Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Methylene Blue Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
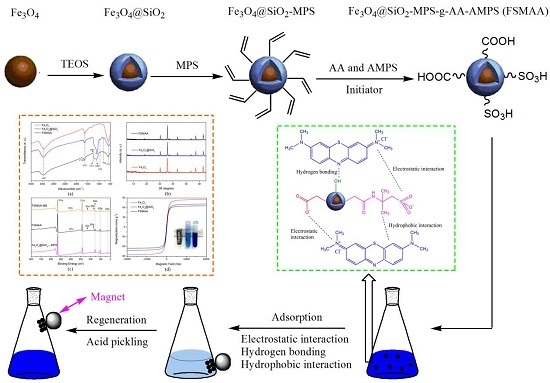
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetic Adsorbent
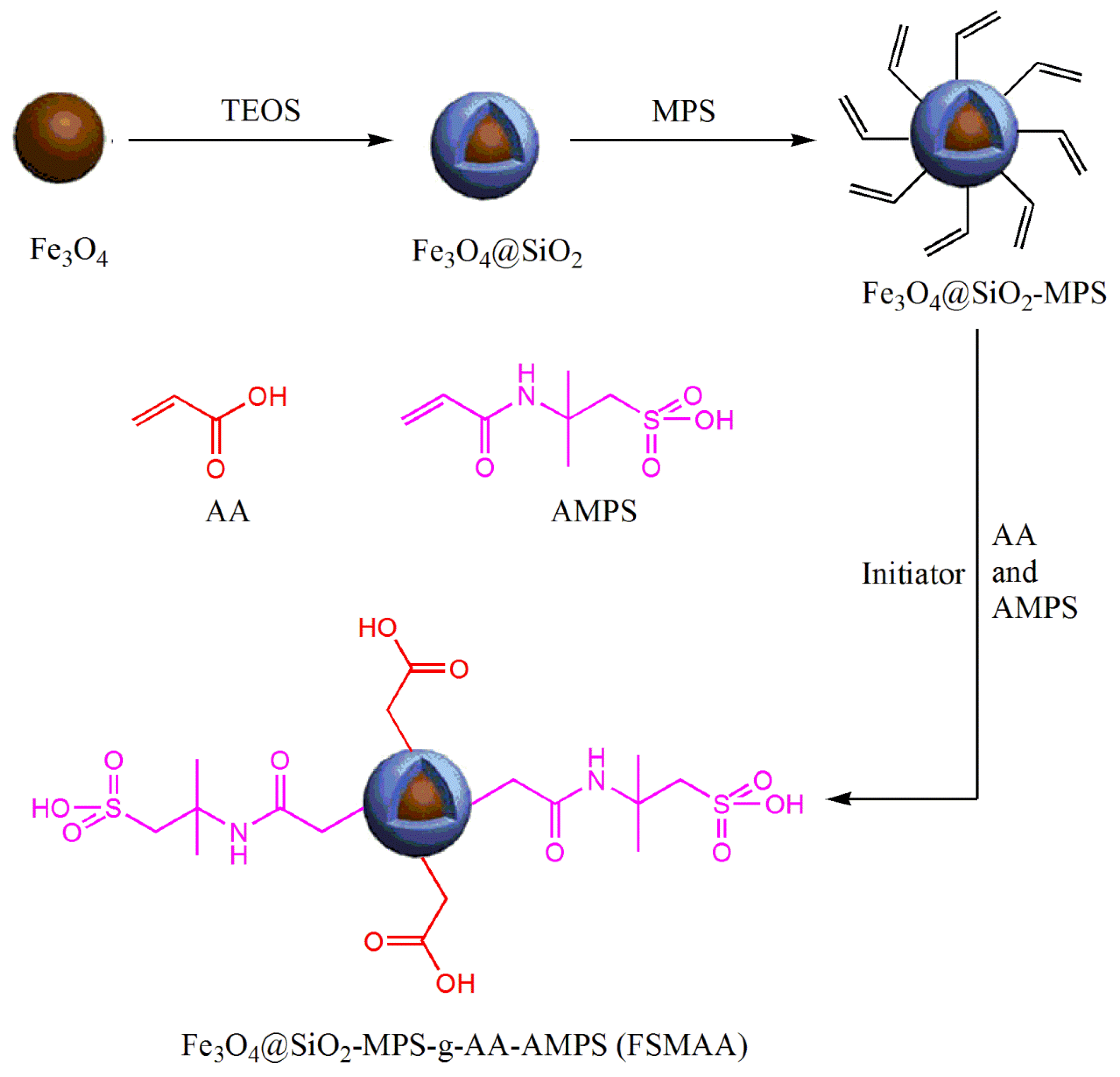
2.2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2 MNPs
2.2.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2-MPS MNPs
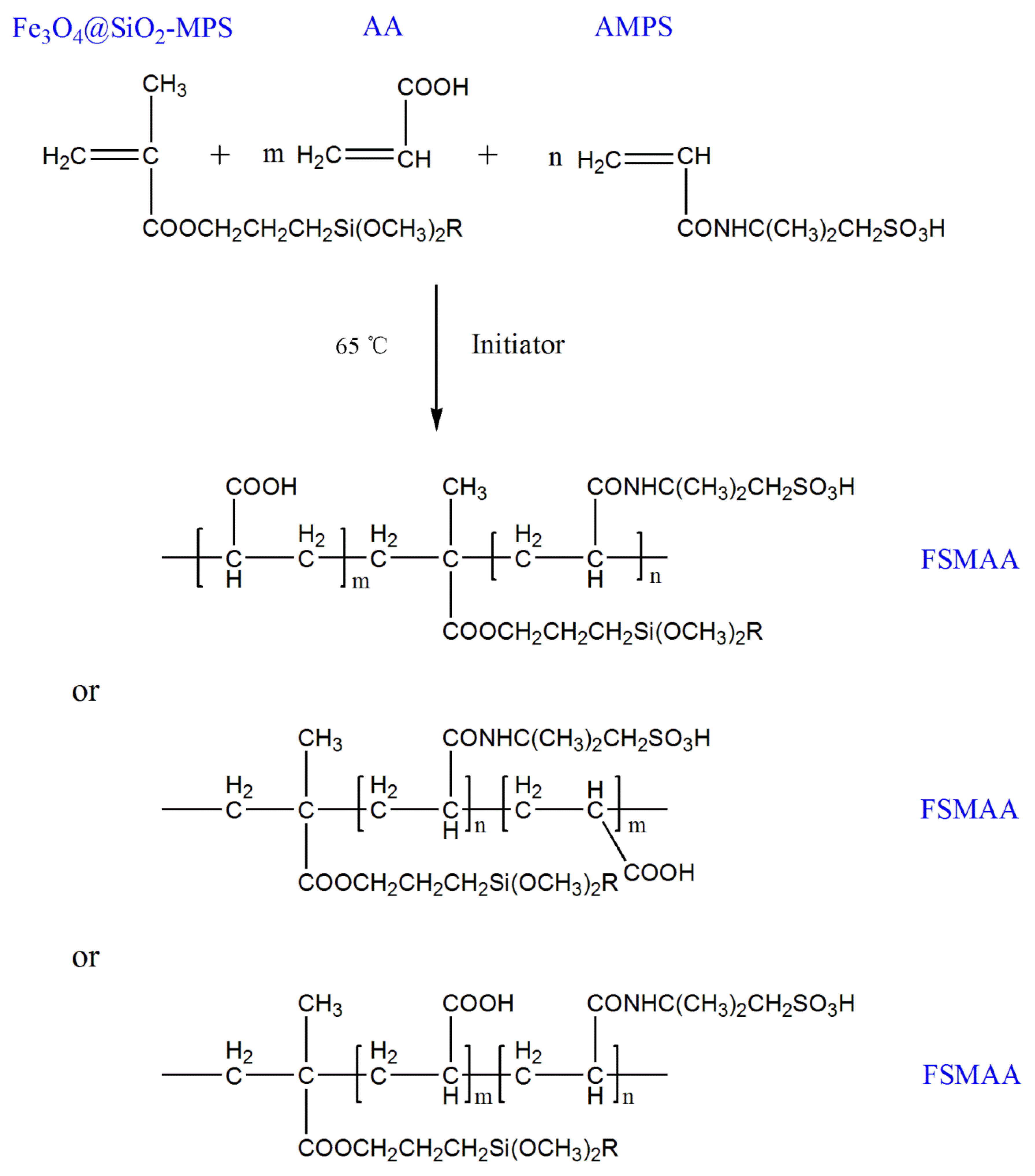
2.2.3. Synthesis of FSMAA MNPs
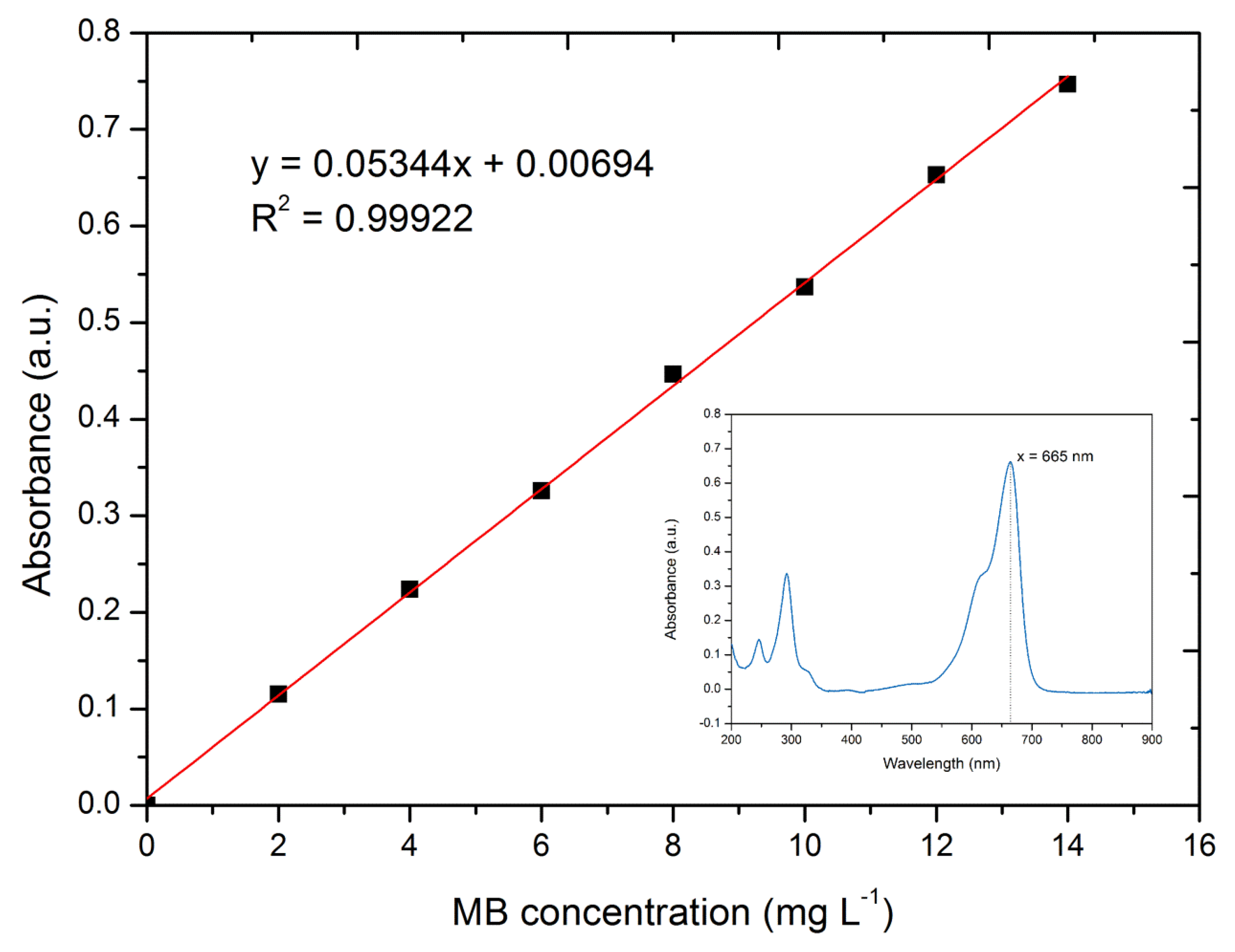
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Effects of Grafted Monomer Concentration and Solution pH
2.4.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.3. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Stability and Regeneration Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
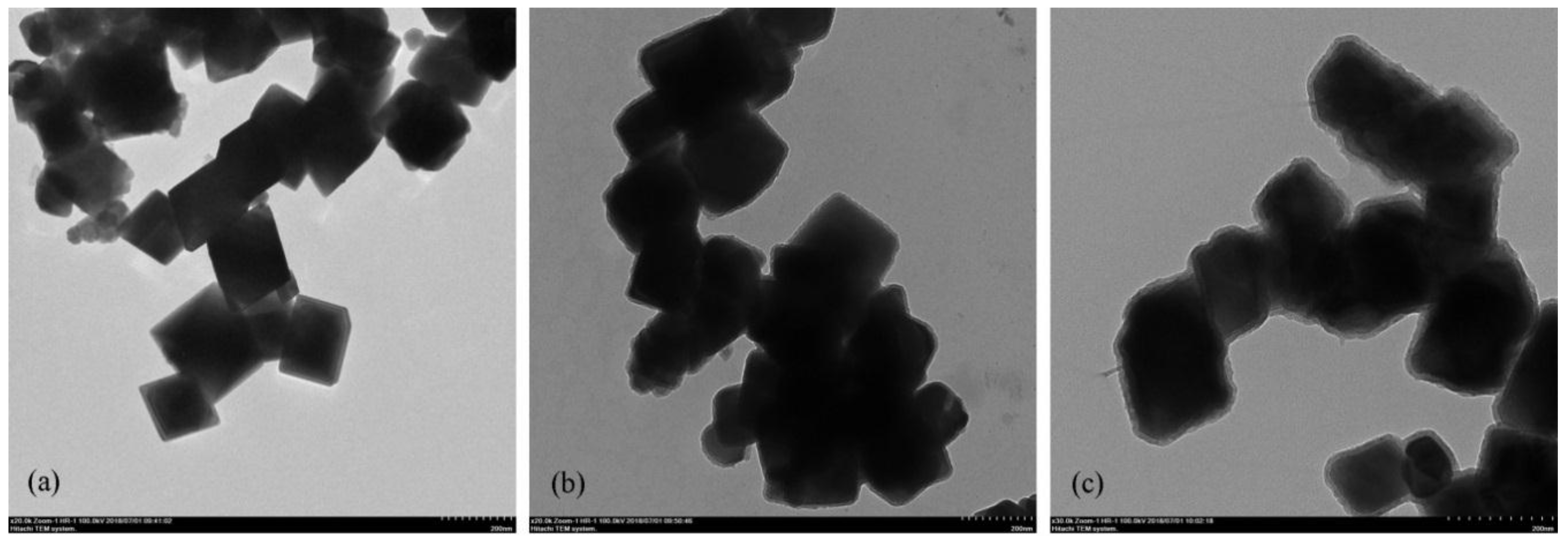
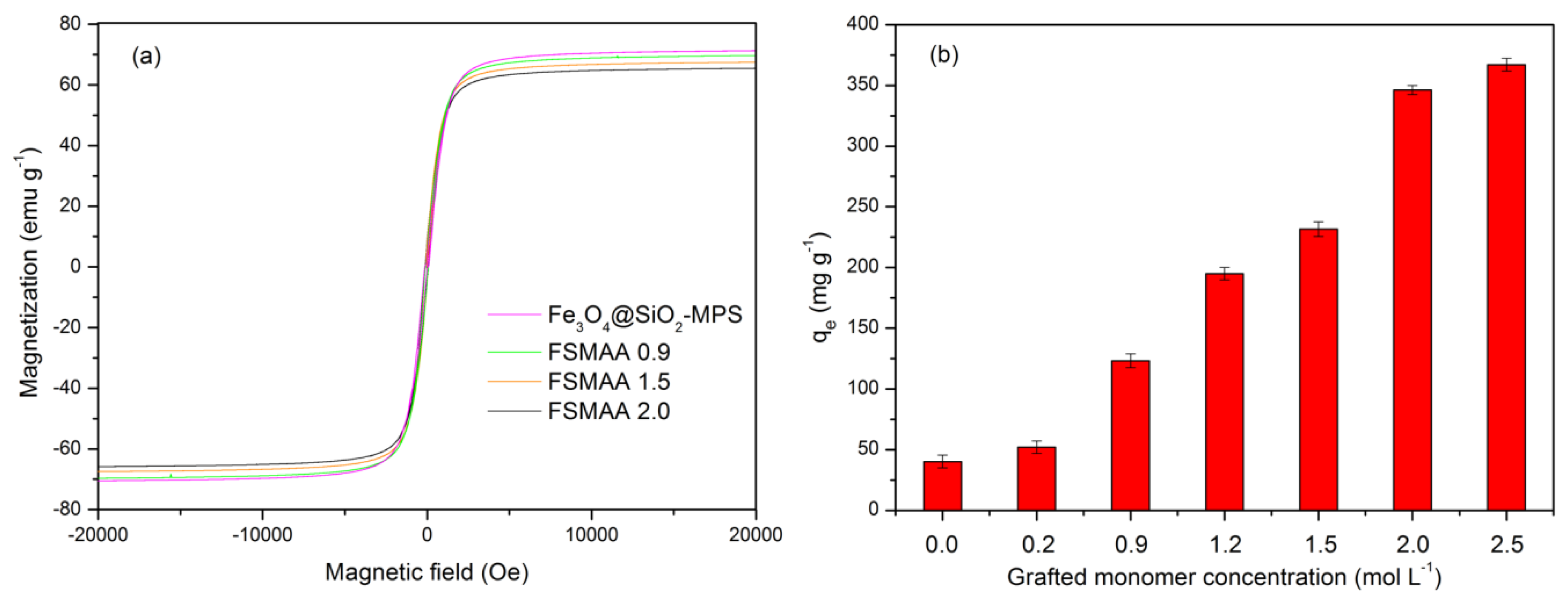
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Adsorption of MB
3.2.1. Effect of Grafted Monomer Concentration on Adsorption
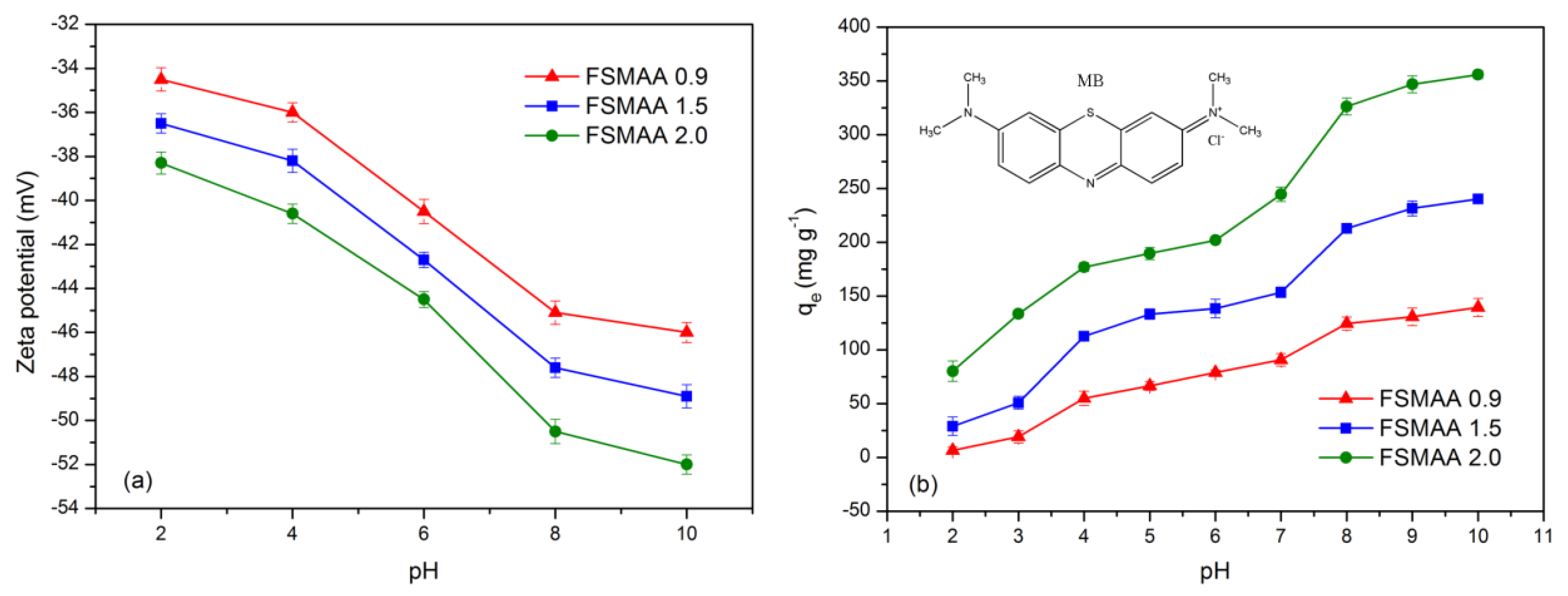
3.2.2. Effect of Solution pH on Adsorption
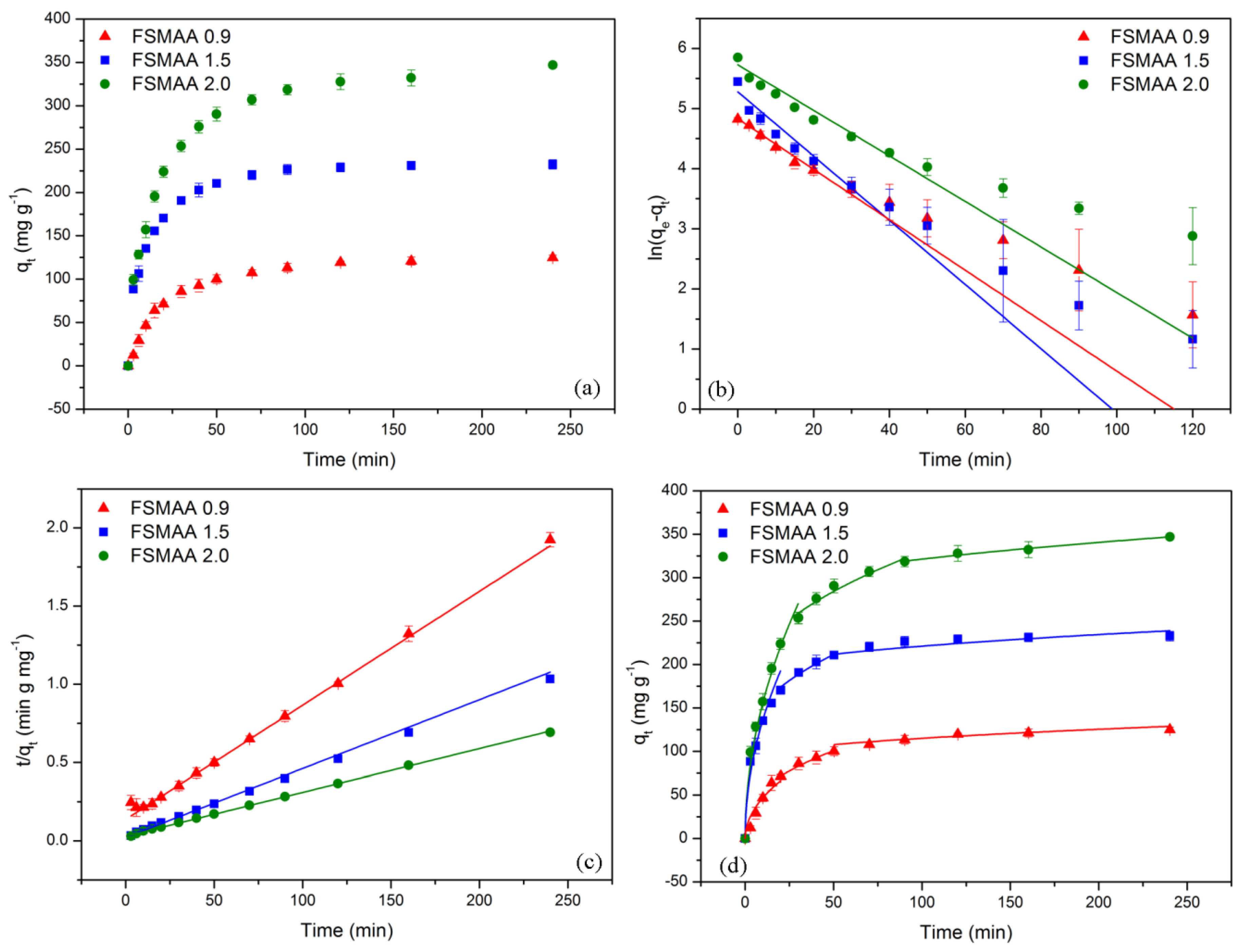
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
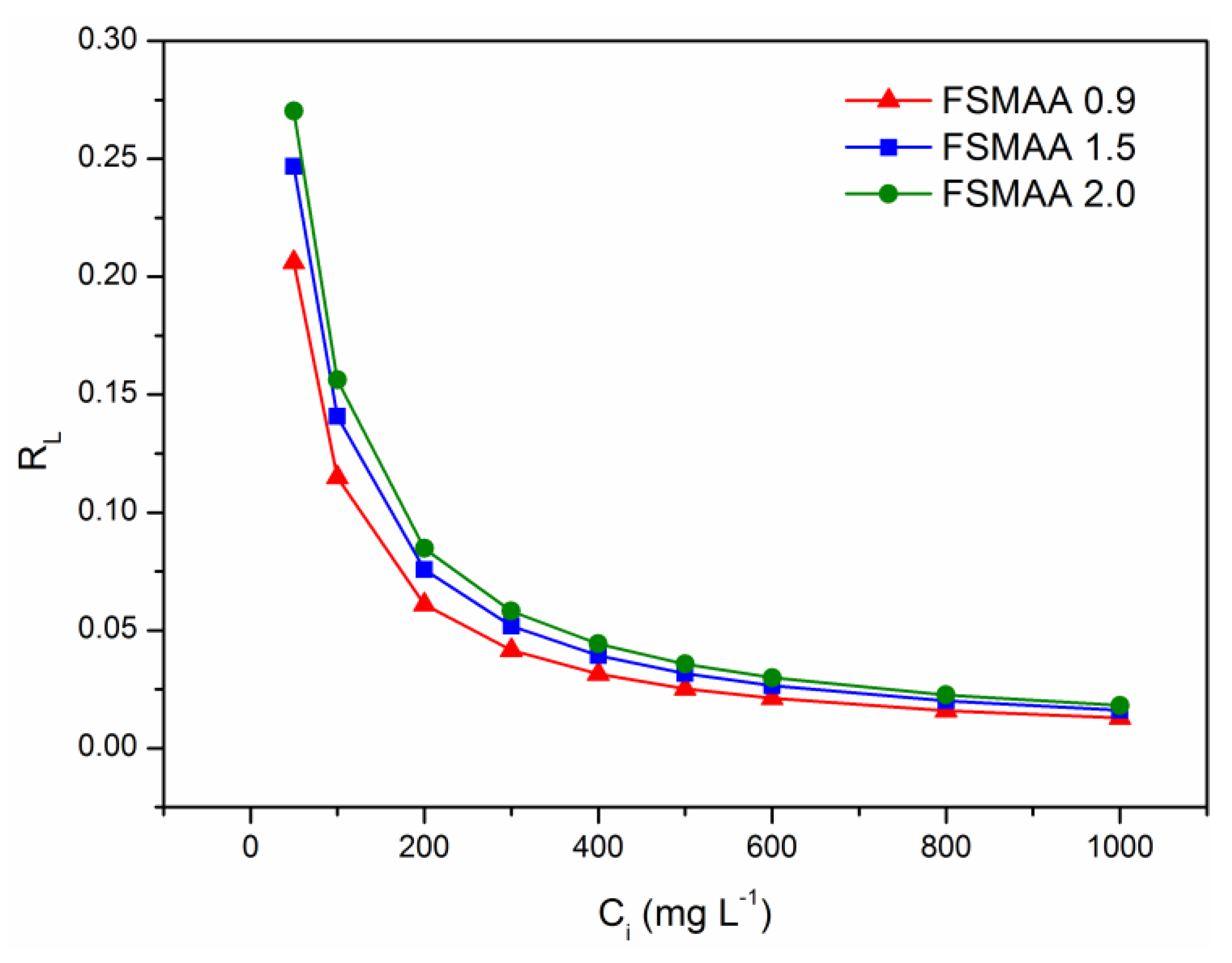
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
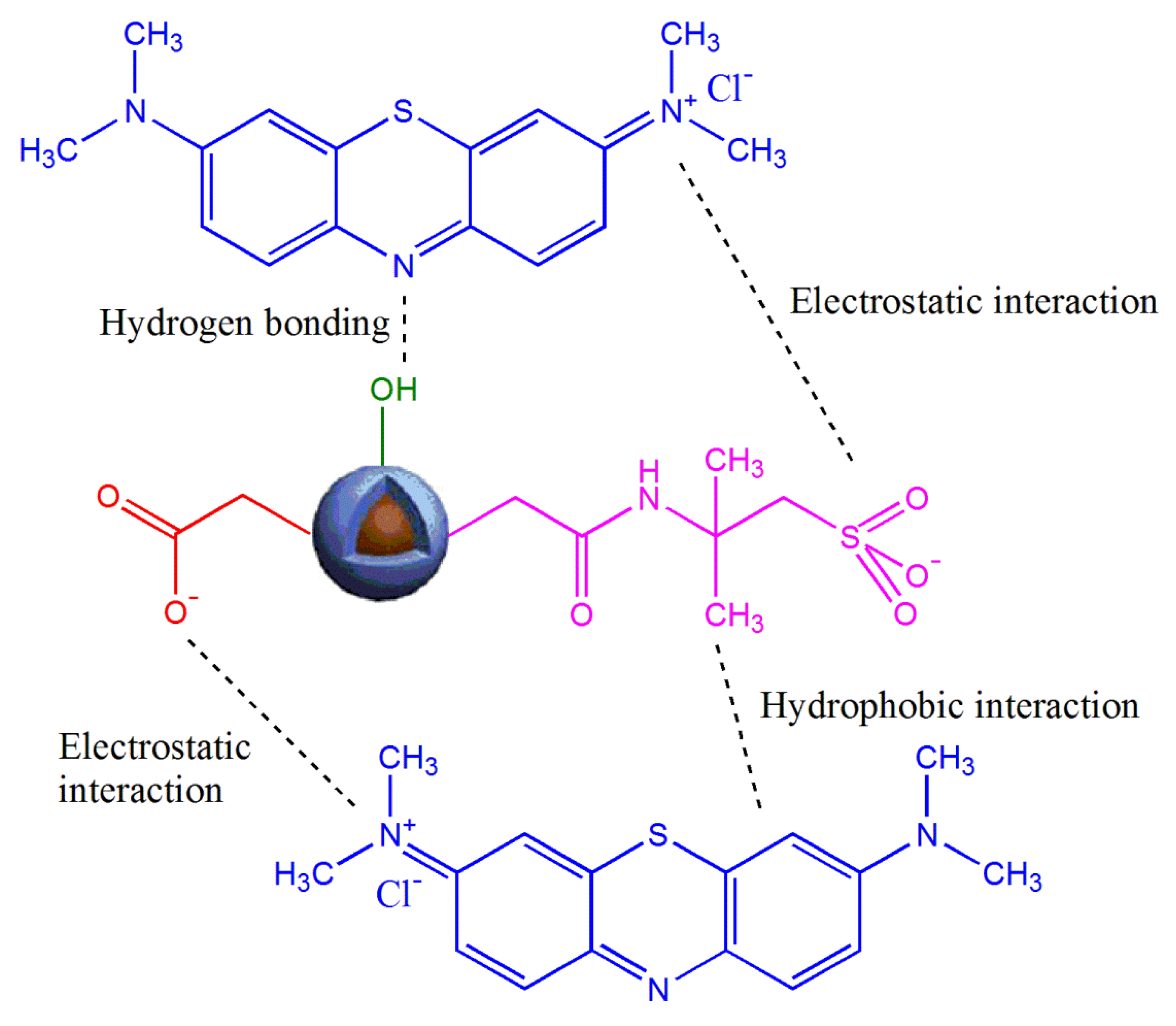
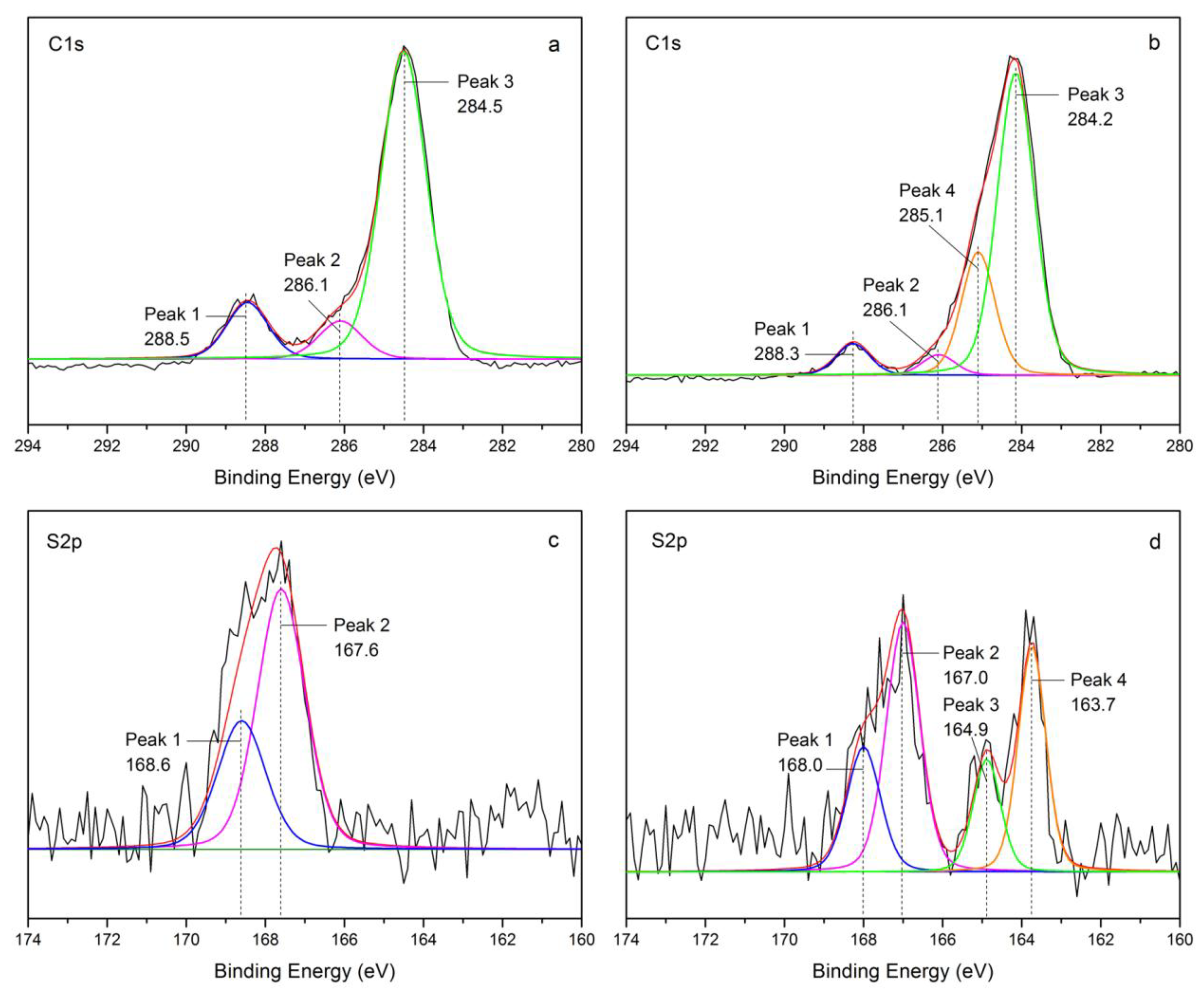
3.2.5. Adsorption Mechanism
3.3. Stability and Regeneration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, S.; Gao, B.; Xing, X.; Xing, L.; Shuang, H.; Duan, P.; Song, W.; Jia, R. Adsorption–desorption behavior of magnetic amine/Fe3O4 functionalized biopolymer resin towards anionic dyes from wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bibi, I.; Bhatti, H.N.; Asgher, M. Decolourisation of direct dyes with manganese peroxidase from white rot basidiomycete Ganoderma lucidum IBL-5. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 87, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.X.; Lei, L.; Zhou, P.X.