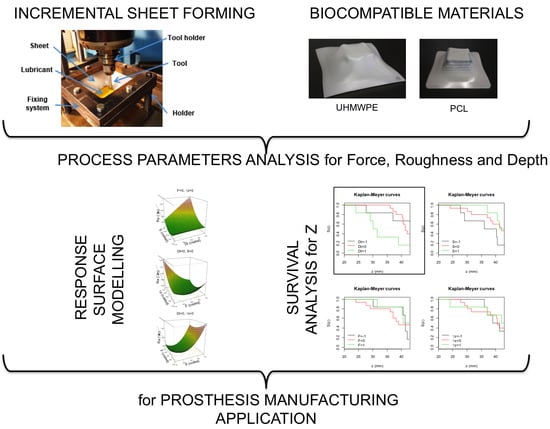
Process Parameter Effects on Biocompatible Thermoplastic Sheets Produced by Incremental Forming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
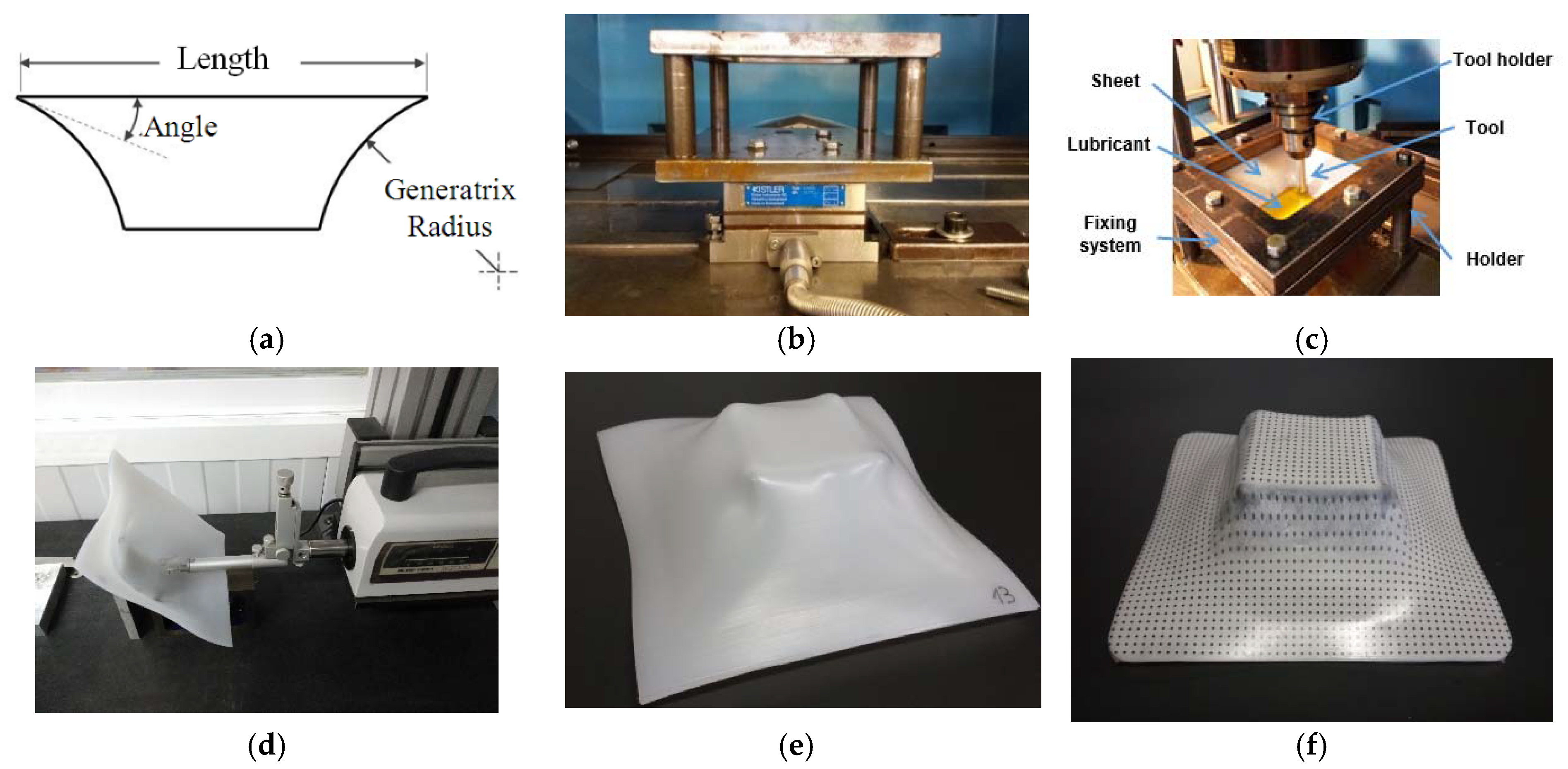
2.1. Geometry and Materials
- varying wall angle along the part’s depth.
