Effects of Cr and Zr Addition on Microstructures, Compressive Properties, and Abrasive Wear Behaviors of In Situ TiB2/Cu Cermets
Abstract
1. Introduction
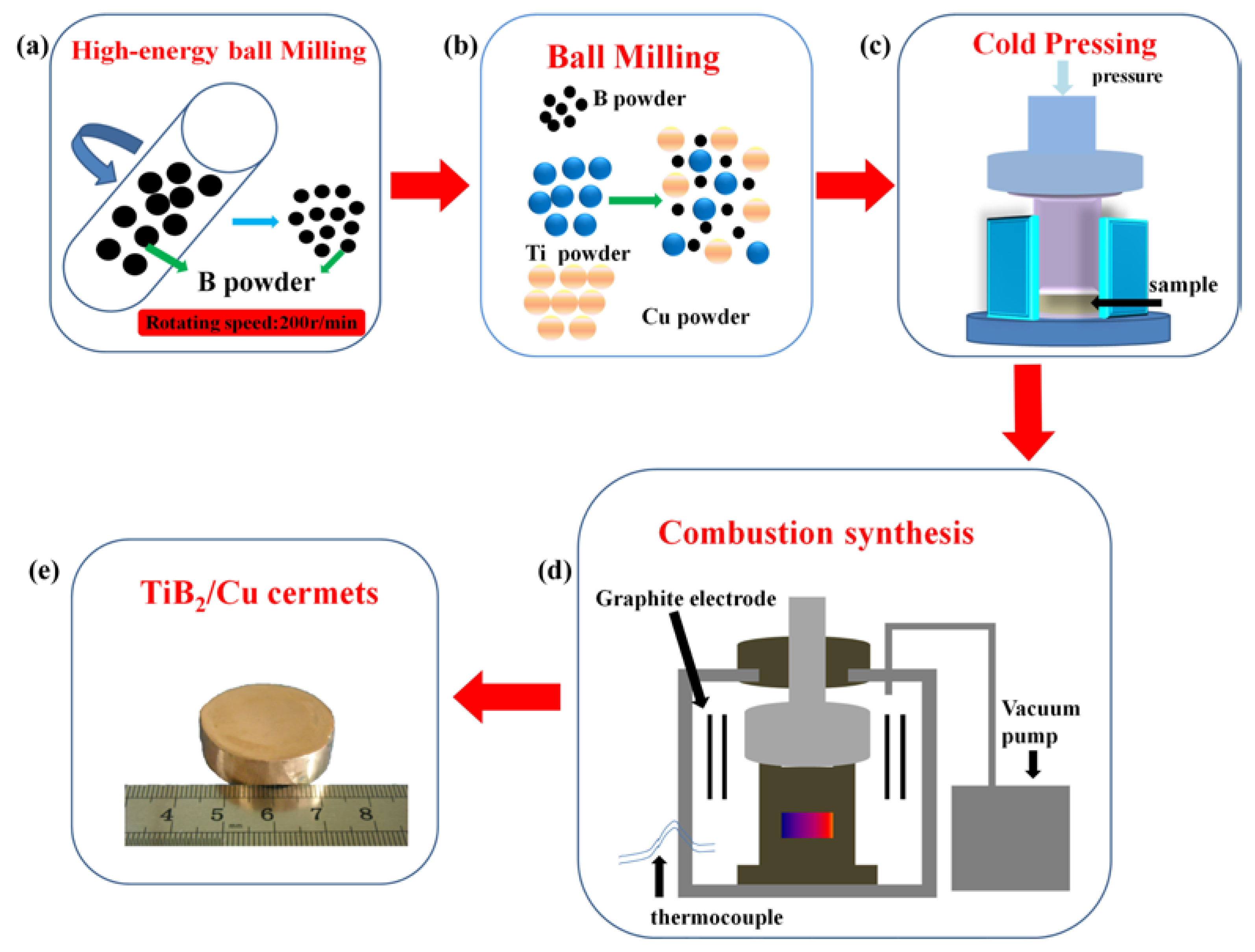
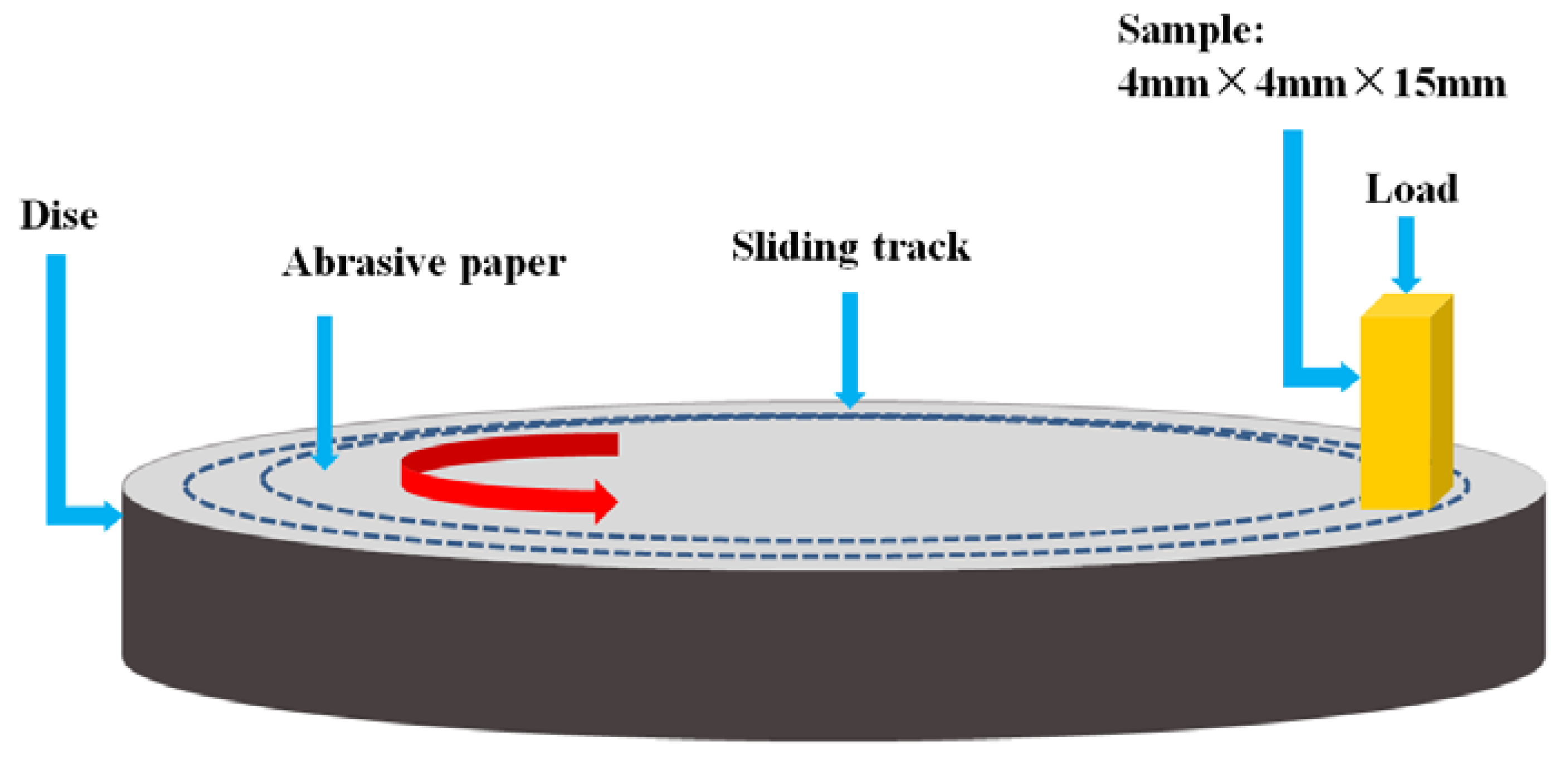
2. Experimental Procedures
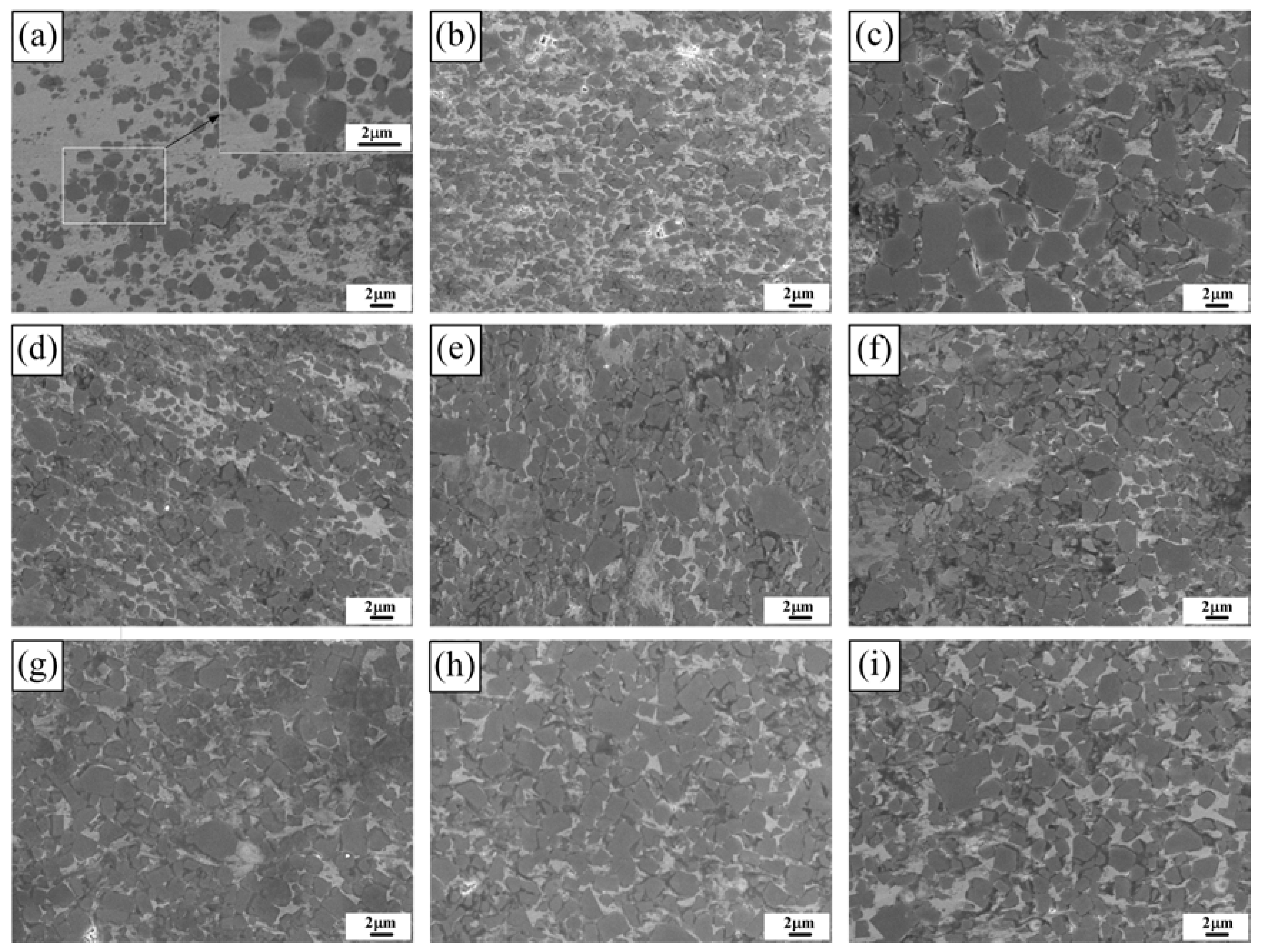
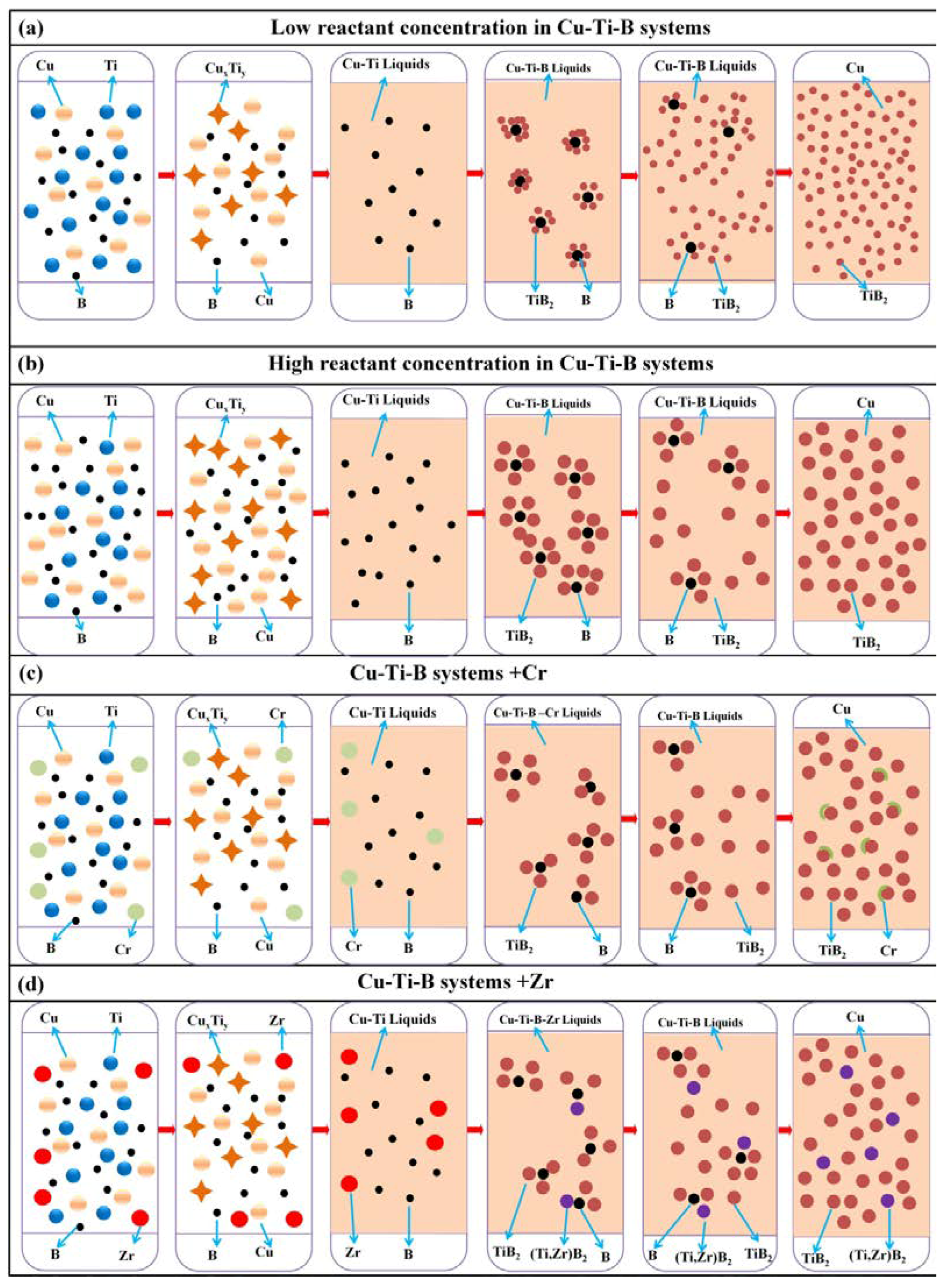
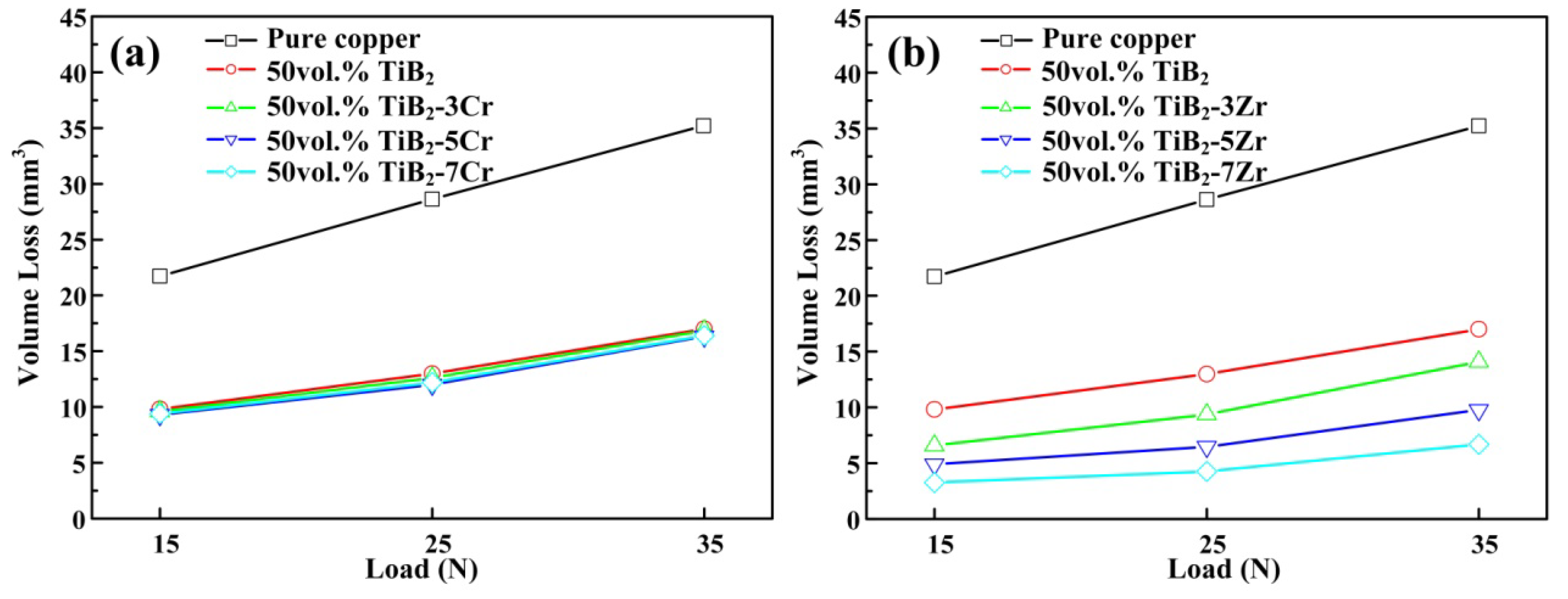
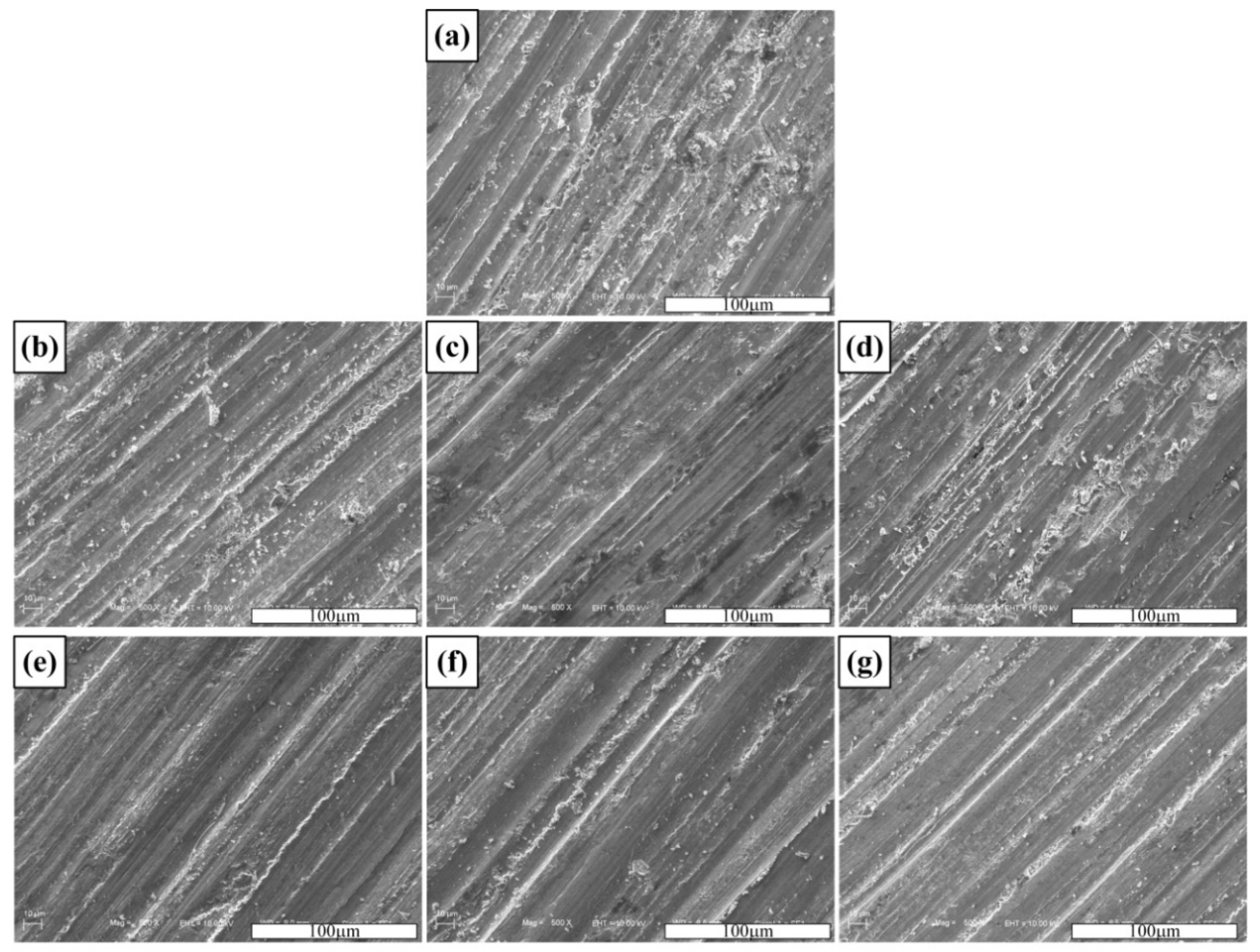
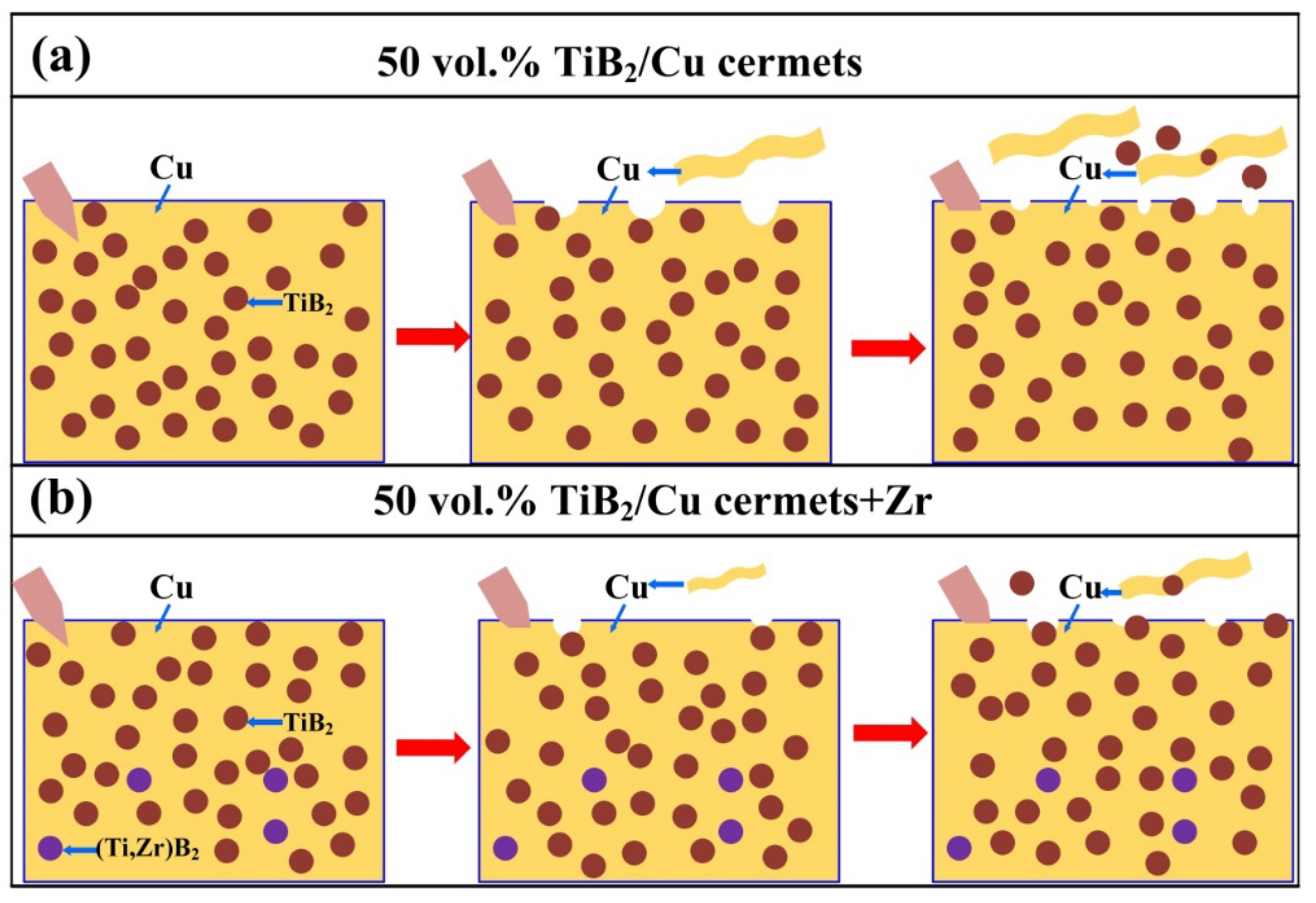
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, S.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Tong, C.Z.; Qiu, F. Fabrication of TiCx-TiB2/Al composites for application as a heat sink. Materials 2016, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.L.; Shi, L. Emerging challenges and materials for thermal management of electronics. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Tong, H.T.; Gao, Y.Y.; Zou, Q.; Dong, B.X.; Li, Q.; Chu, J.G.; Chang, F.; Shu, S.L.; Jiang, Q.C. Microstructures and compressive properties of Al matrix composites reinforced with bimodal hybrid In-Situ nano-/micro-sized TiC particles. Materials 2018, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Qiu, F.; Liu, T.S.; Chu, J.G.; Zhao, Q.L.; Jiang, Q.C. Effects of carbon source on TiC particles’ distribution, tensile, and abrasive wear properties of In Situ TiC/Al-Cu nanocomposites prepared in the Al-Ti-C system. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejado, E.; Müller, A.V.; You, J.H.; Pastor, J.Y. Evolution of mechanical performance with temperature of W/Cu and W/CuCrZr composites for fusion heat sink applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, J.C.; Jheng, S.K. Cooling performance and characteristics of metal piezoelectric fans in a heat sink-equipped handheld projector. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 84, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejado, E.; Müller, A.V.; You, J.H.; Pastor, J.Y. The thermo-mechanical behaviour of W-Cu metal matrix composites for fusion heat sink applications: The influence of the Cu content. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 498, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Bai, F.; Sun, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.G. Compression properties and electrical conductivity of in-situ 20 vol. % nano-sized TiCx/Cu composites with different particle size and morphology. Materials 2017, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.Y.; Inoue, A.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V. Investigation of the structure and mechanical properties of as-cast Ti-Cu-based alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamgaliev, R.K.; Buchgraber, W.; Kolobov, Y.R.; Amirkhanov, N.M.; Sergueeva, A.V.; Ivanov, K.V.; Grabovetskaya, G.P. Deformation behavior of Cu-based nano composite processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 319, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhao, C.J.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. The dry sliding wear properties of nano-sized TiCp/Al-Cu composites at elevated temperatures. Materials 2017, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Ren, L.Q. Microstructures and wear behavior of the TiC ceramic particulate locally reinforced steel matrix composites from a Cu-Ti-C system. Tetsu-to-Hagane 2015, 55, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, W.J. Wear characteristic of in situ synthetic TiB2 particulate-reinforced Al matrix composite formed by laser cladding. Wear 2006, 260, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Raju, G.B.; Suri, A.K. Processing and properties of monolithic TiB2 based materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 51, 