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.Q. Preparation and characterization of poly(AA co PVP)/PGS composite and its application for methylene blue adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 443, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Chang, Y.Y.; Koduru, J.R.; Yang, J.K. Potential degradation of methylene blue (MB) by nano-metallic particles: A kinetic study and possible mechanism of MB degradation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnoli, A.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Bashkova, S. Adsorption of methylene blue on cashew nut shell based carbons activated with zinc chloride: The role of surface and structural parameters. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Qi, Y.; Sun, W.; Men, Y. Preparation of κ-carrageenan/graphene oxide gel beads and their efficient adsorption for methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Martín, I.; Moretti, E.; Talon, A.; Storaro, L.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Infantes-Molina, A. Au and AuCu nanoparticles supported on SBA-15 ordered mesoporous titania-silica as catalysts for methylene blue photodegradation. Materials 2018, 11, 890–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Yang, J.K.; Chang, Y.Y.; Koduru, J.R. Fenton-like degradation of methylene blue by ultrasonically dispersed nano zero-valent metals. Environ. Process. 2017, 4, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Ren, N. E-Fenton degradation of MB during filtration with Gr/PPy modified membrane cathode. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaidia, S.; Delimi, R.; Benredjem, Z.; Mehellou, A.; Djemel, A.; Barbari, K. Use of a PbO2 electrode of a lead-acid battery for the electrochemical degradation of methylene blue. Sep. Sci. 2017, 52, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanocomposite of chitosan/SiO2/carbon