N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
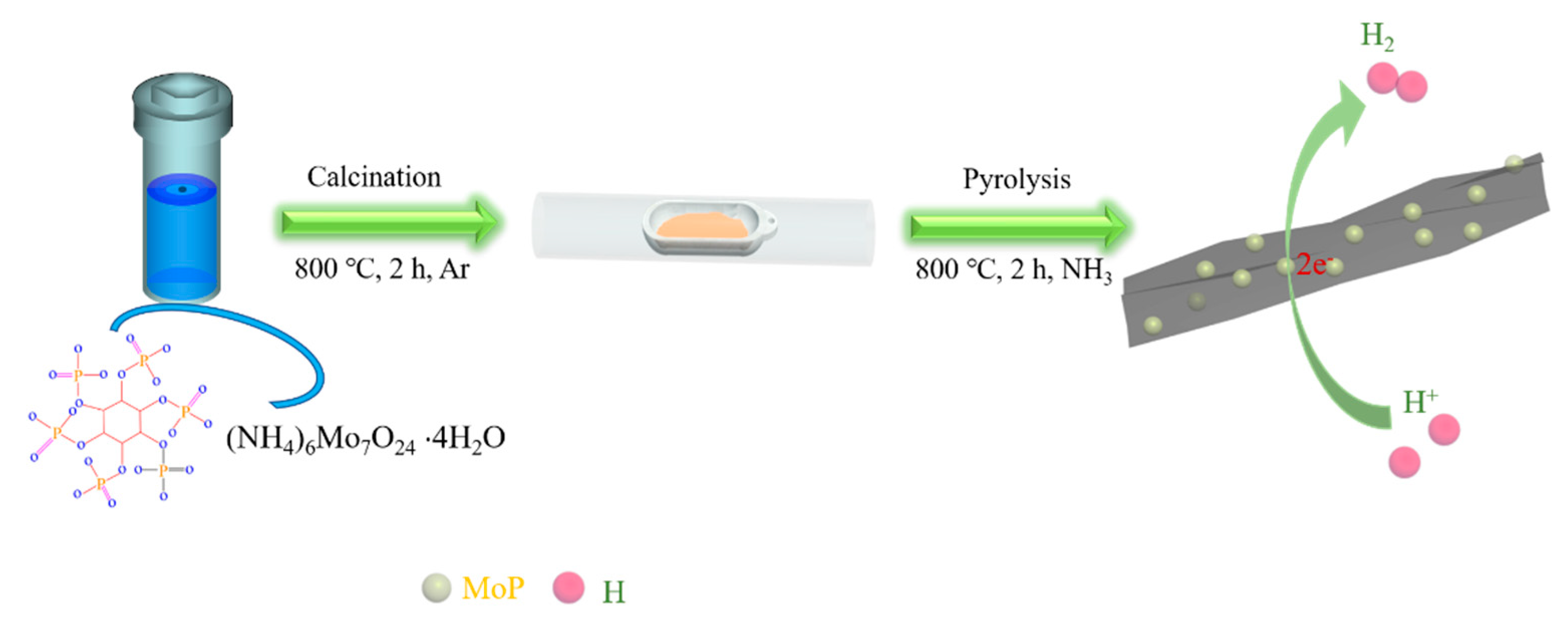
2.1. Synthesis of Catalysts
2.2. Characterization of Catalysts
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
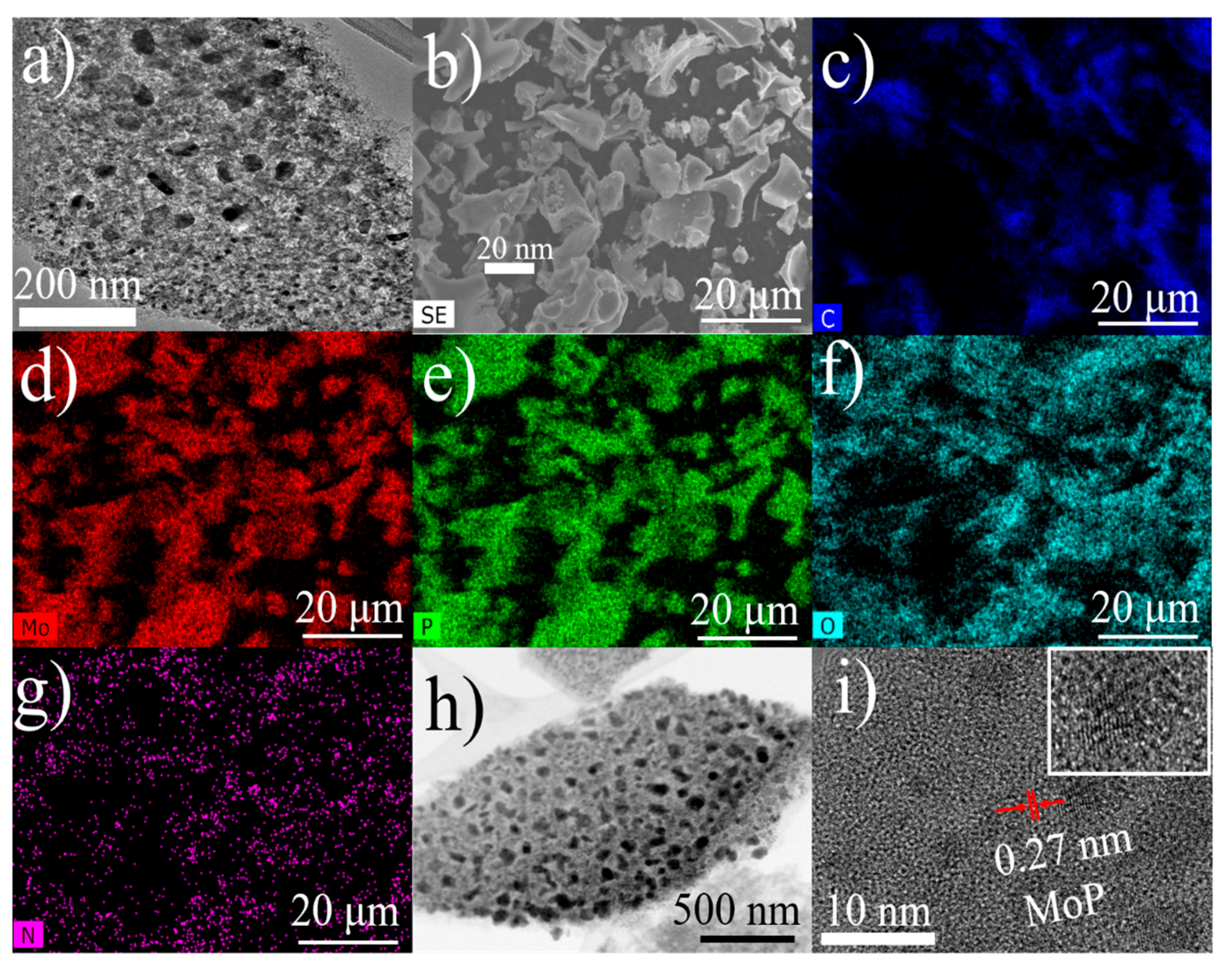
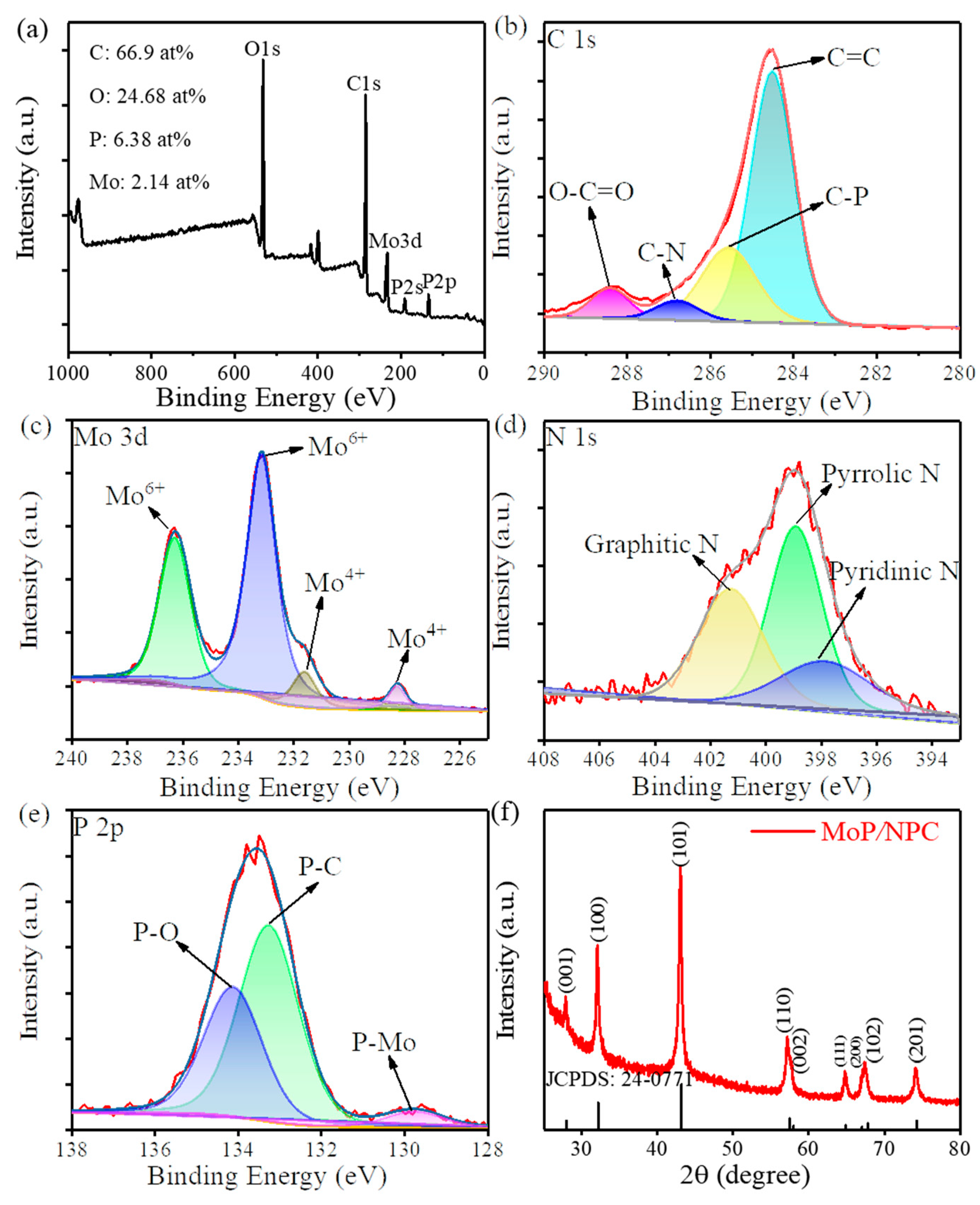
3.1. Characterization of Catalysts
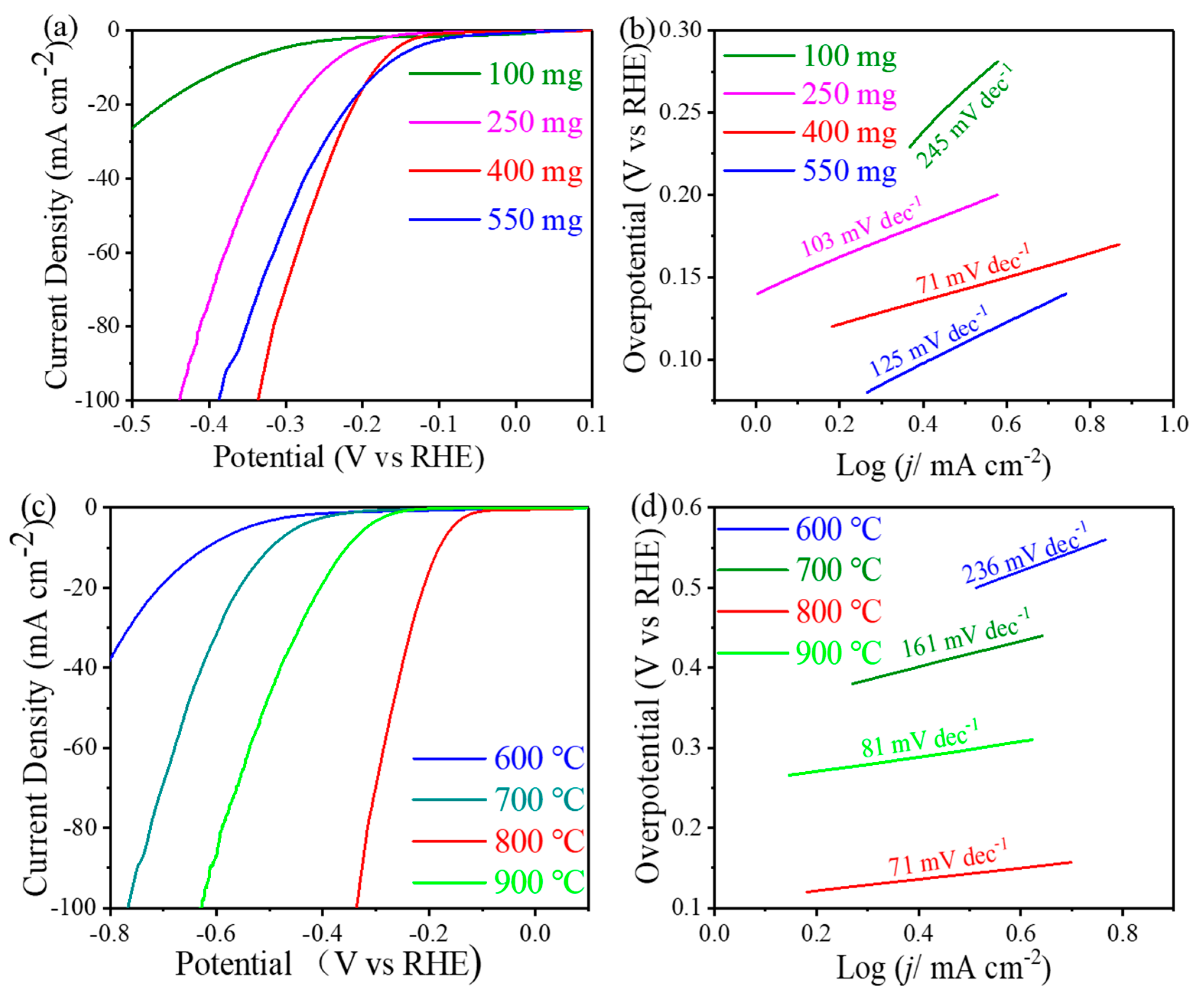
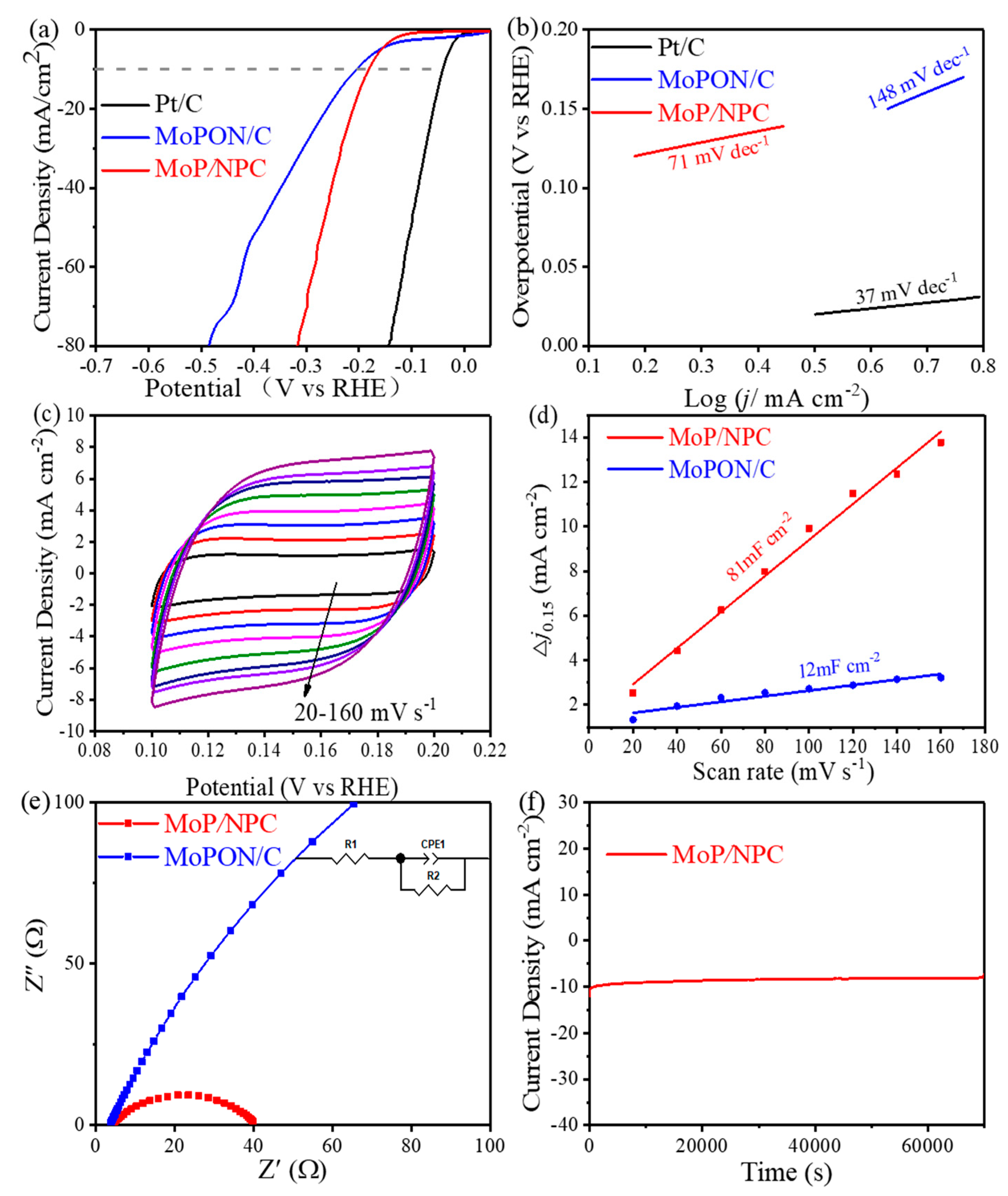
3.2. Electrocatalytic Properties of Catalysts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N.Y.; Han, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S.T.; Zhong, J.; Kang, Z.H. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway. Science 2015, 347, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, I.; Shipman, M.A.; Symes, M.D. Earth-abundant catalysts for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Dai, L. Multifunctional carbon-based metal-free electrocatalysts for simultaneous oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Song, X.; Feng, K.; Nie, K.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Zhong, J.; Li, Y. Mo2C nanoparticles dispersed on hierarchical carbon microflowers for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11337–11343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H.; Shen, M.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Tang, Y. Porous nanoMoC@graphite shell derived from a MOFs-directed strategy: An efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 6006–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Z.; Wan, L.J.; Hu, J.S. Pomegranate-like N,P-doped Mo2C@C nanospheres as highly active electrocatalysts for alkaline hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8851–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Xu, Y.F.; Rao, H.S.; Xu, W.J.