352–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, S.A.; Biswas, K.; Basu, B. Microstructure-hardness-fretting wear resistance correlation in ultrafine grained Cu–TiB2–Pb composites. Wear 2014, 319, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, L.; Gotman, I.; Horvitz, D. In situ processing of TiB2/TiC ceramic composites by thermal explosion under pressure: experimental study and modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, H.; He, L. Effect of sintering process on the microstructures and properties of in situ TiB2-TiC reinforced steel matrix composites produced by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Ren, L.Q. Effect of B4C particle size on the reaction behavior of self-propagation high-temperature synthesis of TiC-TiB2 ceramic/Cu composites from a Cu-Ti-B4C system. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard 2014, 46, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.F.; Wang, W.H.; Jiang, R.S.; Lin, K.Y. A study on cutting force of machining in situ TiB2 particle-reinforced 7050Al alloy matrix composites. Metals 2017, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ren, L.Q. Effect of Ti and C particle sizes on reaction behavior of thermal explosion reaction of Cu-Ti-C system under Ar and air atmospheres. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 679, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Nanda, T.; Pandey, O.P. Effect of particle size on dry sliding wear behaviour of sillimanite reinforced aluminium matrix composites. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Zhao, Q.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Ren, L.Q. Dry sliding friction and wear mechanism of TiC-TiB2 particulate locally reinforced Mn-steel matrix composite from a Cu-Ti-B4C system via a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) casting route. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Gao, X.; Tang, J.; Gao, Y.Y.; Shu, S.