser writing technique. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 23057–23065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, T. RE3+-ion-doped YAG ceramic lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J.J. Optimization of passively Q-switched lasers. IEEE. J. Quantum Electron. 1995, 31, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, N.; Saikawa, J.; Kurimura, S.; Taira, T. High average power diode end-pumped composite Nd:YAG laser passively Q-switched by Cr4+:YAG saturable sbsorber. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspan, M.A.; Welford, D.; Russell, J.A. Passively Q-switched microlaser performance in the presence of pump-induced bleaching of the saturable absorber. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapaport, A.; Zhao, S.; Xiao, G.; Howard, A.; Bass, M. Temperature dependence of the 1.06-μm stimulated emission cross section of neodymium in YAG and in GSGG. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7052–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Taira, T. Temperature dependencies of stimulated emission cross section for Nd-doped solid-state laser materials. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, N.; Tsunekane, M.; Taira, T. Enhancing performances of a passively Q-switched Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG microlaser with a volume Bragg grating output coupler. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausas, A.; Taira, T. Giant-pulse Nd:YVO4 microchip laser with MW-level peak power by emission cross-sectional control. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 3137–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
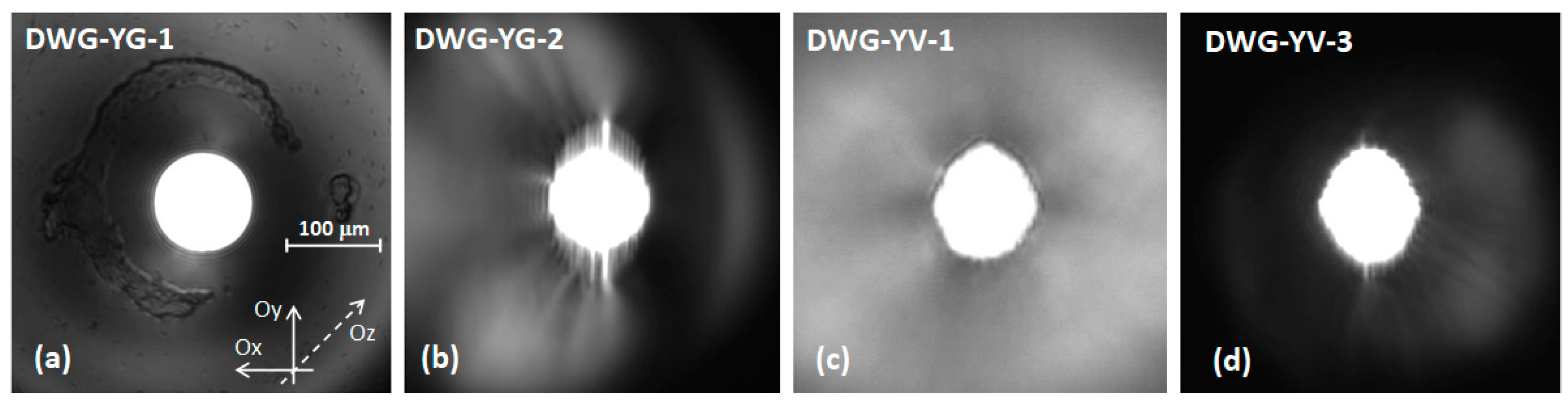

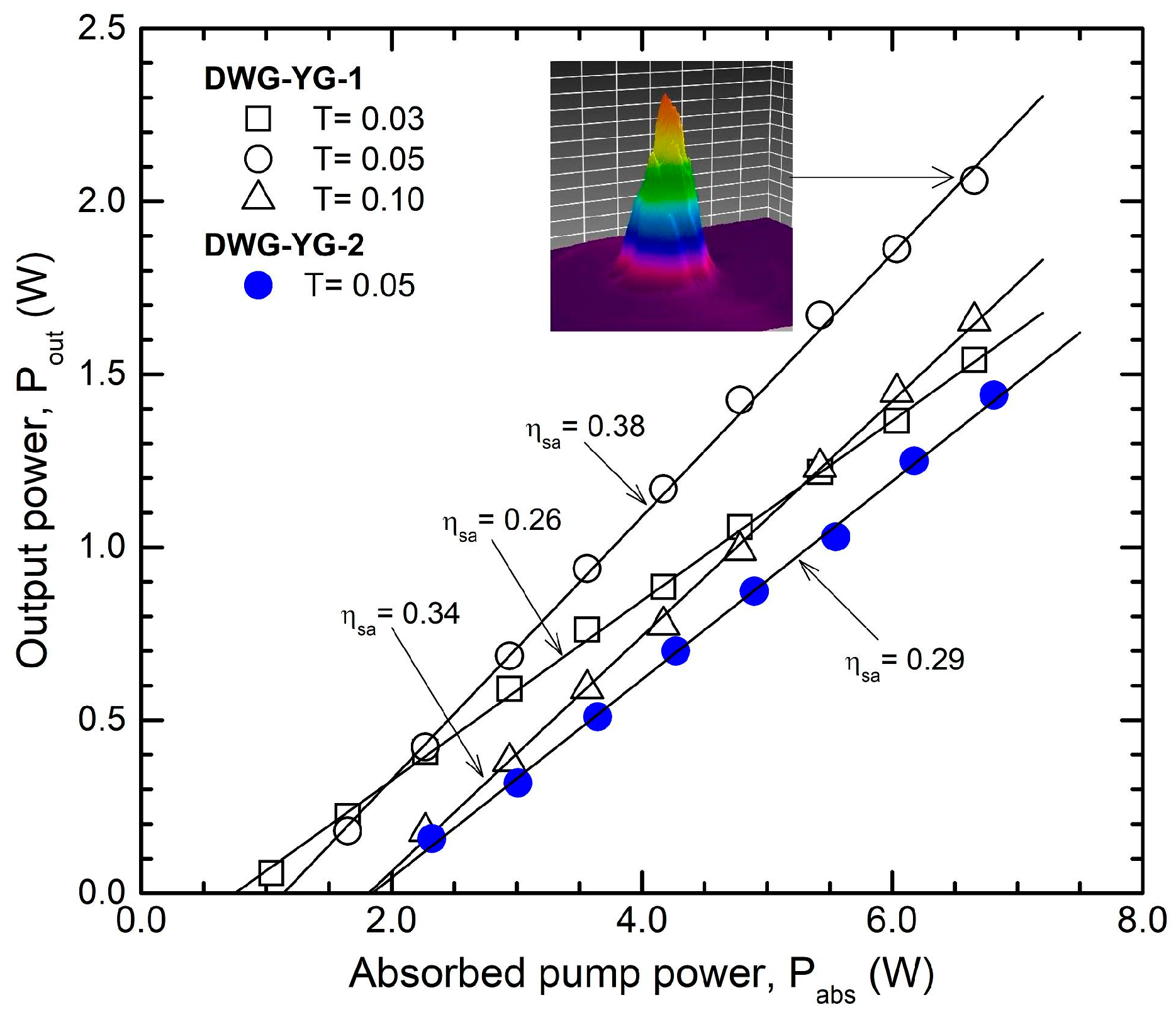
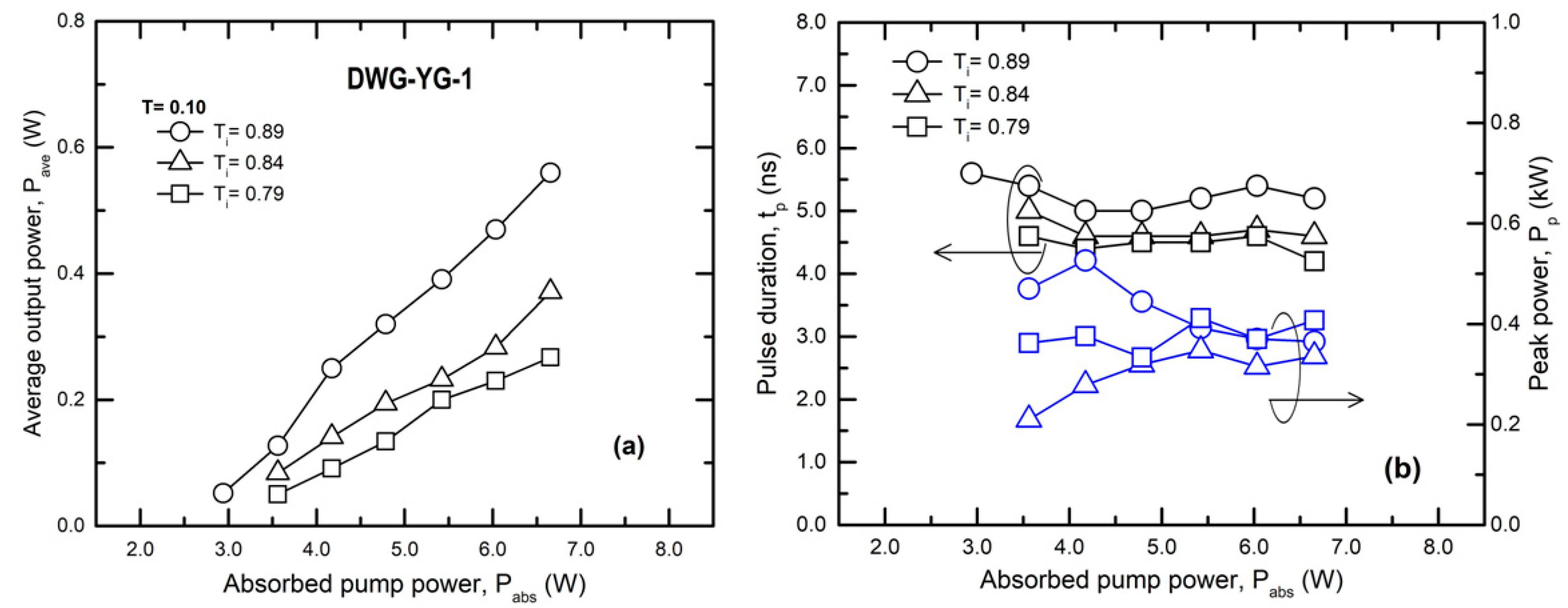
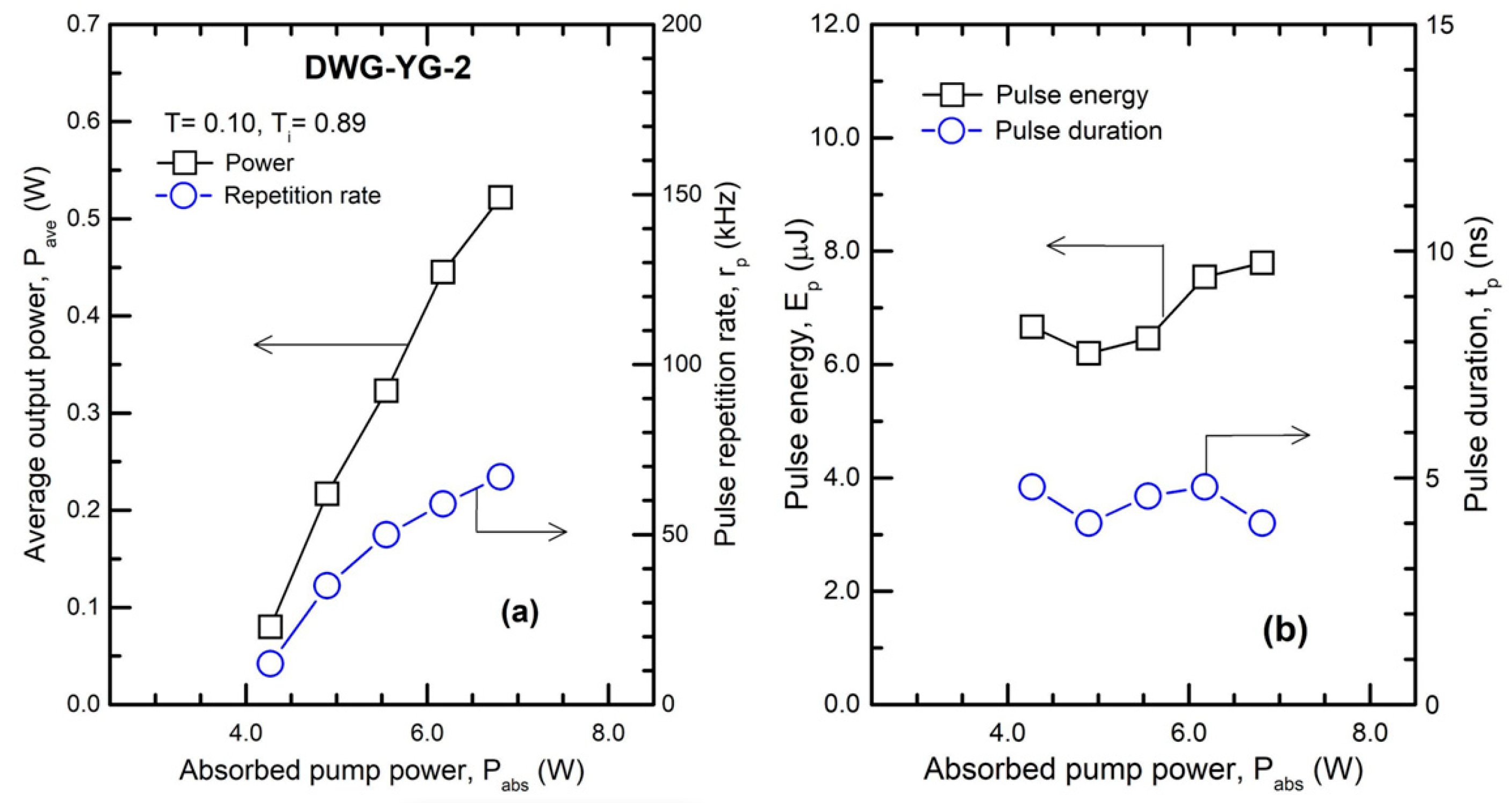
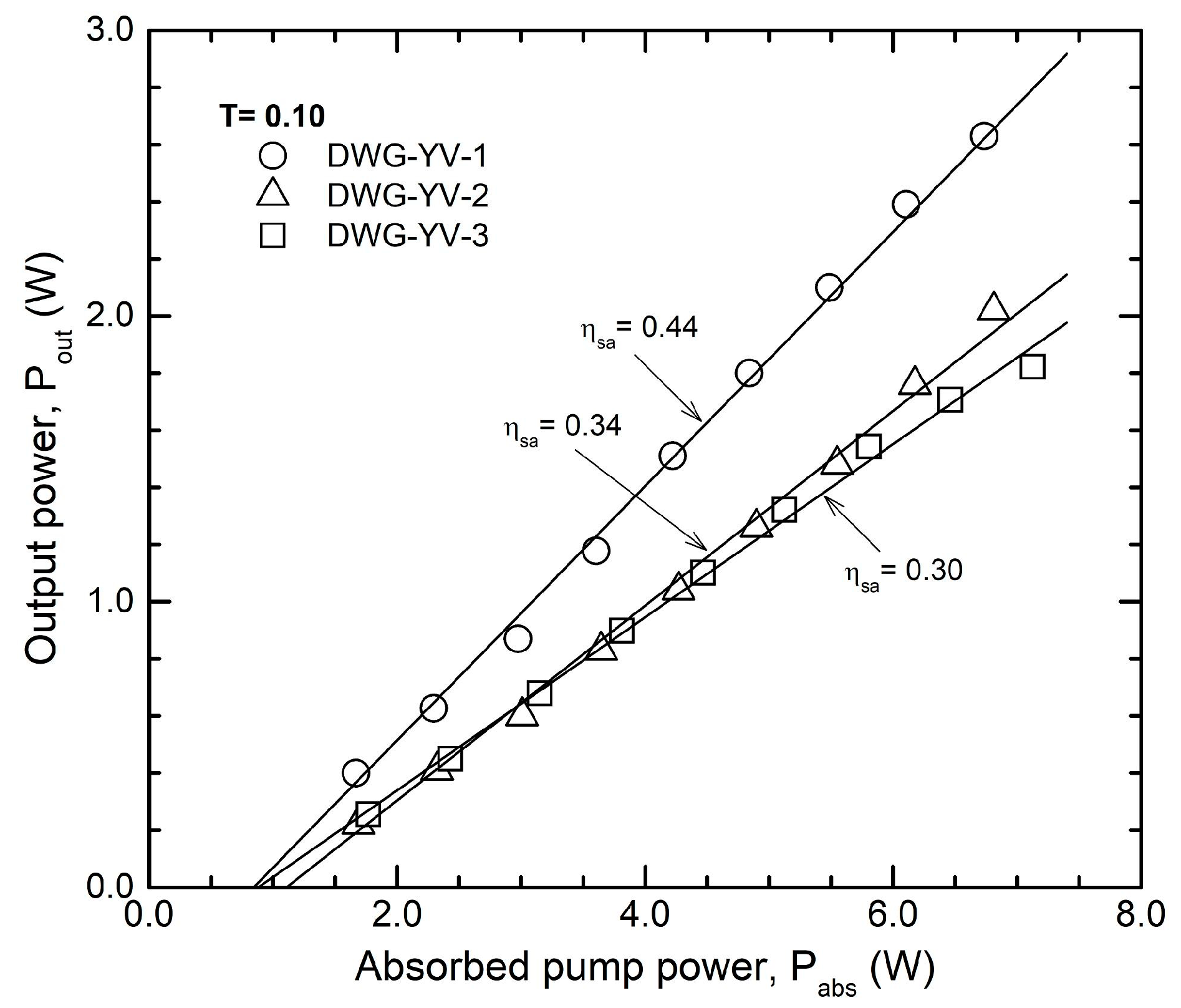
| Laser Medium | Waveguide | Cw Output Power, Pcw (W) | Absorbed Pump Power, Pabs (W) | Absorption Efficiency, ηa | Optical Efficiency, ηoa | Slope, ηsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1-at % Nd:YAG, 4.5 mm | DWG-YG-1 | 2.05 | 6.65 | 0.85 | 0.31 | 0.38 |
| 1.1-at % Nd:YAG, 4.8 mm | DWG-YG-2 | 1.45 | 6.80 | 0.87 | 0.21 | 0.29 |
| 0.5-at % Nd:YVO4, 6.9 mm | DWG-YV-1 | 2.90 | 6.75 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 0.44 |
| 0.7-at % Nd:YVO4, 4.6 mm | DWG-YV-2 | 2.0 | 6.80 | 0.87 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| 1.0-at % Nd:YVO4, 3.4 mm | DWG-YV-3 | 1.85 | 7.10 | 0.91 | 0.26 | 0.30 |