nanotubes and its application for dyes removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 145, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Zu, B.; Zhou, C.; Dou, X. AM-DMC-AMPS multi-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for efficient purification of complex multiphase water system. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaheri, F.; Hassanajili, S. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2@MPS@P4VP nanoparticles for nitrate removal from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 44330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Yan, H.; Yang, H.; Xiao, S.; Li, A. Preparation of chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide magnetic composite microspheres for enhanced selective removal of mercury ions from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 455, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yang, W. Boronic acid-functionalized core-shell-shell magnetic composite microspheres for the selective enrichment of glycoprotein. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8351–8358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafaei, M.; Hosseini, S.N.; Khatami, M.; Javidanbardan, A.; Sepahy, A.A.; Asadi, E. Isolation of recombinant Hepatitis B surface antigen with antibody-conjugated superparamagnetic Fe3O4/SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 145, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lu, J.; Li, S.; Tong, Y.; Ye, B. Synthesis of magnetic microspheres with sodium alginate and activated carbon for removal of methylene blue. Materials 2017, 10, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Koduru, J.R.; Choo, K.H.; Lee, B. Activated carbons impregnated with iron oxide nanoparticles for enhanced removal of bisphenol A and natural organic matter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, N.; Chi, Y.; Geng, W.; Yan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Dong, B. Effect of large pore size of multifunctional mesoporous microsphere on removal of heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Sang, B.