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Kuang, D.B.; Su, C.Y. Novel porous molybdenum tungsten phosphide hybrid nanosheets on carbon cloth for efficient hydrogen evolution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, G.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Sun, D.; Tang, Y. Facile synthesis based on novel carbon-supported cyanogel of structurally ordered Pd3Fe/C as electrocatalyst for formic acid oxidation. Nano Res. 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Lei, W.; Zhu, J.; Xia, K.; Wang, D. Controllable synthesis of molybdenum-based electrocatalysts for a hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4879–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, J.; Fisher, A.; Sritharan, T.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Z.J. A multisite strategy for enhancing the hydrogen evolution reaction on a nano-Pd surface in alkaline media. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, W.; Xiong, T.; Wang, A.; Chen, S.; Chu, B. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity of Co@N-doped carbon nanotubes by ultrasmall defect-rich TiO2 nanoparticles for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z. In situ O2-emission assisted synthesis of molybdenum carbide nanomaterials as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen production in both acidic and alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, G. One-dimensional earth-abundant nanomaterials for water-splitting electrocatalysts. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wei, G.; Chen, Z.; Humphrey, M.G.; Zhang, C. Ultrafast synthesis of molybdenum carbide nanoparticles for efficient hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 22805–22812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Pan, J.; He, T.; Yan, Y.; Xia, B.Y.; Wang, X. Molybdenum carbide-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 10947–10961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, M.A.R.