-L.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.-C. Microstructures and tensile properties of Al-Cu matrix composites reinforced with nano-sized SiCp fabricated by semisolid stirring process. Metals 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiao, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Tribological behavior of nano-sized SiCp/7075 composite parts formed by semisolid processing. Metals 2018, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, T.; Trindade, B.; Weißgärber, T.; Kieback, B. Interfacial design of Cu-based composites prepared by powder metallurgy for heat sink applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 475, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharvandi, H.R.; Hadian, A.M. Pressureless sintering of TiB2-B4C ceramic matrix composite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2007, 17, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeepour, F.; Abachi, P.; Purazrang, K.; Moghanian, A.H. Production and properties of Cu/Cr2O3 nano-composites. Powder Technol. 2012, 222, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-Y.; Qiu, F.; Shu, S.-L.; Wang, L.; Chang, F.; Hu, W.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Q.-C. Mechanical properties and abrasive wear behaviors of in situ nano-TiCx/Al-Zn-Mg-Cu composites fabricated by combustion synthesis and hot press consolidation. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminikia, B. Investigation of the pre-milling effect on synthesis of nanocrystalline TiB2-TiC composite prepared by SHS method. Power Technol. 2012, 232, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Huang, L.; Jiang, Q.C. In situ synthesis of TiB2-TiC particulates locally reinforced medium carbon steel-matrix composites via the SHS reaction of Ni-Ti-B4C system during casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 407, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzari, M.; Cipolloni, G. Tribological behaviour of Cu based materials produced by mechanical milling/alloying and spark plasma sintering. Wear 2017, 376, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Han, Z.W.