- 105 mm in length.
- 45° for the initial wall angle
- 80 mm generatrix radius.
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Design of Experiments
- Dt: Tool diameter (6, 10, 14 mm)
- S: Spindle speed (Free*, 1000, 2000 rpm)
- F: Feed rate (1500, 2250, 3000 mm/min)
- Δz: Step down (0.2, 0.35, 0.5 mm).
2.4. Analysis Procedure
- Estimation of the full model with first order, two-way interactions and pure quadratic terms.
- Sequentially removal of the non-significant terms based on the tests on individual regression and groups of coefficients. Each model was evaluated in terms of the fit statistics: R2, R2-adjusted, R2-predicted and RMSE. In addition, the test for significance of regression (p-value associated to Model in the ANOVA table) was observed: a p-value < α indicated that the regression was significant. The lack of fit test was also examined as an indicator of the tentative model satisfactorily describing the data when its p-value was high.
- Model adequacy checking: last squares regression assumptions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Maximum Axial Force (Fz Max)
3.1.1. PCL
3.1.2. UHMWPE
3.2. Surface Roughness (Ra)
3.2.1. PCL
3.2.2. UHMWPE
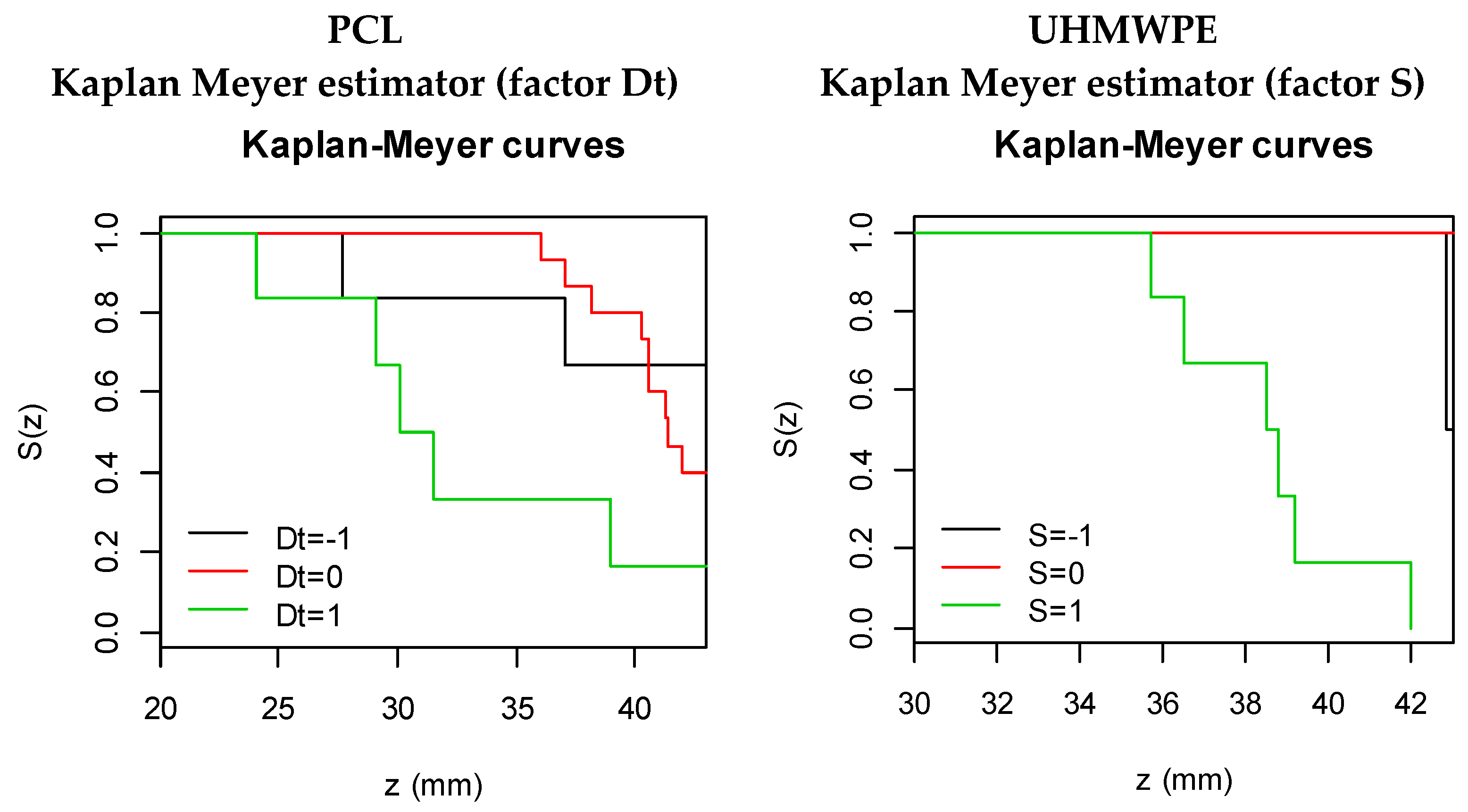
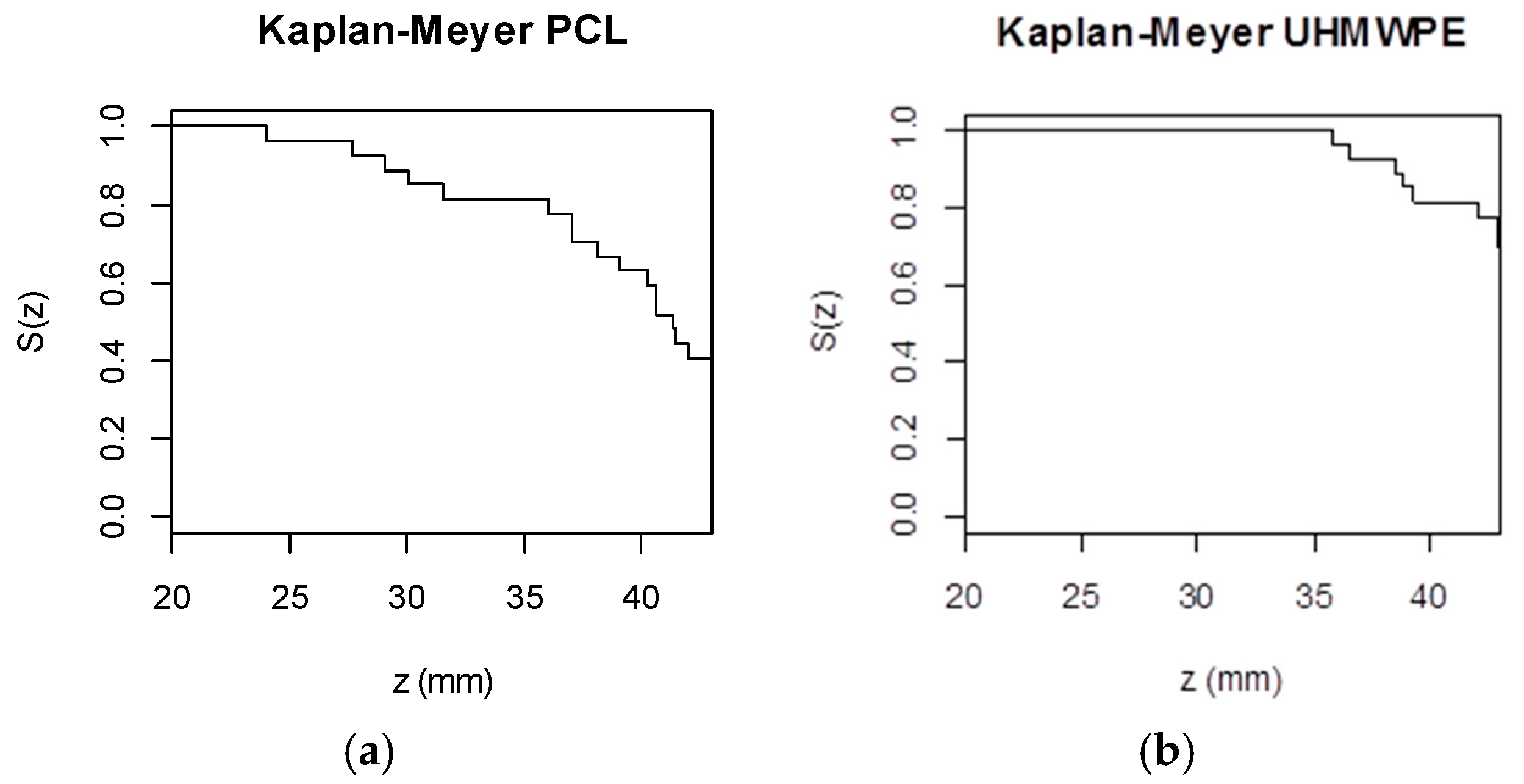
3.3. Maximum Achieved Depth (Zmax)
3.3.1. PCL
3.3.2. UHMWPE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, S.J. Evolving Paradigms of Manufacturing: From Mass Production to Mass Customization and Personalization. Procedia CIRP 2013, 7, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarpisheh, M.; Abdolhoseini, M.J.; Amini, S. Experimental and numerical investigation of the hot incremental forming of Ti-6Al-4V sheet using electrical current. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 83, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.B.; Martinho, T.M.; Martins, P.A.F. Incremental forming of hole-flanges in polymer sheets. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerens, R.; Eyckens, P.; Van Bael, A.; Duflou, J.R. Force prediction for single point incremental forming deduced from experimental and FEM observations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 46, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Daniel, W.J.T.; Liu, S.; Meehan, P. Efficient force prediction for incremental sheet forming and experimental validation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 73, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Daniel, W.J.T.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Meehan, P. Deformation mechanics and efficient force prediction in single point incremental forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahloul, R.; Arfa, H.; BelHadjSalah, H. A study on optimal design of process parameters in single point incremental forming of sheet metal by combining Box–Behnken design of experiments, response surface methods and genetic algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 163–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, G.; Bagudanch, I.; Martínez-Donaire, A.J.; García-Romeu, M.L.; Vallellano, C. Critical analysis of necking and fracture limit strains and forming forces in single-point incremental forming. Mater. Des. 2014, 63, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagudanch, I.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Centeno, G.; Elías-Zúñiga, A.; Ciurana, J. Forming force and temperature effects on single point incremental forming of polyvinylchloride. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 219, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagudanch, I.; Sabater, M.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L. Incremental forming of polymers: Process parameters selection from the perspective of electric energy consumption and cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, M.A.; Mirkouei, A.; Yu, X.; Malhotra, R.; Pilla, S. Effects of incremental depth and tool rotation on failure modes and microstructural properties in single point incremental forming of polymers. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 222, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yanle, L.; Meehan, P.A. Modeling and Optimization of Surface Roughness in Incremental Sheet Forming using a Multi-objective Function. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, M.C.; Cristea, I. Processing Metal Sheets by SPIF and Analysis of Parts Quality. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echrif, S.B.M.; Hrairi, M. Significant Parameters for the Surface Roughness in Incremental Forming Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanasio, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Mazzoni, L.; Ceretti, E.; Giardini, C. Design of an Equipment for Forces Measurement in TPIF Process. Int. Conf. Technol. Plast. 2008, 9, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Sánchez, L.M.; Bagudanch, I.; Sustaita, A.O.; Iturbe-Ek, J.; Elizalde, L.E.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Single-Point Incremental Forming of Two Biocompatible Polymers: An insight into their thermal and structural properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Behnken, D.W. Some New Three Level Designs for the Study of Quantitative Variables. Technometrics 1960, 2, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd ed.; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2016).