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.S. BCN network-encapsulated multiple phases of molybdenum carbide for efficient hydrogen evolution reactions in acidic and alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13122–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A. Electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 11053–11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cui, J.; Guo, C.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, R.; Xu, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Ultrasmall Cu7S4@MoS2 hetero-nanoframes with abundant active edge sites for ultrahigh-performance hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6502–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.J.; Peng, Z.W.; Ye, R.Q.; Zhou, H.Q.; Guo, X. M3C (M: Fe, Co, Ni) Nanocrystals Encased in Graphene Nanoribbons: An Active and Stable Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7407–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Fa, W.; Ge, S. High-efficiency and stable alloyed nickel based electrodes for hydrogen evolution by seawater splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 732, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Cong, W.; Fujita, T.; Tang, Z.; Chen, M. High catalytic activity of nitrogen and sulfur co-doped nanoporous graphene in the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Enhancing electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution of WP2 three-dimensional nanowire arrays via Mo doping. Mater. Lett. 2018, 213, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Suen, N.-T.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xu, G.; Cai, W.; et al. In situ engineering of double-phase interface in Mo/Mo2C heteronanosheets for boosted hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liu, N.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gao, Q. Cobalt-doping in molybdenum-carbide nanowires toward efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5590–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ye, C.; Xu, M.; Bao, S. MoP nanoparticles with a P-rich outermost atomic layer embedded in N-doped porous carbon nanofibers: Self-supported electrodes for efficient hydrogen generation. Nano Res. 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Ding, F.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Ni, W.; Yan, H.; Sun, K.; Yan, Y.-M. Templated-preparation of a three-dimensional molybdenum phosphide sponge as a high performance electrode for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Xia, K.; Xuan, C.; Guo, J.; Lei, W.; Wang, D. Facile preparation of carbon sphere supported molybdenum compounds (P, C and S) as hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts in acid and alkaline electrolytes. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. A novel CoP/MoS2-CNTs hybrid catalyst with Pt-like activity for hydrogen evolution. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnaney, J.M.; Crompton, J.C.; Callejas, J.F.; Popczun, E.J.; Biacchi, A.J.; Lewis, N.S.; Schaak, R.E. Amorphous molybdenum phosphide nanoparticles for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4826–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Guo, J.; Xiao, W.; Xuan, C.; Lei, W.; Wang, D. Highly efficient and stable MoP-rGO nanoparticles as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Xia, K.; Lei, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. MoS2-MoP heterostructured nanosheets on polymer-derived carbon as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Li, S.H.; Tan, H.Q.; Khan, S.U.