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ren, L.Q. Study on the reaction mechanism of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of TiC in the Cu-Ti-C system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.B.; Shu, S.L.; Qiu, F.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, Q.C. Compression properties and abrasive wear behavior of high volume fraction TiCx-TiB2/Cu composites fabricated by combustion synthesis and hot press consolidation. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Bai, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, W.Q. Grain refinement and mechanical properties of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys with different nano-sized TiCp addition. Materials 2017, 10, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, F. Microstructure evolution and wear properties of in situ synthesized TiB2 and TiC reinforced steel matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 459, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Liu, H.L.; Sun, L.P.; Bai, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.G. Shape-controlled TiCx particles fabricated by combustion synthesis in the Cu-Ti-C system. Crystals 2017, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.H.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Ren, L.Q. Effect of Cu content in Cu-Ti-B4C system on fabricating TiC/TiB2 particulates locally reinforced steel matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toozandehjani, M.; Matori, K.A.; Ostovan, F.; Abdul, A.S.; Mamat, M.S. Effect of milling time on the microstructure, physical and mechanical properties of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposite synthesized by ball milling and powder metallurgy. Materials 2017, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.O.; Nguyen, H.V.; Kim, J.S.; Dudina, D. Structural investigations of TiC-Cu nanocomposites prepared by ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Metals 2017, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.J.; Ren, L.Q. Study on the impact resistance of bionic layered composite of TiC-TiB2/Al from Al-Ti-B4C system. Materials 2016, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.M. Fabrication and mechanical properties of microalloyed and ceramic particulate reinforced NiAl-based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 440, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Chu, J.-G.; Hu, W.; Lu, J.-B.; Li, X.-D.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Q.-C. Study of effect of Zr addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of (TiCx-TiB2)/Cu composites by combustion synthesis and hot press consolidation in the Cu-Ti-B4C-Zr system. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Han, Y.; Cheng, A.; Lu, J.B.; Jiang, Q.C. Effect of Cr content on the compression properties and abrasive wear behavior of the high-volume fraction (TiC-TiB2)/Cu Composites. Acta. Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2014, 27, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.L.; Huang, C.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Zou, B.; Zhu, H.T.; Wang, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot pressed TiB2-SiC composite ceramic tool materials at room and elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 606, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, W. Effects of Thermo-mechanical treatment on microstructure and properties of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloys. Phys. Procedia 2013, 50, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, L.