- Centeno, G.; Martínez-Donaire, A.J.; Bagudanch, I.; Morales-Palma, D.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Vallellano, C. Revisiting formability and failure of AISI304 sheets in SPIF: Experimental approach and numerical validation. Metals 2017, 7, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharudin, B.T.H.T.; Azpen, Q.M.; Sulaima, S.; Mustapha, F. Experimental investigation of forming forces in frictional stir incremental forming of aluminum alloy AA6061-T6. Metals 2017, 7, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagudanch, I.; Vives-Mestres, M.; Sabater, M.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L. Polymer Incremental Sheet Forming Process: Temperature Analysis Using Response Surface Methodology. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 32, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, B.M.; Ham, M.; Wilkinson, M.G. Small Data Set Analysis in Surface Metrology: An Investigation Using a Single Point Incremental Forming Case Study. Scanning 2010, 32, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Material | Vicat Softening Temperature (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL | 44.3 | 15.2 | 375 |
| UHMWPE | 80 | 19 | 700 |
| ID | Tool Diameter, Dt (mm) | Spindle Speed, S (rpm) | Feed Rate, F (mm/min) | Step Down, Δz (mm) | PCL | UHMWPE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fz Max (N) | Ra (μm) | Zmax * (mm) | Fz max (N) | ΔRa (μm) | Zmax * (mm) | |||||
| 1 | 6 | Free | 2250 | 0.35 | 208.72 | 0.498 | 27.7 (0) | 485.33 | 0.437 | 42.7 (1) |
| 2 | 14 | Free | 2250 | 0.35 | 439.14 | 0.627 | 29.1 (0) | 1027.50 | 0.750 | 42.7 (1) |
| 3 | 6 | 2000 | 2250 | 0.35 | 190.95 | 0.41 | 42.7 (1) | 414.58 | 0.916 | 42.0 (0) |
| 4 | 14 | 2000 | 2250 | 0.35 | 329.64 | 2.23 | 43.0 (1) | 697.15 | −0.194 | 35.7 (0) |
| 5 | 10 | 1000 | 1500 | 0.20 | 314.38 | 0.608 | 41.4 (0) | 635.68 | 0.511 | 43.0 (1) |
| 6 | 10 | 1000 | 3000 | 0.20 | 309.16 | 0.622 | 43.0 (1) | 596.08 | 0.242 | 43.0 (1) |
| 7 | 10 | 1000 | 1500 | 0.50 | 293.05 | 1.393 | 42.0 (0) | 636.66 | 0.391 | 43.0 (1) |
| 8 | 10 | 1000 | 3000 | 0.50 | 291.63 | 0.509 | 43.0 (1) | 591.00 | 0.324 | 43.0 (1) |
| 9 | 10 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.35 | 325.57 | 0.585 | 38.2 (0) | 643.44 | 0.477 | 42.7 (1) |
| 10 | 6 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.20 | 214.14 | 0.453 | 43.0 (1) | 491.68 | 0.508 | 43.0 (1) |
| 11 | 14 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.20 | 425.94 | 1.114 | 39.0 (0) | 765.37 | 0.739 | 43.0 (1) |
| 12 | 6 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.50 | 197.63 | 0.484 | 37.0 (0) | 399.84 | 0.373 | 43.0 (1) |
| 13 | 14 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.50 | 390.87 | 1.549 | 24.0 (0) | 858.88 | 0.635 | 43.0 (1) |
| 14 | 10 | Free | 1500 | 0.35 | 320.78 | 1.023 | 40.6 (0) | 818.05 | 0.332 | 42.7 (1) |