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Sun, L.; Zou, X. Fabrication of autofluorescent porous silica nanoparticles for redox-responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. Removal of various cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using a kind of fully biodegradable magnetic composite microsphere. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Lin, W.S.; Xiao, W.; Chen, Y.N. Antibacterial effects of magnetically-controlled Ag/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Materials 2018, 11, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, B.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H. Ultrasound-assisted polymerization of P(AM-DMDAAC): Synthesis, characterization and sludge dewatering performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5439–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jia, Y.; Jing, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, J. Kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption by cobalt-hectorite composite. Dyes Pigment. 2012, 93, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Cong, H. Multifunctional PMMA@Fe3O4@DR magnetic materials for efficient adsorption of dyes. Materials 2017, 10, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Koduru, J.R.; Choi, Y.L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Yang, J.K. Studies on removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) using graphene oxide based inverse spinel nickel ferrite nano-composite as sorbent. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Chang, Y.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Singh, J.; Choi, E.H.; Shiratani, M.; Koduru, J.R.; Attri, P. Biogenic reductive preparation of magnetic inverse spinel iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption removal of heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Stewart, C.E.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Applicability of five models to simulate water infiltration into soil with added biochar. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Xiao, L.; Cao, Q. Co-polymerization of catechol and polyethylenimine on magnetic nanoparticles for efficient selective removal of anionic dyes from water. Powder Technol. 2017, 310, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zou, J.; Liu, D.; Niu, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X. Preparation of Congo red functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle and its application for the removal of methylene blue. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 550, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Alharbi, N.S.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, Y. Silica coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanospheres for high removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.M.; Man, C.; Hu, Z.B. Effective removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repo, E.; Warchol, J.K.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.E.T. Adsorption of Co(II) and Ni(II) by EDTA- and/or DTPA-modified chitosan: Kinetic and equilibrium modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M. Application of synthetic layered sodium silicate magadiite nanosheets for environmental remediation of methylene blue dye in water. Materials 2017, 10, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandimurugan, R.; Thambidurai, S. Synthesis of seaweed-ZnO-PANI hybrid composite for adsorption of methylene blue dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1332–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qiu, H.; Sun, M. Fabrication of novel magnetic chitosan grafted with graphene oxide to enhance adsorption properties for methyl blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Miao, S.; Yu, S.; Ma, L.P.