-C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, T.-T.; Chen, C.-G.; Hao, J.-J.; Shao, H.-P.; Guo, Z.-M.; Luo, J.; Sun, J.-B. Influence of nano-Al2O3-reinforced oxide-dispersion-strengthened Cu on the mechanical and tribological properties of Cu-based composites. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2016, 23, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.F.; Zhang, F.G.; Chen, Z.; Ji, G.; Wang, M.L.; Wu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, H. Microstructure of multi-pass friction-stir-processed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys reinforced by nano-sized TiB2 particles and the effect of T6 heat treatment. Metals 2017, 7, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.X.; Luo, Z.Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, D. Improving the mechanical properties of Cu-15Ni-8Sn alloys by addition of Titanium. Materials 2017, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, R.; Vedani, M. Metal matrix composites reinforced by nano-particles—A review. Metals 2014, 4, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muolo, M.L.; Ferrera, E.; Novakovic, R.; Passerone, A. Wettability of zirconium diboride ceramics by Ag, Cu and their alloys with Zr. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, A.P. Precursor film of tin-based active solder wetting on ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 28, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasovskyy, V.P.; Naidich, Y.V.; Krasovskaya, N.A. Surface tension and density of copper-zirconium alloys in contact with fluoride refractories. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 2367–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


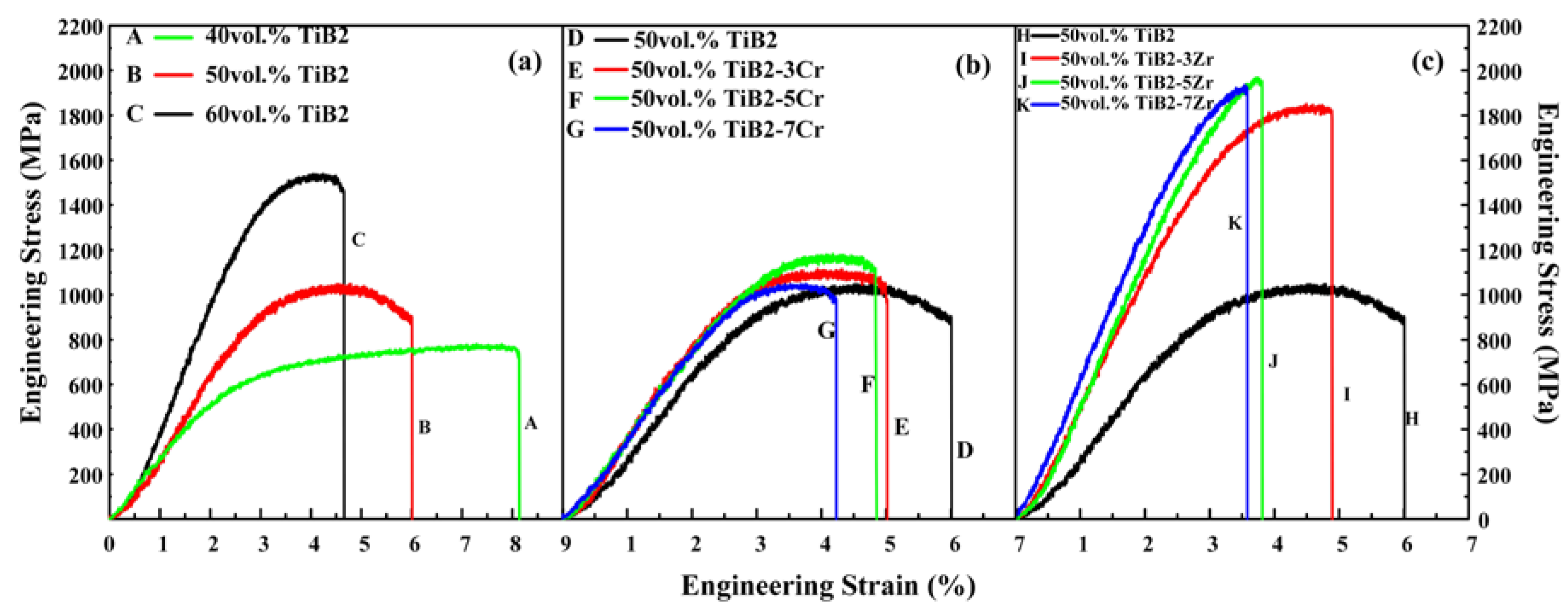