| 15 | 10 | 2000 | 1500 | 0.35 | 275.32 | 1.880 | 41.3 (0) | 581.63 | 0.230 | 38.5 (0) |
| 16 | 10 | Free | 3000 | 0.35 | 343.10 | 0.716 | 40.3 (0) | 747.58 | 0.198 | 42.7 (1) |
| 17 | 10 | 2000 | 3000 | 0.35 | 282.30 | 1.735 | 40.6 (0) | 558.92 | 0.420 | 39.2 (0) |
| 18 | 10 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.35 | 296.22 | 0.464 | 42.7 (1) | 595.00 | 0.524 | 42.7 (1) |
| 19 | 6 | 1000 | 1500 | 0.35 | 227.42 | 0.527 | 42.7 (1) | 486.95 | 0.354 | 42.7 (1) |
| 20 | 14 | 1000 | 1500 | 0.35 | 418.57 | 1.385 | 30.1 (0) | 802.43 | 0.863 | 42.7 (1) |
| 21 | 6 | 1000 | 3000 | 0.35 | 240.99 | 0.330 | 42.7 (1) | 449.30 | 0.231 | 42.7 (1) |
| 22 | 14 | 1000 | 3000 | 0.35 | 381.09 | 0.902 | 31.5 (0) | 830.85 | 0.956 | 42.7 (1) |
| 23 | 10 | Free | 2250 | 0.20 | 330.25 | 0.859 | 36.0 (0) | 727.72 | 0.115 | 42.8 (0) |
| 24 | 10 | 2000 | 2250 | 0.20 | 281.23 | 1.775 | 37.0 (0) | 554.77 | 0.549 | 38.8 (0) |
| 25 | 10 | Free | 2250 | 0.50 | 355.89 | 0.579 | 43.0 (1) | 774.19 | 0.801 | 43.0 (1) |
| 26 | 10 | 2000 | 2250 | 0.50 | 266.34 | 2.102 | 43.0 (1) | 587.48 | 0.407 | 36.5 (0) |
| 27 | 10 | 1000 | 2250 | 0.35 | 280.30 | 0.598 | 42.7 (1) | 611.80 | 0.440 | 42.7 (1) |
| PCL | UHWMPE | ||||||||||
| Parameter estimates | Parameter estimates | ||||||||||
| Coefficient | p-value | Coefficient | Pr (>|t|) | ||||||||
| (Intercept) | 304.84 | <0.001 | (Intercept) | 626.33 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Dt | 92.12 | <0.001 | Dt | 187.88 | <0.001 | ||||||
| S | −31.01 | <0.001 | S | −98.82 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Dt·S | −22.93 | 0.009 | F | −15.64 | 0.033 | ||||||
| Δz | 6.40 | 0.359 | |||||||||
| Dt·S | −64.90 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Dt·Δz | 46.34 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| S2 | 38.24 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Analysis of variance | Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F value | p-value | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F value | p-value | ||
| Model | 3 | 115,468 | 38,489 | 149.76 | <0.001 | Model | 7 | 579,363 | 82,766 | 148.86 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 23 | 5918 | 257 | Residuals | 19 | 10,570 | 556 | ||||
| Lack of fit | 5 | 1185 | 237 | 0.90 | 0.502 | Lack of fit | 17 | 9360 | 551 | 0.91 | 0.644 |
| Pure Error | 18 | 4733 | 263 | Pure Error | 2 | 1210 | 605 | ||||
| Summary of fit | Summary of fit | ||||||||||
| R2 | 0.95 | RMSE | 16.04 | R2 | 0.98 | RMSE | 23.59 | ||||
| Adj, R2 | 0.94 | Pred. R2 | 0.93 | Adj, R2 | 0.98 | Pred. R2 | 0.96 | ||||
 |  | ||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| PCL | UHWMPE | ||||||||||
| Parameter estimates | Parameter estimates | ||||||||||
| Coefficient | p-value | Coefficient | p-value | ||||||||