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanoparticles attached to graphene oxide and its use as an adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 379, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Liu, J.H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Yu, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, S.T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Hydrothermal preparation of magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for dye adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Xi, P.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Huang, L.; Shi, Y.; Hou, F.; Zeng, Z.; Shao, C.; Wang, J. A facile chemical method to produce superparamagnetic graphene oxide–Fe3O4 hybrid composite and its application in the removal of dyes from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 22, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, F.; Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C. The preparation of novel adsorbent materials with efficient adsorption performance for both chromium and methylene blue. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 141, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Rohani, S.; Lu, J. Fe3O4@SiO2@CS-TETA functionalized graphene oxide for the adsorption of methylene blue (MB) and Cu(II). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Villoslada, I.; Torres, C.; González, F.; Shibue, T.; Nishide, H. Binding of methylene blue to polyelectrolytes containing sulfonate groups. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; You, L.; Xiang, H.; Jiang, Y. Comparison of dye adsorption by mesoporous hybrid gels: Understanding the interactions between dyes and gel surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S. Rapid and efficient removal of heavy metal and cationic dye by carboxylate-rich magnetic chitosan flocculants: Role of ionic groups. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zong, P.; Ren, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X. Rapid and high-efficient preconcentration of Eu(III) by core-shell structured Fe3O4@humic acid magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6891–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

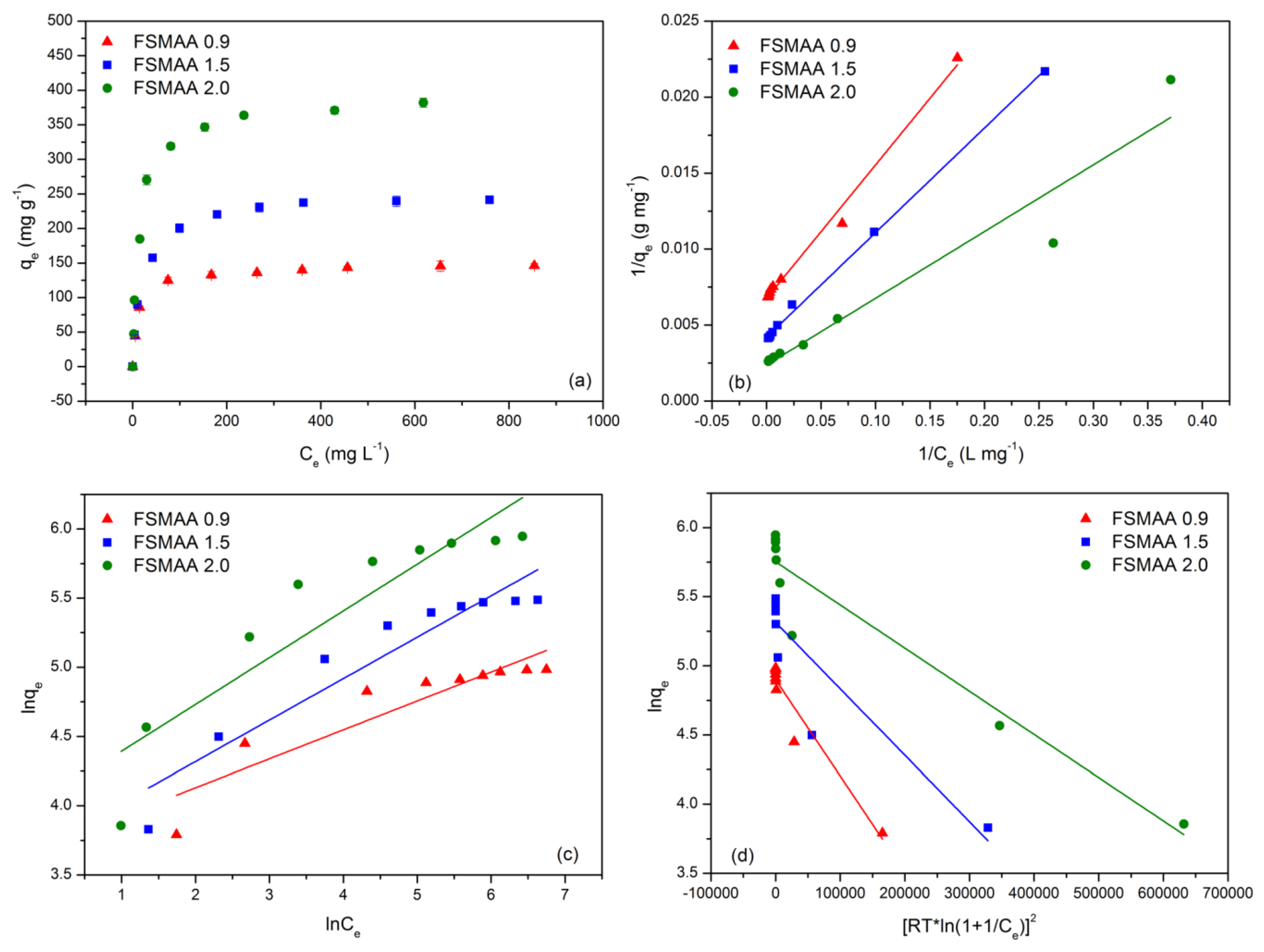

| Monomer Concentration (mol L−1) | qe,exp (mg g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Intraparticle Diffusion Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe1,cal (mg g−1) | k1 × 102 (min−1) | R2 | Reduced Chi-Sqr | qe2,cal (mg g−1) | k2 × 104 (g mg−1 min−1) | R2 | Reduced Chi-Sqr | ki,1 | ki,2 | ki,3 | ||
| (mg g−1 min−1/2) | ||||||||||||
| 0.9 | 124.8 ± 3.0 | 125.0 ± 2.6 | 4.20 ± 0.32 | 0.939 | 4.642 | 137.4 ± 1.5 | 3.84 ± 0.16 | 0.998 | 0.500 | 14.82 ± 1.36 | 11.20 ± 0.60 | 2.50 ± 0.70 |
| 1.5 | 232.3 ± 5.5 | 195.7 ± 13.2 | 5.34 ± 0.72 | 0.832 | 14.218 | 227.3 ± 4.0 | 8.83 ± 0.51 | 0.996 | 8.888 | 43.10 ± 2.86 | 14.44 ± 1.58 | 3.22 ± 0.60 |
| 2.0 | 346.8 ± 3.0 | 307.2 ± 14.8 | 3.79 ± 0.50 | 0.837 | 52.516 | 358.4 ± 4.7 | 2.56 ± 0.15 | 0.998 | 2.691 | 49.30 ± 1.19 | 15.69 ± 1.64 | 4.65 ± 0.21 |
| Monomer Concentration (mol L−1) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | D-R Model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | Reduced Chi-Sqr | n | KF | R2 | Reduced Chi-Sqr | qD (mg g−1) | KD (mol2 kJ−2) | R2 | Reduced Chi-Sqr | |
| 0.9 | 147.9 ± 4.2 | 0.077 ± 0.003 | 0.991 | 2.479 × 10−7 | 4.79 ± 0.81 | 40.95 ± 7.36 | 0.819 | 0.028 | 134.3 ± 5.5 | 6.97 ± 0.73 | 0.919 | 0.013 |
| 1.5 | 238.1 ± 5.2 | 0.061 ± 0.001 | 0.998 | 5.762 × 10−8 | 3.34 ± 0.43 | 41.28 ± 7.76 | 0.884 | 0.038 | 203.2 ± 19.0 | 4.80 ± 0.84 | 0.798 | 0.067 |
| 2.0 | 421.9 ± 19.4 | 0.054 ± 0.005 | 0.929 | 2.704 × 10−6 | 2.96 ± 0.50 | 57.73 ± 14.19 | 0.819 | 0.097 | 314.9 ± 26.0 | 3.12 ± 0.34 | 0.911 | 0.048 |