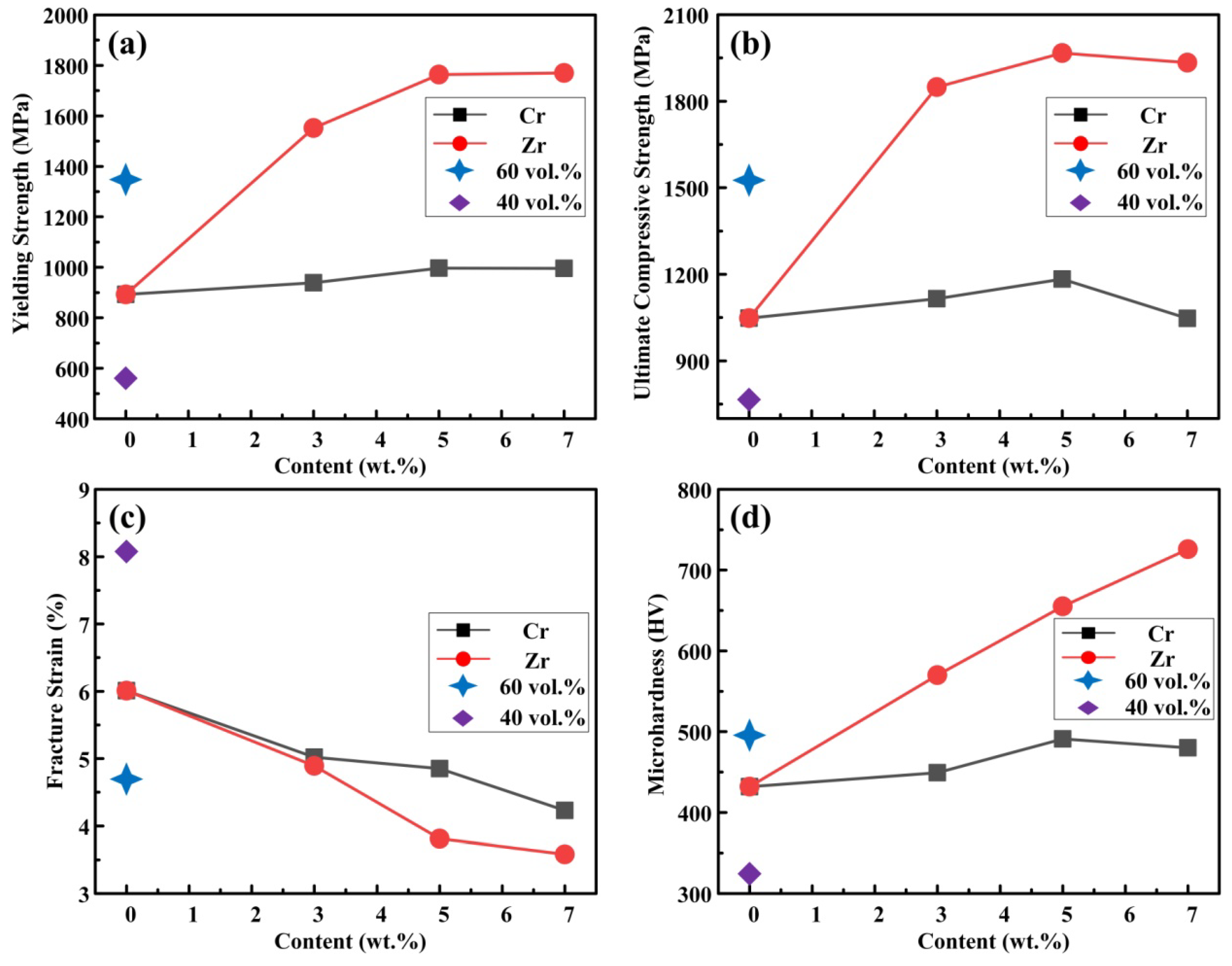
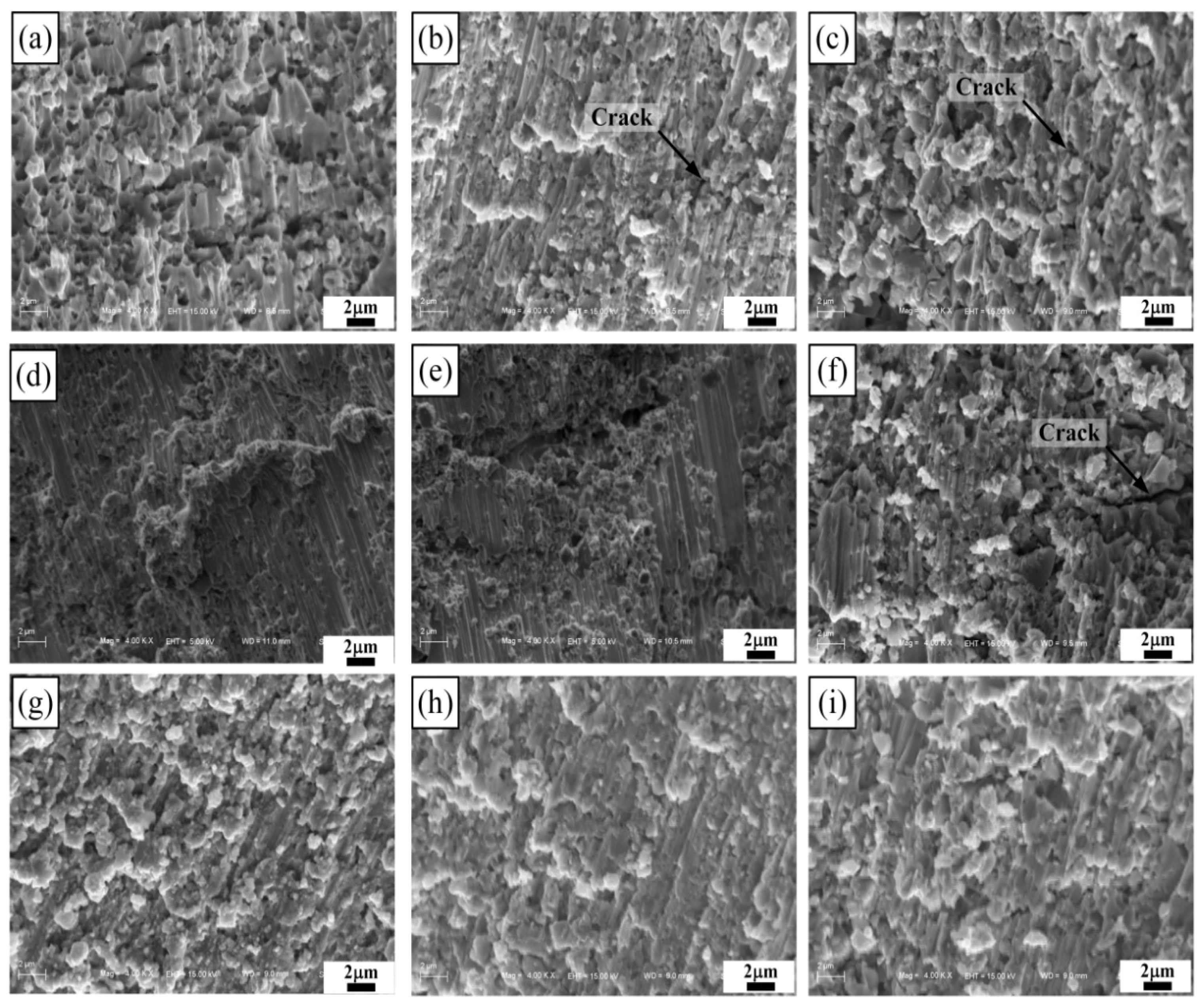

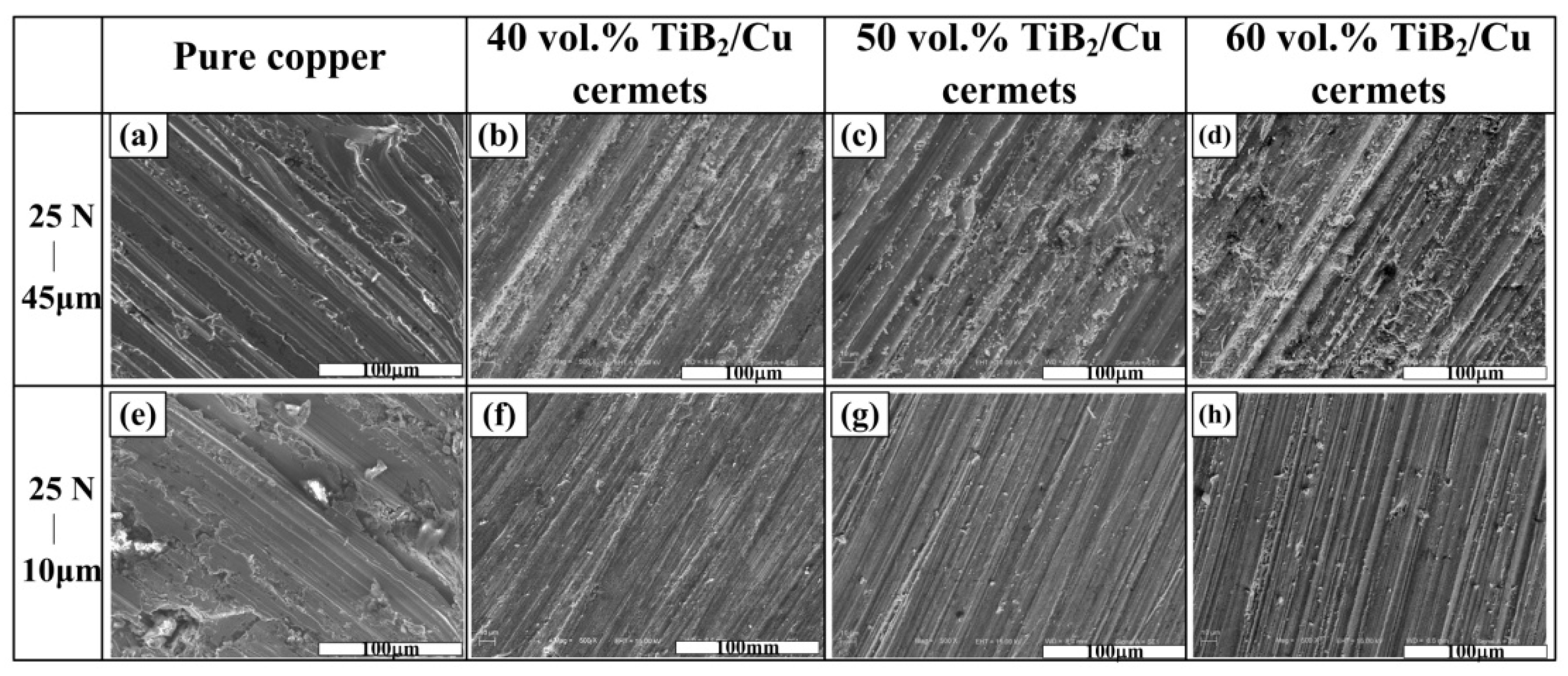
| Samples | σ0.2 (MPa) | σUCS (MPa) | εf (%) | Hv |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 vol % TiB2 | 321 ± 8 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2 | 432 ± 10 | |||
| 60 vol % TiB2 | 493 ± 9 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+3Cr | 449 ± 9 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+5Cr | 491 ± 8 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+7Cr | 480 ± 10 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+3Zr | 570 ± 12 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+5Zr | 655 ± 11 | |||
| 50 vol % TiB2+7Zr | 726 ± 9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, F.; Duan, X.; Dong, B.; Yang, H.; Lu, J.; Li, X. Effects of Cr and Zr Addition on Microstructures, Compressive Properties, and Abrasive Wear Behaviors of In Situ TiB2/Cu Cermets. Materials 2018, 11, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081464
Qiu F, Duan X, Dong B, Yang H, Lu J, Li X. Effects of Cr and Zr Addition on Microstructures, Compressive Properties, and Abrasive Wear Behaviors of In Situ TiB2/Cu Cermets. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081464
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Feng, Xiangzheng Duan, Baixin Dong, Hongyu Yang, Jianbang Lu, and Xiujuan Li. 2018. "Effects of Cr and Zr Addition on Microstructures, Compressive Properties, and Abrasive Wear Behaviors of In Situ TiB2/Cu Cermets" Materials 11, no. 8: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081464
APA StyleQiu, F., Duan, X., Dong, B., Yang, H., Lu, J., & Li, X. (2018). Effects of Cr and Zr Addition on Microstructures, Compressive Properties, and Abrasive Wear Behaviors of In Situ TiB2/Cu Cermets. Materials, 11(8), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081464