| Laser Medium | Waveguide | Average Output Power, Pave (W) | Repetition Rate, rp (kHz) | Pulse Energy, Ep (μJ) | Pulse Duration, tp (ns) | Peak Power, Pp (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1-at % Nd:YAG, 4.5 mm | DWG-YG-1 | 0.56 | 295 | 1.89 | 5.2 | 0.36 |
| 1.1-at % Nd:YAG, 4.8 mm | DWG-YG-2 | 0.52 | 67 | 7.79 | 4.0 | 1.95 |
| 0.5-at % Nd:YVO4, 6.9 mm | DWG-YV-1 | 0.74 | 178 | 4.15 | 14.0 | 0.29 |
| 0.7-at % Nd:YVO4, 4.6 mm | DWG-YV-2 | 0.56 | 152 | 3.68 | 8.2 | 0.45 |
| 1.0-at % Nd:YVO4, 3.4 mm | DWG-YV-3 | 0.77 | 83 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 1.36 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
, G.C.; Pavel, N. Passive Q-Switching by Cr4+:YAG Saturable Absorber of Buried Depressed-Cladding Waveguides Obtained in Nd-Doped Media by Femtosecond Laser Beam Writing. Materials 2018, 11, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091689
GC, Pavel N. Passive Q-Switching by Cr4+:YAG Saturable Absorber of Buried Depressed-Cladding Waveguides Obtained in Nd-Doped Media by Femtosecond Laser Beam Writing. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091689
Chicago/Turabian Style(Salamu), Gabriela Croitoru, and Nicolaie Pavel. 2018. "Passive Q-Switching by Cr4+:YAG Saturable Absorber of Buried Depressed-Cladding Waveguides Obtained in Nd-Doped Media by Femtosecond Laser Beam Writing" Materials 11, no. 9: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091689
APA Style, G. C., & Pavel, N. (2018). Passive Q-Switching by Cr4+:YAG Saturable Absorber of Buried Depressed-Cladding Waveguides Obtained in Nd-Doped Media by Femtosecond Laser Beam Writing. Materials, 11(9), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091689