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, Y.G. MoP/Mo2C@C: A New Combination of Electrocatalysts for Highly Efficient Hydrogen Evolution over the Entire pH Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16270–16279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-Y.; Wu, C.-X.; Feng, X.-J.; Tan, H.-Q.; Yan, L.-K.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.-H.; Wang, E.-B.; Li, Y.-G. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from seawater by a low-cost and stable CoMoP@C electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Teng, X.; Dong, H.; He, X.; Chen, Z. N,P-doped molybdenum carbide nanofibers for efficient hydrogen production. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14632–14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Tian, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, A.; Meng, M.; Zhao, L.; Fu, H. Phosphorus-modified tungsten nitride/reduced graphene oxide as a high-performance, non-noble-metal electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6325–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Pyridinic and pyrrolic nitrogen-rich ordered mesoporous carbon for efficient oxygen reduction in microbial fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14669–14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Cai, J.; Zheng, X.; Han, D.; Wu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; et al. Tailoring the d-band centers enables Co4N nanosheets to be highly active for hydrogen evolution catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5076–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Q.; Ye, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Bao, S.J. Nanosized metal phosphides embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Wen, Z.; Cui, S.; Ci, S.; Mao, S.; Chen, J. An advanced nitrogen-doped graphene/cobalt-embedded porous carbon polyhedron hybrid for efficient catalysis of oxygen reduction and water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.; Yan, D.Y.; Wang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, L.; Mao, J.; Liu, H.; Du, X.-W.; et al. Activating cobalt(ii) oxide nanorods for efficient electrocatalysis by strain engineering. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, I.A.J.; Grugeon, S.; Takenouti, H.; Tribollet, B.; Armand, M.; Davoisne, C.; Débart, A.; Laruelle, S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy response study of a commercial graphite-based negative electrode for li-ion batteries as function of the cell state of charge and ageing. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 223, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X. N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Materials 2018, 11, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081316
Wang S, Wang J, Li P, Wu Z, Liu X. N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081316
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuai, Jia Wang, Ping Li, Zexing Wu, and Xien Liu. 2018. "N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction" Materials 11, no. 8: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081316
APA StyleWang, S., Wang, J., Li, P., Wu, Z., & Liu, X. (2018). N,P-Codoped Carbon Layer Coupled with MoP Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Materials, 11(8), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081316