| (Intercept) | 0.57 | <0.001 | (Intercept) | 0.46 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Dt | 0.43 | <0.001 | Dt | 0.08 | 0.259 | ||||||
| S | 0.49 | <0.001 | S | −0.03 | 0.707 | ||||||
| F | −0.17 | 0.010 | F | −0.03 | 0.703 | ||||||
| Δz | 0.10 | 0.105 | Dt·S | −0.36 | 0.006 | ||||||
| Dt·S | 0.42 | 0.001 | |||||||||
| F· Δz | −0.22 | 0.038 | |||||||||
| S2 | 0.51 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| F2 | 0.16 | 0.070 | |||||||||
| Δz 2 | 0.21 | 0.020 | |||||||||
| Analysis of variance | Analysis of variance | ||||||||||
| Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F value | p-value | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F value | p-value | ||
| Model | 9 | 7.97 | 0.89 | 22.24 | <0.001 | Model | 4 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 2.77 | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 17 | 0.68 | 0.04 | Residuals | 22 | 1.18 | 0.05 | ||||
| Lack of fit | 15 | 0.67 | 0.04 | 8.14 | 0.115 | Lack of fit | 14 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 1.89 | 0.184 |
| Pure Error | 2 | 0.01 | 0.01 | Pure Error | 8 | 0.27 | 0.03 | ||||
| Summary of fit | Summary of fit | ||||||||||
| R2 | 0.92 | RMSE | 0.20 | R2 | 0.33 | RMSE | 0.23 | ||||
| Adj, R2 | 0.88 | Pred. R2 | 0.74 | Adj, R2 | 0.21 | Pred. R2 | −0.33 | ||||
 |  | ||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Intercept | Dt | S | F | Δz | S2 | F2 | Δz2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fz max | |||||||||||
| PCL | |||||||||||
| UHMWPE | |||||||||||
| Ra | |||||||||||
| PCL | |||||||||||
| UHMWPE (ΔRa) | |||||||||||
| Z max (Survival analysis) | |||||||||||
| PCL | × | ||||||||||
| UHMWPE | × |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabater, M.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Vives-Mestres, M.; Ferrer, I.; Bagudanch, I. Process Parameter Effects on Biocompatible Thermoplastic Sheets Produced by Incremental Forming. Materials 2018, 11, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081377
Sabater M, Garcia-Romeu ML, Vives-Mestres M, Ferrer I, Bagudanch I. Process Parameter Effects on Biocompatible Thermoplastic Sheets Produced by Incremental Forming. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081377
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabater, Marc, M. Luisa Garcia-Romeu, Marina Vives-Mestres, Ines Ferrer, and Isabel Bagudanch. 2018. "Process Parameter Effects on Biocompatible Thermoplastic Sheets Produced by Incremental Forming" Materials 11, no. 8: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081377
APA StyleSabater, M., Garcia-Romeu, M. L., Vives-Mestres, M., Ferrer, I., & Bagudanch, I. (2018). Process Parameter Effects on Biocompatible Thermoplastic Sheets Produced by Incremental Forming. Materials, 11(8), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081377