| Adsorbent | pH | Temperature (K) | Equilibrium Time (min) | Adsorption Capacity (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNCM | 6.0 | 323 | 30 | 20.0 | [36] |
| SW-ZnO-PANI | 7.0 | 305 | 100 | 20.6 | [37] |
| GO-CS-Fe3O4 | 5.3 | 303 | 60 | 95.2 | [38] |
| Fe3O4/SiO2-GO | N.A. a | 333 | 70 | 111.1 | [39] |
| Fe3O4@C NPs | 6.0 | 298 | 180 | 117.0 | [40] |
| GO-Fe3O4 | N.A. a | 298 | 30 | 167.2 | [41] |
| CS-Glu-MCMs | 7.0 | 293 | 5 | 182.5 | [22] |
| MG-ILs-OH | 12.0 | 303 | 60 | 243.3 | [42] |
| FSMAA 2.0 | 9.0 | 303 | 90 | 421.9 | This study |
| Sample | Peak for C1s Spectra | Peak for S2p Spectra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | ||
| FSMAA | BE (eV) | 288.5 | 286.1 | 284.5 | — | 168.6 | 167.6 | — | — |
| RAP (%) | 13.04 | 9.26 | 77.70 | — | 33.33 | 66.67 | — | — | |
| FSMAA-MB | BE (eV) | 288.3 | 286.1 | 284.2 | 285.1 | 168.0 | 167.0 | 164.9 | 163.7 |
| RAP (%) | 6.23 | 4.04 | 65.45 | 24.28 | 19.14 | 38.29 | 14.19 | 28.38 | |
| Assignment | C=O | C–OH/C–N/C–S | C–H/C–C | phenylalk-ane | S=O | sulfoether/S–H | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Methylene Blue Adsorption. Materials 2018, 11, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081312
Zheng X, Zheng H, Zhao R, Sun Y, Sun Q, Zhang S, Liu Y. Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Methylene Blue Adsorption. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081312
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xinyu, Huaili Zheng, Rui Zhao, Yongjun Sun, Qiang Sun, Shixin Zhang, and Yongzhi Liu. 2018. "Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Methylene Blue Adsorption" Materials 11, no. 8: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081312
APA StyleZheng, X., Zheng, H., Zhao, R., Sun, Y., Sun, Q., Zhang, S., & Liu, Y. (2018). Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Methylene Blue Adsorption. Materials, 11(8), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081312